Investigating the Mediating Role of Cardiometabolic Traits in the Causal Link Between SHBG Levels and Stroke Risk via Network Mendelian Randomization
Abstract
1. Introduction
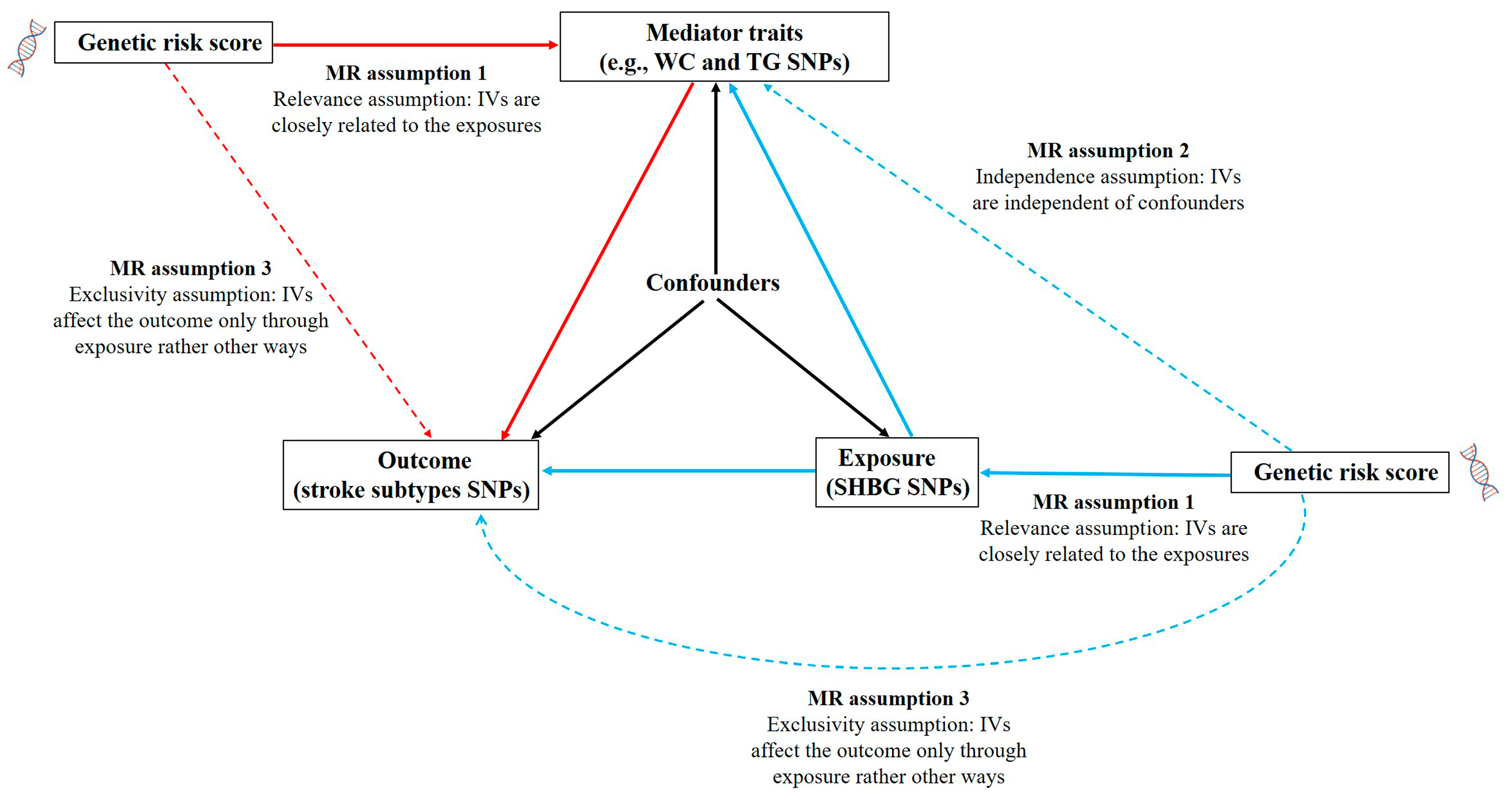
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Selection of Instrument Variables (IVs)
2.3. MR Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
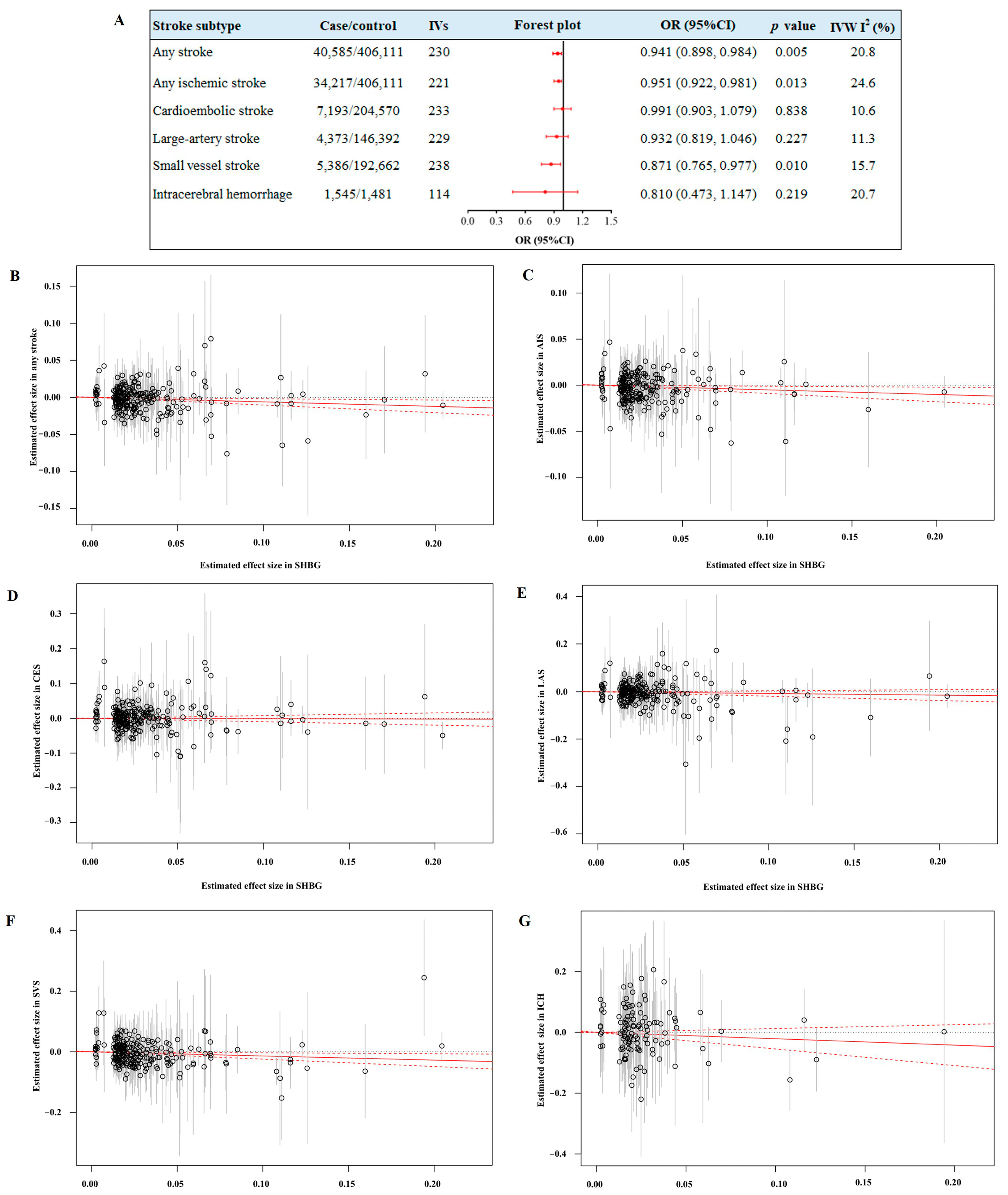
3.1. A Protective Effect of Genetically Elevated SHBG Levels on Stroke Risk
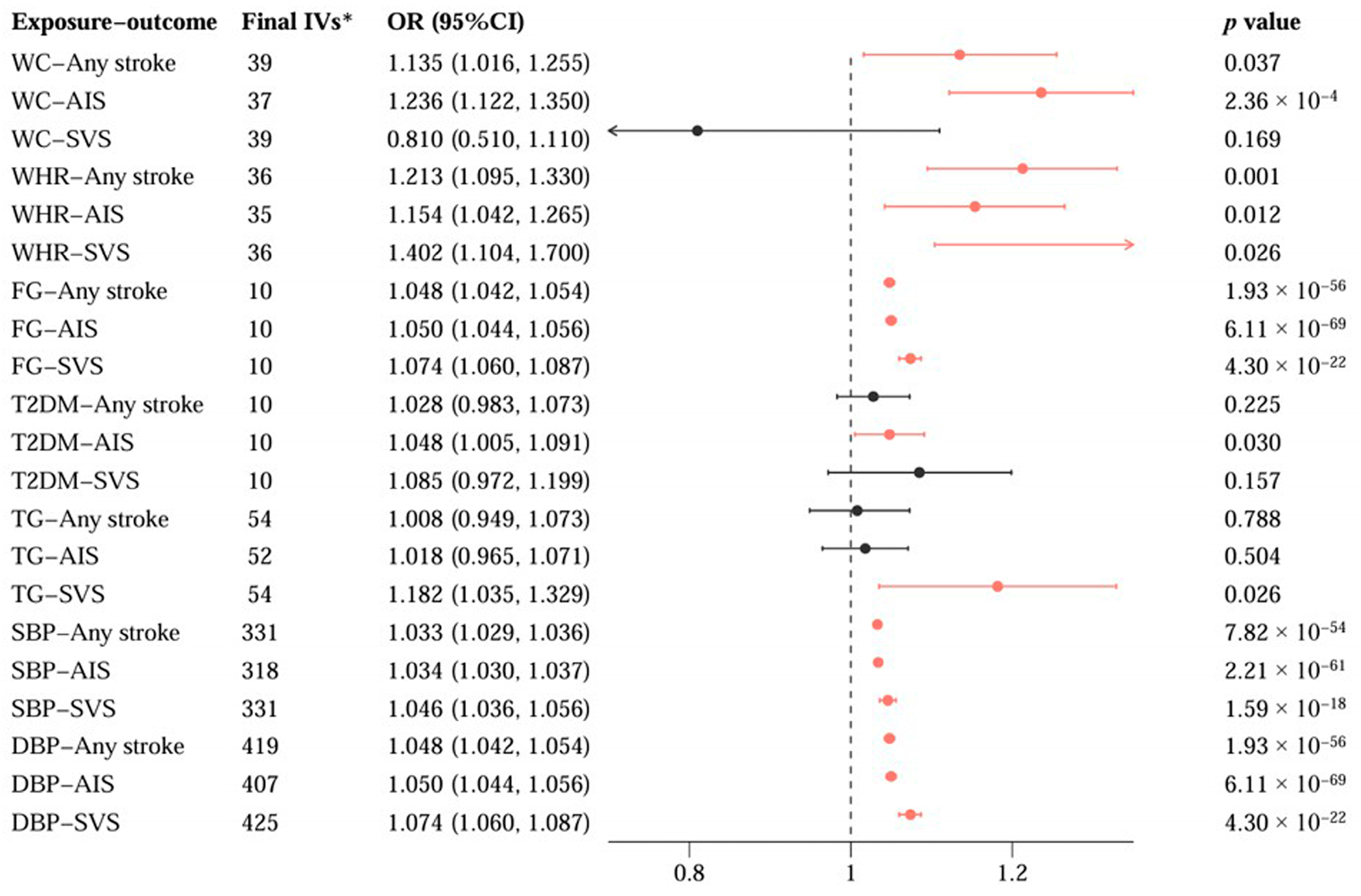
3.2. Causal Associations Between SHBG Levels and Cardiometabolic Traits
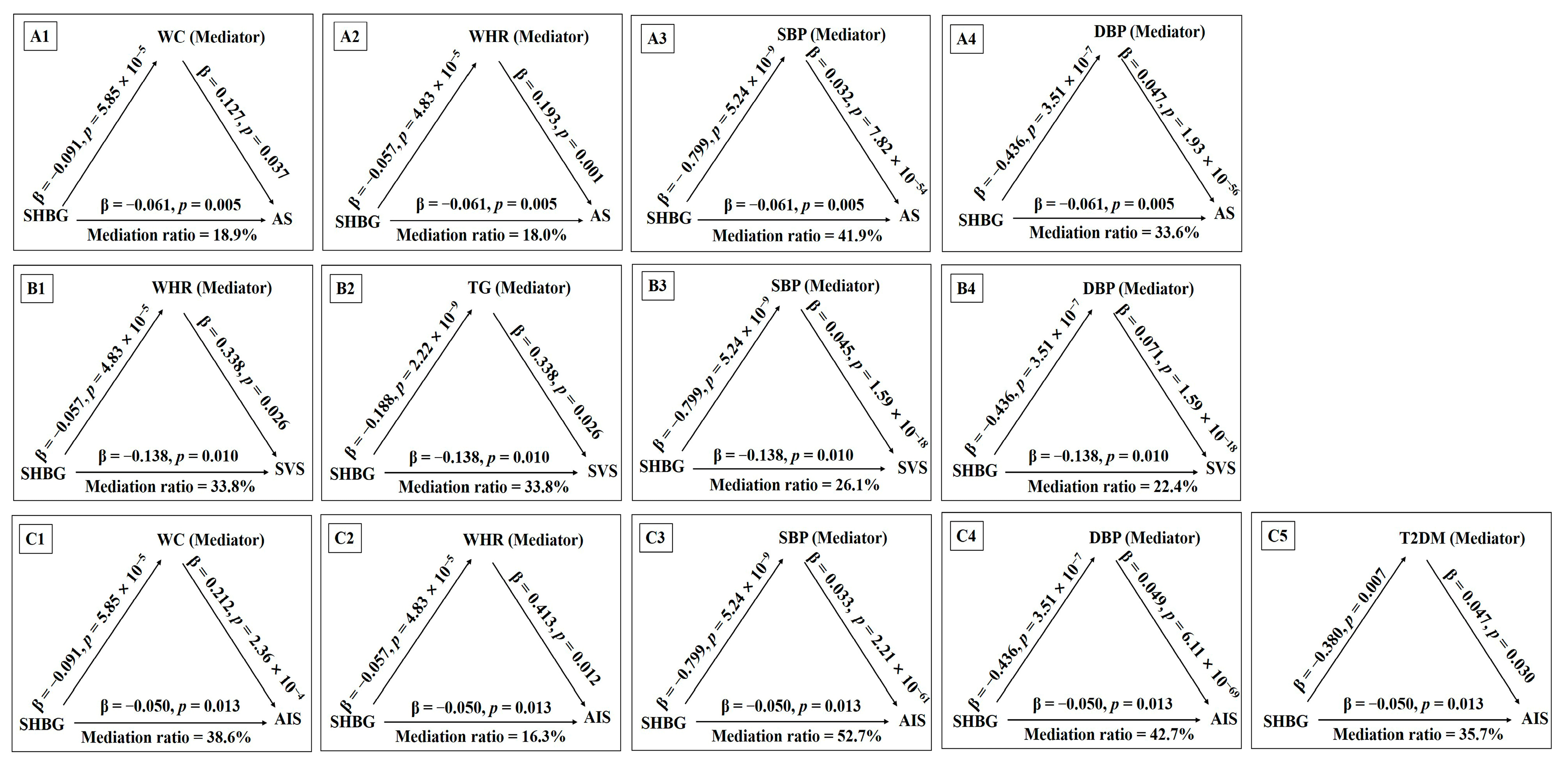
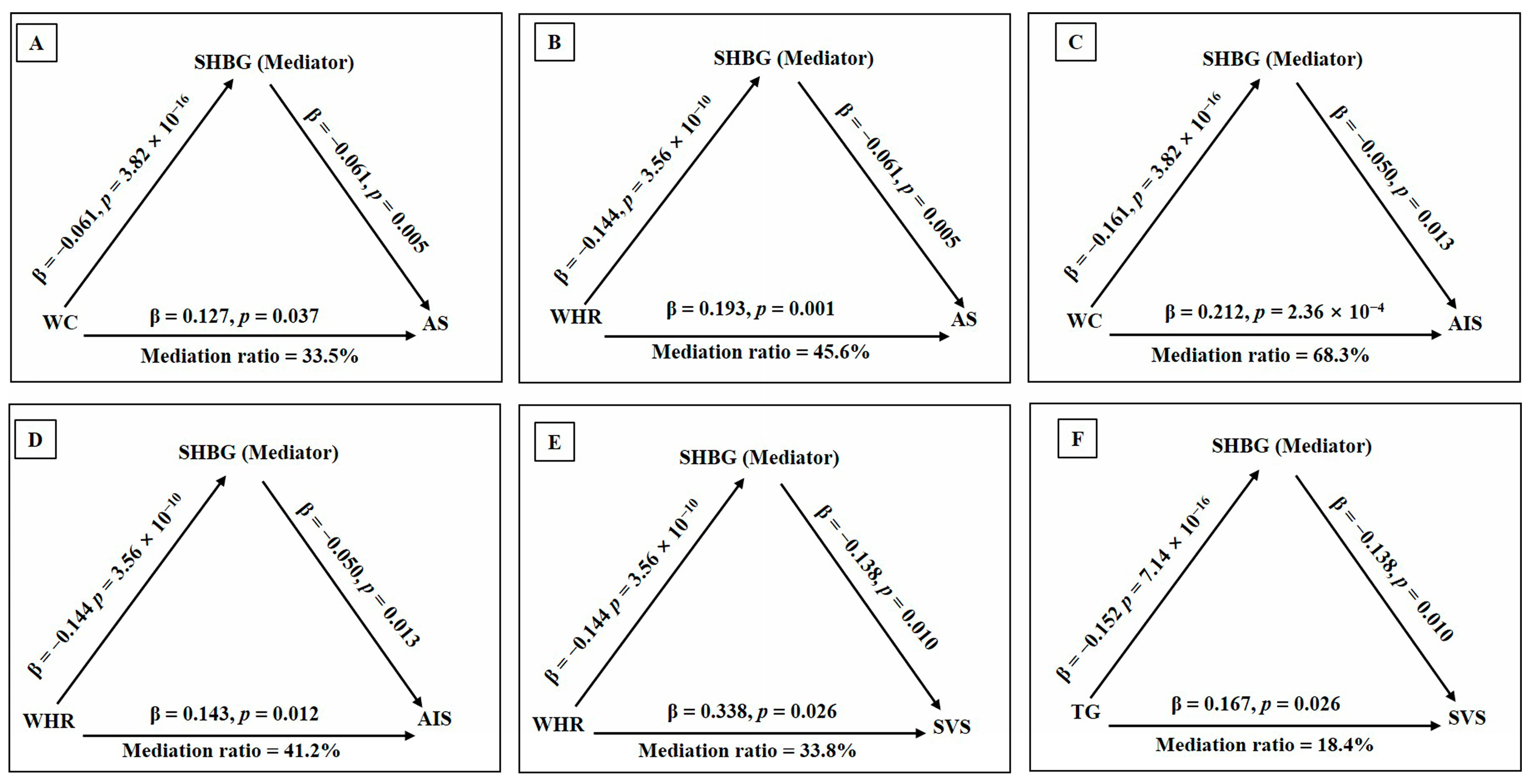
3.3. Causal Pathways from SHBG Levels to Stroke via Cardiometabolic Traits
3.4. Causal Effects of the Cardiometabolic Mediators on Stroke Risk via SHBG
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2021 Nervous System Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of disorders affecting the nervous system, 1990-2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 344–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, K.S.; Singh, A.; Marwaha, G.S.; Ravendranathan, N.; Sandhu, I.S.; Kim, K.; Singh, E.; Frisbee, J.C.; Singh, K.K. Different Mechanisms in Doxorubicin-Induced Neurotoxicity: Impact of BRCA Mutations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montellano, F.A.; Ungethüm, K.; Ramiro, L.; Nacu, A.; Hellwig, S.; Fluri, F.; Whiteley, W.N.; Bustamante, A.; Montaner, J.; Heuschmann, P.U. Role of Blood-Based Biomarkers in Ischemic Stroke Prognosis: A Systematic Review. Stroke 2021, 52, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, T.L.; Hsu, C.K.; Lu, W.J.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Hsiao, G.; Chou, D.S.; Wu, G.J.; Sheu, J.R. Neuroprotective effects of xanthohumol, a prenylated flavonoid from hops (Humulus lupulus), in ischemic stroke of rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Gu, H.; Hu, B.; Li, Y. The Interrelation of Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Albumin Ratio with Three-Month Clinical Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke Cases: A Secondary Analytical Exploration Derived from a Prospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 17, 5333–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tan, S.; Li, X.; Sun, T.; Li, D.; Du, J.; Wei, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B. Calcitonin gene-related peptide inhibits the cardiac fibroblasts senescence in cardiac fibrosis via up-regulating klotho expression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 843, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Ma, W.; Li, X.; Jiang, C.; Sun, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, W. Involvement of ROS/NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Pathway in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2020, 20, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Deng, F.; Chen, Y.; Kong, Y.; Pan, L.; Liao, Q.; Rao, Z.; Xie, L.; Yao, C.; Li, S.; et al. NF-κB pathway activation during endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in a rat model of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Xie, N.; Sun, T.; Ma, W.; Zhang, B.; Li, W. Xanthohumol Inhibits TGF-β1-Induced Cardiac Fibroblasts Activation via Mediating PTEN/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 5431–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Lü, H.; Lv, K. Multitargeted Immunomodulatory Therapy for Viral Myocarditis by Engineered Extracellular Vesicles. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 2782–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Ge, C.; Pei, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, M.; Zhu, X.; Lv, K. M2 macrophage exosome-derived lncRNA AK083884 protects mice from CVB3-induced viral myocarditis through regulating PKM2/HIF-1α axis mediated metabolic reprogramming of macrophages. Redox Biol. 2024, 69, 103016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, Y.; Fujiu, K. Innate immune memory in macrophage differentiation and cardiovascular diseases. Inflamm. Regen. 2025, 45, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, V.; Sawhney, A.; Nebuwa, C.; Borra, V.; Deb, N.; Halder, A.; Rajak, K.; Jha, M.; Wajid, Z.; Thachil, R.; et al. Association between testosterone replacement therapy and cardiovascular outcomes: A meta-analysis of 30 randomized controlled trials. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2024, 85, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Han, F.; Xue, M.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y. The benefits and risks of menopause hormone therapy for the cardiovascular system in postmenopausal women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Womens Health 2024, 24, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassertheil-Smoller, S.; Hendrix, S.L.; Limacher, M.; Heiss, G.; Kooperberg, C.; Baird, A.; Kotchen, T.; Curb, J.D.; Black, H.; Rossouw, J.E.; et al. Effect of estrogen plus progestin on stroke in postmenopausal women: The Women’s Health Initiative: A randomized trial. JAMA 2003, 289, 2673–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Yaffe, K.; Lui, L.Y.; Cauley, J.; Taylor, B.; Browner, W.; Cummings, S.; Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Group. Prospective study of endogenous circulating estradiol and risk of stroke in older women. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D.R. Structure, function, and regulation of androgen-binding protein/sex hormone-binding globulin. Vitam. Horm. 1994, 49, 197–280. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, J.R.; Weedon, M.N.; Langenberg, C.; Jackson, A.U.; Lyssenko, V.; Sparsø, T.; Thorleifsson, G.; Grallert, H.; Ferrucci, L.; Maggio, M.; et al. Genetic evidence that raised sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) levels reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Si, S.; Hou, L.; Yuan, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Xue, F. Causal effect of sex hormone-binding globulin and testosterone on coronary heart disease: A multivariable and network Mendelian randomization analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 339, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimou, N.L.; Papadimitriou, N.; Gill, D.; Christakoudi, S.; Murphy, N.; Gunter, M.J.; Travis, R.C.; Key, T.J.; Fortner, R.T.; Haycock, P.C.; et al. Sex hormone binding globulin and risk of breast cancer: A Mendelian randomization study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arathimos, R.; Granell, R.; Haycock, P.; Richmond, R.C.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Relton, C.L.; Tilling, K. Genetic and observational evidence supports a causal role of sex hormones on the development of asthma. Thorax 2019, 74, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Huang, J.; Yang, F.; Hong, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, S. Sex hormone-binding globulin and arthritis: A Mendelian randomization study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, T.E.; Luo, X.; Huang, M.; Park, K.E.; Stefanick, M.L.; Manson, J.E.; Liu, S. Circulating SHBG (Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin) and Risk of Ischemic Stroke: Findings From the WHI. Stroke 2020, 51, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osganian, S.K.; Stampfer, M.J.; Rimm, E.; Spiegelman, D.; Hu, F.B.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C. Vitamin C and risk of coronary heart disease in women. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossouw, J.E.; Anderson, G.L.; Prentice, R.L.; LaCroix, A.Z.; Kooperberg, C.; Stefanick, M.L.; Jackson, R.D.; Beresford, S.A.; Howard, B.V.; Johnson, K.C.; et al. Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women: Principal results From the Women’s Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2002, 288, 321–333. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D.M.; Davey Smith, G. Mendelian Randomization: New Applications in the Coming Age of Hypothesis Free Causality. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2015, 16, 327–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.; Song, Y.M. Genetic effects on serum testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin in men: A Korean twin and family study. Asian J. Androl. 2016, 18, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijper, E.A.; Lambalk, C.B.; Boomsma, D.I.; van der Sluis, S.; Blankenstein, M.A.; de Geus, E.J.; Posthuma, D. Heritability of reproductive hormones in adult male twins. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 2153–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Timpson, N.