Chronic Exposure of Renal Progenitor Cells (HRTPT) to As (III) Implicates Microfibril Associated Protein 5 (MFAP5) in the Activation of Carcinoembryonic Antigen Related Cell Adhesion Molecules (CEACAM 5 and 6)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Light Microscopic Evidence Shows Fibroblast-like Growth in Human Renal Progenitor Cells at Passage (P3) and (P8)
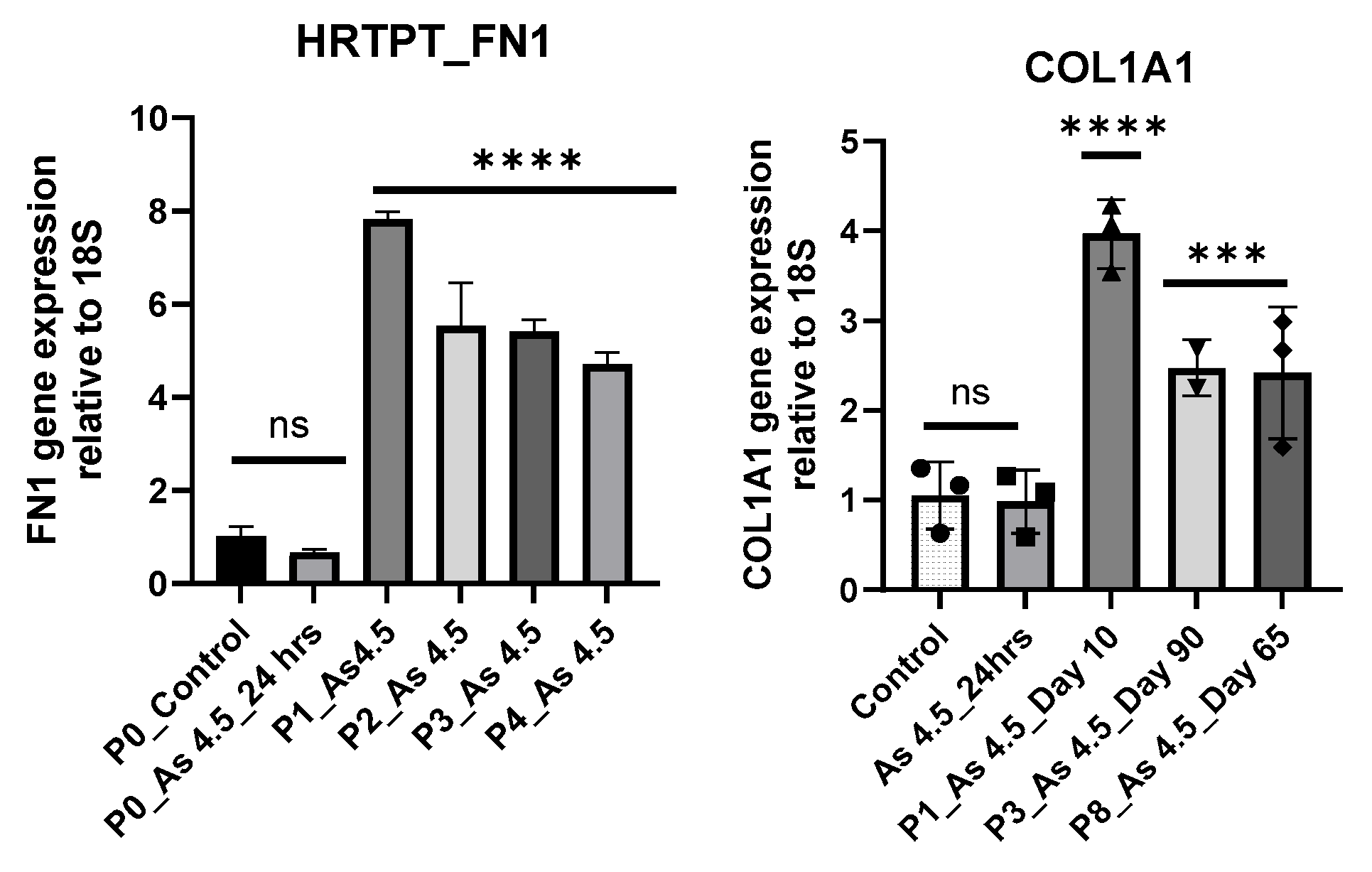
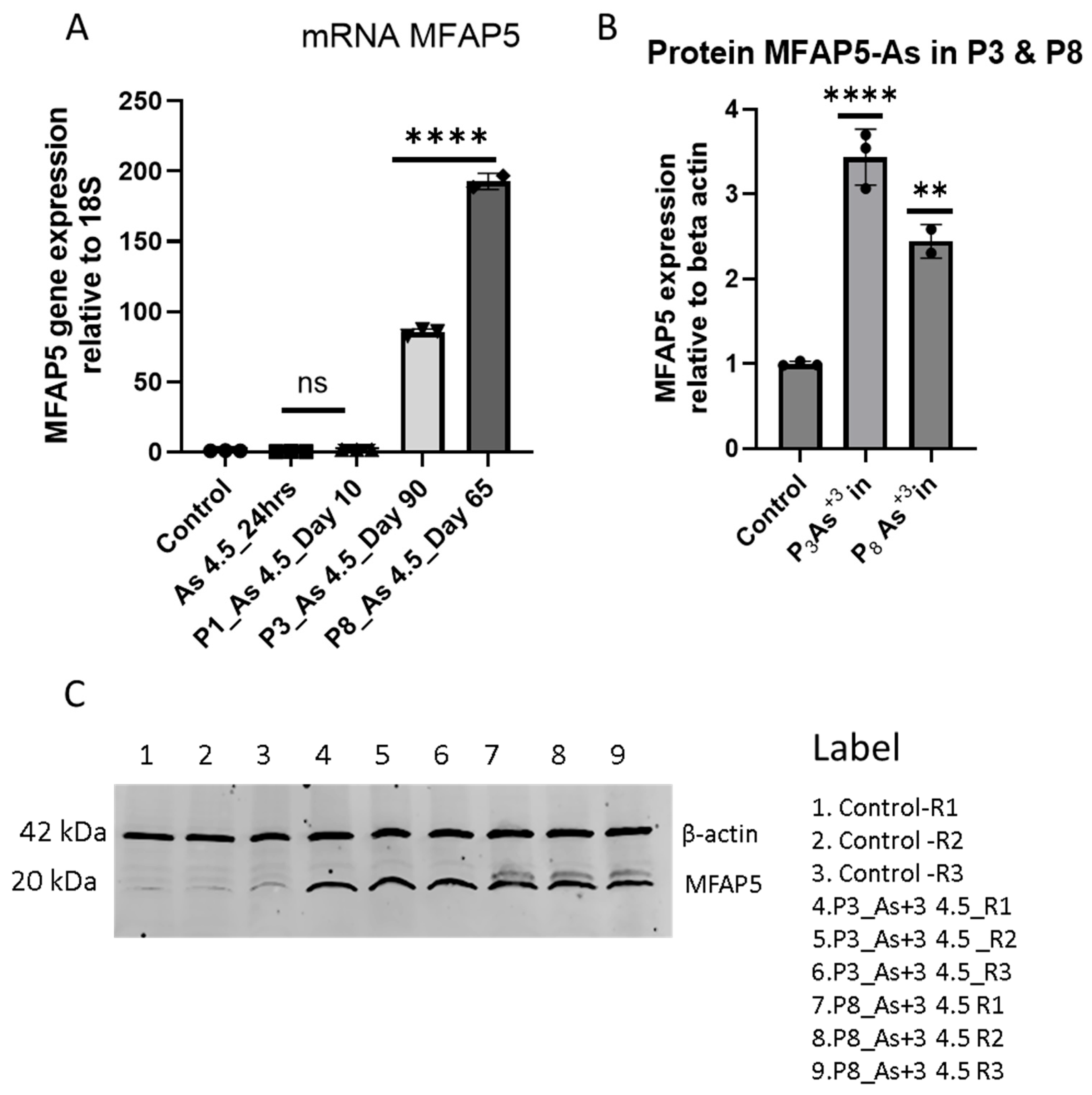
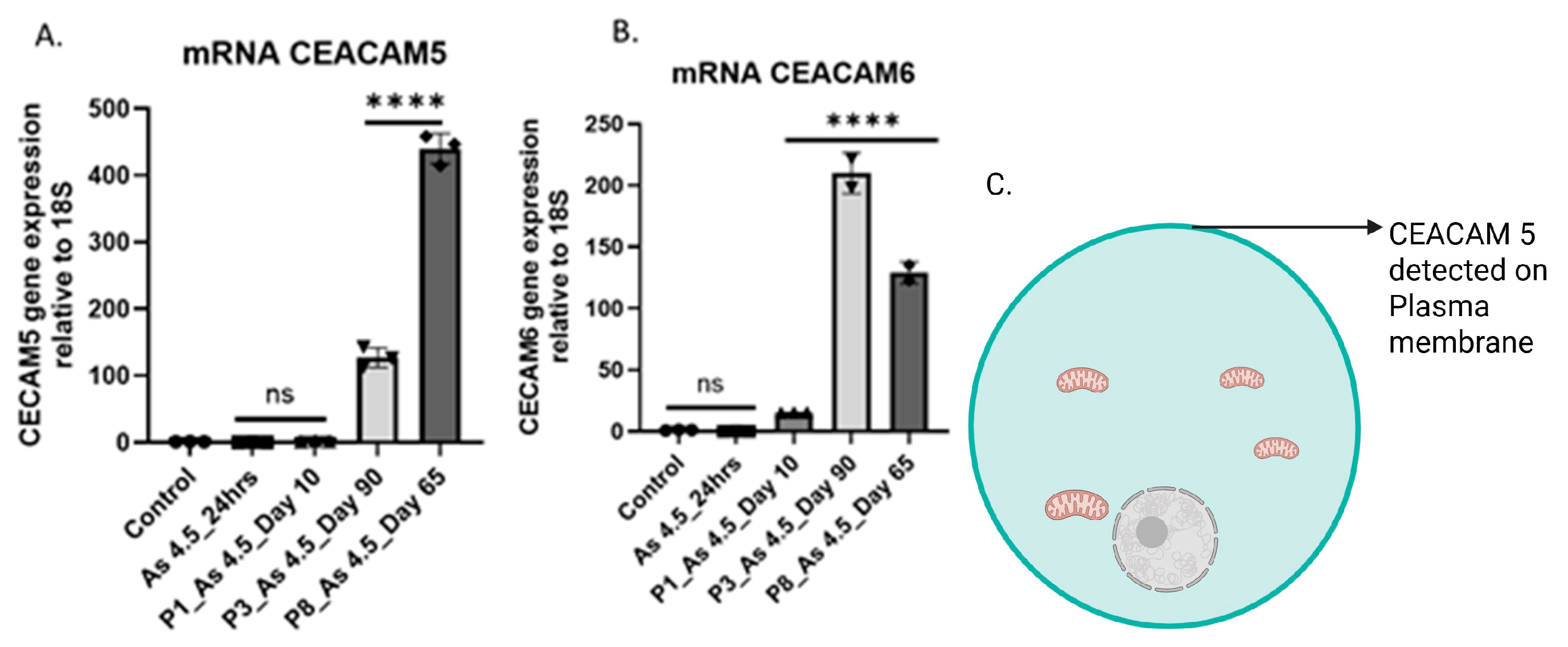
3.2. Arsenite Exposure Increased the Expression of MFAP5, CEACAM 5, and CEACAM 6
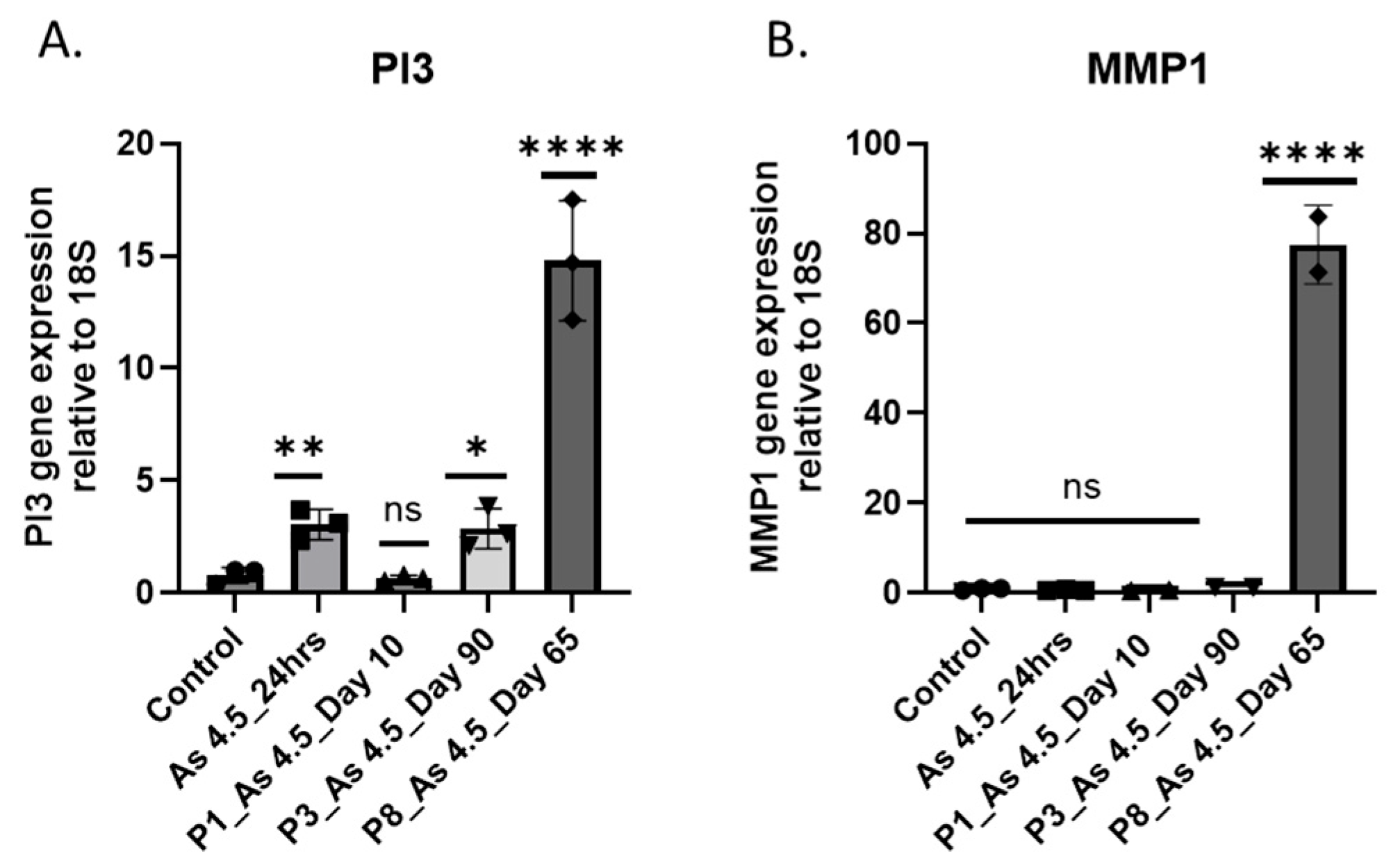
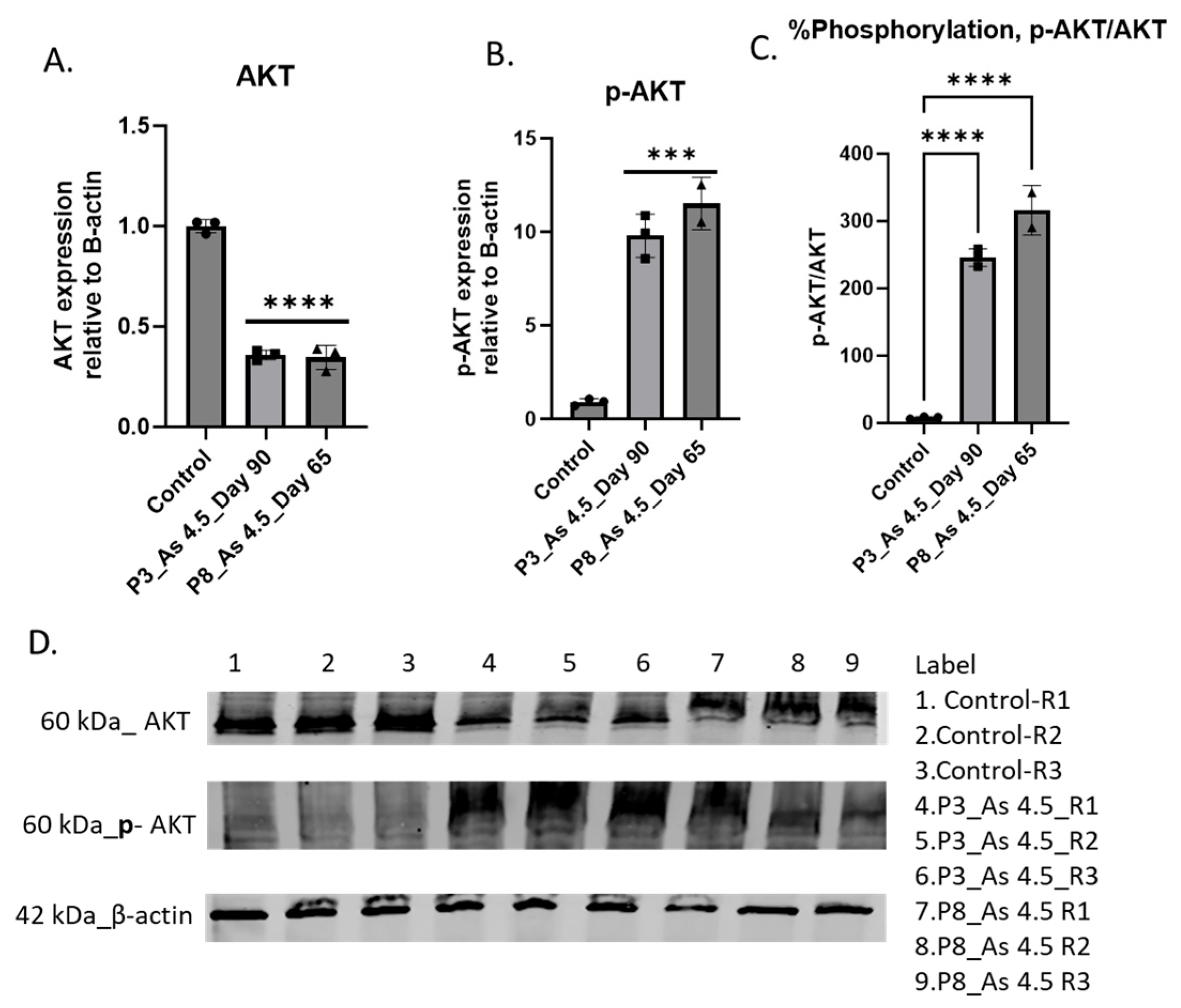
3.3. As (III) Exposure Increased the Expression of PI3K and MMP1
