Sepsis Associated Delirium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology
2.1. Endothelial Dysfunction and Cerebral Perfusion
2.2. Neurotransmission
2.3. Microglial Activation
3. Diagnosis
4. Subsyndromal Delirium
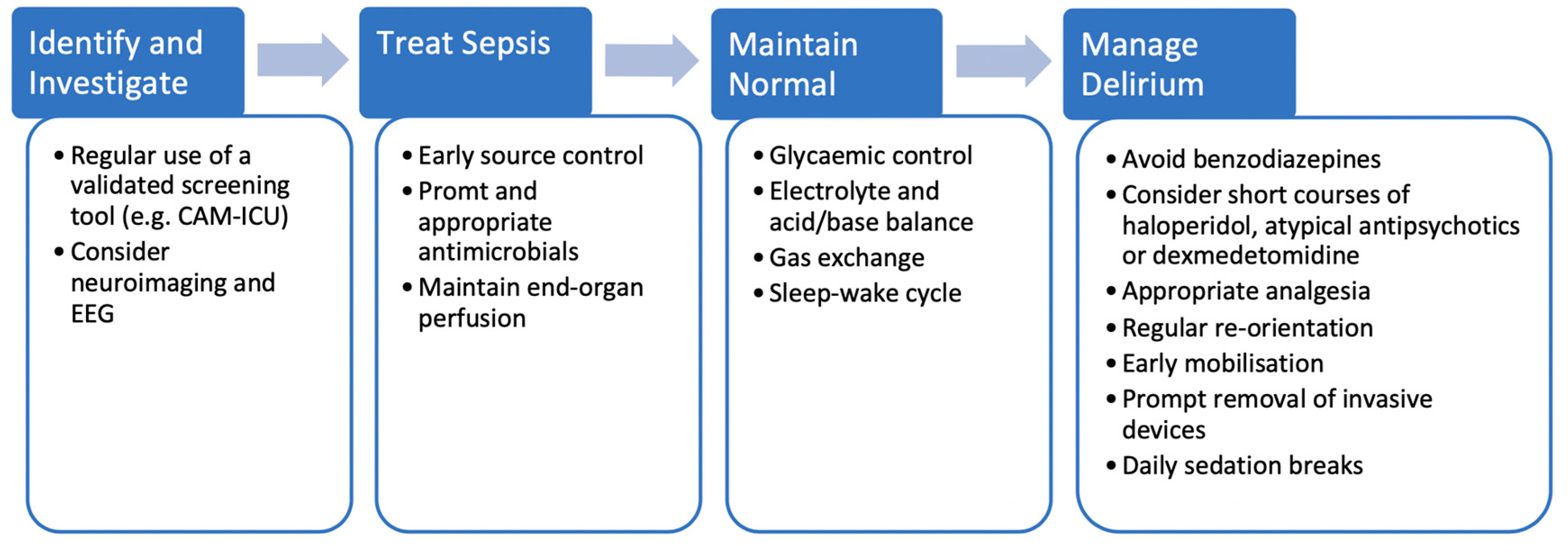
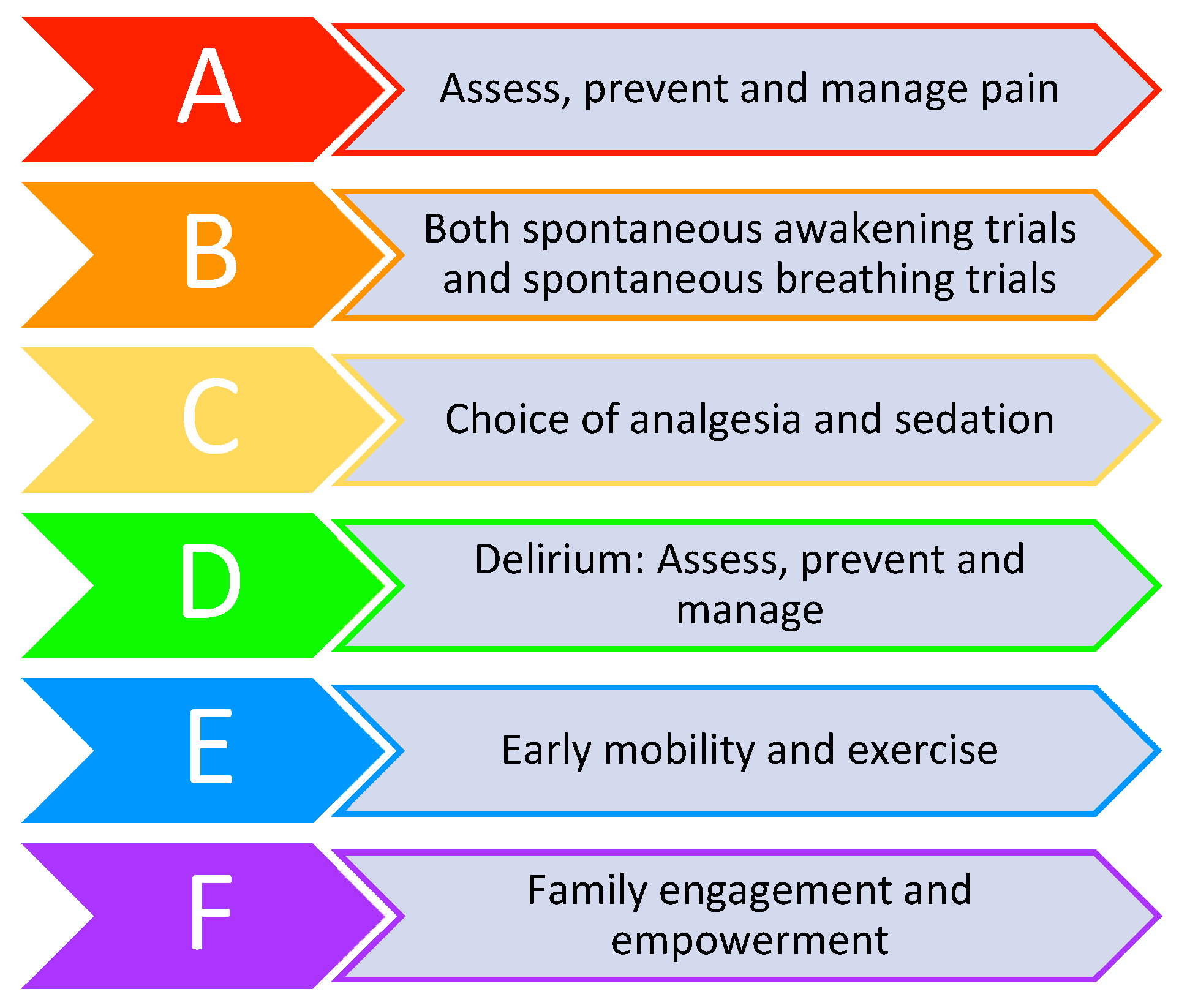
5. Treatment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Annane, D.; Sharshar, T. Cognitive decline after sepsis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijdicks, E.F.; Stevens, M. The role of hypotension in septic encephalopathy following surgical procedures. Arch. Neurol. 1992, 49, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janz, D.R.; Abel, T.W.; Jackson, J.C.; Gunther, M.L.; Heckers, S.; Ely, E.W. Brain autopsy findings in intensive care unit patients previously suffering from delirium: A pilot study. J. Crit. Care 2010, 25, 538.e7-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharshar, T.; Annane, D.; de la Grandmaison, G.L.; Brouland, J.P.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Françoise, G. The neuropathology of septic shock. Brain Pathol. 2004, 14, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.G.; Morandi, A.; Girard, T.D.; Riedel, B.; Thompson, J.L.; Shintani, A.K.; Pun, B.T.; Ely, E.W.; Pandharipande, P.P. Association between endothelial dysfunction and acute brain dysfunction during critical illness. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, D.; Siegemund, M.; Dell-Kuster, S.; Smielewski, P.; Rüegg, S.; Strebel, S.P.; Marsch, S.C.; Pargger, H.; Steiner, L.A. Cerebral perfusion in sepsis-associated delirium. Crit. Care 2008, 12, R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, P.; Klein, K.U.; Falkenberg, L.; Berres, M.; Closhen, D.; Werhahn, K.J.; David, M.; Werner, C.; Engelhard, K. Impaired cerebrovascular autoregulation in patients with severe sepsis and sepsis-associated delirium. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrakos, C.; Attou, R.; Decorte, L.; Kolyviras, A.; Malinverni, S.; Gottignies, P.; Devriendt, J.; De Bels, D. Transcranial Doppler to assess sepsis-associated encephalopathy in critically ill patients. BMC Anesthesiol. 2014, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, D.; Brown, C.; Ono, M.; Rappold, T.; Sieber, F.; Gottschalk, A.; Neufeld, K.J.; Gottesman, R.; Adachi, H.; Hogue, C.W. Arterial pressure above the upper cerebral autoregulation limit during cardiopulmonary bypass is associated with postoperative delirium. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 113, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler, A.; Frisch, C.; Debeir, T.; Ramanathan, M.; Okulla, T.; Klockgether, T.; Heneka, M.T. Long-term cognitive impairment, neuronal loss and reduced cortical cholinergic innervation after recovery from sepsis in a rodent model. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 204, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandharipande, P.P.; Morandi, A.; Adams, J.R.; Girard, T.D.; Thompson, J.L.; Shintani, A.K.; Ely, E.W. Plasma tryptophan and tyrosine levels are independent risk factors for delirium in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 1886–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, R.M.; Taudorf, S.; Bailey, D.M.; Lundby, C.; Larsen, F.S.; Pedersen, B.K.; Møller, K. Cerebral net exchange of large neutral amino acids after lipopolysaccharide infusion in healthy humans. