Therapeutic Potential of 7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin in Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha-Induced Trigeminal Neuralgia in a Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals Used
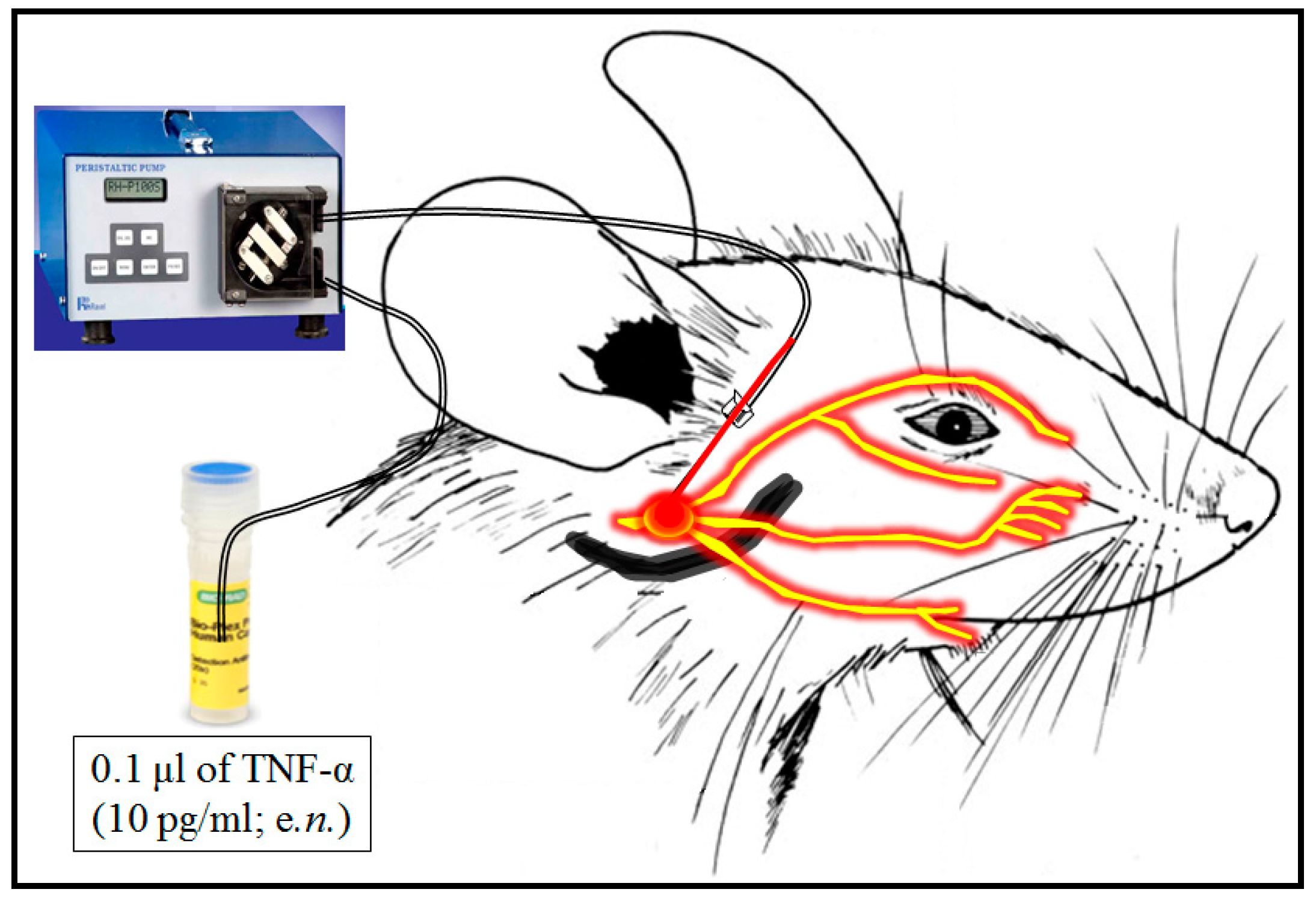
2.2. Induction of Trigeminal Neuralgia
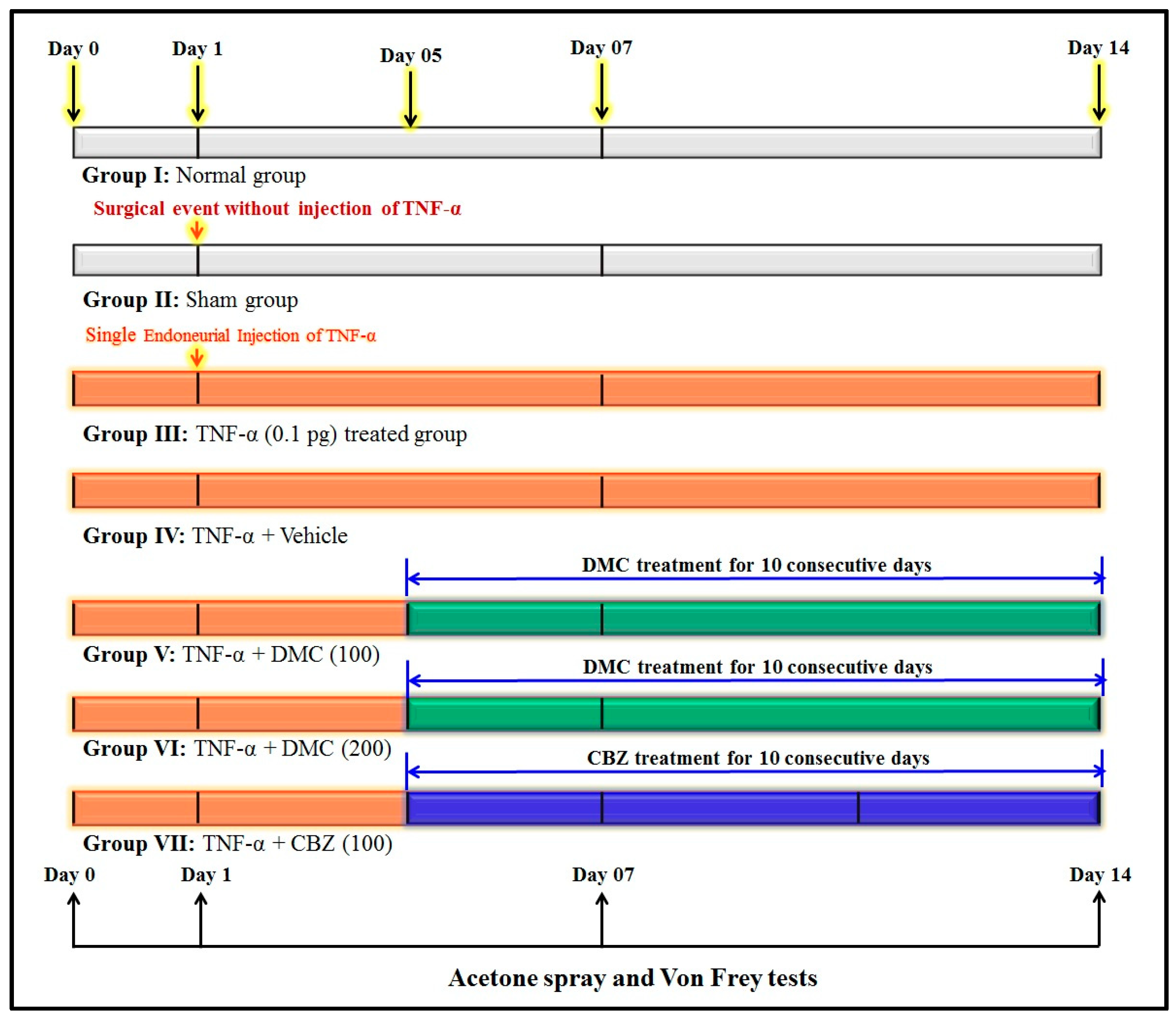
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Behavioural Assessment
2.4.1. Acetone Drop Test
2.4.2. Von Frey Hair Filament Test
2.5. Biochemical Estimation
2.5.1. Estimation of TBARS Level
2.5.2. Estimation of GSH Level
2.5.3. Estimation of TNF-α Level
2.5.4. Estimation of Tissue Total Proteins
2.5.5. Evaluation of Histopathological Changes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
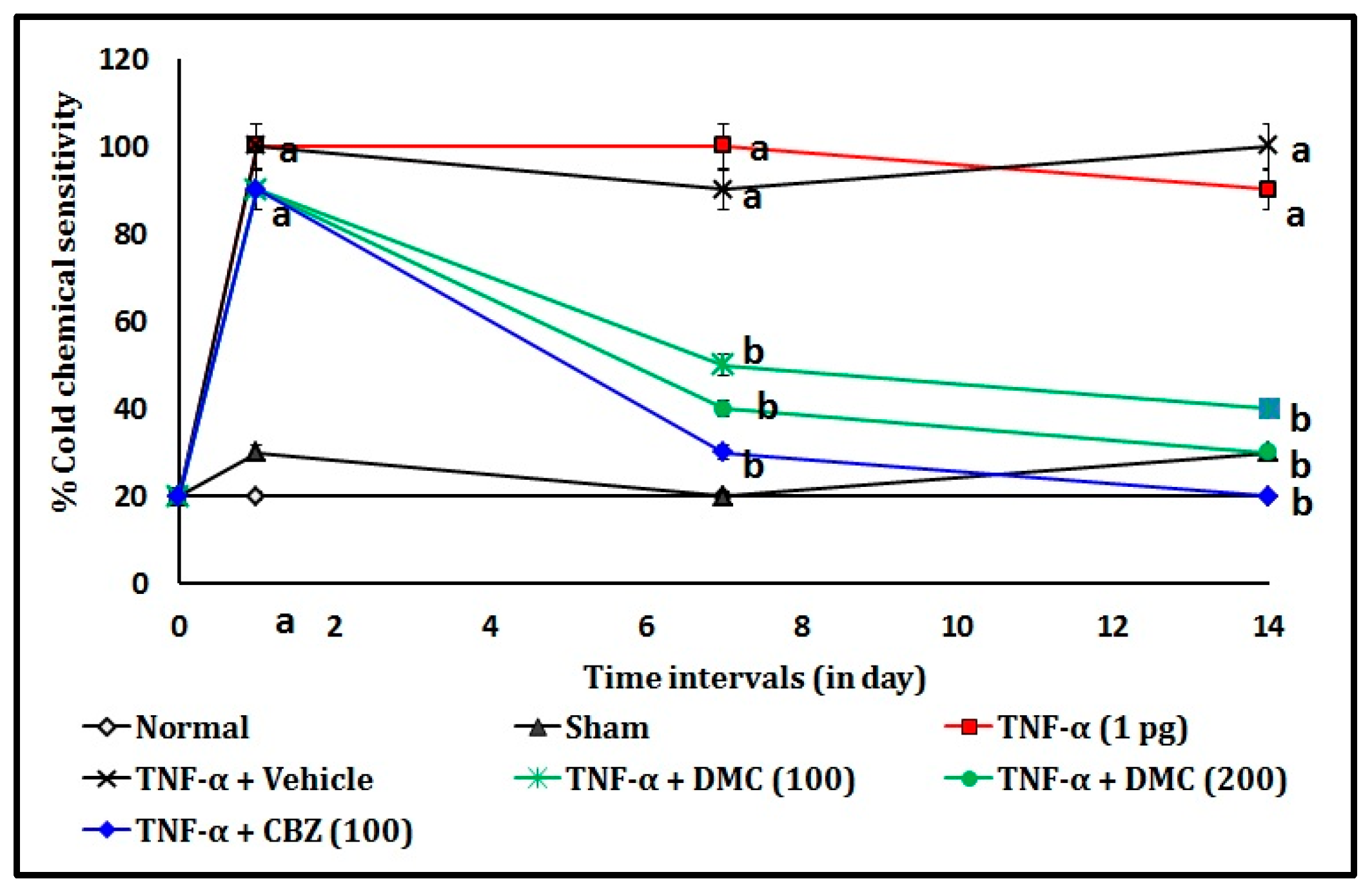
3.1. Effect of DMC in TNF-α-Induced Acetone Drop Test
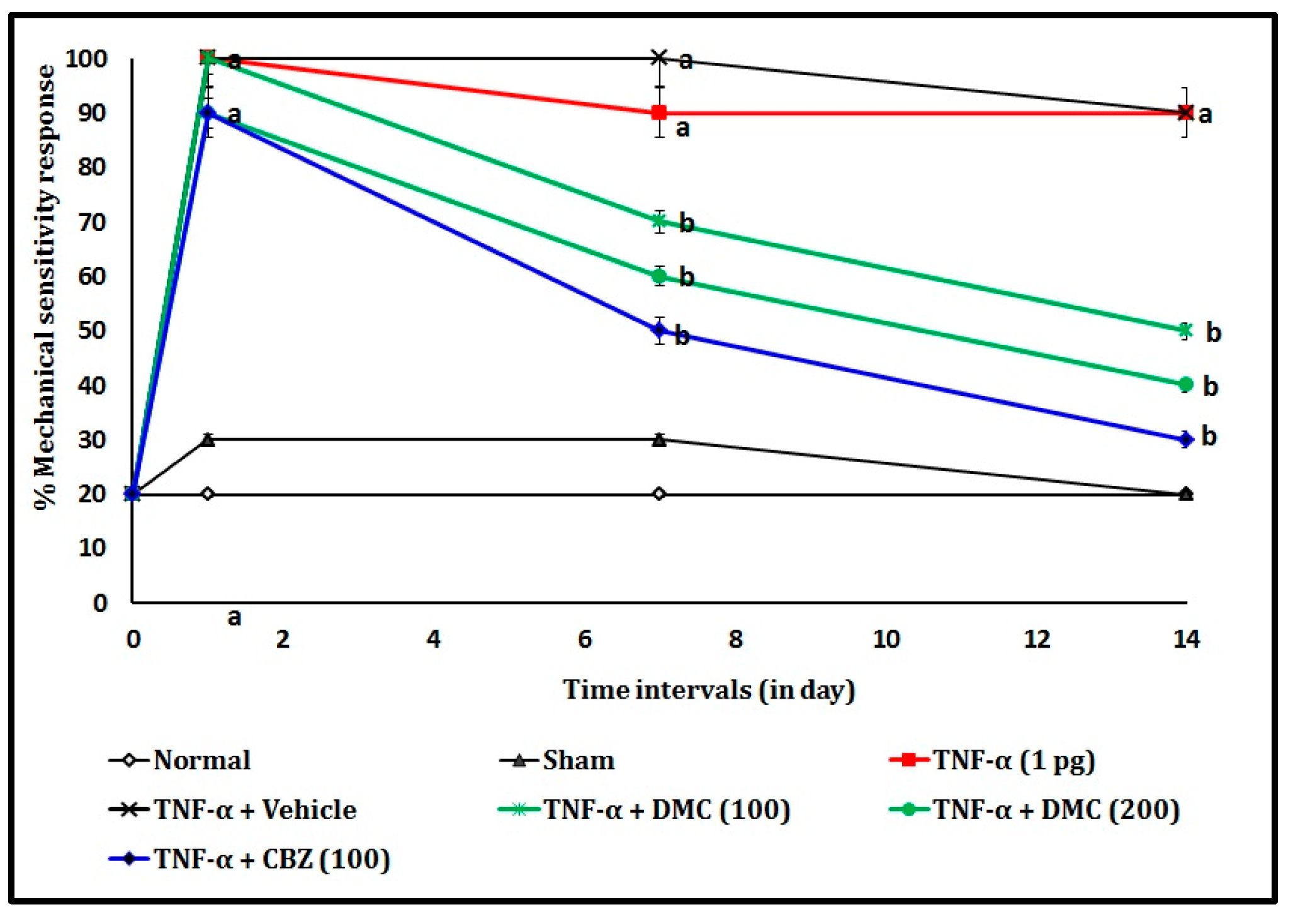
3.2. Effect of DMC in TNF-α-Induced Von Frey Hair Test
3.3. Effect of DMC in TNF-α-Induced Tissue Biomarker Changes
3.4. Effect of DMC in TNF-α-Induced Histopathological Changes
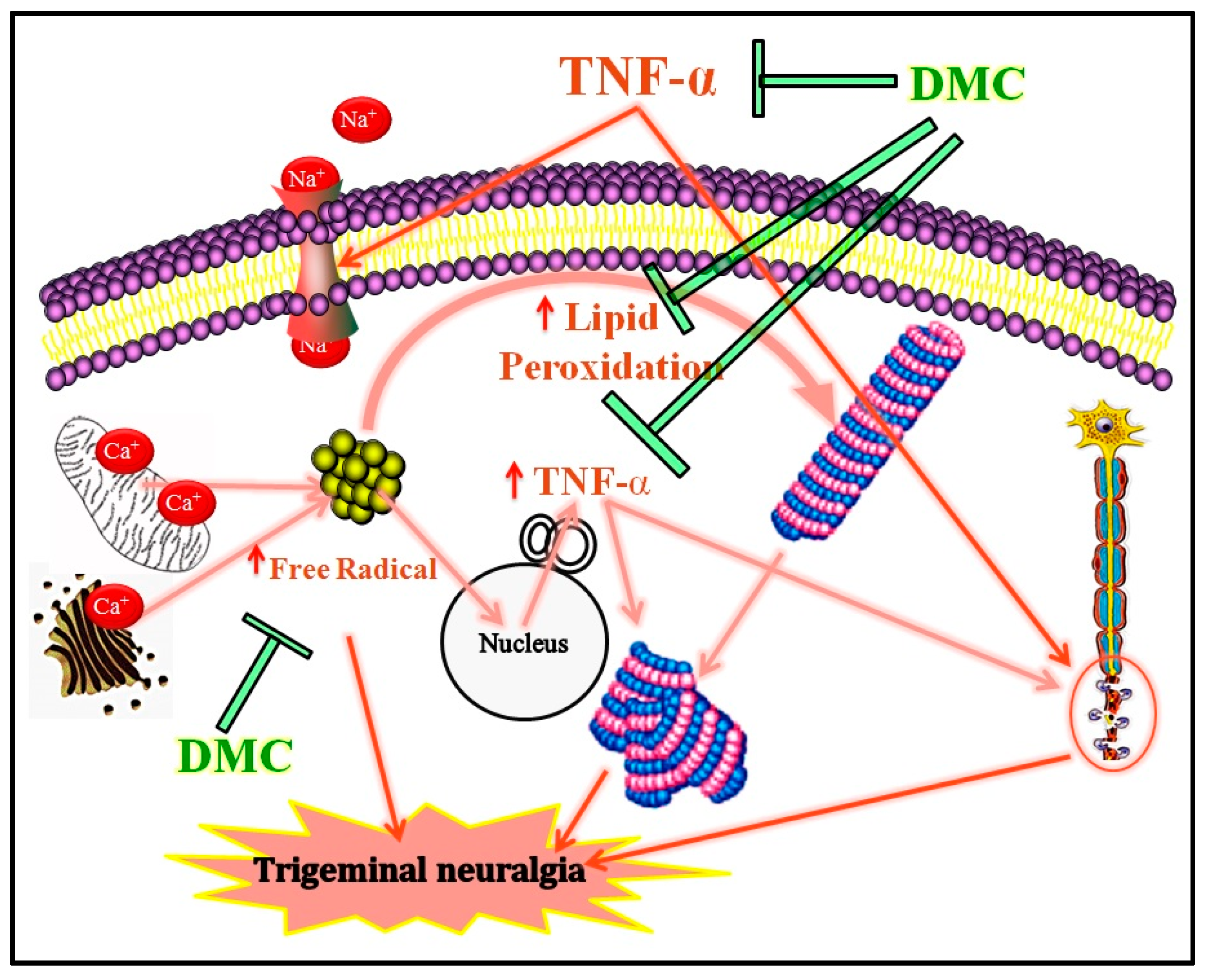
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMC | 7,8-dimethoxy coumarin |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| TBARS | Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances |
| GSH | Reduced glutathione |
| CBZ | Carbamazepine |
| NMDA | N-methyl-d-aspartate |
| IAEC | Institutional animal ethics committee |
| p.o. | Per oral |
| TCA | Trichloroacetic acid |
| TBA | Thiobarbituric acid |
| HCL | Hydrochloric acid |
| DTNB | 5,5′-dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid) |
| SD | Standard deviations |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| pg | picogram |
References
- Breton-Piette, A.; Gélinas, C.; Aita, M. The complexity of the neonatal pain construct: A commentary on Glenzel et al. (2023). Pain Manag. Nurs. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macionis, V. Nociplastic Pain: Controversy of the Concept. Korean J. Pain 2025, 38, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, K.J.A.; Signer, R.; Huckins, L.M. Chronic overlapping pain conditions and nociplastic pain. Hum. Genet. Genom. Adv. 2025, 6, 100381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcangio, M.; Sideris-Lampretsas, G. How microglia contribute to the induction and maintenance of neuropathic pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2025, 26, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Bajorat, R.; Müller-Graf, F.; Zitzmann, A.R.; Müller, V.; Pickhardt, A.