3.4. Determine How i-As (III) Increased the Expression of Phospho-Stress-Activated Protein Kinase/Jun N-Terminal Kinase (p-SAPK/JNK)
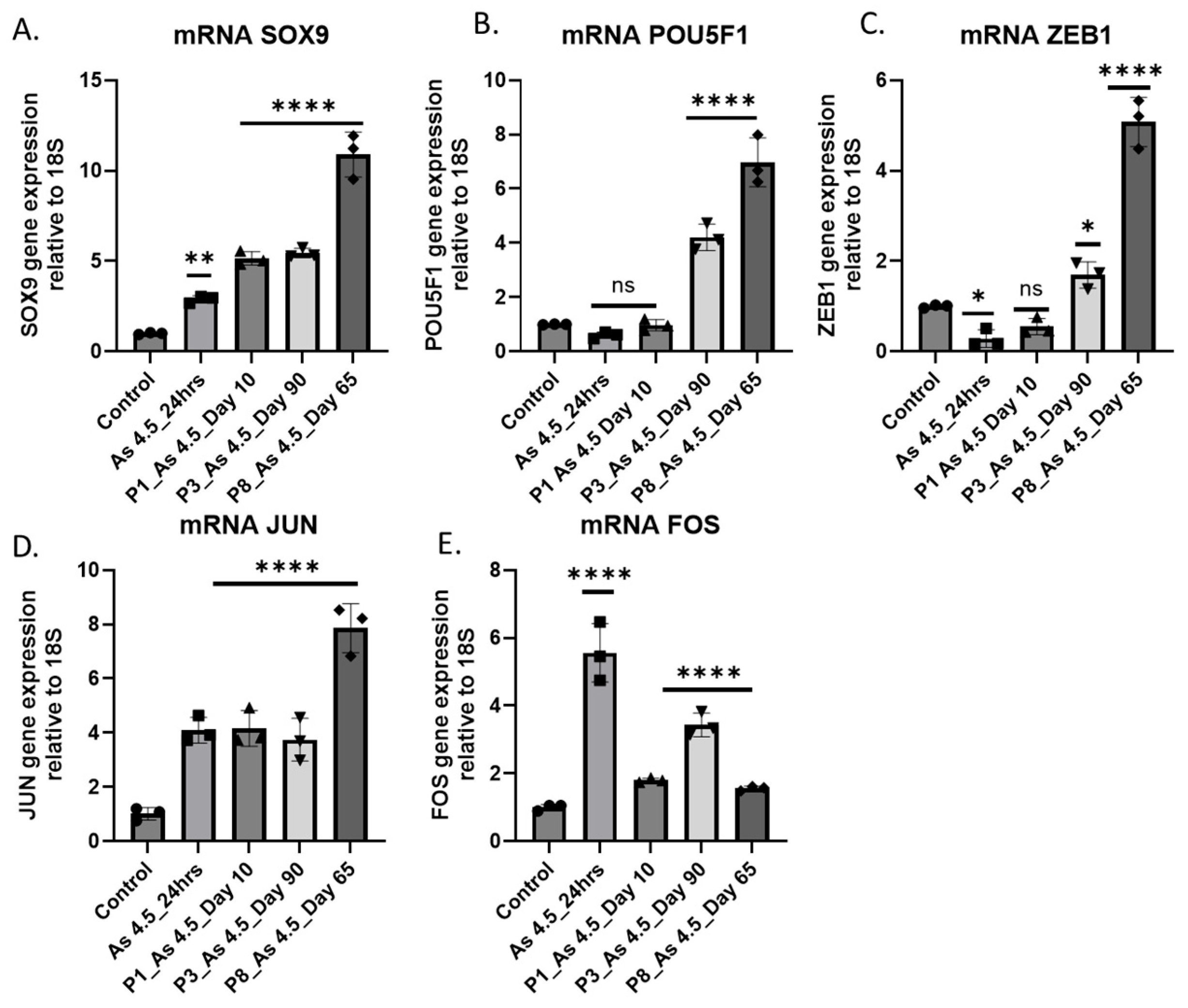
3.5. Expression of Transcription Factors (TFs) in Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Activation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| p-Value | FDR p-Value | Overall F-Test | Overall FDR F-Test | Public Gene IDs | Gene Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.42 × 10−21 | 1.16 × 10−16 | 3.11 × 10−22 | 1.05 × 10−17 | NM_001297709-12 | MFAP5 |
| 1.10 × 10−20 | 4.97 × 10−16 | 5.30 × 10−21 | 9.00 × 10−17 | NM_001306129-32 | FN1 |
| 1.94 × 10−20 | 6.57 × 10−16 | 6.44 × 10−25 | 8.74 × 10−20 | NM_000064 | C3 |
| 1.10 × 10−16 | 6.81 × 10−13 | 1.09 × 10−17 | 2.55 × 10−14 | NM_001291484 | CEACAM5 |
