Abstract
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA, also known as thioctic acid) was discovered nearly 90 years ago and began to be used in clinical practice in the late 1950s. Numerous nonclinical and clinical studies have investigated ALA for treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) and various other diseases. The rising global prevalence of DPN necessitates timely treatment; however, there is currently no effective cure. Current guideline-recommended therapies for DPN provide symptom relief rather than modifying the disease. Among the pathogenesis-oriented therapies, ALA holds a unique position as a universal antioxidant, essential for every cell in the body. This review highlights the ongoing issues and challenges in using ALA to treat DPN. While confronting a complex disease with poorly understood pathophysiology, we also have an endogenous substance with pleiotropic effects on all cells in the human body. It becomes clear that this is a highly multifactorial process that will likely never be precisely defined. This does not diminish the significance of ALA in treating DPN but underscores the need for a deeper understanding of when to start therapy, dosage, duration, and monitoring. In this comprehensive review, we evaluate the achievements of the past 70 years and highlight gaps in ALA’s role in treating DPN.
1. Introduction
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA or thioctic acid) has been extensively studied since its first isolation in 1951 [1,2]. ALA is an essential endogenous substance biosynthesized in mitochondria and exhibits an impressive range of pleiotropic biological effects that undoubtedly influence whole-body physiology [3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. ALA’s specific mechanisms and effects across various pathological conditions are not fully clarified. Its antioxidant properties seem to underlie its beneficial health effects in managing various pathological conditions [2,8,10,11,12,13,14,15]. ALA and its metabolite dihydrolipoic acid (DHLA) are considered “universal antioxidants” and function as biological antioxidants, metal chelators, regenerators of other antioxidants, and modulators of several signaling pathways.
Several pre-clinical in vitro and in vivo studies, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials, and subsequent systematic reviews and meta-analyses demonstrate ALA’s potential in preventing or delaying the onset of diabetic complications, namely diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) [15,16,17]. DPN is the most prevalent form of neuropathic pain, affecting around 50% of diabetic patients [18,19,20]. It typically manifests as a chronic, symmetrical, length-dependent sensorimotor polyneuropathy and represents a significant cause of non-traumatic amputations [21,22,23]. However, the mechanisms by which diabetes leads to these complications and disease progression remain largely unclear. These processes are complex, stemming from an interplay of various interacting factors. A general problem with all preclinical and clinical studies is the selection of the optimal dose of ALA, treatment duration, trial outcomes, and the specific metabolism of the antioxidant, which results in somewhat contradictory patient outcomes [24].
Structurally, as a sulfur-containing substance, ALA is considered a thiol compound. It exists as two enantiomers: (R)-(+)-lipoic acid (R-ALA) and (S)-(−)-lipoic acid (S-ALA), and as a racemic mixture. Only the R-(+)-enantiomer is synthesized in small amounts by microorganisms, plants, animals, and humans, and it is biologically active. Racemic ALA and its biologically active enantiomer, R-ALA, are marketed globally as both therapeutic agents and nutritional supplements in various dosage forms ranging from 100 to 600 mg [25,26].
This review is based on a literature search in PubMed, where approximately 1000 published articles exist for the period of 1950 to 1990 and nearly 6500 for the subsequent 35 years, including over 700 reviews. This indicates the enormous interest in the pharmacological effects and clinical application of ALA. The keywords we used were related to all aspects of preclinical and clinical efficacy and safety data, like lipoic acid or thioctic acid, and pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, toxicity, efficacy, and clinical trials. Additionally, the references of the selected articles were reviewed, and relevant articles were further searched. Only publications in English were considered.
This comprehensive review aims to address the ongoing challenges and concerns related to the use of ALA for treating DPN. We will assess the knowledge gained over the last 70 years while highlighting the existing gaps in ALA’s effectiveness and application in DPN treatment.
2. Biosynthesis and Synthesis of ALA
2.1. Biosynthesis of ALA
ALA is biosynthesized in mitochondria through sequential steps: mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis type II (FAS II) produces octanoate, which is then transferred to the glycine cleavage H protein as the initial acceptor. Two sulfhydryl groups are subsequently added to the nonpolar octanoic acid side chain to form lipoate, which is finally transferred from the H protein to the E2 subunits of 2-oxoacid dehydrogenase complexes [27]. However, some of these reactions have been poorly characterized, and there are still some open questions.
The first step is the formation of malonyl-CoA, catalyzed in humans by malonyl-CoA synthetase (ACSF3), although alternative sources may exist [28]. Malonyl-CoA:acyl-carrier protein acyltransferase (MCAT) transfers the malonyl group to the acyl-carrier-protein (ACP) [29], followed by a series of enzymatic reactions: condensation to 3-ketoacyl-ACP by 3-oxoacyl-acyl-carrier-protein synthase (OXSM) [30], reduction to 3-hydroxyacyl-ACP by 3-oxoacyl-acyl-carrier-protein reductase [31], dehydration of 3-hydroxyacyl-ACP by 3-hydroxyacyl-thioester dehydratase to 2-trans-enoyl-ACP [32,33], and a final reduction by trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase which catalyzes the reduction of 2-transenoyl-ACP to acyl-ACP [34]. The product is used for elongation with two further carbons by reaction with another malonyl-ACP at step 3. This cycle repeats three times to yield octanoyl-ACP.
The octanoyl moiety is then transferred to a conserved lysine residue in the glycine cleavage H protein by octanoyl transferase (LIPT2) [35]. This protein-bound octanoate is then sulphurated twice at positions C6 and C8 by lipoic acid (LA) synthetase and produces exclusively the R-enantiomer, which is the biologically active form of LA [36].
The final step involves transfer of the lipoate moiety from the H protein to other mitochondrial proteins requiring lipoylation by lipoyl transferase [35].
ALA cycles between three forms: oxidized (with an intramolecular disulfide bond), intermediate (with substrate bound to one sulfur atom), and reduced (containing two sulfhydryl groups). Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (DLD) regenerates the oxidized form using NAD+ as an electron acceptor, completing the catalytic cycle [37].
Studies in model organisms, particularly yeast, have significantly advanced our understanding of this pathway [38], though some aspects of human ALA biosynthesis remain under investigation. Defects in genes encoding these enzymes can disrupt mitochondrial energy metabolism and cause severe diseases [27].
2.2. Synthesis of ALA
While ALA is often produced as a racemate in large-scale manufacturing, the isolation or synthesis of its chiral R-form offers advantages in therapeutic potency for several applications, including its uses as an antioxidant, anti-diabetic agent, and cofactor [8,23,39]. Various approaches have been developed for the synthesis of R-ALA, as described in the comprehensive review of Wang et al. [40].
2.2.1. Chemical Resolution
Industrial production of R-ALA primarily relies on the chemical resolution of racemic ALA using chiral resolving agents. The most common method employs R-(+)-methylbenzylamine (RAMBA) to form diastereomeric salts with ALA, and releasing R-ALA upon subsequent acid hydrolysis [41].
2.2.2. Enzymatic Resolution
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions offer stereoselective alternatives. Lipases from Candida rugosa and Aspergillus oryzae have been used for enantioselective esterification of racemic ALA, though with moderate selectivity toward S-ALA [42]. More efficient approaches utilize enzymatic resolution of precursors like ethyl 8-chloro-6-hydroxy octanoate with Novozym 435, achieving excellent enantiomeric excess (>94% ee) [43].
2.2.3. Chiral Pool Synthesis
Starting from naturally occurring chiral compounds allows for controlled stereochemistry. Examples include syntheses from S-malic acid [44] or D-mannitol [45]. These approaches leverage existing stereochemistry but often require multiple steps.
2.2.4. Chemical Asymmetric Catalysis
Modern asymmetric methods have dramatically improved R-ALA synthesis efficiency. Sharpless asymmetric epoxidation [46], BINOL-Ti-catalyzed allylation [47], and asymmetric hydrogenation using BINAP-Ru catalysts [48] achieve high enantioselectivity. Organocatalytic methods using L-proline have also proven effective [49].
2.2.5. Enzymatic Asymmetric Catalysis
Biocatalytic approaches include Baker’s yeast reduction of β-keto esters [50] and engineered ketoreductases like CpAR2 from Candida parapsilosis, which can reduce ethyl 8-chloro-6-oxooctanoate with >99% ee at industrial scale [41]. Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenases from Pseudomonas species offer another enzymatic route [51].
While chemical resolution remains the primary industrial method for R-ALA production [40], enzymatic approaches—particularly engineered ketoreductases—show promise for more sustainable manufacturing. The highest enantioselectivity (>99% ee) has been achieved using enzymatic reduction with space-time yields exceeding 500 g L−1 d−1 [41].
R-ALA is the active form synthesized by the body, with absorption enhanced when taken with S-ALA. Breithaupt-Grogler et al. [52] found that volunteers receiving 600 mg of ALA isomers had plasma concentrations of R-ALA nearly 1.5 times higher, although this enantiomer was cleared more rapidly [3]. S-ALA can inhibit the reduction of R-ALA, preventing its binding to reduction enzymes, though this occurs mainly at high S-ALA concentrations. In a racemic mixture, where R-ALA and S-ALA are equal, R-ALA reduction in mitochondria-rich tissues is generally unaffected. This implies that the body’s mechanisms for reducing R-ALA can overcome S-ALA’s inhibitory effects at physiological levels [3].
3. Pharmacokinetics
ALA exhibits highly variable pharmacokinetic values that depend on various endogenous and exogenous factors [53,54]. Human studies have shown that ALA is rapidly absorbed, with limited oral bioavailability (~30%) due to its low solubility and short blood half-life, which result from extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism and elevated systemic elimination [8,55,56,57]. There is no evidence that ALA is a substrate of CYP450. The ease with which ALA is metabolized by oxidation, particularly beta-oxidation, is believed to be the leading cause of its unfavorable pharmacokinetic characteristics.
After absorption, ALA enters cells where it is converted into its reduced form, known as DHLA. Depending on the chemical characteristics of the internal environment, either may be present in living organisms. Because both versions can perform biological functions in various settings, they often refer to the pair ALA/DHLA without indicating any distinctions [8,58]. A Tmax peaks within an hour and then declines rapidly [52,57,59,60]. ALA exhibits a high degree of plasma protein binding, primarily to albumin, which affects its distribution and bioavailability. ALA is widely distributed in various tissues, with significant concentrations found in the liver, heart, and skeletal muscle. These tissues are associated with high levels of oxidative metabolism, where ALA functions as a cofactor for mitochondrial enzyme complexes [7]. The ability of ALA to penetrate different tissues and convert to DHLA is crucial for its antioxidant and therapeutic effects. This conversion process, facilitated by redox-related enzymes (such as glutathione reductase, thioredoxin reductase, or dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase), underscores the importance of ALA in maintaining cellular redox balance. ALA is rapidly eliminated from the body through renal and non-renal routes [3,57,61]. ALA pharmacokinetics remain unchanged by renal clearance, indicating no dose adjustment is needed for patients with renal dysfunction [62].
The significant impact of food on ALA absorption underscores the recommendation to take it on an empty stomach to enhance its bioavailability [62]. The bioavailability and Cmax of ALA are significantly affected and are higher in individuals over 75 than in young adults aged 18 to 45. Age-related pharmacokinetic changes necessitate dosage adjustments in the elderly to prevent potential toxicity [56,63].
4. Mechanism of Action
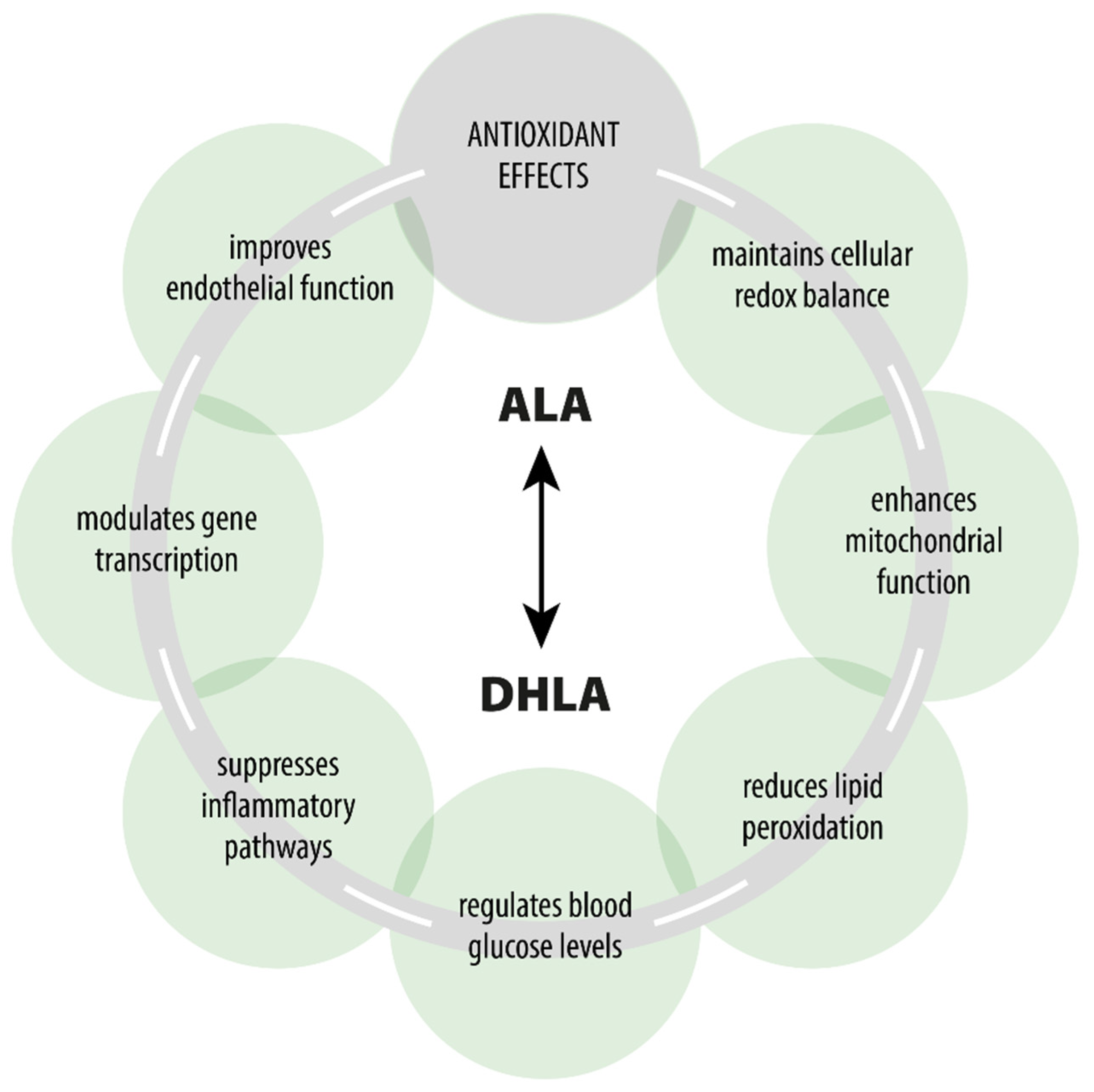
ALA is a naturally occurring compound that plays a key role in every human cell and exhibits various pharmacodynamic effects beyond its primary role as an antioxidant [7,14,64,65] (Figure 1). ALA participates in the Krebs cycle, fulfills crucial functions in numerous chemical reactions, and serves as a cofactor for certain enzymatic complexes that are essential for energy production within the cell [8].
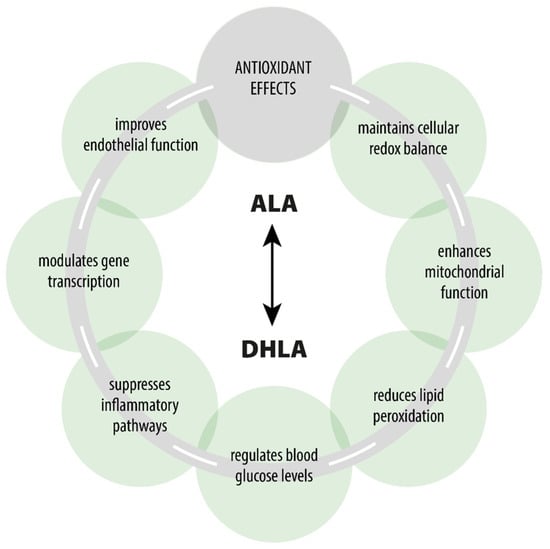
Figure 1.
