Autonomic and Cognitive Function Response to Normobaric Hyperoxia Exposure in Healthy Subjects. Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
2.2. Study Group
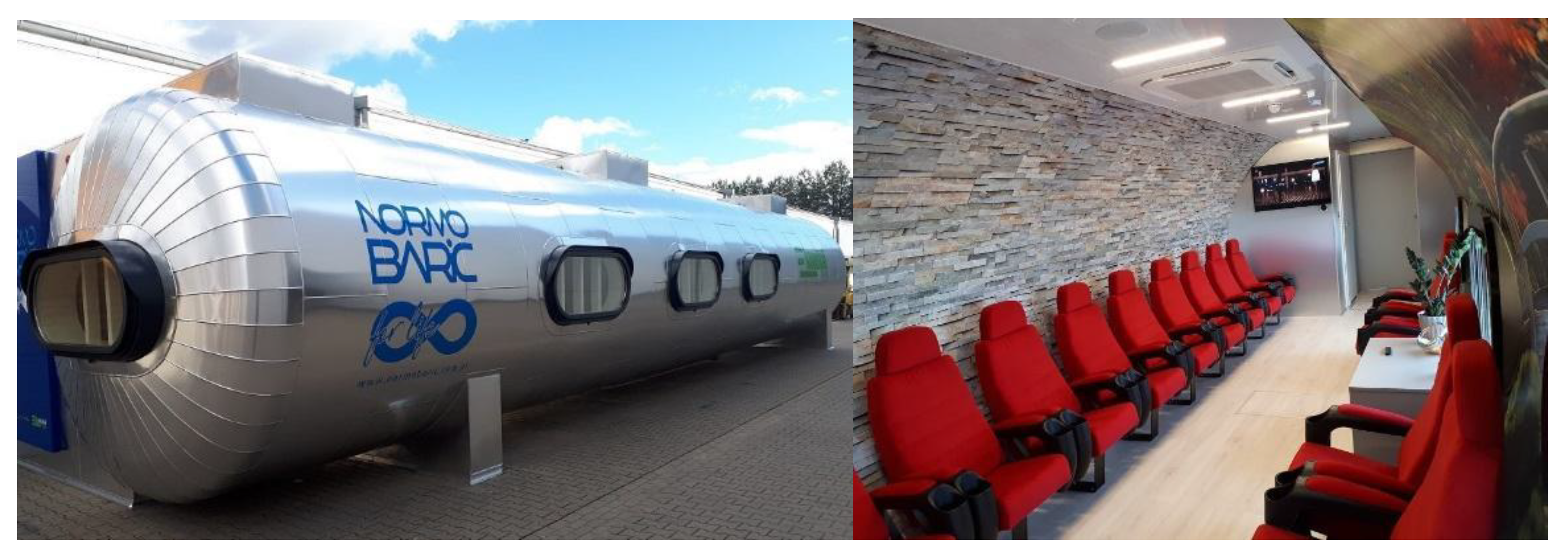
2.3. Intervention—Ten Normobaric Exposures
2.4. Body Composition Analysis
2.5. Cognitive Function and Fatigue Measurements
2.6. Cardiovascular Measurements
2.7. Biochemical Parameters
2.8. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing and Spirometry
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taccone, F.S.; Crippa, I.A.; Vincent, J.L. Normobaric hyperoxia after stroke: A word of caution. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2018, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.K.; Dunn, A.K.; Jones, P.B.; Boas, D.A.; Lo, E.H.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Ayata, C. Normobaric hyperoxia improves cerebral blood flow and oxygenation, and inhibits peri-infarct depolarizations in experimental focal ischaemia. Brain 2007, 130 Pt 6, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueckl, C.; Kaestle, S.; Kerem, A.; Habazettl, H.; Krombach, F.; Kuppe, H.; Kuebler, W.M. Hyperoxia-induced reactive oxygen species formation in pulmonary capillary endothelial cells in situ. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 34, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperlich, B.; Calbet, J.; Boushel, R.; Holmberg, H.C. Is the use of hyperoxia in sports effective, safe and ethical? Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klugar, M.; Nytra, I.; Bocková, S.; Klugarová, J.; Kelnarová, Z.; Marecková, J. The effectiveness of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on mortality in adults with craniotrauma: A systematic review protocol. JBI Database Syst. Rev. Implement. Rep. 2014, 12, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyboer, M., III; Sharma, D.; Santiago, W.; McCulloch, N. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Side effects defined and quantified. Adv. Wound Care 2017, 6, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delis, D.C.; Kramer, J.H.; Kaplan, E.; Thompkins, B.A.O. CVLT: California verbal learning test-adult version: Manual. Psychol. Corp. 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinas-Regla, J.; Vilalta-Franch, J.; Lopez-Pousa, S.; Calvo-Perxas, L.; Torrents Rodas, D.; Garre-Olmo, J. The Trail Making Test. Assessment 2017, 24, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezak, M.D.; Howieson, D.B.; Loring, D.W.; Fischer, J.S. Neuropsychological Assessment; Oxford University Press: Cary, NC, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-19-511121-7. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, S.; Kottorp, A.; Lee, K.A.; Gay, C.L.; Lerdal, A. Can the Fatigue Severity Scale 7-item version be used across different patient populations as a generic fatigue measure-a comparative study using a Rasch model approach. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2014, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.; Marte, W.; Grullenberger, R. Continuous non-invasive blood pressure monitoring using concentrically interlocking control loops. Comput. Biol. Med. 2006, 36, 941–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parati, G.; Omboni, S.; Frattola, A.; Di Rienzo, M.; Zanchetti, A.; Mancia, G. Dynamic evaluation of the baroreflex in ambulant subjects. Blood Press. Heart Rate Var. 1992, 4, 123–137. [Google Scholar]
- Parati, G.; Di Rienzo, M.; Mancia, G. How to measure baroreflex sensitivity: From the cardiovascular laboratory to daily life. J. Hypertens. 2000, 18, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, R.; Kusumi, F.; Hosmer, D. Maximal oxygen intake and nomographic assessment of functional aerobic impairment in cardiovascular disease. Am. Heart J. 1973, 85, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 4 February 2020).
