Impact of Polydeoxyribonucleotides on the Morphology, Viability, and Osteogenic Differentiation of Gingiva-Derived Stem Cell Spheroids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Utilizing Gingiva-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
2.2. Stem Cell Spheroid Fabrication
2.3. Assessment of Qualitative and Quantitative Cell Viability
2.4. Levels of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity and Calcium Deposition
2.5. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction for RUNX2 and COL1A1
2.6. Isolation, Library Preparation, Sequencing, and Data Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
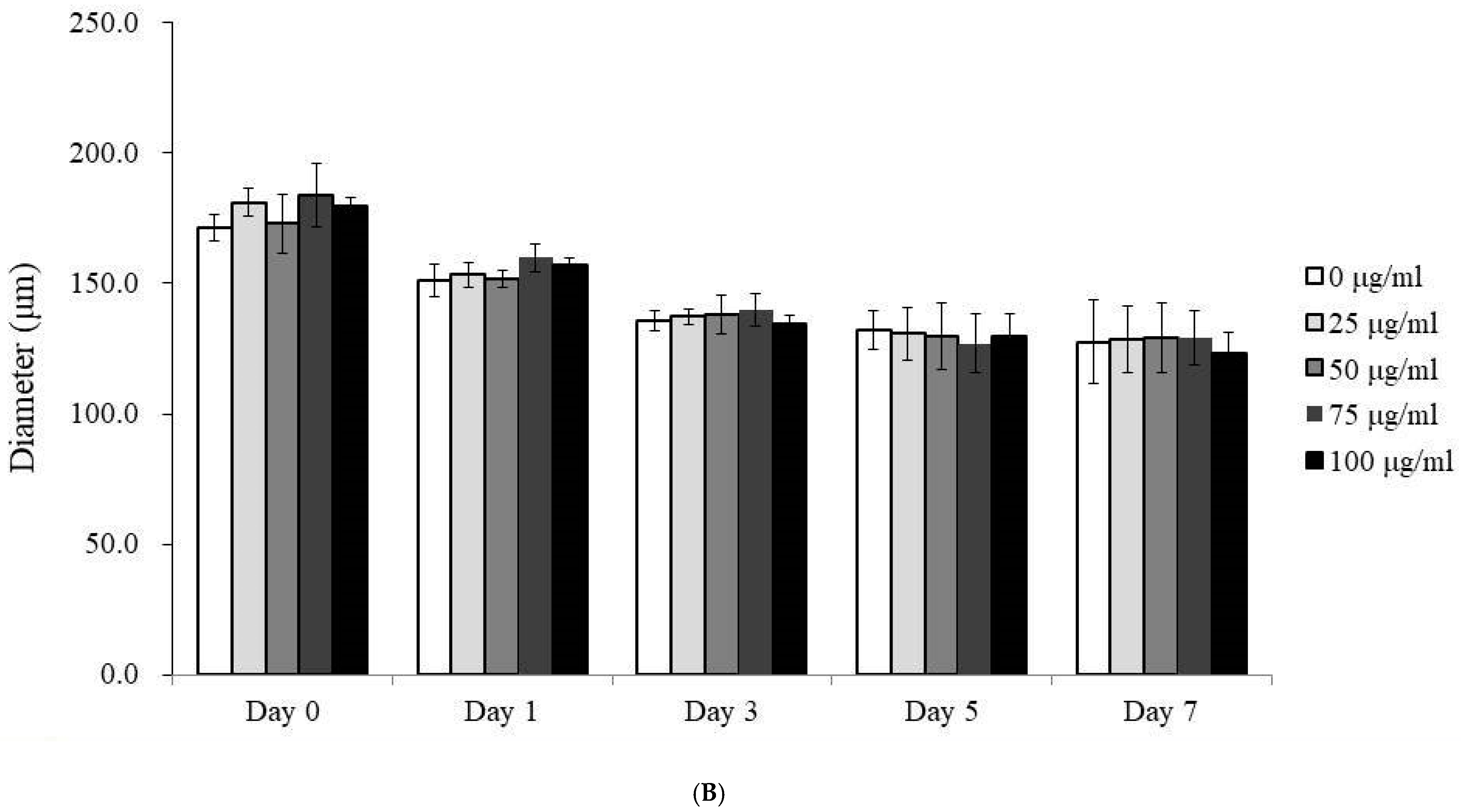
3.1. Morphological Analysis of Human Gingiva-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids
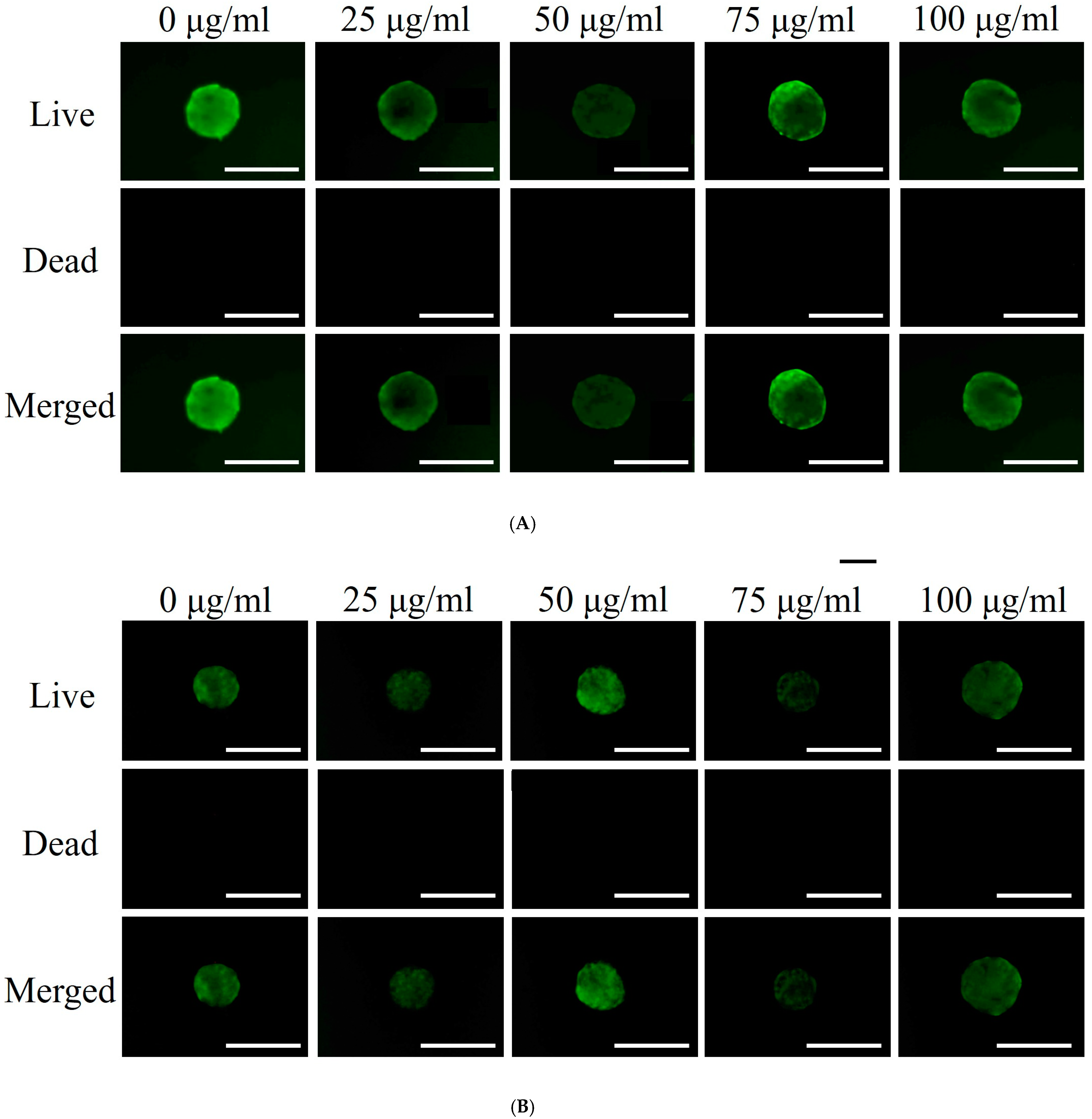
3.2. Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of Cell Viability
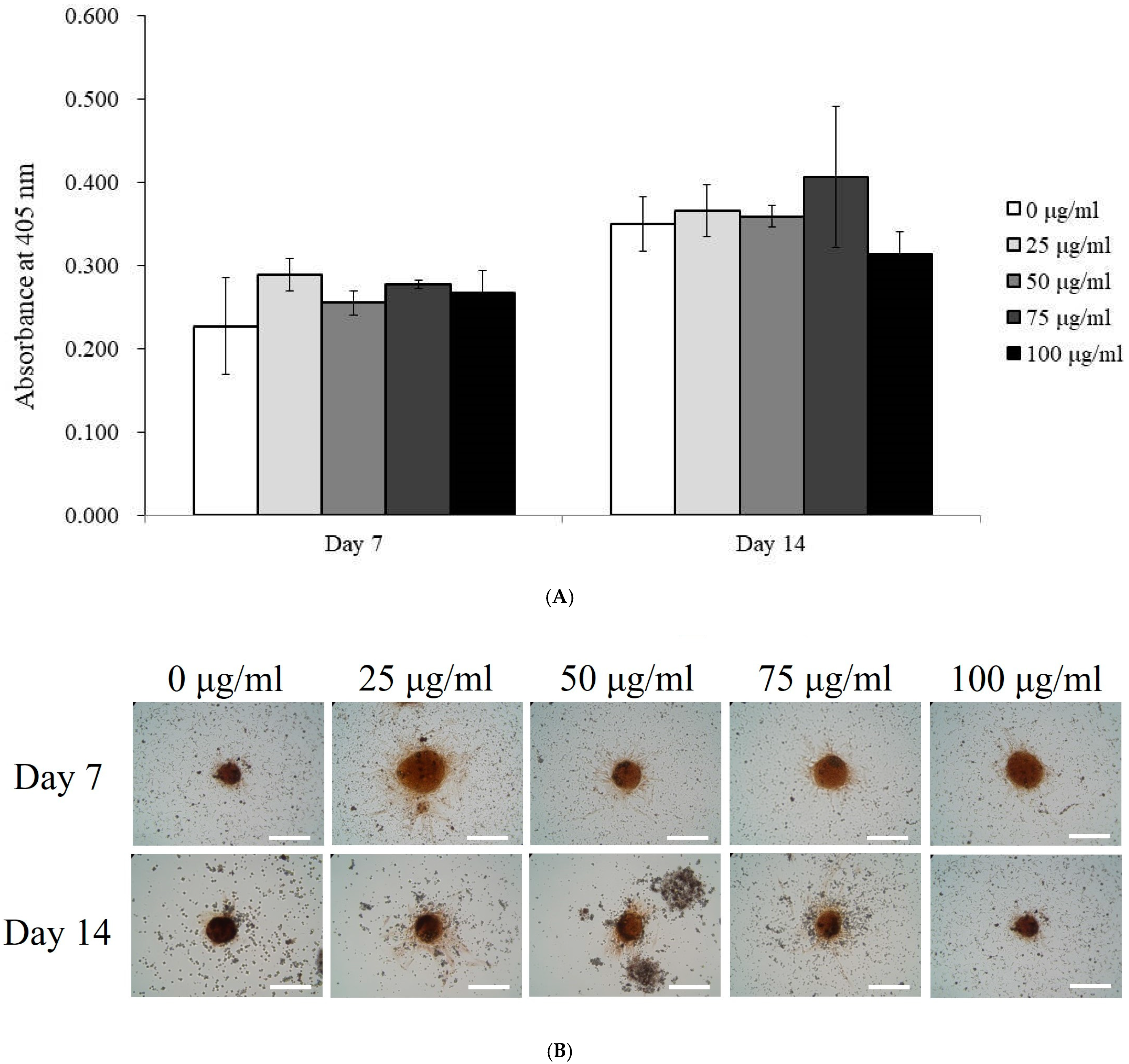
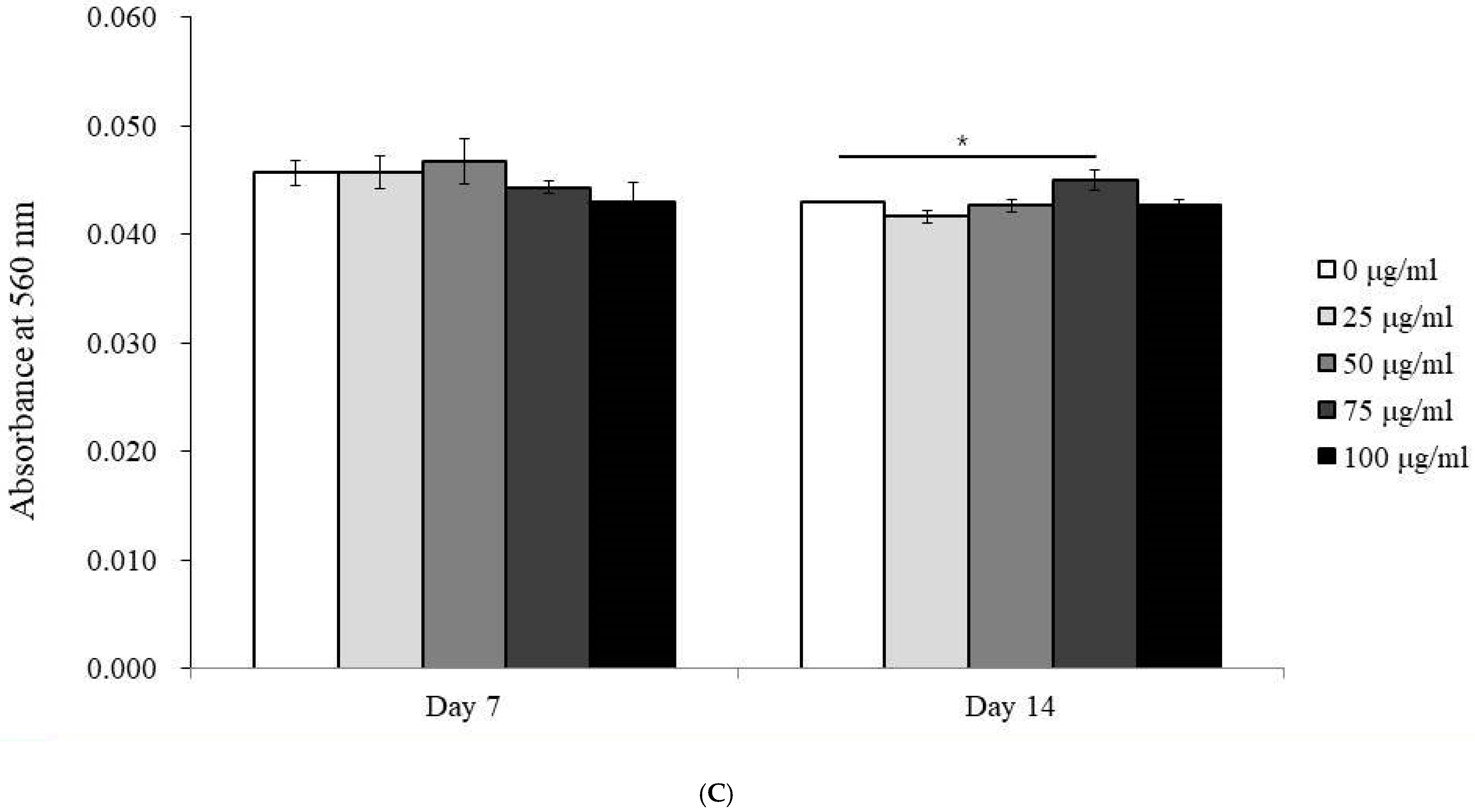
3.3. Alkaline Phosphatase Activity and Calcium Deposition
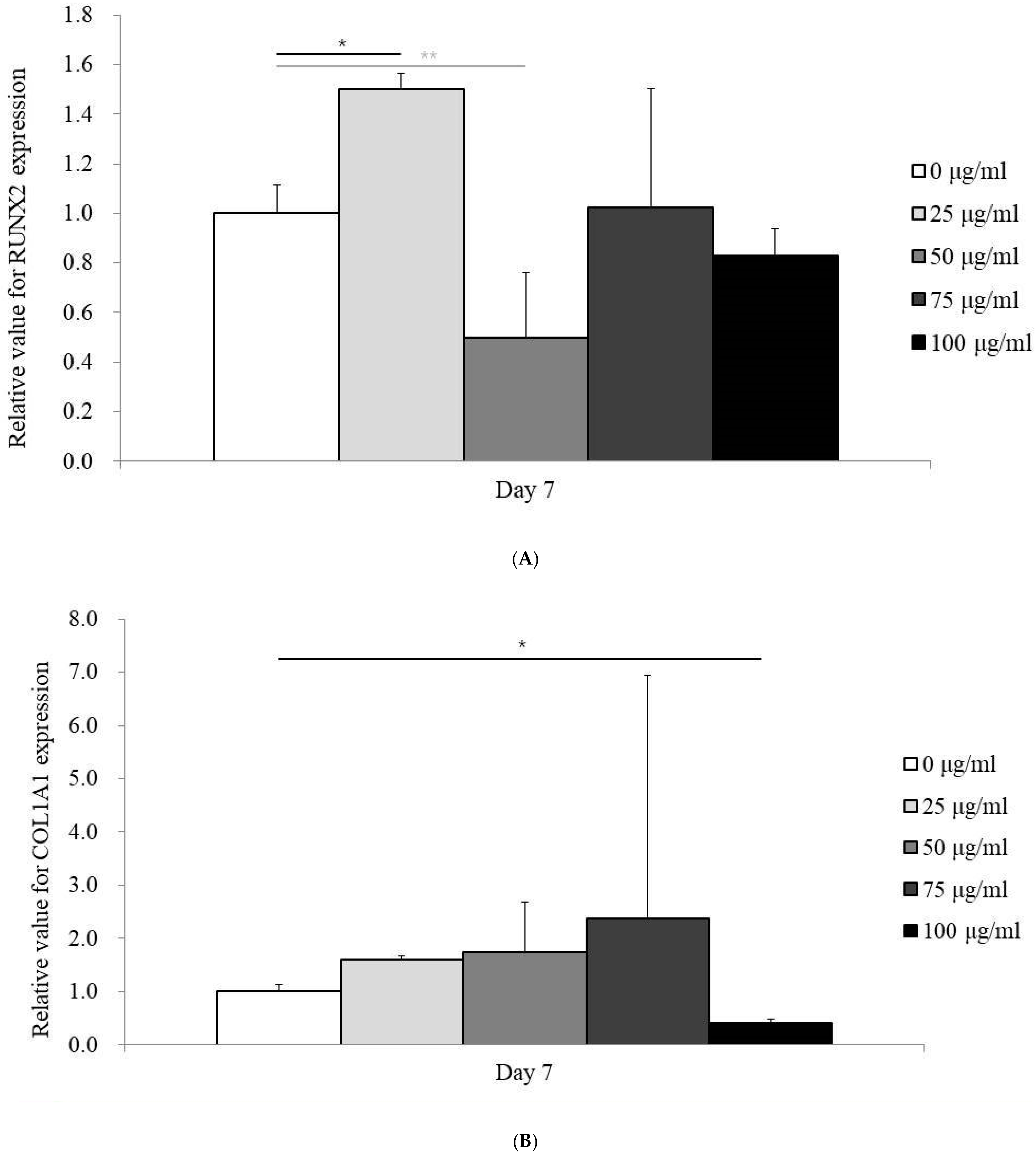
3.4. Expression of RUNX2 and COL1A1 mRNA by qPCR
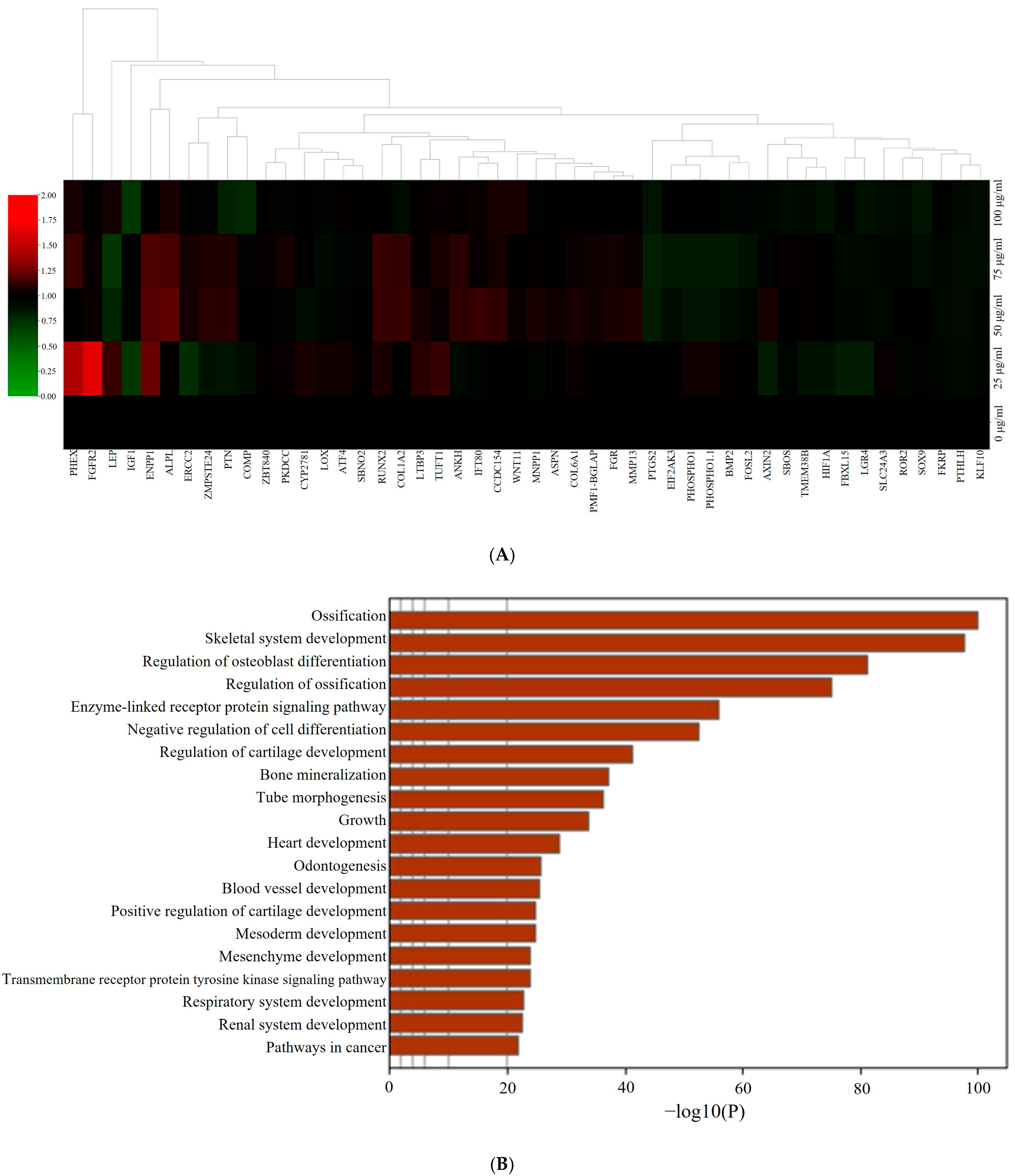
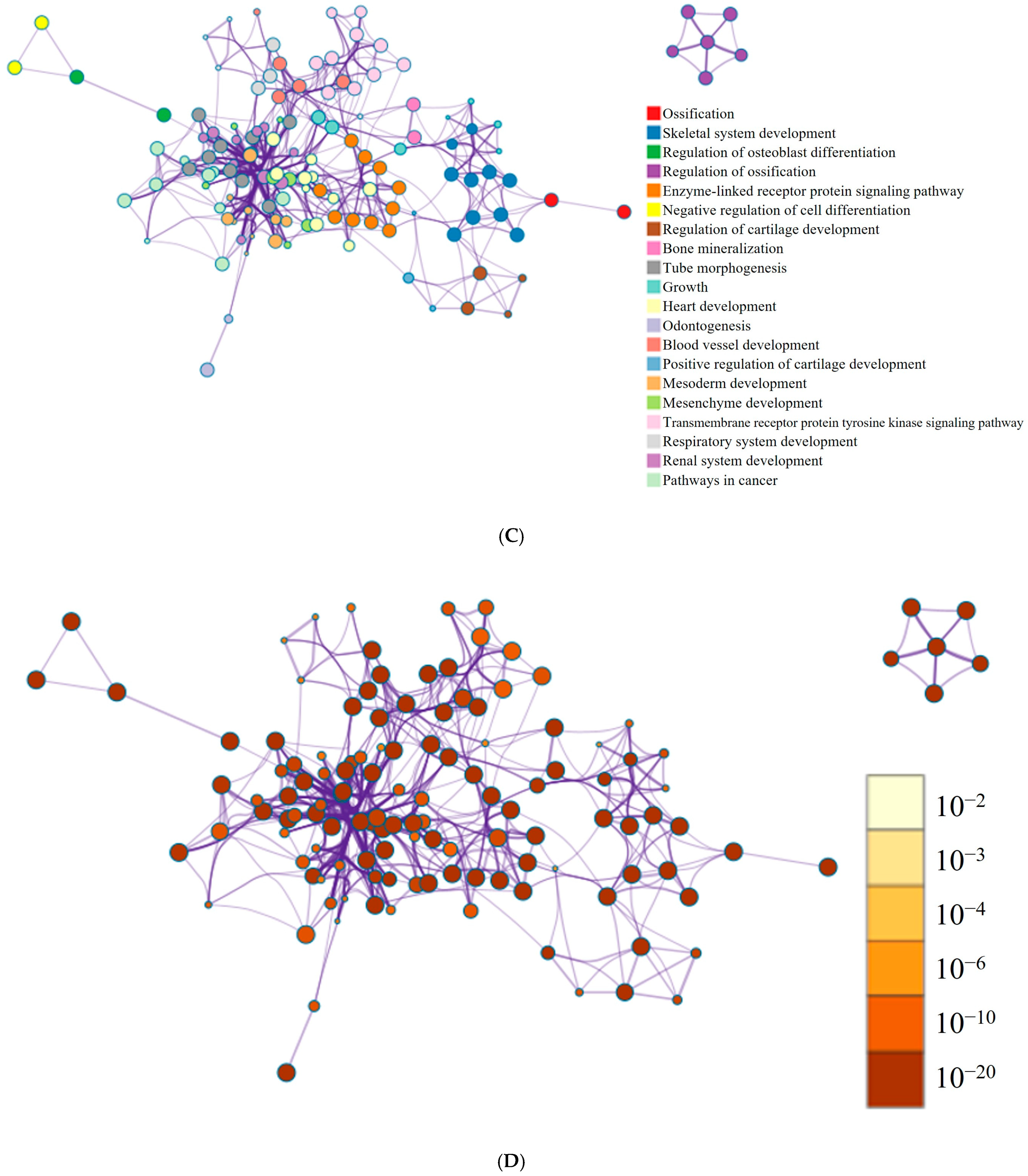
3.5. RNA Sequencing Data Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, T.H.; Heo, S.Y.; Oh, G.W.; Heo, S.J.; Jung, W.K. Applications of Marine Organism-Derived Polydeoxyribonucleotide: Its Potential in Biomedical Engineering. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Wang, G.; Zhou, F.; Gong, L.; Zhang, J.; Qi, L.; Cui, H. Polydeoxyribonucleotide: A promising skin anti-aging agent. Chin. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 4, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.M.; Baek, E.J.