Systemic Oxidative Stress Markers in Cirrhotic Patients with Hepatic Encephalopathy: Possible Connections with Systemic Ammoniemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients and Healthy Subjects
2.2. Measurement of Oxidative Stress Markers
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Oxidative Stress-Related Markers
3.3. Correlations between Oxidative Stress-Related Markers and Serum Ammonia Level
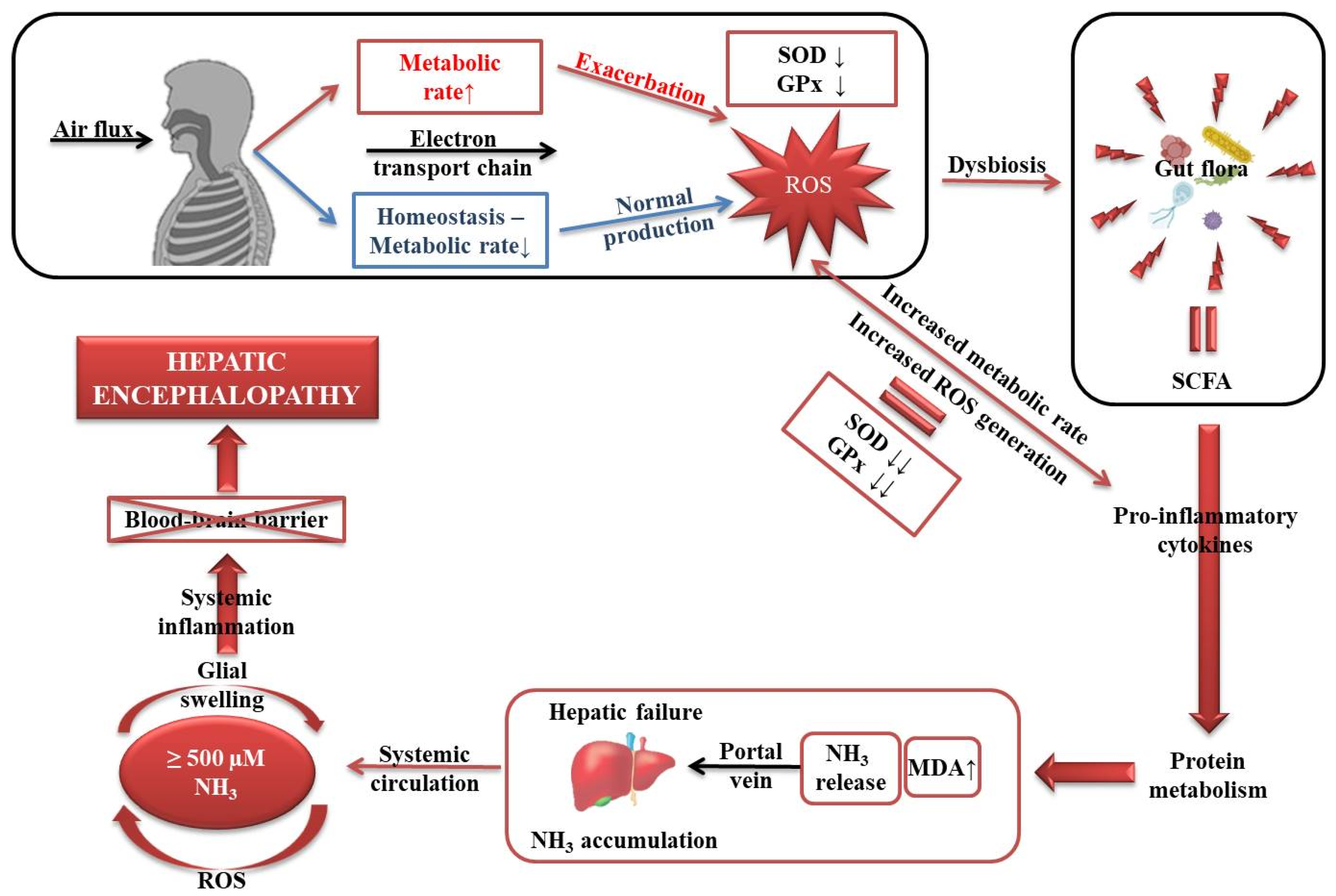
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Availability of Data and Materials
References
- Elwir, S.; Rahimi, R.S. Hepatic encephalopathy: An update on the pathophysiology and therapeutic options. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2017, 5, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldridge, D.R.; Tranah, E.J.; Shawcross, D.L. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy: Role of ammonia and systemic inflammation. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2015, 5, S7–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemberg, A.; Alejandra Fernández, M. Hepatic encephalopathy, ammonia, glutamate, glutamine and oxidative stress. Ann. Hepatol. 2009, 8, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyan, A.S.; Hughes, R.D.; Shawcross, D.L. Changing face of hepatic encephalopathy: Role of inflammation and oxidative stress. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 3347–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichoż-Lach, H.; Michalak, A. Current pathogenetic aspects of hepatic encephalopathy and noncirrhotic hyperammonemic encephalopathy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosenko, E.; Kaminski, Y.; Lopata, O.; Muravyov, N.; Felipo, V. Blocking NMDA receptors prevents the oxidative stress induced by acute ammonia intoxication. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosenko, E.; Kaminsky, M.; Kaminsky, A.; Valencia, M.; Lee, L.; Hermenegildo, C.; Felipo, V. Superoxide production and antioxidant enzymes in ammonia intoxication in rats. Free Radic. Res. 1997, 27, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosenko, E.; Venediktova, N.; Kaminsky, Y.; Montoliu, C.; Felipo, V. Sources of oxygen radicals in brain in acute ammonia intoxication in vivo. Brain Res. 2003, 981, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, S.J.; Connor, J.R. An in vitro model for analysis of oxidative death in primary mouse astrocytes. Brain Res. 1998, 788, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norenberg, M.D.; Jayakumar, A.R.; Rao, K.R. Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2004, 19, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, R.; Gram Pedersen, M.; Luciani, D.S.; Sherman, A. A simplified model for mitochondrial ATP production. J. Theor. Biol. 2006, 243, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skulachev, V.P. Role of uncoupled and non-coupled oxidations in maintenance of safely low levels of oxygen and its one-electron reductants. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1996, 29, 169–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenger, K.J.P.; Clermont-Dejean, N.; Allard, J.P. The role of the gut microbiome in chronic liver disease: The clinical evidence revised. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, R. Brain mitochondria as potential therapeutic targets for managing hepatic encephalopathy. Life Sci. 2019, 218, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, S.; Alden, N.; Lee, K. Pathways and functions of gut microbiota metabolism impacting host physiology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 36, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Blacher, E.; Elinav, E. Microbiome, metabolites and host immunity. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 35, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belizário, J.E.; Faintuch, J.; Garay-Malpartida, M. Gut Microbiome dysbiosis and immunometabolism: New frontiers for treatment of metabolic diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 2037838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, A.H. Blood ammonia levels and hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2004, 19, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häussinger, D.; Görg, B. Interaction of oxidative stress, astrocyte swelling and cerebral ammonia toxicity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görg, B.; Qvartskhava, N.; Keitel, V.; Bidmon, H.J.; Selbach, O.; Schliess, F.; Häussinger, D. Ammonia induces RNA oxidation in cultured astrocytes and brain in vivo. Hepatology 2008, 48, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinehr, R.; Görg, B.; Becker, S.; Qvartskhava, N.; Bidmon, H.J.; Selbach, O.; Haas, H.L.; Schliess, F.; Häussinger, D. Hypoosmotic