-L.; Reuter, D.A.; Böhm, S.H.; Vollmar, B. The role of microcirculatory dysfunction during paclitaxel treatment as a critical co-factor for the development of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Geburtshilfe Und Frauenheilkd. 2025, 85, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmland, M.E.; Kreutzfeldt, M.D.; Brask-Thomsen, P.K.; Jensen, T.S.; Bach, F.W.; Sindrup, S.H.; Finnerup, N.B. Signs of hyperpathia in chronic peripheral neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pain 2025, 29, e4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birangane, R.; Parkarwar, P. Craniofacial Neuralgia; Crow Publishing: London, UK, 2025; ISBN 9364269098. [Google Scholar]
- Pergolizzi, J.V.; LeQuang, J.A.K.; El-Tallawy, S.N.; Ahmed, R.S.; Wagner, M.; Varrassi, G. The challenges in clinical diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia: A review. Cureus 2024, 16, e61898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, G.; Ren, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, B.; Feng, J.; Wu, D.; Xu, X.; Ou, C. Amelioration of central neurodegeneration by docosahexaenoic acid in trigeminal neuralgia rats through the regulation of central neuroinflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 114, 109544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermann, M. Recent advances in understanding/managing trigeminal neuralgia. F1000Research 2019, 8, F1000 Faculty Rev-505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaechi, O. Trigeminal neuralgia: Rapid evidence review. Am. Fam. Physician 2025, 111, 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Mayoral, V.; Galvez, R.; Ferrándiz, M.; Vázquez, X.M.; Cordero-García, C.; Montero, A.A.; Pérez, C.; Pérez-Páramo, M. Pregabalin vs. gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of effectiveness and safety. Front. Pain Res. 2025, 5, 1513597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, A.; Weaver, J. Pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic management of neuropathic pain. Semin. Neurol. 2025, 45, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, K.; Gada, U.; Culakova, E.; Burnette, B.; Jorgensen, C.; Shah, D.; Morrow, G.; Mustian, K.; Sohn, M.B.; Edwards, R.R.; et al. Personalized outcomes in neuropathic pain: A clinical relevance and assay sensitivity analysis from a randomized controlled trial. Pain Med. 2025, 26, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergolizzi, J.V.J.; LeQuang, J.A.; El-Tallawy, S.N.; Wagner, M.; Ahmed, R.S.; Varrassi, G. An update on pharmacotherapy for trigeminal neuralgia. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2024, 24, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbo, J.; Ibrahim, Z.G.; Magaji, S.Y.; Mutalub, Y.B.; Mshelia, P.P.; Mhya, D.H. Therapeutic efficacy of voltage-gated sodium channel inhibitors in epilepsy. Acta Epileptol. 2023, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, J.M.; Smith, K.G.; Robinson, P.P. The effect of carbamazepine on injury-induced ectopic discharge in the lingual nerve. Brain Res. 2005, 1051, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Farias, J.B.; Loeza-Alcocer, E.; Nagarajan, V.; Gold, M.S.; Sekula, R.F. Mechanisms underlying the selective therapeutic efficacy of carbamazepine for attenuation of trigeminal nerve injury pain. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 8991–9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Guan, M.; Chen, Y.; Qin, H.; Huang, S. Efficacy and safety of pregabalin vs carbamazepine in patients with central post-stroke pain. Neurol. Res. 2024, 46, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freynhagen, R.; Baron, R.; Huygen, F.; Perrot, S. Narrative review of the efficacy and safety of the high-concentration (179mg) capsaicin patch in peripheral neuropathic pain with recommendations for clinical practice and future research. Pain Rep. 2025, 10, e1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, Z.; Bukhari, S.A.; Malik, S.A.; Hussain, G.; Kamal, S. Improved gut microbiota escalates muscle function rehabilitation and ameliorates oxidative stress following mechanically induced peripheral nerve injury in mice. Pak. Vet. J. 2023, 43, 707–713. [Google Scholar]
- Heir, R.; Abbasi, Z.; Komal, P.; Altimimi, H.F.; Franquin, M.; Moschou, D.; Chambon, J.; Stellwagen, D. Astrocytes are the source of TNF mediating homeostatic synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2024, 44, e2278222024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-Y.; Hsueh, S.-C.; Parekh, P.; Batsaikhan, B.; Tweedie, D.; Luo, W.; Patel, C.; Chiang, Y.-H.; Bambakidis, N.; Hoffer, B.J. 3-Monothiopomalidomide, a new immunomodulatory imide drug (IMiD), blunts inflammation and mitigates ischemic stroke in the rat. GeroScience 2025, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogulescu, A.; Blidisel, A.; Soica, C.; Mioc, A.; Voicu, A.; Jojic, A.; Voicu, M.; Banciu, C. Neurological side effects of tnf-α inhibitors revisited: A review of case reports. Medicina 2024, 60, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, G.; Saeed, A.; Khurshid, A.; Ahmad, S.; Kashtoh, H.; Ataya, F.S.; Bathiha, G.E.-S.; Ullah, A.; Khan, A. Efficacy assessment of novel methanimine derivatives in chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic model: An in-vivo, ex-vivo and in-silico approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 198, 106797. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, C.D.; Buijs, R.M.; Sitges, M. The anti-seizure drugs vinpocetine and carbamazepine, but not valproic acid, reduce inflammatory IL-1β and TNF-α expression in rat hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y. Treatment of neuropathic pain by traditional Chinese medicine: An updated review on their effect and putative mechanisms of action. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 2962–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.; Badruddeen, U.; Akhtar, J.; Khan, M.I.; Ahmad, M.; Islam, A.; Ahmad, A. Diabetic neuropathy: An overview of molecular pathways and protective mechanisms of phytobioactives. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2024, 24, 758–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, M.; Khan, A.; Shah, F.A. Pharmacological investigation of natural compounds for therapeutic potential in neuropathic pain. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairuae, N.; Noisa, P.; Palachai, N. Phytosome-encapsulated 6-gingerol- and 6-shogaol-enriched extracts from Zingiber officinale roscoe protect against oxidative stress-induced neurotoxicity. Molecules 2024, 29, 6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, H.; Israr, B.; Butt, M.S.; Faisal, M.N. Therapeutic intervention of Opuntia Ficus Indica (L.) fruit and seed powder against CCl 4-induced acute liver injury in Wistar rats. Pak. Vet. J. 2024, 44, 364–376. [Google Scholar]
- AlMasoud, N.; Rabail, R.; Alomar, T.S.; Munir, S.; Hassan, S.A.; Aadil, R.M. Therapeutic impact of bitter gourd seed-fortified crackers on alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Pak. Vet. J. 2024, 44, 629–636. [Google Scholar]
- Şahin, İ.O.; Tunalı, M.B.; Aktaş, A.; Tüfekci, K.K.; Kaplan, S. The effects of curcumin on hyperglycaemia-induced optic nerve damage in Wistar albino rats: An electron microscopic and stereological study. Pak. Vet. J. 2024, 44, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Zekeya, N.; Ibrahim, M.; Mamiro, B.; Ndossi, H.; Kilonzo, M.; Mkangara, M.; Chacha, M.; Chilongola, J.; Kideghesho, J. Potential of natural phenolic antioxidant compounds from Bersama Abyssinica (Meliathacea) for treatment of chronic diseases. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 103273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, M. 7,8-dihydroxycoumarin improves neurological function in a mouse model of sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2012, 7, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.; Malik, H.; Ahmed, Z.; Tokhi, A.; Arif, M.; Huma, Z.; Rauf, K.; Sewell, R. 6,7,8-Trimethoxycoumarin attenuates vincristine induced peripheral neuropathic pain, potential role of 5HT3 and opioid receptors and monoamines. J. Xi’an Shiyou Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2023, 19, 425–464. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, M.; Malik, H.; Tokhi, A.; Arif, M.; Huma, Z.; Rauf, K.; Sewell, R.D.E. 5,7-Dimethoxycoumarin ameliorates vincristine induced neuropathic pain: Potential role of 5HT3 receptors and monoamines. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1213763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraman, A.; Sood, S.; Ramesh, M.; Puri, K.D.S.; Peters, A.; Chauhan, A.; Arora, P.K.; Rana, A. Therapeutic potential of 7,8-dimethoxycoumarin on cisplatin- and ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced acute renal failure in rats. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2012, 385, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Chung, Y.C.; Kang, C.I.; Park, S.; Hyun, C. 7,8-dimethoxycoumarin attenuates the expression of IL-6, IL-8, and CCL2/MCP-1 in TNF-α-treated HaCaT cells by potentially targeting the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Myers, R.R. Endoneurial injection of TNF-alpha produces neuropathic pain behaviors. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 2897–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorkin, L.S.; Doom, C.M. Epineurial application of TNF elicits an acute mechanical hyperalgesia in the awake rat. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2000, 5, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.Y.; Fan, J.; Yu, L.H.; Ma, B.; Cheng, L.M. The up-regulation of TNF-α maintains trigeminal neuralgia by modulating MAPKs phosphorylation and BKCa channels in trigeminal nucleus caudalis. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 764141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Yang, L.; Chen, Q.; Hu, K.; Liu, Y.; Bao, E.; Wang, C.; Mao, J.; Shen, S. Foramen lacerum impingement of trigeminal nerve root as a rodent model for trigeminal neuralgia. JCI. Insight 2023, 8, e168046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damjanovska, M.; Cvetko, E.; Hadzic, A.; Seliskar, A.; Plavec, T.; Mis, K.; Vuckovic Hasanbegovic, I.; Stopar Pintaric, T. Neurotoxicity of perineural vs intraneural-extrafascicular injection of liposomal bupivacaine in the porcine model of sciatic nerve block. Anaesthesia 2015, 70, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C.; Wook, Y.T.; Sik, N.H.; Ho, K.S.; Mo, C.J. Behavioral signs of ongoing pain and cold allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain 1994, 59, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Ling, J.; Gu, J.G. Assessment of orofacial nociceptive behaviors of mice with the sheltering tube method: Oxaliplatin-induced mechanical and cold allodynia in orofacial regions. Mol. Pain 2024, 20, 17448069241261688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.W.; Pogrel, J.W.; Chung, J.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehaus, W.G.J.; Samuelsson, B. Formation of malonaldehyde from phospholipid arachidonate during microsomal lipid peroxidation. Eur. J. Biochem. 1968, 6, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, E.; Duron, O.; Kelly, B.M. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1963, 61, 882–888. [Google Scholar]
- Muthuraman, A.; Ramesh, M. Ischemic-reperfusion of unilateral external iliac artery in rat: A new model for vasculitic femoral neuropathy. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 628, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, D.; Little, P.; Sills, R. Subsite awareness in neuropathology evaluation of national toxicology program (NTP) studies: A review of select neuroanatomical structures with their functional significance in rodents. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 42, 487–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, A.; Toledo, R.N.; de Faria, S.D.; Testa, J.R.G.; Cruz, O.L.M. Behavioral and histologic experimental model of facial nerve regeneration in rats. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 72, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, C.M.; Kelleher, E.; Irani, A.; Schrepf, A.; Clauw, D.J.; Harte, S.E. Deciphering nociplastic pain: Clinical features, risk factors and potential mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Xia, Y.; Ding, Z.; Qian, J.; Gu, X.; Bai, H.; Jiang, M.; Yao, D. Inflammation in the peripheral nervous system after injury. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.N.; Tahir, F. The therapeutic effect of Gymnema Sylvestre extract against hyperglycemia: In Vivo Study. Agrobiol. Rec. 2023, 14, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, U.C.; Bhol, N.K.; Swain, S.K.; Samal, R.R.; Nayak, P.K.; Raina, V.; Panda, S.K.; Kerry, R.G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. Oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders: Mechanisms and implications. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, C.-C.; Dai, S.-P.; Yen, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Chang, S.