Pharmacological effects of ALA/DHLA.
4.1. Antioxidant Properties
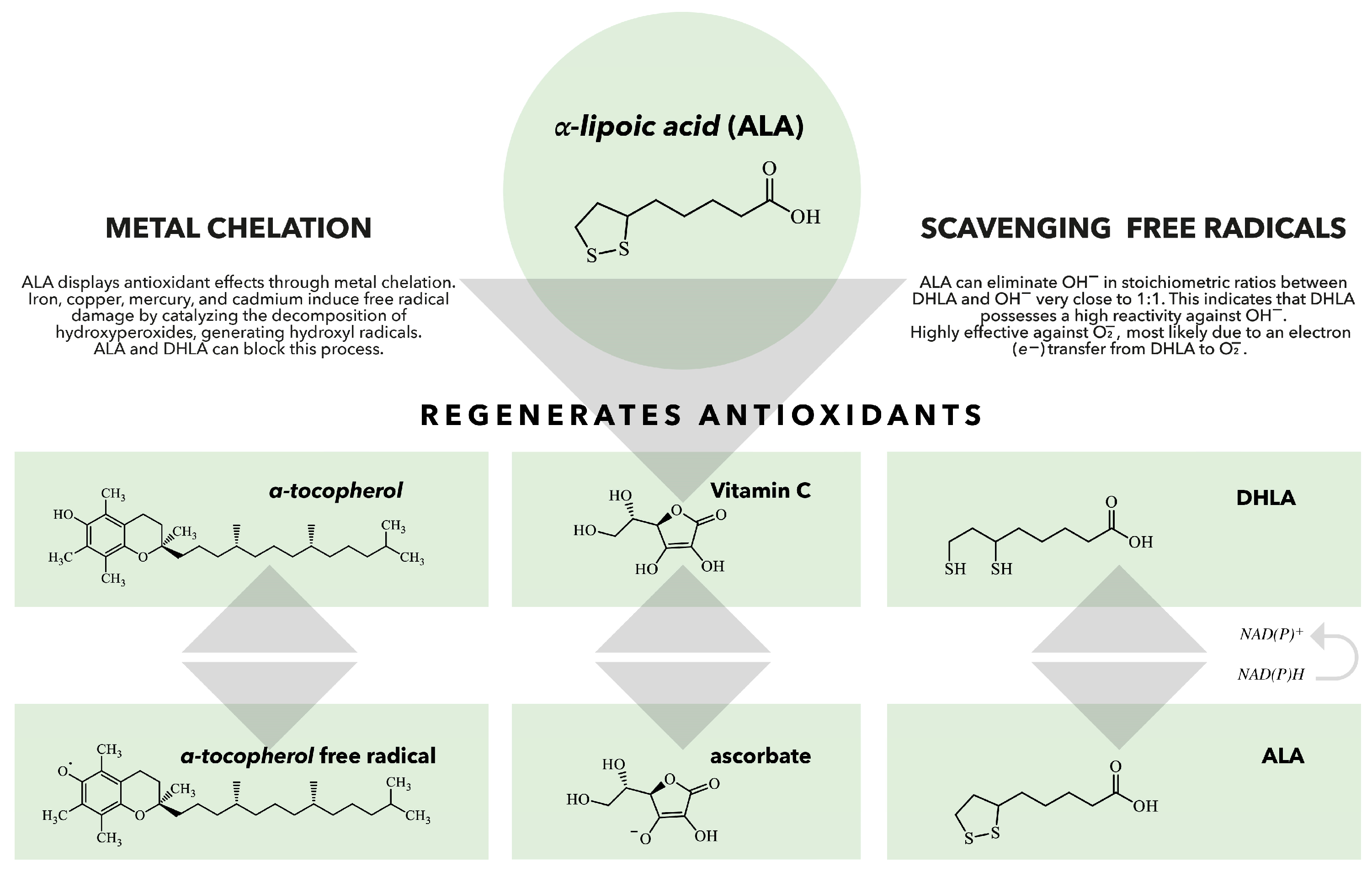
There is a vast body of literature on ALA/DHLA antioxidant effects [2,10,66,67,68,69]. ALA scavenges free reactive radicals, which can induce oxidative stress and contribute to various diseases, including diabetes, cardiovascular diseases (CVD), and neurodegenerative disorders [14,15,70,71,72]. ALA serves as both a water-soluble and fat-soluble antioxidant, allowing it to function effectively in both aqueous and lipid environments, such as plasma membranes, cytosol, and mitochondria [68]. It also recycles other antioxidants, such as glutathione (GSH), and vitamins C and E, thereby enhancing their antioxidant capacities and repairing oxidative damage (Figure 2) [14,68,73]. The presence of thiol groups in ALA accounts for its metal-chelating abilities [66]. The interactions of ALA with transition metals are particularly complex, as ALA’s ability to act as an effective scavenger often involves complex synergism with essential trace elements [74]. Moreover, it can increase the levels of GSH within the cells, which chelate and eliminate a wide range of toxins, particularly toxic metals [2,68].
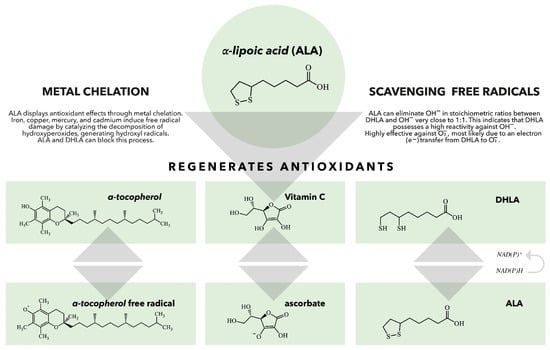
Figure 2.
The role of ALA/DHLA in the regeneration of antioxidants. When vitamin E scavenges a peroxyl radical, it produces a vitamin E radical that can be regenerated by various antioxidants, including vitamin C, ubiquinol, and glutathione (GSH). DHLA can reduce all these antioxidants and can also be regenerated by several enzymes, such as lipoamide reductase, GSH reductase, and thioredoxin reductase. This demonstrates that ALA and DHLA play crucial roles in the body’s antioxidant network [75].
Oxidative stress occurs in experimental diabetic neuropathy (EDN) due to ischemic and autooxidative lipid peroxidation, with resultant neuropathy. Experimental studies in diabetic rats demonstrate that ALA (100–350 mg/kg/day) improves nerve blood flow (NBF), vascular relaxation, and motor nerve conduction velocity while reducing oxidative markers like thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) [76]. In lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced oxidative stress, ALA (60 mg/kg, IV) treatment alleviated neurophysiological symptoms, normalized TBARS and H2O2 levels, and improved the GSH/GSSG ratio, indicating enhanced antioxidant defense [77]. Treatment with ALA (20, 50, and 100 mg/kg, IP, five times per week) results in a dose-dependent normalization of GSH in EDN [73]. These findings highlight oxidative stress as a unifying mechanism in neuropathy and support antioxidant interventions, particularly ALA, as a therapeutic strategy.
4.2. Regulation of Cellular Redox Status
ALA regulates cellular redox status by modulating the ratio of reduced to oxidized glutathione (GSH/GS-SG) levels, which is critical for cellular defense against oxidative stress [68,73,78]. ALA also enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase. This regulation protects cells from oxidative damage and promotes overall redox homeostasis [3,14]. It is also involved in regulating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a transcription factor that controls the expression of several antioxidant genes [79]. A systematic review and meta-analysis, including 15 studies, performed by Zonooz et al. [80], suggested that ALA supplementation may improve lipid peroxidation. By inhibiting lipid peroxidation, ALA preserves membrane integrity and protects cells from oxidative injury, which is especially important in DPN, where oxidative damage is a significant pathological contributor [3,14].
4.3. Mitochondrial Function and Energy Production
ALA has been shown to protect mitochondrial function. ALA acts as a cofactor in the mitochondrial enzyme complexes involved in the Krebs cycle (e.g., pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase). It facilitates the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, thereby supporting cellular energy metabolism [3,7,14,81]. Supporting mitochondrial function and reducing mitochondrial oxidative stress enhances cellular energy production and prevents energy deficits in peripheral nerves [7,82].
4.4. Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Metabolism
ALA enhances glucose uptake into cells by activating the insulin receptor signaling pathway and improving insulin sensitivity [83,84]. This action reduces insulin resistance and helps regulate blood glucose levels, potentially mitigating hyperglycemia that contributes to nerve damage in DPN [39,69,85].
4.5. Effects on Gene Transcription
ALA induces apoptosis in some cancer cells while protecting against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. It enhances DNA fragmentation and decreases cell viability. Additionally, ALA enhances nuclear levels of apoptosis-inducing factor and activates the caspase-dependent pathway, leading to increased cleavage of cytochrome C and PARP-1. It also activates the caspase-independent pathway by overexpressing poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Hence, intracellular Ca2+ mediates both mechanisms of ALA’s apoptotic effects [86].
5. Pharmacodynamics
Multiple preclinical studies show agents can prevent or enhance diabetic neuropathy by targeting underlying pathophysiology [87]. ALA has been shown to improve neuropathy symptoms by modulating endoneural blood flow, thereby improving vascular dysfunction, reducing oxidative stress, and counteracting the harmful effects of lipid peroxidation [1,88]. Clinical trials have been carried out on the effects of ALA on DPN, and its use for this condition is approved in many countries [22,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96].
5.1. Neuroprotective Effects
ALA has been demonstrated to have neuroprotective effects through multiple mechanisms. It protects neurons from hyperglycemia-induced damage, reduces advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), and mitigates mitochondrial dysfunction, significantly contributing to DPN [97]. In streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats, ALA (100 mg/kg orally) demonstrated superior peripheral nerve protection compared to insulin, improving nerve conduction velocity (NCV) and promoting regeneration, even under persistent hyperglycemia [98]. Additionally, ALA has been shown to upregulate neurotrophins, such as nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). These neurotrophins play a crucial role in the survival, repair, and regeneration of peripheral nerves, enhancing neuronal health and functional recovery [99,100,101]. Stevens et al. [102] reported selective effects of ALA (i.p. 100 mg/kg/day for 6 weeks) on STZ-injected diabetic rats. ALA improved digital sensory nerve conduction velocity (NCV) but not sciatic-tibial, corrected endoneurial nutritive but not composite NBF, increased mitochondrial oxidative state without fixing nerve energy depletion, and enhanced polyol pathway intermediate accumulation without depleting myoinositol or taurine. Thus, interactions between nerve biochemistry and perfusion defects from STZ-induced diabetes, corrected by ALA, have differential impacts on nerve fiber populations. Cameron & Cotter [103] studied ALA’s potential for treating diabetic neuropathy by administering it orally at a dose of 100 mg/kg to STZ-induced diabetic rats. The results showed that ALA improved nerve blood flow (NBF) and conduction velocity, which are key indicators of peripheral nerve function. Gorąca & Asłanowicz-Antkowiak [104] found that ALA (60 mg/kg, IV) increased brain-SH groups in LPS-treated rats, demonstrating ALA’s potential to limit nerve tissue damage from oxidative stress. Wang et al. [105] confirm ALA’s neuroprotective effects in a chronic constriction injury model, suggesting its use in chronic neuropathic pain management and supporting its clinical application. However, it showed be noted that in animal models, there is a vast diversity of markers, both in serum (lipid profile, glucose, redox, etc.) as well as in tissues (redox activity—SOD, catalase, glutathione peroxidase—GPx, MDA, carbonylated proteins, AGEs, 4-Hydroxynonenal—4-HNE, among others—inflammatory—TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, etc.) or gene expression markers (proteins involved in pro or anti-inflammatory activity, glucose, and lipid metabolism, etc.), in addition to mitochondrial redox markers (8-OHdG, mitochondrial membrane potential, NADPH activity) that have been studied. However, and probably due to this diversity and also the specific characteristics of each tissue analyzed, biomarkers do not always show sensitivity to the ALA action [68,106,107,108,109,110,111].
Clinical studies have indicated that ALA can improve nerve conduction velocity (NCV), restore electrophysiological function in damaged peripheral nerves, and alleviate neuropathic symptoms such as pain, numbness, and burning sensations. This effect is achieved through its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory actions. ALA helps maintain the structural integrity of the myelin sheath, which is essential for efficient nerve conduction [87,112]. It has been explored in treating neuropathy and neurodegenerative diseases [75,113].
5.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
ALA lowers pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which are elevated in diabetes, and inhibits the NF-κB pathway [114,115,116,117,118]. By suppressing these inflammatory pathways, ALA alleviates inflammation-induced nerve damage, promotes healing, and prevents further progression of neuropathy [14,64]. Zhang et al. [115] found that ALA (30–120 mg/kg for one week, IP) alleviates neuropathic pain in STZ-induced diabetic rats by downregulating TRPV1 receptors via NF-κB pathways, reducing neuronal excitability. TRPV1 modulation is crucial in diabetic neuropathic pain, involving ROS and cytokine pathways [119,120].
Further studies highlight ALA’s role in neuropathic pain reduction via BDNF-TrkB-ERK signaling [101] and sciatic nerve repair in compression injury models [121].
5.3. Effects on Microcirculation
ALA enhances blood flow and oxygen delivery to peripheral nerves by improving endothelial function and reducing vascular dysfunction, which is often compromised in diabetes. It increases nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability by mitigating oxidative stress and preventing NO degradation by ROS. This vasodilatory effect helps restore proper blood flow and oxygen delivery to peripheral nerves, which is essential for nerve repair and function. Additionally, ALA has been shown to decrease vascular endothelial damage by lowering levels of AGEs and inflammatory cytokines, both of which contribute to vascular stiffness and impaired perfusion in diabetes [82,97,122].
In clinical practice, ALA has demonstrated beneficial effects on cardiovascular health, reproductive health, cognitive function, aging processes, detoxification, inflammation reduction, obesity, cancer prevention, and neuroprotection [1,12,122,123,124,125].
6. Drug Interactions
ALA is a powerful antioxidant that has been studied for various health benefits; however, it may also interact with certain medications (Table 1). ALA possesses functional pleiotropism across various signal transduction pathways. Evidence is limited that ALA may inhibit specific cytochrome P450 enzymes, potentially altering the metabolism of drugs that are substrates for these enzymes. The inhibition mechanism can relate to the interaction of ALA with sulfhydryl groups due to its dithiolane structure [126]. Makhova et al. [127] demonstrated no significant effect of ALA on individual stages and processes of catalysis of cytochrome P450 3A4, the primary drug-metabolizing enzyme. Phua et al. [128] explored the interaction between ALA (50 mg/kg IV) and valproate (50 mg/kg IV) in rats, finding that ALA increased the AUC 0–6 h for valproate. ALA reduced the in vitro formation of valproate-CoA in a concentration-dependent manner, with no significant distribution-level interactions noted in preliminary protein binding studies. Metabolic stability studies indicated valproate’s metabolism is not primarily eliminated through CYP450, suggesting that the in vivo interaction likely results from inhibition of β-oxidation or glucuronidation. In vitro tests confirmed that ALA significantly inhibited β-oxidation, reducing the metabolic clearance of valproate. Studies on Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast cells (line D 7) revealed that ALA within the 1 nM–10 μM concentration range does not affect cells’ cytochrome P450 content [129]. However, higher concentrations of ALA (1 mM) proved cytotoxic and destroyed this enzyme [68]. In summary, there is insufficient detailed information regarding ALA’s impact on the metabolism of exogenous substances. It is essential to remember that this process is multifactorial since ALA is present in the diet (as the biologically active form R-ALA), dietary supplements, and drugs. The impact of ALA on metabolism becomes even more complex, given that ALA is an essential endogenous substance for all living cells and functions as a cofactor in various enzyme systems [1]. It is crucial to recognize that ALA may impact liver function in a dose- and concentration-dependent manner, which may also be relevant for potential drug interactions.

Table 1.
Drug Interactions of ALA.
