Combined Bioinformatic and Experimental Approaches to Analyze miR-182-3p and miR-24-3p Expression and Their Target Genes in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Iron Deficiency Anemia During Pregnancy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Mining
2.2. Expression Profiling of Selected miRNA
2.2.1. Sample Collection
2.2.2. RNA Extraction
2.2.3. RT-PCR
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Prediction of miRNA Targets
2.5. Identification of Gene Expression Profile and Hub Genes
3. Results
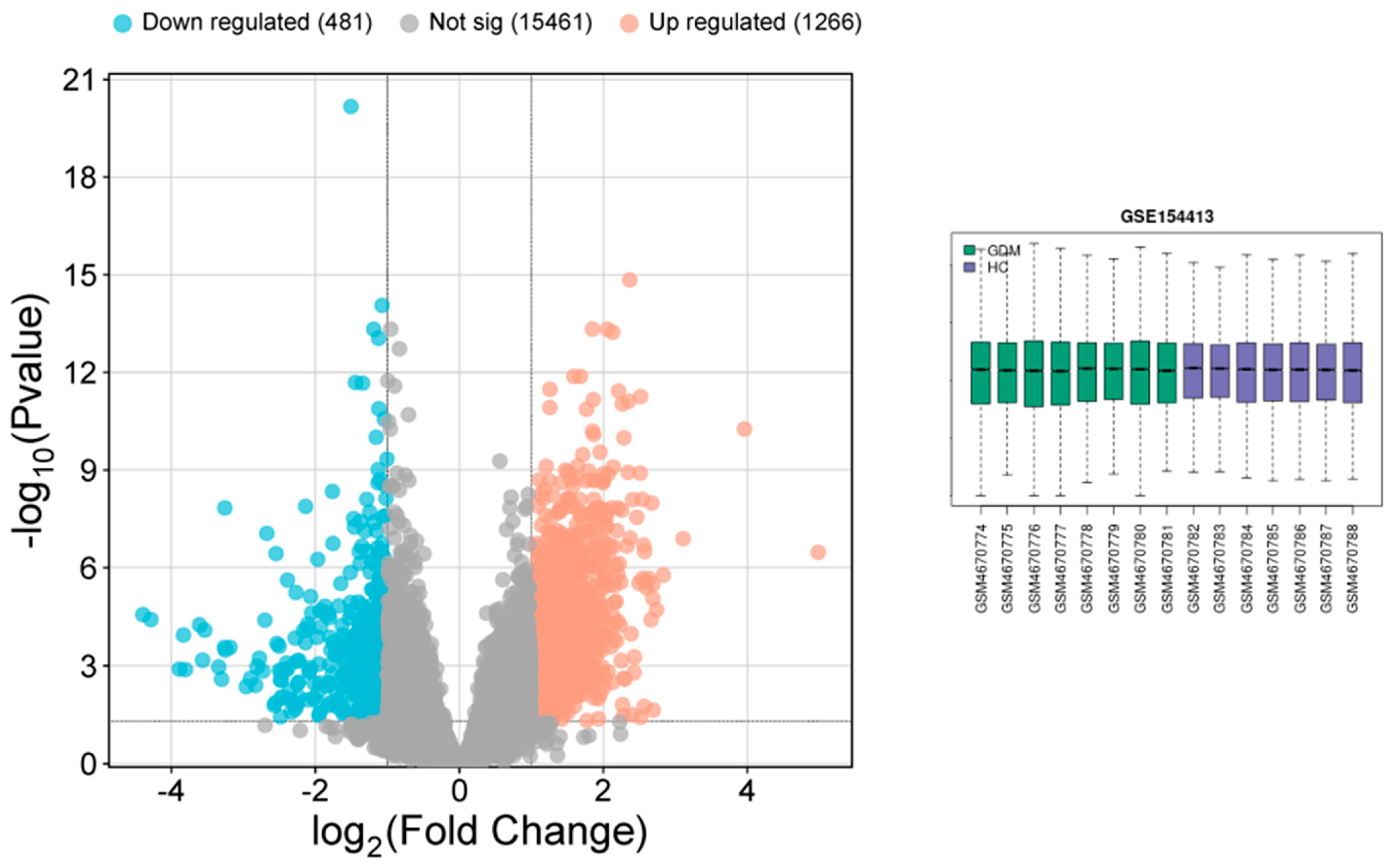
3.1. Data Analysis
3.2. Sample Collection
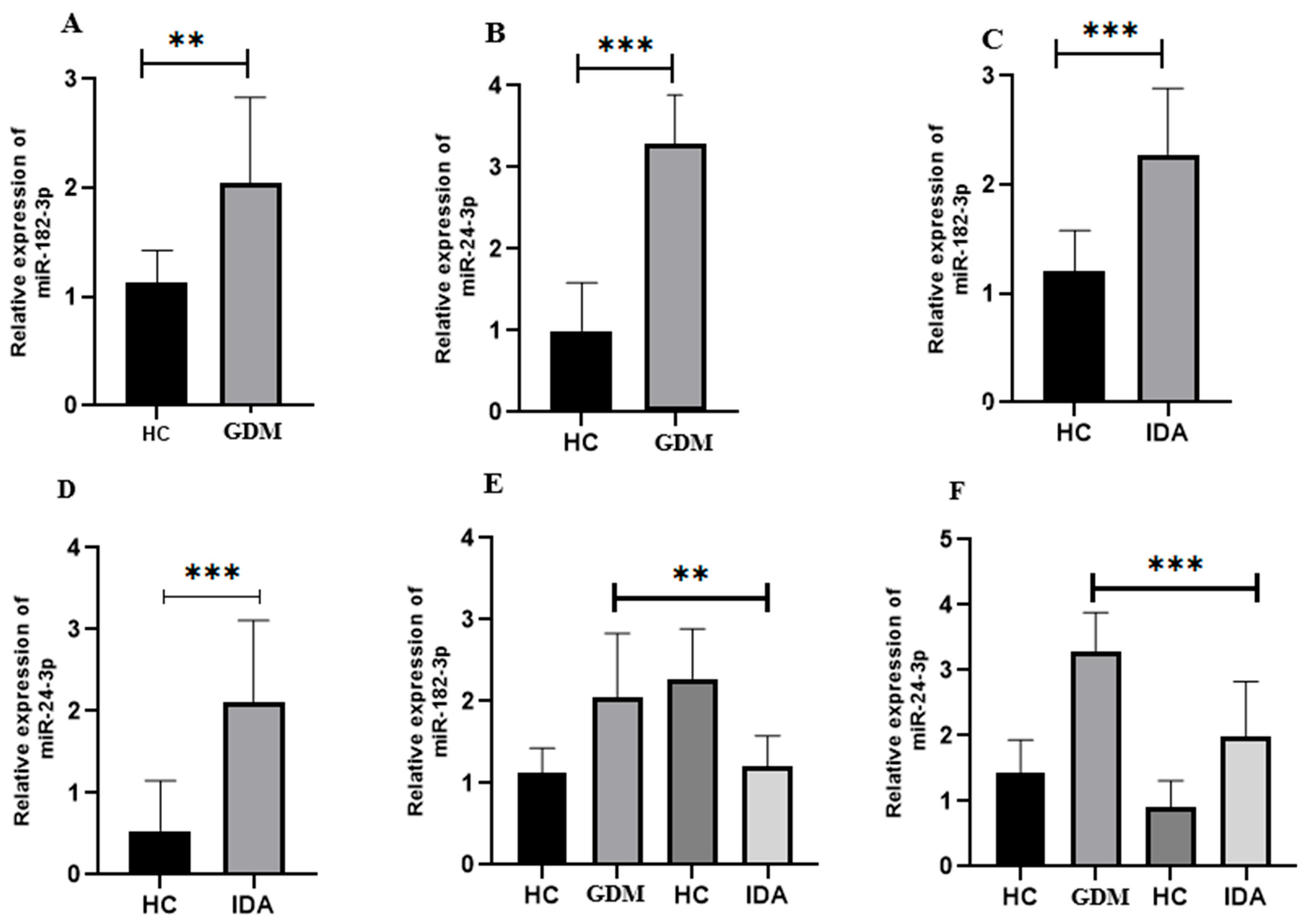
3.3. Expression Analysis of Selected miRNA in GDM
3.4. Expression Analysis of Selected miRNA in Pregnant Women with IDA
3.5. Comparison of the Relative Expression of Selected miRNA in Pregnant Women with GDM and IDA
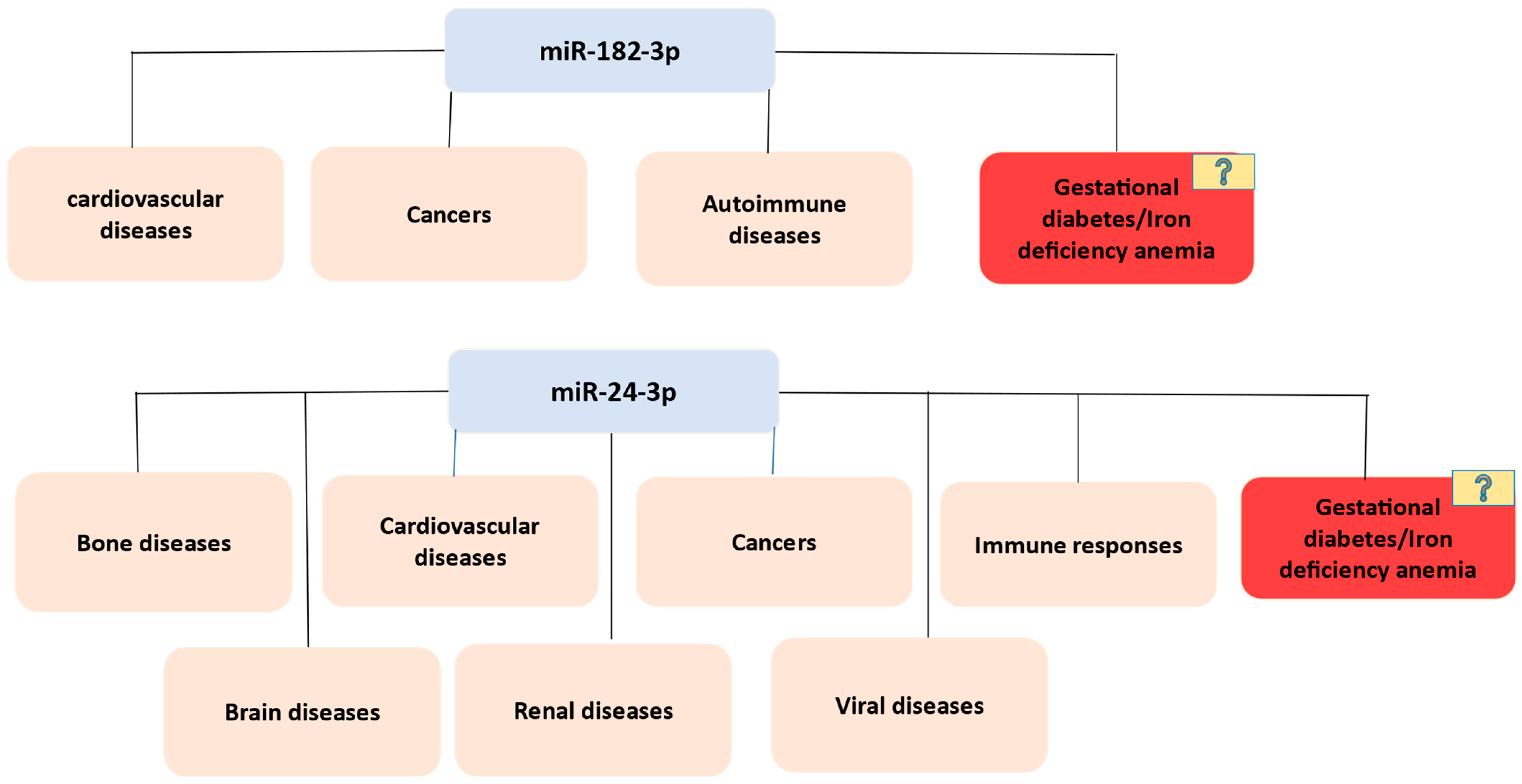
3.6. Exploring miRNA Gene Targets
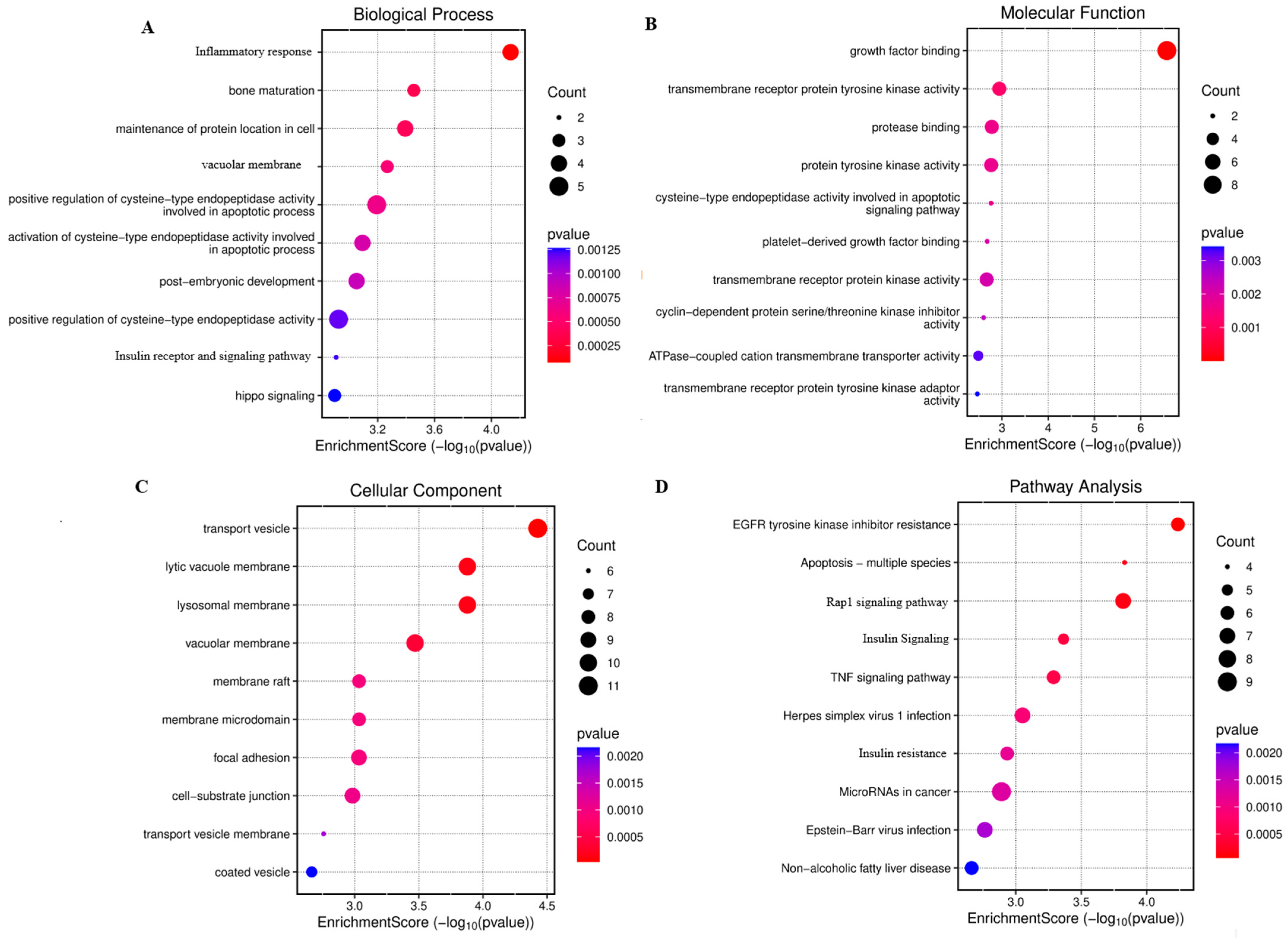
3.7. Analysis of Gene Expression Profile Data
3.8. PPI Network and Hub Genes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GDM | gestational diabetes mellitus |
| IDA | iron deficiency anemia |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| TP53 | tumor protein p53 |
| IRS1 | Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 |
| PIK3CA | phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha |
| CASP3 | Caspase-3 |
| PDGFRB | platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta |
| MAPK7 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 7 |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
References
- Darbandi, M.; Rezaeian, S.; Dianatinasab, M.; Yaghoobi, H.; Soltani, M.; Etemad, K.; Valadbeigi, T.; Taherpour, N.; Hajipour, M.; Saeidi, R. Prevalence of gestational diabetes and its association with stillbirth, preterm birth, macrosomia, abortion and cesarean delivery: A national prevalence study of 11 provinces in Iran. