Initial Experience of Robot-Assisted Transabdominal Preperitoneal (TAPP) Inguinal Hernia Repair by a Single Surgeon in South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Statistics and Ethical Considerations
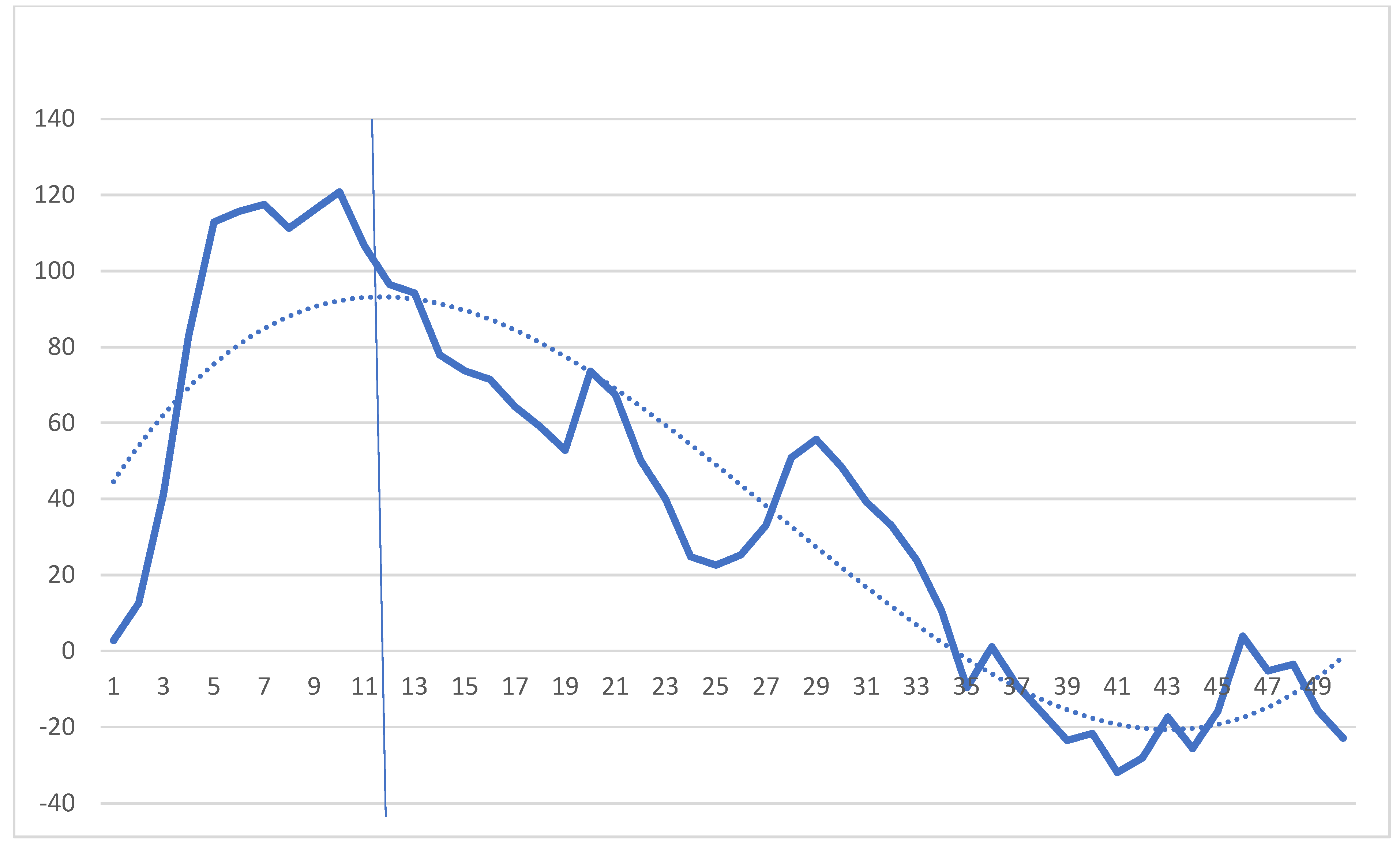
2.4. Cumulative Sum (CUSUM) Analysis
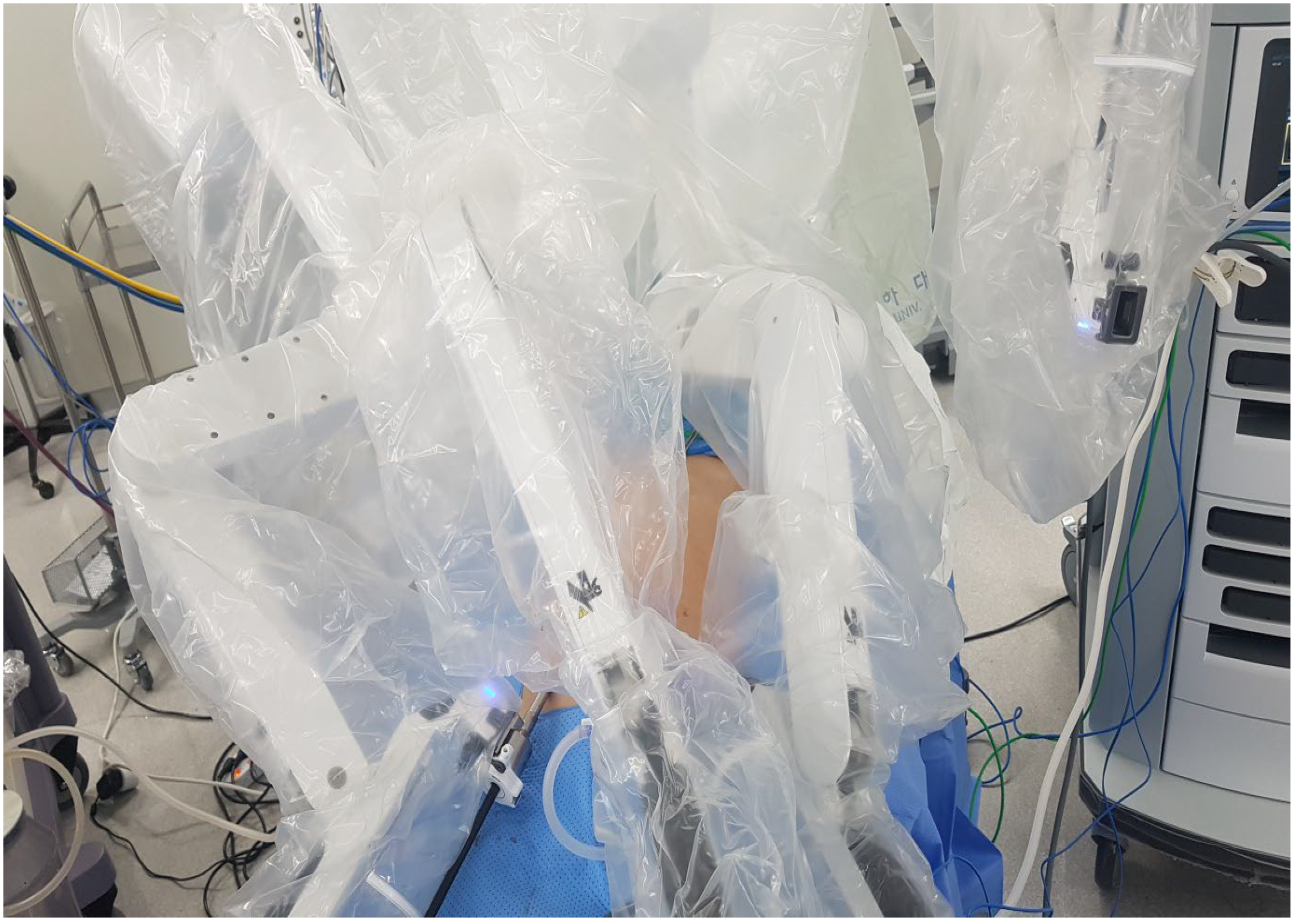
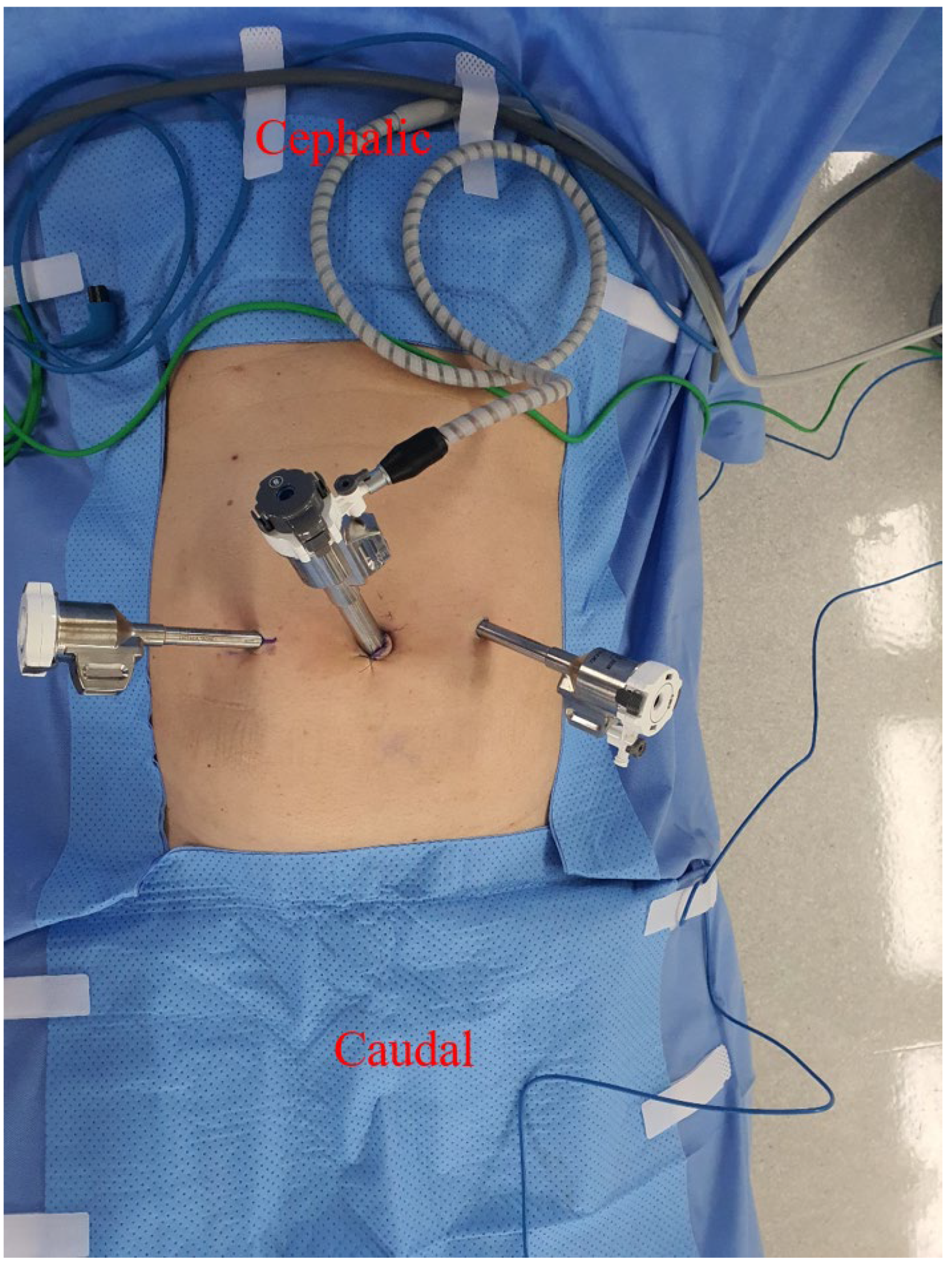
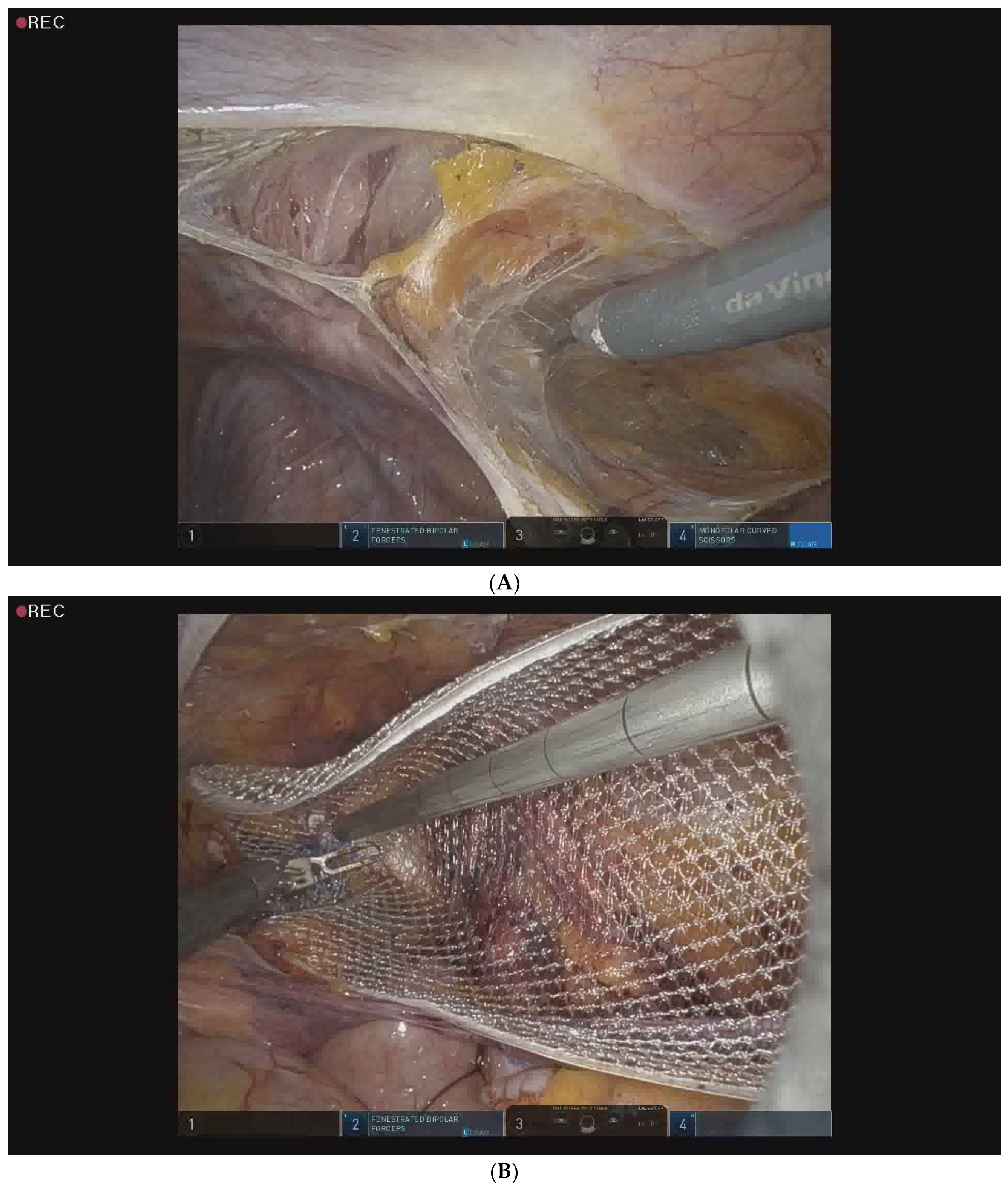
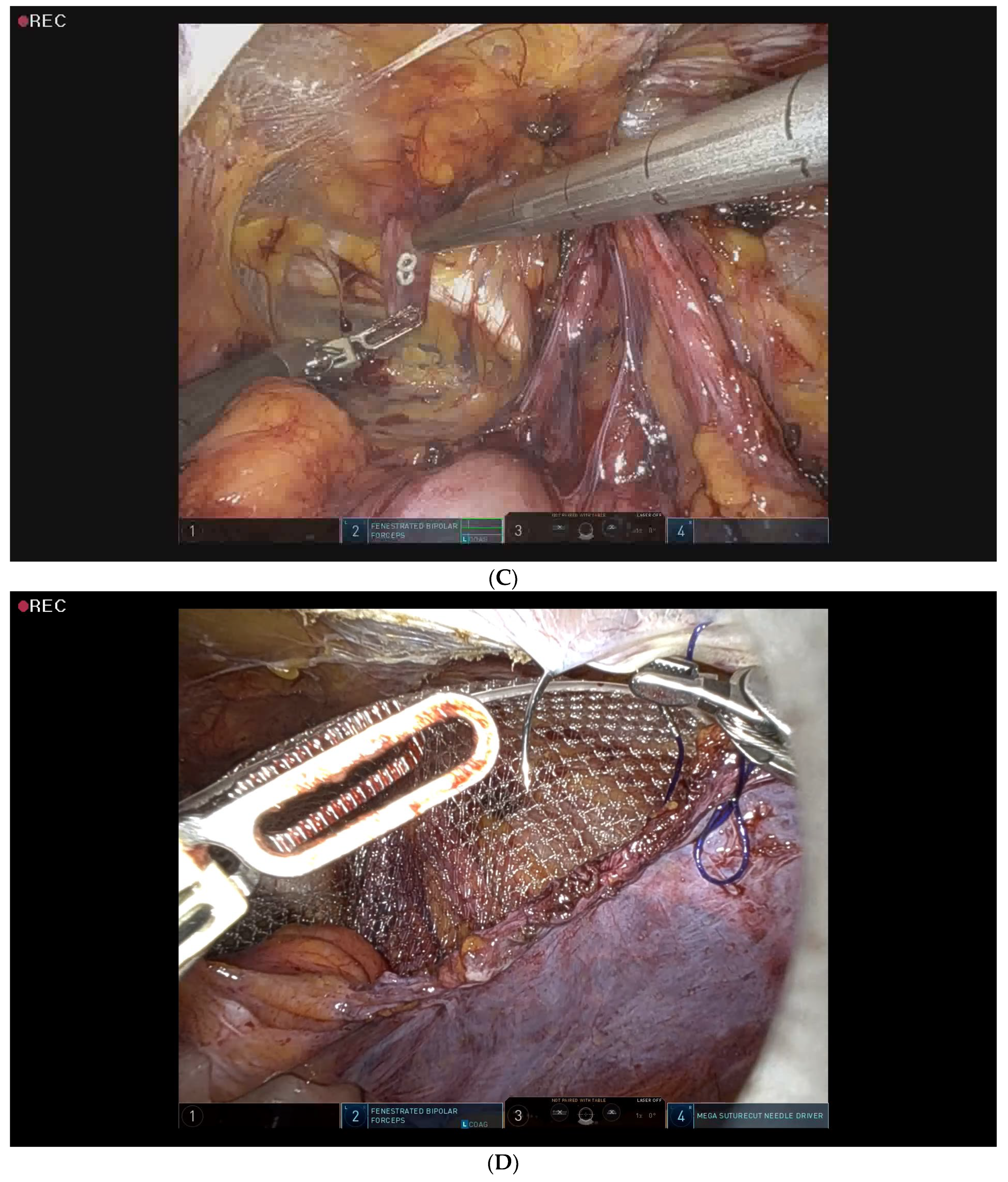
2.5. Surgical Procedure for Robotic-Assisted TAPP Inguinal Hernia Repair
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International guidelines for groin hernia management. Hernia 2018, 22, 1–165. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsnorth, A.; LeBlanc, K. Hernias: Inguinal and incisional. Lancet 2003, 362, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumpelick, V.; Treutner, K.H.; Arlt, G. Inguinal hernia repair in adults. Lancet 1994, 344, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.R.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, N.H.; Shin, S.; Yoo, R.N.; Kim, G.; Cho, H.M. Inguinal hernia surgery in Korea: Nationwide data from 2007–2015. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2019, 97, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. Korea Healthcare Bigdata Hub [Internet]; Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service: Wonju, Republic of Korea, 2021. Available online: http://opendata.hira.or.kr/ (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Ger, R. Laparoscopic