Treatment of Unstable Pediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures with Titanium Elastic Nails
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Population
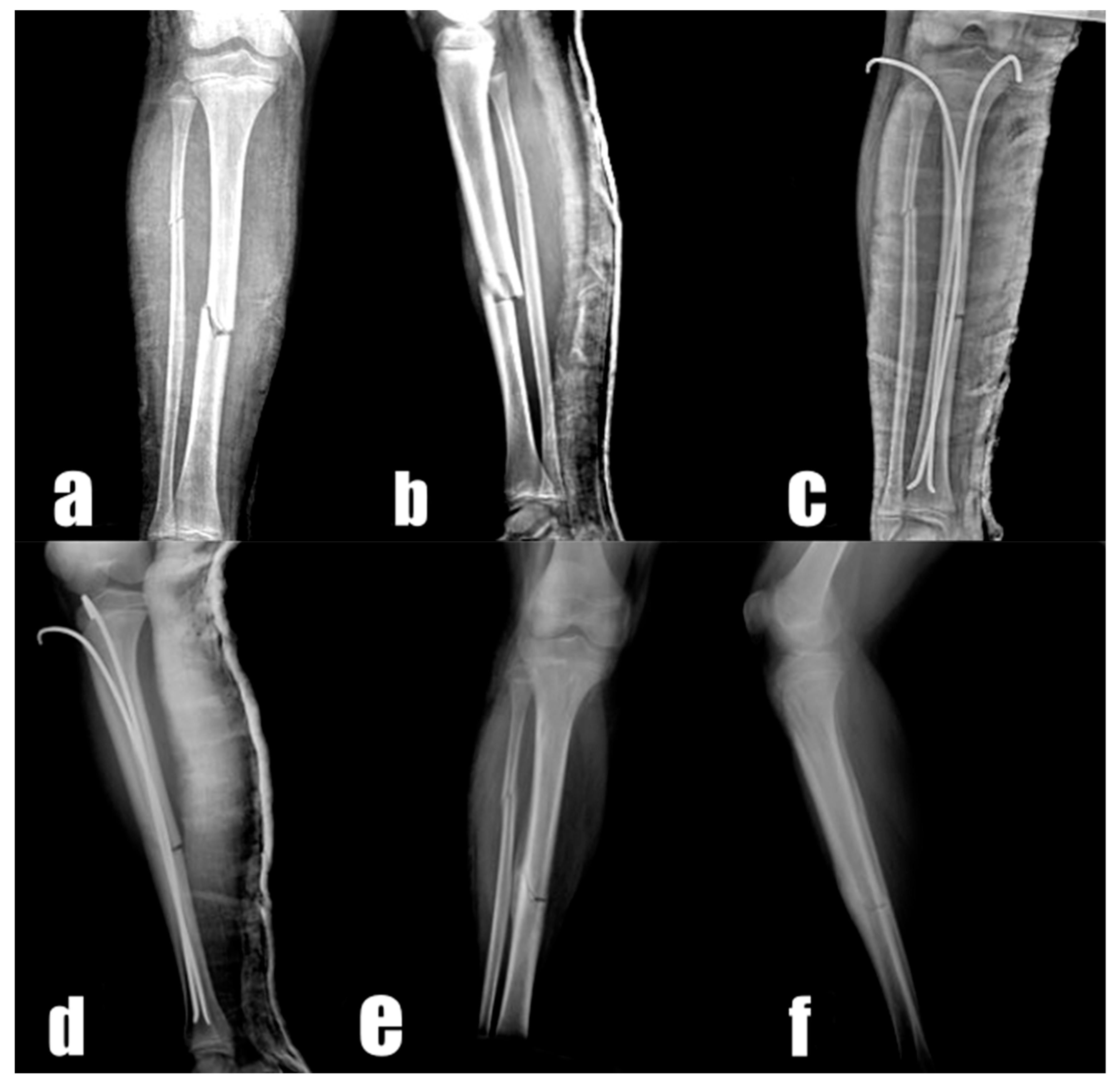
2.2. Surgical Technique
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joeris, A.; Lutz, N.; Wicki, B.; Slongo, T.; Audigé, L. An epidemiological evaluation of pediatric long bone fractures—A retrospective cohort study of 2716 patients from two Swiss tertiary pediatric hospitals. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galano, G.J.; Vitale, M.A.; Kessler, M.W.; Hyman, J.E.; Vitale, M.G. The Most Frequent Traumatic Orthopaedic Injuries from a National Pediatric Inpatient Population. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2005, 25, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mashru, R.P.; Herman, M.J.; Pizzutillo, P.D. Tibial Shaft Fractures in Children and Adolescents. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2005, 13, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandya, N.K.; Edmonds, E.W. Immediate Intramedullary Flexible Nailing of Open Pediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2012, 32, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.; Oh, C.-W.; Park, K.-H.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.-C.; Park, I.-H. Elastic nailing of tibia shaft fractures in young children up to 10 years of age. Injury 2016, 47, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubiak, E.N.; Egol, K.A.; Scher, D.; Wasserman, B.; Feldman, D.; Koval, K.J. Operative Treatment of Tibial Fractures in Children: Are Elastic Stable Intramedullary Nails an Improvement Over External Fixation? J. Bone Surg. Am. 2005, 87, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, S.H.; Spiegel, D.; Flynn, J.M. External Fixation of High-Energy Tibia Fractures. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2007, 27, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligier, J.; Metaizeau, J.; Prévot, J.; Lascombes, P. Elastic Stable Intramedullary Pinning of Long Bone Shaft Fractures in Children. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1985, 40, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.K.; Horstman, J.; Kuester, V.; Sambandam, S.; Mounasamy, V. Pediatric tibial shaft fractures. Indian J. Orthop. 2018, 52, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.E.; Gregush, R.V.; Schoenecker, P.L.; Dobbs, M.B.; Luhmann, S.J. Complications After Titanium Elastic Nailing of Pediatric Tibial Fractures. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2007, 27, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, N.K.; Edmonds, E.W.; Mubarak, S.J. The incidence of compartment syndrome after flexible nailing of pediatric tibial shaft fractures. J. Child. Orthop. 2011, 5, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustilo, R.B.; Anderson, J.T. Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones: retrospective and prospective analyses. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1976, 58, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.M.; Hresko, T.; Reynolds, R.A.K.; Blasier, R.D.; Davidson, R.; Kasser, J. Titanium Elastic Nails for Pediatric Femur Fractures: A Multicenter Study of Early Results with Analysis of Complications. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2001, 21, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, P.; De Graaf, J.; Leemans, R. The use of elastic intramedullary nailing in the stabilisation of paediatric fractures. Injury 2005, 36, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swindells, M.G.; Rajan, R.A. Elastic intramedullary nailing in unstable fractures of the paediatric tibial diaphysis: a systematic review. J. Child. Orthop. 2009, 4, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, S.; Debbarma, S.; Sarkar, A. Titanium elastic nailing osteosynthesis for diaphyseal tibial fracture in pediatrıc age group-our experience. Indian J. Appl. Res. 2017, 7, 52–53. [Google Scholar]
