Which Should Be Used First for ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Chemotherapy or Targeted Therapy? A Meta-Analysis of Five Randomized Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analysis
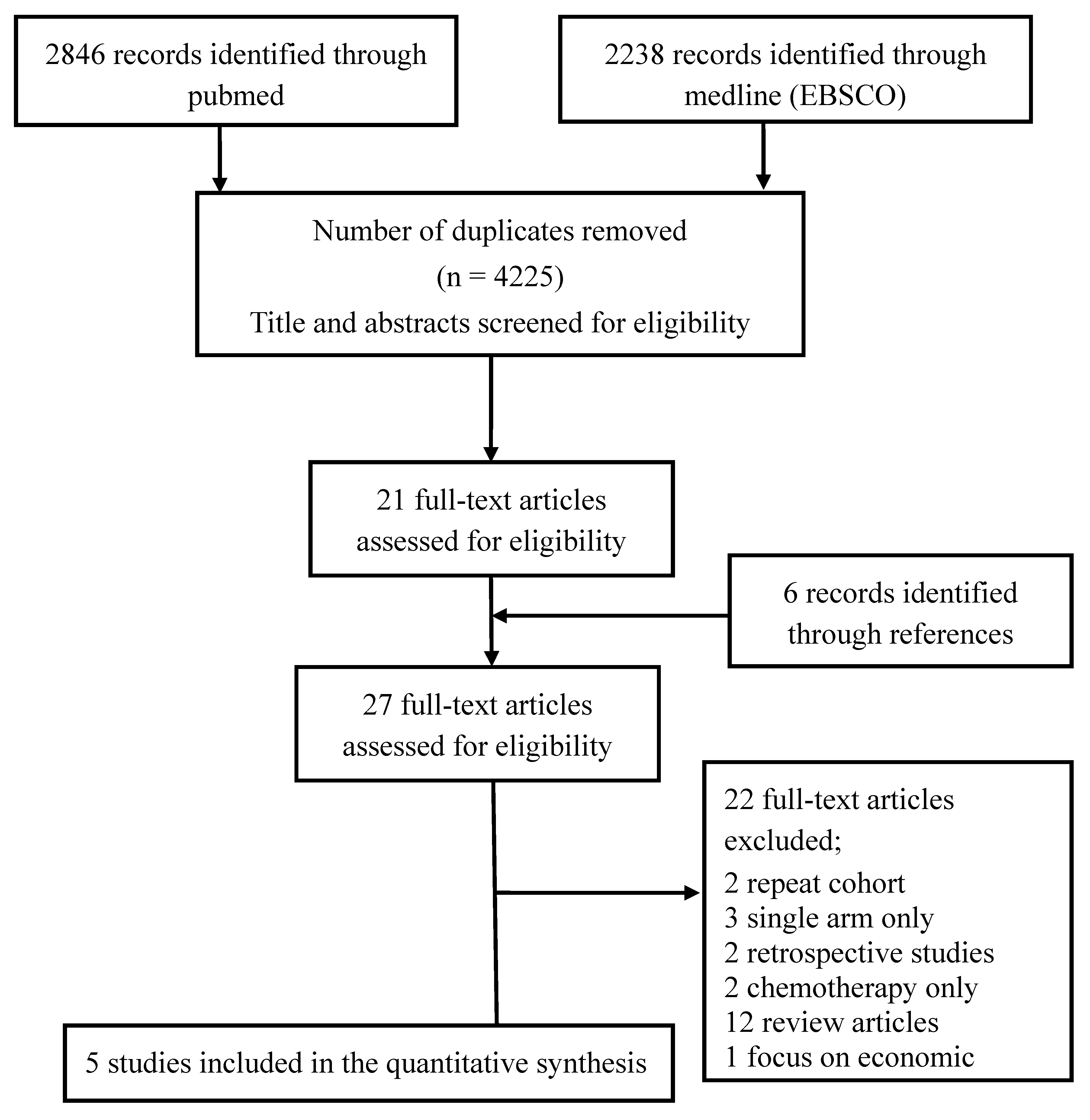
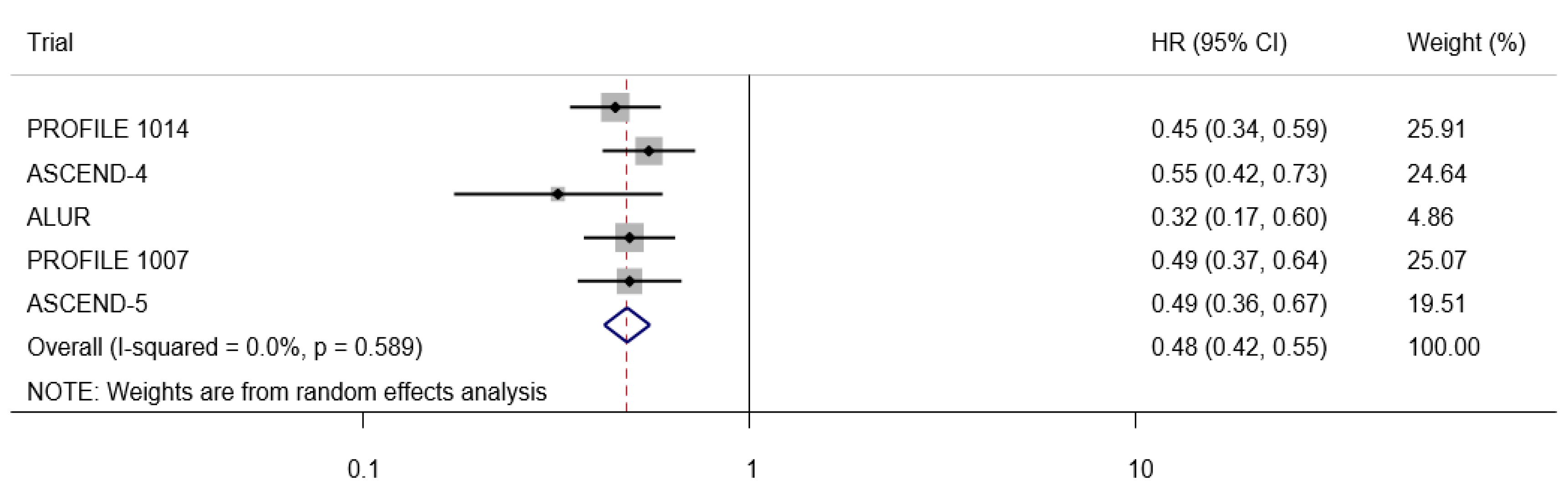
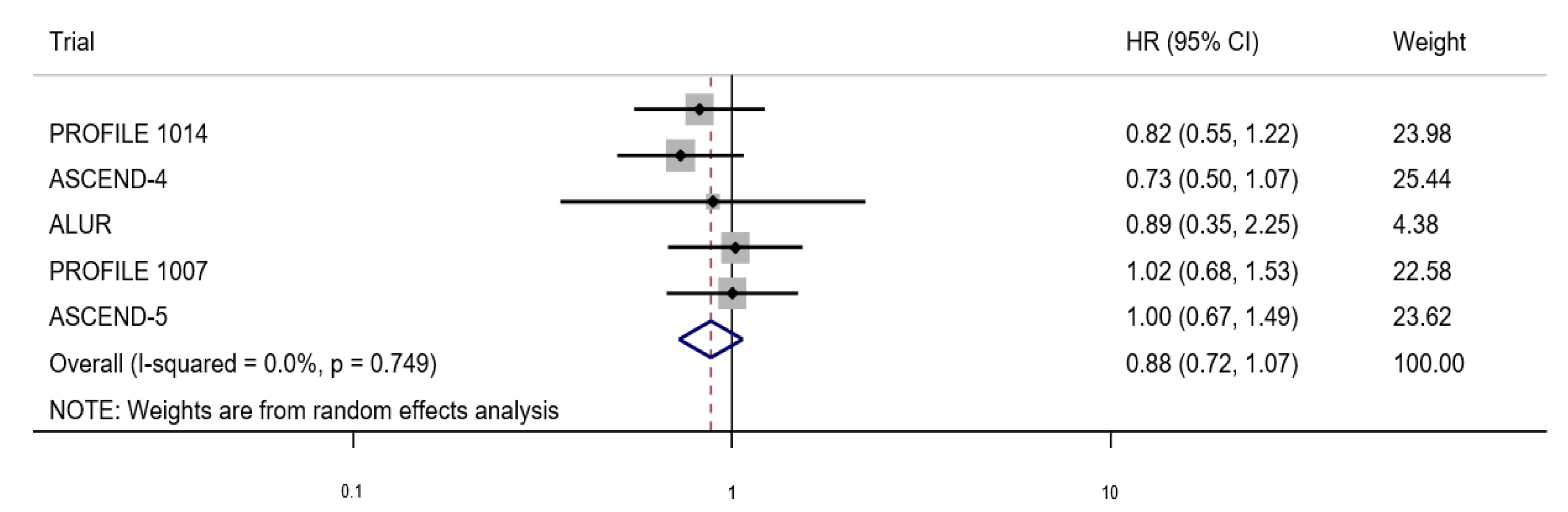
3. Results
Search Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Yeap, B.Y.; Solomon, B.J.; Riely, G.J.; Gainor, J.; Engelman, J.A.; Shapiro, G.I.; Costa, D.B.; Ou, S.H.; Butaney, M.; et al. Effect of crizotinib on overall survival in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring ALK gene rearrangement: A retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadad, A.R.; Moore, R.A.; Carroll, D.; Jenkinson, C.; Reynolds, D.J.; Gavaghan, D.J.; McQuay, H.J. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary? Control. Clin. Trials 1996, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, S.; Mazieres, J.; Oh, I.J.; de Castro, J.; Migliorino, M.R.; Helland, A.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Griesinger, F.; Kotb, A.; Zeaiter, A.; et al. Alectinib versus chemotherapy in crizotinib-pretreated anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from the phase III ALUR study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.J.; et al. First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Nakagawa, K.; Seto, T.; Crino, L.; Ahn, M.J.; De Pas, T.; Besse, B.; Solomon, B.J.; Blackhall, F.; et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, T.M.; Crino, L.; Gridelli, C.; Kiura, K.; Liu, G.; Novello, P.S.; Bearz, A.; Gautschi, O.; Mok, T.; et al. Ceritinib versus chemotherapy in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer previously given chemotherapy and crizotinib (ASCEND-5): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kono, S.A.; Lu, X.; Okuyama, S.; Baron, A.E.; Oton, A.B.; Davies, A.M.