Overlapping Case of Advanced Systemic Sclerosis and IgG4-Related Disease after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
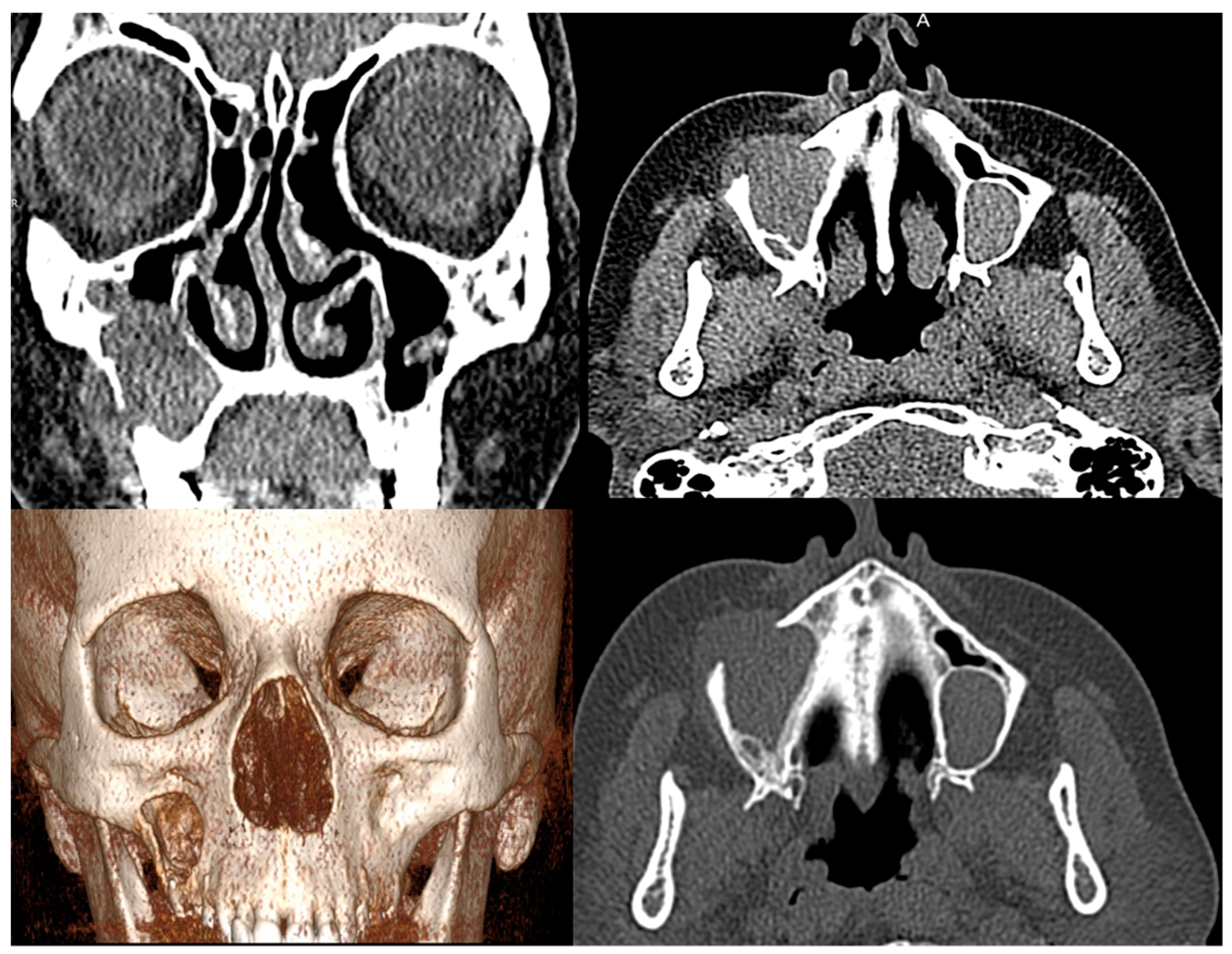
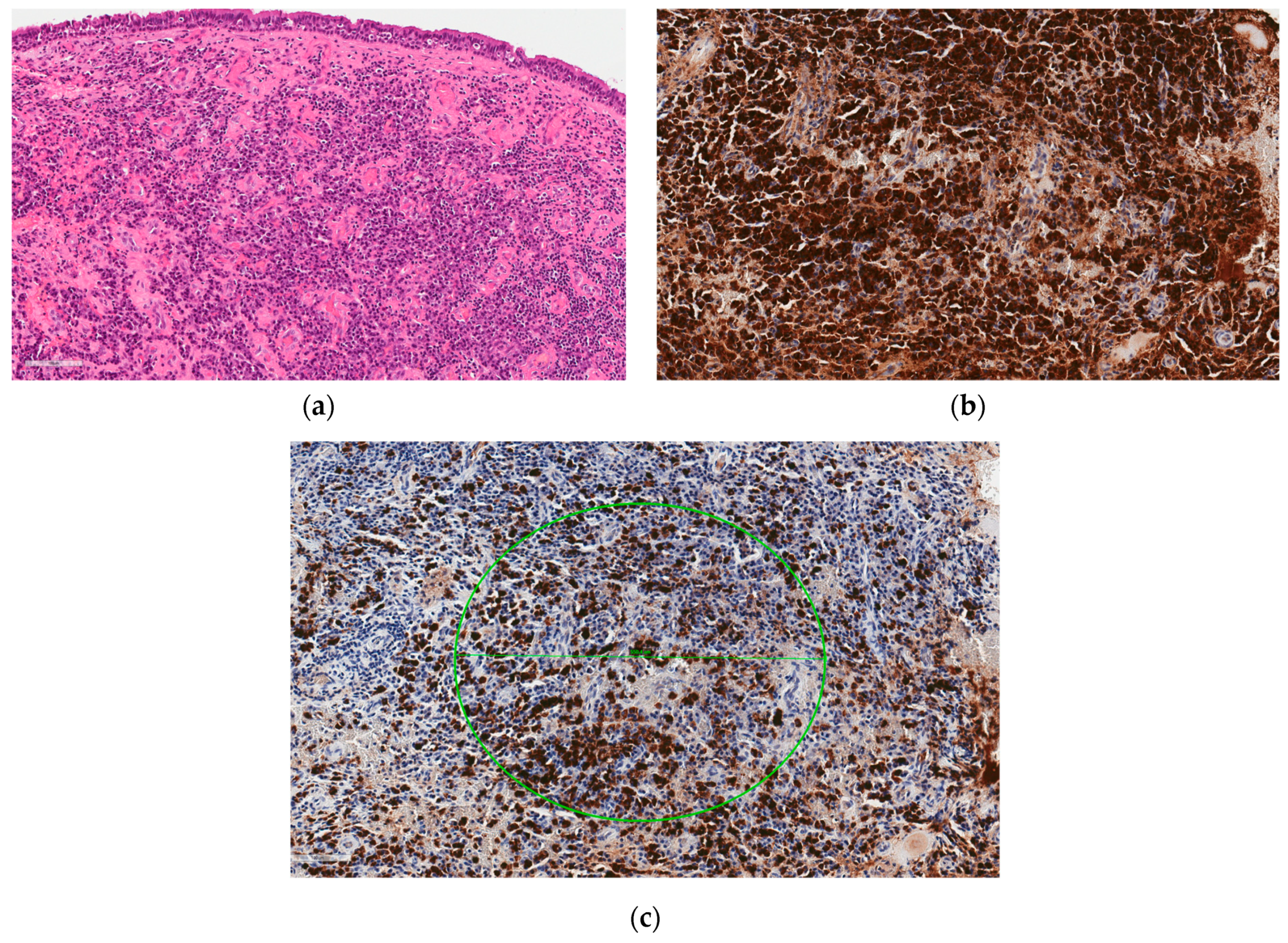
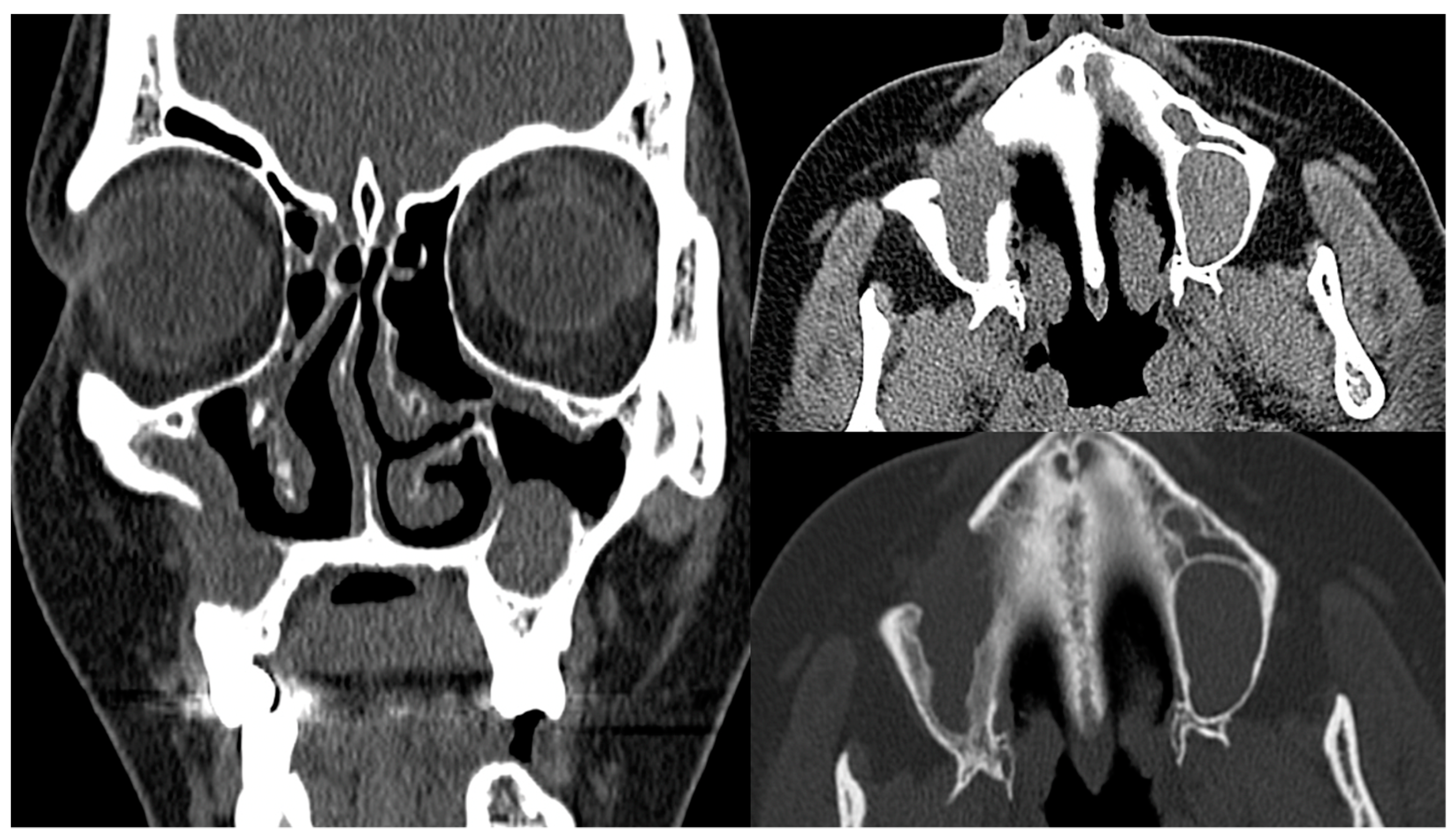
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudel, D.R.; Jayakumar, D.; Danve, A.; Sehra, S.T.; Derk, C.T. Determinants of mortality in systemic sclerosis: A focused review. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 1847–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelas, A.; Silver, R.M.; Arrossi, A.V.; Highland, K.B. Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 304–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Wu, J.; Wu, H.; Sawalha, A.H.; Lu, Q. Clinical Treatment Options in Scleroderma: Recommendations and Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 62, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shouval, R.; Furie, N.; Raanani, P.; Nagler, A.; Gafter-Gvili, A. Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Fransen, J.; Avouac, J.; Becker, M.; Kulak, A.; Allanore, Y.; Distler, O.; Clements, P.; Cutolo, M.; Czirjak, L.; et al. Update of EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, R.K.; Shah, S.J.; Dill, K.; Grant, T.; Gheorghiade, M.; Schroeder, J.; Craig, R.; Hirano, I.; Marshall, K.; Ruderman, E.; et al. Autologous non-myeloablative haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation compared with pulse cyclophosphamide once per month for systemic sclerosis (ASSIST): An open-label, randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Laar, J.M.; Farge, D.; Sont, J.K.; Naraghi, K.; Marjanovic, Z.; Larghero, J.; Schuerwegh, A.J.; Marijt, E.W.; Vonk, M.C.; Schattenberg, A.V.; et al. Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation vs intravenous pulse cyclophosphamide in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014, 311, 2490–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.M.; Goldmuntz, E.A.; Keyes-Elstein, L.; McSweeney, P.A.; Pinckney, A.; Welch, B.; Mayes, M.D.; Nash, R.A.; Crofford, L.J.; Eggleston, B.; et al. Myeloablative Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation for Severe Scleroderma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzillotta, M.; Mancuso, G.; Della-Torre, E. Advances in the diagnosis and management of IgG4 related disease. BMJ 2020, 369, m1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.; Perugino, C.A.; Naden, R.; Choi, H.K.; Stone, J.H.; ACR/EULAR IgG4-RD Classification Criteria Committee. Clinical phenotypes of IgG4-related disease: An analysis of two international cross-sectional cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyronel, F.; Fenaroli, P.; Maritati, F.; Schleinitz, N.; Vaglio, A. IgG4-related disease: Advances in pathophysiology and treatment. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 19, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Naden, R.P.; Chari, S.; Choi, H.; Della-Torre, E.; Dicaire, J.F.; Hart, P.A.; Inoue, D.; Kawano, M.; Khosroshahi, A.; et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, K.; Kakkar, A.; Manchanda, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Kaur, H.; Mishra, D.; Verma, H.; Kumar, R.; Sagar, P.; Jain, D.; et al. Sinonasal IgG4-related disease: A rare and emerging entity broadening the differential diagnosis in the sinonasal universe. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 2883–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, A.; Sakai, O.; Chapman, M.N.; Sugimoto, H. IgG4-related disease of the head and neck: CT and MR imaging manifestations. Radiographics 2012, 32, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, V.; Zen, Y.; Chan, J.K.; Yi, E.E.; Sato, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Klöppel, G.; Heathcote, J.G.; Khosroshahi, A.; Ferry, J.A.; et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielosz, E.; Majdan, M.; Dryglewska, M.; Targońska-Stępniak, B. Overlap syndromes in systemic sclerosis. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. Dermatol. Alergol. 