Peripheral Blood Exosomal miR-184-3p in Methamphetamine Use Disorder: Biomarker Potential and CRTC1-Mediated Neuroadaptation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants and Ethical Statement
2.2. Scale Administration
2.3. Blood Sample Collection and Preparation
2.4. Isolation of Circulating Exosomes
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) for Exosome Characterization
2.6. RNA Extraction
2.7. miRNA Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.8. Quantification and Differential Expression Analysis of miRNA
2.9. Prediction and Functional Analysis of miRNA-Targeted Genes
2.10. Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR
2.11. The Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics and Clinical Data Analysis of the Study Population
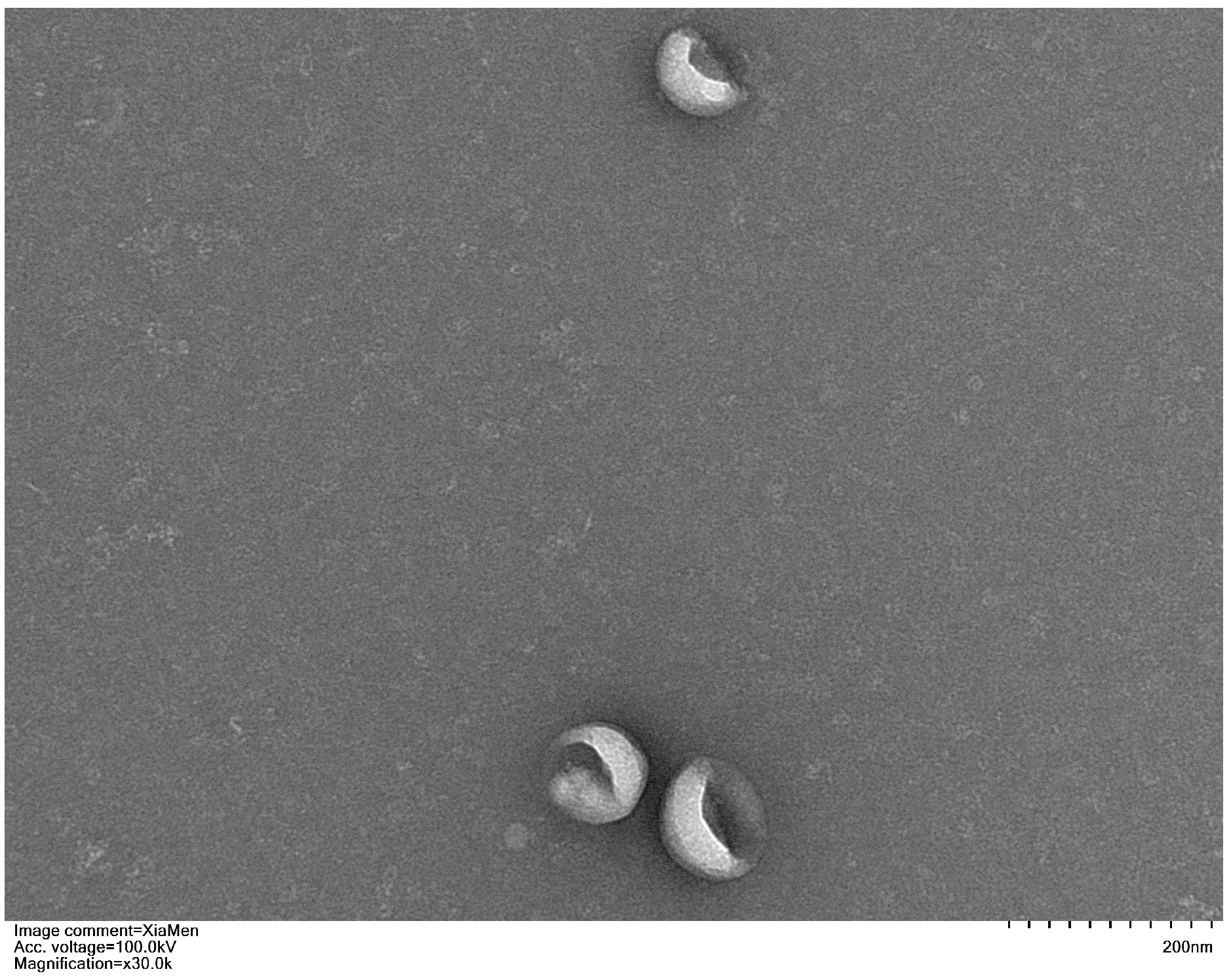
3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis of Exosomes
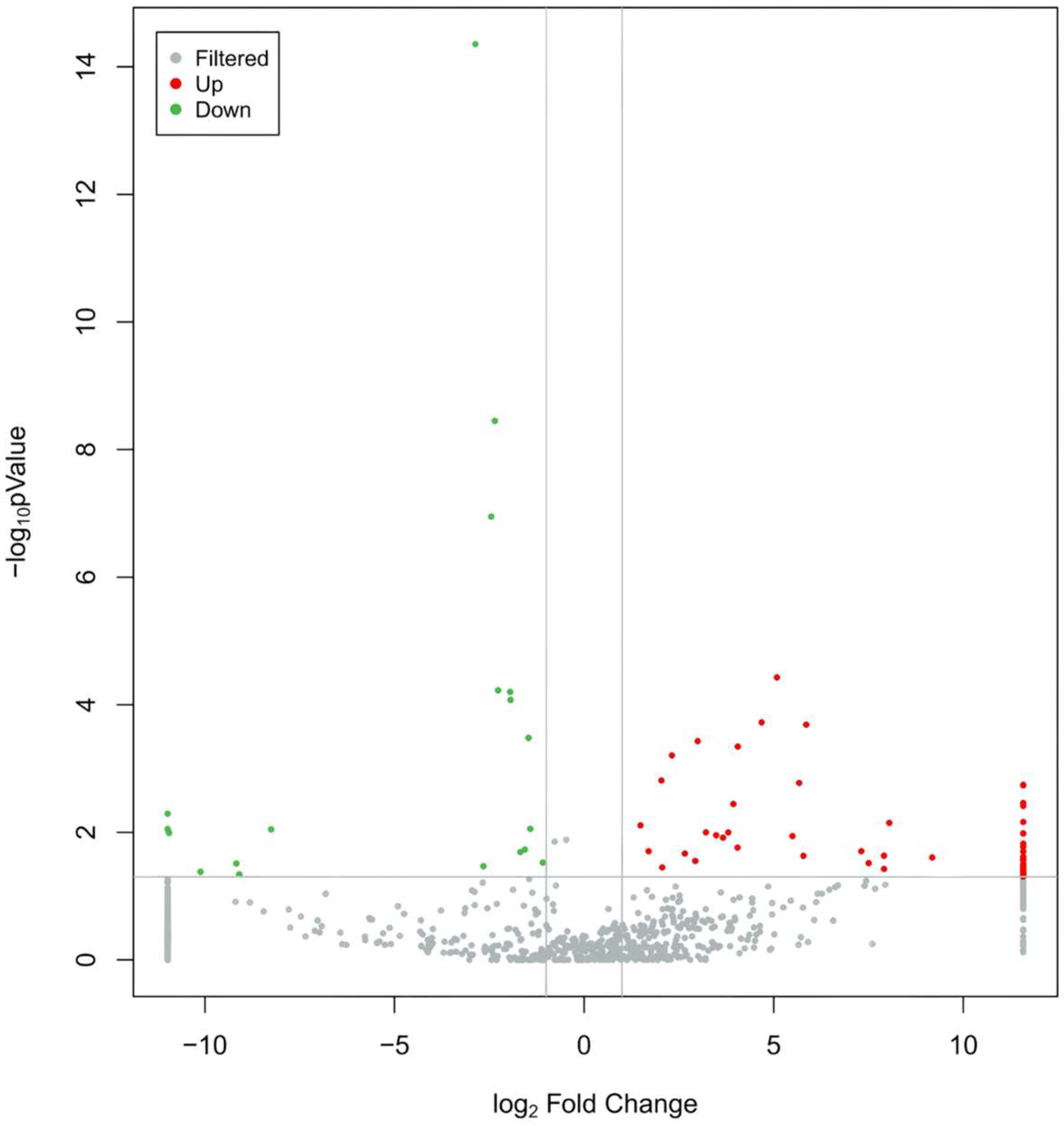
3.3. Differential Expression of Exosomal miRNAs Between MUD and HC
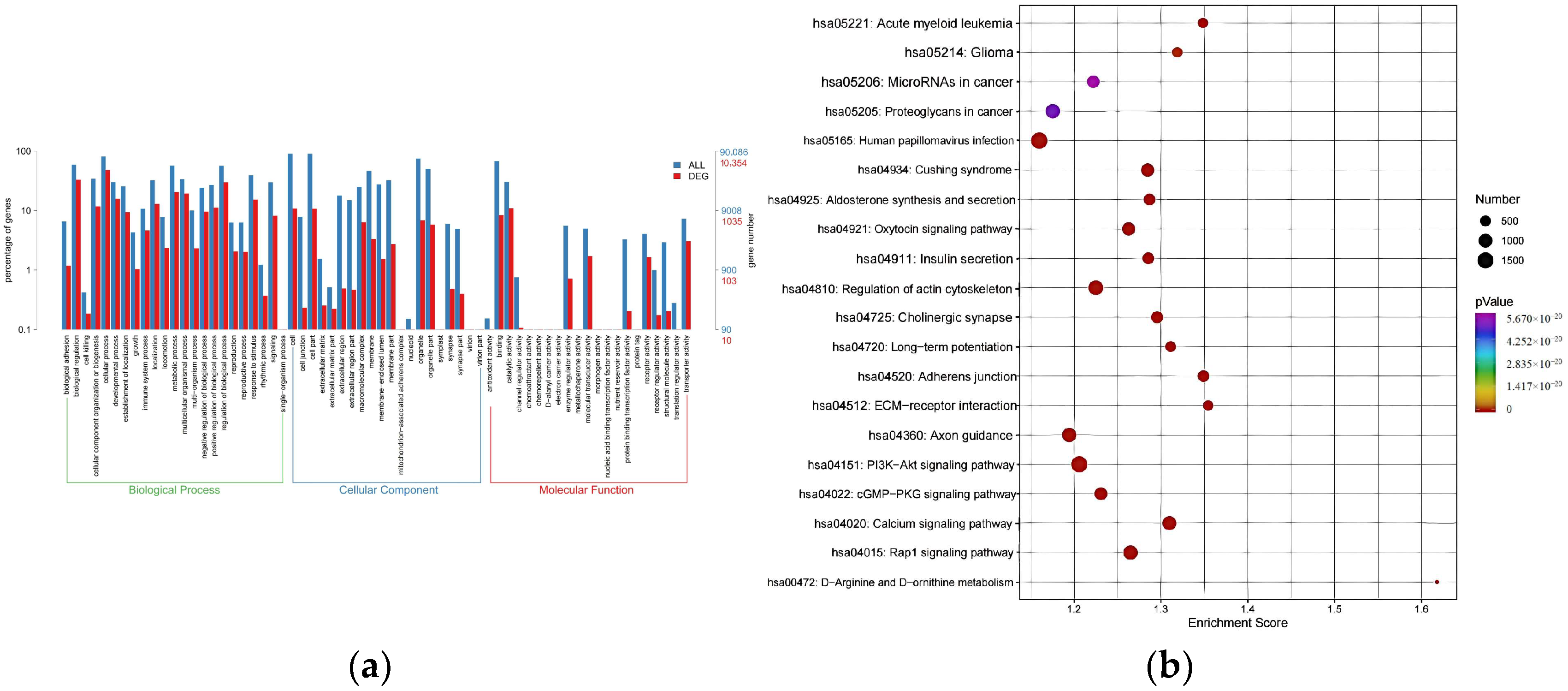
3.4. Potential Regulatory Roles of DE-miRNAs
3.5. Selection of Target Exosomal miRNAs
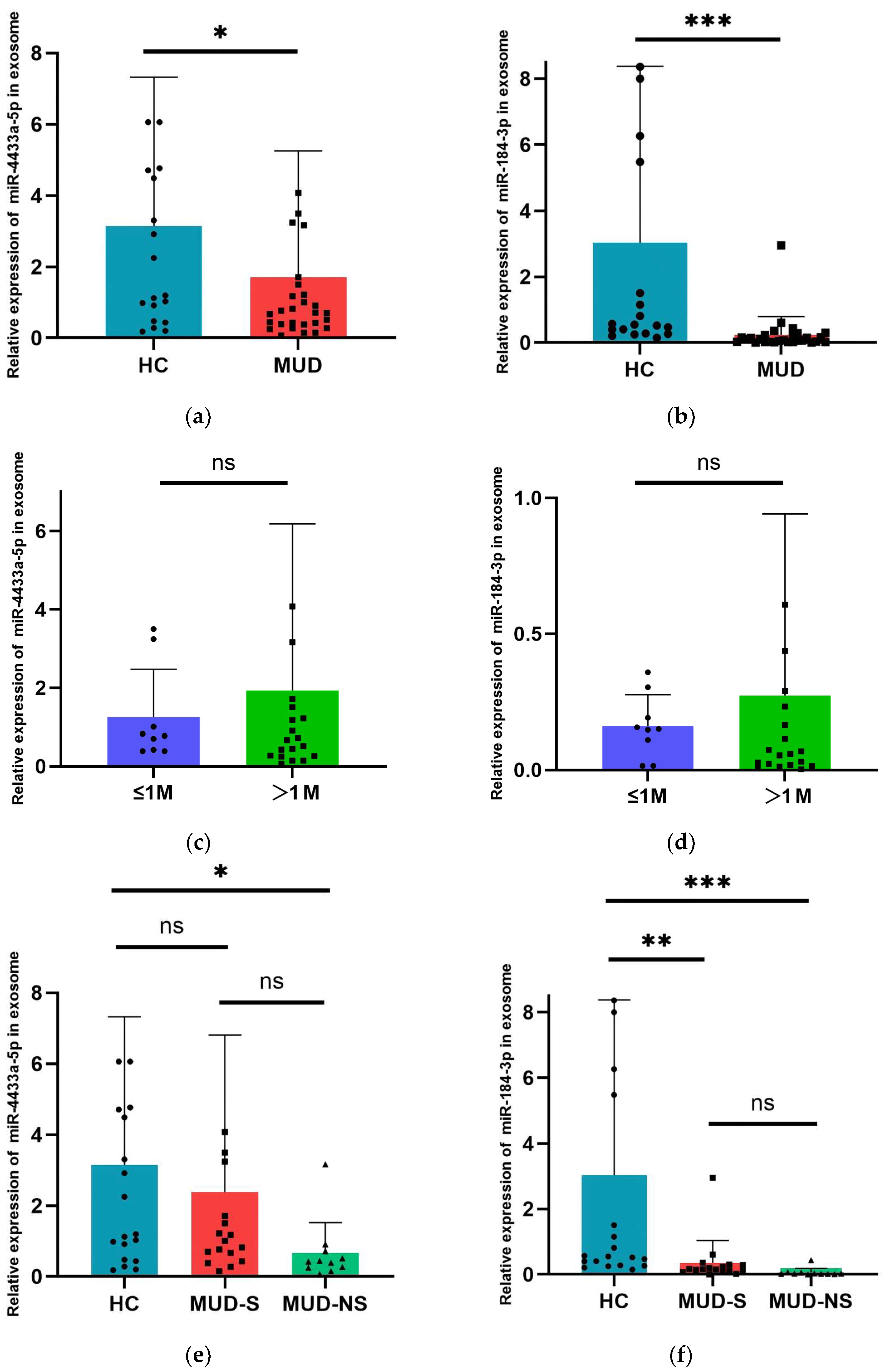
3.6. Alteration of Exosomal miR-4433a-5p and miR-184-3p Expression in MUD Patients
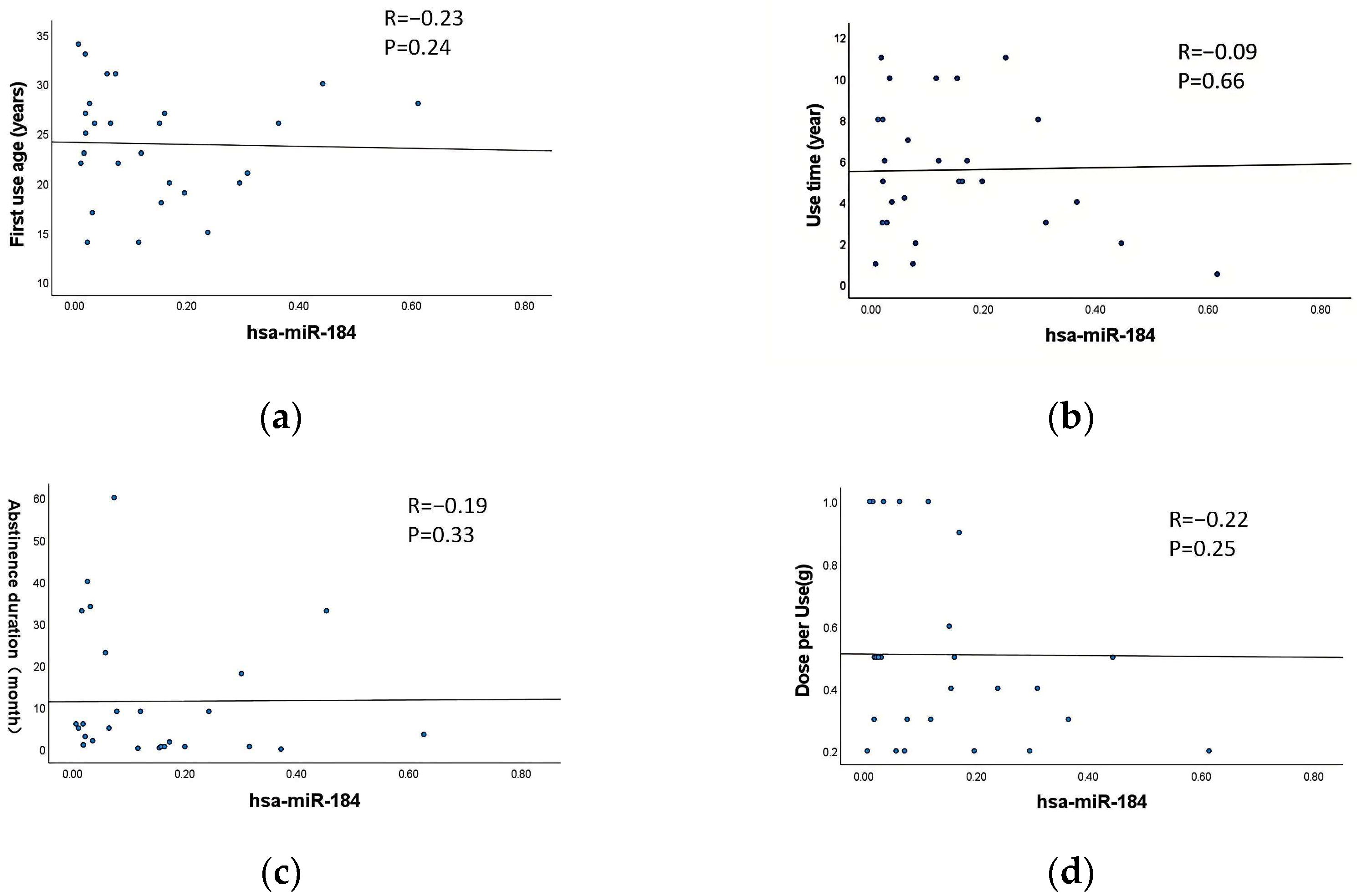
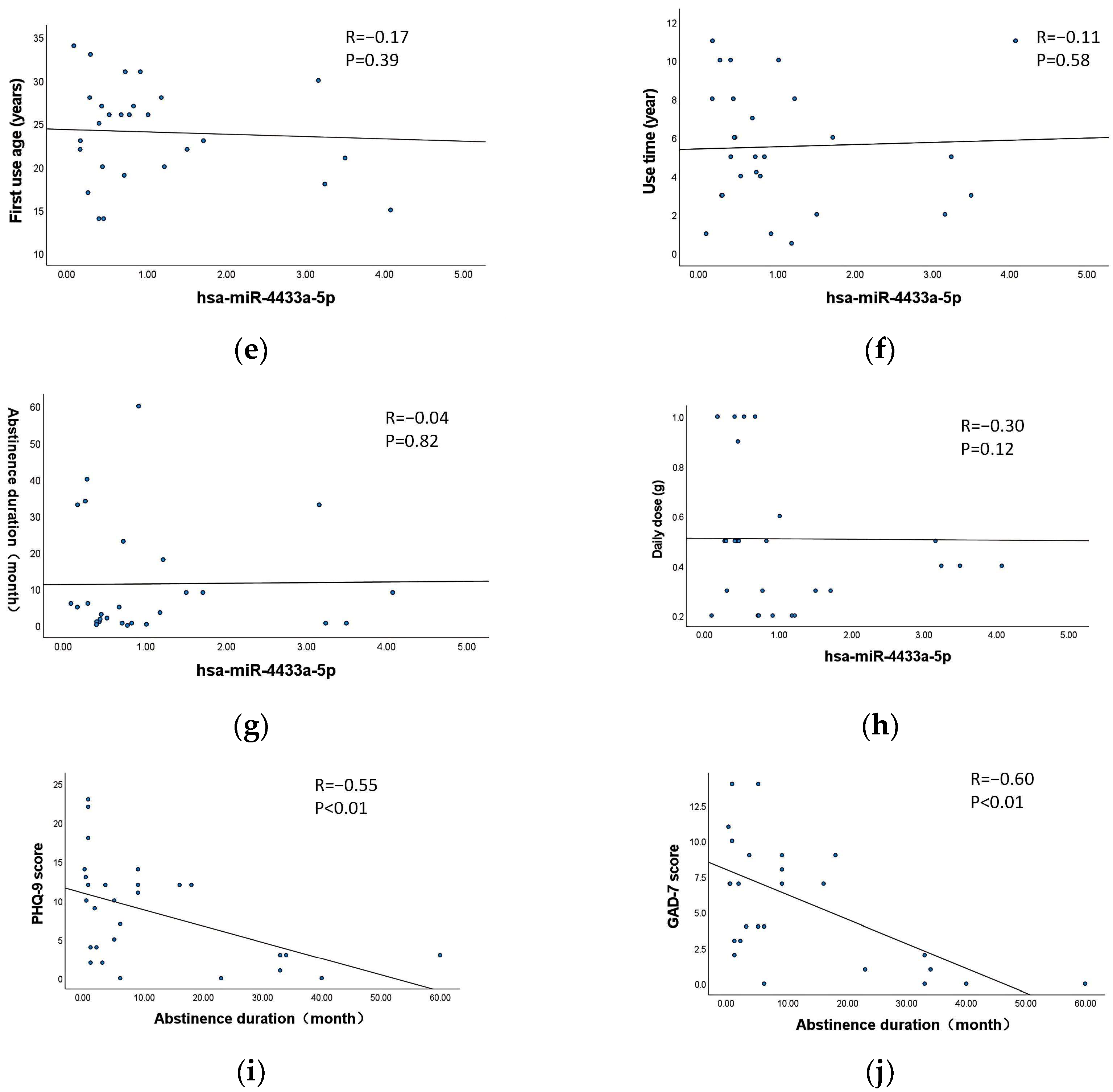
3.7. Correlation Between Exosomal DE-miRNAs and the Characteristics of MA Use
3.8. Correlation Between Withdrawal Duration and the Scores of PHQ-9 and GAD-7
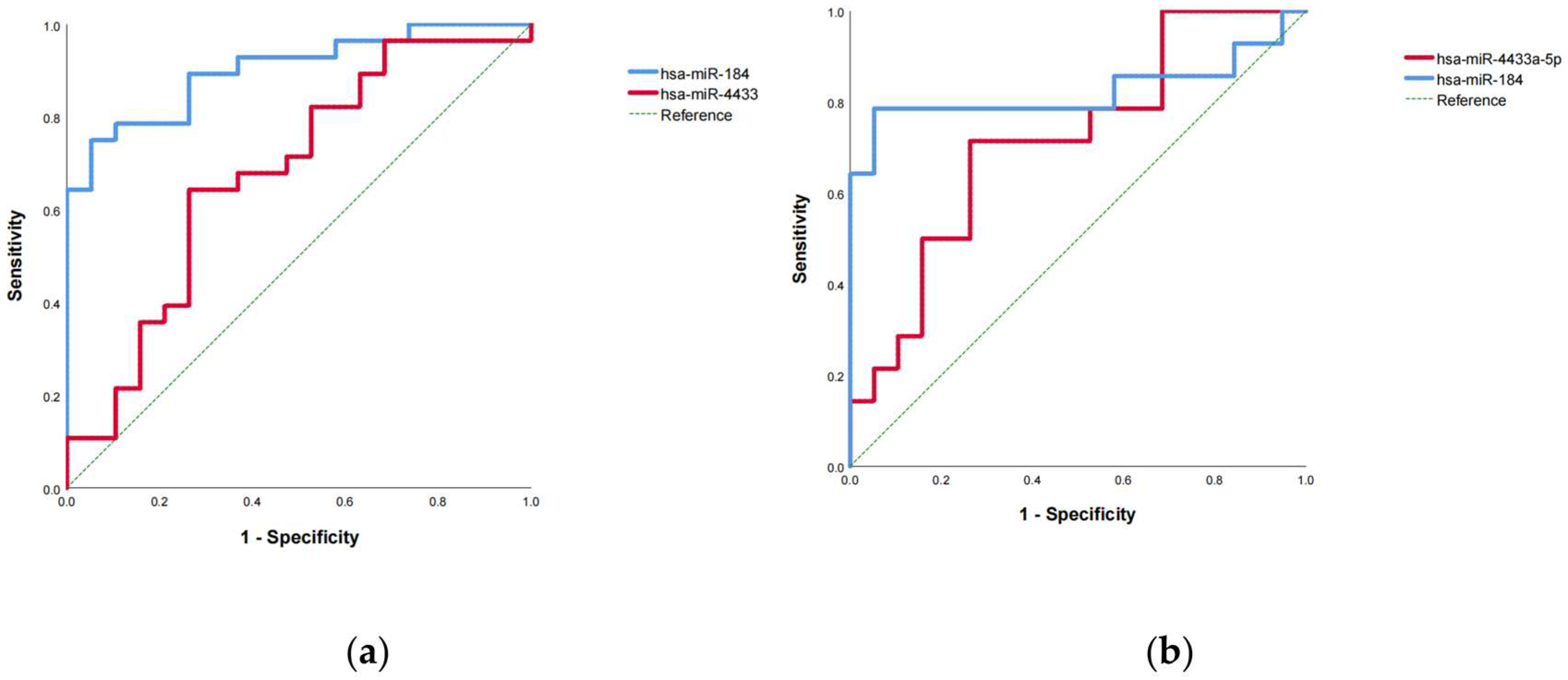
3.9. Diagnostic Accuracy of miR-4433a-5p and miR-184-3p as Diagnostic Biomarkers
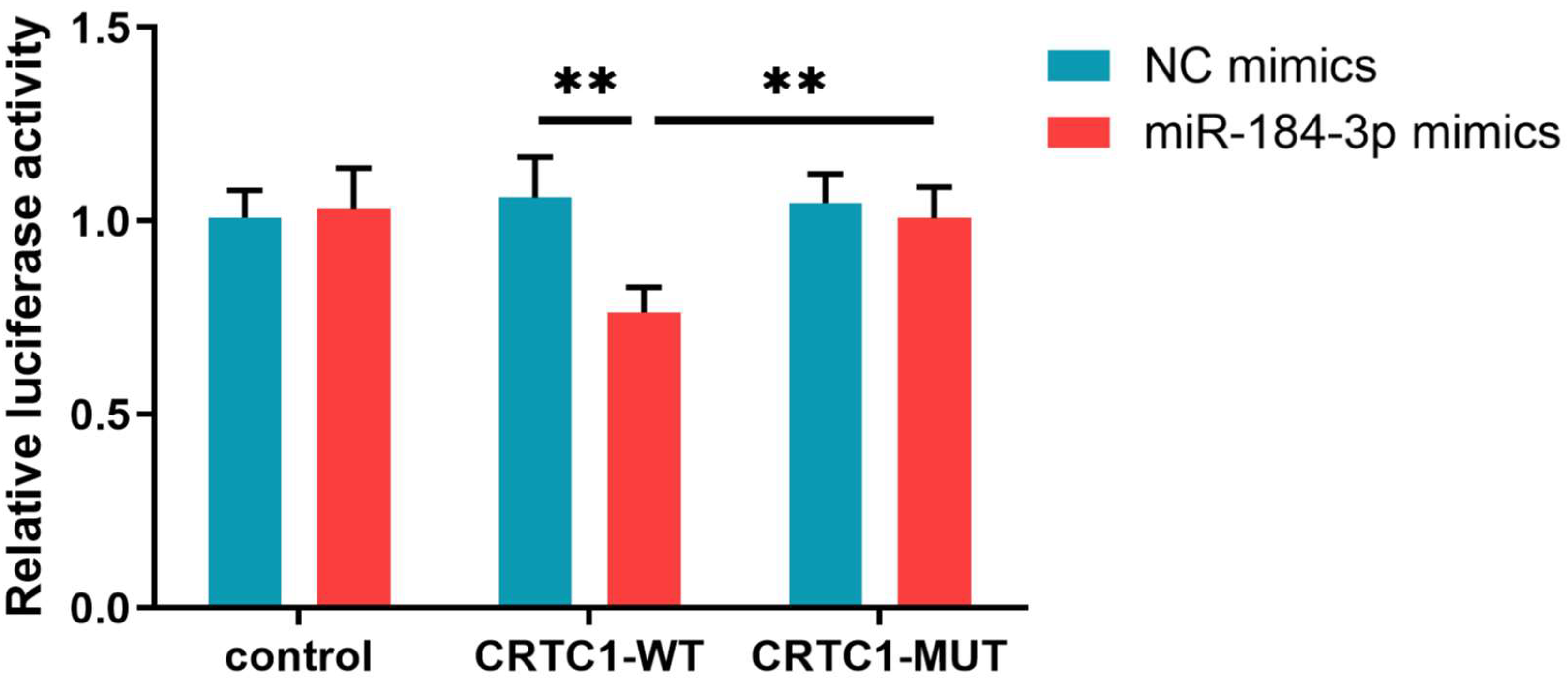
3.10. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MUD | Methamphetamine use disorder |
| HC | Healthy control |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic curve |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| MA | Methamphetamine |
| SUD | Substance use disorder |
| PHQ-9 | Patient Health Questionnaire-9 |
| GAD-7 | Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale |
| LTP | Long-term potentiation |
| CREB | cAMP response element binding protein |
| CRTC1 | CREB regulated transcription coactivator 1 |
References