- Patil, I.; Powell, C. Ggstatsplot: ‘ggplot2’ Based Plots with Statistical Details. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggstatsplot (accessed on 4 February 2020). [CrossRef]
- Morten, K.J.; Potter, M.; Badder, L.; Sivathondan, P.; Dragovic, R.; Neumann, A.; Gavin, J.; Shrestha, R.; Reilly, S.; Phadwal, K.; et al. Insights into pancreatic β cell energy metabolism using rodent β cell models. Welcome Open Res. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, P.M.; Parasuraman, R. Neuronal and cognitive plasticity: A neurocognitive framework for ameliorating cognitive aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2010, 2, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, R.H.; Zgaljardic, D.J. Practice effects during repeated administrations of memory tests with and without alternate forms. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 1998, 20, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunstad, J.; Benitez, A.; Smith, J.; Glickman, E.; Spitznagel, M.B.; Alexander, T.; Murray, L. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor is associated with cognitive function in healthy older adults. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2008, 21, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinoff, A.; Herrmann, N.; Swardfager, W.; Liu, C.S.; Sherman, C.; Chan, S.; Lanctôt, K.L. The effect of exercise training on resting concentrations of peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, J. Digit Symbol Substitution Test: The Case for Sensitivity over Specificity in Neuropsychological Testing. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 38, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gignac, G.E.; Weiss, L.G. Digit Span is (mostly) related linearly to general intelligence: Every extra bit of span counts. Psychol. Assess. 2015, 27, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszko, K.; Piątkowska, A.; Koźluk, E.; Opolski, G. Entropy in investigation of vasovagal syndrome in passive head up tilt test. Entropy 2017, 19, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszko, K.; Piątkowska, A.; Koźluk, E.; Fabiszak, T.; Opolski, G. The complexity of hemodynamic response to the tilt test with and without nitroglycerine provocation in patients with vasovagal syncope. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broeckaert, F.; Bernard, A. Clara cell secretory protein (CC16): Characteristics and perspectives as lung peripheral biomarker. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, L.; Gordin, D.; Bordino, M.; Rosengård-Bärlund, M.; Sandelin, A.; Forsblom, C.; Groop, P.H. Oxygen-induced impairment in arterial function is corrected by slow breathing in patients with type 1 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kropski, J.A.; Fremont, R.D.; Calfee, C.S.; Ware, L.B. Clara cell protein (CC16), a marker of lung epithelial injury, is decreased in plasma and pulmonary edema fluid from patients with acute lung injury. Chest 2009, 135, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurowski, M.; Jurczyk, J.; Jarzębska, M.; Moskwa, S.; Makowska, J.S.; Krysztofiak, H.; Kowalski, M.L. Association of serum Clara cell protein CC16 with respiratory infections and immune response to respiratory pathogens in elite athletes. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, C.; Petrek, M.; Kolek, V.; Weynand, B.; Pieters, T.; Lambert, M.; Bernard, A. Serum Clara cell protein (CC16), a marker of the integrity of the air-blood barrier in sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 18, 507–514.29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarkova, Z.; Engler, I.; Calkovska, A.; Mokra, D.; Drgova, A.; Hodas, P.; Lehotsky, J.; Dobrota, D.; Kaplan, P. Effect of long-term normobaric hyperoxia on oxidative stress in mitochondria of the guinea pig brain. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 36, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahotupa, M.; Mantyla, E.; Peltola, V.; Puntala, A.; Toivonen, H. Pro-oxidant effects of normobaric hyperoxia in rat tissues. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1992, 145, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapo, J.D.; Barry, B.E.; Foscue, H.A.; Shelburne, J. Structural and biochemical changes in rat lungs occurring during exposures to lethal and adaptive doses of oxygen. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1980, 122, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.; Liu, K.J. Does normobaric hyperoxia increase oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke? A critical review of the literature. Med. Gas Res. 2015, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaria, A.; Tolias, C.M. Normobaric hyperoxia therapy for traumatic brain injury and stroke: A review. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 23, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Mandeville, E.T.; Geng, X.; Luo, Y.; Arai, K.; Wang, X.; Ji, X.; Singhal, A.B.; Lo, E.H. Effect of normobaric oxygen therapy in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2011, 42, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, L.; Rosengård-Bärlund, M.; Sandelin, A.; Mäkinen, V.P.; Forsblom, C.; Groop, P.H.; FinnDiane Study Group. Short-term oxygen administration restores blunted baroreflex sensitivity in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2164–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, B.; Stannard, S.R.; Morton, R.H.; North, N. Hyperoxia during recovery improves peak power during repeated wingate cycle performance. Braz. J. Biomotricity 2008, 2, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Oussaidene, K.; Prieur, F.; Bougault, V.; Borel, B.; Matran, R.; Mucci, P. Cerebral oxygenation during hyperoxia-induced increase in exercise tolerance for untrained men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, V.; Kentala, E.; Scheinin, H.; Klossner, J.; Sariola-Heinonen, K.; Jalonen, J. Hyperbaric oxygen increases parasympathetic activity in professional divers. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2000, 170, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, D.P.; Joyner, M.J.; Claus, P.L.; Curry, T.B. Vasoconstrictor responsiveness during hyperbaric hyperoxia in contracting human muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 114, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, W.; Kizuk, S.A.; MacLean, J.; Dickson, C.T.; Mathewson, K. Electrophysiological Correlates of hyperoxia during Resting-state EEG in Awake Human Subjects. Preprint. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2019/01/14/355941.full.pdf (accessed on 22 February 2019).
