Protective Effects of Inula japonica Leaf Extract Against PM10-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Keratinocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Plant Material and UHPLC-Orbitrap-MS Analysis
2.3. Selection of Proteins Associated with Active Compounds
2.4. Collection of Psoriasis-Related Genes
2.5. Construction of Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
2.6. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway Analysis
2.7. Cell Culture and Sample Preparation
2.8. Cell Viability
2.9. ROS Inhibition Assay
2.10. Western Blot
2.11. qRT-PCR Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
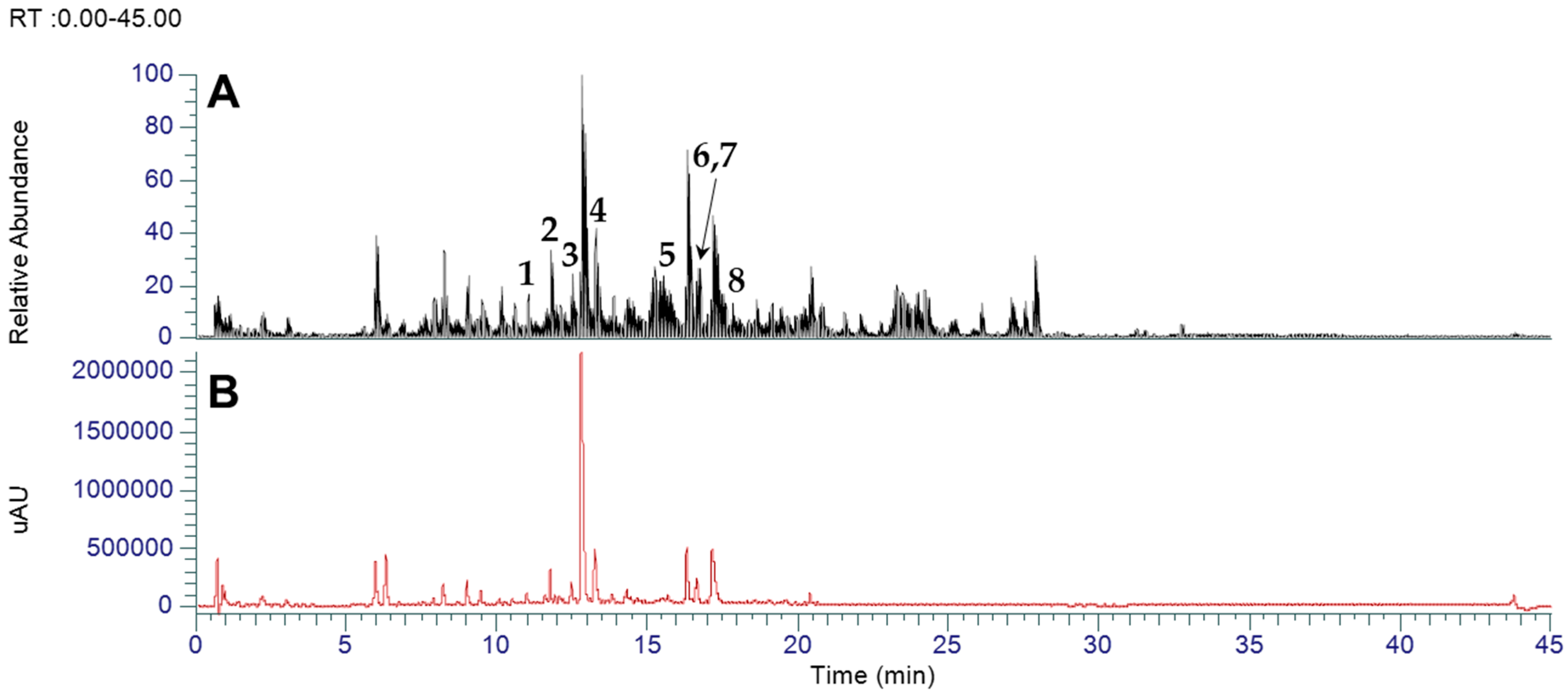
3.1. LC-MS-Based Identification of Flavonoids in Inula japonica Leaves
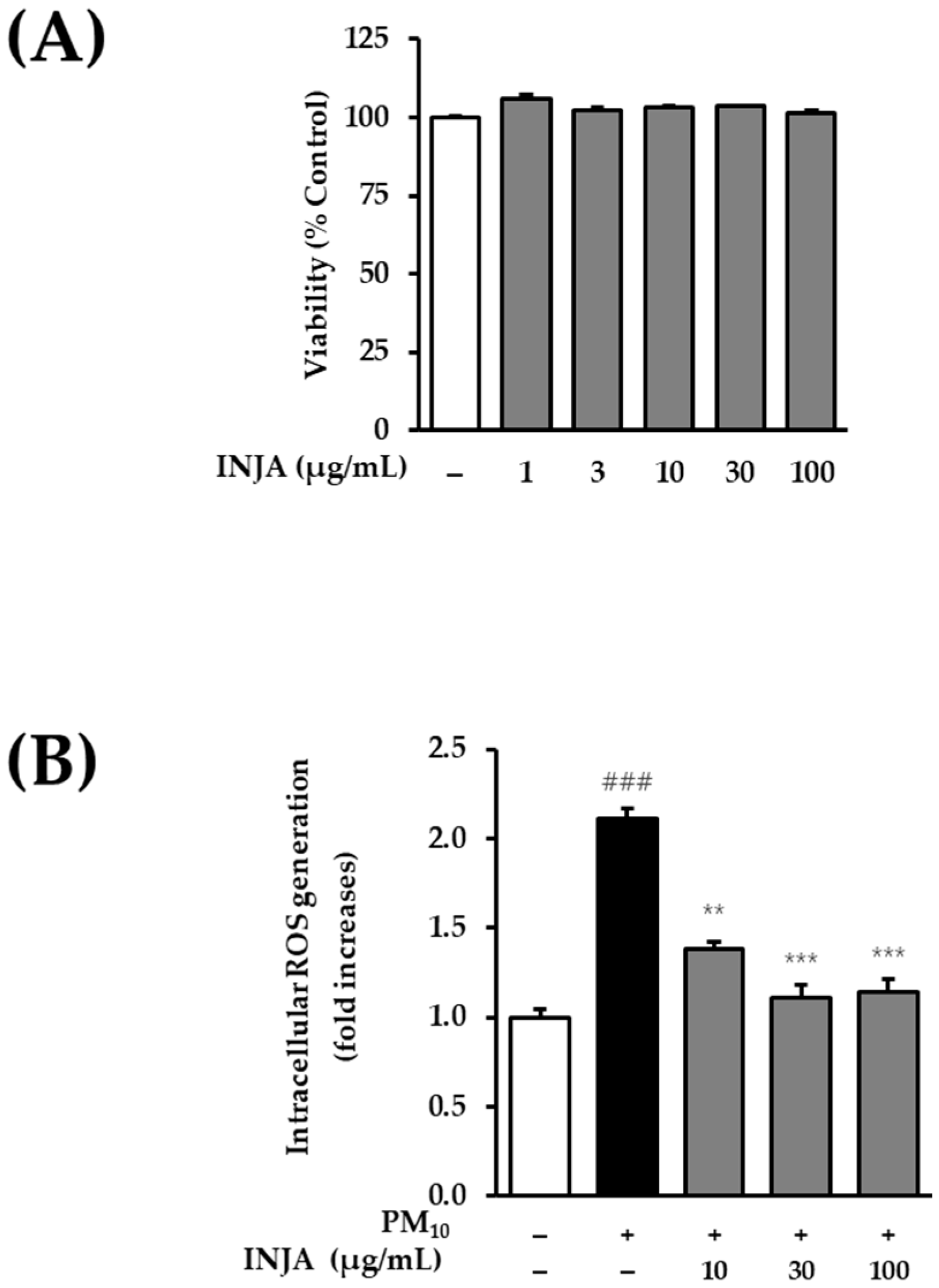
3.2. Effects of Inula japonica Leaf Extract on Cell Viability and Intracellular ROS Generation in PM10-Induced Human Keratinocytes
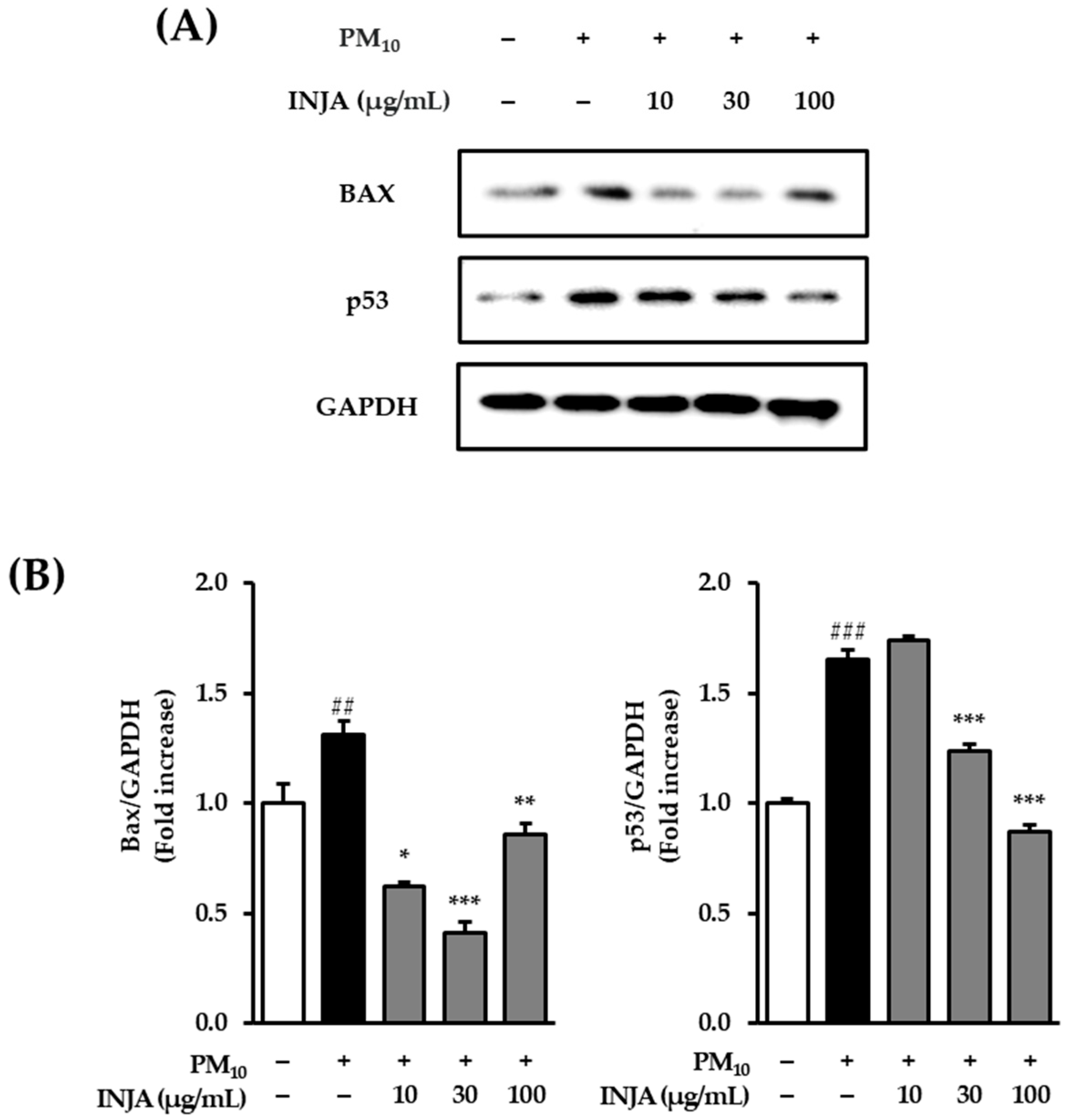
3.3. Effects of Inula japonica Leaf Extract on Bax and p53 Protein Expression in PM10-Induced Human Keratinocytes
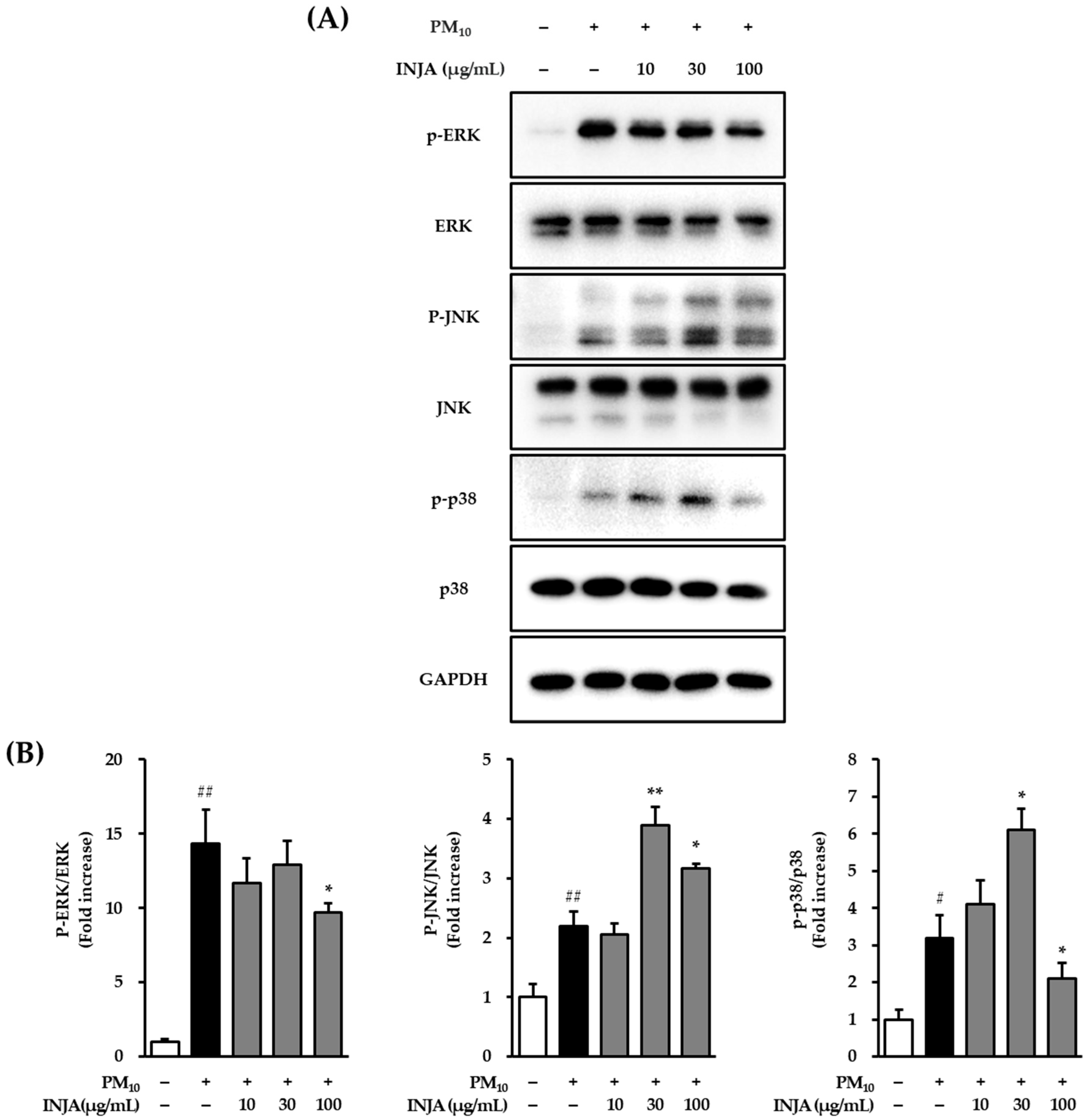
3.4. Effects of Inula japonica Leaf Extract on Phosphorylation of MAPKs Proteins in PM10-Induced Human Keratinocytes
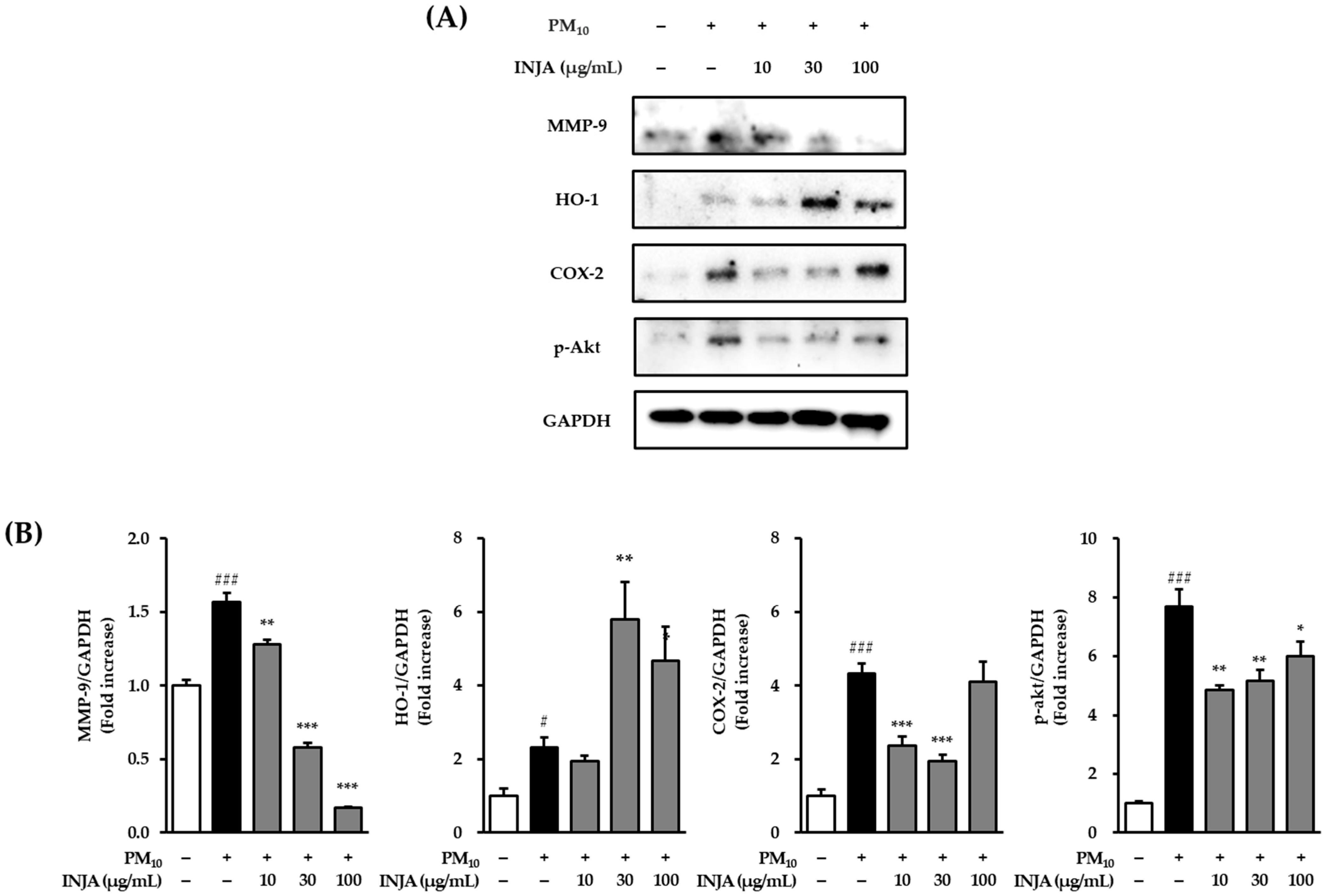
3.5. Effects of Inula japonica Leaf Extract on MMP-9, HO-1, COX-2, and Phosphorylated AKT Expression in PM10-Induced Human Keratinocytes
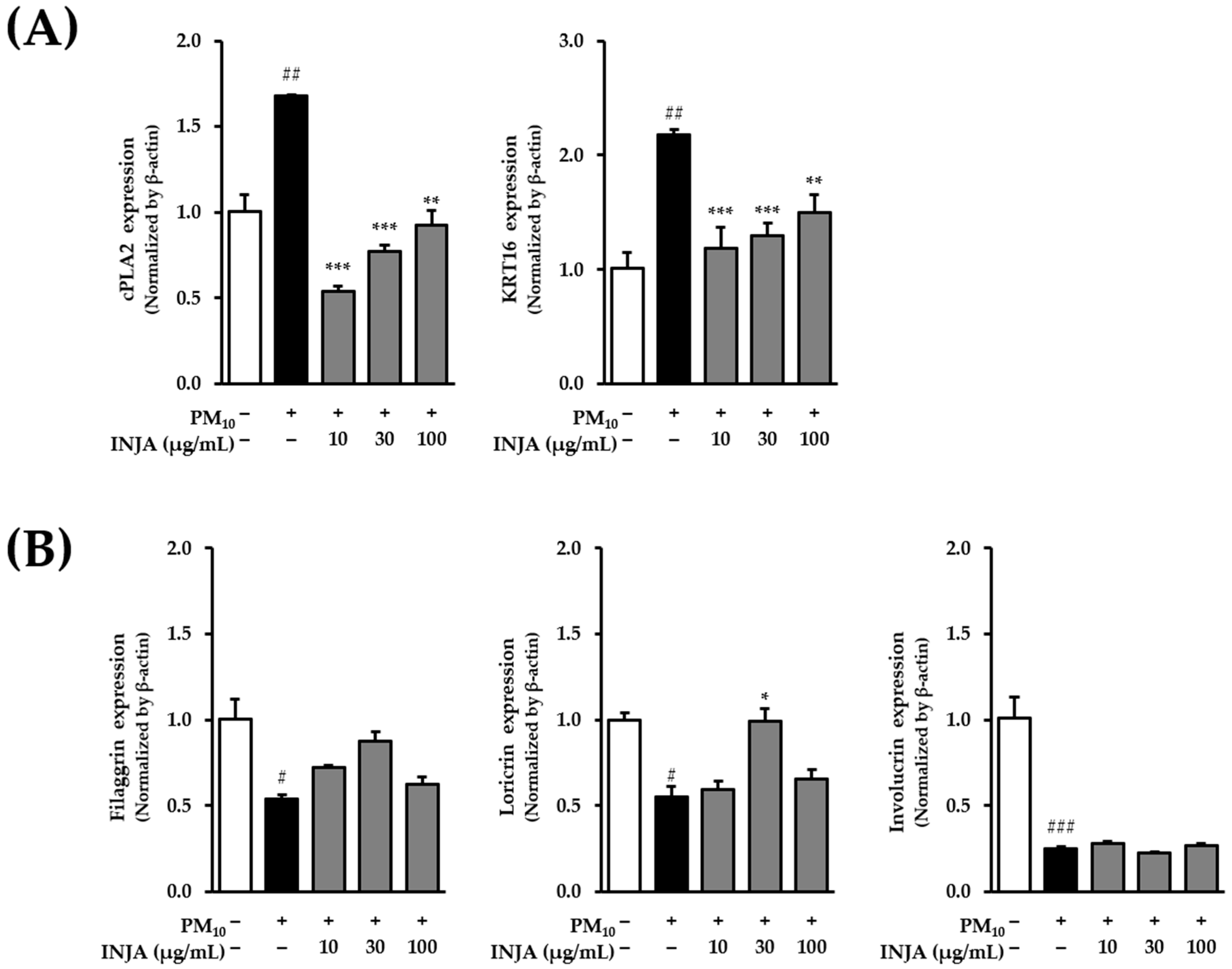
3.6. Effects of Inula japonica Leaf Extract on cPLA2, KRT16, Filaggrin, Loricrin, and Involucrin mRNA Expression in PM10-Induced Human Keratinocytes
3.7. Database-Driven Screening of Inulae Flos
3.8. Target Protein Prediction for Active Compounds of Inulae Flos Using the STITCH Database
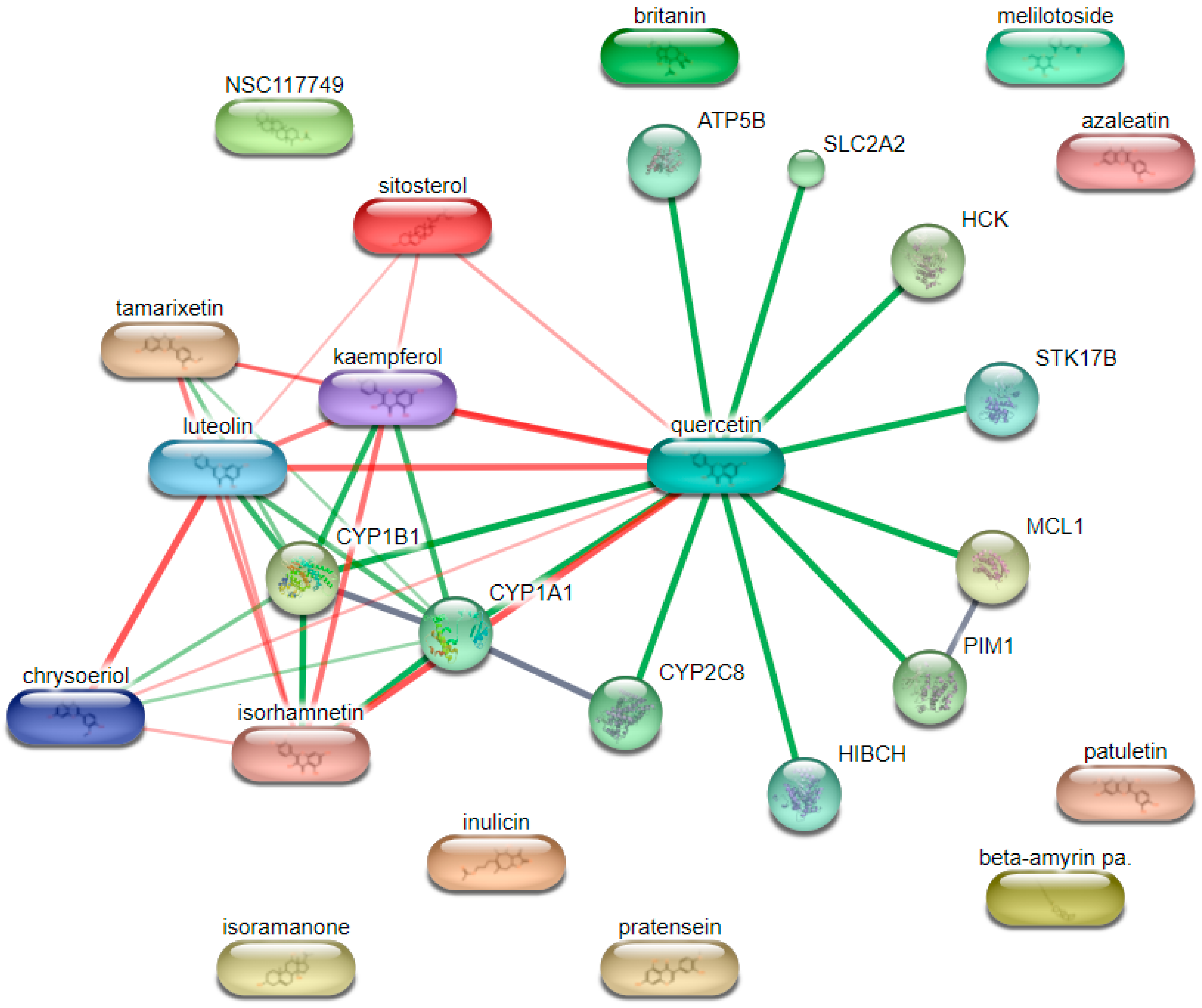
3.9. Identification of Common Targets and Network Analysis Between Inulae Flos Compounds and Psoriasis-Associated Genes
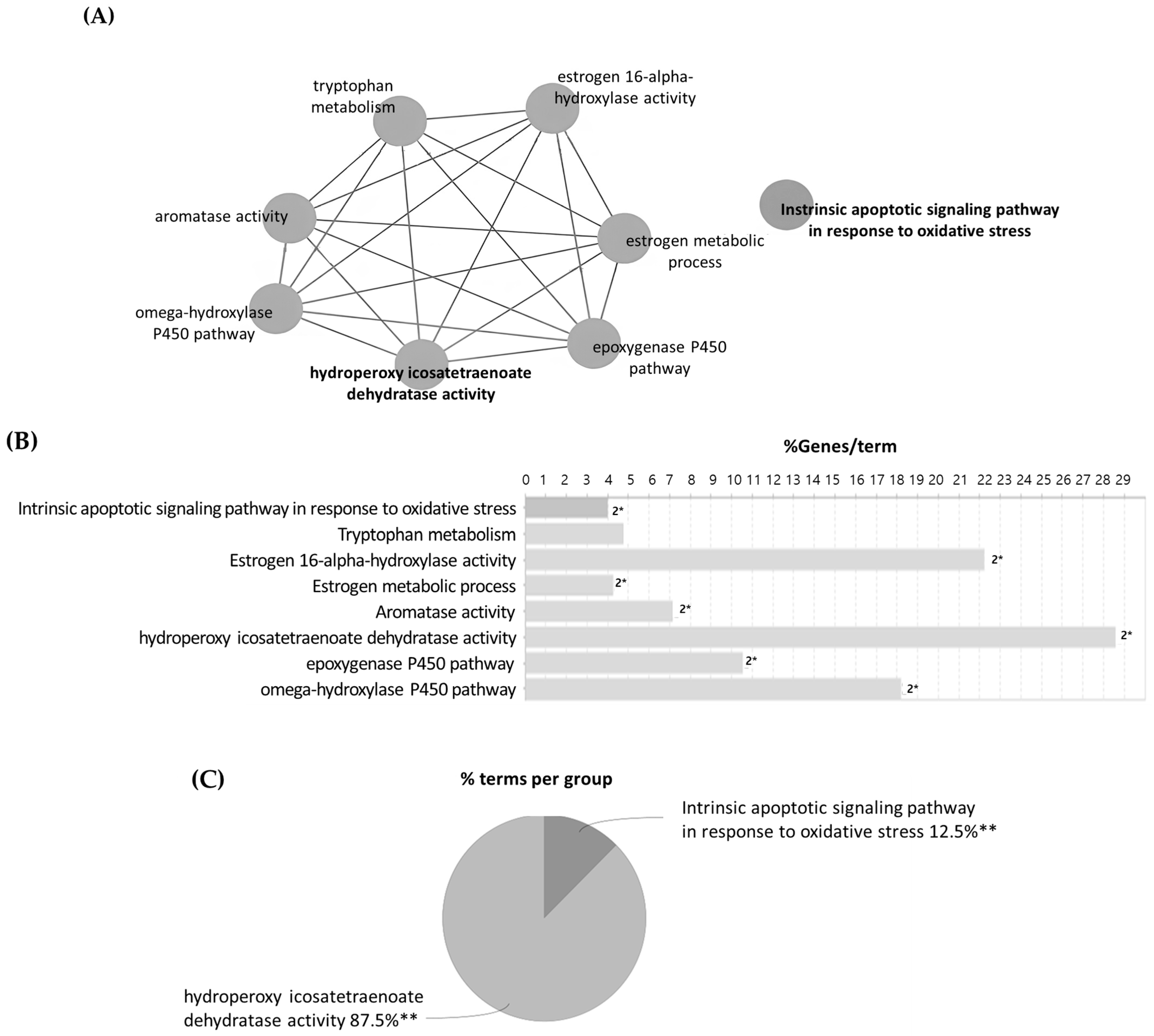
3.10. Prediction of the Mechanism of Action of Active Compounds from Inulae Flos Using ClueGO
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATP5B | ATP synthase subunit beta |
| Bax | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
| ClueGO | Clustering with Gene Ontology |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| cPLA2 | Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 |
| CYP2C8 | Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 8 |
| CYP1A1 | Cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 1 |
| CYP1B1 | Cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily B member 1 |
