Protective Effect of Hepcidin on Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury via Activating the Nrf2/GPX4 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animal
2.2. Cell Lines
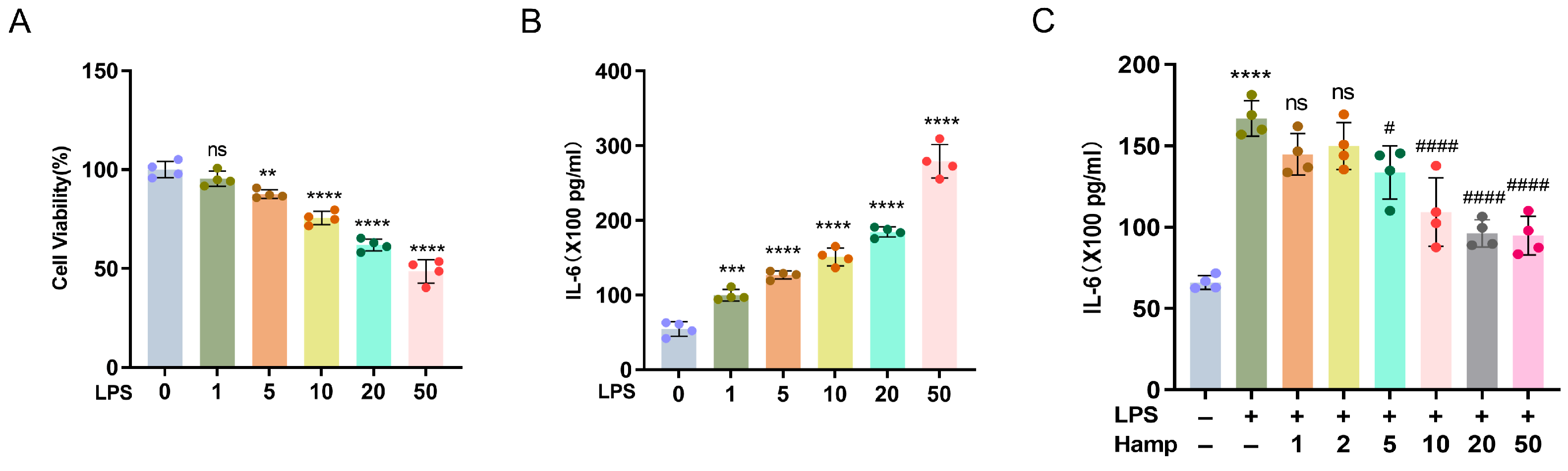
2.3. Cell Viability
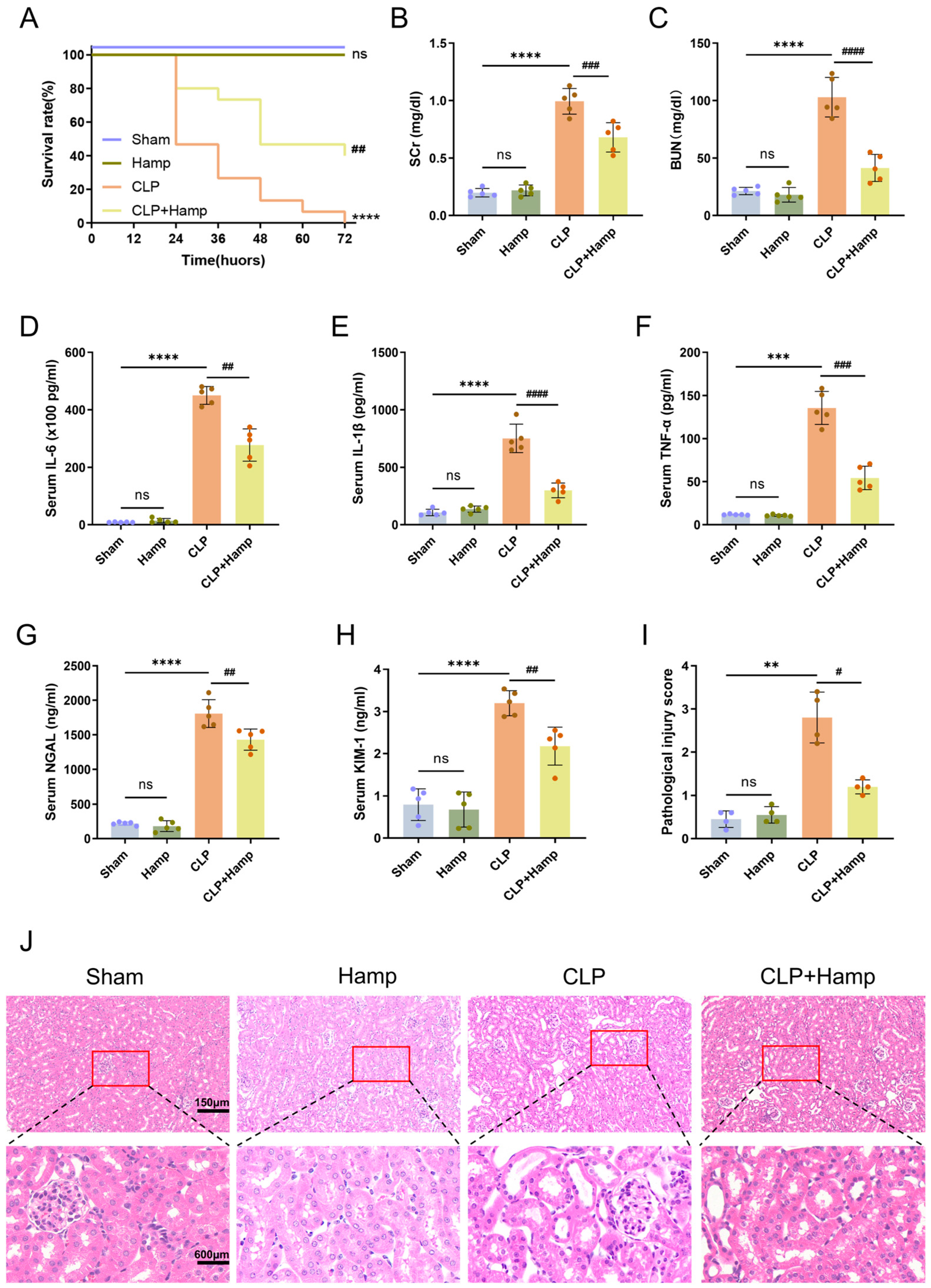
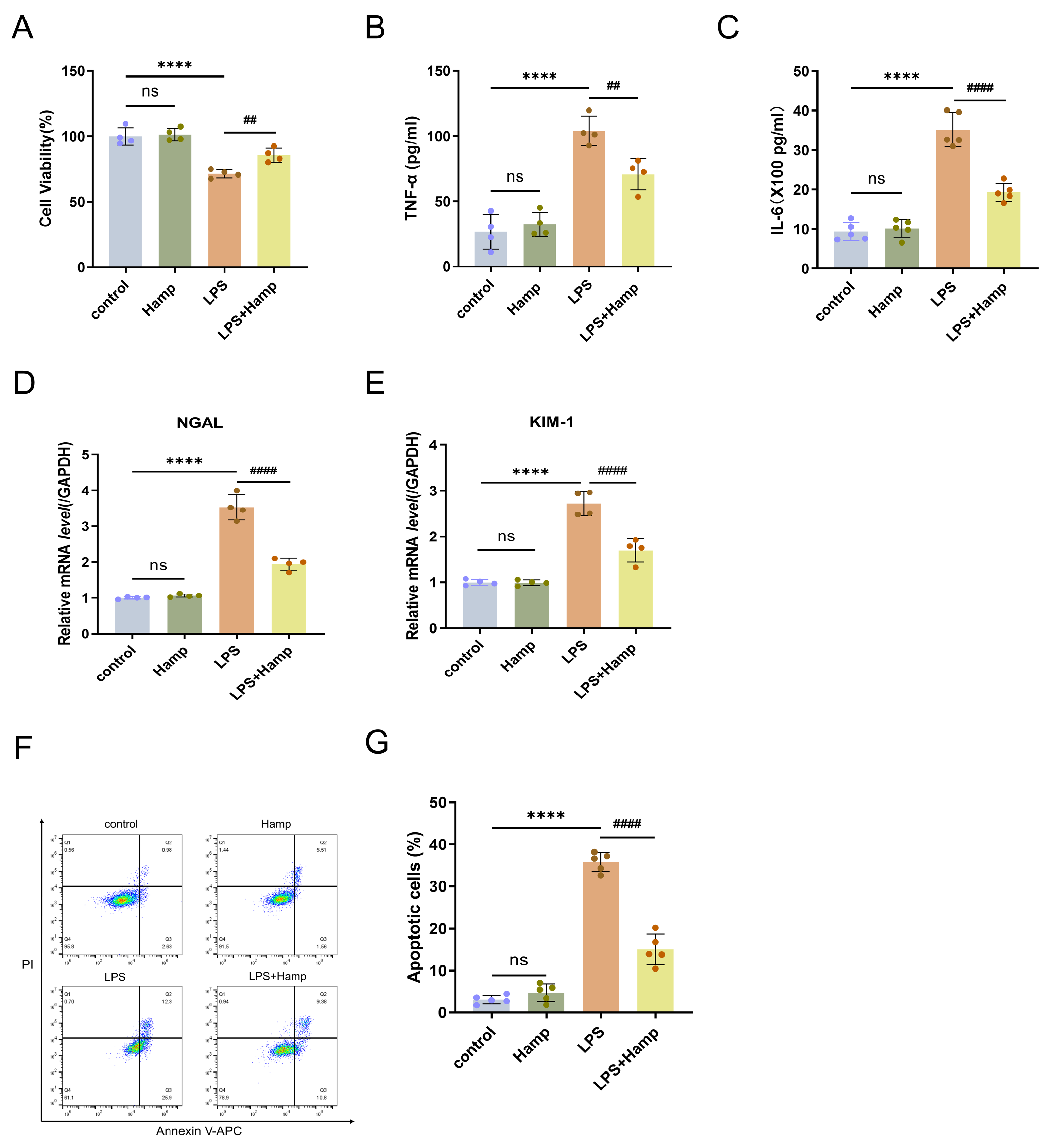
2.4. ELISA Assay
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
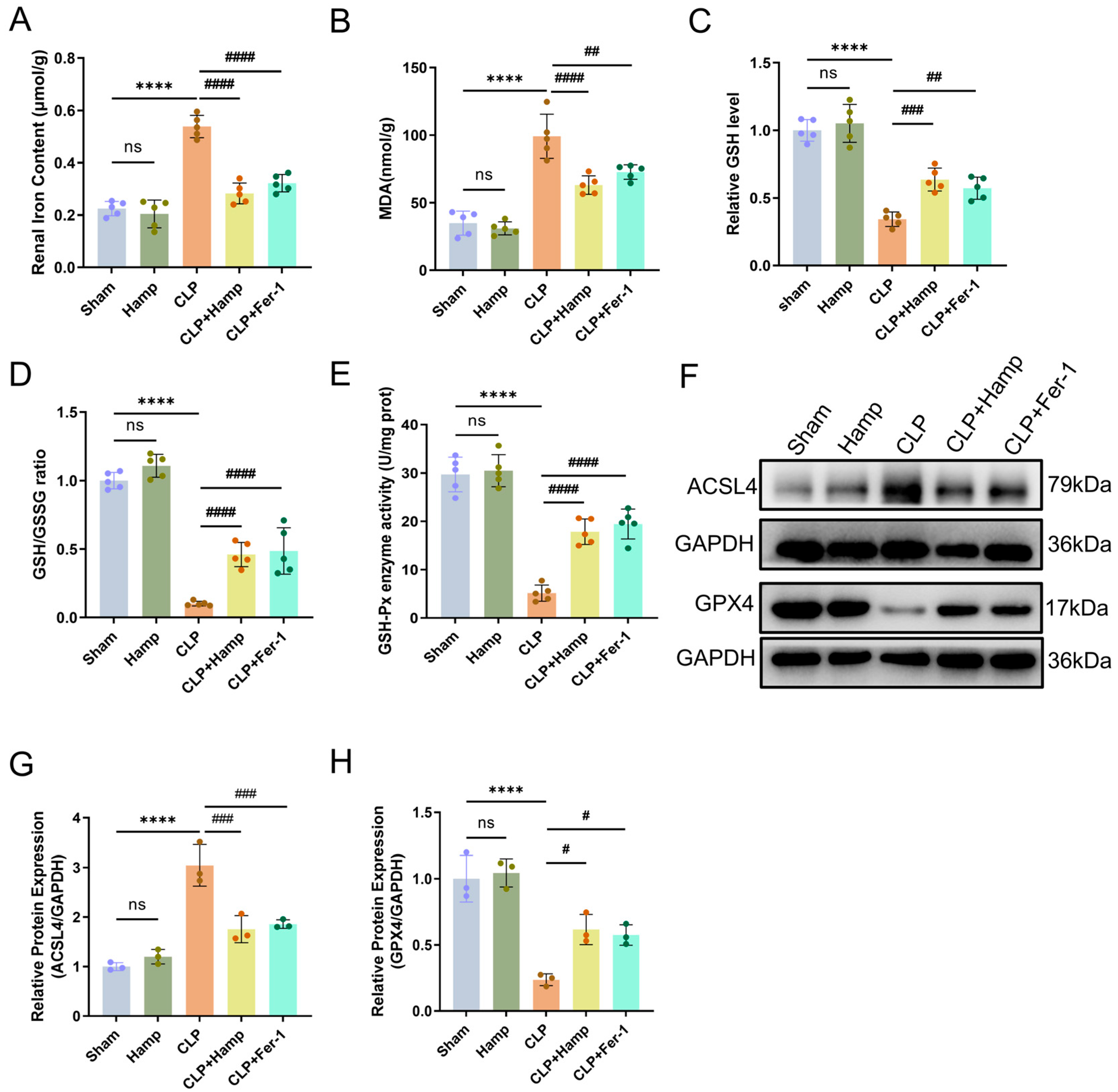
2.6. Ferrous Iron (Fe2+) Content in Renal Tissue
2.7. GSH-Px Activity Assay
2.8. Detection of Lipid Peroxidation Product MDA and GSSH/GSSG Ratio
2.9. Lipid ROS Assay
2.10. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.11. Western Blot
2.12. Immunohistochemistry
2.13. Apoptosis Rates
2.14. RT-qPCR
2.15. Survival Analysis
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hepcidin Ameliorates SAKI in Mice
3.2. Hepcidin Inhibits Ferroptosis in SAKI Mice
3.3. Hepcidin Protects HK-2 Cells from the Damage That Is Induced by LPS
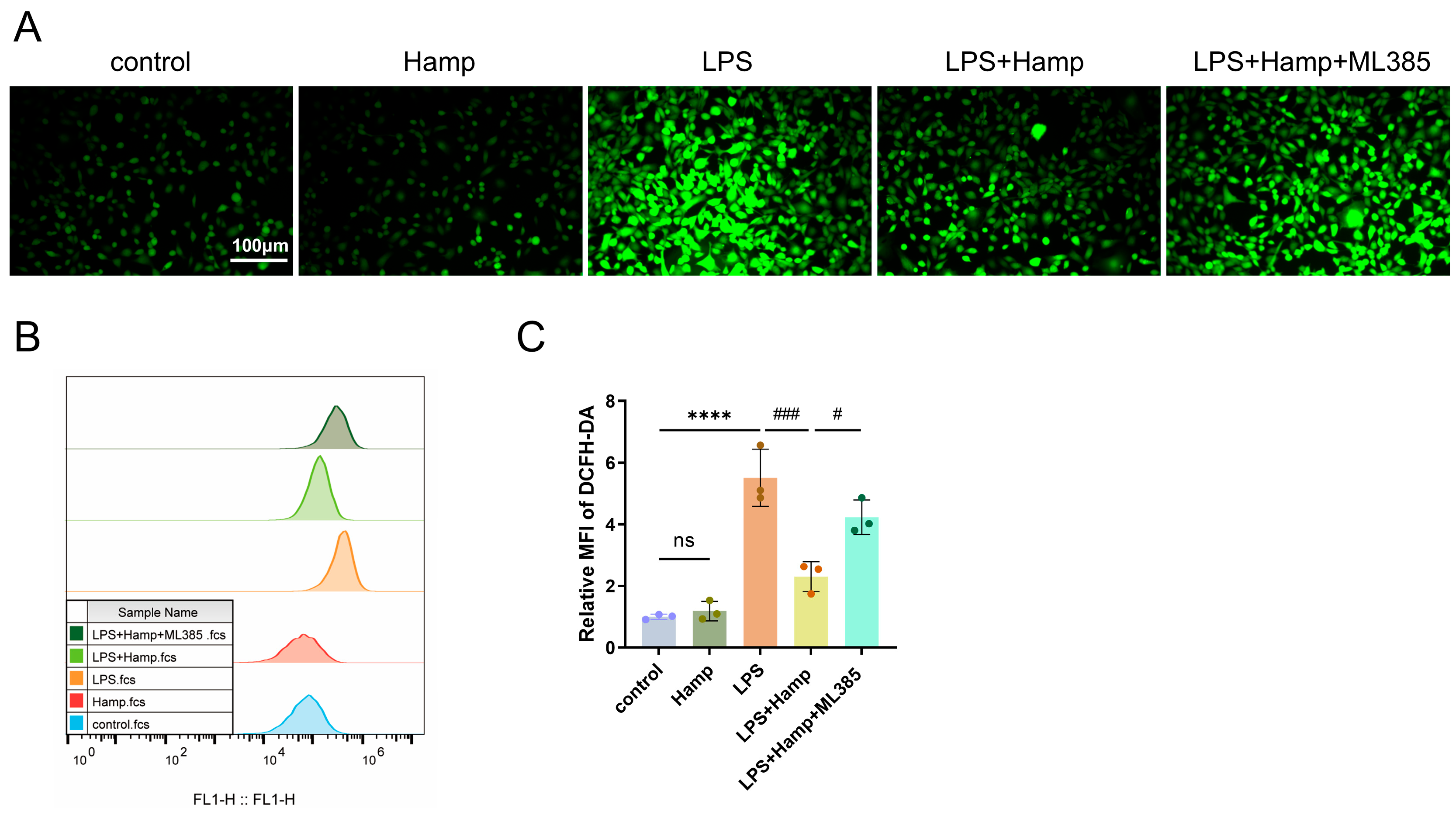
3.4. Hepcidin Alleviates LPS-Induced Ferroptosis by Activating the Nuclear Translocation of Nrf2
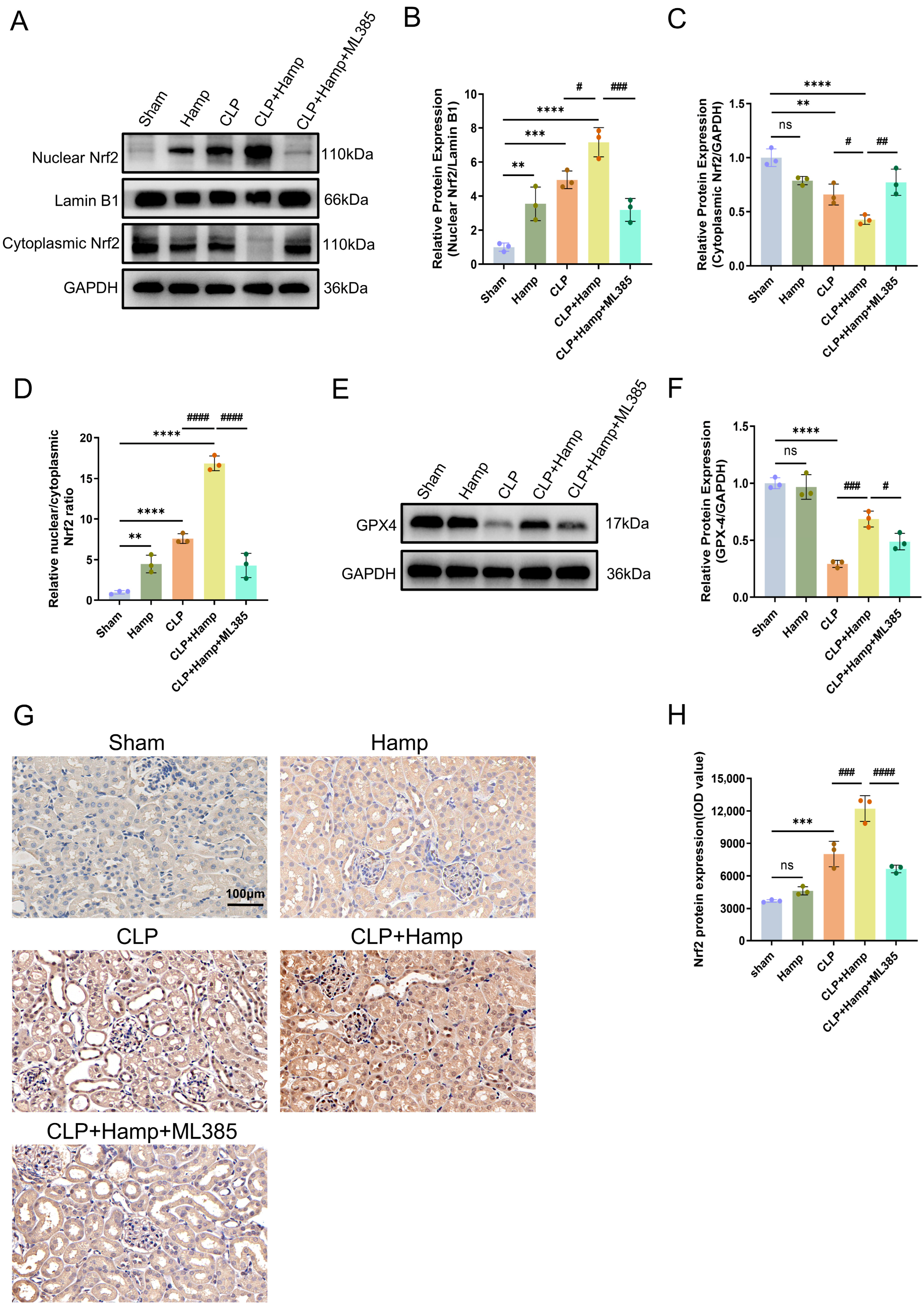
3.5. Hepcidin Inhibits Ferroptosis in SAKI via Activation of Nuclear Translocation of Nrf2
4. Discussion
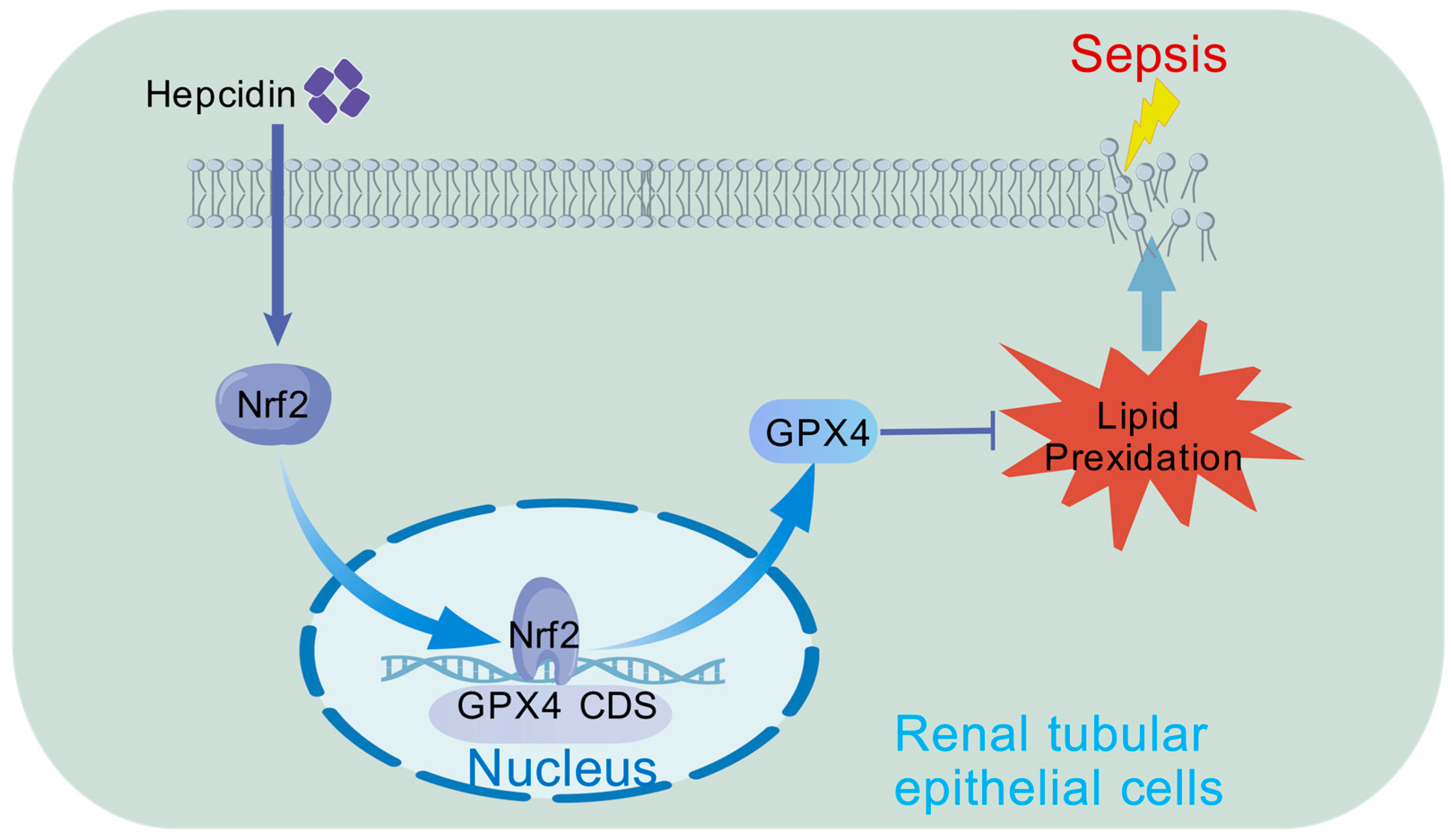
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
Appendix A.2

Appendix A.3

References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Nadim, M.K.; Pickkers, P.; Gomez, H.; Bell, S.; Joannidis, M.; Kashani, K.; Koyner, J.L.; Pannu, N.; Meersch, M.; et al. Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: Consensus report of the 28th Acute Disease Quality Initiative workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Nie, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Xu, G.; Zha, Y.; Qian, J.; Liu, B.; Han, S.; Xu, A.; et al. Epidemiology and Clinical Correlates of AKI in Chinese Hospitalized Adults. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2015, 10, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagshaw, S.M.; Uchino, S.; Bellomo, R.; Morimatsu, H.; Morgera, S.; Schetz, M.; Tan, I.; Bouman, C.; Macedo, E.; Gibney, N.; et al. Septic acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: Clinical characteristics and outcomes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2007, 2, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, H.; Yang, Y.; Luo, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Du, S.; You, J.; Zhang, G.; Ye, Q.; et al. Modulatory role of radioprotective 105 in mitigating oxidative stress and ferroptosis via the HO-1/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis in sepsis-mediated renal injury. Cell Death Discov. 2025, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, N.N.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Gao, L.; Yu, D.X.; Xu, D.X.; Xu, S. Mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species are involved in renal cell ferroptosis during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 107, 108687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; An, S.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Yu, B.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lin, B.; Lin, X.; Gao, Y. Melatonin suppresses ferroptosis via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in the mouse model of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 112, 109162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Lv, C.; Liu, L.; Miao, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J. PGE2 pathway mediates oxidative stress-induced ferroptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E.; Tuttle, M.S.; Powelson, J.; Vaughn, M.B.; Donovan, A.; Ward, D.M.; Ganz, T.; Kaplan, J. Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. Science 2004, 306, 2090–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Yong, C.; Zhang, R.; Qi, D.; Wang, D. Hepcidin Alleviates LPS-Induced ARDS by Regulating the Ferritin-Mediated Suppression of Ferroptosis. Shock 2022, 57, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scindia, Y.; Wlazlo, E.; Ghias, E.; Cechova, S.; Loi, V.; Leeds, J.; Ledesma, J.; Helen, C.; Swaminathan, S. Modulation of iron homeostasis with hepcidin ameliorates spontaneous murine lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanova, D.; Raychev, A.; Deville, J.; Humphries, R.; Campeau, S.; Ruchala, P.; Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T.; Bulut, Y. Hepcidin Protects against Lethal Escherichia coli Sepsis in Mice Inoculated with Isolates from Septic Patients. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00253-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Motohashi, H. The KEAP1-NRF2 System: A Thiol-Based Sensor-Effector Apparatus for Maintaining Redox Homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1169–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnaser, M.; Alaaeldin, R.; Attya, M.E.; Fathy, M. Modulating Nrf-2/HO-1, apoptosis and oxidative stress signaling pathways by gabapentin ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wei, W.; Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Ci, X. Isoorientin Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Through the Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via Activating the SIRT1/SIRT6/Nrf-2 Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Liu, X.H.; Wang, L. CBX7 suppression prevents ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress through the Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2020, 318, F1531–F1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittirsch, D.; Huber-Lang, M.S.; Flierl, M.A.; Ward, P.A. Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and puncture. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.; Nemeth, E.; Gabayan, V.; Lopez, M.A.; Farshidi, D.; Ganz, T. Synthetic hepcidin causes rapid dose-dependent hypoferremia and is concentrated in ferroportin-containing organs. Blood 2005, 106, 2196–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Le, J.W.; Zhu, J.H. Protective Effect of N-Acetylcysteine Pretreatment on Acute Kidney Injury in Septic Rats. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 254, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Rao, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Fu, S.; Xiao, J. Attenuation of Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Exogenous H2S via Inhibition of Ferroptosis. Molecules 2023, 28, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, M.; Deng, Z.; Kang, H. Immunotherapy in the context of sepsis-induced immunological dysregulation. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1391395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Venkatesh, B.; McCreary, E.K. Acute Kidney Injury with Empirical Antibiotics for Sepsis. JAMA 2023, 330, 1531–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, A.H.; Li, X.; Delozier, N.L.; Toto, R.D.; Moe, O.W.; Yee, J.; Neyra, J.A. Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Disease and Long-term Kidney Outcomes. Kidney Med. 2021, 3, 507–514.e501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, H.; Bamba, Y.; Nagano, K.; Hakamata, M.; Ogata, H.; Shibata, S.; Cho, H.; Aoki, N.; Sato, M.; Ohshima, Y.; et al. Dynamics of iron metabolism in patients with bloodstream infections: A time-course clinical study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Liu, H. The effects of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) IL-6 trans-signaling on immunity and iron metabolism via JAK/STAT3 pathway. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 131, 104372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, I.; Zhang, T.Y.; Koening, C.L.; Branch, R.W.; London, N.; Lo, E.; Daynes, R.A.; Kushner, J.P.; Li, D.; Ward, D.M.; et al. Hepcidin mediates transcriptional changes that modulate acute cytokine-induced inflammatory responses in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2395–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Sun, X.; Yan, Y. Study on the regulation of renal tubular cell apoptosis by SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway in septic acute kidney injury. Ren. Fail. 2025, 47, 2499904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, W.; Ma, X.; Diao, R.; Luo, X.; Shen, Q.; Xu, M.; Yin, M.; Jin, Y. NDUFS3 alleviates oxidative stress and ferroptosis in sepsis induced acute kidney injury through AMPK pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, F.; Maiorino, M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Bao, D.; She, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, S.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; et al. Role of Hippo/ACSL4 axis in ferroptosis-induced pericyte loss and vascular dysfunction in sepsis. Redox Biol. 2024, 78, 103353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.K.; Cao, X.; Wan, L.; Diao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Kan, Y.; Ye, L.L.; Mao, Y.M.; Dong, X.Q.; Xiong, Q.W.; et al. Autophagy of OTUD5 destabilizes GPX4 to confer ferroptosis-dependent kidney injury. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiongyue, Z.; Xin, Y.; Meng, P.; Sulin, M.; Yanlin, W.; Xinyi, L.; Xuemin, S. Post-treatment with Irisin Attenuates Acute Kidney Injury in Sepsis Mice Through Anti-Ferroptosis via the SIRT1/Nrf2 Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 857067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalakeche, R.; Hato, T.; Rhodes, G.; Dunn, K.W.; El-Achkar, T.M.; Plotkin, Z.; Sandoval, R.M.; Dagher, P.C. Endotoxin uptake by S1 proximal tubular segment causes oxidative stress in the downstream S2 segment. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2011, 22, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Qin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Su, B. NOX4 is a potential therapeutic target in septic acute kidney injury by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation. Theranostics 2023, 13, 2863–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Shi, H.; Sha, N.; Li, F.; Gu, X.; Lin, H. Ursodeoxycholic acid protects against sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by activating Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibiting NF-κB pathway. BMC Nephrol. 2025, 26, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Zhou, S.; Yu, M.; Qiu, X.; Jiang, S.; Wang, X.; Tang, C.; Li, S.; et al. Dihydromyricetin attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and ferroptosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2023, 473, 116595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Wakabayashi, N.; Katoh, Y.; Ishii, T.; Igarashi, K.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. Keap1 represses nuclear activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, P.; Huang, H.; Zhao, H.; Liu, R.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhang, Z. Edaravone dexborneol protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced blood-brain barrier damage by inhibiting ferroptosis via activation of nrf-2/HO-1/GPX4 signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 217, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.C.; Zhang, J.C.; Huang, T.; Lin, X.M.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, L.F.; Hong, X.Y.; Lin, X.F.; Zheng, H.J.; Zhou, K.L.; et al. Complement C5aR blockade attenuates LPS-induced acute kidney injury by regulating ferroptosis via nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 239, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, D.; Zhu, Y.; Pan, T.; Xia, D.; Cai, T.; Lin, H.; Lin, J.; Jin, X.; Wu, F.; et al. GPX4-Regulated Ferroptosis Mediates S100-Induced Experimental Autoimmune Hepatitis Associated with the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6551069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Mao, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, D. Salidroside Mediated the Nrf2/GPX4 Pathway to Attenuates Ferroptosis in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2024, 49, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.X.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.J.; Su, H.Y.; Zhang, W.H.; Pan, Q.; Liu, H.F. Protection of procyanidin B2 on mitochondrial dynamics in sepsis associated acute kidney injury via promoting Nrf2 nuclear translocation. Aging 2020, 12, 15638–15655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, X.; Luo, Y.; Ji, J.; Li, J.; Lai, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Dexmedetomidine inhibits ferroptosis and attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via activating the Nrf2/SLC7A11/FSP1/CoQ10 pathway. Redox Rep. Commun. Free Radic. Res. 2024, 29, 2430929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Du, X.; Hou, H.; Cao, M.; Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Gu, J.; et al. Carboxymethyl Poria cocos polysaccharides protect against septic kidney injury by regulating the Nrf2-NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 143030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer | Sequences 5’-3’ | PrimerBank ID |
|---|---|---|
