SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in Children under 5 Years Old—A Regional Seroepidemiological Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Ethical Principles
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/table (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- National Institute of Public Health. Analysis of COVID-19 Cases (Weekly Report). Available online: https://insp.gov.ro/download/raport-saptamanal-episaptamana03_2024/ (accessed on 26 January 2024).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker. Available online: https://qap.ecdc.europa.eu/public/extensions/COVID-19/vaccine-tracker.html#age-group-tab (accessed on 26 January 2024).
- Oran, D.P.; Topol, E.J. The Proportion of SARS-CoV-2 Infections That Are Asymptomatic: A Systematic Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofin, F.; Nastase, E.-V.; Vâță, A.; Iancu, L.S.; Luncă, C.; Buzilă, E.R.; Vlad, M.A.; Dorneanu, O.S. The Immune, Inflammatory and Hematological Response in COVID-19 Patients, According to the Severity of the Disease. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofin, F.; Nastase, E.V.; Roșu, M.F.; Bădescu, A.C.; Buzilă, E.R.; Miftode, E.G.; Manciuc, D.C.; Dorneanu, O.S. Inflammatory Response in COVID-19 Depending on the Severity of the Disease and the Vaccination Status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asseri, A.A.; Alsabaani, A. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 among Children Visiting a Tertiary Hospital during the Prevaccination Period, Southwest Region, Saudi Arabia. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairy, A.; Elhussein, N.; Elbadri, O.; Mohamed, S.; Malik, E.M. Epidemiology of COVID-19 among Children and Adolescents in Sudan 2020–2021. Epidemiologia 2023, 4, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathanielsz, J.; Toh, Z.Q.; Do, L.A.H.; Mulholland, K.; Licciardi, P.V. SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children and Implications for Vaccination. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeland, M.R.; Bannister, S.; Clifford, V.; Dohle, K.; Mulholland, K.; Sutton, P.; Curtis, N.; Steer, A.C.; Burgner, D.P.; Crawford, N.W.; et al. Innate Cell Profiles during the Acute and Convalescent Phase of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofin, F.; Dorneanu, O.S.; Constantinescu, D.; Nastase, E.V.; Luncă, C.; Iancu, L.S.; Andrioaie, I.-M.; Duhaniuc, A.; Cianga, C.M.; Pavel-Tanasa, M.; et al. Cytokines and Chemokines in Breastmilk of SARS-CoV-2 Infected or COVID-19 Vaccinated Mothers. Vaccines 2022, 10, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofin, F.; Nastase, E.V.; Iancu, L.S.; Constantinescu, D.; Cianga, C.M.; Lunca, C.; Ursu, R.G.; Cianga, P.; Dorneanu, O.S. Anti-RBD IgA and IgG Response and Transmission in Breast Milk of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Vaccinated Mothers. Pathogens 2022, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, D.E.; Cîtu, C.; Jura, A.M.C.; Lungu, N.; Navolan, D.; Craina, M.; Semenescu, A.; Gorun, F.; Jura, M.-A.; Belengeanu, V.; et al. The Benefits of Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 during Pregnancy in Favor of the Mother/Newborn Dyad. Vaccines 2022, 10, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.T.; Garcia-Carreras, B.; Hitchings, M.D.T.; Yang, B.; Katzelnick, L.C.; Rattigan, S.M.; Borgert, B.A.; Moreno, C.A.; Solomon, B.D.; Trimmer-Smith, L.; et al. A Systematic Review of Antibody Mediated Immunity to Coronaviruses: Kinetics, Correlates of Protection, and Association with Severity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, K.J.; van de Sandt, C.E.; Lemke, M.M.; Lee, C.Y.; Shoffner, S.K.; Chua, B.Y.; Davis, S.K.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Rowntree, L.C.; Hensen, L.; et al. Systems Serology Detects Functionally Distinct Coronavirus Antibody Features in Children and Elderly. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, C.B.; Bragard, E.; Jaber, R.; Gray, A. COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy among Parents of Children under Five Years in the United States. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Chen, S.; Chan, P.S.-F.; Fang, Y.; Cao, H.; Chen, H.; Hu, T.; Chen, Y.; et al. Changes in Parents’ COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy for Children Aged 3–17 Years before and after the Rollout of the National Childhood COVID-19 Vaccination Program in China: Repeated Cross-Sectional Surveys. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolescu, L.S.C.; Zaharia, C.N.; Dumitrescu, A.I.; Prasacu, I.; Radu, M.C.; Boeru, A.C.; Boidache, L.; Nita, I.; Necsulescu, A.; Medar, C.; et al. COVID-19 Parental Vaccine Hesitancy in Romania: Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines 2022, 10, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Epidemiological Update—19 January 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update---19-january-2024 (accessed on 26 January 2024).