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. World Drug Report 2024. Accessed: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/world-drug-report-2024.html (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Cruickshank, C.C.; Dyer, K.R. A review of the clinical pharmacology of methamphetamine. Addiction 2009, 104, 1085–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, A.C.; Ma, Y.; Marshall, F.M.; London, E.D. An evaluation of the evidence that methamphetamine abuse causes cognitive decline in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, N.J.; Han, E. A commentary on the effects of methamphetamine and the status of methamphetamine abuse among youths in South Korea, Japan, and China. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 286, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Fowler, J.S.; Wang, G.J.; Swanson, J.M.; Telang, F. Distribution and pharmacokinetics of methamphetamine in the human body: Clinical implications. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, G.P.; Henshall, D.C. MicroRNAs as regulators of brain function and targets for treatment of epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.I.; Kenny, P.J. MicroRNAs in neuronal function and dysfunction. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krützfeldt, J.; Stoffel, M. MicroRNAs: A new class of regulatory genes affecting metabolism. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.Y.; Hwang, T.J.; Tsai, G.E.; Tsai, S.J. MicroRNA expression aberration as potential peripheral blood biomarkers for schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smaele, E.; Ferretti, E.; Gulino, A. MicroRNAs as biomarkers for CNS cancer and other disorders. Brain Res. 2010, 1338, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J. Evidence for selective microRNAs and their effectors as common long-term targets for the actions of mood stabilizers. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunsberger, J.G.; Stahl, D.R.; Wolkowitz, O.M.; Spiegel, D.R.; Burke, H.M.; Epel, E.S.; Reus, V.I.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Mahan, L.C.; Young, M.S. MicroRNAs in mental health: From biological underpinnings to potential therapies. Neuromol. Med. 2009, 11, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, J.L. New insights into the roles of microRNAs in drug addiction and neuroplasticity. Genome Med. 2010, 2, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, G.; Guzel, E.; Creighton, C.J.; Ozturk, Y.E.; Kucuk, C.; Asliyuksek, H. MDMA Abuse in Relation to MicroRNA Variation in Human Brain Ventral Tegmental Area and Nucleus Accumbens. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 1989–1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, H.; Du, J.; Na, Z.; Hao, W. Decreased Expression of Plasma MicroRNA in Patients with Methamphetamine (MA) Use Disorder. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, C.; Sun, G.; Qiu, C.; Fan, J.; Jin, Y. Increased expression of plasma mir-9-3p and let-7b-3p in methamphetamine use disorder and its clinical significance. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.J.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, C. Altered serum microRNA expression profile in subjects with heroin and methamphetamine use disorder. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocucci, E.; Meldolesi, J. Ectosomes and exosomes: Shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthikumar, S.; Chisanga, D.; Ariyaratne, H.; Alahakoon, D.; Harsha, C.; de Fonseka, N.; Perera, A.; Liyanage, T.; Opathella, N.; Nirmalathas, A.; et al. ExoCarta: A Web-Based Compendium of Exosomal Cargo. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.; Keerthikumar, S.; Ang, C.S.; Gangoda, L.; Quek, C.Y.; Williamson, N.A.; Mourad, O.; Alajez, N.M.; Simpson, R.J.; Salim, A.S. Vesiclepedia 2019: A compendium of RNA, proteins, lipids and metabolites in extracellular vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D516–D519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Balkom, B.W.; Eising, E.; van Dalum, G.; Waasdorp, T.; van der Pol, E.; van Leeuwen, J.; van der Vos, K.E.; Wauben, M.H.M.; Stoorvogel, W. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of small RNAs in human endothelial cells and exosomes provides insights into localized RNA processing, degradation and sorting. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasda, E.; Parker, R. Circular RNAs co-precipitate with extracellular vesicles: A possible mechanism for circRNA clearance. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, 6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Min, Y.; Sinha, A.; Lee, Q.Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L. Elucidation of Exosome Migration across the Blood-Brain Barrier Model In Vitro. Cell Mol. Bioeng. 2016, 9, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Li, X. Macrophage exosomes as natural nanocarriers for protein delivery to inflamed brain. Biomaterials 2017, 142, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X. Characteristics and Roles of Exosomes in Cardiovascular Disease. DNA Cell Biol. 2017, 36, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, F.; Li, Q. Exosomes as Diagnostic Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 998, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kanninen, K.M.; Puhakka, S.; Pulkki, K.; Ylä-Herttuala, S. Exosomes as new diagnostic tools in CNS diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitts, C.A.; Boriack, R.L.; Kline, E.R.; Boriack, J.L.; Kline, D.E. Exploiting Exosomes in Cancer Liquid Biopsies and Drug Delivery. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2019, 8, e1801268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, L.; Vassalli, G. Exosomes: Therapy delivery tools and biomarkers of diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 174, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, S.W.; Nguyen, J. Exosomes as therapeutics: The implications of molecular composition and exosomal heterogeneity. J. Control Release 2016, 228, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X. Comprehensive toxicity and immunogenicity studies reveal minimal effects in mice following sustained dosing of extracellular vesicles derived from HEK293T cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1324730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendt, M.; Kuo, J.S.; Marsh, J.C.; Wang, J.; Patel, S.A.; Kuo, S.M.; Qiao, X.; Zhao, Y.D.; Chen, I.Y.; Gimble, J.M.; et al. Generation and testing of clinical-grade exosomes for pancreatic cancer. JCI Insight. 2018, 3, e99263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordelas, L.; Rebmann, V.; Ludwig, A.K.; Radtke, S.; Ruesing, J.; Doeppner, T.R.; Epple, M.; Horn, P.A.; Beelen, D.W.; Giebel, B. MSC-derived exosomes: A novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia 2014, 28, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Li, X. Circulating plasma and exosome levels of the miR-320 family as a non-invasive biomarker for methamphetamine use disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1160341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K.; Spitzer, R.L.; Williams, J.B. The PHQ-9: Validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2001, 16, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, C.; Ma, Y.; Cui, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) in the general population. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2014, 36, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, R.L.; Kroenke, K.; Williams, J.B.W.; Löwe, B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, L.A.; Brown, T.A. Psychometric properties of the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale-7 (GAD-7) in outpatients with anxiety and mood disorders. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2017, 39, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, K.A.; Steinmann, M.; Magistretti, P.J.; Halfon, O.; Cardinaux, J.R. TORC1 is a calcium- and cAMP-sensitive coincidence detector involved in hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4700–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Green, T.A.; Huang, Y.; Wu, G.Y. Requirement of TORC1 for late-phase long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e0000016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.W.; Li, J.; Li, X. MiR-184-3p in the paraventricular nucleus participates in the neurobiology of depression via regulation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis. Neuropharmacology 2024, 260, 110129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Li, J.; Li, X. A Research of Methamphetamine Induced Psychosis in 1430 Individuals with Methamphetamine Use Disorder: Clinical Features and Possible Risk Factors. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, C.; Roberts, A.J.; Batten, A.; Hermann, D. The nature, time course and severity of methamphetamine withdrawal. Addiction 2005, 100, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, J.; London, E.D.; Berman, S.M.; Mandelkern, M.A.; Bartzokis, G.; Huang, Y.T.; Hwang, J.S.; Ling, W. Open-label pilot study of modafinil for methamphetamine dependence. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2009, 29, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salo, R.; Nordahl, T.E.; Natsuaki, M.; Galloway, G.P.; Moore, C.D.; Buonocore, M.H.; Gouzoulis-Mayfrank, E.; Daumann, J. Psychiatric comorbidity in methamphetamine dependence. Psychiatry Res. 2011, 186, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasner-Edwards, S.; Mooney, L.J.; Rawson, R.A.; Ling, W. Anxiety disorders among methamphetamine dependent adults: Association with post-treatment functioning. Am. J. Addict. 2010, 19, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.; Colledge, S.M.; Hall, W.D.; Whiteford, H.A. Methamphetamine exposure and depression-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol. Rev. 2023, 42, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.C.K.; Chui, W.H.; Chan, P.C.W. Causal inference with observational data in addiction research. Addiction 2022, 117, 2736–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, Z.; Kollins, S.H.; McClernon, F.J.; Calhoun, V.D. A narrative systematic review of associations and temporality between use of methamphetamine, ecstasy/MDMA, or cocaine with anxiety or depressive symptoms. Addict. Behav. 2024, 153, 107988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorick, T.; Nestor, L.; Miotto, K.; Rawson, R. Withdrawal symptoms in abstinent methamphetamine-dependent subjects. Addiction 2010, 105, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellem, T.L. A Review of Methamphetamine Dependence and Withdrawal Treatment: A Focus on Anxiety Outcomes. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2016, 71, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, Z.; Kollins, S.H.; McClernon, F.J.; Calhoun, V.D. Health Service Use for Mental Health Reasons in a Cohort of People Who Use Methamphetamine Experiencing Moderate to Severe Anxiety or Depression. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2024, 22, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieco, G.E.; Kwon, N.J.; Han, E.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.H. Reduced miR-184-3p expression protects pancreatic β-cells from lipotoxic and proinflammatory apoptosis in type 2 diabetes via CRTC1 upregulation. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conkright, M.D.; Gu, Z.; Flechner, L.; Su, S.; Girard, J.M.; Sealy, L.; Gunton, J.E.; Kahn, C.R.; Montminy, M. TORCs: Transducers of regulated CREB activity. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iourgenko, V.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Li, J. Identification of a family of cAMP response element-binding protein coactivators by genome-scale functional analysis in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12147–12152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gu, Z.; Gu, Z. The insulin-regulated CREB coactivator TORC promotes stress resistance in Drosophila. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, W.; Morantte, I.; Rodrigues, A.P.; Manning, G.; Bennett, K.; Ruvkun, G.; Walker, D.W. Lifespan extension induced by AMPK and calcineurin is mediated by CRTC-1 and CREB. Nature 2011, 470, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gu, Z.; Gu, Z. TORC1 regulates activity-dependent CREB-target gene transcription and dendritic growth of developing cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2334–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollander, J.A.; Im, H.I.; Amelio, A.L.; Kocerha, J.; Bali, P.; Lu, Q.; Willoughby, D.; Conkright, M.D.; Blendy, J.A.; Steffan, J.S. Striatal microRNA controls cocaine intake through CREB signaling. Nature 2010, 466, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachostergios, P.J.; Ntoufa, S.; Kastrinaki, M.C.; Chatzaki, E.; Kotsantis, P.; Koutsilieris, M. Non-Invasive miRNA Profiling for Differential Diagnosis and Prognostic Stratification of Testicular Germ Cell Tumors. Genes 2024, 15, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, J.; Li, X. A novel m7G-related miRNA prognostic signature for predicting clinical outcome and immune microenvironment in colon cancer. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 6086–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, J.; Li, X. Exosomal MicroRNA signature acts as an efficient biomarker for non-invasive diagnosis of gallbladder carcinoma. iScience 2022, 25, 104816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X. Proteomic analysis and microRNA expression profiling of plasma-derived exosomes in primary immune thrombocytopenia. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 194, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Li, J.; Li, X. Differential miRNA Profiling Reveals miR-4433a-5p as a Key Regulator of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Progression via PIK3R2-mediated Phenotypic Modulation. Comb. Chem. High. Throughput Screen. 2024, 27, 2323–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.H.; Li, J.; Li, X. Luteolin alleviates methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity by suppressing PI3K/Akt pathway-modulated apoptosis and autophagy in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, S.J.; Nestler, E.J. The addicted synapse: Mechanisms of synaptic and structural plasticity in nucleus accumbens. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, B.F.; Li, J.; Li, X. Stimuli associated with the presence or absence of amphetamine regulate cytoskeletal signaling and behavior. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Salvagno, G.L.; Montagnana, M.; Guidi, G.C. Targeting of the Arpc3 actin nucleation factor by miR-29a/b regulates dendritic spine morphology. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, S.H.; He, L.; Potula, R.; Siddiq, A.; Walter, M.F.; Burow, M.E.; Kishore, R.; Persidsky, Y. Extracellular vesicles: Mediators and biomarkers of pathology along CNS barriers. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X. Targeted exosome-mediated delivery of opioid receptor Mu siRNA for the treatment of morphine relapse. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Li, X. Prognostic serum miRNA biomarkers associated with Alzheimer’s disease shows concordance with neuropsychological and neuroimaging assessment. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, J.; Li, X. Multi-omics study reveals associations among neurotransmitter, extracellular vesicle-derived microRNA and psychiatric comorbidities during heroin and methamphetamine withdrawal. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryani, A.; Denecke, B. Exosomes as a Nanodelivery System: A Key to the Future of Neuromedicine? Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 818–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, S.; Li, J.; Li, X. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes improve neurogenesis and cognitive function of mice with methamphetamine addiction: A novel treatment approach. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | MUD (N = 28) | HC (N = 19) | t/χ2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 32.07 ± 4.39 | 30.00 ± 6.31 | −1.89 | 0.059 |
| Gender (Male) | 25 (89.29%) | 14 (73.68%) | 1.95 | 0.163 |
| Marital Status | 3.81 | 0.149 | ||
| Single | 13 (46.43%) | 11 (57.89%) | ||
| Married | 10 (35.71%) | 8 (42.11%) | ||
| Divorced | 5 (17.86%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Years of Education | 11.68 ± 2.34 | 14.53 ± 2.50 | −3.43 | 0.001 |
| Employment Status (Employed) | 20 (71.43%) | 19 (100.0%) | 6.54 | 0.011 |
| First Use age (years) | 23.82 ± 5.55 | - | - | - |
| Use time (years) | 5.60 ± 3.13 | - | - | - |
| Abstinence Duration (months) | 11.47 ± 15.34 | - | - | - |
| Dose per Use (g) | 0.51 ± 0.28 | - | - | - |
| PHQ-9 Score | 8.50 ± 6.50 | 3.89 ± 3.16 | −2.52 | 0.012 |
| GAD-7 Score | 5.96 ± 4.48 | 1.79 ± 2.15 | −3.25 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, Q.; Su, H.; Chen, T.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Shi, S.; Du, J.; Jiang, H.; et al. Peripheral Blood Exosomal miR-184-3p in Methamphetamine Use Disorder: Biomarker Potential and CRTC1-Mediated Neuroadaptation. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070479
Zhao Y, Zhao Z, Sun Q, Su H, Chen T, Xu X, Li X, Shi S, Du J, Jiang H, et al. Peripheral Blood Exosomal miR-184-3p in Methamphetamine Use Disorder: Biomarker Potential and CRTC1-Mediated Neuroadaptation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070479
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yan, Zhuoming Zhao, Qianqian Sun, Hang Su, Tianzhen Chen, Xiaomin Xu, Xiaotong Li, Sai Shi, Jiang Du, Haifeng Jiang, and et al. 2025. "Peripheral Blood Exosomal miR-184-3p in Methamphetamine Use Disorder: Biomarker Potential and CRTC1-Mediated Neuroadaptation" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070479
APA StyleZhao, Y., Zhao, Z., Sun, Q., Su, H., Chen, T., Xu, X., Li, X., Shi, S., Du, J., Jiang, H., & Zhao, M. (2025). Peripheral Blood Exosomal miR-184-3p in Methamphetamine Use Disorder: Biomarker Potential and CRTC1-Mediated Neuroadaptation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070479






