Effect of Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Chromatin Decondensation on PLCζ Efficacy in Infertile Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Evaluation of Sperm Quality
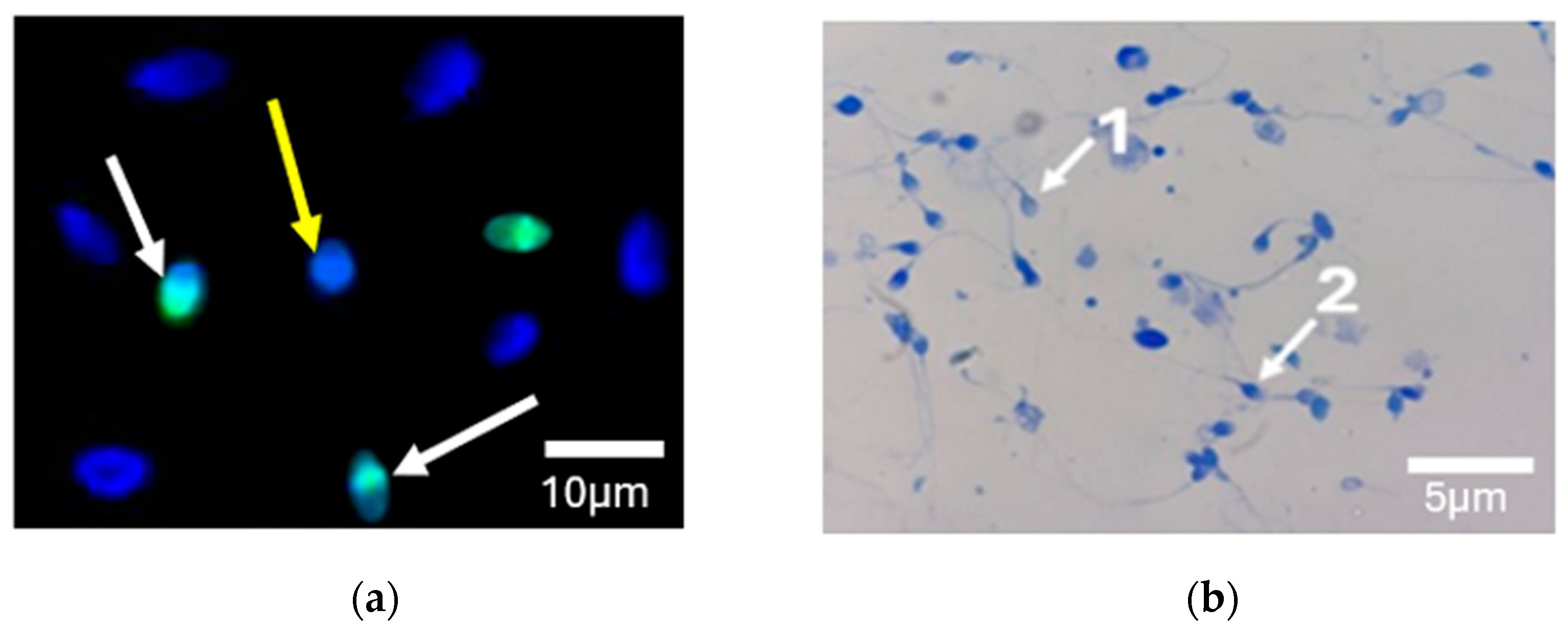
2.3. DNA Fragmentation by TUNEL Assay
2.4. Chromatin Condensation by Aniline Blue Staining
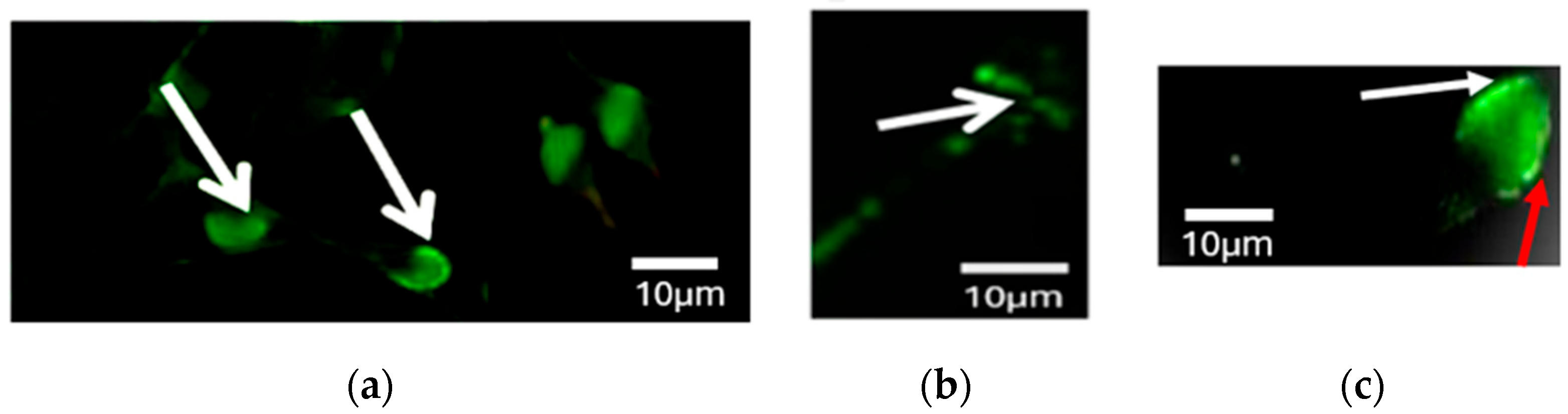
2.5. PLCζ Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Conventional Semen Parameters
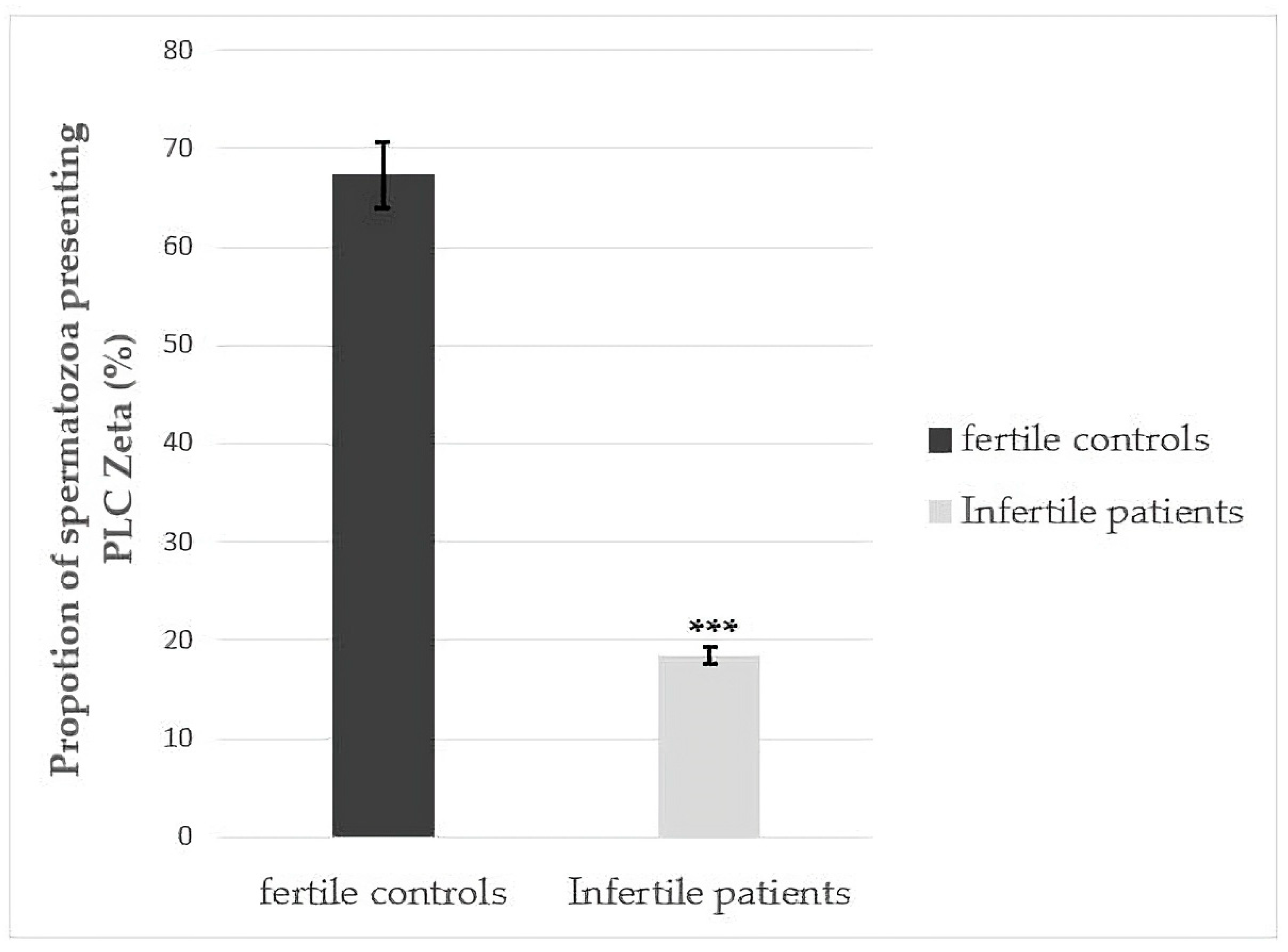
3.2. Differences in Total Number of Sperm Exhibiting PLCζ for Fertile Controls and Infertile Patients
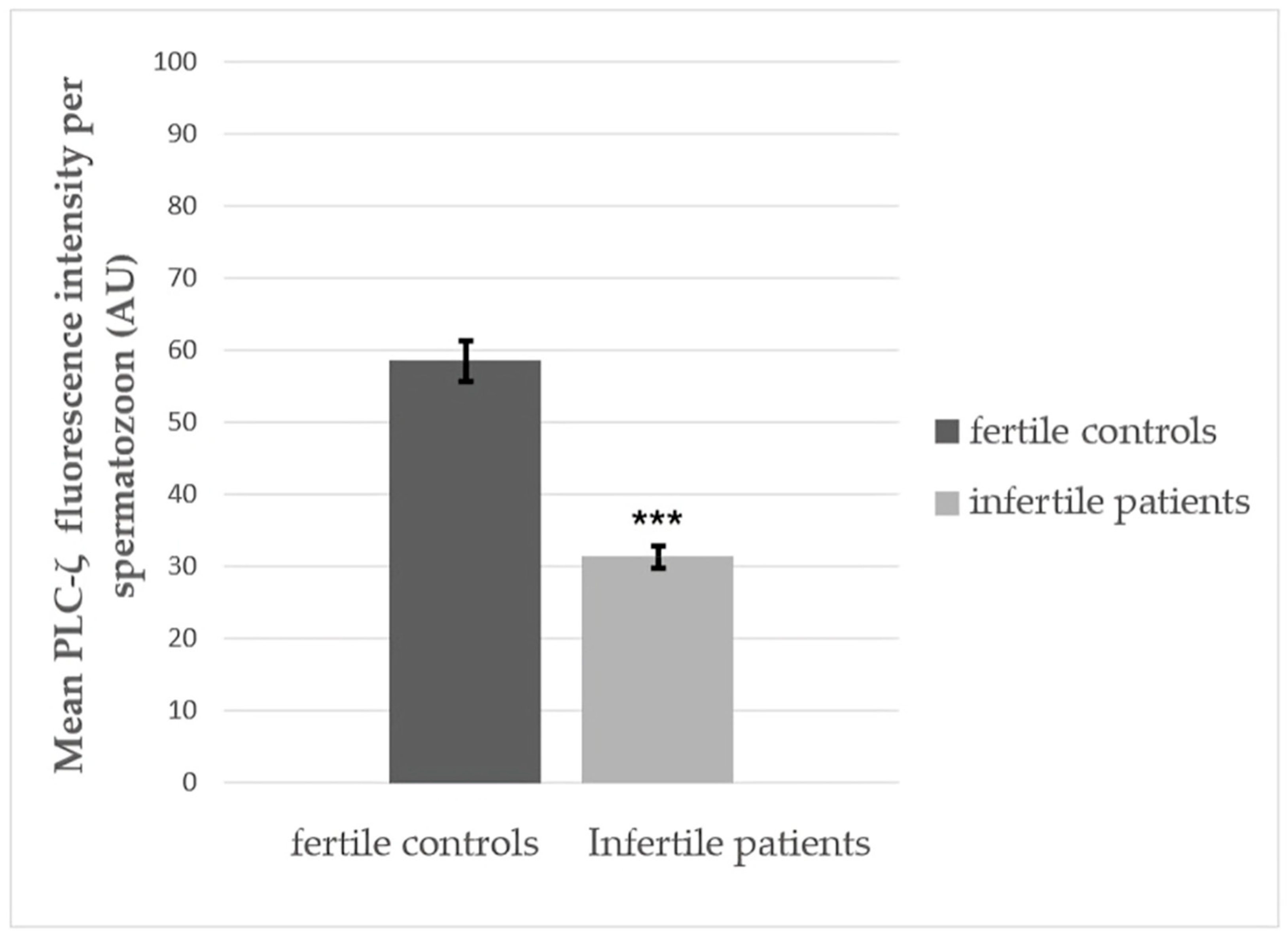
3.3. Quantitative Fluorescence Analysis of PLCζ in Fertile Controls and Infertile Patients
3.4. Differences in PLCζ Localization Patterns in Sperm from Fertile Controls and Infertile Patients
3.5. Correlations Between PLCζ and Sperm Function
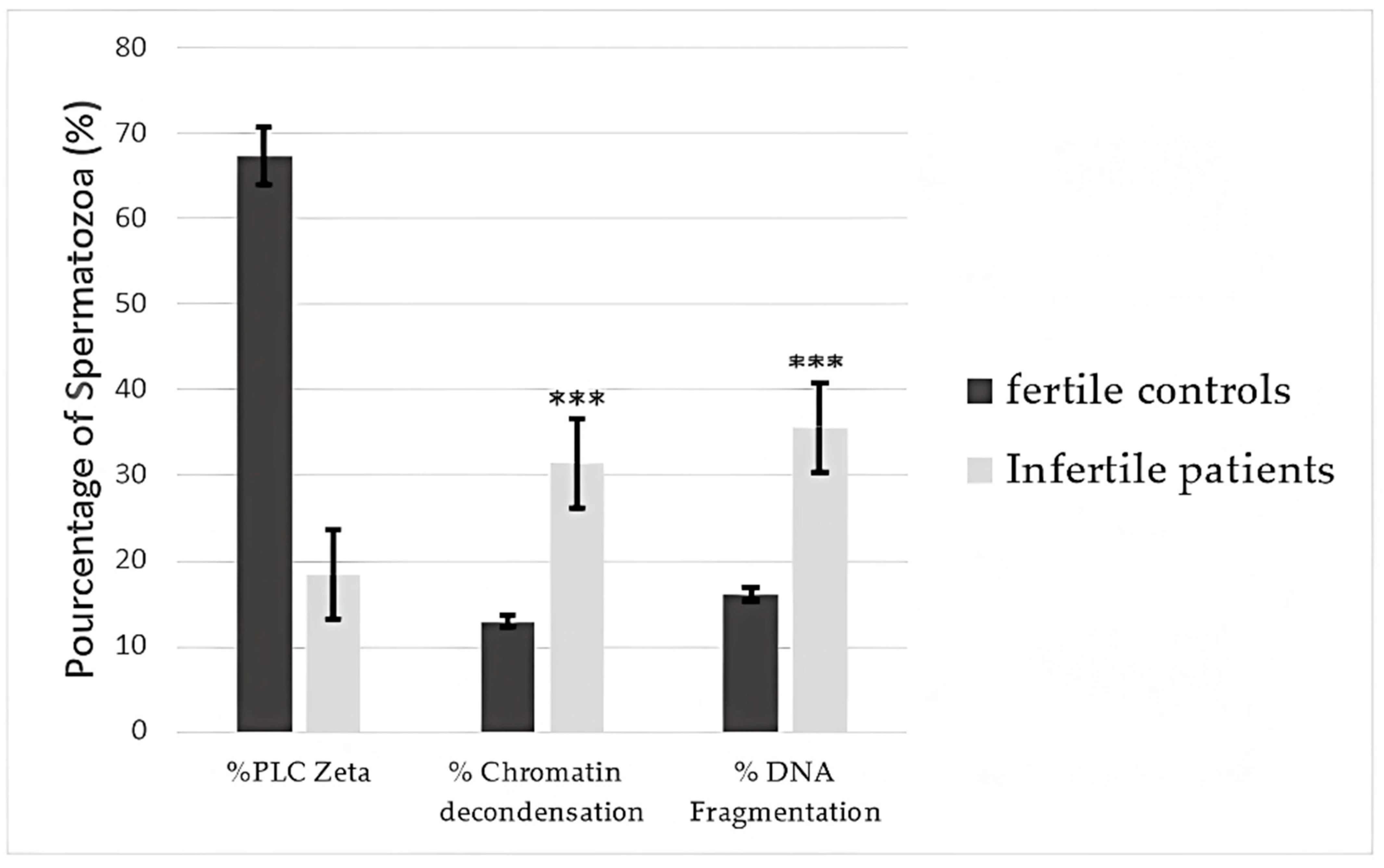
3.6. Correlations of Percentages of Sperm Presenting PLCζ, DNA Fragmentation, and Chromatin Decondensation with Semen Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICSI | intracytoplasmic sperm injection |
| PLCζ | phospholipase C ζ |
| DFI | DNA fragmentation index |
| SCD | sperm chromatin decondensation |
References
- Kashir, J. Increasing Associations between Defects in Phospholipase C Zeta and Conditions of Male Infertility: Not Just ICSI Failure? J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2020, 37, 1273–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdani, S.N.; Yeste, M.; Jones, C.; Coward, K. Phospholipase C Zeta (PLCζ) and Male Infertility: Clinical Update and Topical Developments. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2016, 61, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.; Kashir, J.; Thanassoulas, A.; Safieh-Garabedian, B.; Lai, F.A.; Nomikos, M. Essential Role of Sperm-Specific PLC-Zeta in Egg Activation and Male Factor Infertility: An Update. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azil, S.; Mbaye, M.M.; Louanjli, N.; Ghazi, B.; Benkhalifa, M. Phospholipase C Zeta: A Hidden Face of Sperm for Oocyte Activation and Early Embryonic Development. Korean J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2024, 67, 467–480. [Google Scholar]