- Pennock, A.T.; Bastrom, T.P.; Upasani, V.V. Elastic intramedullary nailing versus open reduction internal fixation of pediatric tibial shaft fractures. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2017, 37, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, T.; Weisman, D.S.; Ronchetti, P.; Piller, C.P.; Maloney, M. Flexible Titanium Nailing for the Treatment of the Unstable Pediatric Tibial Fracture. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2004, 24, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, W.N.; Jones, K.J.; David Horn, B.; Wells, L. Titanium elastic nails for pediatric tibial shaft fractures. J. Child. Orthop. 2007, 1, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başaran, S.H.; Erçin, E.; Çümen, H.; Daşar, U.; Bilgili, M.G.; Avkan, M.C. The titanium elastic nailing in pediatric tibia fractures caused pedestrian versus motor vehicle accidents. Bakirkoy Tip Derg. 2016, 12, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onta, P.R.; Thapa, P.; Sapkota, K.; Ranjeet, N.; Kishore, A.; Gupta, M. Outcome of diaphyseal fracture of tibia treated with flexible intramedullary nailing in pediatrics age group; A prospective study. Am. J. Public Health. 2015, 3, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kc, K.M.; Acharya, P.; Sigdel, A. Titanium elastic nailing system (TENs) for tibia fractures in children: functional outcomes and complications. J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 2016, 55, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallamshetla, V.R.; De Silva, U.; Bache, C.E.; Gibbons, P.J. Flexible intramedullary nails for unstable fractures of the tibia in children: An eight-year experience. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2006, 88, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patients | Gender | Age (year) | Side | Character of Fracture | Fracture Type | Etiology | Fracture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 11 | R | Closed | Transverse | Falling Down | Tibia-Fibula |
| 2 | M | 13 | L | Closed | Oblique | Road Accident | Tibia-Fibula |
| 3 | M | 14 | L | Closed | Transverse | Road Accident | Tibia-Fibula |
| 4 | F | 3 | R | Closed | Oblique | Road Accident | Tibia-Fibula |
| 5 | F | 12 | L | Closed | Spiral | Falling Down | Tibia |
| 6 | M | 10 | L | Closed | Spiral | Road Accident | Tibia-Fibula |
| 7 | M | 8 | L | Closed | Spiral | Falling Down | Tibia-Fibula |
| 8 | M | 8 | L | Closed | Spiral | Falling Down | Tibia |
| 7 | F | 9 | L | Closed | Spiral | Falling Down | Tibia |
| 10 | F | 7 | L | Closed | Oblique | Road Accident | Tibia-Fibula |
| 11 | M | 5 | L | Closed | Transverse | Road Accident | Tibia-Fibula |
| 12 | M | 5 | L | Closed | Spiral | Road Accident | Tibia-Fibula |
| 13 | M | 9 | R | Closed | Spiral | Falling Down | Tibia |
| 14 | M | 7 | L | GRADE 1 | Transverse | Falling Down | Tibia-Fibula |
| 15 | M | 8 | L | GRADE 2 | Spiral | Road Accident | Tibia-Fibula |
| 16 | M | 11 | R | GRADE 2 | Transverse | Road Accident | Tibia-Fibula |
| 17 | M | 12 | R | GRADE 2 | Transverse | Road Accident | Tibia-Fibula |
| 18 | M | 8 | L | GRADE 2 | Spiral | Road Accident | Tibia |