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, R.H.; Berg, R.M.G.; Taudorf, S.; Bailey, D.M.; Lundby, C.; Larsen, F.S.; Møller, K. A reassessment of the blood-brain barrier transport of large neutral amino acids during acute systemic inflammation in humans. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2018, 38, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro da Silva, F.; Machado, M.C.; Velasco, I.T. Neuropeptides in sepsis: From brain pathology to systemic inflammation. Peptides 2013, 44, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, M.; Vieira, A.S.; Vuolo, F.; Zapelini, H.G.; Mendonça, B.; Mina, F.; Dominguini, D.; Steckert, A.; Schuck, P.F.; Quevedo, J.; et al. The role of microglia activation in the development of sepsis-induced long-term cognitive impairment. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 43, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gool, W.A.; van de Beek, D.; Eikelenboom, P. Systemic infection and delirium: When cytokines and acetylcholine collide. Lancet 2010, 375, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Block, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Breese, G.R.; Hong, J.S.; Knapp, D.J.; Crews, F.T. Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia 2007, 55, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemstra, A.W.; Groen in’t Woud, J.C.; Hoozemans, J.J.; van Haastert, E.S.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Eikelenboom, P.; van Gool, W.A. Microglia activation in sepsis: A case-control study. J. Neuroinflamm. 2007, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Henry, C.J.; Huang, Y.; Wynne, A.; Hanke, M.; Himler, J.; Bailey, M.T.; Sheridan, J.F.; Godbout, J.P. Minocycline attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation, sickness behavior, and anhedonia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spronk, P.E.; Riekerk, B.; Hofhuis, J.; Rommes, J.H. Occurrence of delirium is severely underestimated in the ICU during daily care. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 1276–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.W.; Skrobik, Y.; Gélinas, C.; Needham, D.M.; Slooter, A.J.C.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Watson, P.L.; Weinhouse, G.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; Rochwerg, B.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Pain, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption in Adult Patients in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, e825–e873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ely, E.W.; Margolin, R.; Francis, J.; May, L.; Truman, B.; Dittus, R.; Speroff, T.; Gautam, S.; Bernard, G.R.; Inouye, S.K. Evaluation of delirium in critically ill patients: Validation of the Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit (CAM-ICU). Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ely, E.W.; Inouye, S.K.; Bernard, G.R.; Gordon, S.; Francis, J.; May, L.; Truman, B.; Speroff, T.; Gautam, S.; Margolin, R.; et al. Delirium in mechanically ventilated patients: Validity and reliability of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU). JAMA 2001, 286, 2703–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, N.; Dubois, M.J.; Dumont, M.; Dial, S.; Skrobik, Y. Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist: Evaluation of a new screening tool. Intensive Care Med. 2001, 27, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusmao-Flores, D.; Salluh, J.I.; Chalhub, R.; Quarantini, L.C. The confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU) and intensive care delirium screening checklist (ICDSC) for the diagnosis of delirium: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.A.; Perkins, A.J.; Gao, S.; Hui, S.L.; Campbell, N.L.; Farber, M.O.; Chlan, L.L.; Boustani, M.A. The Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU-7 Delirium Severity Scale: A Novel Delirium Severity Instrument for Use in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, Z.; Lange, P.; Watson, R.; Maier, A.B. The use of cerebral imaging for investigating delirium aetiology. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 52, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggstrom, L.; Welschinger, R.; Caplan, G.A. Functional neuroimaging offers insights into delirium pathophysiology: A systematic review. Australas J. Ageing 2017, 36, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr Hosseini, M.; Liebeskind, D.S. The role of neuroimaging in elucidating the pathophysiology of cerebral ischemia. Neuropharmacology 2018, 134 Pt B, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalvas, L.B.; Monroe, T.B. Structural Brain Changes in Delirium: An Integrative Review. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2019, 21, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitchingham, A.; Kumar, V.; Shenkin, S.; Ferguson, K.J.; Caplan, G.A. A systematic review of neuroimaging in delirium: Predictors, correlates and consequences. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2018, 33, 1458–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Shin, J.E.; Yang, K.H.; Kyeong, S.; Lee, W.S.; Chung, T.S.; Kim, J.J. Cortical and subcortical changes in resting-state functional connectivity before and during an episode of postoperative delirium. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2019, 53, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, A.; Rogers, B.P.; Gunther, M.L.; Merkle, K.; Pandharipande, P.; Girard, T.D.; Jackson, J.C.; Thompson, J.; Shintani, A.K.; Geevarghese, S.; et al. The relationship between delirium duration, white matter integrity, and cognitive impairment in intensive care unit survivors as determined by diffusion tensor imaging: The VISIONS prospective cohort magnetic resonance imaging study. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 2182–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, M.L.; Morandi, A.; Krauskopf, E.; Pandharipande, P.; Girard, T.D.; Jackson, J.C.; Thompson, J.; Shintani, A.K.; Geevarghese, S.; Miller, R.R.; et al. The association between brain volumes, delirium duration, and cognitive outcomes in intensive care unit survivors: The VISIONS cohort magnetic resonance imaging study. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 2022–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soiza, R.L.; Sharma, V.; Ferguson, K.; Shenkin, S.D.; Seymour, D.G.; Maclullich, A.M. Neuroimaging studies of delirium: A systematic review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2008, 65, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toft, K.; Tontsch, J.; Abdelhamid, S.; Steiner, L.; Siegemund, M.; Hollinger, A. Serum biomarkers of delirium in the elderly: A narrative review. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, B.A.; Perkins, A.J.; Prasad, N.K.; Shekhar, A.; Campbell, N.L.; Gao, S.; Wang, S.; Khan, S.H.