2018, 35, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naramala, S.; Biswas, S.; Adapa, S.; Gayam, V.; Konala, V.M.; Bose, S. An Overlapping Case of IgG4-Related Disease and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2019, 7, 2324709619862297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.M.; Majhail, N.S.; Bredeson, C.; Carpenter, P.A.; Chatterjee, S.; Crofford, L.J.; Georges, G.E.; Nash, R.A.; Pasquini, M.C.; Sarantopoulos, S.; et al. Systemic Sclerosis as an Indication for Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Position Statement from the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 1961–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowden, J.A.; Saccardi, R.; Allez, M.; Ardizzone, S.; Arnold, R.; Cervera, R.; Denton, C.; Hawkey, C.; Labopin, M.; Mancardi, G.; et al. Haematopoietic SCT in severe autoimmune diseases: Updated guidelines of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012, 47, 770–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farge, D.; Burt, R.K.; Oliveira, M.C.; Mousseaux, E.; Rovira, M.; Marjanovic, Z.; de Vries-Bouwstra, J.; Del Papa, N.; Saccardi, R.; Shah, S.J.; et al. Cardiopulmonary assessment of patients with systemic sclerosis for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Recommendations from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Autoimmune Diseases Working Party and collaborating partners. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 52, 1495–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henes, J.; Oliveira, M.C.; Labopin, M.; Badoglio, M.; Scherer, H.U.; Del Papa, N.; Daikeler, T.; Schmalzing, M.; Schroers, R.; Martin, T.; et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for progressive systemic sclerosis: A prospective non-interventional study from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Autoimmune Disease Working Party. Haematologica 2021, 106, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdo, F.D.; Lescoat, A.; Conaghan, P.G.; Ananyeva, L.P.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Bertoldo, E.; Boyadzhieva, V.; Castellví, I.; Colic, J.; Denton, C.P.; et al. Op0234 2023 Update of Eular Recommendations for the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82 (Suppl. S1), 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, D.M.; Cardona, D.M.; Burchette, J.L.; Puri, P.K. Scleroderma and IgG4-related disease. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2013, 35, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, P. T cell abnormalities in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plichta, D.R.; Somani, J.; Pichaud, M.; Wallace, Z.S.; Fernandes, A.D.; Perugino, C.A.; Lähdesmäki, H.; Stone, J.H.; Vlamakis, H.; Chung, D.C.; et al. Congruent microbiome signatures in fibrosis-prone autoimmune diseases: IgG4-related disease and systemic sclerosis. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressenberger, P.; Jud, P.; Kovacs, G.; Kreuzer, S.; Brezinsek, H.P.; Guetl, K.; Muster, V.; Kolesnik, E.; Schmidt, A.; Odler, B.; et al. Rituximab as a Treatment Option after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in a Patient with Systemic Sclerosis. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Before AHSCT | After AHSCT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date (Time after AHSCT) | 2014 01 | 2014 09 (8 mo.) | 2015 04 (15 mo.) | 2019 04 (63 mo.) |
| Hand injury, Raynaud’s syndrome, skin conditions | Advanced sclerodactyly with flexural contractures, osteolysis, deep scarring, cutaneous fibrosis over the whole body, restricted movement | Softer hands and body skin, greater range of movement | Skin induration is reduced all over the body, acral contractures are reduced, wrinkles appear on the face, the amplitude of the yawning increases | Raynaud’s syndrome persistence, mild cutaneous induration; sclerodactyly with flexural contractures, multiple scars, osteolysis of the fingertips (overall positive dynamic) |
| DLCO, %, | 67% mild reduction | 61% mild reduction | 63% mild reduction | 73% mild reduction |
| Pulmonary function test assessment | FVC 2.6 (81% Ref 3.23), FEV1 1.77 (64% Ref 2.78), FEV1/FVC 68% Ref 81% | FVC 2.71 (84% Ref 3.23), FEV1 1.75 (63% Ref 2.78), FEV1/FVC 65% Ref 81% | FVC 2.6 (81% Ref 3.21), FEV1 1,74 (64% Ref 2.75), FEV1/FVC 67% Ref 81% | FVC 2.39 (77% Ref 3.1), FEV1 1.68 (63% Ref 2.65), FEV1/FVC 70% Ref 80% |
| The patient subjectively assessed her condition | Worsening | 50–60% improvement | 90% improvement | 30% improvement |
