Functional Characterization of Two Glutamate Dehydrogenase Genes in Bacillus altitudinis AS19 and Optimization of Soluble Recombinant Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Plasmids
2.2. Enzymes and Reagents
2.3. Medium
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis of Glutamate Dehydrogenase Genes and Protein Characterization
2.5. Primer Design and Synthesis
2.6. Target Gene Amplification
2.7. Recombinant Plasmid Construction and Verification
2.8. Soluble Expression Optimization and Purification of Recombinant GdhA and GudB Proteins
2.9. Western Blot Analysis and Mass Spectrometry Identification
2.10. Detection of Enzyme Activity of Recombinant Protein
3. Results
3.1. Bioinformatics Analysis of GdhA and GudB
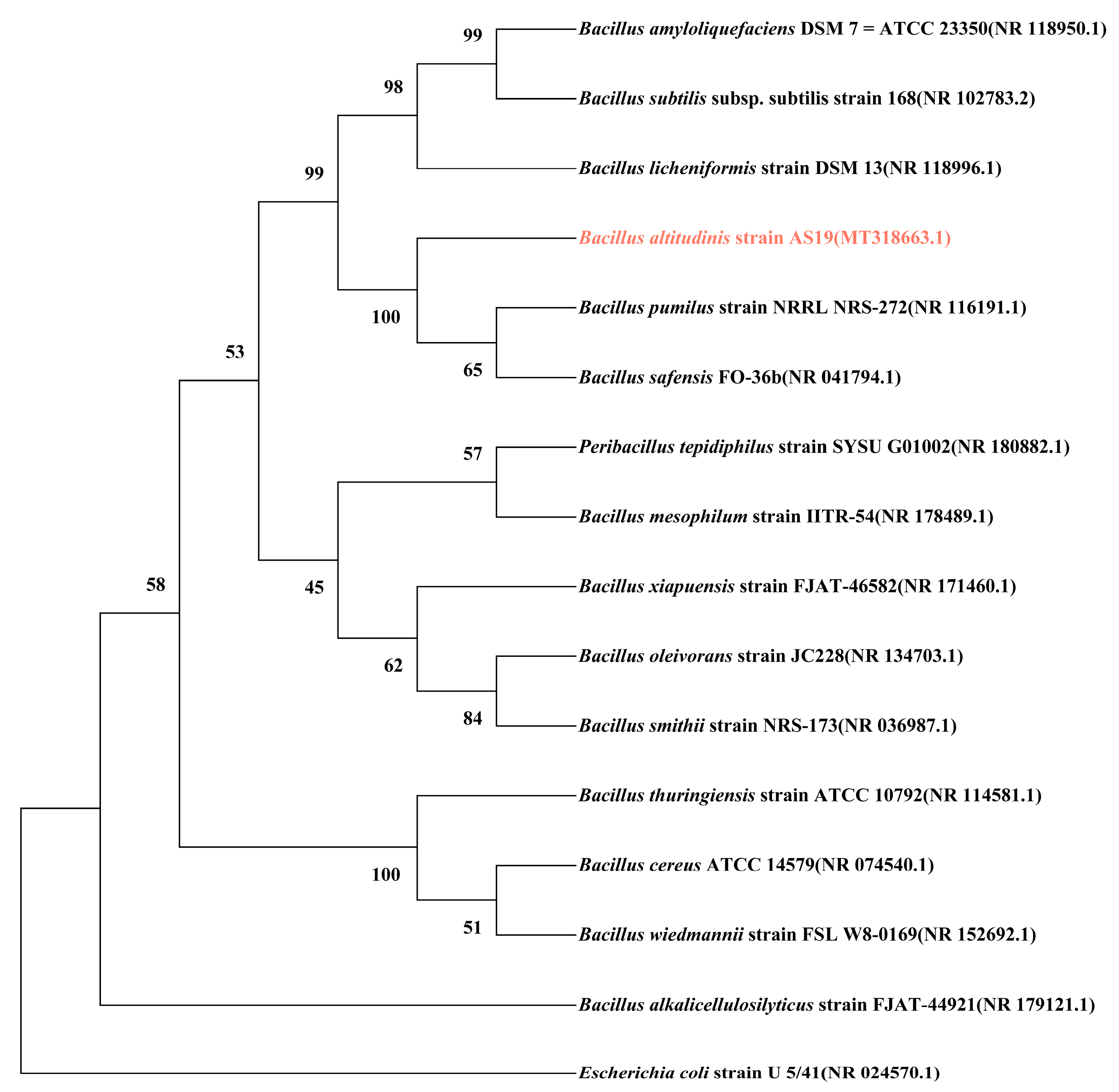
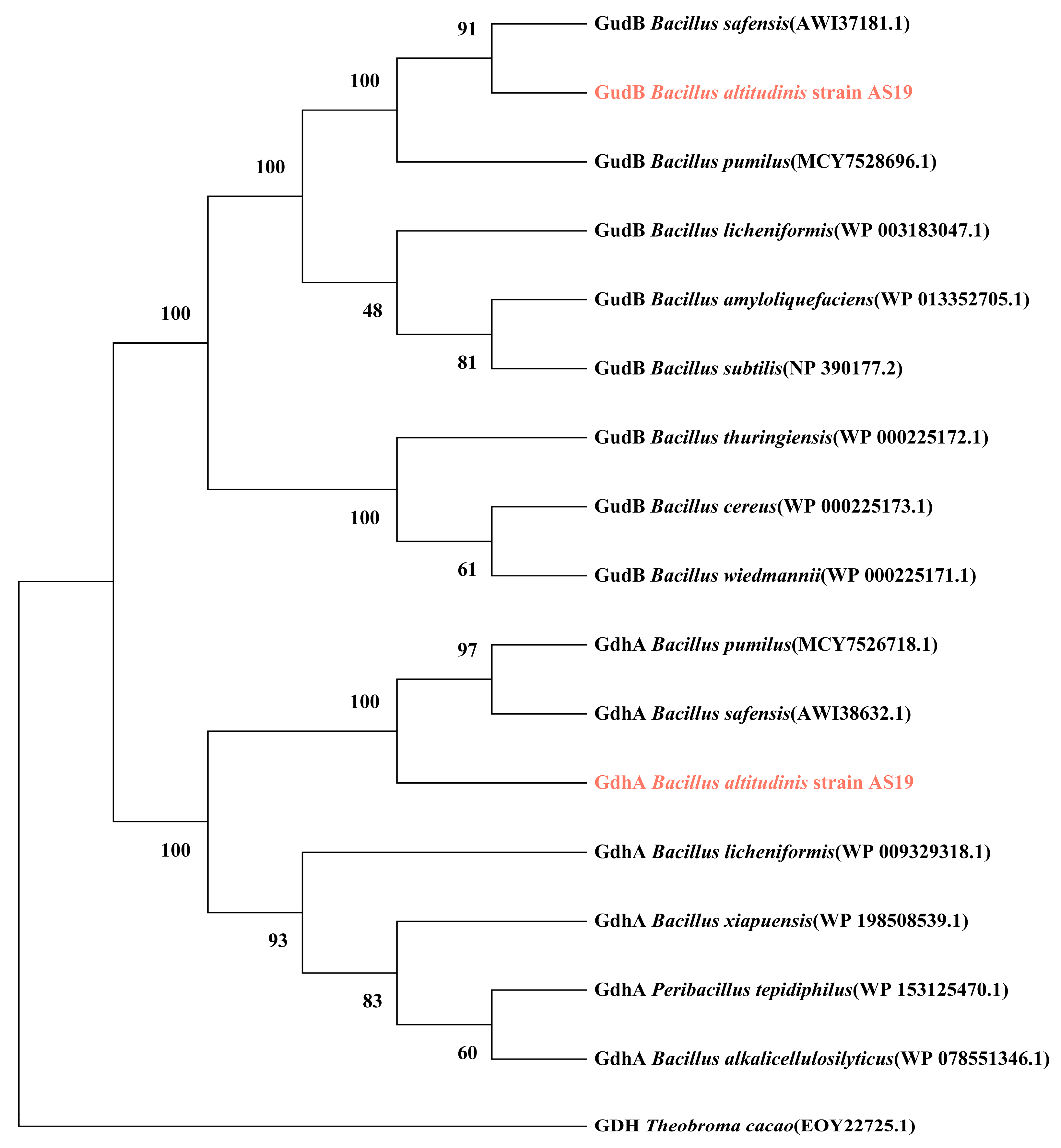
3.1.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of Glutamate Dehydrogenase GdhA and GudB
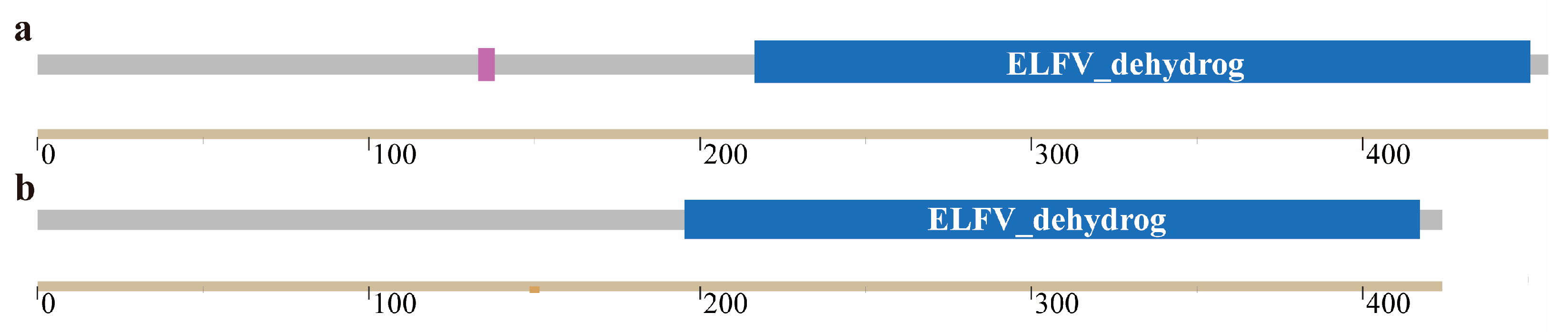
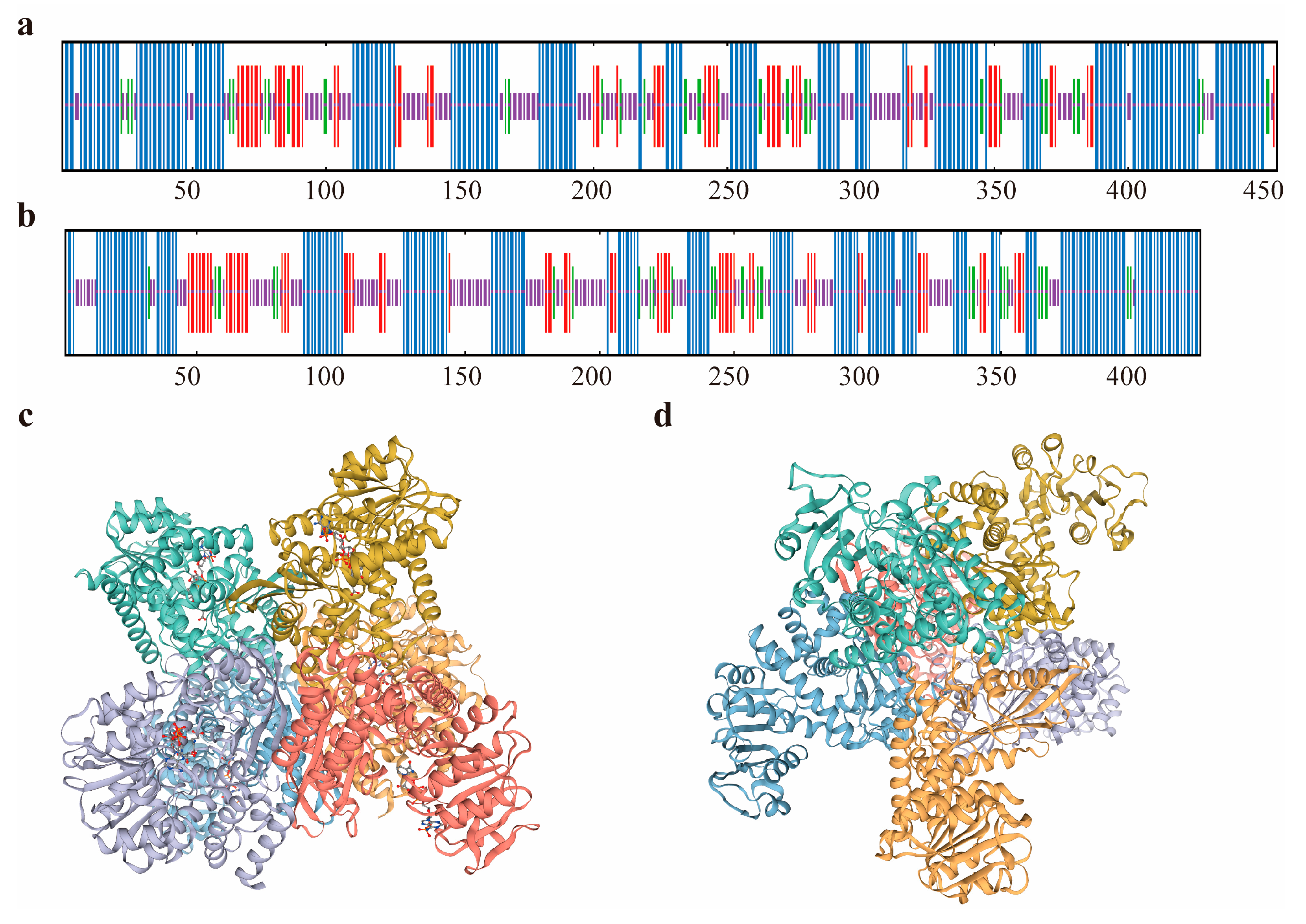
3.1.2. Basic Physicochemical Properties and Structural Analysis of Two Glutamate Dehydrogenases
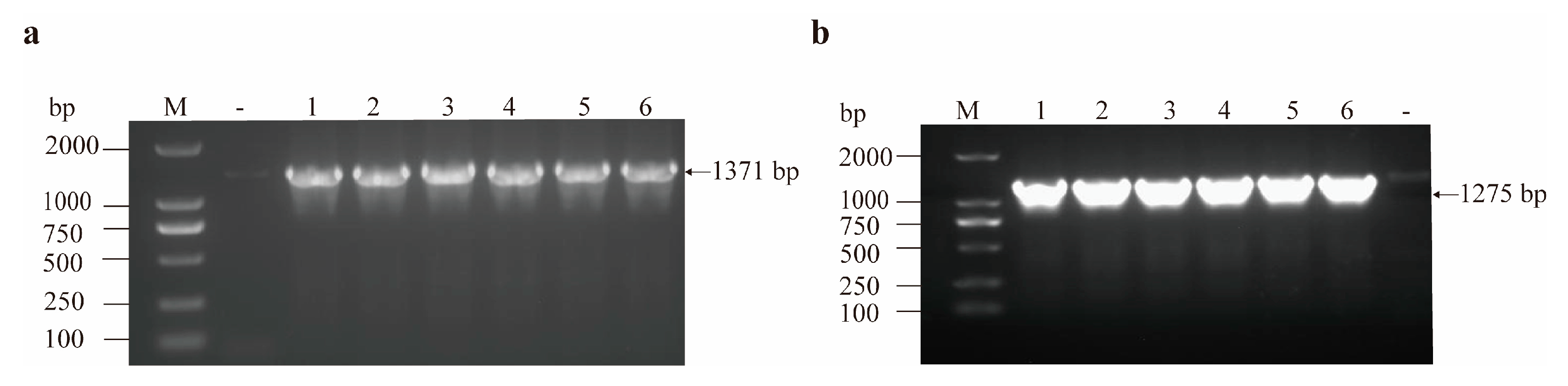
3.2. Results of gdhA and gudB Gene Amplification
3.3. Screening and Identification of Recombinant Plasmids
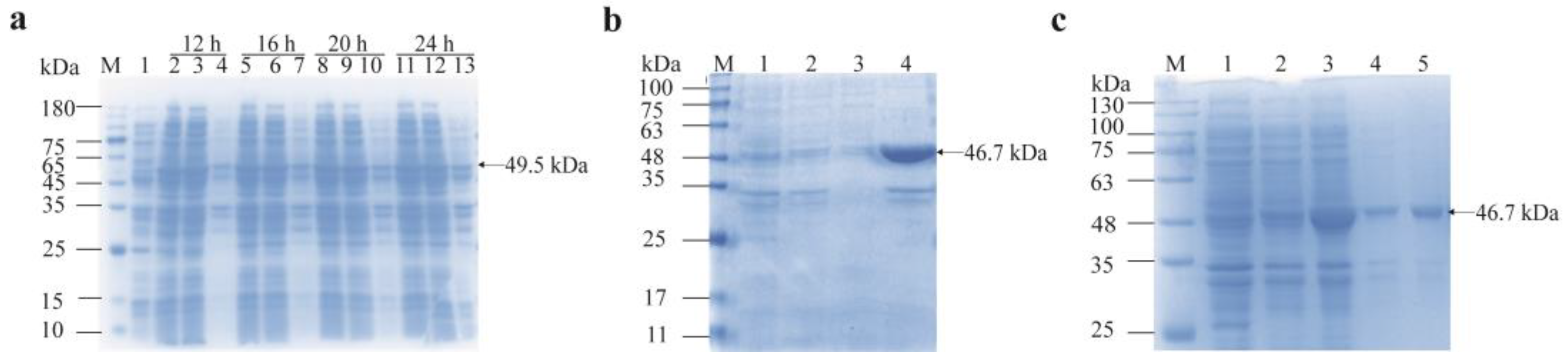
3.4. Soluble Expression and Purification of Recombinant Proteins
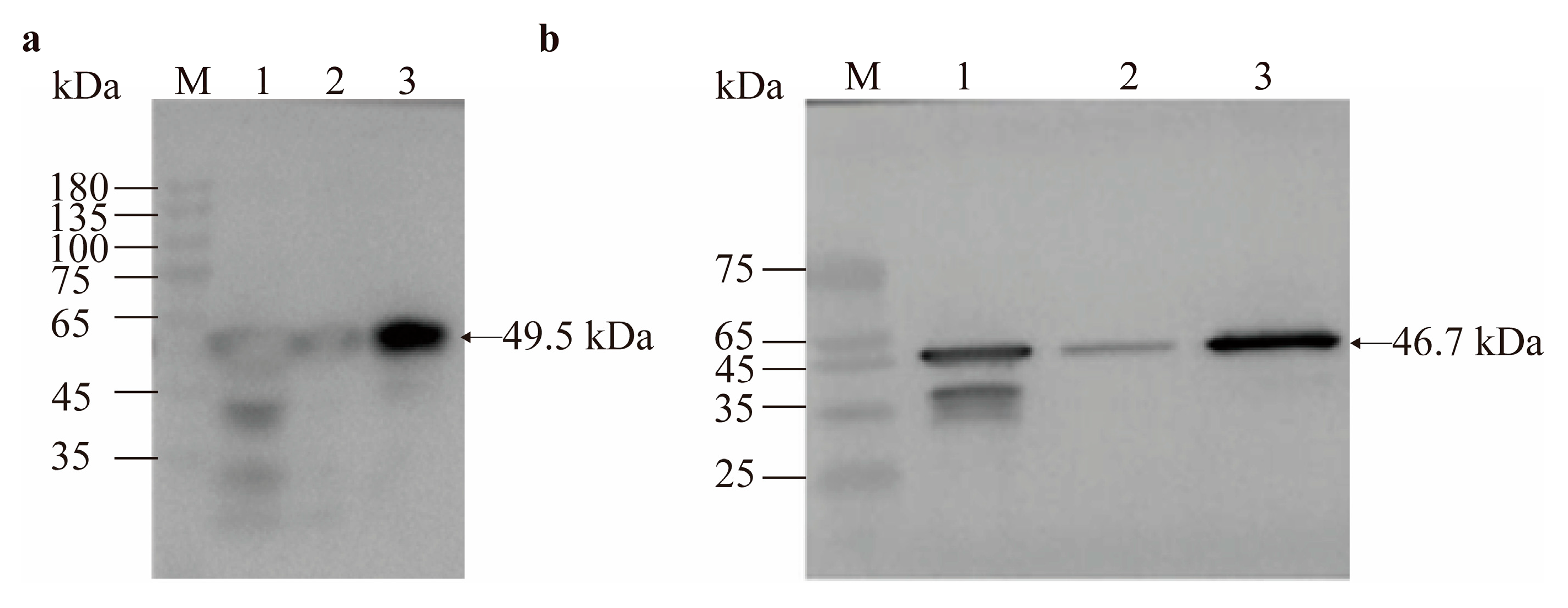
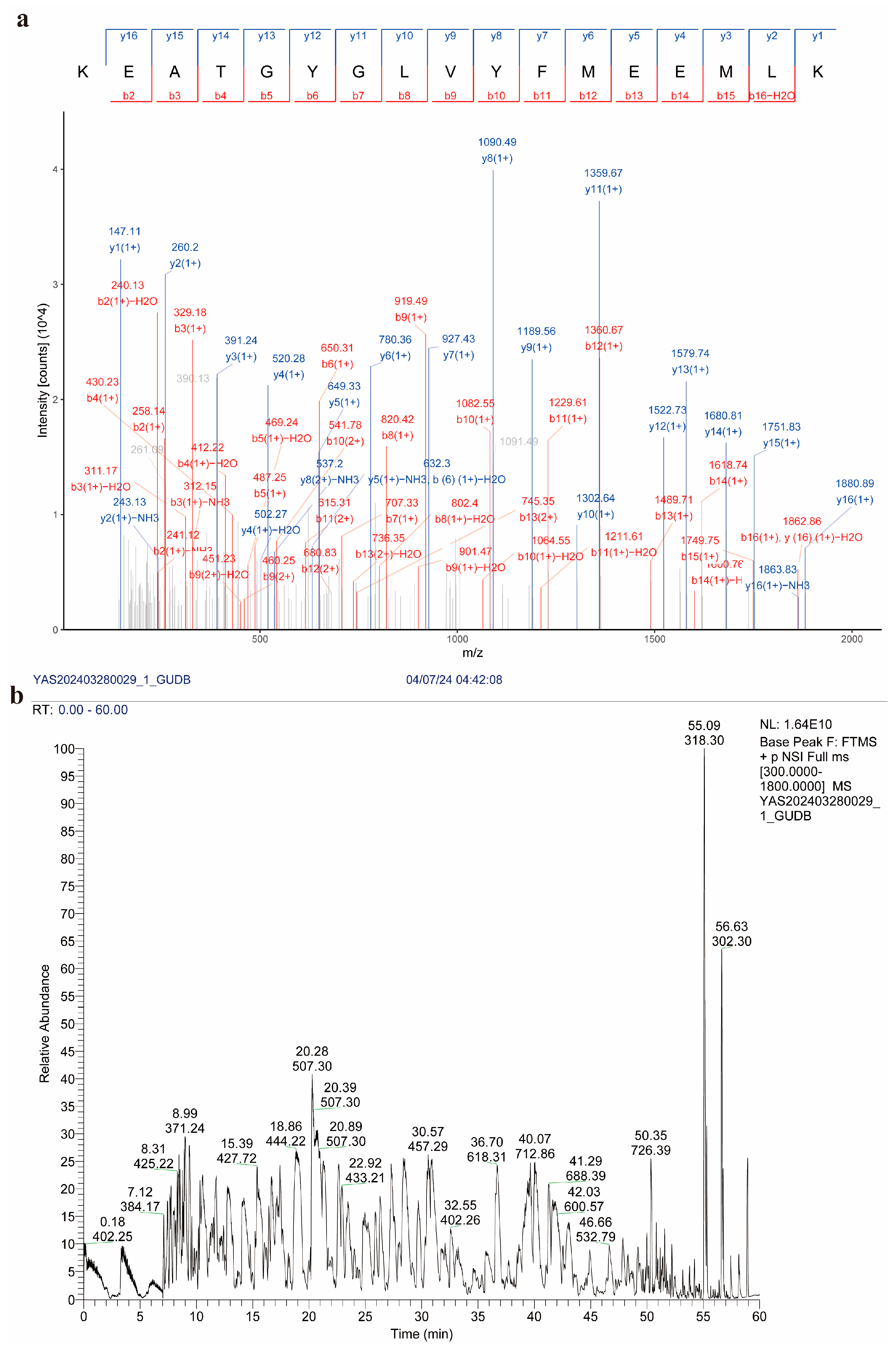
3.5. Western Blot Verification and Mass Spectrometry Identification of Recombinant Proteins
3.6. Enzyme Activity Detection of Recombinant Protein
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GDH | Glutamate dehydrogenase |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic acid |
| GS | Glutamine synthetase |
| GOGAT | Glutamate synthase |
| TBST | Tris-buffered saline with tween-20 |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
Appendix A
| Strains | Glutamate Dehydrogenase Composition | Coding Genes | NCBI Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus pumilus | GDH1 | gdhA | MCY7526718.1 |
| GDH2 | gudB | MCY7528696.1 | |