swelling and ammonia increase oxidative stress by NADPH oxidase in cultured astrocytes and vital brain slices. Glia 2007, 55, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irimia, R.; Ciobica, A.; Carol, S.; Trifan, A. The relevance of oxidative stress in cirrhotic patients with different forms of hepatic encephalopathy. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2013, 65, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Koiri, R.K.; Trigun, S.K. Acute and chronic hyperammonemia modulate antioxidant enzymes differently in cerebral cortex and cerebellum. Neurochem. Res. 2008, 33, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Biochemistry of oxidative stress. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Mohan, S.; Venkataramana, G. Status of lipid peroxidation, glutathione, ascorbic acid, vitamin E and antioxidant enzymes in patients with osteoarthritis. Indian J. Med. Sci. 2007, 61, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
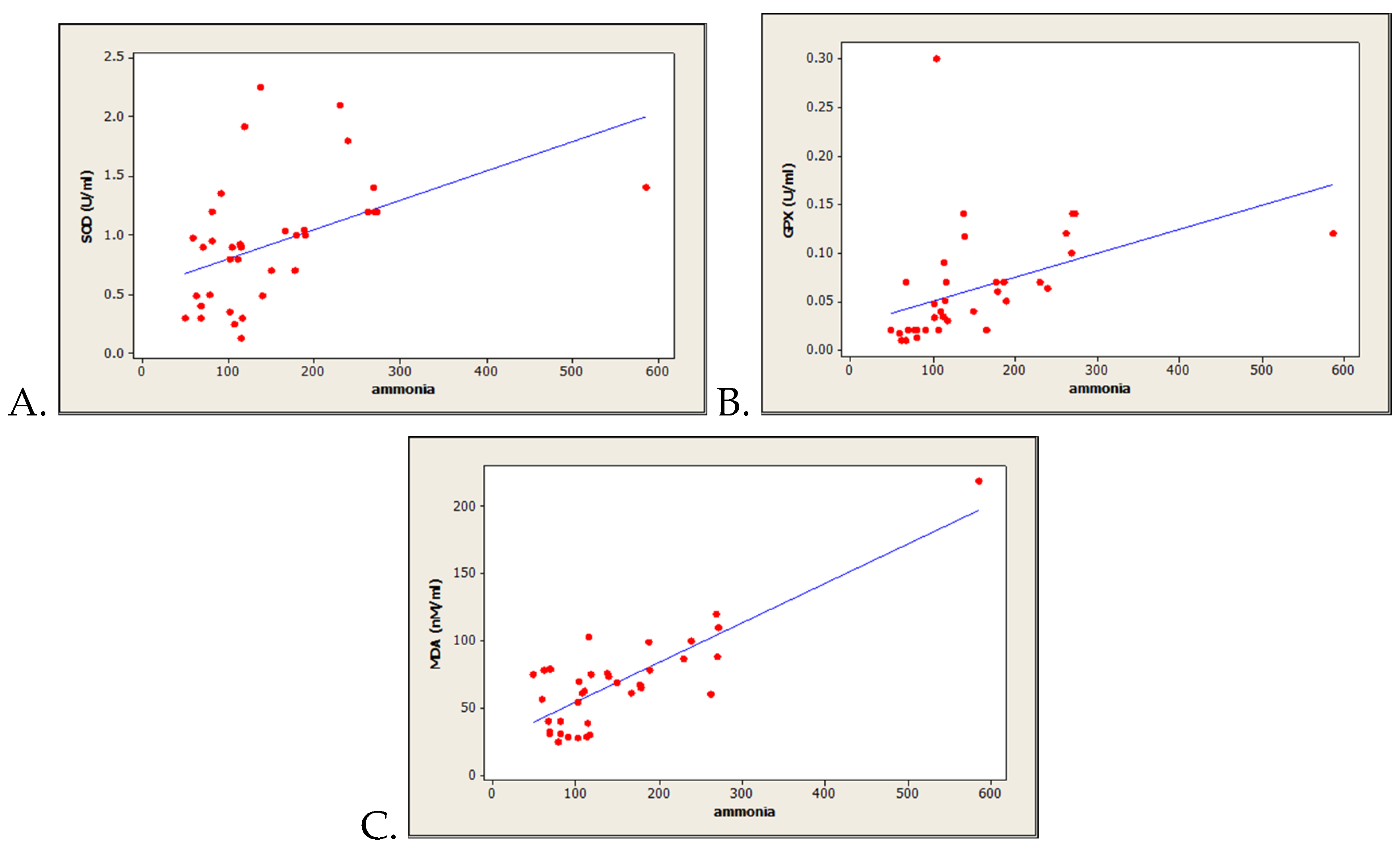
| Parameter | All Patients n = 40 | Study Group A (High Ammoniemia) n = 20 | Study Group B (Normal Ammoniemia) n = 20 | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, Male/Female (%) | 19/21 (47.5/52.5) | 11/9 (55/45) | 8/12 (40/60) | 0.342 C |
| Age, Years, Mean ± SD | 56.0 ± 10.4 | 54.3 ± 9.6 | 57.6 ± 10.4 | 0.305 T |
| Etiology of Cirrhosis, n (%) | 0.322 F | |||
| HCV | 10 (25.0) | 3 (15.0) | 7 (35) | |
| HBV | 6 (15.0) | 3 (15.0) | 3 (15.0) | |
| Alcohol | 24 (60.0) | 14 (70.0) | 10 (50.0) | |
| Child–Pugh Class B/C, n (%) | 15/25 (37.5/62.5) | 4/16 (20/80) | 11/9 (55/45) | 0.022 F |
| Child–Pugh Ccore, Median (Q1/Q3) | 10 (8/15) | 10.5 (9/15) | 9(8/13) | 0.077 M |
| MELD Score, Median (Q1/Q3) | 15 (11/20) | 21 (11/35) | 17 (8/32) | 0.356 M |
| Creatinine (mg/dL),Median (Q1/Q3) | 0.78 (0.11/3.5) | 0.85 (0.12/2.77) | 0.73 (0.11/3.5) | 0.810 M |
| Albumin (g/L), Median (Q1/Q3) | 2.8 (1.59/4.5) | 2.9 (1.5/3.5) | 2.6 (1.96/4.5) | 0.394 M |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL), Median (Q1/Q3) | 4.03 (1.74/24.6) | 2.15 (1.73/24.1) | 4.62 (1.8/16.0) | 0.121 M |
| INR, Median (Q1/Q3) | 1.5 (1.28/1.74) | 1.42 (1.22/1.63) | 1.5 (1.3/1.78) | 0.461 M |
| Ammonia (µmols/L), Median (Q1/Q3) | 117 (91.5/188) | 158 (113.5/234.5) | 69 (60.5/79.5) | 0.001 M |