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Franklin, W.; Doebele, R.C. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene rearrangements in non-small cell lung cancer are associated with prolonged progression-free survival on pemetrexed. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kron, A.; Alidousty, C.; Scheffler, M.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Seidel, D.; Riedel, R.; Ihle, M.A.; Michels, S.; Nogova, L.; Fassunke, J.; et al. Impact of TP53 mutation status on systemic treatment outcome in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2068–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated alk-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J. Treatment of ALK-positive nonsmall cell lung cancer: Recent advances. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leprieur, E.G.; Fallet, V.; Cadranel, J.; Wislez, M. Spotlight on crizotinib in the first-line treatment of ALK-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Patients selection and perspectives. Lung Cancer 2016, 7, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
| Trials, Year | Setting | Regiment | Patient No. | Age (Median) | Cross-Over (%) | Initial Brain Meta (%) | Follow-Up Median Time (m) | PFS (m) | OS (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROFILE 1014, 2014 [1] | First-line | Crizotinib vs. PEM + cisplatin | 172 171 | 52 54 | Yes (70%) | 26 27 | 17.4 16.7 | 10.9 7 | 17.4 16.7 |
| ASCEND-4, 2017 [6] | First-line | Ceritinib vs. PEM + platinum | 189 187 | 55 54 | Yes ((105/187)56%) | 31 33 | NA NA | 16.6 8.1 | NR 26.2 |
| PROFILE 1007, 2013 [5] | Second-line | Crizotinib vs. PEM or TXT | 173 174 | 51 49 | Yes ((112/174)64%) | 35 34 | 12.2 12.1 | 7.7 3.0 | NR NR |
| ALUR, 2018 [4] | Two prior lines, crizotinib, platinum-based doublet | Alectinib vs. PEM or TXT | 72 35 (2:1 block) | 55.5 59 | Yes (70.6%) | 65.3 74.3 | 6.5 5.8 | 7.1 1.6 | 12.6 NR |