| DCFDA | 2′,7′-Dichlorofluorescin Diacetate |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| ECL | Enhanced Chemiluminescence |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| HO-1 | Heme Oxygenase-1 |
| HCK | Hemopoietic cell kinase |
| HIBCH | 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase |
| INJA | Inula japonica leaf extract |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal Kinase |
| KRT16 | Keratin 16 |
| KRT17 | Keratin 17 |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases |
| MMP-9 | Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 |
| MMPs | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| MCL1 | Myeloid cell leukemia 1 |
| NHKs | Normal Human Keratinocytes |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PIM1 | Pim-1 proto-oncogene |
| PM10 | Particulate Matter ≤10 μm in diameter |
| PPI | Protein–Protein Interaction |
| p53 | Tumor protein p53 |
| p-ERK | phosphorylated Extracellular Sig-nal-Regulated Kinase |
| p-JNK | phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| p-p38 | phosphorylated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| p-Akt | phosphorylated Protein Kinase B |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative Real-Time PCR |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| SLC2A2 | Solute carrier family 2 member 2 |
| STK17B | Serine/threonine kinase 17b |
| STRING | Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins |
| TCMSP | Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology |
| TBST | Tris-Buffered Saline with Tween 20 |
| UHPLC | Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
References
- Jin, S.-P.; Li, Z.; Choi, E.K.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.K.; Seo, E.Y.; Chung, J.H.; Cho, S. Urban particulate matter in air pollution penetrates into the barrier-disrupted skin and produces ROS-dependent cutaneous inflammatory response in vivo. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 91, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-Y.; Byun, E.J.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.S. Air pollution, autophagy, and skin aging: Impact of particulate matter (PM10) on human dermal fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Tsoi, L.C.; Billi, A.C.; Ward, N.L.; Harms, P.W.; Zeng, C.; Maverakis, E.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Cytokinocytes: The diverse contribution of keratinocytes to immune responses in skin. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e142067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwandtner, M.; Mildner, M.; Mlitz, V.; Gruber, F.; Eckhart, L.; Werfel, T.; Gutzmer, R.; Elias, P.; Tschachler, E. Histamine suppresses epidermal keratinocyte differentiation and impairs skin barrier function in a human skin model. Allergy 2013, 68, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohania, D.; Chandel, S.; Kumar, P.; Verma, V.; Digvijay, K.; Tripathi, D.; Choudhury, K.; Mitten, S.K.; Shah, D. Ultraviolet radiations: Skin defense-damage mechanism. Ultrav. Light Hum. Health Dis. Environ. 2017, 996, 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, M.K.H.M.; Madusanka, D.M.D.; Han, E.J.; Kim, M.J.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-S.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Ahn, G. (−)-Loliolide isolated from sargassum horneri protects against fine dust-induced oxidative stress in human keratinocytes. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.; Ju, S.-Y.; Park, S.; Jung, W.-K.; Je, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-J. Lysine-Proline-Valine peptide mitigates fine dust-induced keratinocyte apoptosis and inflammation by regulating oxidative stress and modulating the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Tissue Cell 2025, 95, 102837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Jung, D.-H.; Sung, J.; Min, I.S.; Lee, S.-J. Tart cherry extract containing chlorogenic acid, quercetin, and kaempferol inhibits the mitochondrial apoptotic cell death elicited by airborne PM10 in human epidermal keratinocytes. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhasani, R.; Araghi, F.; Tabary, M.; Aryannejad, A.; Mashinchi, B.; Robati, R.M. The impact of air pollution on skin and related disorders: A comprehensive review. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passeron, T.; Krutmann, J.; Andersen, M.; Katta, R.; Zouboulis, C. Clinical and biological impact of the exposome on the skin. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słuczanowska-Głabowska, S.; Salmanowicz, M.; Staniszewska, M.; Pawlik, A. The role of sirtuins in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaštelan, M.; Prpić-Massari, L.; Brajac, I. Apoptosis in psoriasis. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2009, 17, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, A.X.; Hyun, Y.J.; Piao, M.J.; Fernando, P.D.S.M.; Kang, K.A.; Ahn, M.J.; Yi, J.M.; Kang, H.K.; Koh, Y.S.; Lee, N.H. Eckol inhibits particulate matter 2.5-induced skin keratinocyte damage via MAPK signaling pathway. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, J.K.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, Y.M.; Boo, Y.C. Punicalagin and (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate rescue cell viability and attenuate inflammatory responses of human epidermal keratinocytes exposed to airborne particulate matter PM10. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 31, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, I.A.; Ha, J.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Boo, Y.C. Antioxidant effects of Korean propolis in HaCaT keratinocytes exposed to particulate matter 10. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Zhen, A.X.; Fernando, P.D.S.M.; Ahn, M.J.; Koh, Y.S.; Kang, H.K.; Yi, J.M.; Choi, Y.H.; Hyun, J.W. Particulate matter 2.5 mediates cutaneous cellular injury by inducing mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum stress: Protective effects of ginsenoside Rb1. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W. Air pollution and skin disorders. Int. J. Women’s Dermatol. 2021, 7, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Bai, L.; Burnett, R.T.; Kwong, J.C.; Hystad, P.; van Donkelaar, A.; Lavigne, E.; Weichenthal, S.; Copes, R.; Martin, R.V. Air pollution as a risk factor for incident chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. A 15-year population-based cohort study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fongsodsri, K.; Chamnanchanunt, S.; Desakorn, V.; Thanachartwet, V.; Sahassananda, D.; Rojnuckarin, P.; Umemura, T. Particulate matter 2.5 and hematological disorders from dust to diseases: A systematic review of available evidence. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 692008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, X.; Luo, Z.; Wu, D.; Shi, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, C.; Yang, C. Chemical constituents from the flowers of Inula japonica and their anti-inflammatory activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 117052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, M.; Yang, J.H.; Li, X.; Chao, G.H.; Park, H.-H.; Park, Y.N.; Son, J.K.; Lee, E. Inula japonica extract inhibits mast cell-mediated allergic reaction and mast cell activation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, D.-H.; Kim, M.J.; Ahn, J.; Jang, Y.-J.; Ha, T.-Y.; Jung, C.H. Inula japonica Thunb. flower ethanol extract improves obesity and exercise endurance in mice fed a high-fat diet. Nutrients 2018, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.-R.; Kim, K.S.; Jang, D.S.; Lee, S. Caffeoylglucaric and Caffeoylquinic Acids from Inula japonica Leaves and Their Anti-Skin Aging Effects in TNF-α-Induced Normal Human Fibroblast Damage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 13471–13487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, H.