| 8.23 × 10−20 | 2.23 × 10−15 | 1.89 × 10−19 | 1.15 × 10−15 | NM_002483 | CEACAM6 |
| 2.22 × 10−17 | 2.52 × 10−13 | 2.04 × 10−20 | 2.13 × 10−16 | NM_004613 | TGM2 |
| 6.10 × 10−18 | 1.38 × 10−13 | 1.26 × 10−17 | 2.71 × 10−14 | NM_001128588 | SLC14A1 |
| 6.53 × 10−17 | 5.21 × 10−13 | 2.05 × 10−18 | 6.97 × 10−15 | NM_004751 | GCNT3 |
| 1.15 × 10−17 | 1.65 × 10−13 | 7.03 × 10−19 | 3.29 × 10−15 | NM_002994 | CXCL5 |
Appendix B

References
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 101, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairul, I.; Wang, Q.Q.; Jiang, Y.H.; Wang, C.; Naranmandura, H. Metabolism, toxicity and anticancer activities of arsenic compounds. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23905–23926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.-Y.; Huang, N.-C.; Chang, Y.-T.; Sung, J.-M.; Shen, K.-H.; Tsai, C.-C.; Guo, H.-R. Associations between arsenic in drinking water and the progression of chronic kidney disease: A nationwide study in Taiwan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordstrom, D.K. An Overview of Arsenic Mass-Poisoning in Bangladesh and West Bengal, India. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/publication/70198882 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Cohen, S.M.; Arnold, L.L.; Eldan, M.; Lewis, A.S.; Beck, B.D. Methylated arsenicals: The implications of metabolism and carcinogenicity studies in rodents to human risk assessment. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 99–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, N.T.; Han, D.; Xu, X.; Sansom, G.; Roh, T. Relationship between low-level arsenic exposure in drinking water and kidney cancer risk in Texas. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-S.; Song, K.-H.; Chung, J.-Y. Health effects of chronic arsenic exposure. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2014, 47, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.F.; Beck, B.D.; Chen, Y.; Lewis, A.S.; Thomas, D.J. Arsenic exposure and toxicology: A historical perspective. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 305–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayotte, J.D.; Medalie, L.; Qi, S.L.; Backer, L.C.; Nolan, B.T. Estimating the High-Arsenic Domestic-Well Population in the Conterminous United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12443–12454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/arsenic (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Arsenic in Drinking Water. Available online: https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/environment/water/docs/contaminants/arsenicfactsht.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Farkhondeh, T.; Naseri, K.; Esform, A.; Aramjoo, H.; Naghizadeh, A. Drinking water heavy metal toxicity and chronic kidney diseases: A systematic review. Rev. Environ. Health 2021, 36, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012; NBK547852.