- Kashir, J.; Ganesh, D.; Jones, C.; Coward, K. Oocyte Activation Deficiency and Assisted Oocyte Activation: Mechanisms, Obstacles and Prospects for Clinical Application. Hum. Reprod. Open 2022, 2022, hoac003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas-Maynou, J.; Llavanera, M.; Mateo-Otero, Y.; Garcia-Bonavila, E.; Delgado-Bermúdez, A.; Yeste, M. Direct but Not Indirect Methods Correlate the Percentages of Sperm with Altered Chromatin to the Intensity of Chromatin Damage. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 719319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas-Maynou, J.; Garcia-Bonavila, E.; Bonet, S.; Catalán, J.; Salas-Huetos, A.; Yeste, M. The TUNEL Assay Underestimates the Incidence of DNA Damage in Pig Sperm Due to Chromatin Condensation. Theriogenology 2021, 174, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatti, L.M.; Martello, C.L.; Andrade, G.M.; Oliveira, N.P.; Frantz, N. Advanced Paternal Age Affects the Sperm DNA Fragmentation Index and May Lead to Lower Good-Quality Blastocysts. Reprod. Sci. 2023, 30, 2489–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavalaee, M.; Kiani-Esfahani, A.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H. Relationship between Potential Sperm Factors Involved in Oocyte Activation and Sperm DNA Fragmentation with Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection Clinical Outcomes. Cell J. 2016, 18, 588–596. [Google Scholar]
- Tavalaee, M.; Kiani-Esfahani, A.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H. Relationship between Phospholipase C-Zeta, Semen Parameters, and Chromatin Status. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2017, 63, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björndahl, L.; Apolikhin, O.; Baldi, E.; Barratt, C.L.R.; Festin, M.P.R.; Kirkman-Brown, J.C.; Wang, C. WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; p. 276. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Iovine, C.; Agarwal, A.; Henkel, R. TUNEL Assay—Standardized Method for Testing Sperm DNA Fragmentation. Andrologia 2021, 53, e13738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellami, A.; Chakroun, N.; Ben Zarrouk, S.; Sellami, H.; Kebaili, S.; Rebai, T.; Keskes, L. Assessment of Chromatin Maturity in Human Spermatozoa: Useful Aniline Blue Assay for Routine Diagnosis of Male Infertility. Adv. Urol. 2013, 2013, 578631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasa, P.; Coward, K.; Young, C.; Parrington, J. The Pattern of Localization of the Putative Oocyte Activation Factor, Phospholipase Cζ, in Uncapacitated, Capacitated, and Ionophore-Treated Human Spermatozoa. Hum. Reprod. 2008, 23, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelumalai, S.; Yeste, M.; Jones, C.; Amdani, S.N.; Kashir, J.; Mounce, G.; Da Silva, S.J.M.; Barratt, C.L.; McVeigh, E.; Coward, K. Total Levels, Localization Patterns, and Proportions of Sperm Exhibiting Phospholipase C Zeta Are Significantly Correlated with Fertilization Rates after Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 104, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, N.; Meseguer, M.; Alvarez, J.; Simón, C.; Pellicer, A.; Remohí, J. Relationship among Standard Semen Parameters, Glutathione Peroxidase/Glutathione Reductase Activity, and MRNA Expression and Reduced Glutathione Content in Ejaculated Spermatozoa from Fertile and Infertile Men. Fertil. Steril. 2004, 82 (Suppl. S3), 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashir, J.; Nomikos, M.; Lai, F.A. Phospholipase C Zeta and Calcium Oscillations at Fertilisation: The Evidence, Applications, and Further Questions. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2018, 67, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsas, A.; Markou, E.; Kyrgiafini, M.