ALA may influence GIT motility, potentially affecting the absorption of drugs that require specific GIT conditions for optimal absorption. This is especially true for diabetic patients who experience altered gastric emptying and gastric motility. Delayed gastric emptying, however, does not substantially affect the rate and extent of absorption of both ALA enantiomers [148]. Nevertheless, clinical data on this particular interaction is limited.
7. Clinical Implications of ALA
ALA has been used in clinical practice for 70 years to alleviate symptoms associated with various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, cancer, age-related cardiovascular issues, neuromuscular conditions, weight gain caused by antipsychotic medications, and metabolic obesity [1,8,15].
7.1. Effects of ALA on Oxidative Stress
The multifunctional antioxidant properties of ALA highlight its therapeutic potential in oxidative stress-related conditions, particularly DPN [14,64]. Hyperglycemia triggers oxidative stress in mitochondria, which significantly contributes to the development of diabetic microvascular complications [7]. Antioxidants, such as ALA, effectively treat DPN by mitigating oxidative stress [71,122,149,150]. Specifically, ALA enhances GSH, a natural antioxidant involved in antioxidant protection, nutrient metabolism, and the regulation of cellular processes. The RCTs presented in Table 2 clearly demonstrate the effects of ALA on oxidative stress.

Table 2.
RCTs exploring the effects of ALA on oxidative parameters.
The pathogenesis of DPN is influenced by metabolic, vascular, and genetic factors, with oxidative stress playing a significant role in nerve injury [153,154]. DPN is a debilitating condition that adversely affects physical abilities and quality of life [87]. ALA may help correct several mechanisms involved in DPN, including sorbitol accumulation, microvascular damage, oxidative stress, and lipid peroxidation [16]. ALA’s antioxidant properties enhance blood flow, glucose uptake, and energy metabolism [155]. It increases NO production, thereby enhancing endoneural blood flow and potentially alleviating DPN symptoms by protecting endothelial cells and preserving vascular function [82,94,112,156,157]. Additionally, ALA reduces AGEs, which contribute to oxidative stress and neurodegeneration [97,100,122]. By protecting neuronal cells and improving vascular function, ALA helps promote nerve health and function in diabetic animal models [76,158,159].
7.2. ALA in the Treatment of DPN
DPN arises from various mechanisms depending on the type of diabetes. It is increasingly common and progresses faster among individuals with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM), with nearly 100% developing DPN after 15 years, compared to approximately 30% in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) after 25 years [160]. Diabetic neuropathy can affect either the peripheral nervous system, leading to painful diabetic neuropathy [161], or the autonomic nervous system, resulting in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Autonomic neuropathy can cause life-threatening issues, such as sudden cardiac death [23,110,162]. Moreover, clinical studies have revealed that sex is a significant risk factor for DPN in humans. Research suggests that being male may correlate with a greater risk of developing severe diabetic neuropathy at a younger age. Conversely, men tend to show a lower likelihood of developing neuropathic pain symptoms compared to diabetic women, which reinforces the anti-allodynic effects of testosterone and its derivatives [163].
DPN is characterized by axonal dysfunction and degeneration. It primarily affects sensory nerves, leading to progressive symptoms such as sensory loss, pain, and autonomic dysfunction [96,164]. The pathogenesis of DPN is intricate and remains not completely understood. Several studies have proposed underlying mechanisms, including metabolic, neurovascular, and autoimmune pathways [165,166]. The most widely accepted theory is that oxidative stress is induced in mitochondria by hyperglycemia, which, in turn, causes damage to endothelial and neuronal cells, thereby compromising the oxygen and nutrient supply to the nerves [167]. Macrophages infiltrating nerve cells release cytokines that worsen the damage to nerve fibers [20,22,168]. Other factors contributing to peripheral nerve damage include AGEs and microvascular impairment [20]. These conditions disrupt the expression of neurotrophic factors, leading to oxidative stress and inflammation [150,169,170,171]. Considering all these aspects, antioxidants appear to be a pathogenesis-oriented approach to combat the progression and symptoms of DPN [172,173].
Currently, there is no cure for DPN. Managing DPN remains challenging due to its complex and poorly understood pathophysiology, varied clinical manifestations, and underdeveloped staging [23,174]. Management focuses on slowing progression, relieving pain, and addressing complications [166,175]. Improving glycemic control and making lifestyle changes, including dietary changes and moderate physical activity, are recommended to delay the progression of DPN [18,23,96,164,169,176]. Pain relief options include gabapentinoids (gabapentin, pregabalin), SNRIs (duloxetine, desvenlafaxine), TCAs (amitriptyline), and sodium channel antagonists (oxcarbazepine, lamotrigine, lacosamide, valproic acid), as per the 2022 guideline update [166,177]. Second-line therapies include lidocaine, capsaicin patches, and tramadol [164]. These medications show comparable effectiveness, so factors such as tolerability, contraindications, and cost should be considered when making a choice [22,178]. Essential care includes diabetic foot management, chronic ulcer care, and assessing cardiovascular risks [179]. However, only some patients experience significant relief, often encountering side effects that limit the effectiveness of the treatment. High-dose monotherapy or combinations are used for insufficient pain relief, but tolerability issues limit the benefits, leading to high discontinuation rates [166,180,181,182]. Given DPN’s prevalence and severity, a clear need exists for improved treatments to alleviate the burden on patients and society [18]. Topical medications, behavioral approaches, and physical modalities can be particularly advantageous when combined with other treatments due to their minimal side effect profiles [183,184]. Several non-pharmacological treatments may be utilized in managing DPN; however, most possess a weak strength of evidence [185].
Neuropathic pain-relieving drugs are only modestly effective and often do not eliminate pain, leaving a significant unmet need [181,186]. While complete pain resolution is rare, even a slight reduction in pain can improve quality of life [185,187]. Treatment guidelines typically suggest adding a new agent instead of switching, particularly if the initial medication provided some benefit [87,188,189,190]. A multicenter observational prospective study conducted by Checchia et al. [191] highlighted the potential benefits of a multimodal strategy that combines pharmaceutical, physical, and ALA therapy for the treatment of sciatic neuropathy in real-world settings.
Current guideline-recommended therapies for DPN focus on symptom relief rather than modifying the disease. Aside from glycemic control, there is insufficient data on therapies that can prevent the progression of DPN. Among the pathogenesis-oriented therapies, ALA, actovegin, benfotiamine, and epalrestat are currently authorized for the treatment of DPN in several countries [71,110,192].
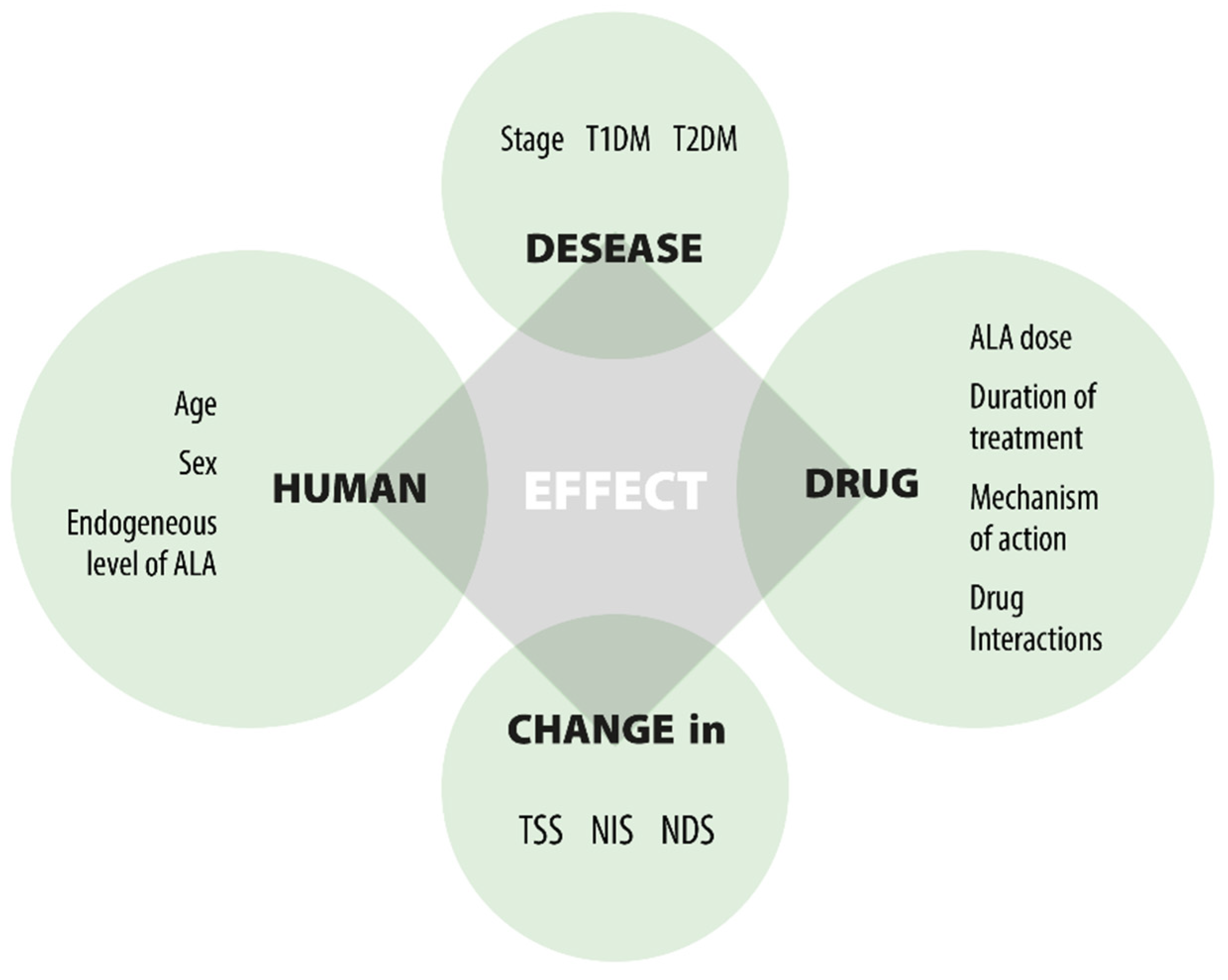
ALA modulates disease and controls symptoms as a therapy focused on pathogenesis. It represents a promising first-line treatment for DPN, preventing early development and progression through both direct and indirect antioxidant effects [8,23,71,87,110] (Figure 3).
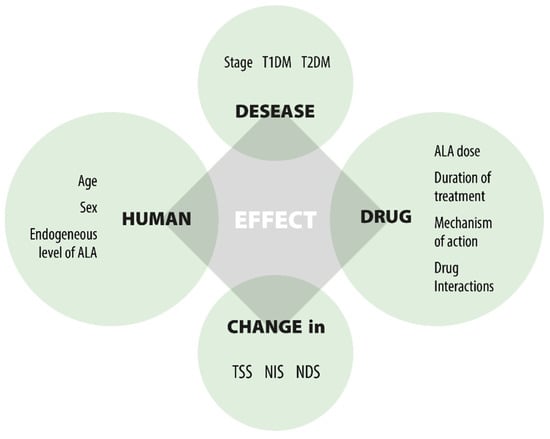
Figure 3.
Factors affecting the effect of ALA.
Several studies provide comprehensive data on the efficacy and safety of ALA across various dosage regimens and modes of administration. Despite differences in sample size, settings, and study duration, they offer substantial evidence supporting the efficacy of oral ALA at 600 mg/day when administered as a tablet once daily. Outcomes were frequently evaluated using the Total Symptom Score (TSS). The TSS is a summary score that assesses the presence, severity, and duration of lancinating pain, burning pain, prickling (paresthesia), and numbness, with a possible score range from 0 to 14.64 [193]. The data supported the finding that an oral dose of 600 mg/day ALA reduces the primary symptoms of DPN, including pain, paresthesia, and numbness, to a clinically relevant level. Additionally, ALA was well-tolerated throughout the studies, leading to a favorable dose-dependent safety profile (Table 3).

Table 3.
Summary of the trials investigating the efficacy and safety of oral ALA.
Numerous clinical trials have been carried out to assess the efficacy and safety of ALA in the treatment of DPN. A key confounding factor leading to inconsistent results is the variety of elements that affect clinical responses, as shown in Figure 3. The three main factors are: (1) the unresolved causes of DPN; (2) the multifunctional effects of ALA; and (3) the lack of precise markers to evaluate the drug’s efficacy in DPN treatment. This leads to challenges when comparing outcomes from different clinical studies. Despite differences in study designs and dosing, the significant findings from the trials include: (1) oral ALA at a dose of 600 mg/day effectively improves nerve conduction; (2) the effect is not dose-dependent beyond 600 mg/day; (3) oral ALA at 600 mg/day is equally effective as IV treatment; (4) oral ALA at 600 mg/day is well tolerated; (5) long-term use of oral ALA at 600 mg/day is safe; (6) there is inadequate evidence on the duration of treatment; (7) benefits do not persist after therapy ends; and (8) the clinical efficacy in severe DPN patients remains unverified.
7.3. Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis
Multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses have evaluated the efficacy and safety of oral 600 mg/day ALA in treating DPN, showing significant improvements in neuropathic pain and NCV [110].
In a meta-analysis of nine studies, oral ALA treatment, compared to placebo, revealed a reduction in the NIS (muscle weakness, reflex loss, sensation loss), the NIS-LL (motor nerve function and reflexes in the lower limbs), and the TSS [58]. Accordingly, treating DPN with oral ALA is considered a beneficial option, as it alleviates pain symptoms and addresses motor and nerve damage while demonstrating an excellent safety profile [204,205]. Furthermore, individuals with diabetes were found to have lower circulating ALA levels, supporting ALA’s positive impact in the management of DPN [206,207]. In a meta-analysis encompassing 24 randomized controlled trials involving patients with metabolic diseases, ALA was observed to enhance glucose homeostasis (resulting in lower fasting blood glucose, insulin levels, HOMA-IR, and HbA1c) and improve the lipid profile (leading to reductions in triglycerides, total cholesterol, and LDL-C) [208]. Its impact on DPN is thought to be more significant when utilized in conjunction with standard treatments (such as gliclazide, SGLT2 inhibitors, metformin, and GLP-1 analogs) for patients with T2DM who are experiencing neuropathic pain [209]. Abubaker et al. [167] reviewed 8 RCTs involving 1500 patients. The findings were inconsistent regarding the effectiveness of ALA in treating DPN, with some trials observing significant improvements and others failing to present any notable evidence. Nearly 30 systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been published regarding ALA’s beneficial effects in managing diabetes and its complications (Table 4). All studies found ALA to be a safe and tolerable intervention.

Table 4.
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses establishing DPN treatment’s effectiveness and safety, including ALA (listed by year).
In addition to monotherapy, numerous studies indicate that combination therapy may improve clinical symptoms in patients with DPN [95,96,110,146,218,219,220,221]. A meta-analysis of 31 RCTs (n = 2676) evaluated the efficacy and safety of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) in combination with ALA for treating DPN. The results demonstrate that the combination therapy (ALA/PGE1) is significantly superior to either monotherapy (p < 0.00001) [222]. A meta-analysis of 13 RCTs (n = 1148) performed by Jiang et al. [223] reveals that combination therapy with fasudil plus methylcobalamin or ALA is well tolerated and superior to methylcobalamin or ALA monotherapy for improving neuropathic symptoms and NCV in patients with DPN, respectively. Another analysis shows that ALA combined with methylcobalamin improves neuropathic symptoms and NCV more effectively than methylcobalamin alone, without increasing severe adverse events in patients with DPN [224]. The combination of ALA with epalrestat has also been demonstrated to significantly improve clinical outcomes and NCV compared to either treatment alone, with no serious adverse events reported [225,226].
7.4. Dosage Regime
7.4.1. Posology in Adults
For adults with sensory disorders caused by DPN, a daily oral dose of 600 mg of ALA is recommended to be taken on an empty stomach (approximately 30 min before the first meal) to enhance absorption [57,85,195,196,227,228,229]. Taking the tablet with food may decrease ALA absorption [6].
If available, initial parenteral therapy with ALA is suggested in cases of severe sensory disturbances [230]. DPN therapy relies on optimal diabetes control. Given the chronic nature of DPN, long-term therapy may be required, along with regular re-evaluation to ensure sustained benefits. Discontinuing ALA after 5 years of treatment led to the recurrence of symptoms after 2 weeks [231].