hernia operation. Der Chirurg; Zeitschrift fur alle Gebiete der Operativen Medizen 1991, 62, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aiolfi, A.; Cavalli, M.; Micheletto, G.; Lombardo, F.; Bonitta, G.; Morlacchi, A.; Bruni, P.G.; Campanelli, G.; Bona, D. Primary inguinal hernia: Systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis comparing open, laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal, totally extraperitoneal, and robotic preperitoneal repair. Hernia 2019, 23, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirolla, E.H.; Patriota, G.P.; Pirolla, F.J.C.; Ribeiro, F.P.G.; Rodrigues, M.G.; Ismail, L.R.; Ruano, R.M. Inguinal Repair via Robotic Assisted Technique: Literature Review. Arq. Bras. Cir. Dig. ABCD Braz. Arch. Dig. Surg. 2018, 31, e1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiolfi, A.; Cavalli, M.; Micheletto, G.; Bruni, P.G.; Lombardo, F.; Perali, C.; Bonitta, G.; Bona, D. Robotic inguinal hernia repair: Is technology taking over? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Hernia 2019, 23, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Rai, B.P.; Stolzenburg, J.U.; Bose, P.; Chlosta, P.L.; Somani, B.K.; Nabi, G.; Qazi, H.A.; Rajbabu, K.; Kynaston, H.; et al. Robotic or open radical cystectomy, which is safer? A systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. J. Endourol. 