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Dimou, N.; Langenberg, C.; et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using mendelian randomisation (STROBE-MR): Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2021, 375, n2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Chauhan, G.; Traylor, M.; Sargurupremraj, M.; Okada, Y.; Mishra, A.; Rutten-Jacobs, L.; Giese, A.K.; van der Laan, S.W.; Gretarsdottir, S.; et al. Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, D.; Falcone, G.J.; Devan, W.J.; Brown, W.M.; Biffi, A.; Howard, T.D.; Anderson, C.D.; Brouwers, H.B.; Valant, V.; Battey, T.W.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies 1q22 as a susceptibility locus for intracerebral hemorrhage. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 94, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, A.E.; Kahali, B.; Berndt, S.I.; Justice, A.E.; Pers, T.H.; Day, F.R.; Powell, C.; Vedantam, S.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Yang, J.; et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature 2015, 518, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shungin, D.; Winkler, T.W.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; Ferreira, T.; Locke, A.E.; Mägi, R.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Pers, T.H.; Fischer, K.; Justice, A.E.; et al. New genetic loci link adipose and insulin biology to body fat distribution. Nature 2015, 518, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuis, J.; Langenberg, C.; Prokopenko, I.; Saxena, R.; Soranzo, N.; Jackson, A.U.; Wheeler, E.; Glazer, N.L.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Gloyn, A.L.; et al. New genetic loci implicated in fasting glucose homeostasis and their impact on type 2 diabetes risk. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, A.K.; Hivert, M.F.; Scott, R.A.; Grimsby, J.L.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Chen, H.; Rybin, D.; Liu, C.T.; Bielak, L.F.; Prokopenko, I.; et al. A genome-wide approach accounting for body mass index identifies genetic variants influencing fasting glycemic traits and insulin resistance. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soranzo, N.; Sanna, S.; Wheeler, E.; Gieger, C.; Radke, D.; Dupuis, J.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Langenberg, C.; Prokopenko, I.; Stolerman, E.; et al. Common variants at 10 genomic loci influence hemoglobin A(1)(C) levels via glycemic and nonglycemic pathways. Diabetes 2010, 59, 3229–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.P.; Voight, B.F.; Teslovich, T.M.; Ferreira, T.; Segrè, A.V.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Khan, H.; Grallert, H.; Mahajan, A.; et al. Large-scale association analysis provides insights into the genetic architecture and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 981–990. [Google Scholar]