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, K.J.; Park, E.J. Polydeoxyribonucleotide exerts opposing effects on ERK activity in human skin keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Mol. Med. Rep. 2023, 28, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeano, M.; Pallio, G.; Irrera, N.; Mannino, F.; Bitto, A.; Altavilla, D.; Vaccaro, M.; Squadrito, G.; Arcoraci, V.; Colonna, M.R.; et al. Polydeoxyribonucleotide: A Promising Biological Platform to Accelerate Impaired Skin Wound Healing. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A.; Polito, F.; Marini, H.; Minutoli, L.; Di Stefano, V.; Irrera, N.; Cattarini, G.; Squadrito, F. Polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN): A safe approach to induce therapeutic angiogenesis in peripheral artery occlusive disease and in diabetic foot ulcers. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 7, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squadrito, F.; Bitto, A.; Irrera, N.; Pizzino, G.; Pallio, G.; Minutoli, L.; Altavilla, D. Pharmacological Activity and Clinical Use of PDRN. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.R.; Han, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, B.C.; Kim, J.M.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, B.J. Polydeoxyribonucleotides Improve Diabetic Wound Healing in Mouse Animal Model for Experimental Validation. Ann. Dermatol. 2019, 31, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squadrito, F.; Bitto, A.; Altavilla, D.; Arcoraci, V.; De Caridi, G.; De Feo, M.E.; Corrao, S.; Pallio, G.; Sterrantino, C.; Minutoli, L.; et al. The effect of PDRN, an adenosine receptor A2A agonist, on the healing of chronic diabetic foot ulcers: Results of a clinical trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E746–E753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Byun, K.A.; Oh, S.; Yang, J.Y.; Park, H.J.; Chung, M.S.