Pre- and Postnatal Fine Particulate Matter Exposure and Renal Fibrogenesis in Adult Male Rats: The Role of Vitamin D Supplementation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PM Collection, Analysis, and Preparation
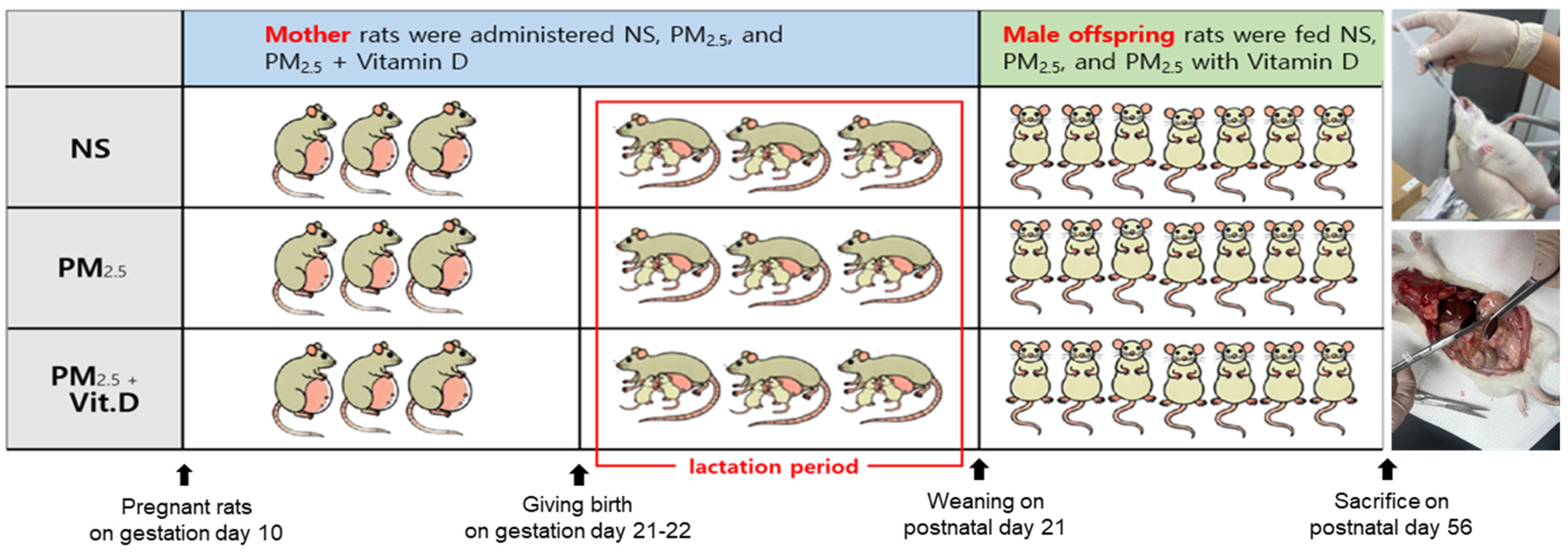
2.2. Animal Preparation
2.3. Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Histological Examination
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of PM2.5
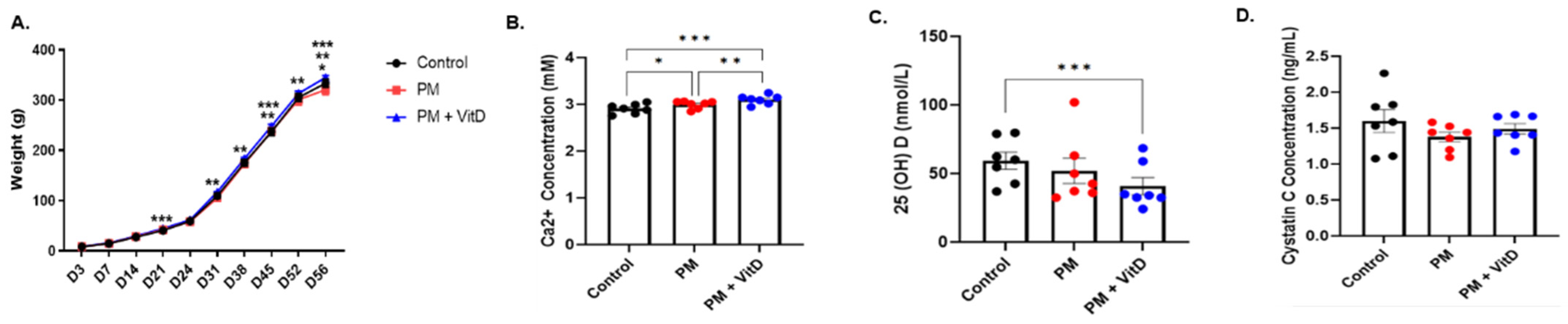
3.2. Body Weight Changes and Biochemical Data
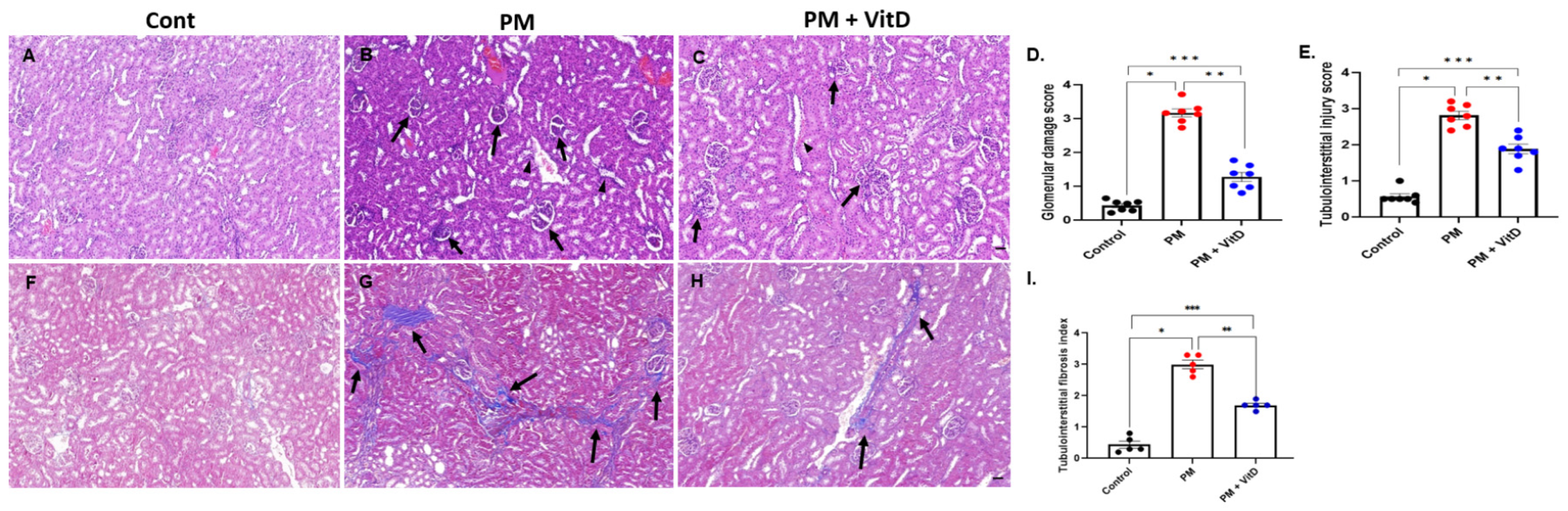
3.3. Renal Histological Alterations
3.4. Renin, ACE, and AT1R Expression
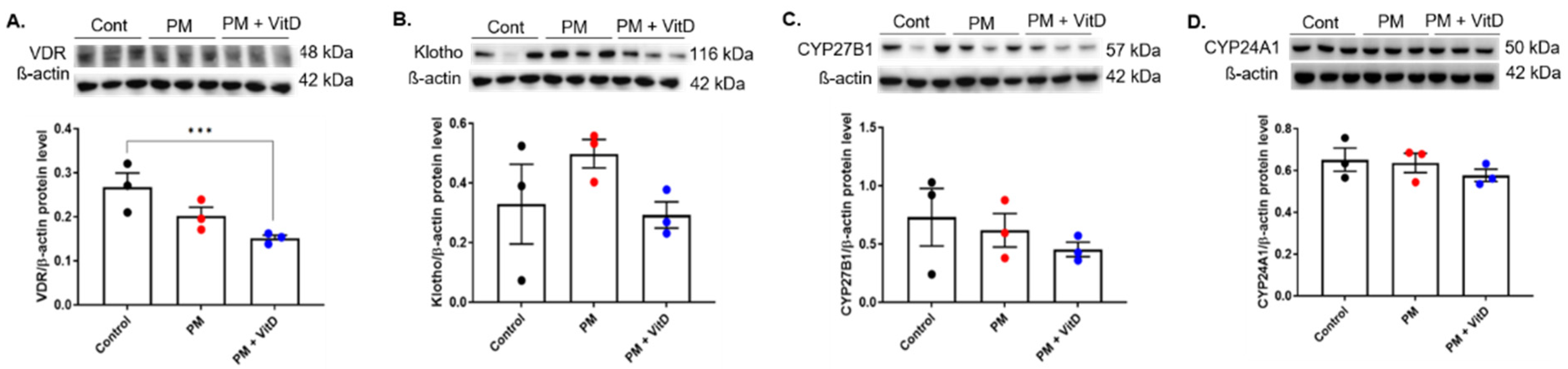
3.5. VDR, Klotho, CYP27B1, and CYP24A1 Expression
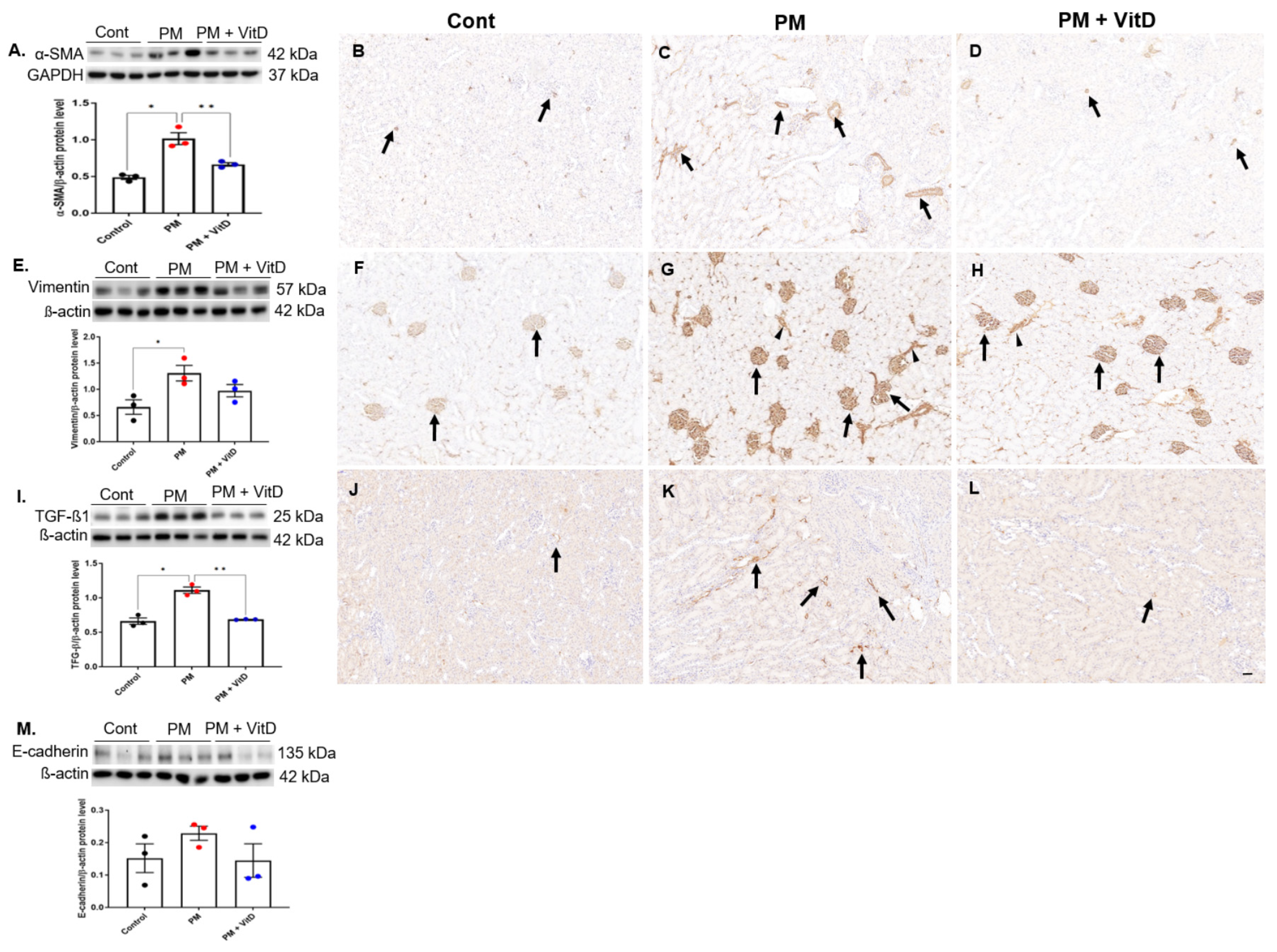
3.6. EMT Markers and TGF-β1 Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| AT1R | Angiotensin II type 1-receptor |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CYP | Cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| MT | Masson’s trichrome |
| NS | Normal saline |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| PM2.5 | Fine particulate matter |
| PRR | Pro renin receptor |
| RAS | Renin-angiotensin system |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| TGF-β1 | Transforming growth factor-β1 |
| VDR | Vitamin D receptor |
| WSOC | Water-soluble organic carbon |
| α-SMA | α-smooth muscle actin |
References
- Garcia, A.; Santa-Helena, E.; De Falco, A.; de Paula Ribeiro, J.; Gioda, A.; Gioda, C.R. Toxicological effects of fine particulate matter (PM2.5): Health risks and associated systemic injuries-systematic review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, V.C.; Kazemiparkouhi, F.; Manjourides, J.; Suh, H.H. Long-term PM2.5 exposure and respiratory, cancer, and cardiovascular mortality in older US adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 186, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wathanavasin, W.; Banjongjit, A.; Phannajit, J.; Eiam-Ong, S.; Susantitaphong, P. Association of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure and chronic kidney disease outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Yao, X.; Qiu, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; et al. The influence of PM2.5 exposure on kidney diseases. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 9603271211069982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ding, W.; Deng, X. PM2.5, Fine particulate matter: A novel player in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition? Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liu, N.; Bao, C.L.; Yang, D.Z.; Ma, G.X.; Yi, W.H.; Xiao, G.Z.; Cao, H.L. Mesenchymal stem cells in fibrotic diseases—The two sides of the same coin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar]
- Balakumar, P.; Sambathkumar, R.; Mahadevan, N.; Muhsinah, A.B.; Alsayari, A.; Venkateswaramurthy, N.; Jagadeesh, G. A potential role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-induced renal abnormalities: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 146, 104314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R.C.; Pastar, I.; Ojeh, N.; Chen, V.; Liu, S.; Garzon, K.I.; Tomic-Canic, M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tissue repair and fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.F.; Tofteng, S.S.; Madsen, K.; Jensen, B.L. Role of the renin-angiotensin system in kidney development and programming of adult blood pressure. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J. How to delay the progression of chronic kidney disease: Focusing on medications. Child. Kidney Dis. 2024, 28, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, L.F.; Francescato, H.D.C.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; de Paula, F.J.A.; da Silva, C.G.A.; Costa, R.S.; Coimbra, T.M. Imbalance of pro- and anti-angiogenic factors due to maternal vitamin D deficiency causes renal microvasculature alterations affecting the adult kidney function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.F.; Francescato, H.D.C.; Silva, R.S.; Silva, C.G.A.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; de Paula, F.J.A. Renal developmental disturbances and their long-term consequences in female pups from vitamin D-deficient mothers: Involved mechanisms. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2019, 10, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, E.; Yim, H.E.; Nam, Y.J.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, J.H.; Son, M.H.; Yoo, K.H. Exposure to airborne particulate matter induces renal tubular cell injury in vitro: The role of vitamin D signaling and renin-angiotensin system. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.H.; Park, E.; Yim, H.E.; Nam, Y.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, E.K.