Post-COVID-19 Spondylodiscitis: A Case Study and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
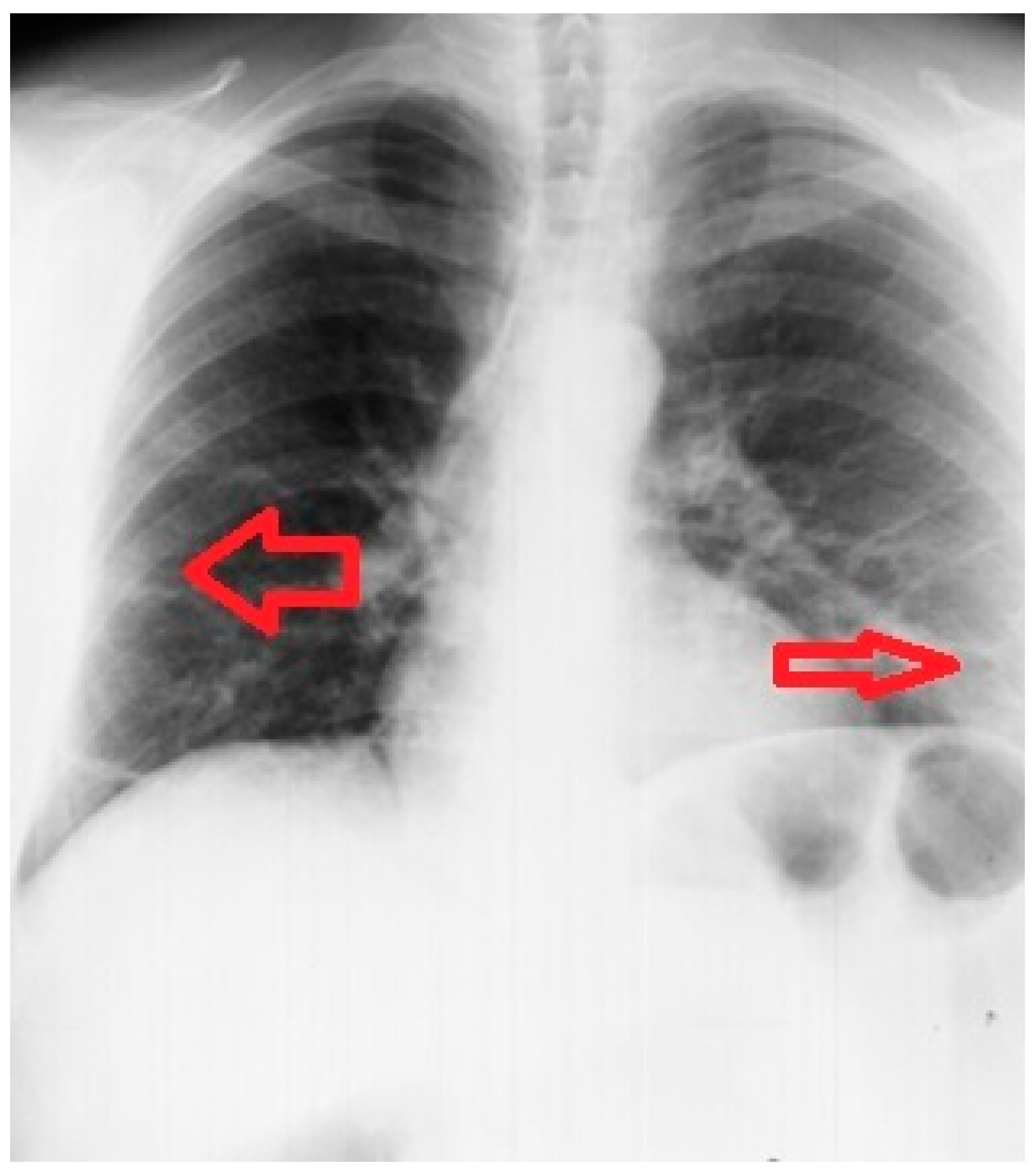
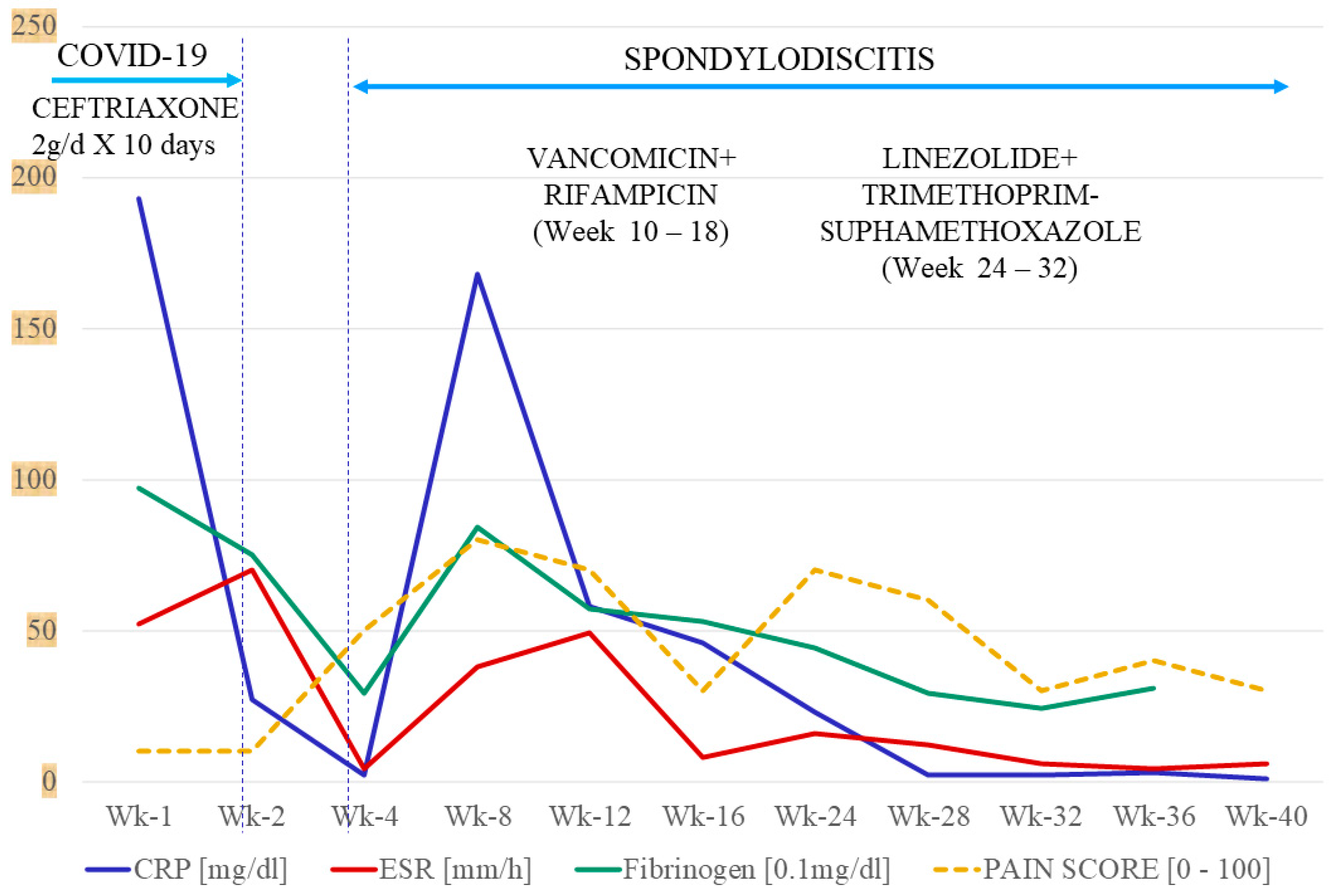
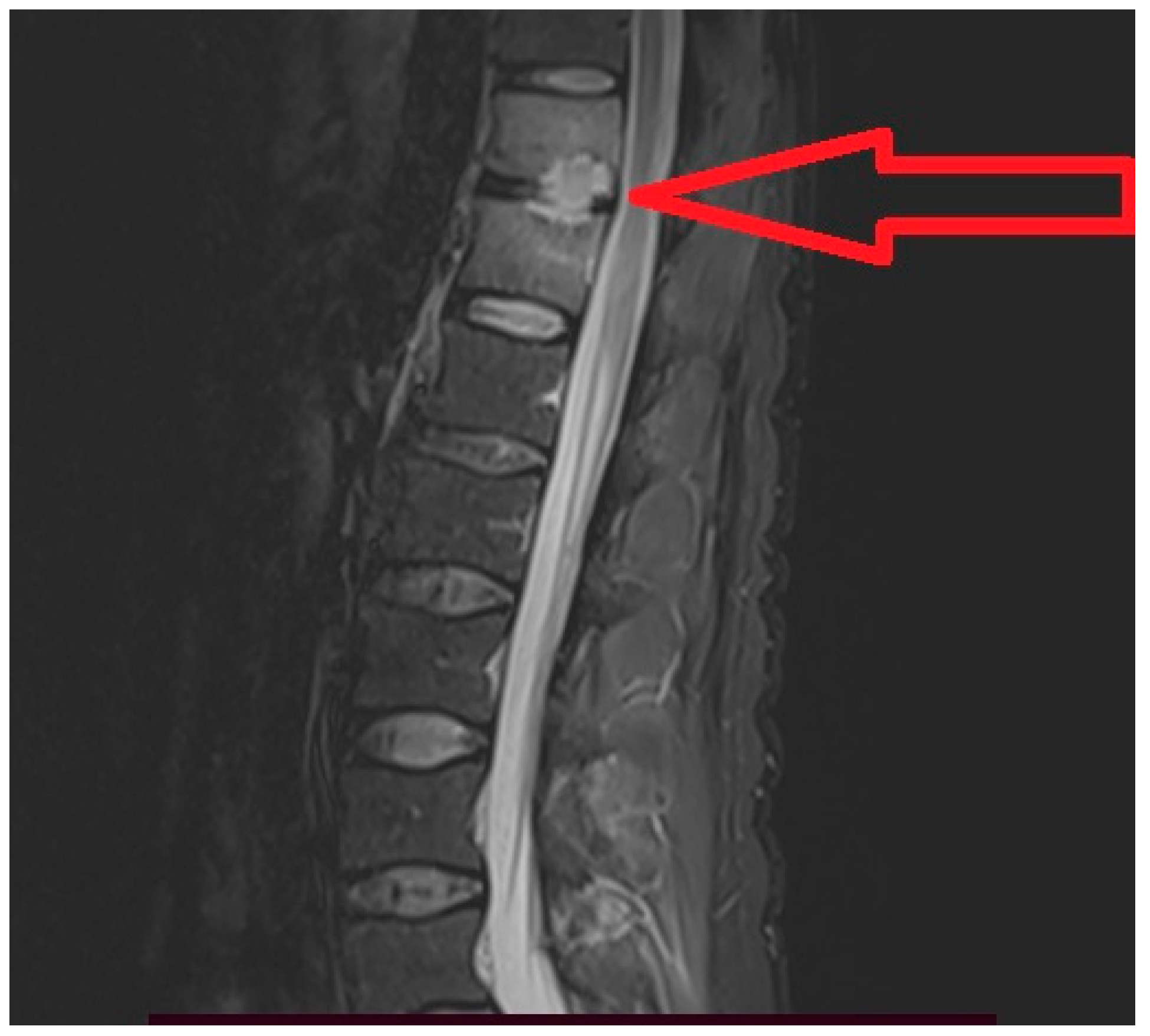
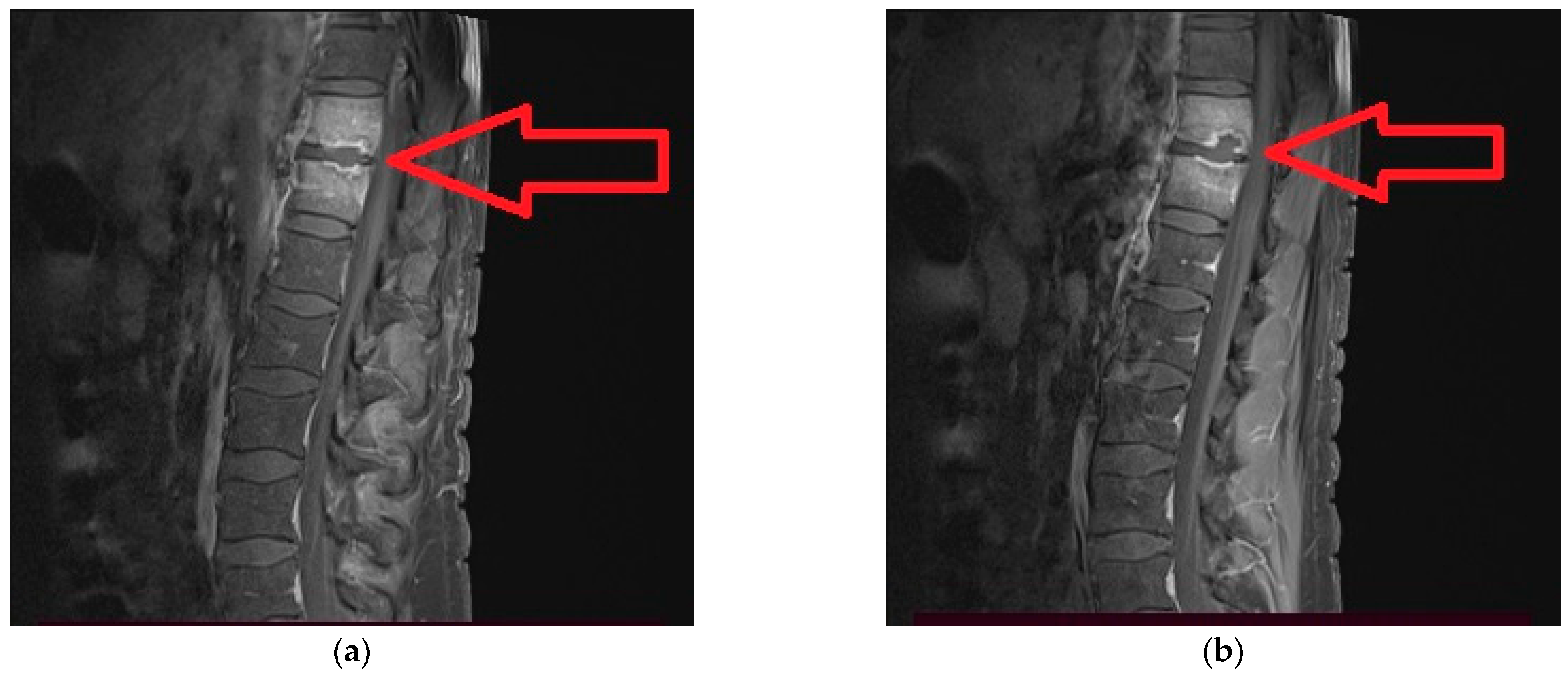
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
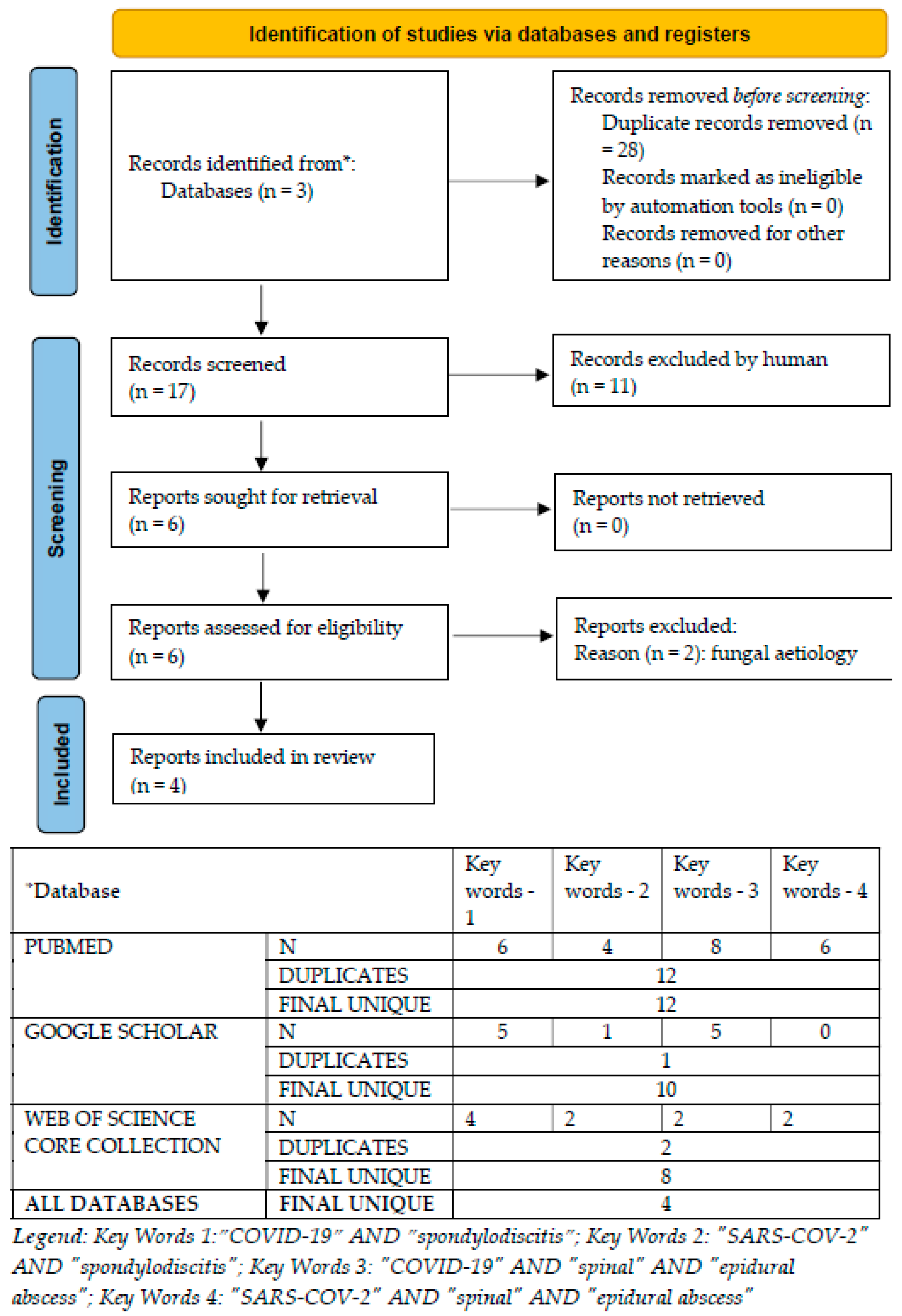
3.1. Systematic Review of Medical Databases
3.2. Particularities of the Reported Case
3.3. Hypothesis of the Linkage between COVID-19 and Spondylodiscitis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Blood Tests | NRV | H-Day1 | H-Day2 | H-Day7 | H-Day 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT [U/L] | 0–50 | 119 | 95 | 289 | 307 |
| AST [U/L] | 14–59 | 98 | 48 | 151 | 72 |
| CK [U/L] | 30–170 | 43 | 27 | 29 | 24 |
| CREATININE [mg/dL] | 0.5–1.25 | 0.98 | 0.81 | 0.95 | 0.85 |
| UREA [mg/dL] | 15/42.9 | 43 | 33.3 | 39.2 | 39.6 |
| GLUCOSE [mg/dL] | 74/106 | 103 | 92 | 67 | 83 |
| LDH [U/L] | 313/618 U/L | 197 | 300 | 236 | |
| CRP [mg/dL] | 0–1 | 193 | 27 | 7 | |
| ESR [mm/h] | 2–10 | 52 | 70 | 18 | |
| Ferritin [ng/mL] | 17.9–464 | 1170 | |||
| FIBRINOGEN [mg/dL] | 200–400 | 967 | 753 | 461 | |
| LEUKOCYTES [/µL] | 4000–10,000 | 16,700 | 16,400 | 10,000 | 12,000 |
| NEUTROPHIL [/µL] | 2000–7000 | 15480.9 | 15793.2 | 8610 | 9180 |
| LYMPHOCYTE [/µL] | 700–5000 | 467.6 | 300.07 | 880 | 1200 |
| Ratio N/Ly | 1–3 | 33.10 | 52.63 | 9.78 | 7.65 |
| Blood Tests | NRV | Wk-4 | Wk-6 | Wk-8 | Wk-10 | Wk-12 | Wk-18 | Wk-24 | Wk-26 | Wk-28 | Wk-32 | Wk-36 | Wk-40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT [U/L] | 0–50 | 419 | 91 | 45 | 157 | 31 | 19 | 17 | 110 | 31 | 29 | ||
| AST [U/L] | 14–59 | 118 | 34 | 27 | 45 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 39 | 22 | 20 | ||
| CK [U/L] | 30–170 | 48 | 29 | 53 | 97 | 142 | 86 | 149 | |||||
| CREATININE [mg/dL] | 0.5–1.25 | 1.05 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 1.15 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 1.02 | |||