| Bacillus safensis | GDH1 | gdhA | AWI38632.1 |
| GDH2 | gudB | AWI37181.1 | |
| Bacillus licheniformis | GDH1 | gdhA | WP_009329318.1 |
| GDH2 | gudB | WP_003183047.1 | |
| Bacillus subtilis | GDH1 | rocG | NP_391659.2 |
| GDH2 | gudB | NP_390177.2 | |
| Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | GDH1 | rocG | WP_013353994.1 |
| GDH2 | gudB | WP_013352705.1 | |
| Peribacillus tepidiphilus | GDH1 | gdhA | WP_153125470.1 |
| GDH2 | - | WP_153126561.1 | |
| GDH3 | - | WP_153122666.1 | |
| Bacillus mesophilum | GDH | - | WP_151573106.1 |
| Bacillus xiapuensis | GDH1 | gdhA | WP_198508539.1 |
| GDH2 | - | WP_100332101.1 | |
| Bacillus oleivorans | GDH | - | WP_097157515.1 |
| Bacillus smithii | GDH | - | WP_048623896.1 |
| Bacillus cereus | GDH | gudB | WP_000225173.1 |
| Bacillus thuringiensis | GDH | gudB | WP_000225172.1 |
| Bacillus wiedmannii | GDH | gudB | WP_000225171.1 |
| Bacillus alkalicellulosilyticus | GDH | gdhA | WP_078551346.1 |
References
- Ye, H.-Y.; Hou, W.; Ruan, B.-F. The basic characteristics of glutamate dehydrogenase and its inhibitors. Drug Inf. 2019, 8, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Gunka, K.; Commichau, F.M. Control of glutamate homeostasis in Bacillus subtilis: A complex interplay between ammonium assimilation, glutamate biosynthesis and degradation. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 85, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, M.A.; Oliveira, T.F.; Engel, P.C.; Khan, A.R. Structure of NADP+-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli--reflections on the basis of coenzyme specificity in the family of glutamate dehydrogenases. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4681–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, M.J.; Wootton, J.C. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli gdhA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983, 11, 5257–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heeswijk, W.C.; Westerhoff, H.V.; Boogerd, F.C. Nitrogen assimilation in Escherichia coli: Putting molecular data into a systems perspective. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 628–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitzer, L. Nitrogen assimilation and global regulation in Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 57, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, V.; Lee, D.J.; Elad, N.; Vimer, S.; Sharon, M.; Fraser, J.S.; Tawfik, D.S. A counter-enzyme complex regulates glutamate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belitsky, B.R.; Sonenshein, A.L. Role and regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamate dehydrogenase genes. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 6298–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stannek, L.; Thiele, M.J.; Ischebeck, T.; Gunka, K.; Hammer, E.; Völker, U.; Commichau, F.M. Evidence for synergistic control of glutamate biosynthesis by glutamate dehydrogenases and glutamate in Bacillus subtilis. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3379–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kingston, A.W.; Helmann, J.D. Glutamate dehydrogenase affects resistance to cell wall antibiotics in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, F.L.; Sun, J.K.; Ren, Y.; He, B.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Li, W. Transcriptomic and enzymatic analysis reveals the roles of glutamate dehydrogenase in Corynebacterium glutamicum. AMB Express 2022, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda-Garcia, L.; Romero Romero, M.L.; Longo, L.M.; Kolodkin-Gal, I.; Tawfik, D.S. Bacilli glutamate dehydrogenases diverged via coevolution of transcription and enzyme regulation. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaustat, D.; Rollet, R. Glutamato deshidrogenasa. Su valor diagnóstico en la diarrea por Clostridioides difficile [Glutamate dehydrogenase. Its diagnostic value in Clostridioides difficile diarrhea]. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2018, 50, 264–268. [Google Scholar]