- Willer, C.J.; Schmidt, E.M.; Sengupta, S.; Peloso, G.M.; Gustafsson, S.; Kanoni, S.; Ganna, A.; Chen, J.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Mora, S.; et al. Discovery and refinement of loci associated with lipid levels. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Evangelou, E.; Warren, H.R.; Mosen-Ansorena, D.; Mifsud, B.; Pazoki, R.; Gao, H.; Ntritsos, G.; Dimou, N.; Cabrera, C.P.; Karaman, I.; et al. Genetic analysis of over 1 million people identifies new loci associated with blood pressure traits. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastani, Z.; Hivert, M.F.; Timpson, N.; Perry, J.R.; Yuan, X.; Scott, R.A.; Henneman, P.; Heid, I.M.; Kizer, J.R.; Lyytikäinen, L.P.; et al. Novel loci for adiponectin levels and their influence on type 2 diabetes and metabolic traits: A multi-ethnic meta-analysis of 45,891 individuals. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikoshi, M.; Mӓgi, R.; van de Bunt, M.; Surakka, I.; Sarin, A.P.; Mahajan, A.; Marullo, L.; Thorleifsson, G.; Hӓgg, S.; Hottenga, J.J.; et al. Discovery and Fine-Mapping of Glycaemic and Obesity-Related Trait Loci Using High-Density Imputation. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, B.P.; Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Bao, Y.; Smart, M.; Zabaneh, D.; Fatemifar, G.; Luan, J.; Wareham, N.J.; Scott, R.A.; Perry, J.R.B.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of health-related biomarkers in the UK Household Longitudinal Study reveals novel associations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, P.R.; Kichaev, G.; Gazal, S.; Schoech, A.P.; Price, A.L. Mixed-model association for biobank-scale datasets. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 906–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhre, K.; Arnold, M.; Bhagwat, A.M.; Cotton, R.J.; Engelke, R.; Raffler, J.; Sarwath, H.; Thareja, G.; Wahl, A.; DeLisle, R.K.; et al. Connecting genetic risk to disease end points through the human blood plasma proteome. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.M.; Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sheehan, N.A.; Tobias, J.H.; Timpson, N.J.; Davey Smith, G.; Sterne, J.A. Using multiple genetic variants as instrumental variables for modifiable risk factors. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2012, 21, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.R. Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 2926–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Choi, I.; Kim, S.; Ko, H.; Shin, J.; Lee, K.; Sung, J.; Song, Y.M. Cross-sectional association between testosterone, sex hormone-binding globulin and metabolic syndrome: The Healthy Twin Study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017, 87, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanya, V.; Zhao, D.; Ouyang, P.; Ying, W.; Vaidya, D.; Ndumele, C.E.; Heckbert, S.R.; Budoff, M.J.; Post, W.S.; Michos, E.D. Association of endogenous sex hormone levels with coronary artery calcium progression among post-menopausal women in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2019, 13, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, B.B.; Marriott, R.J.; Dwivedi, G.; Adams, R.J.; Antonio, L.