2014, 28, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar Dominguez, J.E.; Ramos, M.G.; Seetharamaiah, R.; Donkor, C.; Rabaza, J.; Gonzalez, A. Feasibility of robotic inguinal hernia repair, a single-institution experience. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 4042–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo, R.J.; Robertson, J.C.; Alrajhi, S. First 101 Robotic General Surgery Cases in a Community Hospital. JSLS J. Soc. Laparoendosc. Surg. 2016, 20, e2016.00056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcerito, M.; Changchien, E.; Bernal, O.; Konkoly-Thege, A.; Moon, J. Robotic Inguinal Hernia Repair: Technique and Early Experience. Am. Surg. 2016, 82, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudsi, O.Y.; McCarty, J.C.; Paluvoi, N.; Mabardy, A.S. Transition from Laparoscopic Totally Extraperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair to Robotic Transabdominal Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair: A Retrospective Review of a Single Surgeon’s Experience. World J. Surg. 2017, 41, 2251–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar Dominguez, J.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Donkor, C. Robotic inguinal hernia repair. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 112, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qabbani, A.; Aboumarzouk, O.M.; ElBakry, T.; Al-Ansari, A.; Elakkad, M.S. Robotic inguinal hernia repair: Systematic review and meta-analysis. ANZ J. Surg. 2021, 91, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, A.L.G.; Morrell