- World Health Organization. Interim Statement on COVID-19 Vaccination for Children. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/11-08-2022-interim-statement-on-covid-19-vaccination-for-children (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Furtunescu, F.L.; Pistol, A.; Nicolescu, O.; Leustean, M.; Chifiriuc, M.-C.; Cucu, I.A.; Janta, D.; Vremera, T.; Mitache, M.M. The Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Romania—First Prevalence Survey. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2021, 39, 30902–30908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilla, M.L.; Keetch, C.; Mitchell, G.; McBreen, J.; Shurin, M.R.; Wheeler, S.E. SARS-CoV-2 Serologic Immune Response in Exogenously Immunosuppressed Patients. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2021, 6, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minotti, C.; Tirelli, F.; Barbieri, E.; Giaquinto, C.; Donà, D. How is Immunosuppressive Status affecting Children and Adults in SARS-CoV-2 Infection? A systematic Review. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e61–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, M.H.; Naser, A.Y.; Orabi, M.A.A.; Alwafi, H.; Alyami, H.S. Epidemiology of COVID-19 in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: An Ecological Study. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, U.; Sarioglu, A.A.; Ruh, E.; Sanlidag, B.; Dalkan, C.; Beyitler, I.; Suer, K.; Cakir, N.; Sayan, M.; Sanlidag, T. The pediatric Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 IgG Seropositivity in the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2022, 64, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinszer, K.; McKinnon, B.; Bourque, N.; Pierce, L.; Saucier, A.; Otis, A.; Cheriet, I.; Papenburg, J.; Hamelin, M.E.; Charland, K.; et al. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Among Children in School and Day Care in Montreal, Canada. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2135975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comar, M.; Benvenuto, S.; Lazzerini, M.; Fedele, G.; Barbi, E.; Amaddeo, A.; Risso, F.M.; Strajn, T.; Di Rocco, P.; Stefanelli, P.; et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Italian Pediatric Population: A regional Seroepidemiological Study. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzerini, M.; Benvenuto, S.; Mariani, I.; Fedele, G.; Leone, P.; Stefanelli, P.; Vittori, G.; Schreiber, S.; Tommasini, A.; Rezza, G.; et al. Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 IgG Seroprevalence in Children and Factors Associated with Seroconversion: Results from a Multiple Time-Points Study in Friuli-Venezia Giulia Region, Italy. Children 2022, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante Pinto, V., Jr.; Moura, L.; Cavalcante, R.C.; Lima, J.R.C.; Bezerra, A.S.; de Sousa Dantas, D.R.; Amaral, C.M.L.; Lima, D.F.; Junior, A.B.V.; Florindo Guedes, M.I. Prevalence of COVID-19 in Children, Adolescents and Adults in Remote Education Situations in the City of Fortaleza, Brazil. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sempos, C.T.; Tian, L. Adjusting Coronavirus Prevalence Estimates for Laboratory Test Kit Error. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 190, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banjar, A.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Alruwaily, A.; Alserehi, H.; Al-Qunaibet, A.; Alaswad, R.; Almutlaq, H.; Almudaiheem, A.; Khojah, A.T.; Alsaif, F.; et al. Seroprevalence of Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 among Blood Donors in the early Months of the Pandemic in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 104, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koirala, A.; Gidding, H.F.; Vette, K.; Macartney, K.; Group, P.S. The Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2-specific Antibodies in Children, Australia, November 2020–March 2021. Med. J. Aust. 2022, 217, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dethioux, L.; Dauby, N.; Montesinos, I.; Rebuffat, E.; Hainaut, M. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in Children and their Family Members, July-October 2020, Brussels. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapronova, K.; Kaķe, R.; Pavāre, J.; Grāvele, D.; Šēla, I.; Ērgle, E.; Isarova, D.; Grīnberga, Z.; Zavadska, D. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence among Children in Latvia: A cross-sectional study. Medicine 2023, 102, e32795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimi, R.; Sepidarkish, M.; Mollalo, A.; Parsa, H.; Mahjour, S.; Safarpour, F.; Almukhtar, M.; Mechaal, A.; Chemaitelly, H.; Sartip, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in Children Worldwide: A systematic Review and Meta-analysis. EclinicalMedicine 2023, 56, 101786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franczak, J.; Moppert, J.; Sobolewska-Pilarczyk, M.; Pawłowska, M. The Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies in Children Hospitalized for Reasons Other Than COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.E.N.; Kim, Y.; Jones, J.; Lee, A.; Deng, Y.; Nycz, E.; Iachan, R.; Gundlapalli, A.V.; MacNeil, A.; Hall, A. Pediatric Infection-Induced SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Increases and Seroprevalence by Type of Clinical Care September 2021 to February 2022. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 227, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.C.; Cole, L.D.; Albanese, B.A.; Mahon, A.; Knight, V.; Williams, N.; Severson, R.; Burakoff, A.; Alden, N.B.; Dominguez, S.R. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Compared with Confirmed COVID-19 Cases among Children, Colorado, USA, May–July 2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouge Elton, P.A.; Schmitt, P.A.; Faouzi, M.; Zimmermann, P.; Ritter Schenk, C. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies and Associated Risk Factors in Children less than 6 Years of Age in the Canton of Fribourg, Switzerland (COVPED study): A population-based cross-sectional study. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2022, 152, w30173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.P.; Piñera, C.; De La Maza, V.; Lagomarcino, A.J.; Simian, D.; Torres, B.; Urquidi, C.; Valenzuela, M.T.; O’Ryan, M. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Antibody Prevalence in Blood in a Large School Community Subject to a Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outbreak: A Cross-sectional Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, e458–e465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olariu, T.R.; Craciun, A.C.; Vlad, D.C.; Dumitrascu, V.; Pop, L.L.; Horhat, F.; Lupu, M.A. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in Children from Western Romania, March to June 2021. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2022, 22, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.L.; Jedlicka, A.; Pekosz, A. The Xs and Y of Immune Responses to Viral Vaccines. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, E.N. The X-files in Immunity: Sex-based Differences Predispose Immune Responses. Nat. Rev. Immun. 2008, 8, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Younes, A. Coronavirus COV-19/SARS-CoV-2 affects women less than men: Clinical response to viral infection. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, N.M.; A Selim, L. Characterisation of COVID-19 Pandemic in Paediatric Age Group: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 128, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwati, N.H.; Noprida, D.; Agustia, W.; Imroatun, T.; Sarini, S.; Sahariah, S.; Polapa, D. Impact of Age and Gender on the Incidence of COVID-19 in Children at Pasar