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2022, 62, E885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, H.D.; Catalano, P.; Zhang, C.; Desoye, G.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Damm, P. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.D.; Biggs, B.A.; Tran, T.; Simpson, J.A.; Hanieh, S.; Dwyer, T.; Fisher, J. Impact on infants’ cognitive development of antenatal exposure to iron deficiency disorder and common mental disorders. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiongco, R.E.; Arceo, E.; Clemente, B.; Pineda-Cortel, M.R. Association of maternal iron deficiency anemia with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2019, 299, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, Y.; Wu, Y.; Horskjær, P.D.H.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Ellervik, C. Iron status and gestational diabetes—A meta-analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Cao, J.C.; Aranda, N.; Ribot, B.; Tous, M.; Arija, V. Elevated iron status and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Matern. Child Nutr. 2017, 13, e12400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, K.; Bayraktar, R.; Ferracin, M.; Calin, G.A. Non-coding RNAs in disease: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2024, 25, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Quattrocchi, A.; Agrifoglio, O.; Agodi, A. The role of miRNAs as biomarkers for pregnancy outcomes: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 8067972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masete, M.; Dias, S.; Malaza, N.; Adam, S.; Pheiffer, C. A big role for microRNAs in gestational diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 892587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameti, P.; Tohidast, M.; Amini, M.; Mahdavi, S.Z.B.; Najafi, S.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. The emerging role of MicroRNA-182 in tumorigenesis; a promising therapeutic target. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, R.; Dong, Z.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X. Inhibiting miR-182-3p alleviates gestational diabetes mellitus by improving insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. Balk. Med. J. 2022, 39, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Z.; Zafar, U.; Tauseef, A.; Zaki, S.; Khaliq, S. Micro RNA 182-3-p, 519-d-5p, 378–3p as non-invasive predictors of preeclampsia. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2023, 35, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ru, X.; Wang, S.; Cao, G. miR-24-3p regulation of retinol binding protein 4 in trophoblast biofunction and preeclampsia. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2022, 89, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, Q.; Wu, Z.; Xue, L. miR-92a-3p and miR-182-3p as potential biomarkers for the differential diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus and its correlation with pregnancy outcomes. Ir. J. Med. Sci. (1971–) 2025, 194, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.A.; Lambert, C.; Fernandez-Sanjurjo, M.; Morales-Sanchez, P.; Pujante, P.; Pinto-Hernández, P.; Iglesias-Gutiérrez, E.; Torre, E.M.; Delgado, E. miR-24-3p and body mass index as type 2 diabetes risk factors in Spanish women 15 years after gestational diabetes mellitus diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-L.; Yang, L. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, F.; Nikravesh, A.; Arezumand, R.; Aghaee-Bakhtiari, S.H. Web-based tools for miRNA studies analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 127, 104060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweep, H.; Gretz, N.; Sticht, C. miRWalk database for miRNA–target interactions. RNA Mapp. Methods Protoc. 2014, 1182, 289–305. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C.D.; Cui, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, J.; Zuo, H.; et al. miRTarBase update 2022: An informative resource for experimentally validated miRNA–target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safran, M.; Dalah, I.; Alexander, J.; Rosen, N.; Stein, T.I.; Shmoish, M.; Nativ, N.; Bahir, I.; Doniger, T.; Krug, H.; et al. GeneCards Version 3: The human gene integrator. Database 2010, 2010, baq020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, N.; Twik, M.; Plaschkes, I.; Nudel, R.; Stein, T.I.; Levitt, J.; Gershoni, M.; Morrey, C.P.; Safran, M.; Lancet, D. MalaCards: An amalgamated human disease compendium with diverse clinical and genetic annotation and structured search. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D877–D887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberger, J.S.; Bocchini, C.A.; Schiettecatte, F.; Scott, A.F.; Hamosh, A. OMIM. org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®), an online catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D789–D798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, S.; Kumano, K.; Darden, C.M.; Rahman, I.; Lawrence, M.C.; Naziruddin, B. MicroRNA signatures as future biomarkers for diagnosis of diabetes states. Cells 2019, 8, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, N.U.; Lazrak, M.; Bellitir, S.; El Mir, N.; El Hamdouchi, A.; Barkat, A.; Zeder, C.; Moretti, D.; Aguenaou, H.; Zimmermann, M.B. The opposing effects of acute inflammation and iron deficiency anemia on serum hepcidin and iron absorption in young women. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Hao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, X.; Chen, J. Mild maternal iron deficiency anemia induces DPOAE suppression and cochlear hair cell apoptosis by caspase activation in young guinea pigs. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, D.; Zhuang, C.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, L. The possible involvement of circRNA DMNT1/p53/JAK/STAT in gestational diabetes mellitus and preeclampsia. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itahana, Y.; Itahana, K. Emerging roles of p53 family members in glucose metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, X. p53 tumor suppressor and iron homeostasis. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Fang, C.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, H. The association between maternal/fetal insulin receptor substrate 1 gene polymorphism rs1801278 and gestational diabetes mellitus in a Chinese population. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2021, 86, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Tamemoto, H.; Tobe, K.; Yamamoto-Honda, R.; Kaburagi, Y.; Akanuma, Y.; Yazaki, Y.; Aizawa, S.; Nagai, R.; et al. Restored insulin-sensitivity in IRS-1—Deficient mice treated by adenovirus-mediated gene therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieska, K.; Buczyńska, A.; Krętowski, A.J.; Popławska-Kita, A. Iron homeostasis and insulin sensitivity: Unraveling the complex interactions. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2024, 25, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.; Kang, Z.; Li, L.; Yan, X.; Gao, T.; Pizzo, S.V. PIK3CA regulates development of diabetes retinopathy through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0295813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Bai, C.; Wang, T.; Ruan, F.; Hu, C. Upregulation of MMPs in placentas of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus: Involvement of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, T.R.; Ross, M.G.; Wedekind, L.; Desai, M.; Kjos, S.; Belkacemi, L. Gestational diabetes mellitus alters apoptotic and inflammatory gene expression of trophobasts from human term placenta. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2014, 28, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Leng, P. Research progress on the role of PDGF/PDGFR in type 2 diabetes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | G1 (Control) | G2 (GDM) | G3 (IDA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | N = 17 | N = 30 | N = 30 |