| NGAL For NGAL Rev | GAAGTGTGACTACTGGATCAGGA ACCACTCGGACGAGGTAACT | 108936956c3 |
| KIM-1 For KIM-1 Rev | TGGCAGATTCTGTAGCTGGTT AGAGAACATGAGCCTCTATTCCA | 290560749c1 |
| HO-1 For HO-1 Rev | AAGACTGCGTTCCTGCTCAAC AAAGCCCTACAGCAACTGTCG | 298676487c1 |
| FTH1 For FTH1 Rev | TCCTACGTTTACCTGTCCATGT GTTTGTGCAGTTCCAGTAGTGA | 4503795a2 |
| FSP1 For FSP1 Rev | GATGAGCAACTTGGACAGCAA CTGGGCTGCTTATCTGGGAAG | 4506765a1 |
| SLC7A11 For SLC7A11 Rev | TCTCCAAAGGAGGTTACCTGC AGACTCCCCTCAGTAAAGTGAC | 80861465c1 |
| GAPDH For GAPDH Rev | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG | 378404907c1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, L.-B.; Wu, S.-S.; Xu, F.; Chen, X.-X.; Fan, H. Protective Effect of Hepcidin on Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury via Activating the Nrf2/GPX4 Signaling Pathway. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090772
Guo L-B, Wu S-S, Xu F, Chen X-X, Fan H. Protective Effect of Hepcidin on Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury via Activating the Nrf2/GPX4 Signaling Pathway. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(9):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090772
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Liang-Bo, Shao-Sheng Wu, Feng Xu, Xin-Xing Chen, and Heng Fan. 2025. "Protective Effect of Hepcidin on Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury via Activating the Nrf2/GPX4 Signaling Pathway" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 9: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090772
APA StyleGuo, L.-B., Wu, S.-S., Xu, F., Chen, X.-X., & Fan, H. (2025). Protective Effect of Hepcidin on Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury via Activating the Nrf2/GPX4 Signaling Pathway. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(9), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090772