| UREA [mg/dL] | 15/42.9 | 36 | 33 | 22 | 27 | 30 | 32 | 35 | 37 | 36 | |||
| GLUCOSE [mg/dL] | 74/106 | 103 | 89 | 92 | 92 | 107 | 99 | 86 | 96 | 102 | 92 | ||
| LDH [U/L] | 313/618 U/L | 482 | 326 | 551 | 236 | 220 | 349 | 310 | 323 | 388 | |||
| CRP [mg/dL] | 0–1 | 2 | 168 | 34 | 52 | 46 | 22 | 16.8 | 3.24 | 1.07 | |||
| ESR [mm/h] | 2–10 | 4 | 5 | 38 | 52 | 49 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 6 | 4 | 6 | |
| Ferritin [ng/mL] | 17.9–464 | 713 | 545 | 331 | 249 | 199 | 164 | 306 | 136 | 106 | |||
| FIBRINOGEN [mg/dL] | 200–400 | 287 | 967 | 842 | 720 | 562 | 264 | 532 | 436 | 290 | 235 | 308 | |
| LEUKOCYTES [/µL] | 4000–10,000 | 3900 | 10,540 | 20550 | 12,000 | 7300 | 4200 | 7800 | 6600 | 9800 | 6000 | 4600 | 5300 |
| NEUTROPHIL [/µL] | 2000–7000 | 2300 | 7910 | 17520 | 9180 | 5730 | 2580 | 6290 | 5030 | 7830 | 4770 | 3100 | 3500 |
| LYMPHOCYTE [/µL] | 700–5000 | 880 | 1460 | 1550 | 1200 | 1050 | 1140 | 1000 | 1010 | 1240 | 780 | 1110 | 1300 |
| Ratio N/Ly | 1–3 | 2.61 | 5.41 | 11.30 | 7.65 | 5.45 | 2.26 | 6.29 | 4.98 | 6.31 | 6.11 | 2.79 | 2.69 |
References
- World Health Organization. Clinical Management of COVID-19: Living Guideline, 15 September Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022 (WHO/2019-nCoV/Clinical/2022.2). Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-clinical-2023.1 (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Carsana, L.; Sonzogni, A.; Nasr, A.; Rossi, R.S.; Pellegrinelli, A.; Zerbi, P.; Rech, R.; Colombo, R.; Antinori, S.; Corbellino, M.; et al. Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a series of COVID-19 cases from northern Italy: A two-centre descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Geng, X.; Tan, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, C.; Xu, J.; Hao, L.; Zeng, Z.; Luo, X.; Liu, F.; et al. New understanding of the damage of SARS-CoV-2 infection outside the respiratory system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodigiani, C.; Iapichino, G.; Carenzo, L.; Cecconi, M.; Ferrazzi, P.; Sebastian, T.; Kucher, N.; Studt, J.