-A.; Zikopoulos, A.; Symeonidis, E.N.; Dimitriadis, F.; Zachariou, A.; Sofikitis, N.; Chrisofos, M. Oxidative-Stress-Mediated Epigenetic Dysregulation in Spermatogenesis: Implications for Male Infertility and Offspring Health. Genes 2025, 16, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, D.C.; Ory, J.; Blachman-Braun, R.; Nackeeran, S.; Best, J.C.; Ramasamy, R. Advanced Paternal Age and Sperm DNA Fragmentation: A Systematic Review. World J. Mens. Health 2021, 40, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsas, A.; Moustakli, E.; Zikopoulos, A.; Georgiou, I.; Dimitriadis, F.; Symeonidis, E.N.; Markou, E.; Michaelidis, T.M.; Tien, D.M.B.; Giannakis, I. Impact of Advanced Paternal Age on Fertility and Risks of Genetic Disorders in Offspring. Genes 2023, 14, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashir, J.; Mistry, B.V.; Rajab, M.A.; BuSaleh, L.; Abu-Dawud, R.; Ahmed, H.A.; Alharbi, S.; Nomikos, M.; AlHassan, S.; Coskun, S. The Mammalian Sperm Factor Phospholipase C Zeta Is Critical for Early Embryo Division and Pregnancy in Humans and Mice. Hum. Reprod. 2024, 39, 1256–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, N.; Nazarian, H.; Nazari, L.; Novin, M.G.; Piryaei, A.; Heidari, M.H.; Farahani, R.M.; Sadjadpour, S.S. Evaluation of PAWP and PLCζ Expression in Infertile Men with Previous ICSI Fertilization Failure. Urol. J. 2018, 15, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimizadeh, P.; Topraggaleh, T.R.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Ziarati, N.; Mirshahvaladi, S.; Esmaeili, V.; Seifi, S.; Eftekhari-Yazdi, P.; Shahverdi, A. The Alteration of PLCζ Protein Expression in Unexplained Infertile and Asthenoteratozoospermic Patients: A Potential Effect on Sperm Fertilization Ability. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2020, 87, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, F.; Yan, Z.; Li, M.; Ouyang, J.; Wu, L.; Yin, M.; Zhao, J.; Kuang, Y. Novel Mutations in PLCZ1 Cause Male Infertility Due to Fertilization Failure or Poor Fertilization. Hum. Reprod. 