- Chittick, L.; Okwumabua, O. Loss of expression of the glutamate dehydrogenase (gdh) of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 compromises growth and pathogenicity. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 188, 106565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzi, C.; Bove, C.G.; Marsano, R.M.; Neviani, E. Transcriptional analysis of the gdhA gene in Streptococcus thermophilus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Lao, W.-J.; Zhou, Y.-C.; Sun, Y.-W.; Wang, Q.-J. Glutamate dehydrogenase enables Salmonella to survive under oxidative stress and escape from clearance in macrophages. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazioglu, O.; Kareem, B.O.; Afzal, M.; Shafeeq, S.; Kuipers, O.P.; Ulijasz, A.T.; Andrew, P.W.; Yesilkaya, H. Glutamate dehydrogenase (GdhA) of streptococcus pneumoniae is required for high temperature adaptation. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e0040021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Zhang, G.-Y.; Huang, Y.; Guo, M.; Song, J.-H.; Zhang, T.-T.; Long, Y.-H.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.-M. A potential biofertilizer-siderophilic bacteria isolated from the rhizosphere of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 870413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, F.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combet, C.; Blanchet, C.; Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. NPS@: Network protein sequence analysis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.; Milpetz, F.; Bork, P.; Ponting, C.P. SMART, A simple modular architecture research tool: Identification of signaling domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5857–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwede, T.; Kopp, J.; Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL: An automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3381–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.-M.; Pan, X.-Z.; Wang, C.-J.; Guo, H.-B.; Li, X.-F.; Tang, J.-Q. Cloning, expression and identification of gene encoding the glutamate dehydrogenase of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Chin. J. Zoonoses 2006, 22, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Yu, G.