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. A Mixture of Topical Forms of Polydeoxyribonucleotide, Vitamin C, and Niacinamide Attenuated Skin Pigmentation and Increased Skin Elasticity by Modulating Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-like 2. Molecules 2022, 27, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, M.; Poli, P.P.; Beretta, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Salina, F.E.; Maiorana, C. Polydeoxyribonucleotides Pre-Clinical Findings in Bone Healing: A Scoping Review. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Huh, C.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, M.Y. Histologic study of bone-forming capacity on polydeoxyribonucleotide combined with demineralized dentin matrix. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 38, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Galfo, F.; Oteri, G.; Atteritano, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; D’Amore, A.; Pellegrino, E.; Aliquò, F.; et al. Adenosine Receptor Stimulation Improves Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis in a Rat Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.H.; Jung, J.; Hwang, L.; Ko, I.G.; Nam, O.H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, B.J.; Lee, D.W. Anti-inflammatory effect of polydeoxyribonucleotide on zoledronic acid-pretreated and lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Hyun, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, G.T.; Um, S.; Hong, S.O.; Chun, H.J.; Yang, D.H. The Effect of Polydeoxyribonucleotide Extracted from Salmon Sperm on the Restoration of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciolo, G.; Mannino, F.; Irrera, N.; Altavilla, D.; Minutoli, L.; Vaccaro, M.