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Bauer, D.C.; Bhasin, S.; Biggs, M.L.; Cawthon, P.M.; et al. Associations of Testosterone and Related Hormones with All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality and Incident Cardiovascular Disease in Men: Individual Participant Data Meta-analyses. Ann. Intern. Med. 2024, 177, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Kushiyama, A.; Sakoda, H.; Fujishiro, M.; Yamamotoya, T.; Nakatsu, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Kaneko, S.; Tanaka, H.; Asano, T. Protective Effect of Sex Hormone Binding Globulin against Metabolic Syndrome: In Vitro Evidence Showing Anti-Inflammatory and Lipolytic Effects on Adipocytes and Macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3062319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakis, M.K.; Gill, D.; Rannikmäe, K.; Traylor, M.; Anderson, C.D.; Lee, J.M.; Kamatani, Y.; Hopewell, J.C.; Worrall, B.B.; Bernhagen, J.; et al. Genetically Determined Levels of Circulating Cytokines and Risk of Stroke. Circulation 2019, 139, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esenwa, C.C.; Elkind, M.S. Inflammatory risk factors, biomarkers and associated therapy in ischaemic stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenske, B.; Kische, H.; Gross, S.; Wallaschofski, H.; Völzke, H.; Dörr, M.; Nauck, M.; Keevil, B.G.; Brabant, G.; Haring, R. Endogenous Androgens and Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin in Women and Risk of Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 4595–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Tiainen, M.; Tynkkynen, T.; Puukka, K.; Ruokonen, A.; Viikari, J.; Kähönen, M.; Lehtimäki, T.; et al. Sex hormone-binding globulin associations with 541 circulating lipids and metabolites and the risk for type 2 diabetes: Observational and causal effect estimates. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Ji, S.; Mei, Z.; Li, T. Association of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components with Risk of Stroke 544 Recurrence and Mortality: A Meta-analysis. Neurology 2021, 97, e695–e705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffe, H.V.; Ridker, P.M.; Manson, J.E.; Cook, N.R.; Buring, J.E.; Rexrode, K.M. Sex hormone-binding globulin and serum testosterone are inversely as sociated with C-reactive protein levels in postmenopausal women at high risk for cardiovascular disease. Ann. Epidemiol. 2006, 16, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, R.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, S.; Hou, C.