Olmutinib Reverses Thioacetamide-Induced Cell Cycle Gene Alterations in Mice Liver and Kidney Tissues, While Wheat Germ Treatment Exhibits Limited Efficacy at Gene Level
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model and Experimental Design
2.2. RNA Extraction
2.3. cDNA Synthesis
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis by Real-Time PCR
2.5. Co-Expression Network Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
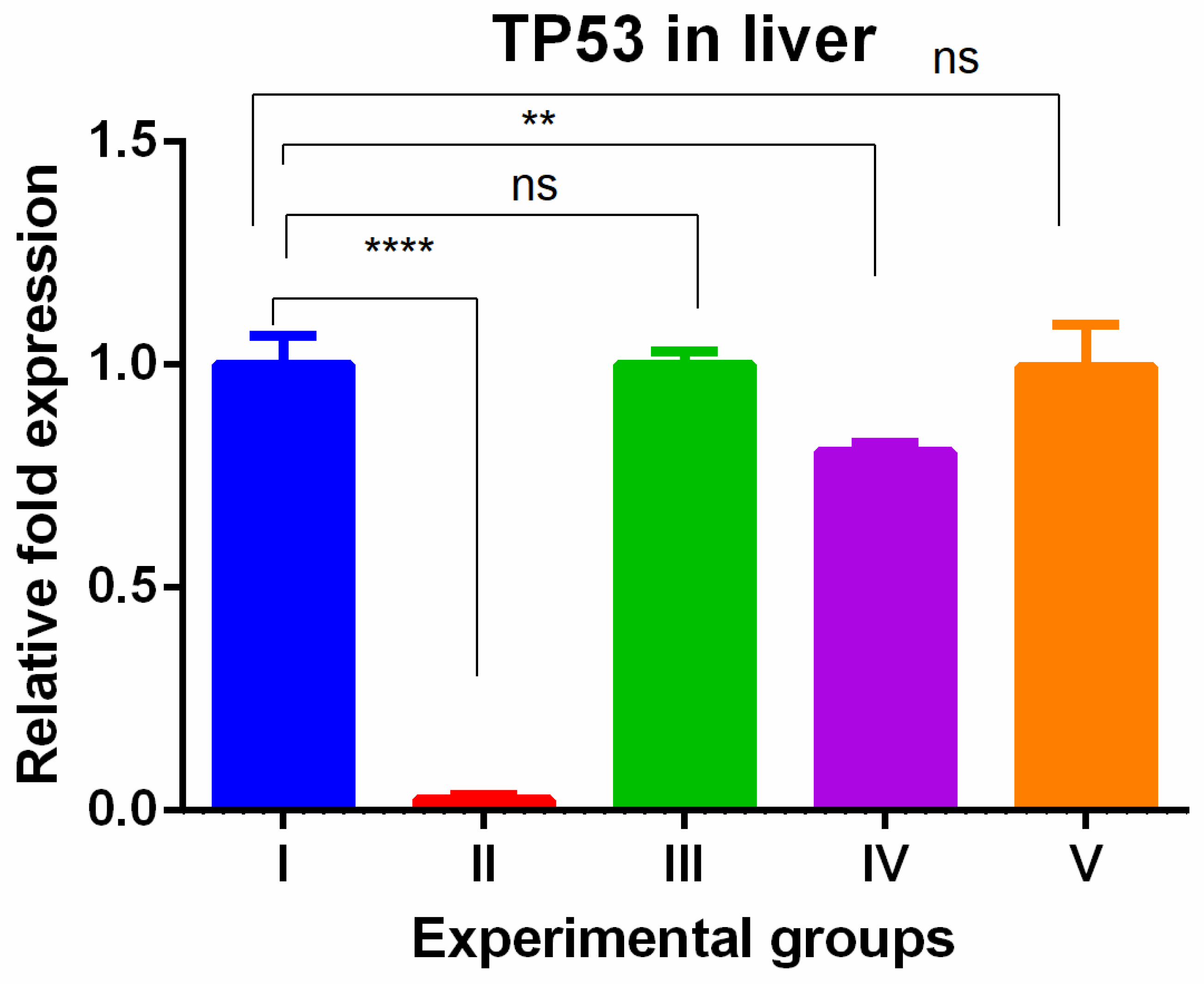
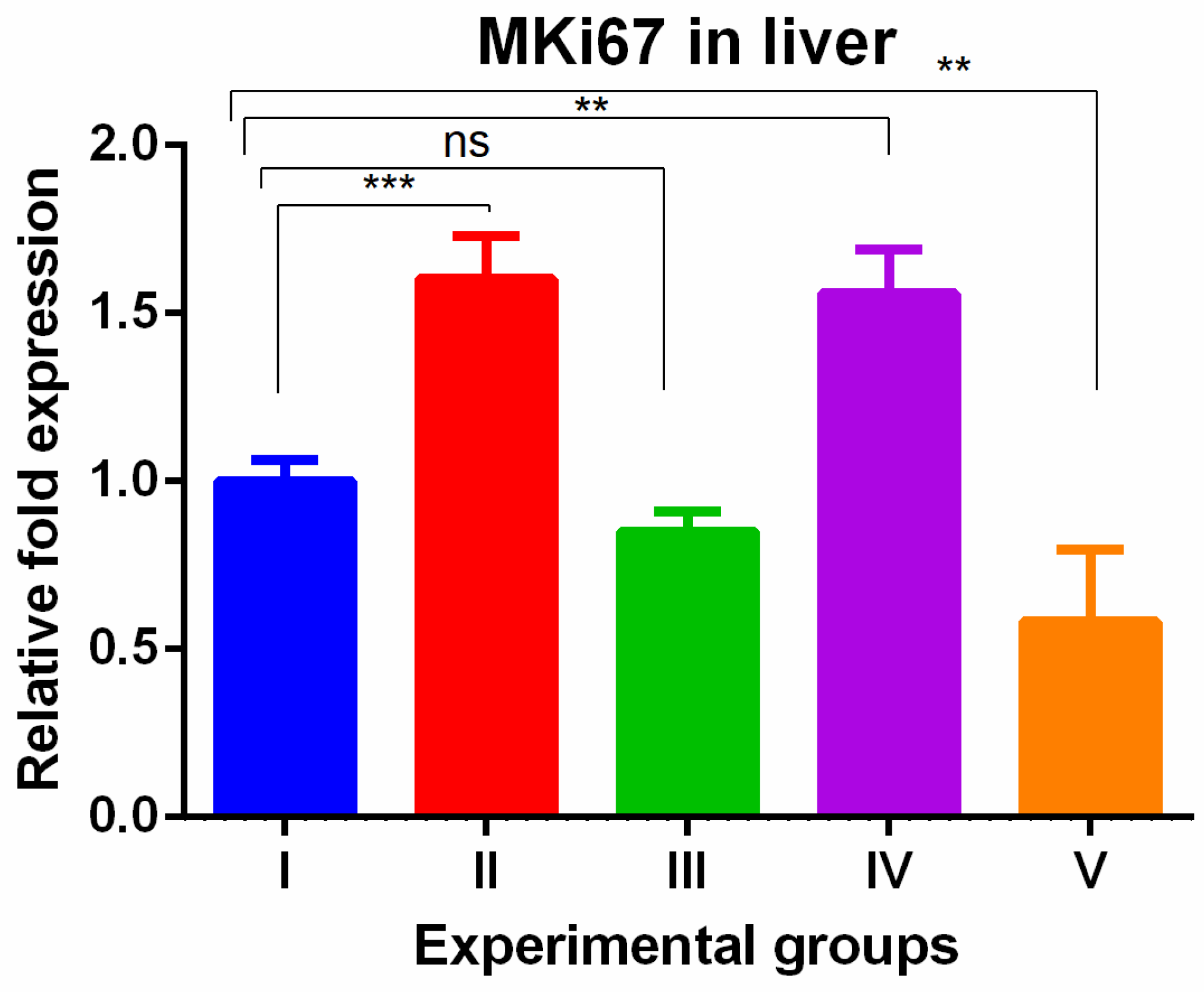
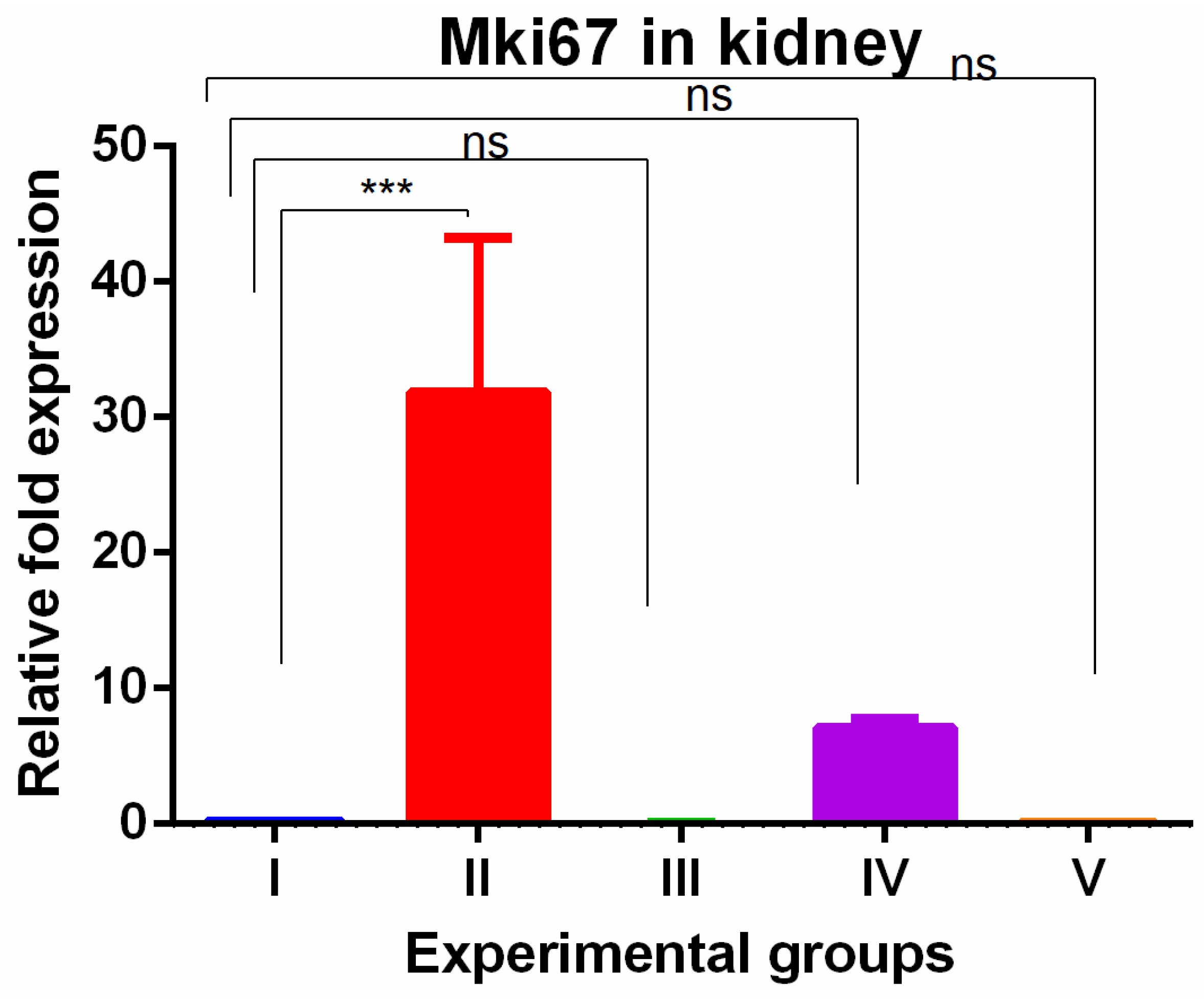
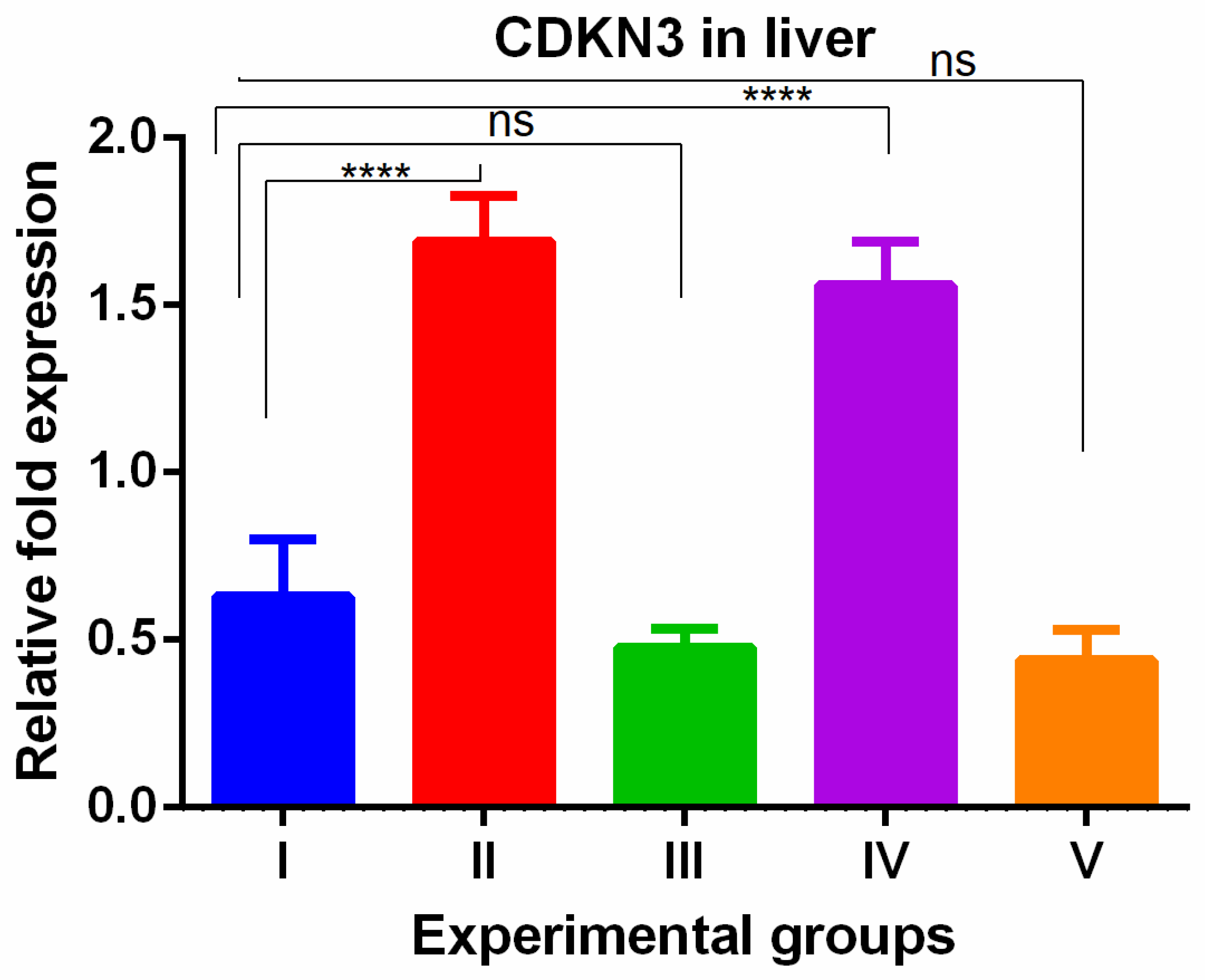
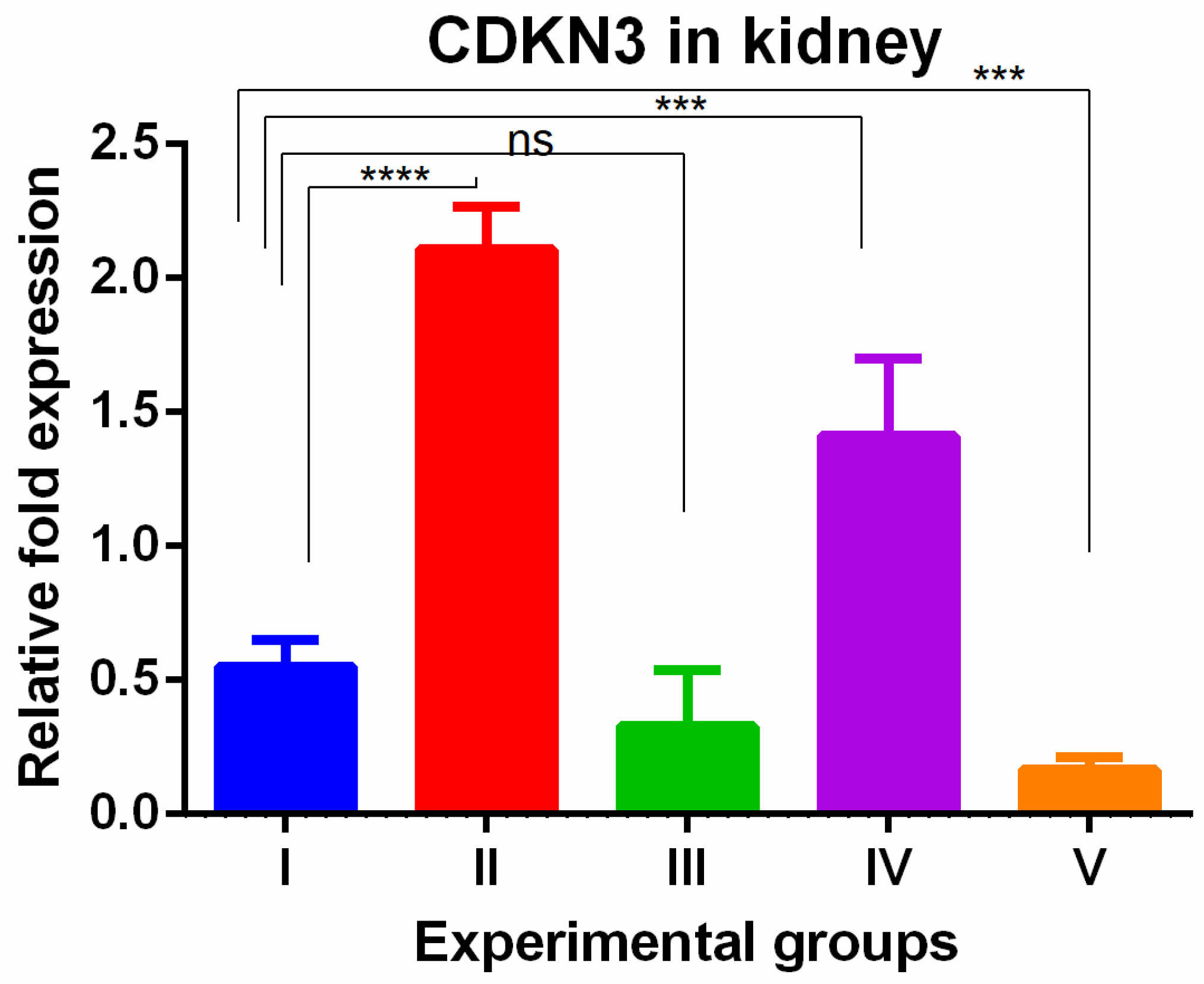
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alamery, S.; Zargar, S.; Yaseen, F.; Wani, T.A.; Siyal, A. Evaluation of the effect of wheat germ oil and olmutinib on the thioacetamide-induced liver and kidney toxicity in mice. Life 2022, 12, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezhilarasan, D. Molecular mechanisms in thioacetamide-induced acute and chronic liver injury models. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 99, 104093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Sharma, D.; Singh, A.P.; Kaur, S. Amelioration of hepatic function, oxidative stress, and histopathologic damages by Cassia fistula L. fraction in thioacetamide-induced liver toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 29930–29945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zargar, S. Protective effect of Trigonella foenum-graecum on thioacetamide induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schyman, P.; Printz, R.L.; Estes, S.K.; Boyd, K.L.; Shiota, M.; Wallqvist, A. Identification of the toxicity pathways associated with thioacetamide-induced injuries in rat liver and kidney. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhao, X.; Gu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, G. The preventive role of hydrogen-rich water in thioacetamide-induced cholangiofibrosis in rat assessed by automated histological classification. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 632045. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Türkmen, N.B.; Hande, Y.; Taşlidere, A.; Şahin, Y.; Çiftçi, O. The ameliorate effects of nerolidol on thioacetamide-induced oxidative damage in heart and kidney tissue. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, A.; Altman, T.; Perlson, E. Looking for answers far away from the soma—The (un) known axonal functions of TDP-43, and their contribution to early NMJ disruption in ALS. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Tan, L.; Tian, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Y. Research progress on rodent models and its mechanisms of liver injury. Life Sci. 2023, 337, 122343. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, A.A.; Ismail, A.F. Protective impact of Spirulina platensis against γ-irradiation and thioacetamide-induced nephrotoxicity in rats mediated by regulation of micro-RNA 1 and micro-RNA 146a. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 10, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Murray, M.G.; Whelan, K.A. Roles for GADD45 in development and cancer. Gadd45 Stress Sens. Genes 2022, 1360, 23–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Lei, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.; Xu, T. BPA and low-Se exacerbate apoptosis and mitophagy in chicken pancreatic cells by regulating the PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J. Adv. Res. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholzen, T.; Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. J. Cell. Physiol. 2000, 182, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Soria, J.-C.; Goldman, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Varga, A.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Solomon, B.J.; Oxnard, G.R.; Dziadziuszko, R. Rociletinib in EGFR-mutated non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fan, Y.-F.; Cai, C.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Teng, Q.-X.; Lei, Z.-N.; Zeng, L.; Gupta, P.; Chen, Z.-S. Olmutinib (BI1482694/HM61713), a novel epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, reverses ABCG2-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Kaur, S.; Sharma, N.; Kaur, J.; Krishania, M.; Tiwari, V.; Garg, M. Effect of processing on the phytochemicals and quality attributes of vermicelli developed from colored wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 108, 103560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.U.; Anjum, F.M.; Zahoor, T. Nutritional assessment of cookies supplemented with defatted wheat germ. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zargar, S.; Wani, T.A.; Rizwan Ahamad, S. An insight into wheat germ oil nutrition, identification of its bioactive constituents and computer-aided multidimensional data analysis of its potential anti-inflammatory effect via molecular connections. Life 2023, 13, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uxa, S.; Castillo-Binder, P.; Kohler, R.; Stangner, K.; Müller, G.A.; Engeland, K. Ki-67 gene expression. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 3357–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babamohamadi, M.; Babaei, E.; Ahmed Salih, B.; Babamohammadi, M.; Jalal Azeez, H.; Othman, G. Recent findings on the role of wild-type and mutant p53 in cancer development and therapy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 903075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Che, W.; Wang, W.; Su, G.; Zhen, T.; Jiang, Z. CDKN3 promotes tumor progression and confers cisplatin resistance via RAD51 in esophageal cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3253–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Sánchez, N.; Fisher, D.; Krasinska, L. Physiological functions and roles in cancer of the proliferation marker Ki-67. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs258932. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.-M.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Q.-N.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Ge, B.-J. A critical role of CDKN3 in gastric cancer and regulates tumor cell proliferation. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 9, 172–178. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, E.Y.L.; Wong, S.C.C.; Chan, C.M.L.; Lam, E.K.Y.; Ho, L.Y.; Lau, C.P.Y.; Au, T.C.C.; Chan, A.K.C.; Tsang, C.M.; Tsao, S.W. TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator promotes proliferation and invasiveness of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 569–574. [Google Scholar]
- Brisco, P.; Sankbeil, J.; Kephart, D. RNA purification: A rapid and versatile protocol for the isolation of total RNA. Promega Notes 1997, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Thermo Scientific. SuperScript™ First-Strand Synthesis System for RT-PCR; Thermo Scientific: Waltham, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Alamery, S.; AlAjmi, A.; Wani, T.A.; Zargar, S. In Silico and In Vitro Exploration of Poziotinib and Olmutinib Synergy in Lung Cancer: Role of hsa-miR-7-5p in Regulating Apoptotic Pathway Marker Genes. Medicina 2023, 59, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donehower, L.A.; Soussi, T.; Korkut, A.; Liu, Y.; Schultz, A.; Cardenas, M.; Li, X.; Babur, O.; Hsu, T.-K.; Lichtarge, O. Integrated analysis of TP53 gene and pathway alterations in the cancer genome atlas. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 1370–1384.e1375. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, K.; Hou, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X. Prognostic value of TP53 concurrent mutations for EGFR-TKIs and ALK-TKIs based targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Hu, M.; Xu, L.; Ren, Y.; Mei, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, C. The Ki-67 proliferation index-related nomogram to predict the response of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors or chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant status. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 728575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Dey, M.K.; Devireddy, R.; Gartia, M.R. Biomarkers in Cancer Detection, Diagnosis, and Prognosis. Sensors 2023, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Cao, H.; He, X.; Sun, P.; Feng, Y.; Chen, L.; Gong, H. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 (CDKN3) plays a critical role in prostate cancer via regulating cell cycle and DNA replication signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Miao, H.; Fang, S.; Fang, T.; Chen, N.; Li, M. CDKN3 expression is negatively associated with pathological tumor stage and CDKN3 inhibition promotes cell survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xia, Z.; Wan, Y.; Huang, P. Identification of hub genes and candidate drugs in hepatocellular carcinoma by integrated bioinformatics analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e27117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montojo, J.; Zuberi, K.; Rodriguez, H.; Kazi, F.; Wright, G.; Donaldson, S.L.; Morris, Q.; Bader, G.D. GeneMANIA Cytoscape plugin: Fast gene function predictions on the desktop. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2927–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annenkov, A. Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signalling in the control of neural stem and progenitor cell (NSPC) development. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 49, 440–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewjanthong, P.; Sooksai, S.; Sasano, H.; Hutvagner, G.; Bajan, S.; McGowan, E.; Boonyaratanakornkit, V. Cell-penetrating peptides containing the progesterone receptor polyproline domain inhibits EGF signaling and cell proliferation in lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name of Gene | Primers | Primer Name | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MKi67 | Forward | AAGAAGAGCCCACAGCACAGAGAA | M_MKi67-E15F |
| Reverse | AAGAAGAGCCCACAGCACAGAGAA | M_MKi67-E16R | |
| CDKN3 | Forward | TTCTGCCATTCTCACCGTGTCCTT | M_CDKN3-E4F |
| Reverse | TGCGATAACAAGCTCCGTCCATCT | M_CDKN3-E6R | |
| TP53 | Forward | AACAATGGCCCGAGTCTAATGGGA | M_TP53-E2F |
| Reverse | ACAGATGTTGCCTGATGTCTGGGT | M_TP53-E4R | |
| GAPDH | Forward | ACCACAGTCCATGCCATCAC | M_GAPDH-F |
| Reverse | ACCACAGTCCATGCCATCAC | M_GAPDH-R | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zargar, S.; Wani, T.A.; Alamery, S.; Yaseen, F. Olmutinib Reverses Thioacetamide-Induced Cell Cycle Gene Alterations in Mice Liver and Kidney Tissues, While Wheat Germ Treatment Exhibits Limited Efficacy at Gene Level. Medicina 2024, 60, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040639
Zargar S, Wani TA, Alamery S, Yaseen F. Olmutinib Reverses Thioacetamide-Induced Cell Cycle Gene Alterations in Mice Liver and Kidney Tissues, While Wheat Germ Treatment Exhibits Limited Efficacy at Gene Level. Medicina. 2024; 60(4):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040639
Chicago/Turabian StyleZargar, Seema, Tanveer A. Wani, Salman Alamery, and Fatimah Yaseen. 2024. "Olmutinib Reverses Thioacetamide-Induced Cell Cycle Gene Alterations in Mice Liver and Kidney Tissues, While Wheat Germ Treatment Exhibits Limited Efficacy at Gene Level" Medicina 60, no. 4: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040639
APA StyleZargar, S., Wani, T. A., Alamery, S., & Yaseen, F. (2024). Olmutinib Reverses Thioacetamide-Induced Cell Cycle Gene Alterations in Mice Liver and Kidney Tissues, While Wheat Germ Treatment Exhibits Limited Efficacy at Gene Level. Medicina, 60(4), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040639