Junior, A.C.; Mendes, J.M.F.; Morrell, A.G.; Morrell, A. Robotic TAPP inguinal hernia repair: Lessons learned from 97 cases. Rev. Col. Bras. Cir. 2021, 48, e20202704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, A.S.; Carbonell, A.; Hope, W.; Warren, J.; Higgins, R.; Jacob, B.; Blatnik, J.; Haskins, I.; Alkhatib, H.; Tastaldi, L.; et al. Robotic Inguinal vs. Transabdominal Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair: The RIVAL Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Surg. 2020, 155, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarian, T.; Nie, L.; McPartland, C.; Brown, A.M.; Yang, J.; Altieri, M.S.; Spaniolas, K.; Docimo, S.; Pryor, A.D. Comparative perioperative and 5-year outcomes of robotic and laparoscopic or open inguinal hernia repair: A study of 153,727 patients in the state of New York. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 7209–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.; Rogers, D.E.; Al-Abbas, A.; Borrebach, J.; Dunn, S.A.; Zureikat, A.H.; Zeh, H.J., 3rd; Hogg, M.E. Robotic Inguinal Hernia Repair: A Large Health System’s Experience With the First 300 Cases and Review of the Literature. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 235, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudsi, O.Y.; Bou-Ayash, N.; Gokcal, F.; Crawford, A.S.; Chung, S.K.; Chudner, A.; Litwin, D. Learning curve of robot-assisted transabdominal preperitoneal (rTAPP) inguinal hernia repair: A cumulative