-M.; Lim, C.-M.; Jeon, K.-B.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Hong, J.-T.; Oh, D.-K.; Yang, Y.; Yoon, D.-Y. Specialized pro-resolving mediator 7S MaR1 inhibits IL-6 expression via modulating ROS/p38/ERK/NF-κB pathways in PM10-exposed keratinocytes. BMB Rep. 2024, 57, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.-W.; Lee, H.-S.; Na, J.-I.; Huh, C.-H.; Park, K.-C.; Choi, H.-R. Resveratrol inhibits particulate matter-induced inflammatory responses in human keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodskii, V.Y.; Terskikh, V.; Vasilyev, A.; Zvezdina, N.; Vorotelyak, E.; Fateeva, V.; Mal’chenko, L. Self-synchronization of the protein synthesis rhythm in HaCaT cultures of human keratinocytes. Russ. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 42, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, H.M.U.L.; Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Zhen, A.X.; Fernando, P.D.S.M.; Kang, H.K.; Yi, J.M.; Hyun, J.W. Hesperidin exhibits protective effects against PM2. 5-mediated mitochondrial damage, cell cycle arrest, and cellular senescence in human HaCaT keratinocytes. Molecules 2022, 27, 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-S.; Liu, Z.-M.; Hong, D.-Y. Blockage of JNK pathway enhances arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in human keratinocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 244, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouda, M.B.; Ford, A.E.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.Y. The JNK signaling pathway in inflammatory skin disorders and cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yin, H.; Li, Y.-T.; Qiao, Y.-X.; Wang, J.; He, Q.-Y.; Xiao, Z.-W.; Kuai, L.; Xiang, Y.-W. Shengjihuayu formula ameliorates the oxidative injury in human keratinocytes via blocking JNK/c-Jun/MMPs signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 326, 117938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, E.-J.; Ju, S.-Y.; Li, Y.; Lee, S.-J. Momordica cochinchinensis extract alleviates oxidative stress and skin damage caused by fine particulate matter. Tissue Cell 2024, 90, 102496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malar, D.S.; Prasanth, M.I.; Verma, K.; Prasansuklab, A.; Tencomnao, T. Hibiscus sabdariffa Extract Protects HaCaT Cells against Phenanthrene-Induced Toxicity through the Regulation of Constitutive Androstane Receptor/Pregnane X Receptor Pathway. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.N.; Naik, P.P.