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Maternal exposure to airborne particulate matter during pregnancy and lactation induces kidney injury in rat dams and their male offspring: The role of vitamin D in pregnancy and beyond. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 43, 648–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exposure Assessment Tools by Routes–Inhalation. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/expobox/exposure-assessment-tools-routes-inhalation (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Grigore, D.; Ojeda, N.B.; Alexander, B.T. Sex differences in the fetal programming of hypertension. Gend. Med. 2008, 5, S121–S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiPietro, J.A.; Voegtline, K.M. The gestational foundation of sex differences in development and vulnerability. Neuroscience 2017, 342, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raij, L.; Azar, S.; Keane, W. Mesangial immune injury, hypertension, and progressive glomerular damage in Dahl rats. Kidney Int. 1984, 26, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, M.; Cabrera, I.; Serrano, D.; Sterin-Speziale, N. Cell proliferation and morphometric changes in the rat kidney during postnatal development. Anat. Embryol. 2002, 205, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P. The laboratory rat: Relating its age with human’s. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Lu, X.; Liu, F.; Gu, D. Ambient air pollution and body weight status in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parasin, N.; Amnuaylojaroen, T.; Saokaew, S. Prenatal PM2.5 Exposure and its association with low birth weight: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Toxics 2024, 12, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, L.; Li, C.; Yang, M.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, J.; Ding, R. Maternal air pollution exposure increases the risk of preterm birth: Evidence from the meta-analysis of cohort studies. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Fang, M.; Ma, Y.; Liu, N.; Yan, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, F. The kidney injury induced by short-term PM2.5 exposure and the prophylactic treatment of essential oils in BALB/c mice. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 9098627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. The renin-angiotensin system and cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome: Focus on early-life programming. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Su, J.; Lu, A.; Lai, Y.; Mo, S.; Pu, M.; Yang, T. Soluble (pro)renin receptor promotes the fibrotic response in renal proximal tubule epithelial cells in vitro via the Akt/β-catenin/Snail signaling pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2020, 319, F941–F953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Miao, J.; Hong, X.; Hou, F.F.; Liu, Y. (Pro)renin receptor is an amplifier of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in kidney injury and fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2393–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yi, X.; Song, S.; Yang, H.; Yu, J.; Xu, C. Principle role of the (pro)renin receptor system in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: An update. Cell Signal. 2024, 124, 111417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, B.; Wang, L.; Tang, G.; Liu, Z.; Song, H.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y. Water-soluble ions in PM2.5 during spring haze and dust periods in Chengdu, China: Variations, nitrate formation and potential source areas. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, N.; Xu, Y.; Hua, L.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, M.; Deng, X. Effects of chronic PM2.5 exposure on pulmonary epithelia: Transcriptome analysis of mRNA-exosomal miRNA interactions. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 316, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, A.; Li, M.; Dong, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Bukhari, A.A.; Cao, C.; Su, D.; et al. Interaction of calcium binding protein S100A16 with myosin-9 promotes cytoskeleton reorganization in renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, M.; Ahmad, R.; Tantry, I.Q.; Ahmad, W.; Siddiqui, S.; Alam, M.; Abbas, K.; Moinuddin Hassan, M.I.; Habib, S.; Islam, S. Apoptosis: A Comprehensive Overview of Signaling Pathways, Morphological Changes, and Physiological Significance and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2024, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docherty, N.G.; Calvo, I.F.; Quinlan, M.R.; Pérez-Barriocanal, F.; McGuire, B.B.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Watson, R.W. Increased E-cadherin expression in the ligated kidney following unilateral ureteric obstruction. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Zhuang, S. New insights into the role and mechanism of partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 569322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Du, L.; Sun, W.; Yu, Z.; He, F.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, D. Maternal exposure to fine particulate air pollution induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition resulting in postnatal pulmonary dysfunction mediated by transforming growth factor-β/Smad3 signaling. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 267, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liang, S.; Duan, J.; Sun, Z. Short-term PM2.5 exposure induces sustained pulmonary fibrosis development during post-exposure period in rats. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 385, 121566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, D.Q.; Chen, L.; Cao, G.; Zhao, H.; Liu, D.; Vaziri, N.D.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.Y. Novel inhibitors of the cellular renin-angiotensin system components, poricoic acids, target Smad3 phosphorylation and Wnt/β-catenin pathway against renal fibrosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2689–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, H.E.; Yoo, K.H.; Bae, I.S.; Hong, Y.S.; Lee, J.W. Effect of angiotensin II inhibition on the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in developing rat kidney. Korean J. Pediatr. 2009, 52, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.H.; Yim, H.E.; Bae, E.S.; Hong, Y.S. Capillary rarefaction and altered renal development: The imbalance between pro- and anti-angiogenic factors in response to angiotensin II inhibition in the developing rat kidney. J. Mol. Histol. 2018, 49, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kett, M.M.; Denton, K.M. Renal programming: Cause for concern? Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 300, R791–R803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, L.L.; Rasch, R. Perinatal ANG II programs adult blood pressure, glomerular number and renal function in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1998, 275, R1593–R1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Ye, S.; Kang, D.H.; Ha, E. Association between exposure to fine particulate matter and kidney function: Results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsen, P.H.; Loft, S.