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, V.; Picciolo, G.; Squadrito, F.; et al. PDRN, a natural bioactive compound, blunts inflammation and positively reprograms healing genes in an “in vitro” model of oral mucositis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.C.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, H.K.; Jeon, G.; Herr, Y.; Chung, J.H. Effect of polydeoxyribonucleotide with xenogeneic collagen matrix on gingival phenotype modification: A pilot preclinical study. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2023, 53, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, J.B. Dimethyl Sulfoxide Leads to Decreased Osteogenic Differentiation of Stem Cells Derived from Gingiva via Runx2 and Collagen I Expression. Eur. J. Dent. 2019, 13, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Shin, K.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, M.Y.; Oh, D.B.; Lim, Y.T. In Situ-Forming Collagen/poly-γ-glutamic Acid Hydrogel System with Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 for Bone Tissue Regeneration in a Mouse Calvarial Bone Defect Model. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 19, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, C.; Qiu, K.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, D. Exosomes Derived from Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Facilitate Diabetic Wound Healing by Angiogenesis and Enrich Multiple lncRNAs. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 20, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Lee, S.H. MMP13-Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhance Bone Tissue Formation in the Presence of Collagen Hydrogel. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 20, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Tae, J.Y.; Min, S.K.; Ko, Y.; Park, J.B. Fibroblast growth factor-4 maintains cellular viability while enhancing osteogenic differentiation of stem cell spheroids in part by regulating RUNX2 and BGLAP expression. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehiamin, M.; Toolee, H.; Azami, M.; Tafti, S.H.A.; Mojaverrostami, S.; Halimi, S.; Barakzai, S.; Sobhani, A.; Abbasi, Y. Chitosan Scaffold Containing Periostin Enhances Sternum Bone Healing and Decreases Serum Level of TNF-α and IL-6 after Sternotomy in Rat. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 19, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Pachter, L.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.; Trapnell, C.; Donaghey, J.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Improving RNA-Seq expression estimates by correcting for fragment bias. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, F.; Zeng, C.; Gu, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, W.; Wu, Y.; Shen, H. RNA Sequencing Reveals the Expression Profiles of circRNAs and Indicates Hsa_circ_0070562 as a Pro-osteogenic Factor in Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 947120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Seo, S.; Hong, H.K.; Yoon, S.J.; Kim, M.; Moon, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Lim, J.; Lee, J.B.; Woo, S.J. Therapeutic Extracellular Vesicles from Tonsil-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Retinal Degenerative Disease. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 20, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, J.; Koo, K.T.; Seol, Y.J.; Lee, Y.M. The impact of polydeoxyribonucleotide on early bone formation in lateral-window sinus floor elevation with simultaneous implant placement. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2023, 53, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, L.; Ko, I.G.; Jin, J.