Valproic Acid as a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Induces ABCB1 Overexpression and De Novo ABCB5 Expression in HeLa Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Total RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and Polymerase Chain Reaction to Evaluate the Expression of Genes Related to Multidrug Resistance Mechanisms
2.4. ABCB5 Sequencing
2.5. ABCB5 Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6. Trypan-Blue Exclusion Method
2.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay of DOX for VPA Sensitization of HeLa Cells
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
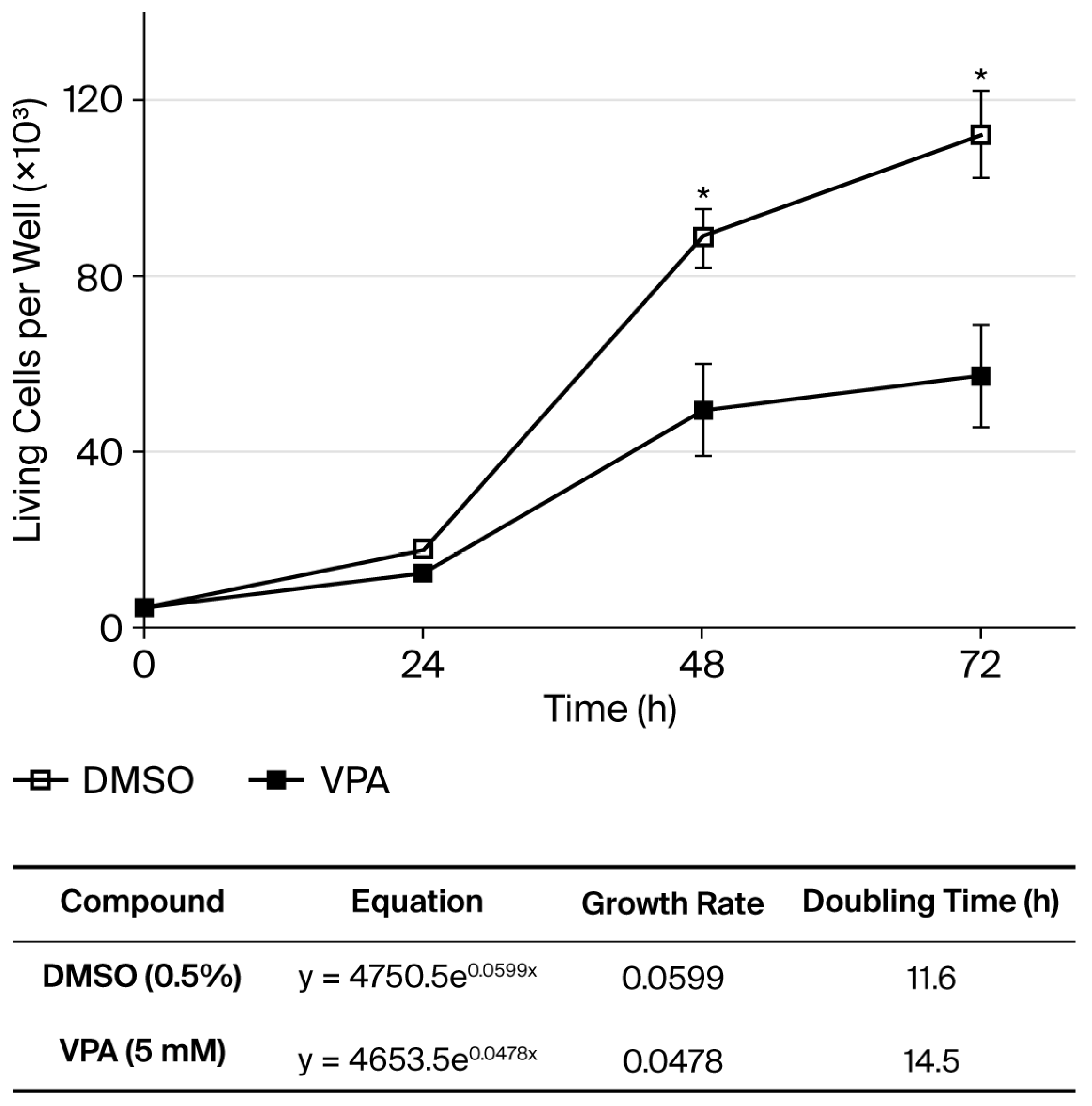
3.1. The Epigenetic Effect of 5 mM Valproic Acid Changes the Expression of the ABCB1 and ABCB5 Pumps in HeLa Cells
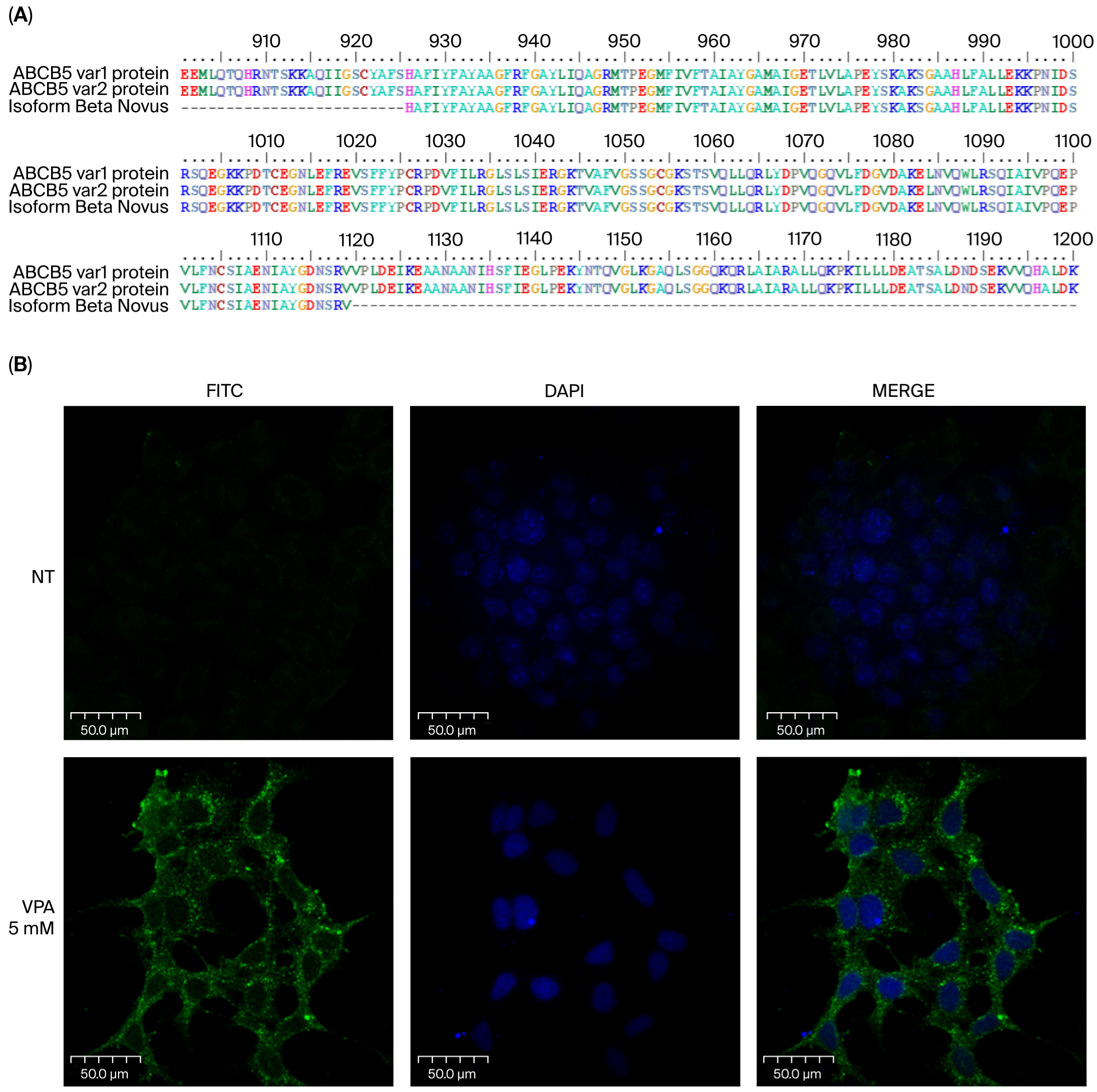
3.2. Sequencing of the ABCB5 Fragment Obtained by RT-PCR Demonstrates That It Is an Amplicon of ABCB5 cDNA
3.3. It Is Possible to Detect the ABCB5 Pump Using a Specific Monoclonal Antibody in HeLa Cells Treated with 5 mM Valproic Acid
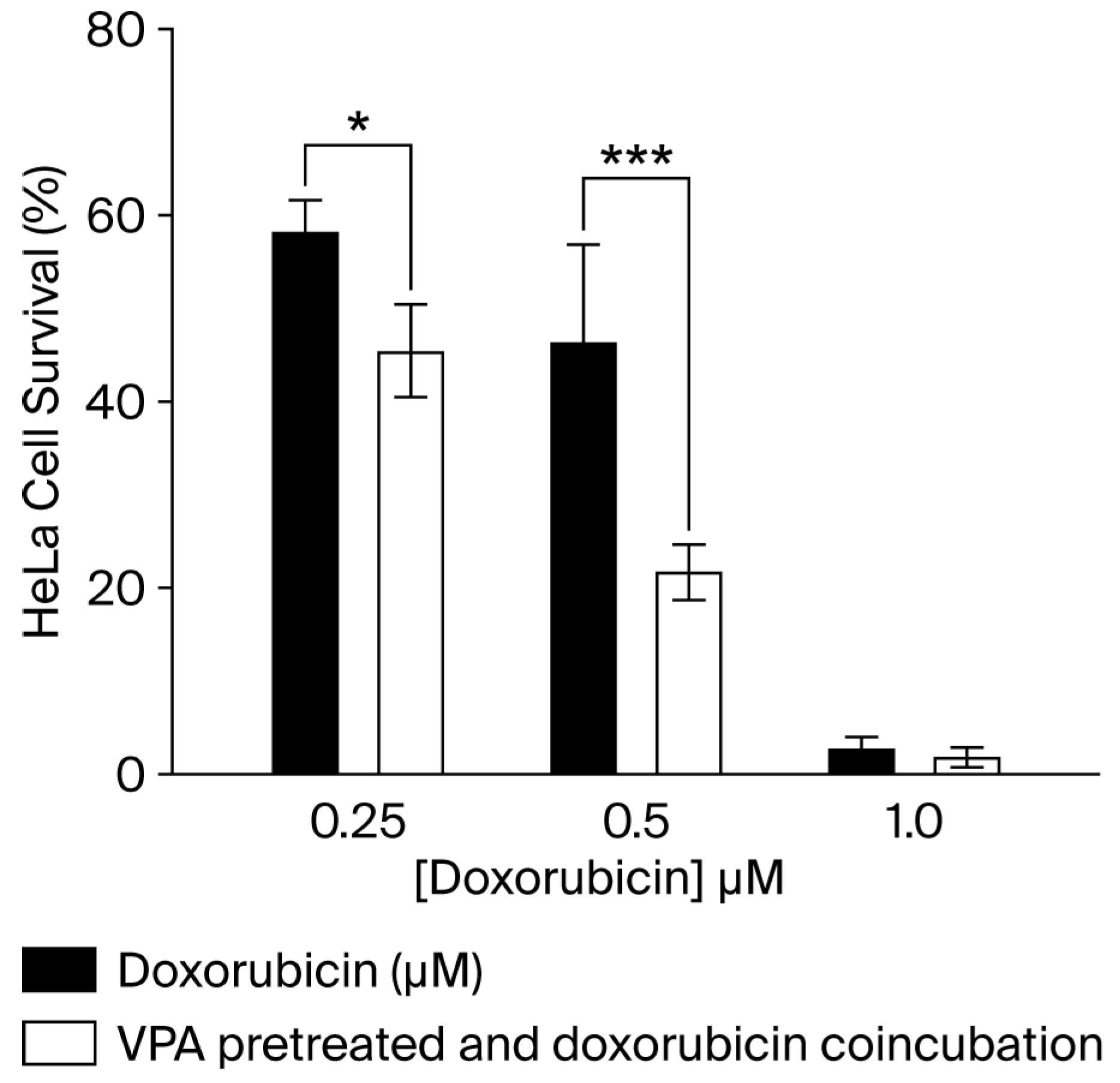
3.4. The Presence of the ABCB5 Pump in HeLa Cells Is Not Sufficient to Confer an Advantage Against Treatment with DOX
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dano, K. Active outward transport of daunomycin in resistant Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1973, 323, 466–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juliano, R.L.; Ling, V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 455, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Drug resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019, 2, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinkel, A.H.; Jonker, J.W. Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family: An overview. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moitra, K.; Scally, M.; McGee, K.; Lancaster, G.; Gold, B.; Dean, M. Molecular Evolutionary Analysis of ABCB5: The Ancestral Gene Is a Full Transporter with Potentially Deleterious Single Nucleotide Polymorphims. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuuchi, H.; Takayanagi, S.I.; Yoshinaga, K.; Taniguchi, N.; Aburatani, H.; Ishikawa, T. ABCC13, an unusual truncated ABC transporter, is highly expressed in fetal human liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 299, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvivier, L.; Gillet, J.P. Deciphering the roles of ABCB5 in normal and cancer cells. Trends Cancer 2022, 8, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Yang, Y.; Cai, C.Y.; Teng, Q.X.; Cui, Q.; Lin, J.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Chen, Z.S. Multidrug resistance proteins (MRPs): Structure, function and the overcoming of cancer multidrug resistance. Drug Resist. Updates 2021, 54, 100743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W. How to explain multidrug resistance in epilepsy? Epilepsy Curr. 2005, 5, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.J.; Schatton, T.; Zhan, Q.; Gasser, M.; Ma, J.; Saab, K.R.; Schanche, R.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; Gold, J.S.; Huang, Q.; et al. ABCB5 identifies a therapy-refractory tumor cell population in colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5307–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Anaya, A.M.; Gerard, L.; Albert, M.; Gaussin, J.F.; Boonen, M.; Gillet, J.P. The β Isoform of Human ATP-Binding Cassette B5 Transporter, ABCB5β, Localizes to the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sana, G.; Madigan, J.P.; Gartner, J.J.; Fourrez, M.; Lin, J.; Qutob, N.; Narayan, J.; Shukla, S.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Xia, D.; et al. Exome Sequencing of ABCB5 Identifies Recurrent Melanoma Mutations that Result in Increased Proliferative and Invasive Capacities. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Shi, X.; Lan, S.; Jin, H.; Wu, D. Effect of melanoma stem cells on melanoma metastasis. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, N.Y.; Margaryan, A.; Huang, Y.; Schatton, T.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; Gasser, M.; Sayegh, M.H.; Sadee, W.; Frank, M.H. ABCB5-mediated doxorubicin transport and chemoresistance in human malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4320–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Yao, X.; Tian, T.; Fu, X.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Shi, T.; Suo, A.; Ruan, Z.; Guo, H.; et al. ABCB5-ZEB1 Axis Promotes Invasion and Metastasis in Breast Cancer Cells. Oncol. Res. 2017, 5, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, P.; Deng, M.; Huang, C.; Hu, T.; Jiang, L.; Li, J. Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family in multidrug resistance: A review of the past decade. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantin, V.R.; Richon, V.M. Mechanisms of resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitors and their therapeutic implications. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 7237–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emran, T.B.; Shahriar, A.; Mahmud, A.R.; Rahman, T.; Abir, M.H.; Siddiquee, M.F.; Ahmed, H.; Rahman, N.; Nainu, F.; Wahyudin, E.; et al. Multidrug Resistance in Cancer: Understanding Molecular Mechanisms, Immunoprevention and Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 891652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriithi, W.; Macharia, L.W.; Heming, C.P.; Echevarria, J.L.; Nyachieo, A.; Filho, P.N.; Neto, V.M. ABC transporters and the hallmarks of cancer: Roles in cancer aggressiveness beyond multidrug resistance. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttlicher, M.; Minucci, S.; Zhu, P.; Kramer, O.H.; Schimpf, A.; Giavara, S.; Sleeman, J.P.; LoCoco, F.; Nervi, C.; Pelicci, P.G.; et al. Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6969–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiel, C.J.; Zhang, F.; Huang, E.Y.; Guenther, M.G.; Lazar, M.A.; Klein, P.S. Histone deacetylase is a direct target of valproic acid, a potent anticonvulsant, mood stabilizer, and teratogen. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36734–36741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Jeffers, M.; Kumar, S.; Hackett, C.; Boldog, F.; Khramtsov, N.; Qian, X.; Mills, E.; Berghs, S.C.; Carey, N.; et al. Determination of the class and isoform selectivity of small-molecule histone deacetylase inhibitors. Biochem. J. 2008, 409, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Adhikary, S.; Singh, V.; Gadad, S.S.; Roy, S.; Das, C. The paradigm of drug resistance in cancer: An epigenetic perspective. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20211812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Palencia, G.R.; Martinez-Ramos, F.; Vásquez-Moctezuma, I.; Fragoso-Vazquez, M.J.; Mendieta-Wejebe, J.E.; Padilla-Martínez, I.I.; Sixto-Lopez, Y.; Mendez-Luna, D.; Trujillo-Ferrara, J.; Meraz-Rios, M.A.; et al. Three amino acid derivatives of valproic acid: Design, synthesis, theoretical and experimental evaluation as anticancer agents. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, V. 2006 Doubling Time Computing. Available online: https://www.doubling-time.com/compute.php (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Eyal, S.; Lamb, J.G.; Smith-Yockman, M.; Yagen, B.; Fibach, E.; Altschuler, Y.; White, H.S.; Bialer, M. The antiepileptic and anticancer agent, valproic acid, induces P-glycoprotein in human tumour cell lines and in rat liver. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benderra, Z.; Faussat, A.M.; Sayada, L.; Perrot, J.Y.; Chaoui, D.; Marie, J.P.; Legrand, O. Breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein in 149 adult acute myeloid leukemias. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2004, 10, 7896–7902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, T.; Gonzales, F.; Barthélémy, A.; Marceau-Renaut, A.; Peyrouze, P.; Guihard, S.; Lepelley, P.; Plesa, A.; Nibourel, O.; Delattre, C.; et al. Clinical Significance of ABCB1 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Comprehensive Study. Cancers 2019, 11, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucha, S.; Sorf, A.; Svoren, M.; Vagiannis, D.; Ahmed, F.; Visek, B.; Ceckova, M. ABCB1 as a potential beneficial target of midostaurin in acute myeloid leukemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 112962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartrain, M.; Riond, J.; Stennevin, A.; Vandenberghe, I.; Gomes, B.; Lamant, L.; Meyer, N.; Gairin, J.E.; Guilbaud, N.; Annereau, J.P. Melanoma chemotherapy leads to the selection of ABCB5-expressing cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, J.L. Understanding and targeting cancer stem cells: Therapeutic implications and challenges. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, L.; Duvivier, L.; Fourrez, M.; Salazar, P.; Sprimont, L.; Xia, D.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Gottesman, M.M.; Gillet, J.P. Identification of two novel heterodimeric ABC transporters in melanoma: ABCB5β/B6 and ABCB5β/B9. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 105594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Palencia, G.R.; Correa-Basurto, J.; Trujillo-Ferrara, J.; Meraz-Ríos, M.A.; Vásquez- Moctezuma, I. Epigenetic Evaluation of N-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-Propylpentanamide, a Valproic Acid Aryl Derivative with Activity Against HeLa Cells. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Blake, M.; Baek, J.H.; Kohlhagen, G.; Pommier, Y.; Carrier, F. Inhibition of histone deacetylase increases cytotoxicity to anticancer drugs targeting DNA. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7291–7300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arce, C.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; González-Fierro, A.; de la Cruz-Hernández, E.; Revilla-Vázquez, A.; Chávez-Blanco, A.; Trejo-Becerril, C.; Pérez-Cárdenas, E.; Taja-Chayeb, L.; Bargallo, E.; et al. A proof-of-principle study of epigenetic therapy added to neoadjuvant doxorubicin cyclophosphamide for locally advanced breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kuramitsu, Y.; Kitagawa, T.; Tokuda, K.; Baron, B.; Akada, J.; Nakamura, K. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Valproic Acid Sensitizes Gemcitabine-Induced Cytotoxicity in Gemcitabine-Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cells Possibly Through Inhibition of the DNA Repair Protein Gamma-H2AX. Target Oncol. 2015, 10, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, Y.; Sung, R.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, D.S.; Park, S.M. HDAC inhibitors induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, C.; Wu, S.; Duan, Q.; Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Shen, Q.; Yin, T. Combination chemotherapy of valproic acid (VPA) and gemcitabine regulates STAT3/Bmi1 pathway to differentially potentiate the motility of pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 50, Erratum in Cell Biosci. 2023, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.M.; Bell, E.L.; Hughes, R.O.; Garfield, A.S. ABC transporters: Human disease and pharmacotherapeutic potential. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 152–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene (Protein) | Forward | Reverse | Size (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ABCC1 (MRP1) | 5′-gACAgAgATTggCgAgAAg-3′ | 5′-ATgTCAgCgTTggAgTACAC-3′ | 90 |