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Jensen, K.A.; Autrup, H.; Ravanat, J.L.; Wallin, H.; Møller, P. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and DNA damage in rats after intratracheal instillation or oral exposure to ambient air and wood smoke particulate matter. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 118, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z. Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Chronic Kidney Disease. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 254, 183–215. [Google Scholar]

| Ion | Liquid Phase Concentration (ppm) | Atmospheric Concentration (μg/m3) | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO3− | 367 | 10.4 | 36.0 |
| WSOC | 325 | 9.4 | 31.9 |
| NH4+ | 137 | 3.93 | 13.4 |
| SO42− | 120 | 3.47 | 11.8 |
| Cl− | 33.3 | 0.91 | 3.26 |
| Ca2+ | 15.1 | 0.24 | 1.48 |
| Na+ | 12.5 | 0.31 | 1.23 |
| K+ | 8.26 | 0.21 | 0.81 |
| Mg2+ | 1.05 | <0.01 | 0.1 |
| F− | 0.49 | <0.01 | 0.05 |
| PO43− | 0.13 | <0.01 | 0.01 |
| Br− | 0.09 | <0.01 | 0.009 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, M.-H.; Yim, H.-E.; Lee, Y.-S.; Nam, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Pre- and Postnatal Fine Particulate Matter Exposure and Renal Fibrogenesis in Adult Male Rats: The Role of Vitamin D Supplementation. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060387
Son M-H, Yim H-E, Lee Y-S, Nam Y-J, Lee J-H. Pre- and Postnatal Fine Particulate Matter Exposure and Renal Fibrogenesis in Adult Male Rats: The Role of Vitamin D Supplementation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(6):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060387
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Min-Hwa, Hyung-Eun Yim, Yu-Seon Lee, Yoon-Jeong Nam, and Ju-Han Lee. 2025. "Pre- and Postnatal Fine Particulate Matter Exposure and Renal Fibrogenesis in Adult Male Rats: The Role of Vitamin D Supplementation" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 6: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060387
APA StyleSon, M.-H., Yim, H.-E., Lee, Y.-S., Nam, Y.-J., & Lee, J.-H. (2025). Pre- and Postnatal Fine Particulate Matter Exposure and Renal Fibrogenesis in Adult Male Rats: The Role of Vitamin D Supplementation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(6), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060387