-D.; Sacco, C.; Bertuzzi, A.; et al. Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; He, W.; Yu, X.; Hu, D.; Bao, M.; Liu, H.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, H. Coronavirus disease 2019 in elderly patients: Characteristics and prognostic factors based on 4-week follow-up. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, M.-C.; Arbune, A.-A.; Lupasteanu, G.; Vlase, C.-M.; Popovici, G.-C.; Arbune, M. Epidemiologic and Clinic Characteristics of the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Hospitalized Patients from Galați County. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention. The novel coronavirus pneumonia emergency response epidemiology team: Vital Surveillances: The epidemiological characteristcs of an outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus diseases (COVID-19)-China. China CDC Weekly 2020, 2, 113–122.u. [Google Scholar]
- Taquet, M.; Geddes, J.R.; Husain, M.; Luciano, S.; Harrison, P.J. 6-month neurological and psychiatric outcomes in 236 379 survivors of COVID-19: A retrospectve cohort study using electronic health records. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelin, D.; Moschopoulos, C.D.; Margalit, I.; Gkrania-Klotsas, E.; Landi, F.; Stahl, J.-P.; Yahav, D. ESCMID rapid guidelines for assessment and management of long COVID. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 955–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, A.; Tsang, K.; Brown, M.; Tzerakis, N. Management of adult spontaneous spondylodiscitis and its rising incidence. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2015, 97, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lener, S.; Hartmann, S.; Barbagallo, G.M.V.; Certo, F.; Thomé, C.; Tschugg, A. Management of spinal infection: A review of the literature. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogenis, A.F.; Megaloikonomos, P.D.; Igoumenou, V.G.; Panagopoulos, G.N.; Giannitsioti, E.; Papadopoulos, A.; Papagelopoulos, P.J. Spondylodiscitis revisited. EFORT Open Rev. 2017, 2, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herren, C.; Jung, N.; Pishnamaz, M.; Breuninger, M.; Siewe, J.; Sobottke, R. Spondylodiscitis: Diagnosis and Treatment Options. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petkova, A.S.; Zhelyazkov, C.B.; Kitov, B.D. Spontaneous Spondylodiscitis—Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Treatment. Folia Medica 2017, 59, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pojskić, M.; Carl, B.; Schmöckel, V.; Völlger, B.; Nimsky, C.; Saβ, B. Neurosurgical Management and Outcome Parameters in 237 Patients with Spondylodiscitis. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homagk, L.; Marmelstein, D.; Homagk, N.; Hofmann, G.O. SponDT (Spondylodiscitis Diagnosis and Treatment): Spondylodiscitis scoring system. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2019, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsantes, A.G.; Papadopoulos, D.V.; Vrioni, G.; Sioutis, S.; Sapkas, G.; Benzakour, A.; Benzakour, T.; Angelini, A.; Ruggieri, P.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; et al. Spinal Infections: An Update. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başak, A.T.; Çakıcı, N.; Özbek, M.A.; Hekimoğlu, M.; Çerezci, Ç.; Ates, O.; Oktenoglu, T.; Sasani, M.; Özer, A.F. A Combined Diagnosis and Treatment Algorithm for Spine Infection Management: A Single-Center Experience. Cureus 2022, 14, e28251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algrmi, S.E.A.; Youssef, M.M.M.T.; Fattah, I.M.A.; Elsayed, E.M. Management of Patients with Spondylodiscitis: An Overview. Eur. J. Mol. Clin. Med. 2021, 8, 3023–3034. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzeri, E.; Bozzao, A.; Cataldo, M.A.; Petrosillo, N.; Manfrè, L.; Trampuz, A.; Signore, A.; Muto, M. Joint EANM/ESNR and ESCMID-endorsed consensus document for the diagnosis of spine infection (spondylodiscitis) in adults. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 46, 2464–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gerven, C.; Eid, K.; Krüger, T.; Fell, M.; Kendoff, D.; Friedrich, M.; Kraft, C.N. Serum C-reactive protein and WBC count in conservatively and operatively managed bacterial spondylodiscitis. J. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharfman, Z.T.; Gelfand, Y.; Shah, P.; Holtzman, A.J.; Mendelis, J.R.; Kinon, M.D.; Krystal, J.D.; Brook, A.; Yassari, R.; Kramer, D.C. Spinal Epidural Abscess: A Review of Presentation, Management, and Medicolegal Implications. Asian Spine J. 2020, 14, 742–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolinsky, D.C.; Liang, S.Y. Musculoskeletal Infections in the Emergency Department. Emerg. Med. Clin. North Am. 2018, 36, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prayag, P.S.; Purandare, B.D.; Patwardhan, S.A.; Pairaiturkar, P.P.; Rege, A.J.; Bhave, A.V.; Ramya, S.; Panchakshari, S.P.; Raja, P.T.; Melinkeri, A.S.; et al. COVID-19 Associated Vertebral Osteomyelitis Caused by Aspergillus Species—A Case Series. Indian J. Orthop. 2022, 56, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gómez, L.M.; Esteban-Sinovas, O.; García-Pérez, D.; García-Posadas, G.; Delgado-Fernández, J.; Paredes, I. Case Report: SARS-CoV-2 Infection—Are We Redeemed? A Report of Candida Spondylodiscitis as a Late Complication. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talamonti, G.; Colistra, D.; Crisà, F.; Cenzato, M.; Giorgi, P.; D’Aliberti, G. Spinal epidural abscess in COVID-19 patients. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 2320–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erok, B.; Kıbıcı, K. COVID-19 Infection Manifesting with Lumbar Spondylodiscitis Complicating with Psoas Abscess without Pneumonia. Indian J. Neurosurg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, S. COVID-19 Infection Leading to Lethal Spondylodiscitis with Spinal Abscess. Iran. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 6, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlee, F.A.M.; Bin Harun, M.H.; Nagaretnam, V.; Lim, T.S.; Aris, H.F.; Tan, C.N. A Case Series of Spinal Infections Following COVID-19: A Delayed Complication. Cureus 2022, 14, e29272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point Prevalence Survey of Healthcareassociated Infections and Antimicrobial Use in European Acute Care Hospitals—Protocol Version 6; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Sharma, G.; Singla, S.; Garg, S. Case Report: Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (sHLH) and Candida auris Fungemia in Post-acute COVID-19 Syndrome: A Clinical Challenge. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 835421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, G.; Mahmood, K.; Gul, H.; Tariq, M.; Ain, Q.U.; Hayat, A.; Rehman, M.U. Pathophysiology of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Superinfection in COVID-19 Patients. Pathophysiology 2022, 29, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.E.; Fenoll, R.G.; Bayo, S.M.; Álvarez, R.M.M.; Millán, V.F.; Usón, M.C.V.; Ruiz, M.P.P.; Mainar, J.M.A.; Jiménez, M.C.M.; Paesa, C.R. Impact of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in COVID-19 patients. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2022, 35, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoop, N.; Zijlstra, H.; Ponds, N.H.; Wolterbeek, N.; Delawi, D.; Kempen, D.H. Long-term quality of life outcome after spondylodiscitis treatment. Spine J. 2021, 21, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalia, G.; Umana, G.E.; Marrone, S.; Graziano, F.; Giuffrida, A.; Ponzo, G.; Giuffrida, M.; Furnari, M.; Galvano, G.; Nicoletti, G.F.; et al. Spontaneous anterior cervicothoracic spinal epidural hematoma extending to clivus in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, T.A.; Andreoni, F.; Acevedo, C.; Scheier, T.C.; Heggli, I.; Maggio, E.M.; Eberhard, N.; Brugger, S.D.; Dudli, S.; Zinkernagel, A.S. Intervertebral disc cell chondroptosis elicits neutrophil response in Staphylococcus aureus spondylodiscitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 908211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, E.; Wubben, R.; Isaza-Correa, J.M.; Melo, A.M.; Mhaonaigh, A.U.; Conlon, N.; O’Donnell, J.S.; Cheallaigh, C.N.; Hurley, T.; Stevenson, N.J.; et al. Neutrophils in COVID-19: Not Innocent Bystanders. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No | Gender | Age | Co-Morbidities | COVID-19 IST | Time Since COV | Fever | HC | Aetiology | Anatomic Site | Antibiotic | Surgery | Evolution | Dx Support | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 48 | AHT Obesity | Tocilizumab HC | Conc. (ICU) | yes | neg | MSSA | Ab T1-T7 | According ABG | Yes | Improve | MRI Ab + culture | Talamonti G, 2021 [27] |
| 2 | M | 47 | AHT Obesity | Tocilizumab Corticosteroid | Conc. (ICU) | no | poz | MSSA | Ab C4-C6 | According ABG | Yes | Improve | MRI Ab + culture | Talamonti G, 2021 [27] |
| 3 | M | 55 | Lymphoma AHT, MI | Tocilizumab | Conc. (ICU) | no | neg | MSSA | Ab C5-T1 | According ABG | Yes | Improve | MRI Ab + culture | Talamonti G, 2021 [27] |
| 4 | M | 56 | AHT, Venous Thrombosis | No | NA | no | neg | MSSA | Ab C1-2; Ab C7-T1 | According ABG | Yes | Pulmonary infarction; deteriorate | MRI Ab + culture | Talamonti G, 2021 [27] |
| 5 | F | 57 | Anaemia | No | NA | no | poz | MSSA | Ab T12-L5 | According ABG | Yes | Improve | MRI Ab + culture | Talamonti G, 2021 [27] |