| 2 | ABCC2 (MRP2) | 5′-AgAgAAgCTgACCATCATCC-3′ | 5′-ACCAggATCTTggATTTCCg-3′ | 255 |
| 3 | ABCC3 (MRP3) | 5′-TgCAggTgACATTTgCTCTg-3′ | 5′-AgCgCACAgAATAATTCCgg-3′ | 192 |
| 4 | ABCC4 (MRP4) | 5′-CTgAgAATgACgCACAgAAg-3′ | 5′-TATgggCTggATTACTTTgg-3′ | 122 |
| 5 | ABCC5 (MRP5) | 5′-TCCgCCACTgTAAgATTCTg-3′ | 5′-CATggCATAgAATCgggAAC-3′ | 242 |
| 6 | ABCC6 (MRP6) | 5′-TgCAgTACAAgTgTgCTgAC-3′ | 5′-CTgTAAAACAggCCCTTCTg-3′ | 313 |
| 7 | ABCC10 (MRP7) | 5′-gAggTgATTACATCCATggg-3′ | 5′-ACTgTCTTgTTggCAAAgCg-3′ | 212 |
| 8 | ABCG2 (BCRP) | 5′-AAggAgATCAgCTACACCAC-3′ | 5′-CACTgCTgAAACACTggTTg-3′ | 232 |
| 9 | ABCB1 (MDR1, Pgp) | 5′-TACTTggTggCACATAAACTC-3′ | 5′-gCATAgTCAggAgCAAATgA-3′ | 113 |
| 10 | ABCB5 | 5′-AggACAAgTgCTgTTTgATg-3′ | 5′-CTCTTgAggAACgATTgCTA-3′ | 85 |
| 11 | GAPDH | 5′-gTATgACAACAgCCTCAAgAT-3′ | 5′-gTCCTTCCACgATACCAAAg-3′ | 104 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luna-Palencia, G.R.; Correa-Basurto, J.; Vásquez-Moctezuma, I. Valproic Acid as a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Induces ABCB1 Overexpression and De Novo ABCB5 Expression in HeLa Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090749
Luna-Palencia GR, Correa-Basurto J, Vásquez-Moctezuma I. Valproic Acid as a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Induces ABCB1 Overexpression and De Novo ABCB5 Expression in HeLa Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(9):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090749
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuna-Palencia, Gabriela Rebeca, José Correa-Basurto, and Ismael Vásquez-Moctezuma. 2025. "Valproic Acid as a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Induces ABCB1 Overexpression and De Novo ABCB5 Expression in HeLa Cells" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 9: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090749
APA StyleLuna-Palencia, G. R., Correa-Basurto, J., & Vásquez-Moctezuma, I. (2025). Valproic Acid as a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Induces ABCB1 Overexpression and De Novo ABCB5 Expression in HeLa Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(9), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090749