| VAS | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| mRSS | 40 | 34 | 30 | 23 |
| HRCT scan (semi-quantitative analysis according to Warrick, 0–30 points) | 14 (GGO, marginal pleural irregularities, intersegmental and subpleural lines) | 13 (slightly less of GGO) | 12 (GGO, pleural thickenings, subpleural lines and solitary subpleural cysts) | 12 |
| Capillaroscopy | Abundant avascular zones, isolated giant capillaries, signs of angiogenesis, marked fibrosis | Increased capillary density and isolated haemorrhages are observed as ischaemia and fibrosis decrease | In dynamics, increasing capillary density, decreasing areas of avascular zones, increasing number of giant capillaries | |
| Anti-Scl-70 and anti-dsDNR positive | Anti-Scl-70 and anti-dsDNR negative | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dulko, A.J.; Butrimiene, I.; Cypiene, A.; Peceliunas, V.; Petroska, D.; Stankeviciene, E.; Rugiene, R. Overlapping Case of Advanced Systemic Sclerosis and IgG4-Related Disease after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Medicina 2024, 60, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60030496
Dulko AJ, Butrimiene I, Cypiene A, Peceliunas V, Petroska D, Stankeviciene E, Rugiene R. Overlapping Case of Advanced Systemic Sclerosis and IgG4-Related Disease after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Medicina. 2024; 60(3):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60030496
Chicago/Turabian StyleDulko, Alisa Julija, Irena Butrimiene, Alma Cypiene, Valdas Peceliunas, Donatas Petroska, Ernesta Stankeviciene, and Rita Rugiene. 2024. "Overlapping Case of Advanced Systemic Sclerosis and IgG4-Related Disease after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation" Medicina 60, no. 3: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60030496
APA StyleDulko, A. J., Butrimiene, I., Cypiene, A., Peceliunas, V., Petroska, D., Stankeviciene, E., & Rugiene, R. (2024). Overlapping Case of Advanced Systemic Sclerosis and IgG4-Related Disease after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Medicina, 60(3), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60030496