| Mean | 25.35 | 29.5 | 24.57 |
| SD | 4.513 | 3.014 | 3.234 |
| SEM | 1.095 | 0.5503 | 0.509 |
| Range | 16 | 11 | 11 |
| Gestational week | |||
| Mean | 25.67 | 26.13 | 26.6 |
| SD | 1.455 | 1.432 | 1.276 |
| SEM | 0.343 | 0.2614 | 0.2329 |
| Range | 4 | 4 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzahrani, B.; Rauff, B.; Ikram, A.; Azam, M. Combined Bioinformatic and Experimental Approaches to Analyze miR-182-3p and miR-24-3p Expression and Their Target Genes in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Iron Deficiency Anemia During Pregnancy. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080610
Alzahrani B, Rauff B, Ikram A, Azam M. Combined Bioinformatic and Experimental Approaches to Analyze miR-182-3p and miR-24-3p Expression and Their Target Genes in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Iron Deficiency Anemia During Pregnancy. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(8):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080610
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzahrani, Badr, Bisma Rauff, Aqsa Ikram, and Mariya Azam. 2025. "Combined Bioinformatic and Experimental Approaches to Analyze miR-182-3p and miR-24-3p Expression and Their Target Genes in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Iron Deficiency Anemia During Pregnancy" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 8: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080610
APA StyleAlzahrani, B., Rauff, B., Ikram, A., & Azam, M. (2025). Combined Bioinformatic and Experimental Approaches to Analyze miR-182-3p and miR-24-3p Expression and Their Target Genes in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Iron Deficiency Anemia During Pregnancy. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(8), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080610



_Kim.png)




