The First Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of the Cyrtomium hemionitis Fern
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
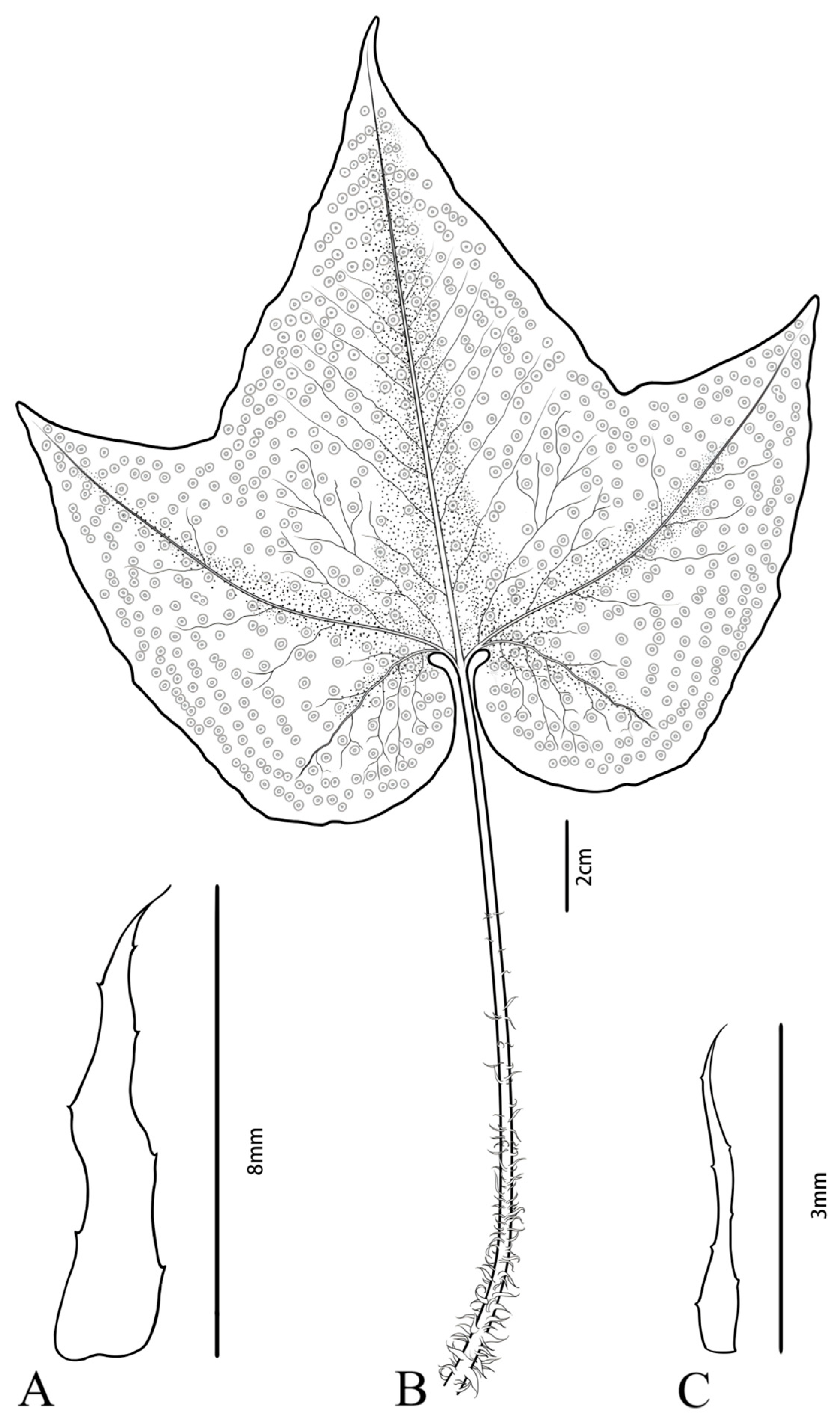
2.1. Plant Materials, DNA Extraction, and Sequencing
2.2. Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.3. Relative Synonymous Codon Usage Analysis
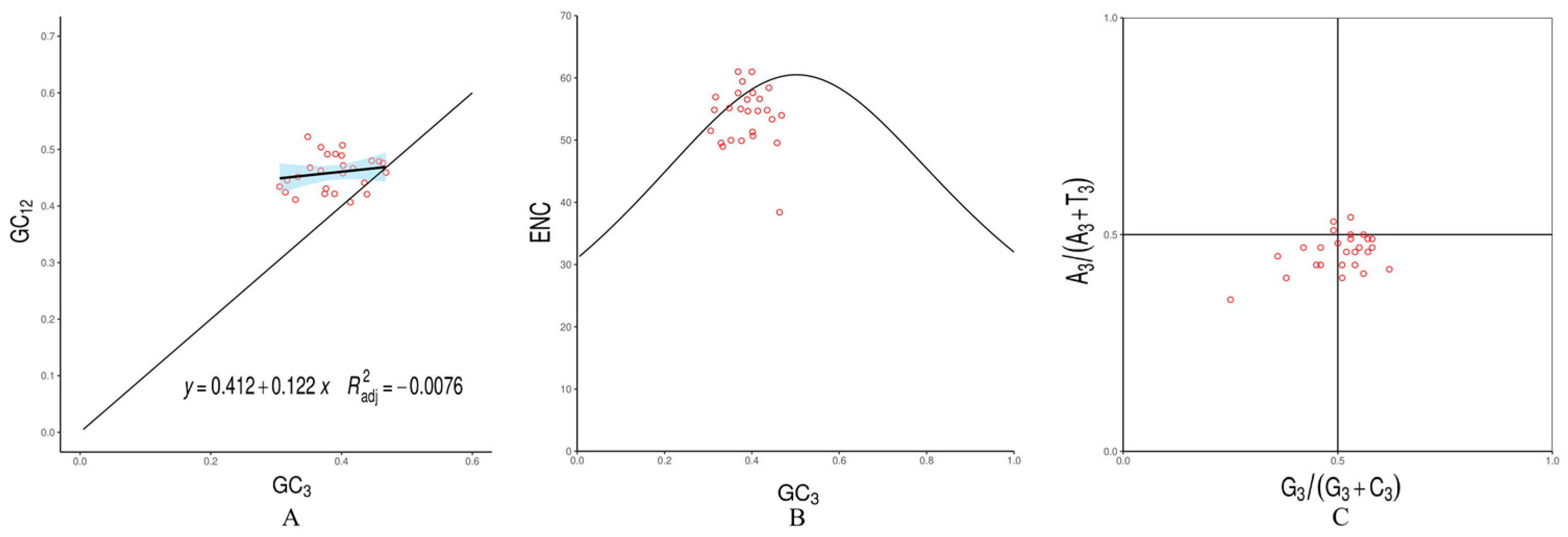
2.4. Neutrality Plot, ENC-Plot, and PR2-Bias Plot Analysis
2.5. Comparative Analysis of Chloroplast Genomes
2.6. The Genomic SSR Markers Detection
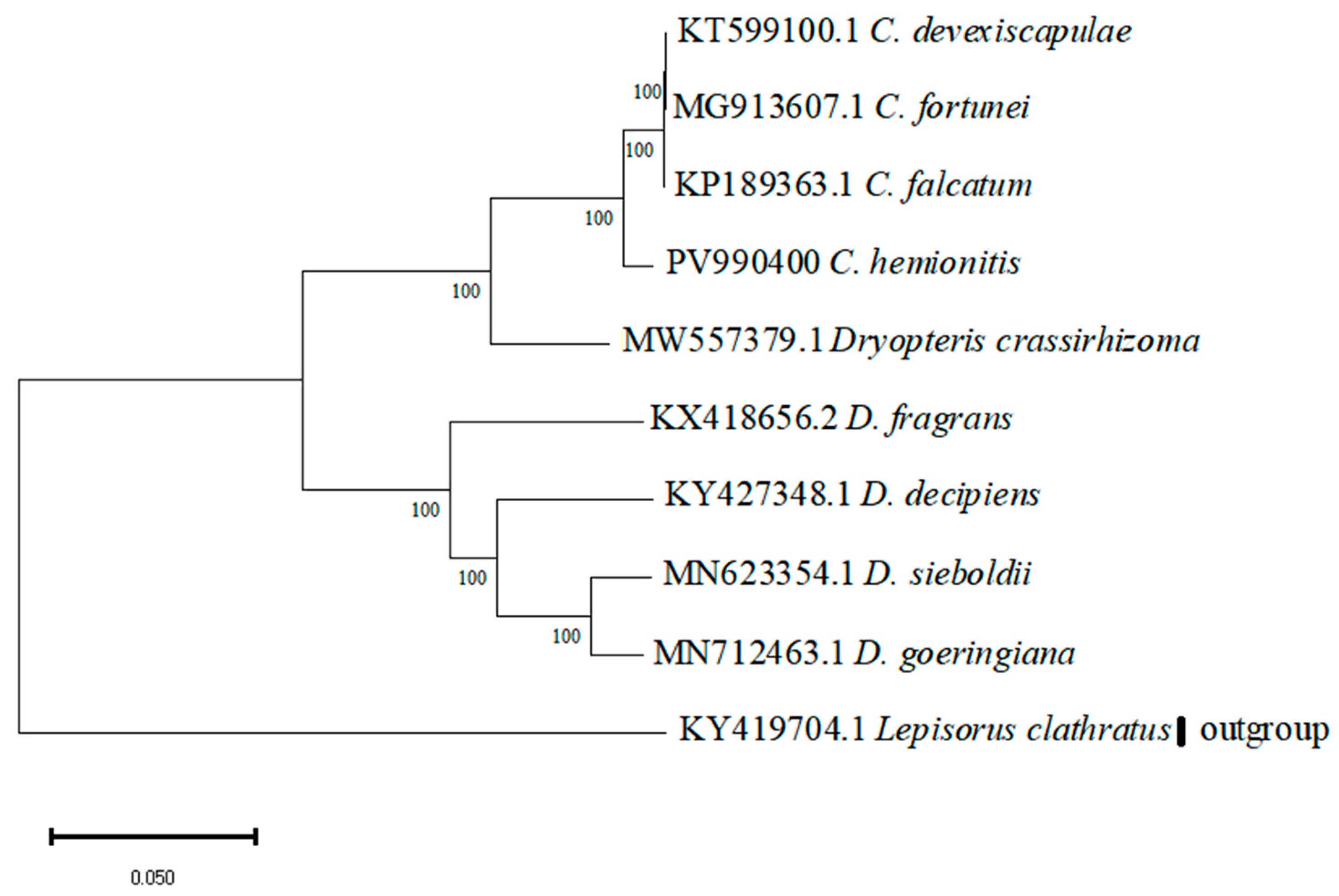
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
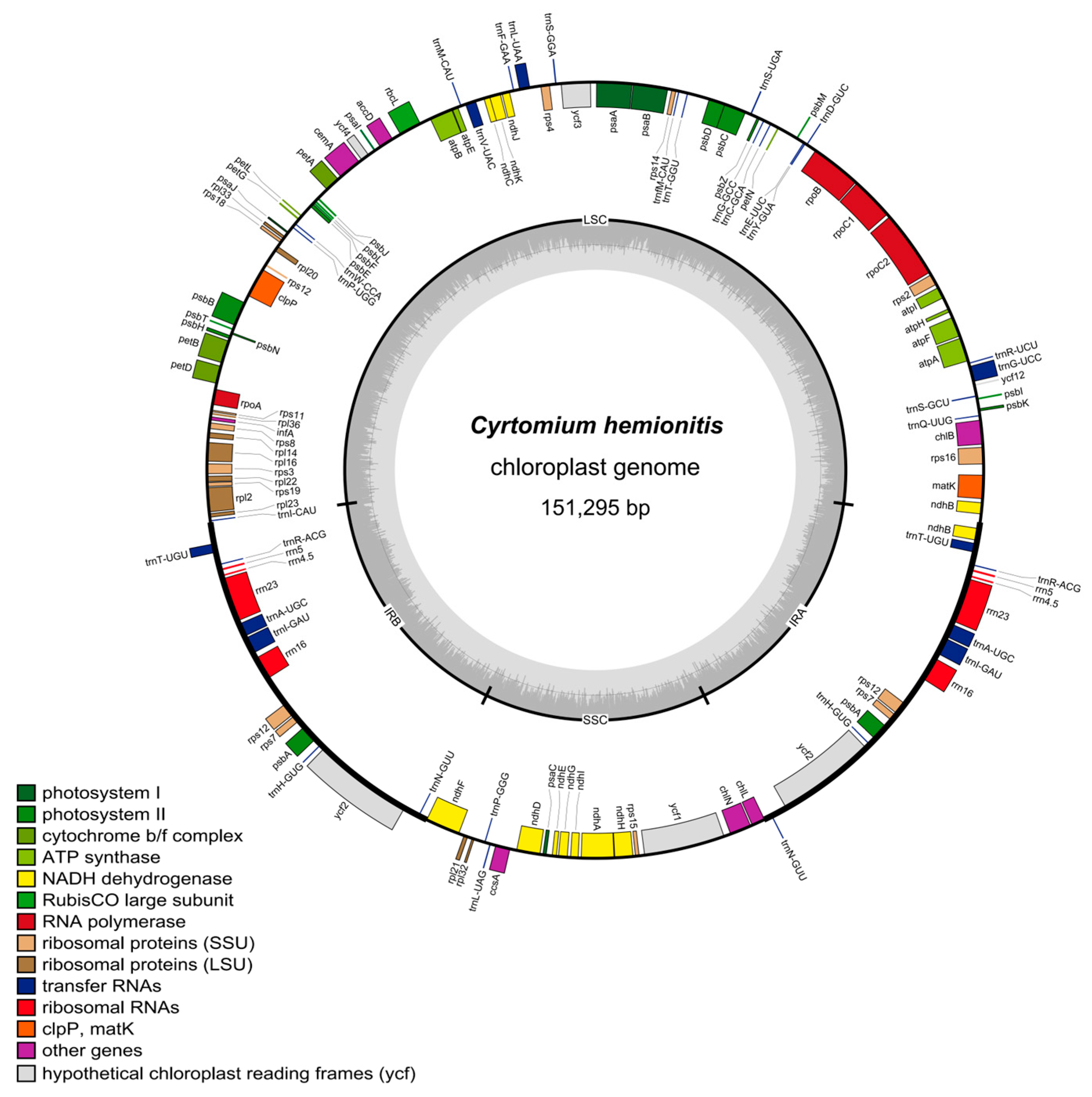
3.1. Characteristics of C. hemionitis Chloroplast Genomes
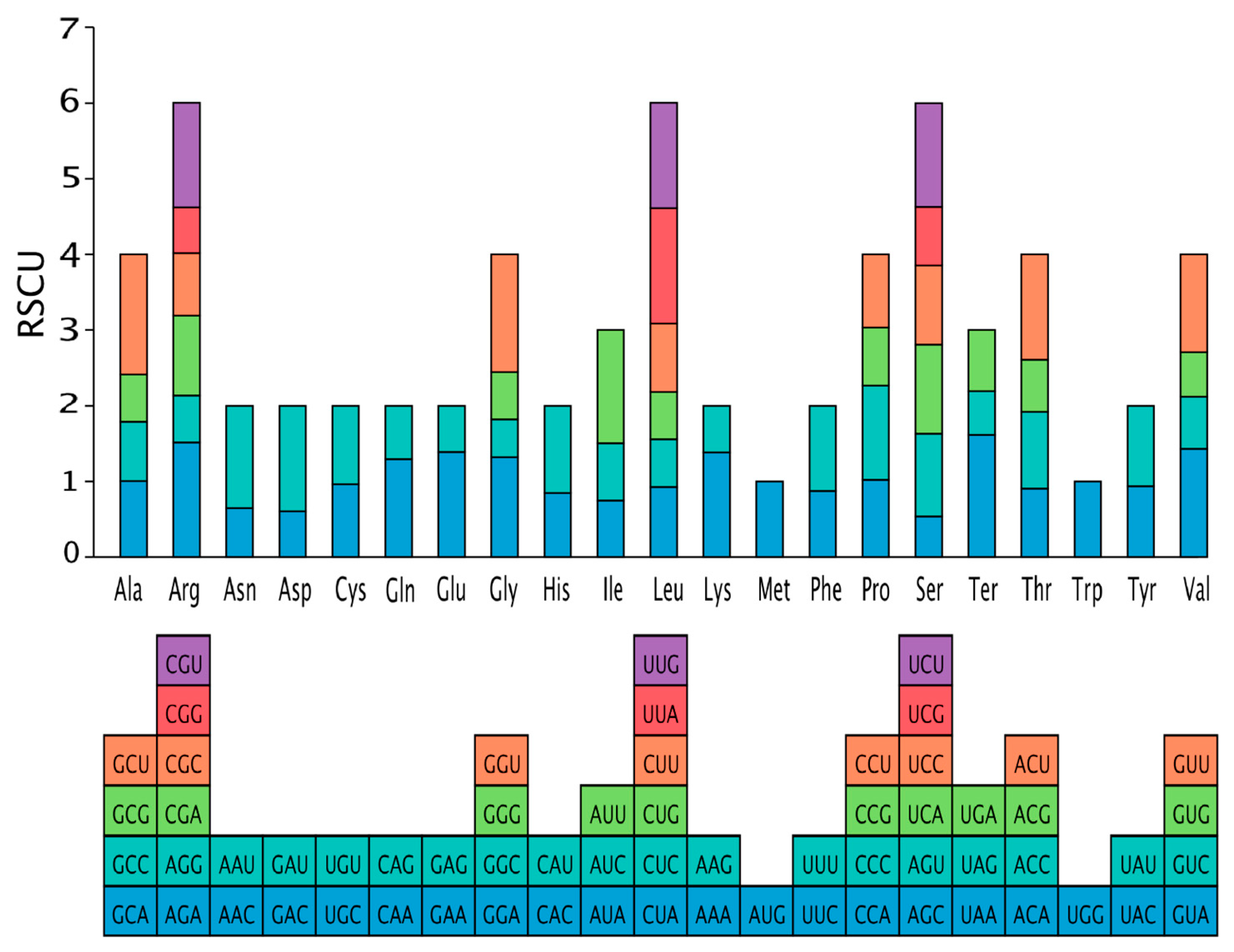
3.2. Codon Preference Analysis
3.3. Codon Usage Bias Analysis
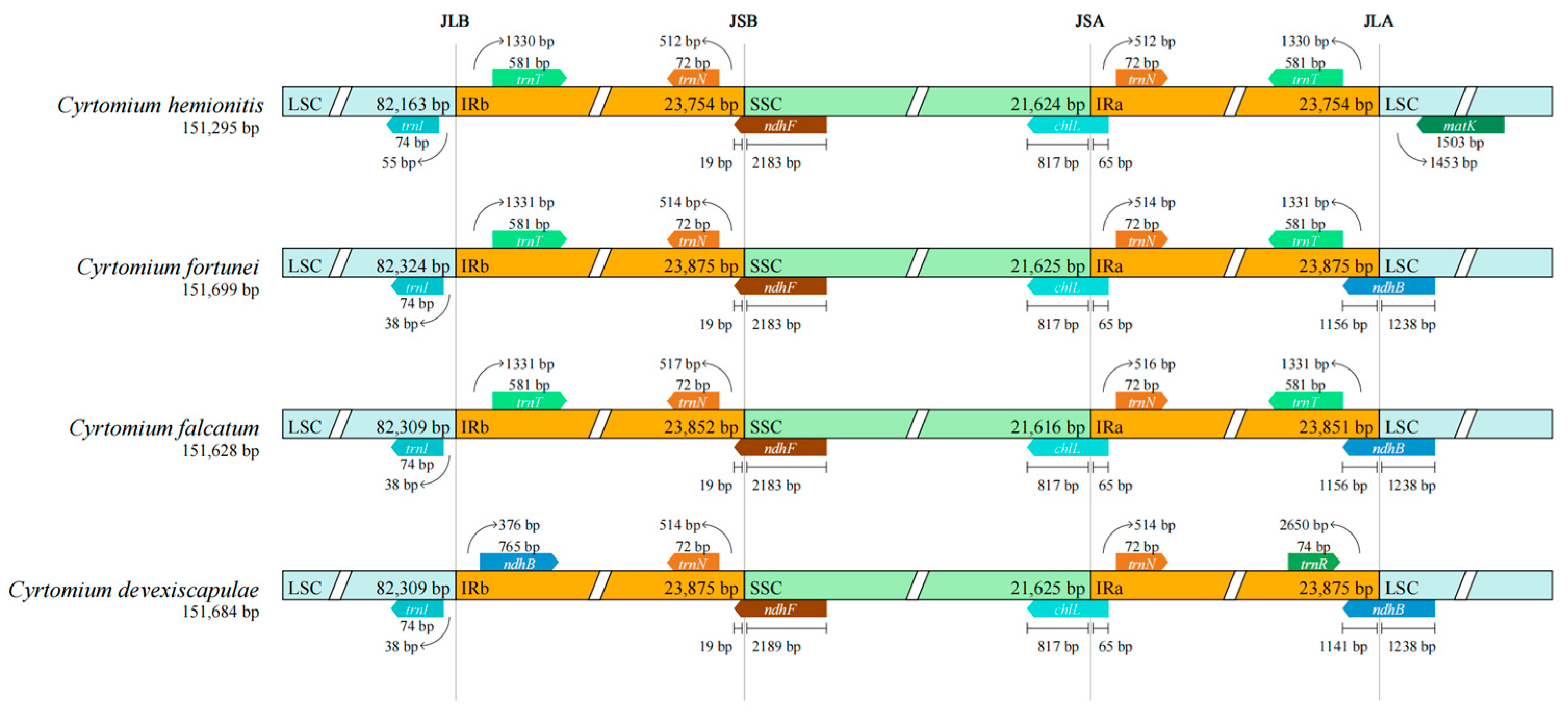
3.4. Expansion and Contraction of IRs
3.5. Genomic SSR Marker Development
3.6. Phylogenetic Relationship Analysis
4. Discussion
Structural Variations in the Chloroplast Genomes of Cyrtomium Species
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Editorial Committee of Flora of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora of China: Volume V, Book II; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001; p. 190. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Su, Y. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Cyrtomium fortunei (Dryopteridaceae), an important medical fern. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2018, 3, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; He, C.; Fan, Y.; Guo, L.; Si, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, H. Immuno-enhancement effects of ethanol extract from Cyrtomium macrophyllum (Makino) Tagawa on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression in BALB/c mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Wan, J.; Song, G.; Lin, H.; Shen, Z.; Tang, C. Analysis of chemical composition and in vitro antidermatophyte activity of ethanol extracts of Dryopteris fragrans (L.) Schott. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 226, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, H.; Ding, C.; Huang, Y.; Liao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, S.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, M. Antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities of polysaccharides from the rhizome of Dryopteris crassirhizoma Nakai. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruang-Areerate, P.; Pinsupa, S.; Kongkachana, W.; Yoocha, T.; Phetchawang, P.; Paenpong, P.; Somta, P.; Laosatit, K.; Tangphatsornruang, S.; Pootakham, W. Assembly and analysis of the complete mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes of Vigna reflexo-pilosa. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0325243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xing, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Kang, T. Plastid genome and composition analysis of two medical ferns: Dryopteris crassirhizoma Nakai and Osmunda japonica Thunb. Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Su, Y.; Wang, T. Comparative genomic analysis of Polypodiaceae chloroplasts reveals fine structural features and dynamic insertion sequences. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Tian, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhan, H. Development and application of simple sequence repeat markers based on whole-genome sequencing in Codonopsis lanceolata. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2024, 71, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, W.; Chang, Y.; Yao, D. Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequences of Three Canna Species: Genome Characterization, Comparative Analyses, and Phylogenetic Relationships Within Zingiberales. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.; Lesin, V.; Nikolenko, S.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Moore, M.J.; Li, D.; Yi, T. PGA: A software package for rapid, accurate, and flexible batch annotation of plastomes. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3. 1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Pan, Z.; Gao, S.; He, Y.; Xia, Q.; Jin, Y.; Yao, H. Analysis of synonymous codon usage of chloroplast genome in Porphyra umbilicali. Genes Genom. 