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, C.J.; Hwang, J.J.; Choi, C.W.; Chang, B.S. Attenuation effect of polydeoxyribonucleotide on inflammatory cytokines and apoptotic factors induced by particulate matter (PM10) damage in human bronchial cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, L.; Jin, J.J.; Ko, I.G.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.A.; Sung, J.S.; Choi, C.W.; Chang, B.S. Polydeoxyribonucleotide Attenuates Airway Inflammation Through A2AR Signaling Pathway in PM10-Exposed Mice. Int. Neurourol. J. 2021, 25, S19–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswamy, R.; Patro, B.P.; Jeyaraman, N.; Gangadaran, P.; Rajendran, R.L.; Nallakumarasamy, A.; Jeyaraman, M.; Ramani, P.; Ahn, B.C. Evolution and Clinical Advances of Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Musculoskeletal Regeneration. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeano, M.; Bitto, A.; Altavilla, D.; Minutoli, L.; Polito, F.; Calò, M.; Lo Cascio, P.; Stagno d’Alcontres, F.; Squadrito, F. Polydeoxyribonucleotide stimulates angiogenesis and wound healing in the genetically diabetic mouse. Wound Repair Regen. Off. Publ. Wound Heal. Soc. Eur. Tissue Repair Soc. 2008, 16, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guizzardi, S.; Galli, C.; Govoni, P.; Boratto, R.; Cattarini, G.; Martini, D.; Belletti, S.; Scandroglio, R. Polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) promotes human osteoblast proliferation: A new proposal for bone tissue repair. Life Sci. 2003, 73, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, J.K.; Jung, J.W.; Baek, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Heo, Y.; Kim, T.H.; Han, D.K. Promotion of Bone Regeneration Using Bioinspired PLGA/MH/ECM Scaffold Combined with Bioactive PDRN. Materials 2021, 14, 4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.M.; Lee, E.H. Transcriptional regulatory cascades in Runx2-dependent bone development. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2013, 19, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimalraj, S.; Arumugam, B.; Miranda, P.J.; Selvamurugan, N. Runx2: Structure, function, and phosphorylation in osteoblast differentiation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devos, H.; Zoidakis, J.; Roubelakis, M.G.; Latosinska, A.; Vlahou, A. Reviewing the Regulators of COL1A1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, J.C.; Forlino, A.; Bächinger, H.P.; Bishop, N.J.; Byers, P.H.; Paepe, A.; Fassier, F.; Fratzl-Zelman, N.; Kozloff, K.M.; Krakow, D.; et al. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.S.; An, S.; Park, S.B.; Kim, T.H.; Rim, J.S.; Lee, S.; et al. Advanced PLGA hybrid scaffold with a bioactive PDRN/BMP2 nanocomplex for angiogenesis and bone regeneration using human fetal MSCs. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabj1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.K.; Kwon, Y.J.; Hong, S.J.; Choi, H.G.; Chung, S.M.; Yang, B.E.; Lee, J.H.; Byun, S.H. Bone regeneration in ceramic scaffolds with variable concentrations of PDRN and rhBMP-2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dananjaya, S.H.S.; Madushani, K.G.P.; Dilrukshi, J.; De Silva, N.D.; Sandamalika, W.M.G.; Kim, D.; Choi, D.; De Zoysa, M.; Attanayake, A.P. Development and characterization of polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) loaded chitosan polyplex: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of wound healing activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.B.; Kim, I.; Lee, W.; Kim, H. Evaluation of the regenerative capacity of stem cells combined with bone graft material and collagen matrix using a rabbit calvarial defect model. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2023, 53, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.S.; Jeong, M.H.; Jin, Y.J.; Na, M.H.; Sim, D.S.; Kim, M.; Cho, K.H.; Hyun, D.Y.; Oh, S.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of an Everolimus-Eluting Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffold Via a Long-Term Rabbit Iliac Artery Model. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 20, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Hwa, S.; Cho, S.; Kim, J.-H.; Song, H.-J.; Ko, Y.; Park, J.-B. Impact of Polydeoxyribonucleotides on the Morphology, Viability, and Osteogenic Differentiation of Gingiva-Derived Stem Cell Spheroids. Medicina 2024, 60, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60101610
Lee H, Hwa S, Cho S, Kim J-H, Song H-J, Ko Y, Park J-B. Impact of Polydeoxyribonucleotides on the Morphology, Viability, and Osteogenic Differentiation of Gingiva-Derived Stem Cell Spheroids. Medicina. 2024; 60(10):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60101610
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Heera, Somyeong Hwa, Sunga Cho, Ju-Hwan Kim, Hye-Jung Song, Youngkyung Ko, and Jun-Beom Park. 2024. "Impact of Polydeoxyribonucleotides on the Morphology, Viability, and Osteogenic Differentiation of Gingiva-Derived Stem Cell Spheroids" Medicina 60, no. 10: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60101610
APA StyleLee, H., Hwa, S., Cho, S., Kim, J.-H., Song, H.-J., Ko, Y., & Park, J.-B. (2024). Impact of Polydeoxyribonucleotides on the Morphology, Viability, and Osteogenic Differentiation of Gingiva-Derived Stem Cell Spheroids. Medicina, 60(10), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60101610