- Cortés, D.O.; Puflea, F.; Donadello, K.; Taccone, F.S.; Gottin, L.; Creteur, J.; Vincent, J.-L.; De Backer, D. Normobaric hyperoxia alters the microcirculation in healthy volunteers. Microvasc. Res. 2014, 98, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergo, G.W.; Tyssebotn, I. Effect of exposure to oxygen at 101 and 150 kPa on the cerebral circulation and oxygen supply in conscious rats. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1995, 71, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, T.F.; Clark, J.M.; Gelfand, R.; Detre, J.A.; Ratcliffe, S.; Guvakov, D.; Lambertsen, C.J.; Eckenhoff, R.G. Independent cerebral vasoconstrictive effects of hyperoxia and accompanying arterial hypocapnia at 1 ATA. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 95, 2453–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.W.; Tang, C.Y.; Ng, J.; Wong, E.; Carpenter, D.; Tao, X. Effects of hyperoxia on resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroreport 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Manaenko, A.; Guo, Z.; Huang, L.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for post concussion symptoms: Issues may affect the results. Med. Gas Res. 2015, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Collet, J.P.; Vanasse, M.; Marois, P.; Amar, M.; Goldberg, J.; Lambert, J.; Lassonde, M.; Hardy, P.; Fortin, J.; Tremblay, S.D. Hyperbaric oxygen for children with cerebral palsy: A randomised multicentre trial. Lancet 2001, 357, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, G.; Cifu, D.; Baugh, L.; Carne, W.; Profenna, L. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen on symptoms after mild traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoesen, K.B.; Camporesi, E.M.; Moon, R.E.; Hage, M.L.; Piantadosi, C.A. Should hyperbaric oxygen be used to treat the