| Ascites, Mild/Medium/ Large, n (%) | 10/14/16 (25/35/40) | 5/8/7 (25/40/35) | 5/6/9 (25/30/45) | 0.536 F |
| SBP, n (%) | 6 (15.0) | 2 (10.0) | 4 (20.0) | 0.096 F |
| HRS, n (%) | 5 (12.5) | 3 (15.0) | 2 (10.0) | 0.633 F |
| UGIB, n (%) | 13 (32.5) | 6 (30.0) | 7 (35.0) | 0.736 F |
| Encephalopathy, n (%) | 0.043 F | |||
| Stage II | 16 (40.0) | 9 (45.0) | 7 (35.0) | |
| Stage III | 15 (37.5) | 4 (20.0) | 11 (55.0) | |
| Stage IV | 9 (22.5) | 7 (35.0) | 2 (10.0) |
| Parameter | Controls n = 21 | All Cirrhotic Patients n = 40 | Study Group A (High Ammoniemia) n = 20 | Study Group B (Normal Ammoniemia) n = 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOD (U/mL) | 1.35 ± 0.08 | 0.90 ± 0.08 | 1.06 ± 0.07 ª | 0.68 ± 0.08 |
| GPx (U/mL) | 0.09 ± 0.006 | 0.061 ± 0.008 | 0.08 ± 0.005 ª | 0.024 ± 0.004 |
| MDA (nmols/mL) | 35.94 ± 1.37 | 68.90 ± 5.68 | 76.93 ± 5.48 | 50.06 ± 5.60 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sfarti, C.; Ciobica, A.; Balmus, I.-M.; Ilie, O.-D.; Trifan, A.; Petrea, O.; Cojocariu, C.; Gîrleanu, I.; Sîngeap, A.M.; Stanciu, C. Systemic Oxidative Stress Markers in Cirrhotic Patients with Hepatic Encephalopathy: Possible Connections with Systemic Ammoniemia. Medicina 2020, 56, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56040196
Sfarti C, Ciobica A, Balmus I-M, Ilie O-D, Trifan A, Petrea O, Cojocariu C, Gîrleanu I, Sîngeap AM, Stanciu C. Systemic Oxidative Stress Markers in Cirrhotic Patients with Hepatic Encephalopathy: Possible Connections with Systemic Ammoniemia. Medicina. 2020; 56(4):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56040196
Chicago/Turabian StyleSfarti, Cătălin, Alin Ciobica, Ioana-Miruna Balmus, Ovidiu-Dumitru Ilie, Anca Trifan, Oana Petrea, Camelia Cojocariu, Irina Gîrleanu, Ana Maria Sîngeap, and Carol Stanciu. 2020. "Systemic Oxidative Stress Markers in Cirrhotic Patients with Hepatic Encephalopathy: Possible Connections with Systemic Ammoniemia" Medicina 56, no. 4: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56040196
APA StyleSfarti, C., Ciobica, A., Balmus, I.-M., Ilie, O.-D., Trifan, A., Petrea, O., Cojocariu, C., Gîrleanu, I., Sîngeap, A. M., & Stanciu, C. (2020). Systemic Oxidative Stress Markers in Cirrhotic Patients with Hepatic Encephalopathy: Possible Connections with Systemic Ammoniemia. Medicina, 56(4), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56040196