2020, 35, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heytens, E.; Parrington, J.; Coward, K.; Young, C.; Lambrecht, S.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Fissore, R.A.; Hamer, R.; Deane, C.M.; Ruas, M. Reduced Amounts and Abnormal Forms of Phospholipase C Zeta (PLCζ) in Spermatozoa from Infertile Men. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 24, 2417–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Dai, C.; Guo, J.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Gong, F.; Lu, G.; Lin, G. Novel Homozygous Variations in PLCZ1 Lead to Poor or Failed Fertilization Characterized by Abnormal Localization Patterns of PLCζ in Sperm. Clin. Genet. 2020, 97, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, G.D.; Neri, Q.V.; Schlegel, P.N.; Rosenwaks, Z. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) in Extreme Cases of Male Infertility. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Deemeh, M.R.; Tavalaee, M. Artificial Oocyte Activation and Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 94, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aras-Tosun, D.; Cakar, Z.; Can, A.; Ozkavukcu, S.; Kaplanoglu, I.; Cinar, O. Phospholipase C-zeta Levels Are Not Correlated with Fertilisation Rates in Infertile Couples. Andrologia 2022, 54, e14269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashir, J.; Jones, C.; Coward, K. Oocyte Activation and Phospholipase C Zeta (PLCζ): Male Infertility and Implications for Therapeutic Intervention. Phospholipases Health Dis. 2014, 263–281. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Kong, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Wu, H.; Tang, D.; Zha, X.; Tan, Q.; et al. A Homozygous Nonsense Mutation of PLCZ1 Cause Male Infertility with Oocyte Activation Deficiency. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2020, 37, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoffier, J.; Lee, H.C.; Yassine, S.; Zouari, R.; Martinez, G.; Karaouzène, T.; Coutton, C.; Kherraf, Z.E.; Halouani, L.; Triki, C.; et al. Homozygous Mutation of PLCZ1 Leads to Defective Human Oocyte Activation and Infertility That Is Not Rescued by the WW-Binding Protein PAWP. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-Vaquer, A.; Barragan, M.; Freour, T.; Vernaeve, V.; Vassena, R. PLCζ Sequence, Protein Levels, and Distribution in Human Sperm Do Not Correlate with Semen Characteristics and Fertilization Rates after ICSI. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2016, 33, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, A.; Frigge, M.L.; Masson, G.; Besenbacher, S.; Sulem, P.; Magnusson, G.; Gudjonsson, S.A.; Sigurdsson, A.; Jonasdottir, A.; Jonasdottir, A. Rate of de Novo Mutations and the Importance of Father’s Age to Disease Risk. Nature 2012, 488, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Chang, J.H.; Jee, B.C.; Kim, S.H. Relationship between Phospholipase C Zeta Immunoreactivity and DNA Fragmentation and Oxidation in Human Sperm. Obs. Gynecol. Sci. 2015, 58, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovova, O.A.; Chernykh, V.B. Genetics of Oocyte Maturation Defects and Early Embryo Development Arrest. Genes 2022, 13, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jonge, C. Biological Basis for Human Capacitation—Revisited. Hum. Reprod. Update 2017, 23, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhedi, F.; Chalas, C.; Petit, J.-M.; Abid, N.; Mokadem, E.; Hizem, S.; Kamoun, H.; Keskes, L.; Dupont, J.-M. Altered Three-Dimensional Organization of Sperm Genome in DPY19L2-Deficient Globozoospermic Patients. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2019, 36, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvaei, I.; Litzky, J.; Esfandiari, N. Advanced Paternal Age: Effects on Sperm Parameters, Assisted Reproduction Outcomes and Offspring Health. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2020, 18, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.T.K.; Robaire, B. Advanced Paternal Age and Future Generations. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 897101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins da Silva, S.; Anderson, R.A. Reproductive Axis Ageing and Fertility in Men. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashir, J.; Mistry, B.V.; Gumssani, M.A.; Rajab, M.; Abu-Dawas, R.; AlMohanna, F.; Nomikos, M.; Jones, C.; Abu-Dawud, R.; Al-Yacoub, N. Advancing Male Age Differentially Alters Levels and Localization Patterns of PLCzeta in Sperm and Testes from Different Mouse Strains. Asian J. Androl. 2021, 23, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, H.; Takarabe, S.; Kageyama, A.; Kawata, Y.; Ito, J. Molecular Mechanism of Oocyte Activation in Mammals: Past, Present, and Future Directions. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.; Thanassoulas, A.; Aliyev, E.; Swann, K.; Naija, A.; Yalcin, H.C.; Lai, F.A.; Nomikos, M. Development of Recombinant PLC-Zeta Protein as a Therapeutic Intervention for the Clinical Treatment of Oocyte Activation Failure. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.T. Mammalian Sperm Contain Two Factors for Calcium Release and Egg Activation: Phospholipase C Zeta and a Cryptic Activating Factor. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 24, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.; Meng, X.; Coward, K. Sperm Factors and Egg Activation: Phospholipase C Zeta (PLCZ1) and the Clinical Diagnosis of Oocyte Activation Deficiency. Reproduction 2022, 164, F53–F66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sperm Parameters | Fertile Controls | Infertile Patients | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sperm concentration (106/mL) | 94.19 ± 57.77 | 59.97 ± 40.45 | 0.015 * |
| Progressive motility (%) | 50.69 ± 11.92 | 42.96 ± 11.29 | 0.46 |
| Viability (%) | 76.58 ± 10.35 | 70.59 ± 9.20 | 0.29 |
| Morphology (%) | 11.30 ± 4.32 | 7.52 ± 3.24 | 0.001 * |