-Q.; Shen, S.-J.; Zhu, J.-B. Cloning and Characterization of the Glutamate Dehydrogenase Gene from Bacillus licheniformis. Sci. China Ser. C Life Sci. 2000, 43, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commichau, F.M.; Gunka, K.; Landmann, J.J.; Stülke, J. Glutamate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis: Gene expression and enzyme activities evolved to avoid futile cycles and to allow rapid responses to perturbations of the system. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 3557–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benachenhou-Lahfa, N.; Forterre, P.; Labedan, B. Evolution of glutamate dehydrogenase genes: Evidence for two paralogous protein families and unusual branching patterns of the archaebacteria in the universal tree of life. J. Mol. Evol. 1993, 36, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.-Y.; Du, L.; Wang, J.-Q.; Chen, Z.-J.; Huang, J.-B.; Chen, Q.-X.; Zou, P.-X.; Han, X.; Zhang, C. Soluble expression strategies for production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. China Biotechnol. 2023, 43, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Villaverde, A.; Carrió, M.M. Protein aggregation in recombinant bacteria: Biological role of inclusion bodies. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, R.; Sabir, J.S.; Bora, R.S.; Saini, K.S. Optimization of culture parameters and novel strategies to improve protein solubility. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1258, 45–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer-Miralles, N.; Saccardo, P.; Corchero, J.L.; Xu, Z.; García-Fruitós, E. General introduction: Recombinant protein production and purification of insoluble proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1258, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo-Pineda, S.; Bando-Campos, C.G.; Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Trujillo-Roldán, M.A. Recombinant production of ESAT-6 antigen in thermoinducible Escherichia coli: The role of culture scale and temperature on metabolic response, expression of chaperones, and architecture of inclusion bodies. Cell Stress Chaperones 2019, 24, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.