| 19 | M | 9 | L | GRADE 2 | Oblique | Falling Down | Tibia-Fibula |
| 20 | M | 9 | R | GRADE 2 | Spiral | Road Accident | Tibia-Fibula |
| Patients | Character of Fracture | Follow up (Month) | Healing Time | Residual Deficiency | Complication | Weight-Bearing Time (Week) | Pin Tract Infection/Irritation | Shortness | Functional Result (Flynn Criteria) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Closed | 22 | 10 | 0/0 | None | 2 | Irritation | None | Excellent |
| 2 | Closed | 60 | 11 | 0/0 | None | 1 | None | None | Excellent |
| 3 | Closed | 30 | 12 | 0/0 | None | 2 | None | None | Excellent |
| 4 | Closed | 30 | 10 | 6/3 | None | 3 | None | None | Satisfactory |
| 5 | Closed | 7 | 14 | 6/8 | None | 2 | None | None | Satisfactory |
| 6 | Closed | 16 | 12 | 9/7 | None | 2 | None | None | Satisfactory |
| 7 | Closed | 18 | 14 | 4/8 | None | 2 | Irritation | None | Satisfactory |
| 8 | Closed | 42 | 7 | 0/8 | None | 2 | None | None | Excellent |
| 7 | Closed | 40 | 6 | 0/0 | None | 1 | None | None | Excellent |
| 10 | Closed | 22 | 20 | 0/0 | None | 1 | None | None | Excellent |
| 11 | Closed | 7 | 7 | 4/4 | None | 3 | Irritation | None | Excellent |
| 12 | Closed | 9 | 6 | 0/0 | None | 1 | None | None | Excellent |
| 13 | Closed | 9 | 9 | 3/5 | None | 2 | None | None | Excellent |
| 14 | Grade I Open | 28 | 8 | 0/0 | None | 1 | None | None | Excellent |
| 15 | Grade II Open | 40 | 10 | 0/0 | None | 2 | None | None | Excellent |
| 16 | Grade II Open | 15 | 10 | 9/3 | None | 3 | Irritation | None | Satisfactory |
| 17 | Grade II Open | 20 | 12 | 6/3 | Wound infection (Superficial) | 2 | None | None | Satisfactory |
| 18 | Grade II Open | 48 | 12 | 8/0 | None | 3 | None | None | Satisfactory |
| 19 | Grade II Open | 7 | 15 | 10/5 | Wound infection (Deep) | 4 | infection | Yes | Satisfactory |
| 20 | Grade II Open | 28 | 12 | 0/0 | Wound infection (Superficial) | 3 | infection | None | Excellent |
| Features | Closed Fracture | Open Fracture | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 13 | 7 | |
| Gender M/F | 9/4 | 7/0 | p > 0.05 |
| Side R/L | 3/10 | 3/4 | p > 0.05 |
| Weight-bearing time (week) | 1.84 ± 0.68 | 2.57 ± 0.97 | p > 0.05 |
| Healing time (week) | 10.61 ± 3.93 | 11.28 ± 2.21 | p > 0.05 |
| Complication | None | 3 | p < 0.05 |
| Residual deficiency (coronal/sagittal angulation) degree | 5 | 4 | p > 0.05 |
| Pin tract infection/irritation | 3 | 3 | p > 0.05 |
| Shortness | No | 1 | p > 0.05 |
| Functional result(Flynn Criteria) | Excellent: 9 | Excellent: 3 | p > 0.05 |
| Satisfactory: 4 | Satisfactory: 4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uludağ, A.; Tosun, H.B. Treatment of Unstable Pediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures with Titanium Elastic Nails. Medicina 2019, 55, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55060266
Uludağ A, Tosun HB. Treatment of Unstable Pediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures with Titanium Elastic Nails. Medicina. 2019; 55(6):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55060266
Chicago/Turabian StyleUludağ, Abuzer, and Hacı Bayram Tosun. 2019. "Treatment of Unstable Pediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures with Titanium Elastic Nails" Medicina 55, no. 6: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55060266
APA StyleUludağ, A., & Tosun, H. B. (2019). Treatment of Unstable Pediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures with Titanium Elastic Nails. Medicina, 55(6), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55060266