pregnant patient for acute carbon monoxide poisoning? A case report and litrature review. JAMA 1989, 261, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

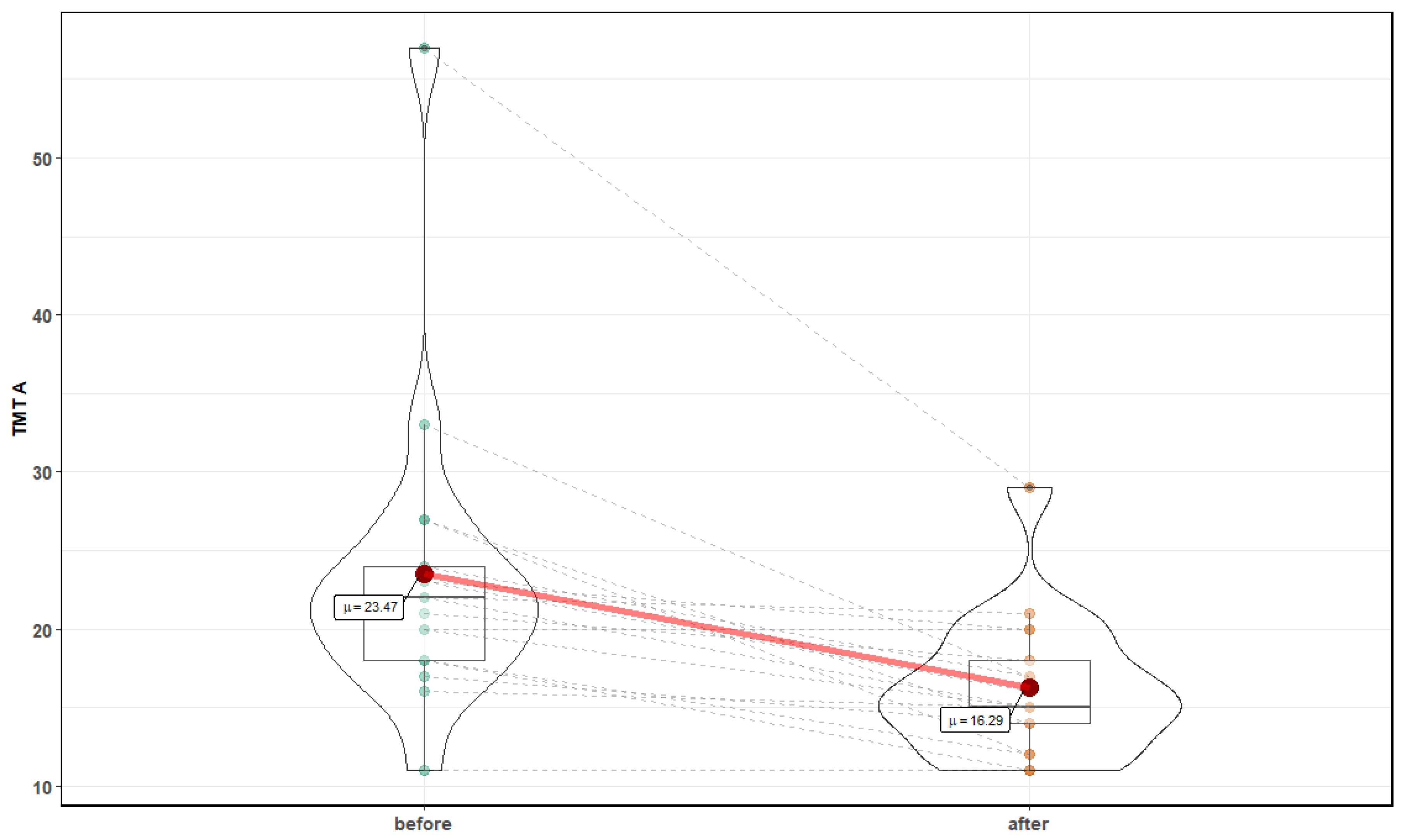
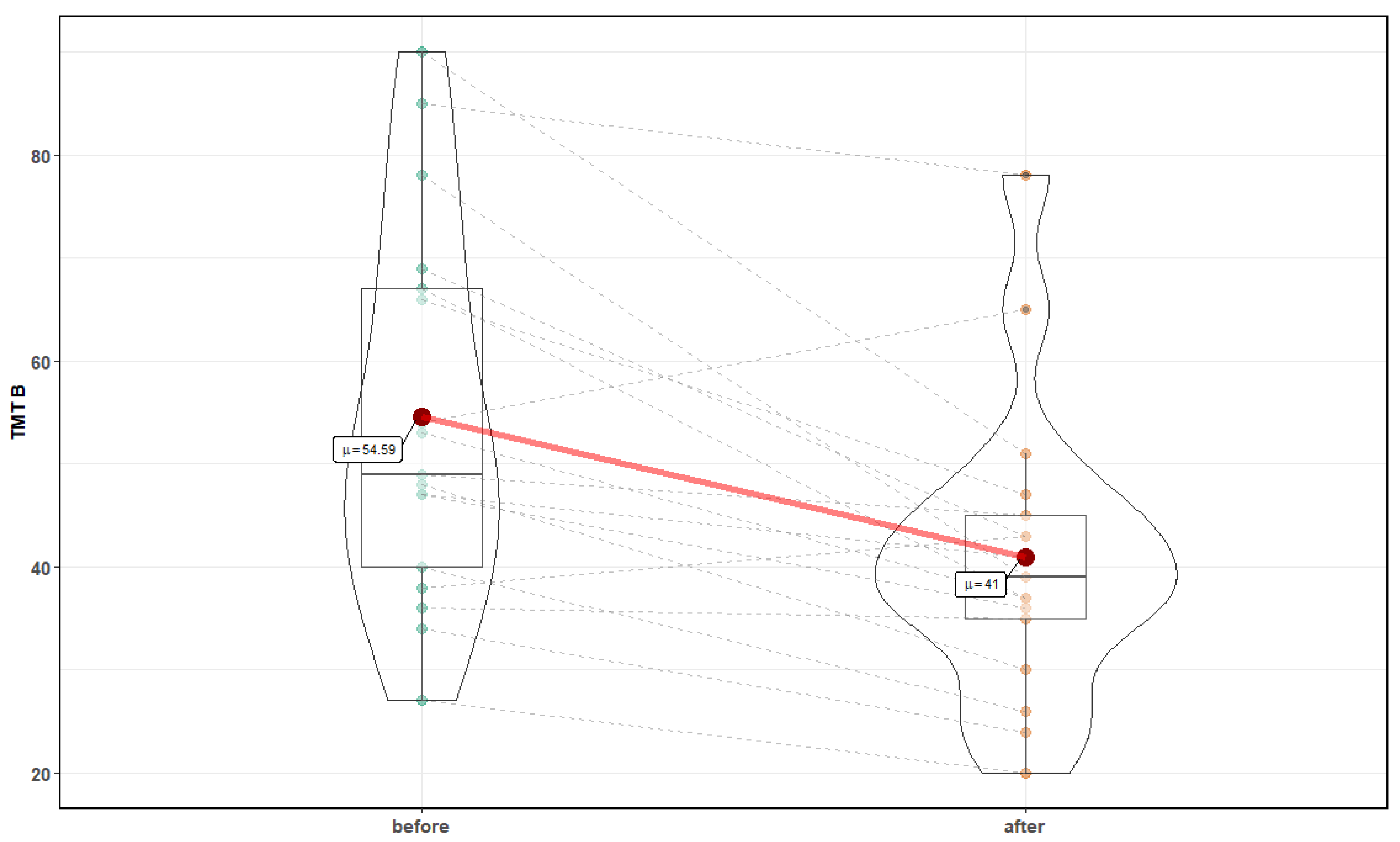
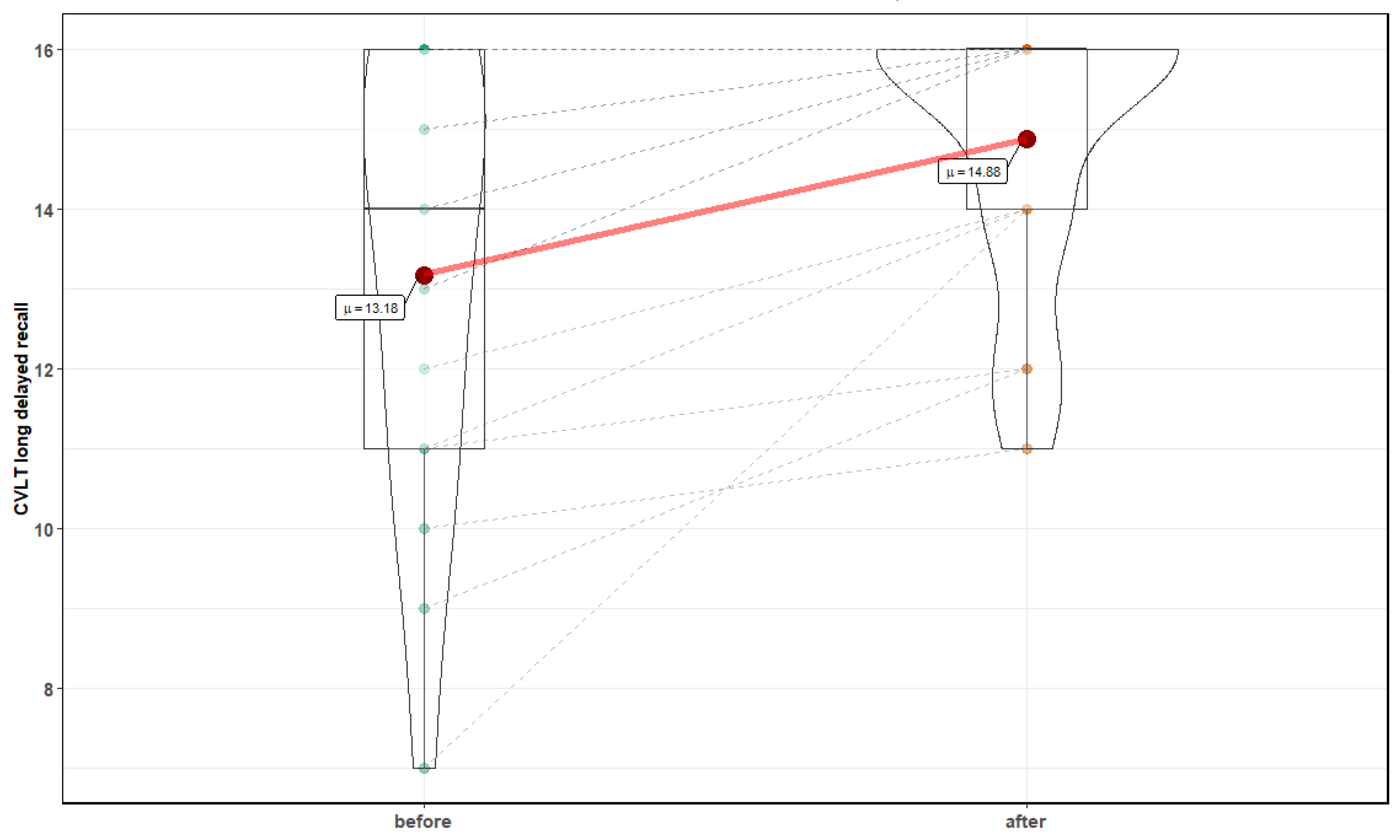
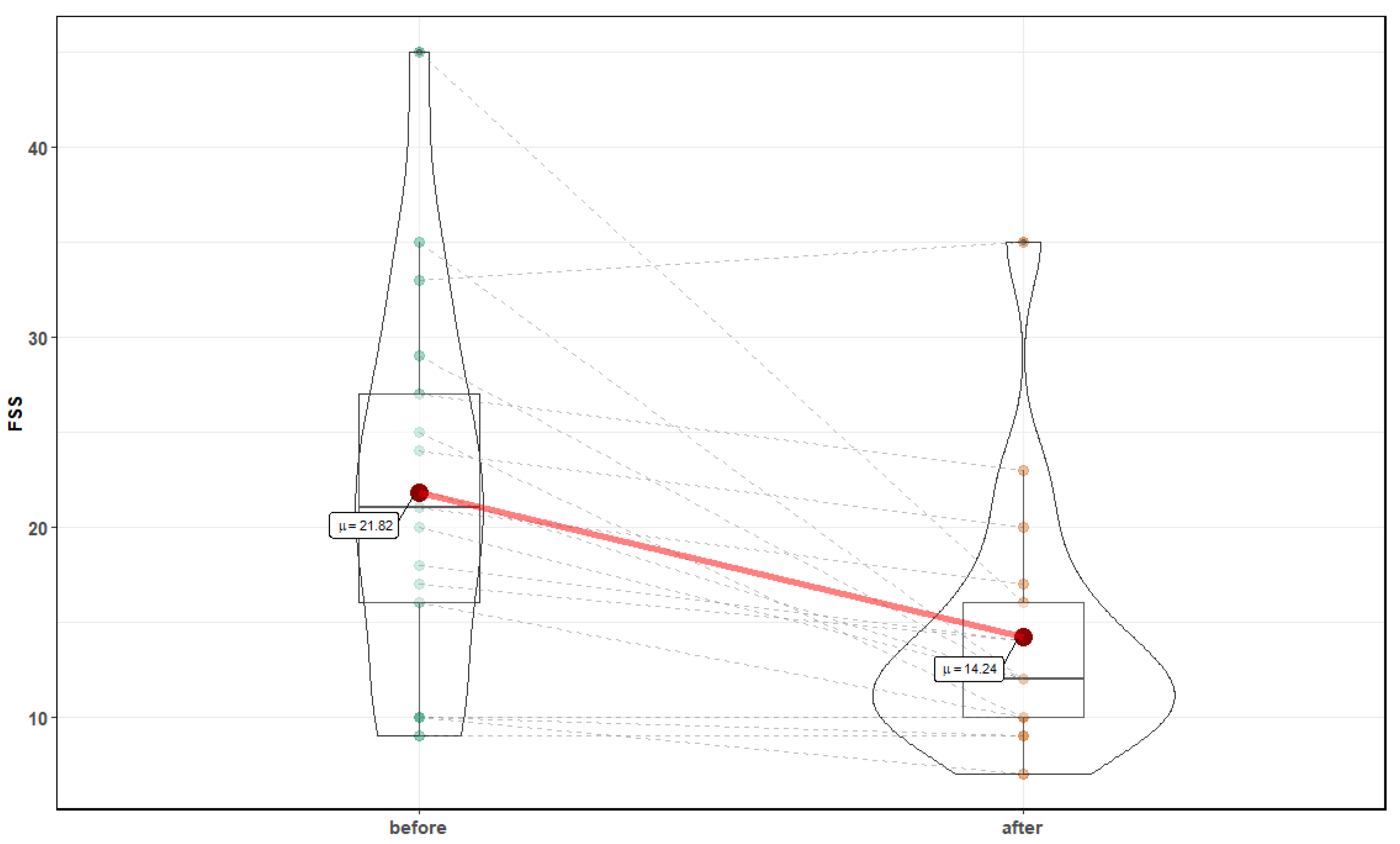

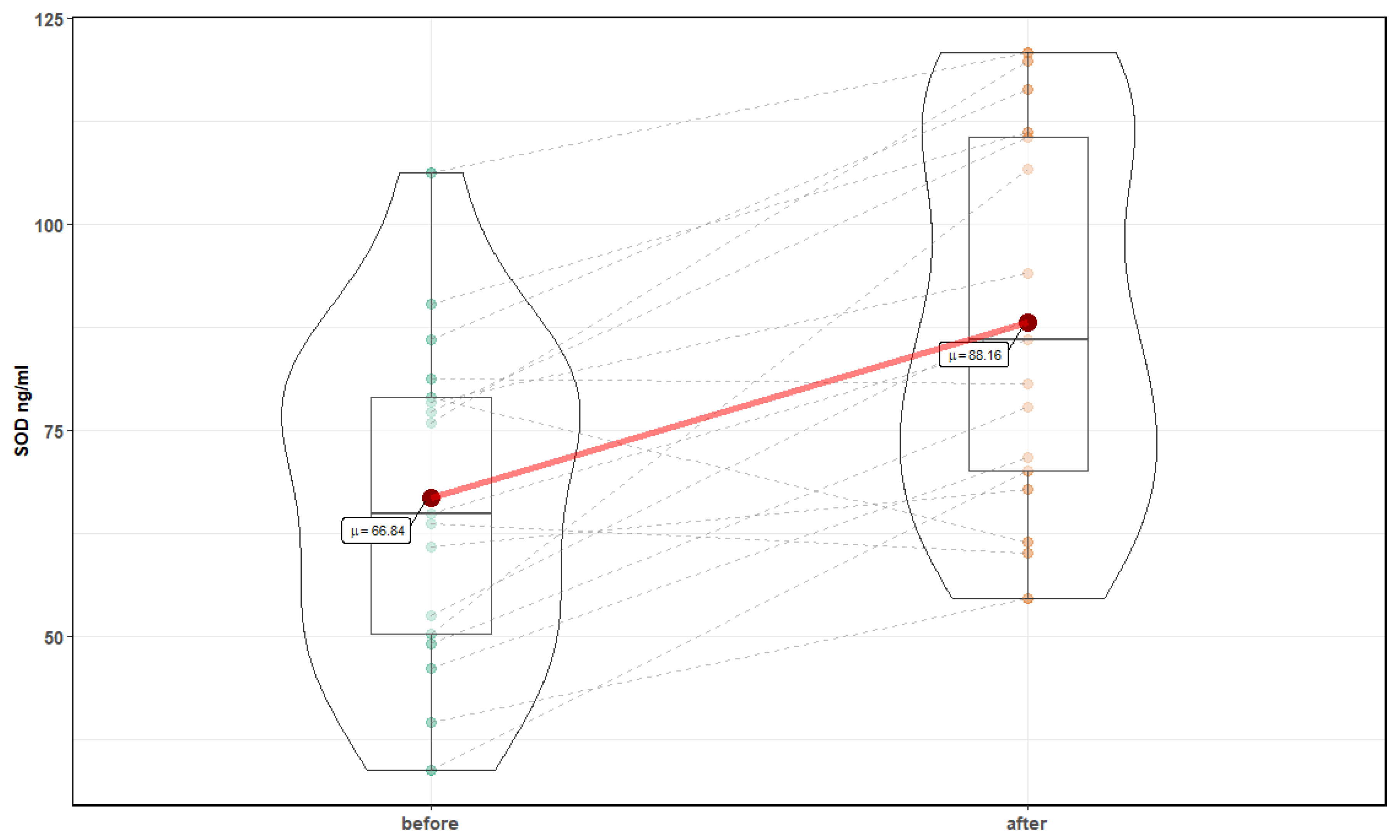
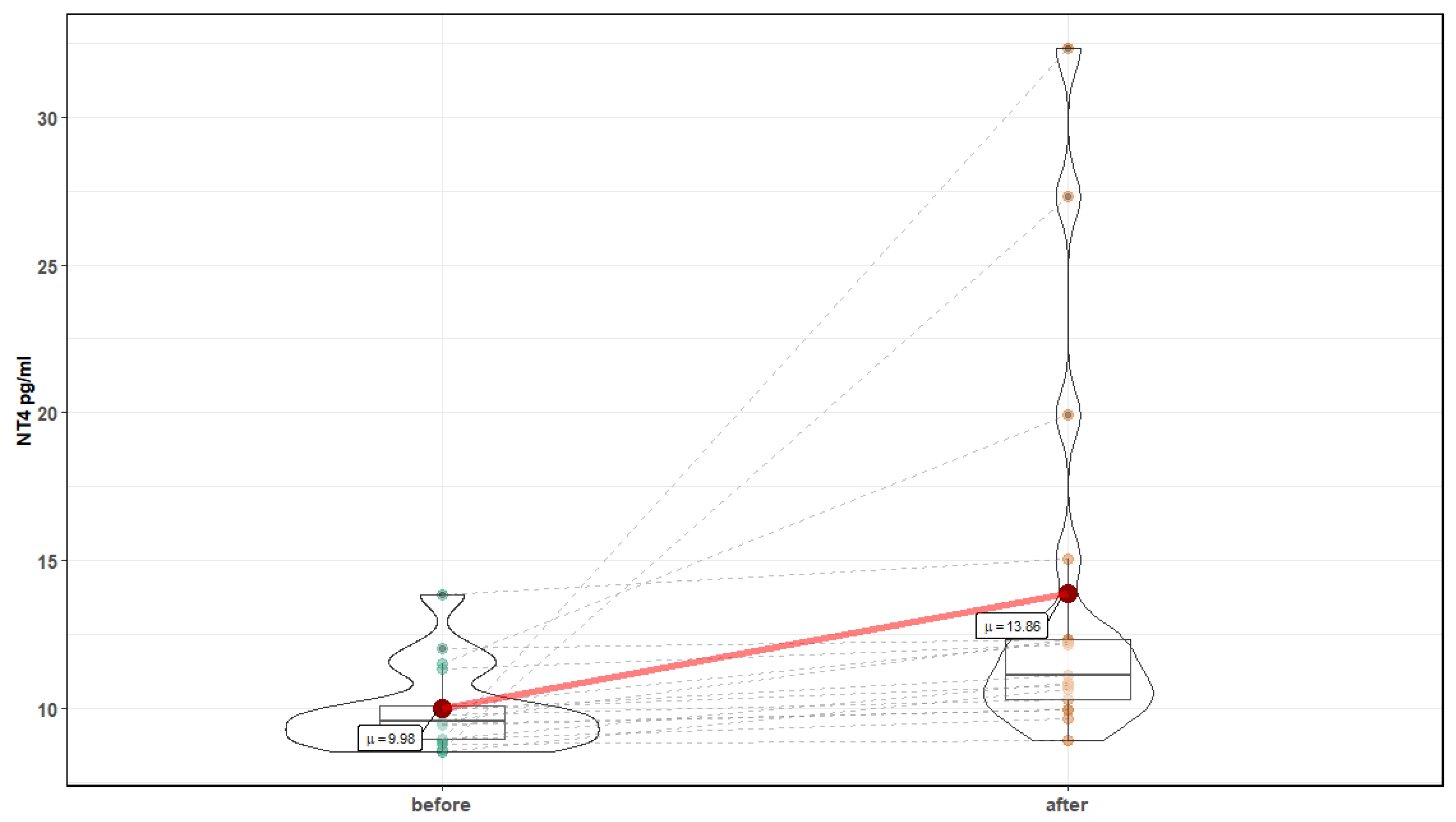
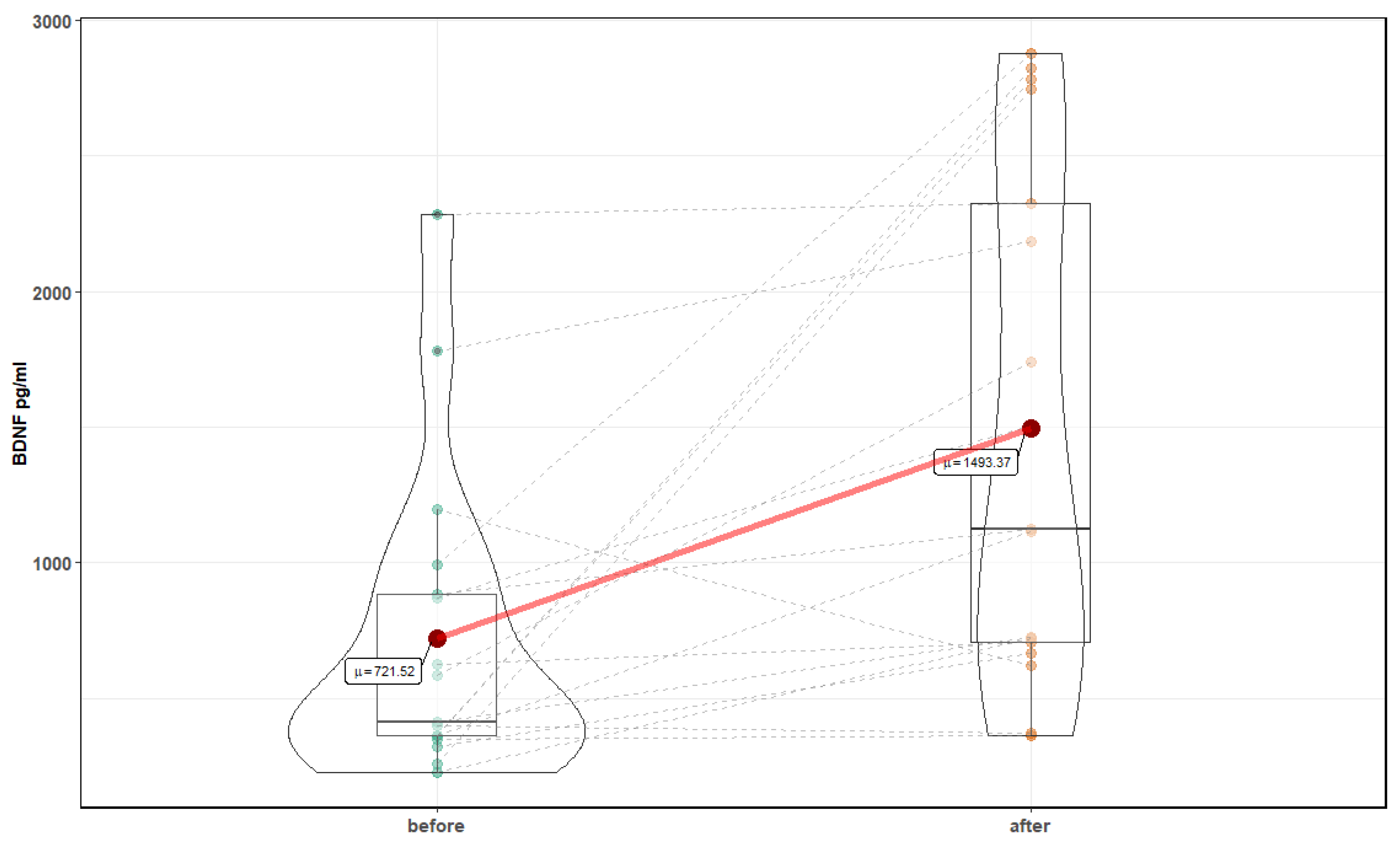
| Parameter | Before Mean ± SD | After Mean ± SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | 81.44±23.5 | 81.01±23.3 | 0.03 |
| BMR (kcal) | 7498.97±1944.2 | 7543.56±1970.4 | 0.35 |
| FatP (%) | 24.86±7.8 | 23.93±7.7 | 0.04 |
| FFM (kg) | 60.32±15.5 | 60.77±15.6 | 0.31 |
| VFatL | 6.88±5.3 | 6.65±4.9 | 0.18 |
| Bone Mass (kg) | 3.00±0.7 | 3.04±0.7 | 0.08 |
| Value | SE | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 11.81 | 0.64 | <0.01 |