-Q.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J. Enhanced production of recombinant Escherichia coli glutamate decarboxylase through optimization of induction strategy and addition of pyridoxine. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamad, P.; Boonchird, C.; Panbangred, W. High level accumulation of soluble diphtheria toxin mutant (CRM197) with co-expression of chaperones in recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 100, 6319–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Hou, J. Molecular chaperone GroEL-GroES enhances the soluble expression of biologically active ovine growth hormone in the prokaryotic system. Protein Expr. Purif. 2022, 195–196, 106097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.-M.; Xie, Q.; Huang, R.-H.; Tao, X.-Y.; Wan, C.-X.; Wei, H. Expression of the glutamate dehydrogenase gene from Lactobacillus plantarumin Escherichia coli. J. Nanchang Univ. 2016, 40, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-L.; Pan, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.-H. Gene cloning, expression and enzyme activity assay of a glutamate dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis natto. J. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. 2010, 28, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, P.C. Glutamate dehydrogenases: The why and how of coenzyme specificity. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.-L.; Meng, Y.-H.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.-Y.; Dong, G.R.; Chen, W.F. Cloning, expression and bioinformatics analysis of glutamate dehydrogenase cDNA from Bacillus subtilis natto. J. Shaanxi Norm. Univ. 2017, 45, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Loughran, S.T.; Bree, R.T.; Walls, D. Purification of polyhistidine-tagged proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1485, 275–303. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, V. Affinity tags for protein purification. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2020, 21, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahns, T. Occurrence of cold-labile NAD-specific glutamate dehydrogenase in Bacillus species. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1992, 75, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primer Name | Primers Sequence(5′-3′) | Restriction Sites |
|---|---|---|
| gdhA-F | CGGGATCCATGTTGACCTTAGATCGAGCAGC | BamH I |
| gdhA-R | CCCAAGCTTTTAAATGACGCCTTGTGCGAT | Hind III |
| gudB-F | CGCGGATCCATTTTAATGGCAGCCG | BamH I |
| gudB-R | CCGGAATTCTTAAATCCAGCCTCTGAATC | EcoR I |
| Strains | Glutamate Dehydrogenase Composition | Coding Genes | Similarity with AS19 GdhA (%) | Similarity with AS19 GudB (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus altitudinis strain AS19 | GDH1 | gdhA | 100 | 30.70 | - |
| GDH2 | gudB | 30.70 | 100 | ||
| Bacillus pumilus | GDH1 | gdhA | 95.83 | 31.12 | - |
| GDH2 | gudB | 32.27 | 99.76 | ||
| Bacillus safensis | GDH1 | gdhA | 95.18 | 31.12 | [12] |
| GDH2 | gudB | 32.04 | 100 | ||
| Bacillus licheniformis | GDH1 | gdhA | 70 | 29.93 | [25] |
| GDH2 | gudB | 32.31 | 91.51 | ||
| Bacillus subtilis | GDH1 | rocG | 30.28 | 74.76 | [26] |
| GDH2 | gudB | 31.36 | 91.80 | ||
| Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | GDH1 | rocG | 31.47 | 74.30 | - |
| GDH2 | gudB | 30.66 | 91.51 | ||
| Peribacillus tepidiphilus | GDH1 | gdhA | 73.26 | 28.95 | - |
| GDH2 | - | 30.58 | 76.65 | ||
| GDH3 | - | 31.74 | 87.76 | ||
| Bacillus mesophilum | GDH | - | 31.44 | 86.82 | - |
| Bacillus xiapuensis | GDH1 | gdhA | 71.30 | 30.07 | - |
| GDH2 | - | 31.49 | 75.36 | ||
| Bacillus oleivorans | GDH | - | 31.89 | 86.32 | - |
| Bacillus smithii | GDH | - | 30.16 | 77.54 | - |
| Bacillus cereus | GDH | gudB | 30.84 | 84.58 | - |
| Bacillus thuringiensis | GDH | gudB | 31.63 | 84.58 | - |
| Bacillus wiedmannii | GDH | gudB | 31.40 | 84.91 | - |
| Bacillus alkalicellulosilyticus | GDH | gdhA | 71.83 | 29.91 | - |
| Physicochemical Properties | GdhA | GudB |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Amino Acids | 456 | 424 |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 49.52 | 46.74 |