7.4.2. Posology in the Pediatric Population
There is limited data on the use, efficacy, posology, and safety of ALA in the pediatric population. This limitation can be explained by the fact that ALA is indicated only for adults. However, a few clinical studies have included pediatric patients. In the study by El Amrousy & El-Afify [124], ALA was administered to 40 obese children (ages 10 to 18 years) at a dose of 300 mg twice daily for 3 months. No treatment-related side effects were observed during the treatment period. Hegazy et al. [232] also studied the effects of 300 mg twice daily for four months in 15 asymptomatic T1DM pediatric patients (ages 10–14) to assess potential protective effects on diabetic cardiomyopathy. In the study by Puliappadamb et al. [233], 300 mg/day ALA combined with 5 mg/day flunarizine was administered to 30 adolescents (ages 10–19) for 12 weeks. The ALA/flunarizine combination resulted in a reduction in the frequency and severity of migraines. In a double- blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled randomized trial, Tromba et al. [234] studied the effect of 800 mg/day ALA for 3 months on cardiovascular risk factors in 32 children aged 8 to 16 with a body mass index greater than the 85th percentile. No adverse events were noted throughout the study period. Scaramuzza et al. [235] evaluated the effects of 400 mg of slow-release ALA, twice daily for 6 months, in 25 T1DM children aged 12 to 19. No severe adverse events were noted during the study period. Huang et al. [236] evaluated the effects of 600 to 1200 mg/day (mean 17 mg/kg/day) on oxidative stress in adolescents (n = 30; mean age 14 ± 2.4) with T1 DM for 3 months. No effects of ALA on oxidative stress were observed, and no adverse events were reported. In the study by Korkina et al. [237], the antioxidant effect of ALA was studied by administering a dose of 400 mg/day for 28 days to 16 children (mean age 11.4 ± 2.1 years) living in the Chernobyl area. ALA significantly lowered urinary radioactivity, normalized liver and kidney functions, and no severe side effects were observed.
8. Safety Pharmacology
Clinical and post-marketing surveillance studies have demonstrated the drug’s highly favorable safety profile [1,85,91,201,231,238,239]. To date, neither animal studies [240,241,242] nor human studies have shown serious side effects from administering ALA [3,14,85,194,196,243,244,245]. A meta-analysis of 71 RCTs performed by Fogacci et al. [205] suggests that ALA supplementation of 600 mg once daily is not associated with an increased risk of any treatment-emergent adverse events. In humans, significant toxicity arises at doses of 1200 mg and 1800 mg once daily. Interestingly, ALADIN III study [85] suggested that high doses of ALA are better tolerated when administered in smaller, divided doses.
In a practical cohort of 443 diabetic individuals suffering from chronic painful neuropathy, treatment was administered orally at ALA 600 mg once daily for an average period of five years [231]. Notably, switching from long-term ALA treatment to central analgesic drugs, such as gabapentin, was associated with significantly higher rates of side effects and treatment discontinuation [231]. These findings suggest that DPN treatment is long-term, even during symptom-free intervals, and requires a drug with pathogenetic properties like ALA. Supporting Ruessmann’s [231] data, a retrospective database analysis conducted by Jermendy et al. [204] from 2009 to 2019 revealed a lower occurrence of cardio- and cerebrovascular morbidity, cancer events, and all-cause mortality in DPN patients treated with ALA (n = 23,843) compared to those receiving symptomatic pharmacotherapies (n = 23,843), primarily gabapentin, pregabalin, and duloxetine. Each patient was followed for a minimum of 1 year.
The most frequently reported side effects of oral ALA supplementation are allergic reactions affecting the skin, including rashes, hives, and itching [9]. The use of ALA should be discontinued immediately if any allergic reaction occurs [207]. Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and vertigo have been reported, with one trial indicating that these symptoms are dose-dependent [195]. Additionally, malodorous urine is observed in those taking 1200 mg/day of ALA [246].
Although few adverse effects are noted in animal studies, it has been observed in thiamine-deficient rats that ALA (20 mg/kg IP) caused fatal complications. In contrast, thiamine-sufficient rats showed no adverse effects from ALA supplementation, and the action of ALA in the deficient rats could be prevented by administering thiamine (250 µg) just before ALA administration [144]. The animals in this study were severely thiamine-deficient, exhibiting frank polyneuritis from thiamine deficiency; it may be prudent that any group likely to be severely thiamine-deficient, such as alcoholics, should receive supplemental thiamine if ALA is given.
Additionally, research conducted on primates demonstrated that high doses (90–100 mg/kg IV) resulted in significant necrotic regions in the thigh muscles, as well as in the liver, heart, and kidneys, suggesting that excessive intravenous ALA can cause symptoms identical to those caused by lower doses [247].
8.1. Effects on the Cardiovascular System
Several studies have evaluated the effects of ALA on cardiac function. In the longest randomized clinical trial ever conducted [196], oral treatment with 600 mg of ALA once daily for DPN patients showed that the incidence of serious AEs related to cardiovascular disorders, blood pressure (BP), and heart rate did not differ between the ALA and placebo groups. Corrected QT interval (QTc) prolongation > 60 ms occurred significantly more often in the placebo group than in the ALA group (5.0% vs. 1.4%; p < 0.05). Dudek et al. (2008) [248] found that ALA (100 mg/kg/day IP for 8 days) did not influence rats’ BP compared to the control group. The same author [249] reported that a single IP dose of ALA 50 mg/kg significantly decreased BP from the 50th minute after drug administration. Consequently, the potential for ALA to reduce BP should be considered, even though it does not cause significant orthostatic hypotension.
In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated ALA’s protective role in lipotoxic cardiomyopathy [250] and in maintaining cardiovascular function under hypoxic conditions [251,252]. While ALA generally exhibits cardioprotective effects, primarily due to its antioxidant properties, it may provoke adverse cardiovascular effects under certain metabolic conditions [253], particularly in diabetic settings where oxidative stress is poorly regulated.
8.2. Effects on the Respiratory System
Years of clinical use have shown that ALA is not expected to negatively impact the respiratory system. Currently, there is no evidence to suggest that ALA itself causes direct adverse effects on lung function or contributes to the development of respiratory diseases. On the contrary, its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties seem beneficial for respiratory health, particularly in conditions involving inflammation and oxidative stress [254,255].
8.3. Effects on the Central Nervous System
ALA has proven to be safe at the recommended therapeutic dose of 600 mg/day. While ALA has potential therapeutic benefits for improving insulin sensitivity and mitochondrial function, its ability to induce hypoglycemia poses risks to the nervous system, especially under fasting conditions [256,257]. These findings highlight the need for careful monitoring of blood glucose levels when using ALA, particularly in populations at risk of hypoglycemia, as the CNS relies heavily on a constant glucose supply for energy production and normal functioning. ALA can induce refractory convulsions in children in cases of intoxication [258].
8.4. Effects on the Liver and Kidneys
A few experimental studies aimed at evaluating the safety of long-term prophylactic treatment with ALA suggest that it may exhibit pro-oxidant properties, cause oxidative stress, disrupt lipid metabolism, and lead to liver steatosis [107,259,260,261,262]. The impact of ALA on methylation pathways suggests a risk of hepatic and renal toxicity, particularly with long-term or high-dose treatments [263]. There is limited clinical experience with patients who have liver impairment. Therefore, when treating individuals with liver issues, ALA should be administered with caution [264].
8.5. Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity
The findings from several preclinical studies suggest that ALA plays a protective role in male reproductive health, particularly under oxidative stress conditions and exposure to environmental toxins [265,266,267,268,269]. ALA positively influences embryo development, oocyte maturation, and reproductive outcomes [125,270,271,272,273,274]. Regular ALA administration normalizes menstrual blood flow and reduces pelvic pain in patients with endometriosis. ALA could offer benefits for infertility as a novel agent, and further clinical research is recommended [9,275,276,277]. According to current evidence, using ALA supplements during pregnancy is safe [245,278,279,280]. Di Tucci et al. (2018) [281] performed a comprehensive literature search and concluded that ALA can safely treat neuropathic pain and serve as dietary support during pregnancy. Nonetheless, additional information is necessary to comprehensively grasp the function of ALA supplementation during this time. There appear to be no published reports on ALA levels in human milk, and the excretion of ALA in human milk remains unknown.
8.6. Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome
ALA can induce insulin autoimmune syndrome (IAS; also known as Hirata’s disease), characterized by hypoglycemia, high concentrations of immunoreactive insulin, and high titers of antibodies to endogenous insulin, even without prior exposure to exogenously administered insulin. ALA activates the insulin receptor by binding to it extracellularly and can also traverse the cell membrane to activate AMPK, which enhances GLUT4 expression and glucose uptake. This leads to increased glycolysis and initiates the Krebs cycle via interaction with pyruvate dehydrogenase. Additionally, ALA may alter insulin by cleaving disulfide bonds, which exposes fragments to the immune system and results in the production of insulin autoantibodies (IAA), contributing to IAS [65]. IAA is a type of IgG antibody with low affinity and high capacity, causing postprandial and nocturnal hypoglycemia in IAS patients. The IAA titer declines gradually, taking between 2 and 36 months after stopping ALA due to the long half-life (3–4 weeks) of IAA [282].
IAS manifests as neurological symptoms, including tremors, palpitations, anxiety, sweating, hunger, and numbness or tingling. The pathogenesis of ALA-induced IAS remains not fully understood. IAS is classified into two types: type 1, caused by antibodies against insulin [283], and type 2, caused by antibodies against the insulin receptor [282]. An individual’s ethnic and genetic background significantly influences their predisposition to IAS [284,285,286]. Individuals with HLA-DRB1*04:03 and HLA-DRB1*04:06 who consume ALA might have a higher risk of developing IAS [284,286,287]. When conducting a differential diagnosis of spontaneous hypoglycemia in individuals taking ALA, IAS should be considered [65,284,288,289]. Since IAS is a type VII hypersensitivity autoimmune disease, it is assumed that the consumed dose does not significantly contribute to the development of IAS. The presence of other autoimmune diseases may predispose to the development of IAS. Drug-induced cases have been reported, linked to carbimazole, methimazole, clopidogrel, propylthiouracil, isoniazid, hydralazine, imipenem, and ALA [283,286,290,291]. However, IAS is not associated with consuming naturally occurring ALA-containing foods [288].
ALA’s disulfide bonds and sulfhydryl (-SH) groups may contribute to its potential to induce autoimmunity through mechanisms such as hapten formation or alterations in protein structure and antigenicity. Li et al. (2021) [292] investigated the clinical characteristics of ALA-induced IAS in 37 patients (23 from Asia, 13 from Europe, and one from South America). The median age of these patients was 61 years (range 32–82), and the median BMI was 26.3 kg/m2 (range 17.8–36.9). The median dose was 600 mg (range 200–600), with a median course of treatment lasting 20 days (range 2–120) and administered through PO or IV routes. Six patients (16.2%) also had autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, anaphylactoid purpura, autoimmune thyroiditis, and glomerulonephritis.
IAS can develop within 1 week to 2 months during ALA use and may also appear a few hours to 2 weeks after discontinuing the medication [282]. IAS is a self-limiting condition with a favorable prognosis. Symptoms of hypoglycemia typically resolve within 3 to 8 months following the cessation of ALA. Steroid treatment and the discontinuation of ALA will, over time, cause IAS to disappear [293]. Refractory cases may require immunomodulators such as rituximab or azathioprine [294]. There is likely an underestimation of IAS occurrences due to a lack of awareness about the disease, resulting in underdiagnosis and underreporting. Due to the limited data available, it is impossible to accurately quantify the risk of developing IAS after consuming ALA. The safe dose of ALA that would not lead to IAS may vary among individuals and cannot be determined based on the current evidence [288].
8.7. Overdosage
The range of toxicity from ALA ingestion is varied and challenging to determine based on existing literature. ALA is generally considered very safe, with intoxication being quite rare [295]. The initial clinical signs of intoxication include psychomotor agitation or impaired consciousness, often accompanied by generalized convulsions and the onset of lactic acidosis [296]. Seizures that progress to status epilepticus have been reported in pediatric patients [258,297,298,299]. Polat et al. [299] presented a case of ALA intoxication in a 16-year-old girl who took a total dose of 1800 mg ALA. Furthermore, hypoglycemia, shock, rhabdomyolysis, hemolysis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, bone marrow depression, thrombocytopenia, and multiple organ failure have been recognized as consequences of high-dose ALA intoxication [298,299,300,301]. The initiation of general poisoning therapy (such as induced vomiting, gastric lavage, and activated charcoal administration), along with prompt hospitalization, is advised if there is even the slightest suspicion of ALA intoxication (for instance, more than 6 g in adults or over 50 mg/kg in children). Treatment for lactic acidosis, generalized seizures, and other potentially life-threatening effects should be symptomatic and follow current intensive care unit guidelines. To date, there is no evidence that hemodialysis, hemoperfusion, or filtration methods are effective in facilitating the removal of ALA.
10. Discussion
Alpha-lipoic acid has been extensively studied for over 70 years, yet significant gaps remain in our understanding of its optimal clinical application for DPN. This comprehensive review reveals several critical considerations that merit further discussion.
The pleiotropic nature of ALA presents both opportunities and challenges in therapeutic applications [8,9,64]. As an endogenous substance with universal antioxidant properties, ALA’s mechanism of action in DPN is multifaceted, involving antioxidant effects [14,15,68], regulation of cellular redox status [68,73,78], improvement of mitochondrial function [3,7,81,82], enhancement of insulin sensitivity [65,83,84], and modulation of inflammatory pathways [114,115,116,117,118]. This complexity makes it difficult to isolate the precise mechanisms responsible for its clinical benefits in DPN. Furthermore, the interaction between ALA and the pathophysiology of DPN, which itself is incompletely understood [165,166], creates additional layers of complexity.
Clinical evidence supports 600 mg/day oral ALA as an effective and well-tolerated treatment for DPN, with efficacy comparable to intravenous administration [94,110,195,211]. However, the optimal treatment duration remains uncertain. While some studies suggest benefits within 3–5 weeks [229], others indicate that long-term therapy (≥6 months) may be necessary for sustained improvements [85,196]. The NATHAN 1 trial’s four-year data demonstrated that ALA had a favorable impact on neuropathic impairments but not on neurophysiological markers [196], suggesting that different aspects of DPN may respond differently to ALA therapy. Additionally, evidence suggests that discontinuation of ALA leads to symptom recurrence [231], indicating that ongoing treatment may be necessary.
The variability in ALA’s pharmacokinetics presents practical challenges for clinical application [53,54]. Factors such as food intake [57,62], age [56,63], genetic variations [284,286,287], and concurrent medications [126,127,128] can significantly affect ALA’s bioavailability and efficacy. The high first-pass metabolism and short half-life of ALA necessitate careful consideration of dosing regimens [52,57,59,60]. Furthermore, the different forms of ALA available commercially (racemic mixture versus R-enantiomer) [25,26] may have different pharmacokinetic profiles and therapeutic efficacies, yet most clinical studies have used the racemic form [302,305].
Safety considerations reveal that while ALA is generally well-tolerated at 600 mg/day [205,216], higher doses may increase the risk of adverse effects [195]. The potential for rare but serious reactions such as IAS [65,282,283,284,285,286], particularly in individuals with specific HLA genotypes [284,286,287], warrants caution. The risk of hypoglycemia, especially when ALA is combined with antidiabetic medications [130,131,132], necessitates careful monitoring. Moreover, the potential pro-oxidant effects of ALA at high doses highlight the importance of appropriate dosing [107,259,260,261,262].
A significant limitation in the current evidence base is the heterogeneity in study designs, patient populations, outcome measures, and treatment protocols [22,193,213]. Many trials have been relatively short-term, potentially underestimating both benefits and risks of long-term ALA therapy [85,194,195,196]. The lack of standardized assessment tools for DPN severity and progression complicates the interpretation of treatment effects across studies [23,174]. Additionally, most studies have focused on symptomatic improvements rather than disease modification or prevention [22,175].