Rebo Hospital, Jakarta. KnE Life Sci. 2022, 7, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour Ghanaie, R.; Boone, I.; Shamshiri, A.R.; Karimi, A.; Amirali, A.; Marhamati, N.; Rostami, M.H.; Pashaei, N.; Janbazi, S.; Azimi, L.; et al. Seroepidemiological and Molecular Survey for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Children in Iran, September 2020 to June 2021: 1-Year Cross-Sectional Study. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boey, L.; Roelants, M.; Merckx, J.; Hens, N.; Desombere, I.; Duysburgh, E.; Vandermeulen, C. Age-dependent Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in School-aged Children from Areas with low and high Community Transmission. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringhini, S.; Zaballa, M.E.; Perez-Saez, J.; Pullen, N.; de Mestral, C.; Picazio, A.; Pennacchio, F.; Wisniak, A.; Richard, A.; Baysson, H.; et al. Specchio-COVID19 Study Group. Seroprevalence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies after the Second Pandemic Peak. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 600–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

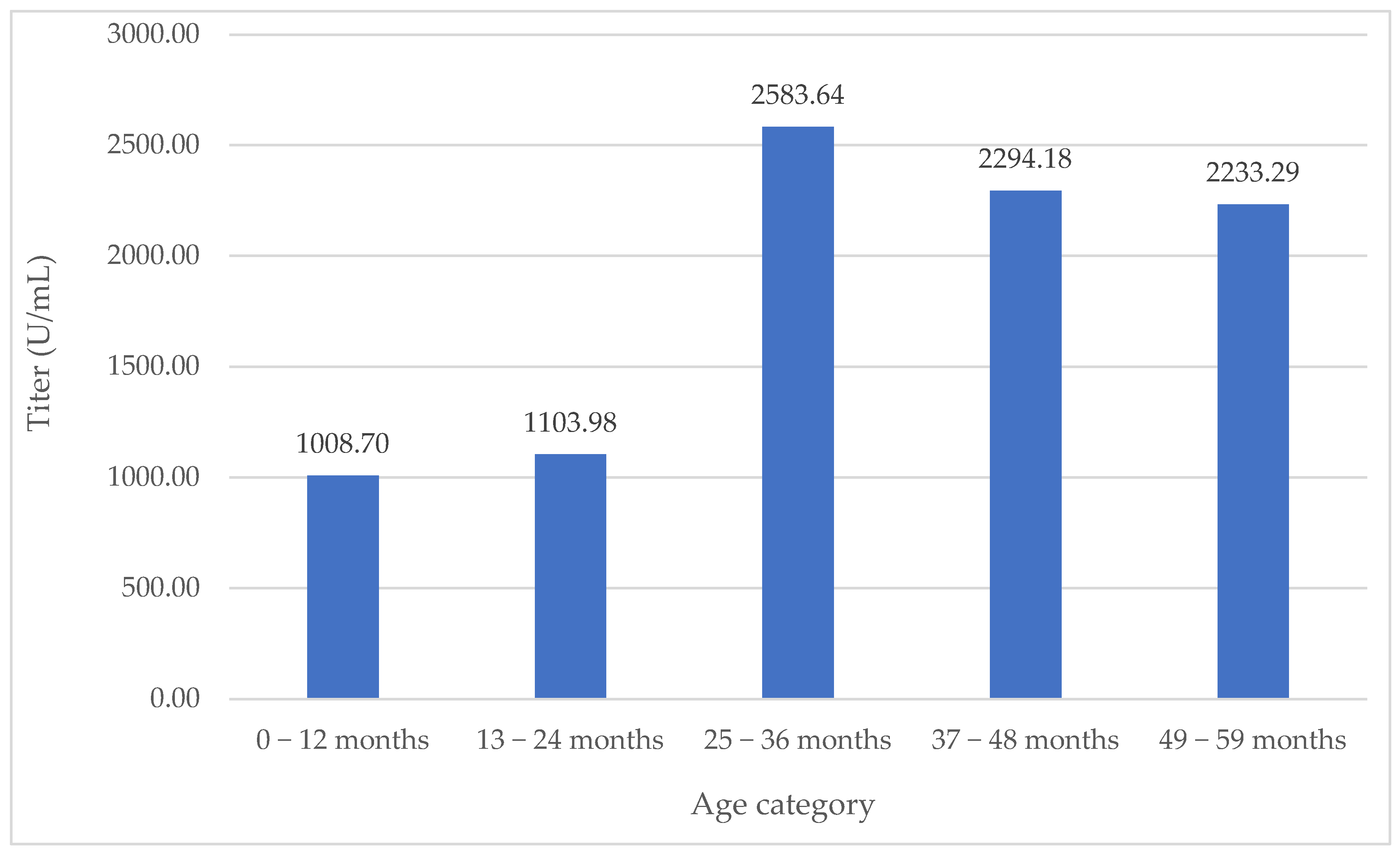
| Statistic Parameters | Age (Months) | Titer (U/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 22.64 | 1558.01 | |
| Std. Error of Mean | 0.60 | 167.77 | |
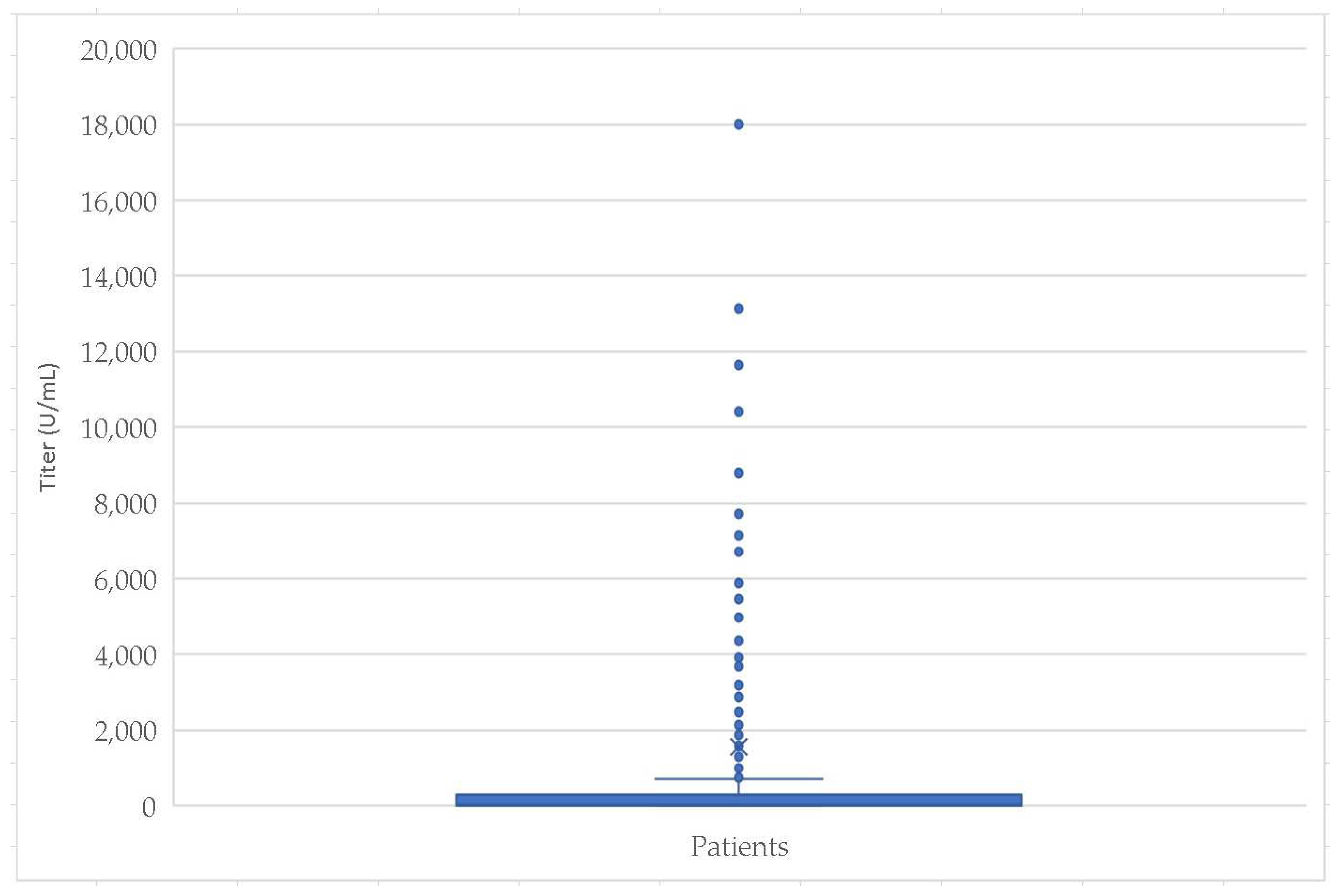
| Median | 21.00 | 22.90 | |
| Std. Deviation | 16.32 | 4573.00 | |
| Range | 57.80 | 18,000.00 | |
| Minimum | 0.20 | 0.00 | |
| Maximum | 58.00 | 18,000.00 | |
| Percentiles | 25 | 9.00 | 6.91 |
| 50 | 21.00 | 22.90 | |
| 75 | 36.00 | 297.10 | |
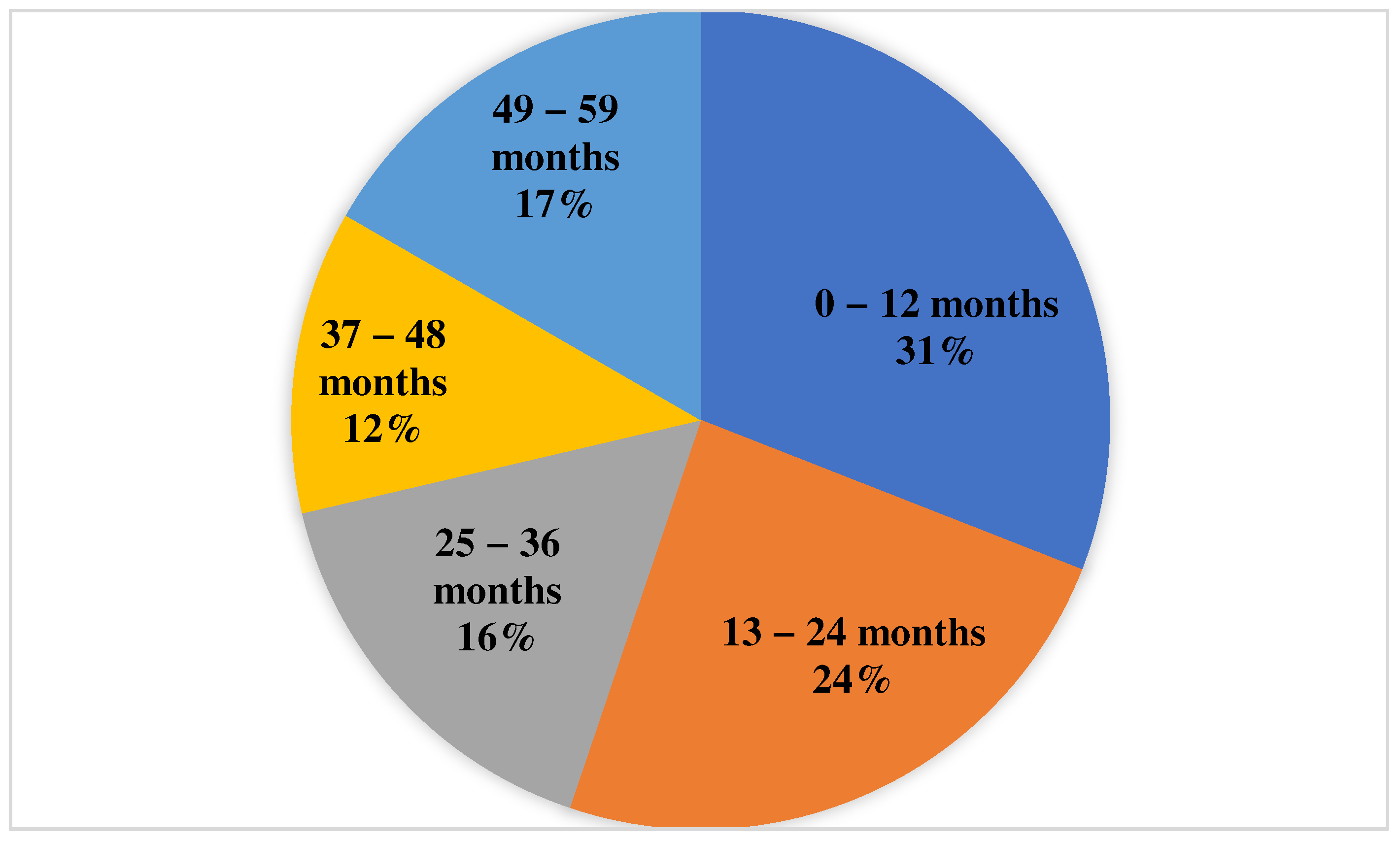
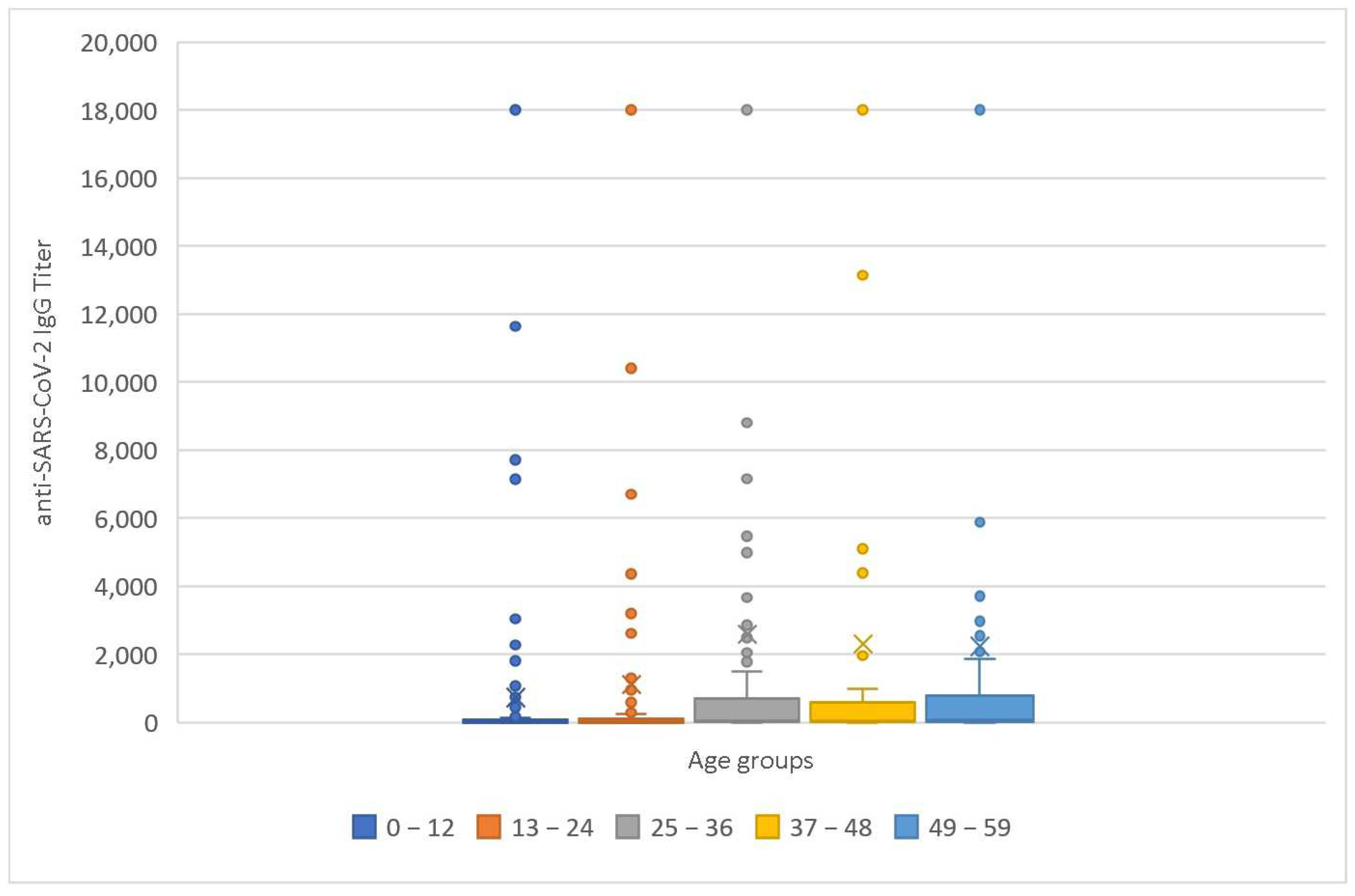
| Age Group (Months) | Sample Size (Patients) | Mean IgG Titer (U/mL) | Median IgG Titer (U/mL) | Mean Age (Months) | Median Age (Months) | Males | Emergency | Admission to ICU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–12 | 230 | 1008.70 | 12.18 | 5.76 | 6 | 51.74% | 38.7% | 7.4% |