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Panda, P.K.; Sinha, N.; Meher, B.R.; Bhutia, S.K. Elimination of dysfunctional mitochondria through mitophagy suppresses benzo [a] pyrene-induced apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 112, 452–463, Erratum in Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 208, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, S.W.; Yu, E.; Kwon, K.; Jang, S.J.; Shin, D.S.; Moh, S.H.; Lee, J. Anti-pollutant activity of Porphyra yezoensis water extract and its active compound, porphyra 334, against urban particulate matter-induced keratinocyte cell damage. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-E.; Ryu, J.J.; Jo, Y.K.; Yeo, H.; Kang, S. 2′-Fucosyllactose attenuates particulate matter-induced inflammation via inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor in keratinocytes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, I.A.; Ha, J.W.; Boo, Y.C. Chlorogenic Acid, a Component of Oenanthe javanica (Blume) DC., Attenuates Oxidative Damage and Prostaglandin E2 Production Due to Particulate Matter 10 in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Y.-C.; Chou, C.-W.; Kumar, K.S.; Fu, K.-T.; Wang, H.-M.; Hsu, L.-S.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-R.; Chen, S.-C.; Yang, H.-L. Ellagic acid protects human keratinocyte (HaCaT) cells against UVA-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis through the upregulation of the HO-1 and Nrf-2 antioxidant genes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, M.J.; Chung, H.S. Fucoidan reduces oxidative stress by regulating the gene expression of HO-1 and SOD-1 through the Nrf2/ERK signaling pathway in HaCaT cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 3255–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-W.; Su, Y.-H.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Lee, I.-T.; Li, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-C.; Hsu, L.-F.; Yan, Y.-L.; Li, H.-Y.; Chen, M.-C. Glycofullerenes inhibit particulate matter induced inflammation and loss of barrier proteins in hacat human keratinocytes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Ko, E.-J.; Lee, D.; Kang, J.; Hwang, J.-K.; Kim, E. Protective Effects of Xanthorrhizol-Rich Extracts Against PM-Induced Skin Damage in Human Keratinocytes and 3D-Reconstructed Skin Models. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coy-Barrera, E.; Ogungbe, I.V.; Schmidt, T.J. Natural products for drug discovery in the 21st century: Innovations for novel therapeutics. Molecules 2023, 28, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beránek, M.; Fiala, Z.; Kremláček, J.; Andrýs, C.; Krejsek, J.; Hamáková, K.; Palička, V.; Borská, L. Serum levels of aryl hydrocarbon receptor, cytochromes P450 1A1 and 1B1 in patients with exacerbated psoriasis vulgaris. Folia Biol. 2018, 64, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawe, H.R.; Di Meglio, P. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR): Peacekeeper of the skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.R.; Park, M.J.; Lee, M.K.; Sung, S.H.; Park, E.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, T.H.; Markelonis, G.J.; Kim, Y.C. Flavonoids of Inula britannica protect cultured cortical cells from necrotic cell death induced by glutamate. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.-H.; Zhu, Q.-M.; Huo, X.-K.; Sun, C.-P.; Ma, X.-C.; Xiao, H.-T. Total flavonoids of Inula japonica alleviated the inflammatory response and oxidative stress in LPS-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting the sEH activity: Insights from lipid metabolomics. Phytomedicine 2022, 107, 154380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Weng, Z.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Mei, X.; Ren, F.; Li, L. Isoalantolactone inhibits UM-SCC-10A cell growth via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wen, Q.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, W.; Li, Q.; Song, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ge, J. Alantolactone induces concurrent apoptosis and GSDME-dependent pyroptosis of anaplastic thyroid cancer through ROS mitochondria-dependent caspase pathway. Phytomedicine 2023, 108, 154528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Genes | Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| Human cPLA2 | Forward Reverse | 5′-GTGATGTGCCTGTGGTAG-3′ 5′-GGTGAGAATACAAGGTTGAC-3′ |
| Human KRT16 | Forward Reverse | 5′-ATGCACAGTTCACTTTGCAGA-3′ 5′-CGCAAGAACAGCTCATTCTCG-3′ |
| Human Filaggrin | Forward Reverse | 5′-GCTGAAGGAACTTCTGGAAAGG-3′ 5′-GTTGTGGTCTATATCCAAGTGATC-3′ |
| Human Loricrin | Forward Reverse | 5′-GTGGGAGCGTCAAGTACTCC-3′ 5′-AGAGTAGCCGCAGACAGAGC-3′ |
| Human Involucrin | Forward Reverse | 5′-CAACTGGAGCTCCCAGAGCAGC-3′ 5′-AACACAGGCTGCTCCAGCTGC-3′ |
| Peak | Identification | tR (min) | Chemical Formula | Experimental m/z | MS/MS Fragment Ions (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quercetin 3-O-glucuronide | 11.68 | C21H18O13 | 477.0660 | 301 |
| 2 | Isoquercetin | 11.88 | C21H20O12 | 463.0870 | 301 |
| 3 | Luteolin 3-O-glucuronide | 12.06 | C21H18O12 | 461.0714 | 85, 285 |
| 4 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside | 13.40 | C22H22O12 | 477.1024 | 243, 314 |
| 5 | Viscidulin III | 15.56 | C17H14O8 | 345.0605 | 164, 287, 315, 345 |