The expanding market for ALA presents challenges related to product quality, standardization, and regulatory oversight [302,303,304,305]. The availability of ALA as both a pharmaceutical and a dietary supplement creates potential confusion among healthcare providers and patients regarding appropriate formulations, dosing, and quality standards. The significant variations in ALA content in nutritional supplements (7–600 mg) compared to the established therapeutic dose (600 mg) may lead to suboptimal treatment outcomes.
Future research should focus on identifying biomarkers that predict response to ALA therapy [87,110], optimizing dosing regimens based on pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling [53,57], and developing extended-release formulations to overcome the limitations of ALA’s short half-life [59,60]. Longitudinal studies investigating the preventive potential of ALA in early-stage DPN [71,87] and studies comparing R-ALA to racemic ALA in clinical settings are warranted [25,56]. Genetic studies could help identify individuals at risk for adverse effects such as IAS [284,286,287]. Additionally, combination therapies that leverage synergistic effects between ALA and other pathogenetically oriented treatments deserve further investigation [95,96,146,218,219,220,221,222,223,224,225,226].
11. Conclusions
Scientific literature offers extensive information on ALA’s pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and safety. ALA represents a valuable therapeutic option for managing DPN, offering benefits through multiple mechanisms that address the pathophysiological processes underlying diabetic neuropathy. The evidence supports oral ALA at 600 mg/day as an effective and well-tolerated treatment that improves neuropathic symptoms. The favorable safety profile of ALA at this dose makes it an attractive option, particularly for long-term management. However, several challenges remain, including optimizing treatment duration, addressing pharmacokinetic variability, managing potential drug interactions, and minimizing rare adverse effects. The heterogeneity in available ALA products and varying regulatory standards across regions complicates clinical implementation. Despite these challenges, ALA holds promise as a pathogenesis-oriented therapy for DPN, offering advantages over purely symptomatic treatments. As our understanding of both ALA and DPN continues to evolve, improved clinical protocols and more targeted approaches may enhance the effectiveness of ALA therapy. Future research should focus on personalized treatment strategies, biomarker development, and combination therapies to maximize the therapeutic potential of this endogenous antioxidant that has withstood 70 years of scientific scrutiny.
12. Limitations
A key limitation of this review is the challenge of covering all areas related to the biological effects and medical implications of ALA. We have endeavored to cite many distinguished reviews; however, several aspects of synthesis, natural sources of ALA, and its applications in various medical and cosmetic fields remain unaddressed in this review, though they are covered by the cited reviews.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.M. and I.N.; original draft preparation, I.M., Y.V. and I.N.; data curation, Y.V., S.I. and I.K.; writing—review and editing, I.K., V.P., S.I. and L.M.; supervision, I.N. and V.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Medical University of Sofia and the European Union—NextGenerationEU through the National Recovery and Resilience Plan of the Republic of Bulgaria, project № BG-RRP-2.004-0004-C01.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Superti, F.; Russo, R. Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Biological Mechanisms and Health Benefits. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafaee, F.; Derakhshani, M.; Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Alpha-lipoic acid, as an effective agent against toxic elements: A review. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 3345–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, K.P.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Smith, A.R.; Hagen, T.M. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2009, 1790, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Selim, M.A.; El-Sayed, N.M. α-Lipoic acid ameliorates oral mucositis and oxidative stress induced by methotrexate in rats. Histological and immunohistochemical study. Life Sci. 2017, 171, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanaida, M.; Lysiuk, R.; Mykhailenko, O.; Hudz, N.; Abdulsalam, A.; Gontova, T.; Oleshchuk, O.; Ivankiv, Y.; Shanaida, V.; Lytkin, D. Alpha-lipoic acid: An antioxidant with anti-aging properties for disease therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2025, 32, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, R.M.; MacLeay, J.M.; Gross, K.L. Alpha-lipoic acid as a nutritive supplement for humans and animals: An overview of its use in dog food. Animals 2021, 11, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmonson, A.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Lipoic acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 7522–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Berkay Yılmaz, Y.; Antika, G.; Boyunegmez Tumer, T.; Fawzi Mahomoodally, M.; Lobine, D.; Akram, M.; Riaz, M.; Capanoglu, E.; Sharopov, F. Insights on the use of α-lipoic acid for therapeutic purposes. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Ray, A.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Bishen, S.M.; Mishra, H.; Khurana, A. Molecular and therapeutic insights of alpha-lipoic acid as a potential molecule for disease prevention. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2023, 33, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biewenga, G.P.; Haenen, G.R.; Bast, A. The pharmacology of the antioxidant lipoic acid. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1997, 29, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea Moura, F.; Queiroz de Andrade, K.; Celia Farias dos Santos, J.; Oliveira Fonseca Goulart, M. Lipoic acid: Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory role and clinical applications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 458–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Karunakaran, U.; Ho Jeoung, N.; Jeon, J.-H.; Lee, I.-K. Physiological effect and therapeutic application of alpha lipoic acid. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 3636–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.B.; Negrato, C.A. Alpha-lipoic acid as a pleiotropic compound with potential therapeutic use in diabetes and other chronic diseases. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorąca, A.; Huk-Kolega, H.; Piechota, A.; Kleniewska, P.; Ciejka, E.; Skibska, B. Lipoic acid–biological activity and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.D.M.; Lauria, P.S.S.; Lima, A.A.d.; Opretzka, L.C.F.; Marcelino, H.R.; Villarreal, C.F. Alpha-lipoic acid as an antioxidant strategy for managing neuropathic pain. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laher, I. Diabetes and alpha lipoic acid. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 15229. [Google Scholar]
- Ensmenger, P.J. Alpha Lipoic Acid: A Review and Comparison to Current Treatment Guidelines of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Master’s Thesis, Arcadia University, Glenside, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroz-Aldave, J.; Durand-Vásquez, M.; Gamarra-Osorio, E.; Suárez-Rojas, J.; Roseboom, P.J.; Alcalá-Mendoza, R.; Coronado-Arroyo, J.; Zavaleta-Gutiérrez, F.; Concepción-Urteaga, L.; Concepción-Zavaleta, M. Diabetic neuropathy: Past, present, and future. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 14, 153. [Google Scholar]
- Anandhanarayanan, A.; Teh, K.; Goonoo, M.; Tesfaye, S.; Selvarajah, D. Diabetic Neuropathies. In Endotext. South Dartmouth; Feingold, K.R., Ahmed, S.F., Anawalt, B., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bodman, M.A.; Dreyer, M.A.; Varacallo, M. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wukich, D.K.; Raspovic, K.M.; Suder, N.C. Patients with diabetic foot disease fear major lower-extremity amputation more than death. Foot Ankle Spec. 2018, 11, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baicus, C.; Purcarea, A.; von Elm, E.; Delcea, C.; Furtunescu, F.L. Alpha-lipoic acid for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2024, 1, CD012967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, A.; Ketenci, A.; Sahin, I.; Sengun, I.S.; Oner, R.I.; Erdem Tilki, H.; Adas, M.; Soyleli, H.; Demir, T. Expert opinion on screening, diagnosis and management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A multidisciplinary approach. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1380929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koufaki, Μ. Therapeutic applications of lipoic acid: A patent review (2011–2014). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2014, 24, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachanderan, R.; Schaefer, B. Lipoic acid. ChemTexts 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, A.L.; Crișan, S.; Bârcă, M.; Ciobanu, A.-M.; Varlas, V.N.; Pop, C.; Pali, M.-A.; Cauni, D.; Ozon, E.A.; Udeanu, D. Evaluation of dissolution profiles of a newly developed solid oral immediate-release formula containing alpha-lipoic acid. Processes 2021, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, J.A.; Feichtinger, R.G.; Tort, F.; Ribes, A.; Sperl, W. Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2014, 37, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, A.; Joshi, A.K.; Smith, S. Mechanism of the β-ketoacyl synthase reaction catalyzed by the animal fatty acid synthase. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 10877–10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Joshi, A.K.; Smith, S. Cloning, expression, characterization, and interaction of two components of a human mitochondrial fatty acid synthase: Malonyltransferase and acyl carrier protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40067–40074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Joshi, A.K.; Hofmann, J.; Schweizer, E.; Smith, S. Cloning, expression, and characterization of the human mitochondrial β-ketoacyl synthase: Complementation of the yeast cem1 knock-out strain. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 12422–12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Leskinen, H.; Liimatta, E.; Sormunen, R.T.; Miinalainen, I.J.; Hassinen, I.E.; Hiltunen, J.K. Myocardial overexpression of Mecr, a gene of mitochondrial FAS II leads to cardiac dysfunction in mouse. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastaniotis, A.J.; Autio, K.J.; Sormunen, R.T.; Hiltunen, J.K. Htd2p/Yhr067p is a yeast 3-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase essential for mitochondrial function and morphology. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autio, K.J.; Kastaniotis, A.J.; Pospiech, H.; Miinalainen, I.J.; Schonauer, M.S.; Dieckmann, C.L.; Hiltunen, J.K. An ancient genetic link between vertebrate mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis and RNA processing. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Kastaniotis, A.J.; Miinalainen, I.J.; Rajaram, V.; Wierenga, R.K.; Hiltunen, J.K. 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 8 and carbonyl reductase type 4 assemble as a ketoacyl reductase of human mitochondrial FAS. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3682–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonauer, M.S.; Kastaniotis, A.J.; Kursu, V.S.; Hiltunen, J.K.; Dieckmann, C.L. Lipoic acid synthesis and attachment in yeast mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23234–23242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, P.; Kriek, M.; Bryant, P.; Roach, P.L. Lipoyl synthase inserts sulfur atoms into an octanoyl substrate in a stepwise manner. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5197–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carothers, D.J.; Pons, G.; Patel, M.S. Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase: Functional similarities and divergent evolution of the pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1989, 268, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltunen, J.K.; Autio, K.J.; Schonauer, M.S.; Kursu, V.S.; Dieckmann, C.L.; Kastaniotis, A.J. Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis and respiration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2010, 1797, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.-J.; Moini, H.; Shon, H.-K.; Chung, A.-S.; Packer, L. α-Lipoic acid decreases thiol reactivity of the insulin receptor and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-Q.; Ling, X.; Wang, H.-J.; Chen, F.-E. α-Lipoic acid chemistry: The past 70 years. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 36346–36363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, W.X.; Zheng, G.W.; Xu, J.H. Identification of an ε-Keto Ester Reductase for the Efficient Synthesis of an (R)-α-Lipoic Acid Precursor. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnavis, N.; Babu, R.L.; Vadivel, S.K.; Deshpande, A.A.; Bhalerao, U. Lipase catalyzed regio-and stereospecific hydrolysis: Chemoenzymatic synthesis of both (R)-and (S)-enantiomers of α-lipoic acid. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1998, 9, 4109–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-J.; Ni, Y.; Zheng, G.-W.; Chen, H.-H.; Zhu, Z.-R.; Xu, J.-H. Enzymatic resolution of a chiral chlorohydrin precursor for (R)-α-lipoic acid synthesis via lipase catalyzed enantioselective transacylation with vinyl acetate. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 99, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, M.H.; Golding, B.T.; Hudson, A.T. Syntheses of α-(R)-and α-(S)-lipoic acid from (S)-malic acid. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1988, 1, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.; Mysorekar, S.V.; Pawar, S.M.; Gurjar, M. Synthesis of (3R, 4R)-1,2-divinylglycol and its unsymmetrical derivatives: An application to the synthesis of R-(+)-α-lipoic acid. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 1990, 9, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, P.C.B.; Rayner, C.M.; Sutherland, I.O. Enantioselective synthesis of R-(+)-α-lipoic acid. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1986, 18, 1408–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, R.; Hain, U.; Berndt, M.; Gewald, R.; Reissig, H.-U. Enantioselective synthesis of (S)-and (R)-6-hydroxy-8-nonene-carboxylates by asymmetric catalysis: A formal synthesis of (R)-α-lipoic acid and its (S)-antipode. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2000, 11, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhya, T.; Nikalje, M.; Sudalai, A. Asymmetric dihydroxylation and hydrogenation approaches to the enantioselective synthesis of R-(+)-α-lipoic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 4891–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Duan, W. An enantioselective formal synthesis of (+)-(R)-α-lipoic acid by an l-proline-catalyzed aldol reaction. Synthesis 2008, 2008, 383–386. [Google Scholar]
- Sih, C.J.; ZHOU, B.N.; Gopalan, A.S.; SHIEH, W.R.; CHEN, C.S.; Girdaukas, G.; Vanmiddlesworth, F. Enantioselective Reductions of β-keto-Esters by Bakers’ Yeast. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1984, 434, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adger, B.; Bes, M.T.; Grogan, G.; McCague, R.; Pedragosa-Moreau, S.; Roberts, S.M.; Villa, R.; Wan, P.W.H.; Willetts, A.J. Application of enzymic Baeyer–Villiger oxidations of 2-substituted cycloalkanones to the total synthesis of (R)-(+)-lipoic acid. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 15, 1563–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breithaupt-Grögler, K.; Niebch, G.; Schneider, E.; Erb, K.; Hermann, R.; Blume, H.H.; Schug, B.S.; Belz, G.G. Dose-proportionality of oral thioctic acid—Coincidence of assessments via pooled plasma and individual data. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 8, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, B.; Sarraçoğlu, N.; Pınarbaşlı, O. Alpha lipoic acid bioequivalence study redesigned: A candidate for highly variable drugs. Istanb. J. Pharm. 2021, 51, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Marracci, G.H.; Munar, M.Y.; Cherala, G.; Stuber, L.E.; Alvarez, L.; Shinto, L.; Koop, D.R.; Bourdette, D.N. Pharmacokinetic study of lipoic acid in multiple sclerosis: Comparing mice and human pharmacokinetic parameters. Mult. Scler. J. 2010, 16, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignini, F.; Nasuti, C.C.; Gioventu, G.; Napolioni, V.; Di Martino, P. Human bioavailability and pharmacokinetic profile of different formulations delivering alpha lipoic acid. J. Bioequiv. Bioavailab. 2012, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hermann, R.; Mungo, J.; Cnota, P.J.; Ziegler, D. Enantiomer-selective pharmacokinetics, oral bioavailability, and sex effects of various alpha-lipoic acid dosage forms. Clin. Pharmacol. Adv. Appl. 2014, 6, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichert, J.; Hermann, R.; Ruus, P.; Preiss, R. Plasma kinetics, metabolism, and urinary excretion of alpha-lipoic acid following oral administration in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 43, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassanego, G.; Rodrigues, P.; Bauermann, L.D.F.; Trevisan, G. Evaluation of the analgesic effect of α-lipoic acid in treating pain disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 177, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, R.; Niebch, G.; Borbe, H.; Fieger-Büschges, H.; Ruus, P.; Nowak, H.; Riethmüller-Winzen, H.; Peukert, M.; Blume, H. Enantioselective pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of different racemic α-lipoic acid formulations in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 4, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brufani, M.; Figliola, R. (R)-α-lipoic acid oral liquid formulation: Pharmacokinetic parameters and therapeutic efficacy. Acta Bio-Medica Atenei Parm. 2014, 85, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zicker, S.C.; Avila, A.; Joshi, D.K.; Gross, K.L. Pharmacokinetics of orally administered DL-α-lipoic acid in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2010, 71, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichert, J.; Tuemmers, T.; Achenbach, H.; Preiss, C.; Hermann, R.; Ruus, P.; Preiss, R. Pharmacokinetics of alpha-lipoic acid in subjects with severe kidney damage and end-stage renal disease. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.J.; Butler, J.A.; Bemer, B.; Dixon, B.; Johnson, S.; Garrard, M.; Sudakin, D.L.; Christensen, J.M.; Pereira, C.; Hagen, T.M. Age and gender dependent bioavailability of R-and R, S-α-lipoic acid: A pilot study. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, G.A.; Iannuzzo, F.; Xerra, F.; Genovese, G.; Pandolfo, G.; Cedro, C.; Muscatello, M.R.A.; Bruno, A. Cognitive and mood effect of alpha-lipoic acid supplementation in a nonclinical elder sample: An open-label pilot study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capece, U.; Moffa, S.; Improta, I.; Di Giuseppe, G.; Nista, E.C.; Cefalo, C.M.; Cinti, F.; Pontecorvi, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Giaccari, A. Alpha-lipoic acid and glucose metabolism: A comprehensive update on biochemical and therapeutic features. Nutrients 2022, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, P.; Tritschler, H.J.; Wolff, S.P. Thioctic (lipoic) acid: A therapeutic metal-chelating antioxidant? Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 50, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, P.A.; Nickander, K.K.; Tritschler, H.J. The roles of oxidative stress and antioxidant treatment in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 1997, 46, S38–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, L.; Witt, E.H.; Tritschler, H.J. Alpha-lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moini, H.; Packer, L.; Saris, N.