-L.; Fang, Y.-T.; Lin, H.-L.; Chen, C.-L. Animal neuropathic pain aroused by conglutinating oxidative regenerative cellulose on dorsal root ganglion. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2025, 84, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, E.; Bellomo, G.; Parola, M.; Carini, R.; Dianzani, M.U. Stimulation of lipid peroxidation increases the intracellular calcium content of isolated hepatocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1091, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumilaar, S.G.; Hardianto, A.; Dohi, H.; Kurnia, D. A Comprehensive review of free radicals, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Overview, clinical applications, global perspectives, future directions, and mechanisms of antioxidant activity of flavonoid compounds. J. Chem. 2024, 2024, 5594386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongchitrat, P.; Chanmee, T.; Govitrapong, P. Molecular mechanisms associated with neurodegeneration of neurotropic viral infection. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 2881–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Muthuraman, A. Anti-neuralgesic effect of ginsenoside rg1 (GRg) in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2018, 10, 3482–3489. [Google Scholar]
- Sood, S.; Muthuraman, A.; Gill, N.S.; Bali, M.; Sharma, P.D. Role of 7,8-dimethoxycoumarin in anti-secretary and anti-inflammatory action on pyloric ligation-induced gastritis in rats. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 12, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Wang, H. 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin prevents chronic mild stress induced depression in rats through increase in the expression of heat shock protein-70 and inhibition of monoamine oxidase-A levels. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheriyan, B.V.; Shanmugasundaram, J.; Ramakrishnan, P.; Ramasamy, K.; Karthikeyan, R.; Venkataraman, S.; Roy, A.; Parthasarathy, P.R. Exploring the potential therapeutic benefits of 7-methoxy coumarin for neuropathy pain: An in vivo, in vitro, and in silico approach. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, J.; Sun, M.; Song, X.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Ji, H.; Liu, G.; Chen, N. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory effects of IMMLG5521, a coumarin derivative. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Yang, H.W.; Ko, S.C.; Ko, Y.J.; Kim, E.A.; Roh, S.W.; Ko, E.Y.; Ahn, G.; Heo, S.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; et al. 6-7-Dimethoxy-4-methylcoumarin suppresses pro-inflammatory mediator expression through inactivation of the NF-κB and MAPK pathways in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. EXCLI J. 2014, 13, 792–800. [Google Scholar]