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Bao, M.; He, B.; Li, S. Mechanisms of inflammatory microenvironment formation in cardiometabolic diseases: Molecular and cellular perspectives. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 11, 1529903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexrode, K.M.; Manson, J.E.; Lee, I.M.; Ridker, P.M.; Sluss, P.M.; Cook, N.R.; Buring, J.E. Sex hormone levels and risk of cardiovascular events in postmenopausal women. Circulation 2003, 108, 1688–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, M.E.; Manson, J.E.; Buring, J.E.; Cook, N.R.; Seely, E.W.; Ridker, P.M.; Rexrode, K.M. Low sex hormone-binding globulin is with the metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women. Metabolism 2006, 55, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakis, M.K.; Gill, D.; Webb, A.J.S.; Evangelou, E.; Elliott, P.; Sudlow, C.L.M.; Dehghan, A.; Malik, R.; Tzoulaki, I.; Dichgans, M. Genetically determined blood pressure, anti-hypertensive drug classes, and risk of stroke subtypes. Neurology 2020, 95, e353–e361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Graham, S.; Wang, X.; Cai, D.; Huang, M.; Pique-Regi, R.; Dong, X.C.; Chen, Y.E.; Willer, C.; et al. Causal relationships between NAFLD, T2D and obesity have implications for disease subphenotyping. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, C.; Yang, L.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, M.; Bovet, P.; Xi, B. Weight status change during four years and left ventricular hypertrophy in Chinese children. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1371286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, R.; Xu, S.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Bao, M.; He, B.; Li, S. Endocrine and metabolic factors and the risk of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1321576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, D.M.; Hogeveen, K.N.; Innis, S.M.; Hammond, G.L. Monosaccharide-induced lipogenesis regulates the human hepatic sex hormone-binding globulin gene. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3979–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A. Commentary: Two-sample Mendelian randomization: Opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.; Chasman, D.I.; Smith, J.D.; Mora, S.; Ridker, P.M.; Nickerson, D.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Stephens, M. A multivariate genome-wide association analysis of 10 LDL subfractions, and their response to statin treatment, in 1868 Caucasians. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, B.L.; Ahsan, H.; Vanderweele, T.J. Power and instrument strength requirements for Mendelian randomization studies using multiple genetic variants. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Karlsson, I.K.; Karlsson, R.; Tillander, A.; Reynolds, C.A.; Pedersen, N.L.; Hägg, S. Exploring the Causal Pathway From Telomere Length to Coronary Heart Disease: A Network Mendelian Randomization Study. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology using Mendelian Randomization (STROBE-MR) Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Outcomes | Causal Estimates in the Discovery Datasets | Causal Estimates in the Replication Datasets # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Sizes | OR/β (95% CI) * | IVW p Value | Sample Sizes | OR/β (95% CI) * | IVW p Value | |