| 13–24 | 180 | 1103.98 | 11.47 | 16.91 | 16 | 56.11% | 42.35% | 4.4% |
| 25–36 | 120 | 2583.64 | 62.21 | 30 | 30 | 55.83% | 37.5% | 5% |
| 37–48 | 89 | 2294.18 | 54.8 | 42 | 42 | 57.3% | 43.8% | 0% |
| 49–59 | 124 | 2233.29 | 63.5 | 54 | 54 | 58.87 | 41.94% | 0.8% |
| Parameters | Seroprevalence | Ab Titer |
|---|---|---|
| Age | p < 0.001 | p = 0.001 |
| Age Group | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Gender | p = 0.675 | p = 0.337 |
| Diagnosis | p = 0.692 | p = 0.743 |
| Parameters | Age | Age Group | Diagnosis | Gender |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Seroprevalence | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.692 | p = 0.675 |
| Parameters | Seroprevalence | Ab Titer | Emergency Room Admission | ICU Admission |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | p = 0.337 | p = 0.330 | p = 0.729 | p = 0.729 |
| Results | Seroprevalence | Study Period | Sample Size | Geographical Area | Age (Years) | Mean Titer | Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Ab Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our study | 52.76% | 1 August 2022–15 September 2023 | 743 | Romania | 0–5 | 1559.01 U/mL | anti-S |
| Sapronova et al. (2023) [34] | 77.80% | March–July 2022 | 81 | Latvia | <5 | anti-N and anti-S | |
| Naeimi et al. (2022) [35] | 11.01% | December 2021–July 2022 | 42,889 | Review | <5 | NA | |
| Franczak et al. (2022) [36] | 57% (69% being < 5 y) | 1 June 2021–30 April 2022 | 272 | Poland | <18 | 539.85 (BAU/mL) | anti-S |
| Clarke et al. (2023) [37] | 68% | February 2022 | 6096 | USA | 1–4 | anti-N | |
| Asseri et al. (2022) [7] | 36% | 1 October 2021–30 November 2021 | 246 | Saudi Arabia | 1–5 | NA | |
| O’Brien et al. (2022) [38] | 39% | 12 May 2021–13 July 2021 | 254 | USA | 1–4 | anti-N and anti-S | |
| Zinszer et al. (2021) [26] | 4.82% | 22 October 2020–22 March 2021 | 1632 | Canada | 2–4 | anti-S | |