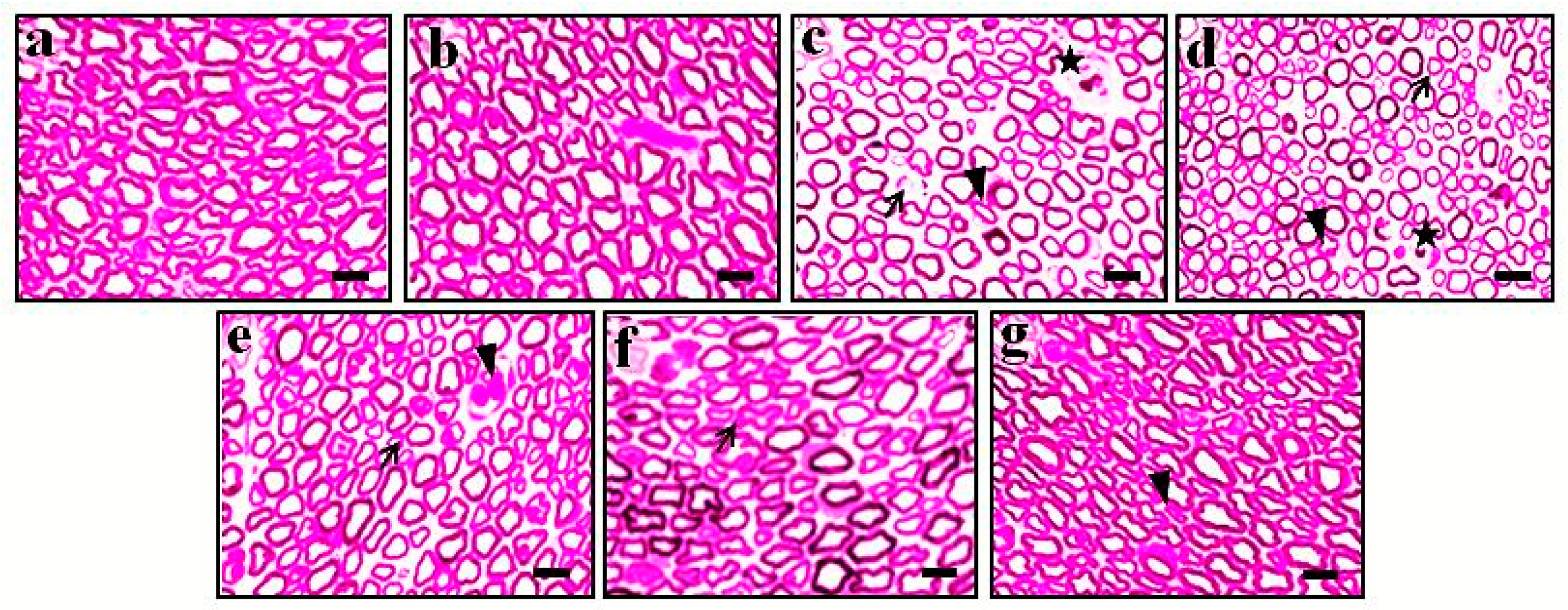
| Groups | TBARS (nmol/mg of Protein) | GSH (µg/mg of Protein) | TNF-α (pg/mg of Protein) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 3.72 ± 0.84 | 73.64 ± 2.92 | 5.04 ± 0.02 |
| Sham | 4.08 ± 0.59 | 70.93 ± 1.86 | 4.98 ± 0.09 |
| TNF-α (0.1 pg) | 19.48 ± 0.26 a | 43.17 ± 2.46 a | 28.84 ± 0.07 a |
| TNF-α + Vehicle | 18.71 ± 0.59 | 45.64 ± 2.34 | 28.61 ± 0.04 |
| TNF-α + DMC (100) | 10.02 ± 0.35 b | 61.92 ± 1.69 b | 11.48 ± 0.08 b |
| TNF-α + DMC (200) | 8.11 ± 0.37 b | 64.73 ± 1.83 b | 9.72 ± 0.07 b |
| TNF-α + CBZ (100) | 5.73 ± 0.28 b | 68.18 ± 2.47 b | 6.35 ± 0.03 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paramakrishnan, N.; Raadhika, K.; Elayaperumal, S.; Sivamani, Y.; Paramaswaran, Y.; Siang, L.J.; Venkata Rathina Kumar, T.; Lim, K.G.; Ramesh, M.; Muthuraman, A. Therapeutic Potential of 7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin in Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha-Induced Trigeminal Neuralgia in a Rat Model. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070518
Paramakrishnan N, Raadhika K, Elayaperumal S, Sivamani Y, Paramaswaran Y, Siang LJ, Venkata Rathina Kumar T, Lim KG, Ramesh M, Muthuraman A. Therapeutic Potential of 7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin in Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha-Induced Trigeminal Neuralgia in a Rat Model. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070518
Chicago/Turabian StyleParamakrishnan, Nallupillai, Kanthiraj Raadhika, Sumitha Elayaperumal, Yuvaraj Sivamani, Yamunna Paramaswaran, Lim Joe Siang, Thiagharajan Venkata Rathina Kumar, Khian Giap Lim, Muthusamy Ramesh, and Arunachalam Muthuraman. 2025. "Therapeutic Potential of 7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin in Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha-Induced Trigeminal Neuralgia in a Rat Model" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070518
APA StyleParamakrishnan, N., Raadhika, K., Elayaperumal, S., Sivamani, Y., Paramaswaran, Y., Siang, L. J., Venkata Rathina Kumar, T., Lim, K. G., Ramesh, M., & Muthuraman, A. (2025). Therapeutic Potential of 7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin in Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha-Induced Trigeminal Neuralgia in a Rat Model. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070518