2019, 41, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Qian, J.; Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Xu, X.; Chen, S. Complete chloroplast genome of medicinal plant Lonicera japonica: Genome rearrangement, intron gain and loss, and implications for phylogenetic studies. Molecules 2017, 22, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Chen, J.; Ran, Z.; Huang, L.; Li, Z. Comparative Analysis of Complete Chloroplast Genomes and Phylogenetic Relationships of 21 Sect. Camellia (Camellia L.) Plants. Genes 2025, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J. Chloroplast Genome Evolution and Codon Usage in the Medicinal Plant Pothos chinensis (Araceae). Genes 2025, 16, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Intrastrand parity rules of DNA base composition and usage biases of synonymous codons. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 40, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Near homogeneity of PR2-bias fingerprints in the human genome and their implications in phylogenetic analyses. J. Mol. Evol. 2001, 53, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, R.; Hu, J.; Chuluunbat, J.; Wu, F.; Qin, B.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, R. Comparative chloroplast genomes and phylogenetic analysis of the Phlegmariurus (Lycopodiaceae) from China and neighboring regions. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1543431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Fan, J.; Chang, P.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, M.; Li, L. Genome Survey Sequencing of Acer truncatum Bunge to Identify Genomic Information, Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers and Complete Chloroplast Genome. Forests 2019, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Lu, X.; Li, W.; Sun, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y. Chloroplast genome diversity and molecular evolution in hypericaceae: New insights from three Hypericum species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Ran, Z.; Yan, C.; Gu, W.; Li, Z. Mitochondrial genome assembly of the Chinese endemic species of Camellia luteoflora and revealing its repetitive sequence mediated recombination, codon preferences and MTPTs. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xue, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, T. Comprehensive Analysis of Chloroplast Genomes in Leguminous Forage Species: Codon Usage, Phylogenetic Relationships, and Evolutionary Insights. Agronomy 2025, 15, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, L.; Lu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, D.; Liu, S. Patterns in genome-wide codon usage bias in representative species of Lycophytes and Ferns. Genes 2024, 15, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ye, H.; Zhang, N.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, G.; Li, M.; Zhao, P. Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes provide comprehensive insights into the adaptive evolution of Paphiopedilum (Orchidaceae). Horticulturae 2022, 8, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Jia, L.; Chen, Z. Comprehensive analysis of the complete chloroplast genome of the cultivated soapberry and phylogenetic relationships of Sapindaceae. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 228, 120952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Q.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Luo, C.; Zhang, J.; Bai, X. Complete chloroplast genomes of 13 species of the Impatiens genus for genomic features and phylogenetic relationships studies. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4258. [Google Scholar]
- Tamboli, A.S.; Youn, J.S.; Kadam, S.K.; Pak, J.H.; Choo, Y.S. Chloroplast genome of Arisaema takesimense: Comparative genomics and phylogenetic insights into the Arisaema. Biochem. Genet. 2025, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Xue, B.; Zhang, X.; Song, W.; Guo, W.; Wu, W. Comparative Analysis of Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Rubus in China: Hypervariable Regions and Phylogenetic Relationships. Genes 2024, 15, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.K.; Tamboli, A.S.; Youn, J.S.; Pak, J.H.; Choo, Y.S. Decoding the Chloroplast Genome of Korean endemic plant Acer okamotoanum: Comparative Genomics, Phylogenetic Insights, and Potential for Marker Development. Mol. Biotechnol. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Gene Group | Gene Name |
|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | Subunits of photosystem I | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ |
| Subunits of photosystem II | psbA(2), psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ | |
| Subunits of NADH dehydrogenase | ndhA*, ndhB*, ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH, ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK | |
| Subunits of cytochrome b/f complex | petA, petB*, petD*, petG, petL, petN | |
| Subunits of ATP synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, atpF*, atpH, atpI | |
| Large subunit of rubisco | rbcL | |
| Subunits photochlorophyllide reductase | chlB, chlL, chlN | |
| Self-replication | Proteins of large ribosomal subunit | rpl14, rpl16*, rpl2*, rpl20, rpl21, rpl22, rpl23, rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 |
| Proteins of small ribosomal subunit | rps11, rps12**(2), rps14, rps15, rps16*, rps18, rps19, rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7(2), rps8 | |
| Subunits of RNA polymerase | rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1*, rpoC2 | |
| Ribosomal RNAs | rrn16(2), rrn23(2), rrn4.5(2), rrn5(2) | |
| Transfer RNAs | trnA-UGC*(2), trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnG-GCC, trnG-UCC*, trnH-GUG(2), trnI-CAU, trnI-GAU*(2), trnL-UAA*, trnL-UAG, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU(2), trnP-GGG, trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG(2), trnR-UCU, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnT-UGU*(2), trnV-UAC*, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA, trnfM-CAU | |
| Other genes | Maturase | matK |
| Protease | clpP** | |
| Envelope membrane protein | cemA | |
| Acetyl-CoA carboxylase | accD | |
| c-type cytochrome synthesis gene | ccsA | |
| Translation initiation factor | infA | |
| Genes of unknown function | Conserved hypothetical chloroplast ORF | ycf1, ycf12, ycf2(2), ycf3**, ycf4 |
| Repeats | Total | Proportion/% |
|---|---|---|
| A | 8 | 16 |
| C | 16 | 32 |
| G | 7 | 14 |
| T | 14 | 28 |
| AT | 3 | 6 |
| TA | 1 | 2 |
| TCTA | 1 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Shi, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhan, H. The First Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of the Cyrtomium hemionitis Fern. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090771
Zhao J, Shi P, Wang X, Zhang S, Zhan H. The First Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of the Cyrtomium hemionitis Fern. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(9):771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090771
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Junxi, Panpan Shi, Xiaoxuan Wang, Shuosheng Zhang, and Haixian Zhan. 2025. "The First Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of the Cyrtomium hemionitis Fern" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 9: 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090771
APA StyleZhao, J., Shi, P., Wang, X., Zhang, S., & Zhan, H. (2025). The First Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of the Cyrtomium hemionitis Fern. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(9), 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090771