sum (CUSUM) analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sánchez, M.; González-Poveda, I.; Mera-Velasco, S.; Cuesta-Vargas, A.I. Comparison of fatigue accumulated during and after prolonged robotic and laparoscopic surgical methods: A cross-sectional study. Surg. Endosc. 2017, 31, 1119–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armijo, P.R.; Huang, C.K.; High, R.; Leon, M.; Siu, K.C.; Oleynikov, D. Ergonomics of minimally invasive surgery: An analysis of muscle effort and fatigue in the operating room between laparoscopic and robotic surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2019, 33, 2323–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.H.; Jung, M.C.; Park, S.Y. Evaluation of surgeon’s muscle fatigue during thoracoscopic pulmonary lobectomy using interoperative surface electromyography. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Joo, H.-j.; Ahn, J.-H.; Kong, H.-J.; Yi, J. Forearm Muscle Activity Patterns during Open Thyroidectomy Using 8-Channel Surface Electromyography. J. Endocr. Surg. 2021, 21, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | All (n = 100) | Laparoscopic TAPP (n = 50) | Robotic TAPP (n = 50) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 59.4 ± 15.2 | 64.4 ± 14.8 | 54.4 ± 14.0 | 0.001 |
| BMI a | 24.3 ± 2.9 | 23.8 ± 2.9 | 24.8 ± 3.0 | 0.116 |
| Gender (%) | ||||
| Male | 99 (99%) | 49 (98%) | 50 (100%) | 0.315 |
| Female | 1 (1%) | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | |
| ASA b score | 2.2 ± 0.5 | 2.3 ± 0.6 | 2.0 ± 0.4 | 0.002 |
| CLASS I (%) | 5 (5%) | 2 (2%) | 3 (6%) | 0.003 |
| CLASS II (%) | 73 (60%) | 30 (60%) | 43 (86%) | |
| CLASS III (%) | 22 (100%) | 18 (36%) | 4 (8%) | |
| Comorbidities (%) | ||||
| HTN c | 44 (43%) | 30 (60%) | 14 (28%) | 0.001 |
| DM d | 14 (13%) | 9 (18%) | 5 (10%) | 0.249 |
| Cardiovascular | 15 (15%) | 10 (20%) | 5 (10%) | 0.161 |
| Pulmonary | 10 (10%) | 7 (14%) | 3 (6%) | 0.182 |
| Renal | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| Liver | 6 (6%) | 3 (6%) | 3 (6%) | 1 |
| Cerebral | 4 (4%) | 3 (6%) | 1 (2%) | 0.307 |
| Other cancer history | 10 (10%) | 6 (12%) | 4 (8%) | 0.505 |
| BPH e | 20 (20%) | 12 (24%) | 8 (16%) | 0.317 |
| Smoking | 34 (34%) | 15 (30%) | 19 (38%) | 0.398 |
| Alcohol | 42 (42%) | 20 (40%) | 22 (44%) | 0.685 |
| Steroid use | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| Variables | All (n = 100) | Laparoscopic TAPP (n = 50) | Robotic TAPP (n = 50) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operation time (minutes, mean ± SD) | 30.8 ± 11.1 | 31.5 ± 10.3 | 30.2 ± 11.9 | 0.56 |
| Conversion rate (%) (Open or Laparoscopic) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| Cost of surgery (USD a) | 209.6 ± 27.5 | 3814.8 ± 172.9 | <0.001 | |
| Type of hernia (%) | 0.829 | |||
| Indirect only | 87 (87%) | 44 (88%) | 43 (86%) | |
| Direct only | 7 (7%) | 3 (6%) | 4 (8%) | |
| Combined direct and indirect | 3 (3%) | 1 (2%) | 2 (4%) | |