- Thakkar, S.; Chen, M.; Fang, H.; Liu, Z.; Roberts, R.; Tong, W. The Liver Toxicity Knowledge Base (LKTB) and drug-induced liver injury (DILI) classification for assessment of human liver injury. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 12, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahter, M.; Concha, G. Role of metabolism in arsenic toxicity. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 89, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curthoys, N.P.; Moe, O.W. Proximal tubule function and response to acidosis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-Y.; Chang, Y.-T.; Cheng, H.-L.; Shen, K.-H.; Sung, J.-M.; Guo, H.-R. Associations between arsenic in drinking water and occurrence of end-stage renal disease with modifications by comorbidities: A nationwide population-based study in Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, G.A.; Pérez, R.D.; Mardirosian, M.; Pérez, C.A.; Marguí, E.; Queralt, I. Comprehensive analysis of renal arsenic accumulation using images based on X-ray fluorescence at the tissue, cellular, and subcellular levels. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2019, 150, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Hsueh, Y.M.; Lai, M.S.; Shyu, M.P.; Chen, S.Y.; Wu, M.M.; Kuo, T.L.; Tai, T.Y. Increased prevalence of hypertension and long-term arsenic exposure. Hypertension 1995, 25, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Jacques, N.; Parker, L.; Brown, P.; Dummer, T.J. Arsenic in drinking water and urinary tract cancers: A systematic review of 30 years of epidemiological evidence. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.H.; Hopenhayn-Rich, C.; Bates, M.N.; Goeden, H.M.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Duggan, H.M.; Wood, R.; Kosnett, M.J.; Smith, M.T. Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 1992, 97, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, M.G.; Cherry, N. Arsenic in drinking water and renal cancers in rural Bangladesh. Occup. Environ. Med. 2013, 70, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pershagen, G. The carcinogenicity of arsenic [Pesticides, drinking water]. Environ. Health Perspect. 1981, 40, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, H. Arsenic Exposure in Drinking Water and Occurrence of Chronic Kidney Disease: The Association and Effect Modifications by Comorbidities. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 3, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts and Figures 2024. American Cancer Society. 2024. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/2024-cancer-facts-figures.html (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Andrianova, N.V.; Buyan, M.I.; Zorova, L.D.; Pevzner, I.B.; Popkov, V.A.; Babenko, V.A.; Silachev, D.N.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; Zorov, D.B. Kidney Cells Regeneration: Dedifferentiation of Tubular Epithelium, Resident Stem Cells and Possible Niches for Renal Progenitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsuyanim, S.; Harari-Steinberg, O.; Buzhor, E.; Omer, D.; Pode-Shakked, N.; Ben-Hur, H.; Halperin, R.; Schneider, D.; Dekel, B. Expression of stem cell markers in the human fetal kidney. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, B.; Boor, P.; Dijkman, H.; Sharma, S.V.; Jirak, P.; Mooren, F.; Berger, K.; Bornemann, J.; Gelman, I.H.; Floege, J.; et al. Proximal tubular cells contain a phenotypically distinct, scattered cell population involved in tubular regeneration. J. Pathol. 2013, 229, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, M.; Darabi, S.; Roozbahany, N.A.; Abbaszadeh, H.A.; Moghadasali, R. Great potential of renal progenitor cells in kidney: From the development to clinic. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 434, 113875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.; Garrett, S.H.; Somji, S.; Schaefer, K.; Bansal, B.; Gill, J.S.; Singhal, S.K.; Sens, D.A. Arsenite Exposure to Human RPCs (HRTPT) Produces a Reversible Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT): In-Vitro and In-Silico Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Singhal, S.; Kalonick, M.; Guyer, R.; Volkert, A.; Somji, S.; Garrett, S.H.; Sens, D.A.; Singhal, S.K. Role of HRTPT in kidney proximal epithelial cell regeneration: Integrative differential expression and pathway analyses using microarray and scRNA-seq. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 10466–10479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Somji, S.; Sens, D.A.; Slusser-Nore, A.; Patel, D.H.; Savage, E.; Garrett, S.H. Human renal tubular cells contain CD24/CD133 progenitor cell populations: Implications for tubular regeneration after toxicant induced damage using cadmium as a model. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 331, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Garrett, S.H.; Sens, D.A.; Zhou, X.D.; Guyer, R.; Somji, S. Characterization and determination of cadmium resistance of CD133+/CD24+ and CD133−/CD24+ cells isolated from the immortalized human proximal tubule cell line, RPTEC/TERT1. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 375, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehus, A.A.; Jones, M.; Trahan, M.; Kinnunen, K.; Berwald, K.; Lindner, B.; Al-Marsoummi, S.; Zhou, X.D.; Garrett, S.H.; Sens, D.A.; et al. Pevonedistat Inhibits SOX2 Expression and Sphere Formation but Also Drives the Induction of Terminal Differentiation Markers and Apoptosis within Arsenite-Transformed Urothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhou, X.D.; Sens, M.A.; Garrett, S.H.; Zheng, Y.; Dunlevy, J.R.; Sens, D.A.; Somji, S. Keratin 6 expression correlates to areas of squamous differentiation in multiple independent isolates of As+3-induced bladder cancer. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasiou, A.D.; Peroukidis, S.; Sirinian, C.; Arkoumani, E.; Chaniotis, D.; Zizi-Sermpetzoglou, A. CD44 Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC) Correlates with Tumor Grade and Patient Survival and Is Affected by Gene Methylation. Genes 2024, 15, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, D.J.; Simon, M.C. Genetic and metabolic hallmarks of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2018, 1870, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sene, A.P.; Hunt, L.; McMahon, R.F.; Carroll, R.N. Renal carcinoma in patients undergoing nephrectomy: Analysis of survival and prognostic factors. Br. J. Urol. 1992, 70, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Xu, W.H.; Ren, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.K.; Cao, D.L.; Shi, G.H.; Qu, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Ye, D.W. Prognostic value of epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Aging 2020, 12, 866–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ying, H.; Xu, J.; Yang, H.; Sun, K.; He, L.; Li, M.; Ji, Y.; Liang, T.; et al. Targeting MFAP5 in cancer-associated fibroblasts sensitizes pancreatic cancer to PD-L1-based immunochemotherapy via remodeling the matrix. Oncogene 2023, 42, 2061–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Ge, J.; Ma, J.; Zheng, J. Carcinoembryonic antigen related cell adhesion molecule 6 promotes the proliferation and migration of renal cancer cells through the ERK/AKT signaling pathway. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2019, 8, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wang, D.; Xiong, F.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y. The emerging roles of CEACAM6 in human cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2024, 64, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Su, L.; Zhu, Z.; Gu, Q.; Liu, B.; Yan, M. CEACAM6 promotes gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Wang, J.; Lei, Y.; Cong, C.; Tan, D.; Zhou, X. Research progress on the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in gynecological cancer (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 4529–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating Downstream. Cell 2007, 129, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.-Y.; Smit, D.J.; Jücker, M. The Role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Bai, X.; Feng, X.; Ni, J.; Beretov, J.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway alleviates ovarian cancer chemoresistance through reversing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and decreasing cancer stem cell marker expression. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.L.; Cantley, L.C. PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: Variations on a theme. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5497–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.-H.; Liu, L.-Z. PI3K/PTEN signaling in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2008, 1784, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Lu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Q.; Sang, X.; Wang, K.; Cao, G. The role of JNK signaling pathway in organ fibrosis. J. Adv. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Camarillo, C.; Ramos-Payán, R.; Romero-Quintana, J.G.; Bermúdez, M.; Lizárraga-Verdugo, E.; Avendaño-Félix, M.; Aguilar-Medina, M.; Ruiz-Garcia, E.; Vergara, D. SOX9 Stem-Cell Factor: Clinical and Functional Relevance in Cancer. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 6754040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, M.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, D.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; et al. SOX on tumors, a comfort or a constraint? Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haque, M.E.; Sens, D.A.; Garrett, S.H. Chronic Exposure of Renal Progenitor Cells (HRTPT) to As (III) Implicates Microfibril Associated Protein 5 (MFAP5) in the Activation of Carcinoembryonic Antigen Related Cell Adhesion Molecules (CEACAM 5 and 6). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060455
Haque ME, Sens DA, Garrett SH. Chronic Exposure of Renal Progenitor Cells (HRTPT) to As (III) Implicates Microfibril Associated Protein 5 (MFAP5) in the Activation of Carcinoembryonic Antigen Related Cell Adhesion Molecules (CEACAM 5 and 6). Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(6):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060455
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaque, Md Ehsanul, Donald A. Sens, and Scott H. Garrett. 2025. "Chronic Exposure of Renal Progenitor Cells (HRTPT) to As (III) Implicates Microfibril Associated Protein 5 (MFAP5) in the Activation of Carcinoembryonic Antigen Related Cell Adhesion Molecules (CEACAM 5 and 6)" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 6: 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060455
APA StyleHaque, M. E., Sens, D. A., & Garrett, S. H. (2025). Chronic Exposure of Renal Progenitor Cells (HRTPT) to As (III) Implicates Microfibril Associated Protein 5 (MFAP5) in the Activation of Carcinoembryonic Antigen Related Cell Adhesion Molecules (CEACAM 5 and 6). Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(6), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060455