| before:after | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.34 |
| BDNF | 0.0015 | 0.0005 | 0.006 |
| Value | SE | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 12.45 | 0.56 | <0.0001 |
| before: after | 1.22 | 0.46 | 0.017 |
| BDNF | 0.0009 | 0.0004 | 0.021 |
| Parameter | Before Mean ± SD | After Mean ± SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR (1/min) | 69.77 ± 11.2 | 68.46 ± 10 | >0.05 |
| sBP (mmHg) | 114.26 ± 16.4 | 113.38 ± 14.4 | >0.05 |
| dBP (mmHg) | 74.25 ± 9.0 | 74.61 ± 8.5 | >0.05 |
| mBP (mmHg) | 90.58 ± 10.8 | 90.50 ± 9.3 | >0.05 |
| SI (ml/m2) | 51.71 ± 12 | 50.39 ± 13.3 | >0.05 |
| CI (l/min/m2) | 3.51 ± 0.6 | 3.36 ± 0.7 | >0.05 |
| TPRI (dyn*s*m2/cm5) | 2110.44 ± 664.4 | 2200 ± 582.1 | >0.05 |
| LF-RRI (ms2) | 506.62 ± 475.1 | 708.18 ± 734.3 | >0.05 |
| HF-RRI (ms2) | 410.35 ± 339.1 | 581.4 ± 580.6 | >0.05 |
| LF/HF | 1.64 ± 1.2 | 1.76 ± 1.3 | >0.05 |
| LF-dBP (mmHg2) | 5.54 ± 5.1 | 6.29 ± 5.8 | >0.05 |