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Twigg, H.L.; et al. Biomarkers of Delirium Duration and Delirium Severity in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, K.S.; van den Boogaard, M.; Hendriksen, E.; Gerretsen, J.; van der Hoeven, J.G.; Pickkers, P.; de Jager, C.P.C. Temporal biomarker profiles and their association with ICU acquired delirium: A cohort study. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulkey, M.A.; Everhart, D.E.; Kim, S.; Olson, D.M.; Hardin, S.R. Detecting Delirium Using a Physiologic Monitor. Dimens Crit. Care Nurs. 2019, 38, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, J.; Engel, G. Delirium: I. Electroencephalographic Data. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1944, 51, 356–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S.A.; Leuchter, A.F.; Walter, D.O. Conventional and quantitative EEG in the diagnosis of delirium among the elderly. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1993, 56, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimchi, E.Y.; Neelagiri, A.; Whitt, W.; Sagi, A.R.; Ryan, S.L.; Gadbois, G.; Groothuysen, D.; Westover, M.B. Clinical EEG slowing correlates with delirium severity and predicts poor clinical outcomes. Neurology 2019, 93, e1260–e1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, R.M.; Urdanibia-Centelles, O.; Vedel-Larsen, E.; Thomsen, K.J.; Møller, K.; Olsen, K.S.; Lauritsen, A.; Eddelien, H.S.; Lauritzen, M.; Benedek, K. Continuous EEG Monitoring in a Consecutive Patient Cohort with Sepsis and Delirium. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 32, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boettger, S.; Nuñez, D.G.; Meyer, R.; Richter, A.; Schubert, M.; Jenewein, J. Subsyndromal delirium in the intensive care setting: Phenomenological characteristics and discrimination of subsyndromal delirium versus no and full-syndromal delirium. Palliat Support Care 2018, 16, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. American Psychiatric Association, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brummel, N.E.; Boehm, L.M.; Girard, T.D.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Jackson, J.C.; Hughes, C.G.; Patel, M.B.; Han, J.H.; Vasilevskis, E.E.; Thompson, J.L.; et al. Subsyndromal Delirium and Institutionalization Among Patients With Critical Illness. Am. J. Crit. Care 2017, 26, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimet, S.; Riker, R.; Bergeron, N.; Bergeon, N.; Cossette, M.; Kavanagh, B.; Skrobik, Y. Subsyndromal delirium in the ICU: Evidence for a disease spectrum. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breu, A.; Stransky, M.; Metterlein, T.; Werner, T.; Trabold, B. Subsyndromal delirium after cardiac surgery. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2015, 49, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafim, R.B.; Soares, M.; Bozza, F.A.; Lapa E Silva, J.R.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Paulino, M.C.; Povoa, P.; Salluh, J.I.F. Outcomes of subsyndromal delirium in ICU: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qadheeb, N.S.; Skrobik, Y.; Schumaker, G.; Pacheco, M.N.; Roberts, R.J.; Ruthazer, R.R.; Devlin, J.W. Preventing ICU Subsyndromal Delirium Conversion to Delirium With Low-Dose IV Haloperidol: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, S.M.; Othman, A.I.; Naoum, D.O. Early treatment with risperidone for subsyndromal delirium after on-pump cardiac surgery in the elderly: A randomized trial. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, A.; Evans, L.E.; Alhazzani, W.; Levy, M.M.; Antonelli, M.; Ferrer, R.; Kumar, A.; Sevransky, J.E.; Sprung, C.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 304–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneville, R.; de Montmollin, E.; Poujade, J.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Souweine, B.; Darmon, M.; Mariotte, E.; Argaud, L.; Barbier, F.; Goldgran-Toledano, D.; et al. Potentially modifiable factors contributing to sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, Y.; Ording, H.; Jennum, P. Sleep disturbances in critically ill patients in ICU: How much do we know? Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2012, 56, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rompaey, B.; Elseviers, M.; Van Drom, W.; Fromont, V.; Jorens, P. The effect of earplugs during the night on the onset of delirium and sleep perception: A randomized controlled trial in intensive care patients. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Boogaard, M.; Slooter, A.J.C.; Bruggemann, R.J.M. Effect of haloperidol on survival among critically ill adults with a high risk of delirium: The REDUCE randomised controlled trial. J. Intensive Care Soc. 2019, 20, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- van Eijk, M.M.; Roes, K.C.; Honing, M.L.; Kuiper, M.A.; Karakus, A.; van der Jagt, M.; Spronk, P.E.; van Gool, W.A.; van der Mast, R.C.; Kesecioglu, J.; et al. Effect of rivastigmine as an adjunct to usual care with haloperidol on duration of delirium and mortality in critically ill patients: A multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweickert, W.D.; Pohlman, M.C.; Pohlman, A.S.; Nigos, C.; Pawlik, A.J.; Esbrook, C.L.; Spears, L.; Miller, M.; Franczyk, M.; Deprizio, D.; et al. Early physical and occupational therapy in mechanically ventilated, critically ill patients: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009, 373, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NICE Guideline (CG103) Delirium: Prevention, Diagnosis and Management. 2010. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg103 (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Pandharipande, P.; Shintani, A.; Peterson, J.; Pun, B.T.; Wilkinson, G.R.; Dittus, R.S.; Bernard, G.R.; Ely, E.W. Lorazepam is an independent risk factor for transitioning to delirium in intensive care unit patients. Anesthesiology 2006, 104, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandharipande, P.P.; Pun, B.T.; Herr, D.L.; Maze, M.; Girard, T.D.; Miller, R.R.; Shintani, A.K.; Thompson, J.L.; Jackson, J.C.; Deppen, S.A.; et al. Effect of sedation with dexmedetomidine vs lorazepam on acute brain dysfunction in mechanically ventilated patients: The MENDS randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2007, 298, 2644–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandharipande, P.P.; Sanders, R.D.; Girard, T.D.; McGrane, S.; Thompson, J.L.; Shintani, A.K.; Herr, D.L.; Maze, M.; Ely, E.W.; investigators, M. Effect of dexmedetomidine versus lorazepam on outcome in patients with sepsis: An a priori-designed analysis of the MENDS randomized controlled trial. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reade, M.C.; O’Sullivan, K.; Bates, S.; Goldsmith, D.; Ainslie, W.R.; Bellomo, R. Dexmedetomidine vs. haloperidol in delirious, agitated, intubated patients: A randomised open-label trial. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, A.; Blinder, H.; Hutton, B.; English, S.W. A Systematic Review of Alpha-2 Agonists for Sedation in Mechanically Ventilated Neurocritical Care Patients. Neurocrit. Care 2018, 28, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reade, M.C.; Eastwood, G.M.; Bellomo, R.; Bailey, M.; Bersten, A.; Cheung, B.; Davies, A.; Delaney, A.; Ghosh, A.; van Haren, F.; et al. Effect of Dexmedetomidine Added to Standard Care on Ventilator-Free Time in Patients With Agitated Delirium: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakob, S.M.; Ruokonen, E.; Grounds, R.M.; Sarapohja, T.; Garratt, C.; Pocock, S.J.; Bratty, J.R.; Takala, J.; Investigators, D.L.-T.S. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam or propofol for sedation during prolonged mechanical ventilation: Two randomized controlled trials. JAMA 2012, 307, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, H.C.; Angus, D.C. Enhancing Recovery From Sepsis: A Review. JAMA 2018, 319, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandharipande, P.P.; Girard, T.D.; Ely, E.W. Long-term cognitive impairment after critical illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Girard, T.D.; Thompson, J.L.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Brummel, N.E.; Jackson, J.C.; Patel, M.B.; Hughes, C.G.; Chandrasekhar, R.; Pun, B.T.; Boehm, L.M.; et al. Clinical phenotypes of delirium during critical illness and severity of subsequent long-term cognitive impairment: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakusic, A.; O’Horo, J.C.; Dziadzko, M.; Volha, D.; Ali, R.; Singh, T.D.; Kashyap, R.; Farrell, A.M.; Fryer, J.D.; Petersen, R.; et al. Potentially Modifiable Risk Factors for Long-Term Cognitive Impairment After Critical Illness: A Systematic Review. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes-Daly, M.A.; Phillips, G.; Ely, E.W. Improving Hospital Survival and Reducing Brain Dysfunction at Seven California Community Hospitals: Implementing PAD Guidelines Via the ABCDEF Bundle in 6064 Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, A.; Piva, S.; Ely, E.W.; Myatra, S.N.; Salluh, J.I.F.; Amare, D.; Azoulay, E.; Bellelli, G.; Csomos, A.; Fan, E.; et al. Worldwide Survey of the “Assessing Pain, Both Spontaneous Awakening and Breathing Trials, Choice of Drugs, Delirium Monitoring/Management, Early Exercise/Mobility, and Family Empowerment” (ABCDEF) Bundle. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, e1111–e1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atterton, B.; Paulino, M.C.; Povoa, P.; Martin-Loeches, I. Sepsis Associated Delirium. Medicina 2020, 56, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56050240
Atterton B, Paulino MC, Povoa P, Martin-Loeches I. Sepsis Associated Delirium. Medicina. 2020; 56(5):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56050240
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtterton, Ben, Maria Carolina Paulino, Pedro Povoa, and Ignacio Martin-Loeches. 2020. "Sepsis Associated Delirium" Medicina 56, no. 5: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56050240
APA StyleAtterton, B., Paulino, M. C., Povoa, P., & Martin-Loeches, I. (2020). Sepsis Associated Delirium. Medicina, 56(5), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56050240