-E.L. Antioxidant and prooxidant activities of α-lipoic acid and dihydrolipoic acid. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2002, 182, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Knezevic, N.N.; Abd-Elsayed, A.; Ray, M.; Patel, K.; Chowdhury, B. Treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy—A narrative review of pharmacological and interventional approaches. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.; Tesfaye, S.; Spallone, V.; Gurieva, I.; Al Kaabi, J.; Mankovsky, B.; Martinka, E.; Radulian, G.; Nguyen, K.T.; Stirban, A.O. Screening, diagnosis and management of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy in clinical practice: International expert consensus recommendations. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 186, 109063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sementina, A.; Cierzniakowski, M.; Rogalska, J.; Piechowiak, I.; Spichalski, M.; Araszkiewicz, A. A novel approach to alpha-lipoic acid therapy in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 91, e714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamatsu, M.; Nickander, K.K.; Schmelzer, J.D.; Raya, A.; Wittrock, D.A.; Tritschler, H.; Low, P.A. Lipoic acid improves nerve blood flow, reduces oxidative stress, and improves distal nerve conduction in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 1995, 18, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, Z.; Ozkaya, A.; Yilmaz, O.; Yuce, A.; Gunes, M. Investigation of the role of α-lipoic acid on fatty acids profile, some minerals (zinc, copper, iron) and antioxidant activity against aluminum-induced oxidative stress in the liver of male rats. J. Basic. Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 28, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, L.; Kraemer, K.; Rimbach, G. Molecular aspects of lipoic acid in the prevention of diabetes complications. Nutrition 2001, 17, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppey, L.J.; Gellett, J.S.; Davidson, E.P.; Dunlap, J.A.; Lund, D.D.; Yorek, M.A. Effect of antioxidant treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats on endoneurial blood flow, motor nerve conduction velocity, and vascular reactivity of epineurial arterioles of the sciatic nerve. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1927–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibska, B.; Kochan, E.; Stanczak, A.; Lipert, A.; Skibska, A. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of α-lipoic acid on lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in rat kidney. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2023, 71, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morcos, M.; Borcea, V.; Isermann, B.; Gehrke, S.; Ehret, T.; Henkels, M.; Schiekofer, S.; Hofmann, M.; Amiral, J.; Tritschler, H. Effect of α-lipoic acid on the progression of endothelial cell damage and albuminuria in patients with diabetes mellitus: An exploratory study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2001, 52, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratantonio, D.; Speciale, A.; Molonia, M.; Bashllari, R.; Palumbo, M.; Saija, A.; Cimino, F.; Monastra, G.; Virgili, F. Alpha-lipoic acid, but not di-hydrolipoic acid, activates Nrf2 response in primary human umbilical-vein endothelial cells and protects against TNF-α induced endothelium dysfunction. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 655, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonooz, S.R.; Hasani, M.; Morvaridzadeh, M.; Pizarro, A.B.; Heydari, H.; Yosaee, S.; Rezamand, G.; Heshmati, J. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on oxidative stress parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhuang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, G.; Cai, W. Alphalipoic acid prevents oxidative stress and peripheral neuropathy in nab-paclitaxel-treated rats through the Nrf2 signalling pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3142732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, N.E.; Jack, A.M.; Cotter, M.A. Effect of α-lipoic acid on vascular responses and nociception in diabetic rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, E.J.; Jacob, S.; Streeper, R.S.; Fogt, D.L.; Hokama, J.Y.; Tritschler, H.J. Stimulation by α-lipoic acid of glucose transport activity in skeletal muscle of lean and obese Zucker rats. Life Sci. 1997, 61, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad, D.; Somwar, R.; Sweeney, G.; Yaworsky, K.; Hayashi, M.; Ramlal, T.; Klip, A. The antihyperglycemic drug α-lipoic acid stimulates glucose uptake via both GLUT4 translocation and GLUT4 activation: Potential role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in GLUT4 activation. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, D.; Hanefeld, M.; Ruhnau, K.-J.; Hasche, H.; Lobisch, M.; Schütte, K.; Kerum, G.; Malessa, R. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: A 7-month multicenter randomized controlled trial (ALADIN III Study). ALADIN III Study Group. Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Yu, J.H.; Kim, H. Mechanism of α-Lipoic Acid-Induced Apoptosis of Lung Cancer Cells: Involvement of Ca2+. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1171, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D. Pathogenetic treatments for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 206, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.Y.; Ha, A.W.; Kim, W.K. α-Lipoic acid reduced weight gain and improved the lipid profile in rats fed with high fat diet. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2012, 6, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlduff, C.E.; Rutkove, S.B. Critical appraisal of the use of alpha lipoic acid (thioctic acid) in the treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2011, 7, 377–385. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, D.; Reljanovic, M.; Mehnert, H.; Gries, F. α-Lipoic acid in the treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy in Germany: Current evidence from clinical trials. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 1999, 107, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, D. Thioctic acid for patients with symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy: A critical review. Treat. Endocrinol. 2004, 3, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.S. Efficacy and safety of α-lipoic acid supplementation in the treatment of symptomatic diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Educ. 2007, 33, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanas, N.; Maltezos, E. α-Lipoic acid, diabetic neuropathy, and Nathan’s prophecy. Angiology 2012, 63, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanas, N.; Ziegler, D. Efficacy of α-lipoic acid in diabetic neuropathy. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 2721–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingali, U.; Kammila, S.; Mekala, P.; Yareeda, S.; Penugonda, S. A study to evaluate the effect of alpha-lipoic acid on neuropathic symptoms in diabetic neuropathy patients on gabapentin or pregabalin. Cureus 2024, 16, e70299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, W.; Du, X.; Luo, Z.; Hu, J.; Peng, S. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Pathogenetic mechanisms and treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1265372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csiha, S.; Hernyák, M.; Molnár, Á.; Lőrincz, H.; Katkó, M.; Paragh, G.; Bodor, M.; Harangi, M.; Sztanek, F.; Berta, E. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Treatment Reduces the Levels of Advanced End Glycation Products in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Neuropathy. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.A.; Lee, N.Y.; Park, T.S.; Jin, H.Y. Comparison of peripheral nerve protection between insulin-based glucose control and alpha lipoic acid (ALA) in the streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rat. Endocrine 2018, 61, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, G.; Vinik, A. Nerve growth factor and diabetic neuropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2003, 4, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, G.; Guo, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, K.; Li, J.; Xiao, Q. α-lipoic acid can greatly alleviate the toxic effect of AGES on SH-SY5Y cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2855–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Smith, M.T. Neurotrophins and neuropathic pain: Role in pathobiology. Molecules 2015, 20, 10657–10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.J.; Obrosova, I.; Cao, X.; Van Huysen, C.; Greene, D.A. Effects of DL-alpha-lipoic acid on peripheral nerve conduction, blood flow, energy metabolism, and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, N.; Cotter, M. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Effects And Combination Therapy With Gamma-Linolenic Acid. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2000, 5, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorąca, A.; Asłanowicz-Antkowiak, K. Prophylaxis with α-lipoic acid against lipopolysaccharide-induced brain injury in rats. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2009, 57, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lou, Z.; Xi, H.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Asakawa, T. Verification of neuroprotective effects of alpha-lipoic acid on chronic neuropathic pain in a chronic constriction injury rat model. Open Life Sci. 2021, 16, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bast, A.; Haenen, G. Lipoic acid: A multifunctional antioxidant. In Thiol Metabolism and Redox Regulation of Cellular Function; Pompella, A., Banhegyi, G., Wellman-Rousseau, M., Eds.; IOS Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Maritim, A.; Sanders, R.; Watkins Iii, J. Effects of α-lipoic acid on biomarkers of oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2003, 14, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pershadsingh, H.A. α-Lipoic acid: Physiologic mechanisms and indications for the treatment of metabolic syndrome. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, L.; Cadenas, E. Lipoic acid: Energy metabolism and redox regulation of transcription and cell signaling. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 48, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.; Porta, M.; Papanas, N.; Mota, M.; Jermendy, G.; Beltramo, E.; Mazzeo, A.; Caccioppo, A.; Striglia, E.; Serhiyenko, V. The role of biofactors in diabetic microvascular complications. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2022, 18, 20–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Singh, T.G.; Dahiya, R.S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. α-Lipoic acid, an organosulfur biomolecule a novel therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative disorders: An mechanistic perspective. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 1853–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haak, E.; Usadel, K.; Kusterer, K.; Amini, P.; Frommeyer, R.; Tritschler, H.; Haak, T. Effects of alpha-lipoic acid on microcirculation in patients with peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2000, 108, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodosis-Nobelos, P.; Papagiouvannis, G.; Tziona, P.; Rekka, E.A. Lipoic acid. Kinetics and pluripotent biological properties and derivatives. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 6539–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, N.E.; Cotter, M.A. Pro-inflammatory mechanisms in diabetic neuropathy: Focus on the nuclear factor kappa B pathway. Curr. Drug Targets 2008, 9, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, P.A.; Wang, X.X.; Xu, G.Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.H. Alpha-lipoic acid downregulates TRPV1 receptor via NF-κB and attenuates neuropathic pain in rats with diabetes. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-J.; Wei, H.; Hagen, T.; Frei, B. α-Lipoic acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory responses by activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4077–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajith, T.A. Alpha-lipoic acid: A possible pharmacological agent for treating dry eye disease and retinopathy in diabetes. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nádró, B.; Lőrincz, H.; Molnár, Á.; Szentpéteri, A.; Zöld, E.; Seres, I.; Páll, D.; Paragh, G.; Kempler, P.; Harangi, M. Effects of alpha-lipoic acid treatment on serum progranulin levels and inflammatory markers in diabetic neuropathy. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 03000605211012213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y. The dual role of TRPV1 in peripheral neuropathic pain: Pain switches caused by its sensitization or desensitization. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2024, 17, 1400118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazğan, B.; Yazğan, Y.; Nazıroğlu, M. Alpha-lipoic acid modulates the diabetes mellitus-mediated neuropathic pain via inhibition of the TRPV1 channel, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in rats. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2023, 55, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacini, A.; Tomassoni, D.; Trallori, E.; Micheli, L.; Amenta, F.; Ghelardini, C.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Traini, E. Comparative assessment of the activity of racemic and dextrorotatory forms of thioctic (Alpha-Lipoic) acid in low back pain: Preclinical results and clinical evidences from an open randomized trial. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 607572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midaoui, A.E.; Elimadi, A.; Wu, L.; Haddad, P.S.; De Champlain, J. Lipoic acid prevents hypertension, hyperglycemia, and the increase in heart mitochondrial superoxide production. Am. J. Hypertens. 2003, 16, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Lu, J.; Chen, B.; Yuan, L.; Chen, L.; Ju, L.; Cai, W.; Wu, J. The Multifaceted Role of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Cancer Prevention, Occurrence, and Treatment. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Amrousy, D.; El-Afify, D. Effects of alpha lipoic acid as a supplement in obese children and adolescents. Cytokine 2020, 130, 155084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos, G.; Schuman, M.L.; Landa, M.S.; Robello, E.; Incardona, C.; Conrad, M.L.; Galleano, M.; García, S.I. Therapeutic effect of alpha lipoic acid in a rat preclinical model of preeclampsia: Focus on maternal signs, fetal growth and placental function. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slepneva, I.A.; Sergeeva, S.V.; Khramtsov, V.V. Reversible inhibition of NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase by α-lipoic acid. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 214, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhova, A.A.; Shikh, E.V.; Bulko, T.V.; Gilep, A.A.; Usanov, S.A.; Shumyantseva, V.V. No effect of lipoic acid on catalytic activity of cytochrome P450 3A4. Drug Metab. Pers. Ther. 2020, 35, 20200105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phua, L.C.; New, L.S.; Goh, C.W.; Neo, A.H.; Browne, E.R.; Chan, E.C. Investigation of the drug–drug interaction between α-lipoic acid and valproate via mitochondrial β-oxidation. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2639–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Croce, C.; Bronzetti, G.; Cini, M.; Caltavuturo, L.; Poi, G. Protective effect of lipoic acid against hydrogen peroxide in yeast cells. Toxicol. in Vitro 2003, 17, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiter, C.H.; Schreeb, K.H.; Freudenthaler, S.; Thomas, M.; Elze, M.; Fieger-Büschges, H.; Potthast, H.; Schneider, E.; Schug, B.S.; Blume, H.H.; et al. Lack of interaction between thioctic acid, glibenclamide and acarbose. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALI, R.S.; Hameed, B.J.; Shari, F.H. Synergistic Antihyperglycemic Effect of Alpha Lipoic Acid with Antidiabetic Agents in the Normoglycemic and Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2023, 80, 483–491. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, T.; Zubair, M.; Tadi, P. Blood Glucose Monitoring. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Camiolo, G.; Tibullo, D.; Giallongo, C.; Romano, A.; Parrinello, N.L.; Musumeci, G.; Di Rosa, M.; Vicario, N.; Brundo, M.V.; Amenta, F. α-Lipoic acid reduces iron-induced toxicity and oxidative stress in a model of iron overload. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multum, C. Alpha Lipoic Acid. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/mtm/alpha-lipoic-acid.html (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- El-Gowelli, H.M.; Saad, E.I.; Abdel-Galil, A.-G.A.; Ibrahim, E.R. Co-administration of α-lipoic acid and cyclosporine aggravates colon ulceration of acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis via facilitation of NO/COX-2/miR-210 cascade. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 288, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werida, R.H.; Elshafiey, R.A.; Ghoneim, A.; Elzawawy, S.; Mostafa, T.M. Role of alpha-lipoic acid in counteracting paclitaxel-and doxorubicin-induced toxicities: A randomized controlled trial in breast cancer patients. Support. Care Cancer 2022, 30, 7281–7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jones, D.; Palmer, J.L.; Forman, A.; Dakhil, S.R.; Velasco, M.R.; Weiss, M.; Gilman, P.; Mills, G.; Noga, S.J. Oral alpha-lipoic acid to prevent chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 22, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateef Al-Awsi, G.R.; Arshed, U.; Arif, A.; Ramírez-Coronel, A.A.; Alhassan, M.S.; Mustafa, Y.F.; Rahman, F.F.; Zabibah, R.S.; Gupta, J.; Iqbal, M.S. The chemoprotective potentials of alpha-lipoic acid against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: A systematic review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024, 31, 3588–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frediani, J.K.; Lal, A.A.; Kim, E.; Leslie, S.L.; Boorman, D.W.; Singh, V. The role of diet and non-pharmacologic supplements in the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain: A systematic review. Pain Pract. 2024, 24, 186–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciftci, H.; Bakal, U. The effect of lipoic acid on macro and trace metal levels in living tissues exposed to oxidative stress. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. (Former. Curr. Med. Chem.-Anti-Cancer Agents) 2009, 9, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Zahabi, E.; Abdollahzad, H. Alpha Lipoic Acid Supplementation and Iron Homeostasis: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2024, 95, 36623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segermann, J.; Hotze, A.; Ulrich, H.; Rao, G. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on the peripheral conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine and on serum lipid-, protein-and glucose levels. Arzneim. Forsch. 1991, 41, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Khoder, N.M.; Sawie, H.G.; Sharada, H.M.; Hosny, E.N.; Khadrawy, Y.A.; Abdulla, M.S. Metformin and alpha lipoic acid ameliorate hypothyroidism and its complications in adult male rats. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GAL, E. Reversal of Selective Toxicity of (â)-α-Lipoic Acid by Thiamine in Thiamine-deficient Rats. Nature 1965, 207, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Edelstein, D.; Brownlee, M. Oral benfotiamine plus α-lipoic acid normalises complication-causing pathways in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1930–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, A.R.; Bungau, S.; Vesa, C.M.; Bondar, A.C.; Pantis, C.; Maghiar, O.; Dimulescu, I.A.; Nistor-Cseppento, D.; Rus, M. Evaluating the efficacy of the treatment with benfotiamine and alpha-lipoic acid in distal symmetric painful diabetic polyneuropathy. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 3108–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zempleni, J.; Trusty, T.A.; Mock, D.M. Lipoic acid reduces the activities of biotin-dependent carboxylases in rat liver. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 1776–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, R.; Wildgrube, H.J.; Ruus, P.; Niebch, G.; Nowak, H.; Gleiter, C.H. Gastric emptying in patients with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and bioavailability of thioctic acid-enantiomers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 6, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.; Evangelopoulos, A.; Koutalas, P. Alpha-lipoic acid and diabetic neuropathy. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2010, 6, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahayu, I.; Arfian, N.; Kustanti, C.Y.; Wahyuningsih, M.S.H. The effectiveness of antioxidant agents in delaying progression of diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. BioImpacts BI 2024, 15, 30129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, H.; Mazloom, Z.; Kazemi, F.; Hejazi, N. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on blood glucose, insulin resistance and glutathione peroxidase of type 2 diabetic patients. Saudi Med. J. 2011, 32, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Porasuphatana, S.; Suddee, S.; Nartnampong, A.; Konsil, J.; Harnwong, B.; Santaweesuk, A. Glycemic and oxidative status of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus following oral administration of alphalipoic acid: A randomized double-blinded placebocontrolled study. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 21, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee, M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Bai, J.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y. THERAPY OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: A systematic review and meta-analysis of α-lipoic acid in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 167, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.; Tritschler, H.J.; King, G.A.; Azzi, A. Antioxidants in Diabetes Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Strokov, I.; Manukhina, E.; Bakhtina, L.Y.; Malyshev, I.Y.; Zoloev, G.; Kazikhanova, S.; Ametov, A. The function of endogenous protective systems in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and polyneuropathy: Effect of antioxidant therapy. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2000, 130, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.L.; Goldfine, I.D. α-Lipoic acid: A multifunctional antioxidant that improves insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2000, 2, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, N.; Cotter, M.; Horrobin, D.; Tritschler, H. Effects of α-lipoic acid on neurovascular function in diabetic rats: Interaction with essential fatty acids. Diabetologia 1998, 41, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, A.; Cotter, M.; Cameron, N.E. Effects of diabetes and treatment with the antioxidant α-lipoic acid on endothelial and neurogenic responses of corpus cavernosum in rats. Diabetologia 1999, 42, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, A. The heterogeneity of diabetic neuropathy. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 4809–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, B.R.; Ang, L.; Pop-Busui, R. Spectrum of diabetic neuropathy: New insights in diagnosis and treatment. Annu. Rev. Med. 2024, 75, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sima, A.A.; Zhang, W. Mechanisms of diabetic neuropathy: Axon dysfunction. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 126, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merlin, E.; Salio, C.; Ferrini, F. Painful Diabetic Neuropathy: Sex-Specific Mechanisms and Differences from Animal Models to Clinical Outcomes. Cells 2024, 13, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Luo, N.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wie, L.J.; Fang, J. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of 2014–2024 publications on therapy for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1434756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, P.; Prasoon, P.; Susuki, K. Understanding and managing diabetic neuropathy: Current perspectives and future directions. Front. Neurosci. 2025, 19, 1582123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, C.A.N. Issues and challenges in diabetic neuropathy management: A narrative review. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubaker, S.A.; Alonazy, A.M.; Abdulrahman, A.; Abubaker, S.; Alonazy, A.; Albasseet, A. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy: A systematic review. Cureus 2022, 14, e25750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, P.; Toyka, K.V.; Blüher, M.; Kosacka, J.; Nowicki, M. Inflammatory mechanisms in the pathophysiology of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DN)—New aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, E.L.; Callaghan, B.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Zochodne, D.W.; Wright, D.E.; Bennett, D.L.; Bril, V.; Russell, J.W.; Viswanathan, V. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, Z.Z.; Menkes, D.L.; Souayah, N. Targeting neuroinflammation in distal symmetrical polyneuropathy in diabetes. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 104087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighatdoost, F.; Hariri, M. The effect of alpha-lipoic acid on inflammatory mediators: A systematic review and meta-analysis on randomized clinical trials. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 849, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.; Papanas, N.; Schnell, O.; Nguyen, B.D.T.; Nguyen, K.T.; Kulkantrakorn, K.; Deerochanawong, C. Current concepts in the management of diabetic polyneuropathy. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, N.; Barma, S.; Konwar, N.; Dewanjee, S.; Manna, P. Mechanistic insight of diabetic nephropathy and its pharmacotherapeutic targets: An update. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 791, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, Z.; Ali, M.N.; Khalid, M. An insight into potential pharmacotherapeutic agents for painful diabetic neuropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 9989272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, R.-Y.; Huang, I.-C.; Chen, C.; Sung, J.-Y. Effects of oral alpha-lipoic acid treatment on diabetic polyneuropathy: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, B.C.; Gallagher, G.; Fridman, V.; Feldman, E.L. Diabetic neuropathy: What does the future hold? Diabetologia 2020, 63, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.; Smith, D.; Franklin, G.; Gronseth, G.; Pignone, M.; David, W.S.; Armon, C.; Perkins, B.A.; Bril, V.; Rae-Grant, A. Oral and topical treatment of painful diabetic polyneuropathy: Practice guideline update summary: Report of the AAN guideline subcommittee. Neurology 2022, 98, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, S.; Raz, I. Management of diabetic neuropathy. Metabolism 2021, 123, 154867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, G.; Selvarajah, D.; Tesfaye, S. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical management of diabetic sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 400–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorek, M. Combination therapy is it in the future for successfully treating peripheral diabetic neuropathy? Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1357859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, D.; Fonseca, V. From guideline to patient: A review of recent recommendations for pharmacotherapy of painful diabetic neuropathy. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2015, 29, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro, L.E.; Wiffen, P.J.; Moore, R.A.; Gilron, I. Combination pharmacotherapy for the treatment of neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD008943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, C.J.; Watson, J.C. Treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2015, 39, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, Y. Analysis of MDA, SOD, TAOC, MNCV, SNCV, and TSS scores in patients with diabetes peripheral neuropathy. Open Life Sci. 2024, 19, 20220945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, F.G.; Riley, D.R.; Azmi, S.; Alam, U. Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Practical guidance and challenges for clinical management. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 1595–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; McNicol, E.; Baron, R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpää, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, J.T.; Young, J.P., Jr.; LaMoreaux, L.; Werth, J.L.; Poole, R.M. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain 2001, 94, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, R.H.; O’Connor, A.B.; Audette, J.; Baron, R.; Gourlay, G.K.; Haanpää, M.L.; Kent, J.L.; Krane, E.J.; LeBel, A.A.; Levy, R.M. Recommendations for the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain: An overview and literature update. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulin, D.; Clark, A.; Gilron, I.; Ware, M.; Watson, C.; Sessle, B.; Coderre, T.; Morley-Forster, P.; Stinson, J.; Boulanger, A. Pharmacological management of chronic neuropathic pain–consensus statement and guidelines from the Canadian Pain Society. Pain Res. Manag. 2007, 12, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Ang, L.; Boulton, A.J.; Feldman, E.L.; Marcus, R.L.; Mizokami-Stout, K.; Singleton, J.R.; Ziegler, D. Diagnosis and treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Am. Diabetes Assoc. 2022, 2022, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checchia, G.; Letizia Mauro, G.; Morico, G.; Lisi, C.; Polimeni, V.; Lucia, M.; Ranieri, M. Observational multicentric study on chronic sciatic pain: Clinical data from 44 Italian centers. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, G.-L.; Li, Y.-P.; Lu, L.-C.; Lan, S.-H. Disease-modifying therapies for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2024, 38, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dy, S.M.; Bennett, W.L.; Sharma, R.; Zhang, A.; Waldfogel, J.M.; Nesbit, S.A.; Yeh, H.-C.; Chelladurai, Y.; Feldman, D.; Wilson, L.M. Preventing Complications and Treating Symptoms of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Reljanovic, M.; Reichel, G.; Rett, K.; Lobisch, M.; Schuette, K.; Möller, W.; Tritschler, H.-J.; Mehnert, H. Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant thioctic acid (α-lipoic acid): A two year multicenter randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial (ALADIN II). Free Radic. Res. 1999, 31, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.; Ametov, A.; Barinov, A.; Dyck, P.J.; Gurieva, I.; Low, P.A.; Munzel, U.; Yakhno, N.; Raz, I.; Novosadova, M. Oral treatment with α-lipoic acid improves symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy: The SYDNEY 2 trial. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.; Low, P.A.; Litchy, W.J.; Boulton, A.J.; Vinik, A.I.; Freeman, R.; Samigullin, R.; Tritschler, H.; Munzel, U.; Maus, J. Efficacy and safety of antioxidant treatment with α-lipoic acid over 4 years in diabetic polyneuropathy: The NATHAN 1 trial. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, P.A.; Kalshetti, S.; Bhatt, J. Supplementation of α-lipoic acid in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A prospective open label randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- El-Nahas, M.R.; Elkannishy, G.; Abdelhafez, H.; Elkhamisy, E.T.; El-Sehrawy, A.A. Oral alpha lipoic acid treatment for symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled study. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord.-Drug Targets Former. Curr. Drug Targets-Immune Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 20, 1531–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.C.; Kwon, H.-S.; Moon, S.-S.; Chun, S.W.; Kim, C.H.; Park, I.B.; Kim, I.J.; Lee, J.; Cha, B.Y.; Park, T.S. γ-Linolenic acid versus α-lipoic acid for treating painful diabetic neuropathy in adults: A 12-week, double-placebo, randomized, noninferiority trial. Diabetes Metab. J. 2020, 44, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, N.; Awais, F.; Shakil, M.; Sarwar, S.; Kakar, N.H.; Ullah, M.I. Effect of anti-oxidant (α-lipoic acid) treatment on improvement of diabetic neuropathic pain. Rawal Med. J. 2021, 46, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Hahm, J.R.; Kim, B.-J.; Kim, K.-W. Clinical experience with thioctacid (thioctic acid) in the treatment of distal symmetric polyneuropathy in Korean diabetic patients. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2004, 18, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Alcala, H.; Santos Vichido, C.I.; Islas Macedo, S.; Genestier-Tamborero, C.N.; Minutti-Palacios, M.; Hirales Tamez, O.; García, C.; Ziegler, D. Treatment with α-lipoic acid over 16 weeks in type 2 diabetic patients with symptomatic polyneuropathy who responded to initial 4-week high-dose loading. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 189857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawy, A.M.; Abd Elmoniem, R.O.; Elsayed, A.M. Alpha lipoic acid and diabetes mellitus: Potential effects on peripheral neuropathy and different metabolic parameters. Alex. J. Med. 2021, 57, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermendy, G.; Rokszin, G.; Fábián, I.; Kempler, P.; Wittmann, I. Morbidity and mortality of patients with diabetic neuropathy treated with pathogenetically oriented alpha-lipoic acid versus symptomatic pharmacotherapies–a nationwide database analysis from Hungary. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 201, 110734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogacci, F.; Rizzo, M.; Krogager, C.; Kennedy, C.; Georges, C.M.; Knežević, T.; Liberopoulos, E.; Vallée, A.; Pérez-Martínez, P.; Wenstedt, E.F. Safety evaluation of α-lipoic acid supplementation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled clinical studies. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugbartey, G.J.; Alornyo, K.K.; N’guessan, B.B.; Atule, S.; Mensah, S.D.; Adjei, S. Supplementation of conventional anti-diabetic therapy with alpha-lipoic acid prevents early development and progression of diabetic nephropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, D.; Low, P.A.; Freeman, R.; Tritschler, H.; Vinik, A.I. Predictors of improvement and progression of diabetic polyneuropathy following treatment with α-lipoic acid for 4 years in the NATHAN 1 trial. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2016, 30, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Ostadmohammadi, V.; Lankarani, K.B.; Tabrizi, R.; Kolahdooz, F.; Khatibi, S.R.; Asemi, Z. The effects of alpha-lipoic acid supplementation on glucose control and lipid profiles among patients with metabolic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Metabolism 2018, 87, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalis, D.T.; Karalis, T.; Karalis, S.; Kleisiari, A.S.; Malakoudi, F.; Maimari, K.E.V. The effect of alpha-lipoic acid on diabetic peripheral neuropathy and the upcoming depressive disorders of type II diabetics. Cureus 2021, 13, e12773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijnhout, G.S.; Kollen, B.J.; Alkhalaf, A.; Kleefstra, N.; Bilo, H.J. Alpha lipoic acid for symptomatic peripheral neuropathy in patients with diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 456279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakici, N.; Fakkel, T.; Van Neck, J.; Verhagen, A.; Coert, J. Systematic review of treatments for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.; Takemoto, J.K. A case for alpha-lipoic acid as an alternative treatment for diabetic polyneuropathy. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 21, 192s–199s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato Nesbit, S.; Sharma, R.; Waldfogel, J.M.; Zhang, A.; Bennett, W.L.; Yeh, H.-C.; Chelladurai, Y.; Feldman, D.; Robinson, K.A.; Dy, S.M. Non-pharmacologic treatments for symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2019, 35, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibril, A.T.; Jayedi, A.; Shab-Bidar, S. Efficacy and safety of oral alpha-lipoic acid supplementation for type 2 diabetes management: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of randomized trials. Endocr. Connect. 2022, 11, e220322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana-Donoso, M.; López-Chaparro, M.; Barahona-Vásquez, M.; Santana-Machuca, A.; Bruna-Mejias, A.; Nova-Baeza, P.; Valenzuela-Fuenzalida, J.J. Effectiveness of alpha-lipoic acid in patients with neuropathic pain associated with type I and type II diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2023, 102, e35368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Viswanatha, G.L.; Kishore, A.; Nandakumar, K. Safety and efficacy of oral Alpha lipoic acid in the management of Diabetic Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, M.B., Jr.; Adiao, K.J.B. Ranking alpha lipoic acid and gamma linolenic acid in terms of efficacy and safety in the management of adults with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Can. J. Diabetes 2024, 48, 233–243.e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H. Using corneal confocal microscopy to compare Mecobalamin intramuscular injections vs oral tablets in treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A RCT. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathos, E.; Tentolouris, A.; Eleftheriadou, I.; Katsaouni, P.; Nemtzas, I.; Petrou, A.; Papanikolaou, C.; Tentolouris, N. Effect of α-lipoic acid on symptoms and quality of life in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilron, I.; Robb, S.; Tu, D.; Holden, R.R.; Jackson, A.C.; Duggan, S.; Milev, R. Randomized, double-blind, controlled trial of a combination of alpha-lipoic acid and pregabalin for neuropathic pain: The PAIN-CARE trial. Pain 2022, 165, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotto, F.; Massone, A. Combination of alpha lipoic acid and superoxide dismutase leads to physiological and symptomatic improvements in diabetic neuropathy. Drugs RD 2012, 12, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.-Q.; Li, M.-X.; Ma, Y.-J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Efficacy and safety of prostaglandin E1 plus lipoic acid combination therapy versus monotherapy for patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 27, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.-Q.; Xu, L.-C.; Jiang, L.-L.; Li, M.-X.; Wang, Y. Fasudil combined with methylcobalamin or lipoic acid can improve the nerve conduction velocity in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Pan, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Zuo, X.; Wu, P.; Deng, H.; Zhang, J.; Ji, A. Meta-analysis of methylcobalamin alone and in combination with lipoic acid in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 101, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawangjit, R.; Thongphui, S.; Chaichompu, W.; Phumart, P. Efficacy and safety of mecobalamin on peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2020, 26, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, J.-Y.; Chu, Y.-D.; Zhu, Y.-B.; Luo, L.; Bu, S.-Z. Efficacy of epalrestat plus α-lipoic acid combination therapy versus monotherapy in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A meta-analysis of 20 randomized controlled trials. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhnau, K.J.; Meissner, H.; Finn, J.R.; Reljanovic, M.; Lobisch, M.; Schütte, K.; Nehrdich, D.; Tritschler, H.; Mehnert, H.; Ziegler, D. Effects of 3-week oral treatment with the antioxidant thioctic acid (α-lipoic acid) in symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabet. Med. 1999, 16, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.; Hanefeld, M.; Ruhnau, K.; Mei\Ner, H.; Lobisch, M.; Schütte, K.; Gries, F.; Group, A.S. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy with the anti-oxidant α-lipoic acid: A 3-week multicentre randomized controlled trial (ALADIN Study). Diabetologia 1995, 38, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ametov, A.S.; Barinov, A.; Dyck, P.J.; Hermann, R.; Kozlova, N.; Litchy, W.J.; Low, P.A.; Nehrdich, D.; Novosadova, M.; O’Brien, P.C.; et al. The sensory symptoms of diabetic polyneuropathy are improved with alpha-lipoic acid: The SYDNEY trial. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazutka, J.R.; Daniūnaitė, K.; Dedonytė, V.; Popandopula, A.; Žukaitė, K.; Visockienė, Ž.; Šiaulienė, L. Effects of Short-Term Treatment with α-Lipoic Acid on Neuropathic Pain and Biomarkers of DNA Damage in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruessmann, H.J. Switching from pathogenetic treatment with α-lipoic acid to gabapentin and other analgesics in painful diabetic neuropathy: A real-world study in outpatients. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2009, 23, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, S.K.; Tolba, O.A.; Mostafa, T.M.; Eid, M.A.; El-Afify, D.R. Alpha-lipoic acid improves subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in asymptomatic patients with type 1 diabetes. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2013, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puliappadamb, H.M.; Satpathy, A.K.; Mishra, B.R.; Maiti, R.; Jena, M. Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of Add-on Alpha-Lipoic Acid on Migraine Prophylaxis in an Adolescent Population: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 63, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tromba, L.; Perla, F.M.; Carbotta, G.; Chiesa, C.; Pacifico, L. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid supplementation on endothelial function and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight/obese youths: A double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaramuzza, A.; Giani, E.; Redaelli, F.; Ungheri, S.; Macedoni, M.; Giudici, V.; Bosetti, A.; Ferrari, M.; Zuccotti, G.V. Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Antioxidant Diet Help to Improve Endothelial Dysfunction in Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes: A Pilot Trial. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 474561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.A.; Gitelman, S.E. The effect of oral alpha-lipoic acid on oxidative stress in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr. Diabetes 2008, 9, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkina, L.G.; Afanas’ef, I.B.; Diplock, A.T. Antioxidant therapy in children affected by irradiation from the Chernobyl nuclear accident. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993, 21, 314S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathmann, W.; Haastert, B.; Delling, B.; Gries, F.; Giani, G. Postmarketing surveillance of adverse drug reactions: A correlational study approach using multiple data sources. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 1998, 7, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Crum, B.A.; Rubin, D.I.; Demaerschalk, B.M. Alpha-lipoic acid may improve symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy. Neurol. 2007, 13, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, D.; Rabeler, R.; Roberts, A.; Lynch, B. Safety evaluation of α-lipoic acid (ALA). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 46, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, D.; Rabeler, R.; Roberts, A.; Lynch, B. Long-term safety of α-lipoic acid (ALA) consumption: A 2-year study. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 46, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, R.M.; MacLeay, J.M.; Jewell, D.E.; Brejda, J.J.; Gross, K.L. Alpha-lipoic acid is an effective nutritive antioxidant for healthy adult dogs. Animals 2021, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derosa, G.; D’Angelo, A.; Preti, P.; Maffioli, P. Safety and efficacy of alpha lipoic acid during 4 years of observation: A retrospective, clinical trial in healthy subjects in primary prevention. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 5367–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.; Nowak, H.; Kempler, P.; Vargha, P.; Low, P. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant α-lipoic acid: A meta-analysis. Diabet. Med. 2004, 21, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parente, E.; Colannino, G.; Picconi, O.; Monastra, G. Safety of oral alpha-lipoic acid treatment in pregnant women: A retrospective observational study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 4219–4227. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, V.; Marracci, G.; Lovera, J.; Woodward, W.; Bogardus, K.; Marquardt, W.; Shinto, L.; Morris, C.; Bourdette, D. Lipoic acid in multiple sclerosis: A pilot study. Mult. Scler. J. 2005, 11, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigil, M.; Berkson, B.M.; Garcia, A.P. Adverse effects of high doses of intravenous alpha lipoic acid on liver mitochondria. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2014, 3, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.; Bednarski, M.; Bilska, A.; Iciek, M.; Sokołowska-Jeżewicz, M.; Filipek, B.; Włodek, L. The role of lipoic acid in prevention of nitroglycerin tolerance. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 591, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotańska, M.; Razny, K.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Iciek, M.; Sapa, J.; Włodek, L.B.; Filipek, B. Hypotensive effect of alpha-lipoic acid after a single administration in rats. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2016, 16, 306–309. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Naseem, R.H.; Park, B.-H.; Garry, D.J.; Richardson, J.A.; Schaffer, J.E.; Unger, R.H. α-Lipoic acid prevents lipotoxic cardiomyopathy in acyl CoA-synthase transgenic mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 344, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badran, M.; Abuyassin, B.; Golbidi, S.; Ayas, N.; Laher, I. Alpha lipoic acid improves endothelial function and oxidative stress in mice exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 4093018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, B.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, H.-F.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Luo, X.-J.; Ma, Q.-L.; Peng, J. Alpha lipoic acid protects heart against myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury through a mechanism involving aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 678, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rasheed, N.M.; Al-Rasheed, N.M.; Attia, H.A.; Hasan, I.H.; Al-Amin, M.; Al-Ajmi, H.; Mohamad, R.A. Adverse cardiac responses to alpha-lipoic acid in a rat-diabetic model: Possible mechanisms? J. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 69, 761–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, T.-H.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, K.-U.; Park, J.Y.; Moon, H.-B. α-Lipoic acid inhibits airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in a mouse model of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- GOR, A.; CA, B.S. Beneficial effect of α-lipoic acid on lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008, 59, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Khamaisi, M.; Rudich, A.; Potashnik, R.; Tritschler, H.J.; Gutman, A.; Bashan, N. Lipoic acid acutely induces hypoglycemia in fasting nondiabetic and diabetic rats. Metabolism 1999, 48, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftin, E.G.; Herold, L.V. Therapy and outcome of suspected alpha lipoic acid toxicity in two dogs. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2009, 19, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolunay, O.; Çelik, T.; Kömür, M.; Gezgin, A.E.; Kaya, M.S.; Çelik, Ü. A rare cause of status epilepticus; alpha lipoic acid intoxication, case report and review of the literature. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2015, 19, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhla, A.; Derbenev, M.; Shih, H.Y.; Vollmar, B. Prophylactic and abundant intake of α-lipoic acid causes hepatic steatosis and should be reconsidered in usage as an anti-aging drug. Biofactors 2016, 42, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakatay, U.; Kayaliı, R. Plasma protein oxidation in aging rats after alpha-lipoic acid administration. Biogerontology 2005, 6, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Çakatay, U. Pro-oxidant actions of α-lipoic acid and dihydrolipoic acid. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 66, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kravchenko, L.V.; Aksenov, I.V.; Nikitin, N.S.; Guseva, G.V.; Avrenyeva, L.I.; Trusov, N.V.; Balakina, A.S.; Tutelyan, V.A. Lipoic acid exacerbates oxidative stress and lipid accumulation in the liver of Wistar rats fed a hypercaloric choline-deficient diet. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabler, S.P.; Sekhar, J.; Allen, R.H.; O’Neill, H.C.; White, C.W. α-Lipoic acid induces elevated S-adenosylhomocysteine and depletes S-adenosylmethionine. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offersen, C.M.; Skjoeth-Rasmussen, J. Evaluation of the risk of liver damage from the use of 5-aminolevulinic acid for intra-operative identification and resection in patients with malignant gliomas. Acta Neurochir. 2017, 159, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.F.; Osman, K.; Das, S.; Othman, A.M.; Majid, N.A.; Rahman, M.P.A. A study of the antioxidant effect of alpha lipoic acids on sperm quality. Clinics 2008, 63, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prathima, P.; Pavani, R.; Sukeerthi, S.; Sainath, S.B. α-Lipoic acid inhibits testicular and epididymal oxidative damage and improves fertility efficacy in arsenic-intoxicated rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deore, M.S.; Keerthana, S.; Naqvi, S.; Kumar, A.; Flora, S. Alpha-lipoic acid protects co-exposure to lead and zinc oxide nanoparticles induced neuro, immuno and male reproductive toxicity in rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 626238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, R.S.; Mohamed, H.A.; Kassem, D.H. Alpha-lipoic acid effectively attenuates ionizing radiation-mediated testicular dysfunction in rats: Crosstalk of NF-ĸB, TGF-β, and PPAR-γ pathways. Toxicology 2020, 442, 152536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, N.; Darmishonnejad, Z.; Tavalaee, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H. The effect of alpha-lipoic acid on sperm functions in rodent models for male infertility: A systematic review. Life Sci. 2023, 323, 121383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Li, Y. Effect of oral alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) on the treatment of male infertility: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e18453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ghafli, M.; Padmanabhan, R.; Kataya, H.; Berg, B. Effects of α-lipoic acid supplementation on maternal diabetes-induced growth retardation and congenital anomalies in rat foetuses. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 261, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, R.; Mohamed, S.; Singh, S. Beneficial effect of supplemental lipoic acid on diabetes-induced pregnancy loss in the mouse. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1084, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Tucci, C.; Galati, G.; Mattei, G.; Bonanni, V.; Capri, O.; D’Amelio, R.; Muzii, L.; Benedetti Panici, P. The role of alpha lipoic acid in female and male infertility: A systematic review. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2021, 37, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozzana, M.; Zaiton, Z.; Rajikin, M.; Fadzilah, S.; Zanariyah, A. Supplementation with alpha lipoic acid improves the in vitro development of embryos in nicotine-treated mice. Biomed. Res. 2005, 16, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cilio, S.; Rienzo, M.; Villano, G.; Mirto, B.F.; Giampaglia, G.; Capone, F.; Ferretti, G.; Di Zazzo, E.; Crocetto, F. Beneficial effects of antioxidants in male infertility management: A narrative review. Oxygen 2022, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.-J.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Wang, Q.-H.; Liao, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Zhang, C.-C.; Liu, L.-R.; Wei, Q.; Bao, Y.-G. Current treatment for male infertility: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Asian J. Androl. 2024, 26, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banihani, S.A. Role of Lipoic Acid in Testosterone Production in Males. World J. Men’s Health 2024, 43, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, M.; Essa, E.A.; Zaki, R.M.; Elkordy, A.A. An overview of the antioxidant effects of ascorbic acid and alpha lipoic acid (in liposomal forms) as adjuvant in cancer treatment. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcaro, G.; Brillo, E.; Giardina, I.; DI IORIO, R. Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA) effects on subchorionic hematoma. Preliminary clinical results. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 3426–3432. [Google Scholar]
- Petca, A.; Bot, M.; Maru, N.; Calo, I.G.; Borislavschi, A.; Dumitrascu, M.C.; Petca, R.-C.; Sandru, F.; Zvanca, M.E. Benefits of α-lipoic acid in high-risk pregnancies. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Tucci, C.; Di Feliciantonio, M.; Vena, F.; Capone, C.; Schiavi, M.C.; Pietrangeli, D.; Muzii, L.; Benedetti Panici, P. Alpha lipoic acid in obstetrics and gynecology. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2018, 34, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Chen, Y.; Ning, J. Insulin autoimmune syndrome: A systematic review. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 2023, 1225676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellani, D.; Sardella, C.; Campopiano, M.; Falorni, A.; Marchetti, P.; Macchia, E. Spontaneously remitting insulin autoimmune syndrome in a patient taking alpha-lipoic acid. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2018, 2018, 18-0122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffa, S.; Improta, I.; Rocchetti, S.; Mezza, T.; Giaccari, A. Potential cause-effect relationship between insulin autoimmune syndrome and alpha lipoic acid: Two case reports. Nutrition 2019, 57, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, D.; Evans, J.L.; Sortino, G.; Goldfine, I.D.; Vigneri, R. Insulin autoimmune syndrome (Hirata Disease) in European Caucasians taking α-lipoic acid. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 81, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchigata, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Omori, Y.; Iwamoto, Y.; Tokunaga, K. Worldwide differences in the incidence of insulin autoimmune syndrome (Hirata disease) with respect to the evolution of HLA-DR4 alleles. Hum. Immunol. 2000, 61, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Feng, C.; Chu, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Xia, J.; Chen, Y. HLA Alleles Associate with Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 3463–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition; Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA); Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; de Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Knutsen, H.K.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; et al. Scientific opinion on the relationship between intake of alpha-lipoic acid (thioctic acid) and the risk of insulin autoimmune syndrome. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06577. [Google Scholar]
- Veltroni, A.; Zambon, G.; Cingarlini, S.; Davì, M. Autoimmune hypoglycaemia caused by alpha-lipoic acid: A rare condition in Caucasian patients. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2018, 2018, 18-0011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, J.; You, W. Insulin autoimmune syndrome: Three case reports. Medicine 2018, 97, e13486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baburaj, K.; MP, J.; MV, V. Alpha-lipoic acid induced insulin autoimmune antibody syndrome. Egypt. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 36, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Su, Y.; Yi, D.; Wu, C.; Fang, W.; Wang, C. Analysis of the clinical characteristics of insulin autoimmune syndrome induced by alpha-lipoic acid. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2021, 46, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food, D.; Safety of Alpha-Lipoic Acid Use in Food Supplements. DTU Doc 2017. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2020-06/labelling-nutrition_vitamins-minerals_add_alpha-lipoic-acid_nfi-da.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Censi, S.; Mian, C.; Betterle, C. Insulin autoimmune syndrome: From diagnosis to clinical management. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emir, D.F.; Ozturan, I.U.; Yilmaz, S. Alpha lipoic acid intoxicatıon: An adult. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 1125.e3–1125.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, R.; Angeletti, C.; Minora, S. Multiple organ failure and shock following acute alpha lipoic acid (ALA) intoxication. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özçetin, M.; Yilmaz, R.; Tetikçok, R.; Karaaslan, E.; Dürer, Z.; Narin, B. Alpha lipoic acid intoxication in a 10 months old infant; a case report. Anatol. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 6, 267–268. [Google Scholar]
- Karaarslan, U.; İşgüder, R.; Bağ, Ö.; Kışla, M.; Ağın, H.; Ünal, N. Alpha lipoic acid intoxication, treatment and outcome. Clin. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, S.; Kılıçaslan, Ö.; Sönmez, F.T. Alpha-lipoic acid intoxication in an adolescent girl: Case report and review of the literature. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. /Türk. Pediatri. Arşivi. 2020, 55, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabi, Z.; El Helou, C.; Al Balushi, H.; Gittinger, M.; Steck, A.R.; Kaakour, A.; Abu-Alfa, A.; El Zahran, T. Alpha lipoic acid toxicity: The first reported mortality in an adult patient after multiorgan failure. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 64, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzik, B.; Grass, H.; Mayatepek, E.; Daldrup, T.; Hoehn, T. Fatal non-accidental alpha-lipoic acid intoxication in an adolescent girl. Klin. Pädiatr. 2014, 226, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpha Lipoic Acid Market Size, Share, Competitive Landscape and Trend Analysis Report, by Product Type and Application: Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2021–2030. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/alpha-lipoic-acid-market-A13701 (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Product (R Alpha Lipoic Acid, S Alpha Lipoic Acid), by Application (Dietary Supplements, Cosmetics), by Region, and Segment Forecasts, 2024–2030. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/alpha-lipoic-acid-market-report# (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Alpha Lipoic Acid Market Research Report Information by Product Type (R Alpha Lipoic Acid And S Alpha Lipoic Acid), by Application (Dietary Supplements, Cosmetics, Pharmaceuticals, and Others), and by Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Rest of the World)–Market Forecast Till 2032. Available online: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/alpha-lipoic-acid-market-22178 (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid Market Size and Share Analysis—Growth Trends and Forecasts (2025–2032). Available online: https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/industry-reports/alpha-lipoic-acid-market (accessed on 16 April 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).