| HF-dBP (mmHg2) | 0.94 ± 0.9 | 1.41 ± 1.1 | >0.05 |
| LF-sBP (mmHg2) | 8.25 ± 7.7 | 6.45 ± 4.7 | >0.05 |
| HF-sBP (mmHg2) | 2.91 ± 3.6 | 2.49 ± 1.6 | >0.05 |
| Total Slope Mean (ms/mmHg) | 17.91 ± 9.1 | 22.13 ± 9.2 | 0.003 |
| Parameter | Before Mean ± SD | After Mean ± SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Δ HR (1/min) | −14.50 ± 5.7 | −13.64 ± 5.3 | >0.05 |
| Δ sBP (mmHg) | −17.63 ± 8.9 | −16.51 ± 7.5 | >0.05 |
| Δ dBP (mmHg) | −19.95 ± 5.7 | −18.96 ± 7.9 | >0.05 |
| Δ mBP (mmHg) | −18.82 ± 6.7 | −17.46 ± 7.6 | >0.05 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kujawski, S.; Słomko, J.; Morten, K.J.; Murovska, M.; Buszko, K.; Newton, J.L.; Zalewski, P. Autonomic and Cognitive Function Response to Normobaric Hyperoxia Exposure in Healthy Subjects. Preliminary Study. Medicina 2020, 56, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56040172
Kujawski S, Słomko J, Morten KJ, Murovska M, Buszko K, Newton JL, Zalewski P. Autonomic and Cognitive Function Response to Normobaric Hyperoxia Exposure in Healthy Subjects. Preliminary Study. Medicina. 2020; 56(4):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56040172
Chicago/Turabian StyleKujawski, Sławomir, Joanna Słomko, Karl J. Morten, Modra Murovska, Katarzyna Buszko, Julia L. Newton, and Paweł Zalewski. 2020. "Autonomic and Cognitive Function Response to Normobaric Hyperoxia Exposure in Healthy Subjects. Preliminary Study" Medicina 56, no. 4: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56040172
APA StyleKujawski, S., Słomko, J., Morten, K. J., Murovska, M., Buszko, K., Newton, J. L., & Zalewski, P. (2020). Autonomic and Cognitive Function Response to Normobaric Hyperoxia Exposure in Healthy Subjects. Preliminary Study. Medicina, 56(4), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56040172