| ASCEND-5, 2017 [7] | 1 or 2 chemotherapy, and crizotinib resistance | Ceritinib vs. PEM or TXT | 115 116 | 54 54 | Yes (64.7%) | 57 59 | 19.7 | 5.4 1.6 | 18.1 20.1 |
| Trials, Year | Was the Study Described as Randomized? | Method to Generate the Sequence of Randomization was Described and Appropriate | Was the Study Described as a Double Blind? | Method of Double Blinding was Described and Appropriate | Was There a Description of Withdrawal and Dropouts? | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROFILE 1014, 2014 [1] | * | - | - | - | * | 2 |
| ASCEND-4, 2017 [6] | * | * | - | - | * | 3 |
| PROFILE 1007, 2013 [5] | * | - | - | - | * | 2 |
| ALUR, 2018 [4] | * | - | - | - (note) | - | 1 |
| ASCEND-5, 2017 [7] | * | * | - | - (note) | * | 3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-C.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Lee, Y.-L.; Li, C.-Y. Which Should Be Used First for ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Chemotherapy or Targeted Therapy? A Meta-Analysis of Five Randomized Trials. Medicina 2019, 55, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55020029
Lee Y-C, Hsieh C-C, Lee Y-L, Li C-Y. Which Should Be Used First for ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Chemotherapy or Targeted Therapy? A Meta-Analysis of Five Randomized Trials. Medicina. 2019; 55(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yen-Chien, Chung-Cheng Hsieh, Yen-Ling Lee, and Chung-Yi Li. 2019. "Which Should Be Used First for ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Chemotherapy or Targeted Therapy? A Meta-Analysis of Five Randomized Trials" Medicina 55, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55020029
APA StyleLee, Y.-C., Hsieh, C.-C., Lee, Y.-L., & Li, C.-Y. (2019). Which Should Be Used First for ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Chemotherapy or Targeted Therapy? A Meta-Analysis of Five Randomized Trials. Medicina, 55(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55020029