| Femoral | 1 (1%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (2%) | |
| Spigelian | 1 (1%) | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Hernia site (%) | 0.483 | |||
| Right | 61 (61%) | 32 (64%) | 29 (58%) | |
| Left | 31 (31%) | 13 (26%) | 18 (36%) | |
| Bilateral | 8 (8%) | 5 (10%) | 3 (6%) | |
| Previous contralateral hernia (%) | 10 (10%) | 4 (8%) | 6 (12%) | 0.505 |
| Complex hernia (%) | ||||
| Recurrent hernia | 8 (8%) | 5 (10%) | 3 (6%) | 0.461 |
| Incarceration | 9 (9%) | 4 (8%) | 5 (10%) | 0.727 |
| Prostatectomy history | 8 (8%) | 6 (12%) | 2 (4%) | 0.14 |
| Variables | All (n = 100) | Laparoscopic TAPP (n = 50) | Robotic TAPP (n = 50) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital stay (days, mean ± SD) | 3.4 ± 1.6 | 3.5 ± 2.2 | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 0.658 |
| VAS a score | ||||
| Operation day (0–10, mean ± SD) | 4.7 ± 1.0 | 4.6 ± 1.1 | 4.8 ± 0.9 | 0.243 |
| Postoperative 1 day (0–10, mean ± SD) | 2.7 ± 0.7 | 2.9 ± 0.5 | 2.5 ± 0.7 | 0.015 |
| Readmission within 30 days (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| Hernia recurrence (%) | 1 (1%) | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 0.315 |
| Postoperative outcome (%) | ||||
| Infection (Surgical site, Mesh) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| Seroma | 2 (2%) | 2 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.153 |
| Hematoma | 4 (4%) | 3 (6%) | 1 (2%) | 0.307 |