| 6 | F | 78 | AHT, Obesity, Diabetes | No | NA | no | neg | MSSA | Ab T7-12 | According ABG | Yes | Improve | MRI Ab + culture | Talamonti G, 2021 [27] |
| 7 | F | 60 | No | No | 10 w | no | poz | MSSA | SD L4-5; Ab L3-2 | Pip/Taz; Cefazolin; Cloxacillin * | Yes | Improve | MRI | Ramlee M, 2022 [30] |
| 8 | M | 69 | IC, Bone metastases, prostate cancer | No | 12 w | no | neg | UN | SD L3-4-5 | Ceftriaxone | Yes | Improve | MRI | Ramlee M, 2022 [30] |
| 9 | F | 24 | No | No | 12 w | no | neg | TB | SD T2-7 | HRZE | Yes | Improve | MRI, HP exam | Ramlee M, 2022 [30] |
| 10 | M | 43 | No | No | Conc (ICU) | yes | neg | UN | SD L3-4 Psoas abscess | NA | Yes | Improve | MRI | Erok B, 2021 [28] |
| 11 | M | 71 | No | HC | Conc (ICU) | yes | neg | UN | Multiple SD and Ab | Meronem + Vancomycin | Yes | MSOF Death | MRI | Naderi S, 2020 [29] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popovici, G.-C.; Georgescu, C.-V.; Arbune, A.-A.; Vasile, M.-C.; Olteanu, I.; Arbune, M. Post-COVID-19 Spondylodiscitis: A Case Study and Review of the Literature. Medicina 2023, 59, 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59030616
Popovici G-C, Georgescu C-V, Arbune A-A, Vasile M-C, Olteanu I, Arbune M. Post-COVID-19 Spondylodiscitis: A Case Study and Review of the Literature. Medicina. 2023; 59(3):616. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59030616
Chicago/Turabian StylePopovici, George-Cosmin, Costinela-Valerica Georgescu, Anca-Adriana Arbune, Mihaela-Camelia Vasile, Ionut Olteanu, and Manuela Arbune. 2023. "Post-COVID-19 Spondylodiscitis: A Case Study and Review of the Literature" Medicina 59, no. 3: 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59030616
APA StylePopovici, G.-C., Georgescu, C.-V., Arbune, A.-A., Vasile, M.-C., Olteanu, I., & Arbune, M. (2023). Post-COVID-19 Spondylodiscitis: A Case Study and Review of the Literature. Medicina, 59(3), 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59030616