| BMI | 322,154 | −0.058 (−0.093, −0.023) | 0.001 | 87,048 | −0.005 (−0.046, 0.036) | 0.820 |
| WC | 232,101 | −0.091 (−0.136, −0.046) | 5.85 × 10−5 | 336,639 | −0.039 (−0.057, −0.021) | 2.04 × 10−5 |
| WHR | 210,082 | −0.057 (−0.084, −0.030) | 4.83 × 10−5 | 502,773 | −0.065 (−0.094, −0.036) | 2.56 × 10−5 |
| FG | 41,486 | −0.034 (−0.054, −0.014) | 0.007 | 87,048 | −0.029 (−0.049, −0.009) | 0.006 |
| FI | 51,750 | −0.028 (−0.046, −0.010) | 0.002 | 87,048 | −0.017 (−0.039, 0.005) | 0.123 |
| HbA1c | 46,368 | 0.020 (0.010, 0.030) | 1.31 × 10−5 | 9436 | −0.040 (−0.095, 0.015) | 0.162 |
| T2DM | 69,033 | 0.684 (0.400, 0.968) | 4.77 × 10−3 | 298,957 | 0.834 (0.749, 0.918) | 2.27 × 10−5 |
| TC | 94,595 | −0.023 (−0.080, 0.034) | 0.221 | NA | NA | NA |
| TG | 94,595 | −0.188 (−0.249, −0.127) | 2.22 × 10−9 | 9796 | −0.131 (−0.213, −0.049) | 0.002 |
| LDL-C | 94,595 | −0.027 (−0.068, 0.014) | 0.201 | NA | NA | NA |
| HDL-C | 94,595 | 0.141 (0.094, 0.188) | 5.64 × 10−9 | 403,943 | 0.103 (−0.024, 0.230) | 0.113 |
| SBP | 757,601 | −0.799 (−1.068, −0.530) | 5.24 × 10−9 | 436,419 | −0.055 (−0.075, −0.035) | 1.70 × 10−8 |
| DBP | 757,601 | −0.436 (−0.605, −0.267) | 3.51 × 10−7 | 436,424 | −0.027 (−0.041, −0.013) | 9.37 × 10−5 |
| Hypertension | 361,194 | 1.000 (0.999, 1.000) | 0.857 | NA | NA | NA |
| Adiponectin | 39,883 | 0.037 (0.008, 0.066) | 0.014 | 1000 | 0.207 (−0.020, 0.434) | 0.075 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, P.; Liang, H.; Li, M. Investigating the Mediating Role of Cardiometabolic Traits in the Causal Link Between SHBG Levels and Stroke Risk via Network Mendelian Randomization. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070494
Pan P, Liang H, Li M. Investigating the Mediating Role of Cardiometabolic Traits in the Causal Link Between SHBG Levels and Stroke Risk via Network Mendelian Randomization. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070494
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Peijiang, Hao Liang, and Mingli Li. 2025. "Investigating the Mediating Role of Cardiometabolic Traits in the Causal Link Between SHBG Levels and Stroke Risk via Network Mendelian Randomization" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070494
APA StylePan, P., Liang, H., & Li, M. (2025). Investigating the Mediating Role of Cardiometabolic Traits in the Causal Link Between SHBG Levels and Stroke Risk via Network Mendelian Randomization. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070494