| Prolonged ileus | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| Bowel obstruction | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| Bladder injury | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (2%) | 0.315 |
| Urinary retention | 8 (8%) | 5 (10%) | 3 (6%) | 0.461 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.S.; Kim, K.D.; Choi, M.S.; Heo, Y.S.; Yi, J.W.; Choe, Y.-M. Initial Experience of Robot-Assisted Transabdominal Preperitoneal (TAPP) Inguinal Hernia Repair by a Single Surgeon in South Korea. Medicina 2023, 59, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59030582
Choi YS, Kim KD, Choi MS, Heo YS, Yi JW, Choe Y-M. Initial Experience of Robot-Assisted Transabdominal Preperitoneal (TAPP) Inguinal Hernia Repair by a Single Surgeon in South Korea. Medicina. 2023; 59(3):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59030582
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Yun Suk, Kyeong Deok Kim, Moon Suk Choi, Yoon Seok Heo, Jin Wook Yi, and Yun-Mee Choe. 2023. "Initial Experience of Robot-Assisted Transabdominal Preperitoneal (TAPP) Inguinal Hernia Repair by a Single Surgeon in South Korea" Medicina 59, no. 3: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59030582
APA StyleChoi, Y. S., Kim, K. D., Choi, M. S., Heo, Y. S., Yi, J. W., & Choe, Y.-M. (2023). Initial Experience of Robot-Assisted Transabdominal Preperitoneal (TAPP) Inguinal Hernia Repair by a Single Surgeon in South Korea. Medicina, 59(3), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59030582