| 6 | Luteolin | 16.50 | C15H10O6 | 285.0395 | 133, 151 |
| 7 | Quercetin | 16.57 | C15H9O7 | 301.0344 | 107, 121, 139, 151, 178 |
| 8 | 4,5,7-Trihydroxy-3,6-dimethoxyflavone | 17.88 | C17H14O7 | 329.0656 | 164, 271, 299 |
| NO. | Name | OB (%) | DL |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chryseriol | 35.85 | 0.27 |
| 2 | Pratensein | 39.06 | 0.28 |
| 3 | Isorhamnetin | 49.6 | 0.31 |
| 4 | Beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| 5 | Amyrin Palmitate | 32.68 | 0.3 |
| 6 | Isoramanone | 39.97 | 0.51 |
| 7 | Tamarixetin | 32.86 | 0.31 |
| 8 | Inulicin | 30.12 | 0.22 |
| 9 | 3-[(3aS,4R,5R,8aR)-4-hydroxy-5,7-dimethyl-3-methylene-2-oxo-4,5,8,8a-tetrahydro-3aH-cyclohepta[b]furan-6-yl]propyl acetate | 73.35 | 0.22 |
| 10 | [(3aR,4R,7aR)-5-[(1S)-4-acetoxy-1-methyl-butyl]-6-methyl-3-methylene-2-oxo-3a,4,7,7a-tetrahydrobenzofuran-4-yl] acetate | 39.03 | 0.31 |
| 11 | Azaleatin | 54.28 | 0.3 |
| 12 | Britanin | 33.73 | 0.41 |
| 13 | Epifriedelanol acetate | 31.18 | 0.74 |
| 14 | Melilotoside | 36.85 | 0.28 |
| 15 | Patuletin | 53.11 | 0.34 |
| 16 | Kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 |
| 17 | [(3S,4aR,6aR,6aR,6bR,8aR,12S,12aR,14aR,14bR)-4,4,6a,6b,8a,12,14b-heptamethyl-11-methylene-1,2,3,4a,5,6,6a,7,8,9,10,12,12a,13,14,14a-hexadecahydropicen-3-yl] Acetate | 43.08 | 0.74 |
| 18 | Luteolin | 36.16 | 0.25 |
| 19 | Quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.J.; Son, S.-R.; Lee, S.; Jang, D.S. Protective Effects of Inula japonica Leaf Extract Against PM10-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Keratinocytes. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080639
Choi YJ, Son S-R, Lee S, Jang DS. Protective Effects of Inula japonica Leaf Extract Against PM10-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Keratinocytes. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(8):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080639
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Yea Jung, So-Ri Son, Sullim Lee, and Dae Sik Jang. 2025. "Protective Effects of Inula japonica Leaf Extract Against PM10-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Keratinocytes" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 8: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080639
APA StyleChoi, Y. J., Son, S.-R., Lee, S., & Jang, D. S. (2025). Protective Effects of Inula japonica Leaf Extract Against PM10-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Keratinocytes. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(8), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080639