| Isoelectric Point | 5.09 | 5.31 |
| Molecular Formula | C2191H3440N596O668S22 | C2075H3293N561O629S18 |
| Instability Coefficient | 35.86 | 26 |
| Fat-Solubility Index | 83.20 | 89.69 |
| Average Hydrophilicity Value | −0.16 | −0.19 |
| Number of Signal Peptides | 0 | 0 |
| Transmembrane Region | 0 | 0 |
| Target Protein | Protein ID | Protein Name | Gene Name | Sequence Coverage (%) | Number of Peptide | Molecular Weight (kDa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GdhA | A0A1K2A8A6 | Glutamate dehydrogenase | gdhA | 72.0 | 40 | 49.6 |
| GudB | A0A5K1NAB7 | Glutamate dehydrogenase | gudB | 82.8 | 31 | 46.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Lv, X.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Long, Y.; Liu, H. Functional Characterization of Two Glutamate Dehydrogenase Genes in Bacillus altitudinis AS19 and Optimization of Soluble Recombinant Expression. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080603
Wang F, Lv X, Guo Z, Wang X, Long Y, Liu H. Functional Characterization of Two Glutamate Dehydrogenase Genes in Bacillus altitudinis AS19 and Optimization of Soluble Recombinant Expression. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(8):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080603
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fangfang, Xiaoying Lv, Zhongyao Guo, Xianyi Wang, Yaohang Long, and Hongmei Liu. 2025. "Functional Characterization of Two Glutamate Dehydrogenase Genes in Bacillus altitudinis AS19 and Optimization of Soluble Recombinant Expression" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 8: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080603
APA StyleWang, F., Lv, X., Guo, Z., Wang, X., Long, Y., & Liu, H. (2025). Functional Characterization of Two Glutamate Dehydrogenase Genes in Bacillus altitudinis AS19 and Optimization of Soluble Recombinant Expression. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(8), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080603