| Elton et al. (2023) [39] | 21% | 11 January 2021–14 March 2021 | 871 | Switzerland | 0–5 | anti-S | |
| Comar et al. (2021) [27] | 9.50% | 5 January 2021–31 January 2021 | 169 | Italy | <18 | 482.3 ± 387.1 BAU/mL | anti-S |
| Cavalcante Pinto Junior et al. (2021) [29] | 22.70% | 9 November 2020–9 December 2020 | 423 | Brazil | <9 | anti-N | |
| Torres et al. (2020) [40] | 12.30% | 4 May 2020–19 May 2020 | 1009 | Chile | <5 | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trofin, F.; Luncă, C.; Păduraru, D.; Anton-Păduraru, D.-T.; Buzilă, E.R.; Nastase, E.V.; Lupu, A.; Lupu, V.V.; Dorneanu, O.S. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in Children under 5 Years Old—A Regional Seroepidemiological Study. Medicina 2024, 60, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60030384
Trofin F, Luncă C, Păduraru D, Anton-Păduraru D-T, Buzilă ER, Nastase EV, Lupu A, Lupu VV, Dorneanu OS. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in Children under 5 Years Old—A Regional Seroepidemiological Study. Medicina. 2024; 60(3):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60030384
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrofin, Felicia, Cătălina Luncă, Diana Păduraru, Dana-Teodora Anton-Păduraru, Elena Roxana Buzilă, Eduard Vasile Nastase, Ancuta Lupu, Vasile Valeriu Lupu, and Olivia Simona Dorneanu. 2024. "SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in Children under 5 Years Old—A Regional Seroepidemiological Study" Medicina 60, no. 3: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60030384
APA StyleTrofin, F., Luncă, C., Păduraru, D., Anton-Păduraru, D.-T., Buzilă, E. R., Nastase, E. V., Lupu, A., Lupu, V. V., & Dorneanu, O. S. (2024). SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in Children under 5 Years Old—A Regional Seroepidemiological Study. Medicina, 60(3), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60030384