| PLCζ Localization | Fertile Controls (n Positive/n Total) | Infertile Patients (n Positive/n Total) | χ2 (df) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 50/65 | 4/70 | 70.011 (1) | <0.001 * |
| Eq | 16/65 | 9/70 | 1.951 (1) | 0.162 |
| A + Eq | 27/65 | 8/70 | 13.691 (1) | <0.001 * |
| Sperm Concentration (106/mL) | Progressive Motility (%) | Viability (%) | Morphology (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLCζ (%) | p = 0.043 * | p = 0.4 | p= 0.056 | p = 0.04 * |
| DFI (%) | p = 0.011 * | p = 0.715 | p = 0.017 * | p = 0.119 |
| SCD (%) | p = 0.036 * | p = 0.438 | p = 0.074 | p = 0.219 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azil, S.; Kaarouch, I.; Montjean, D.; Pagé, M.-H.G.; Cabry, R.; Louanjli, N.; Ghazi, B.; Benkhalifa, M. Effect of Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Chromatin Decondensation on PLCζ Efficacy in Infertile Patients. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090707
Azil S, Kaarouch I, Montjean D, Pagé M-HG, Cabry R, Louanjli N, Ghazi B, Benkhalifa M. Effect of Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Chromatin Decondensation on PLCζ Efficacy in Infertile Patients. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(9):707. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090707
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzil, Soukaina, Ismail Kaarouch, Debbie Montjean, Marie-Hélène Godin Pagé, Rosalie Cabry, Noureddine Louanjli, Bouchra Ghazi, and Moncef Benkhalifa. 2025. "Effect of Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Chromatin Decondensation on PLCζ Efficacy in Infertile Patients" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 9: 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090707
APA StyleAzil, S., Kaarouch, I., Montjean, D., Pagé, M.-H. G., Cabry, R., Louanjli, N., Ghazi, B., & Benkhalifa, M. (2025). Effect of Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Chromatin Decondensation on PLCζ Efficacy in Infertile Patients. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(9), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090707







