Astragalus in Acute Pancreatitis: Insights from Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Meta-Analysis Validation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioactive Ingredients and Action Targets of Astragalus
2.2. Identification of AP Disease Targets
2.3. Acquisition of Therapeutic Targets
2.4. Construction of Protein–Protein Interaction Network and Identification of Core Targets
2.5. GO Enrichment Analysis and KEGG Pathway Analysis
2.6. Molecular Docking
2.7. Meta-Analysis
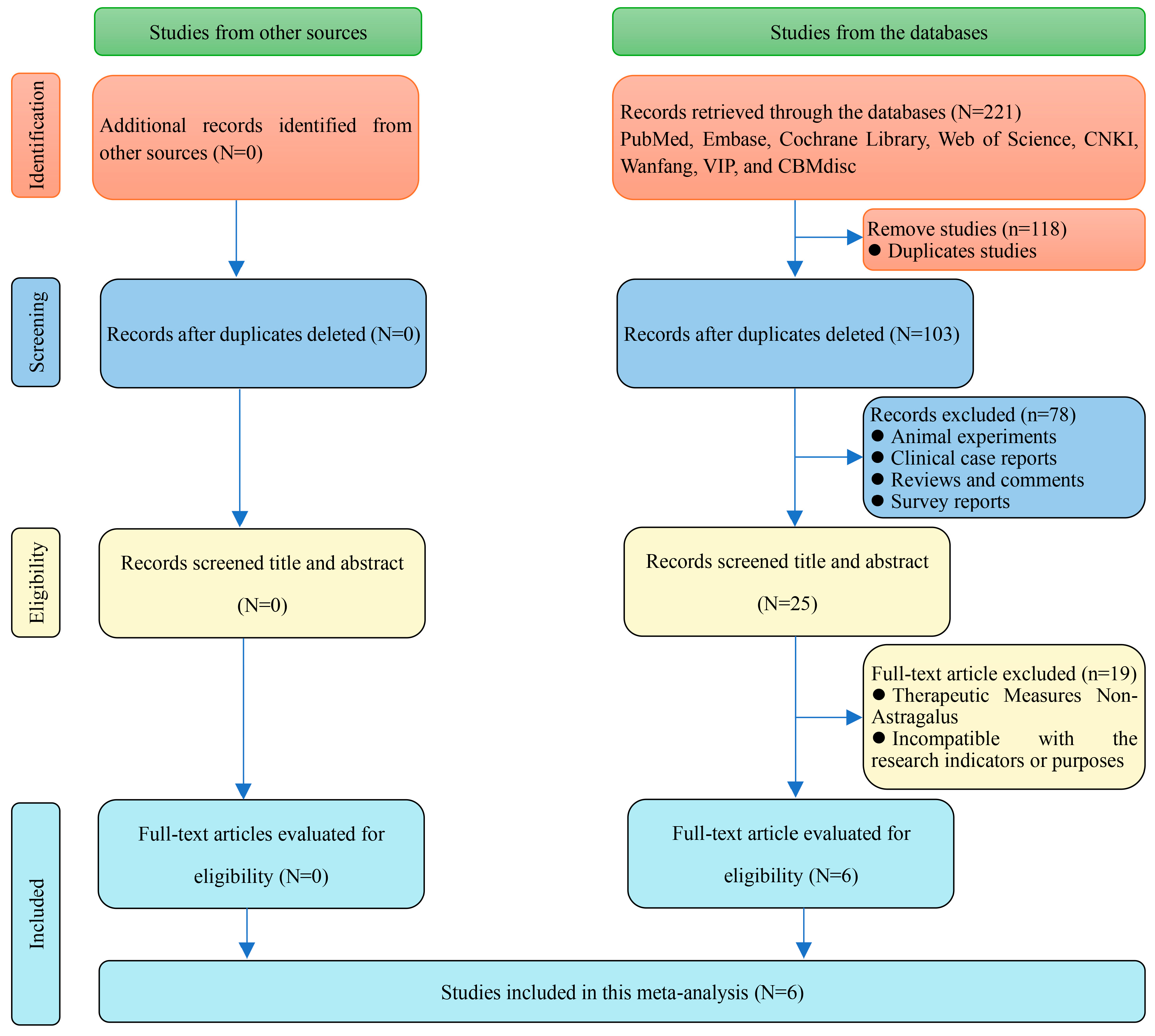
2.7.1. Literature Retrieval
2.7.2. Study Selection
2.7.3. Date Extraction
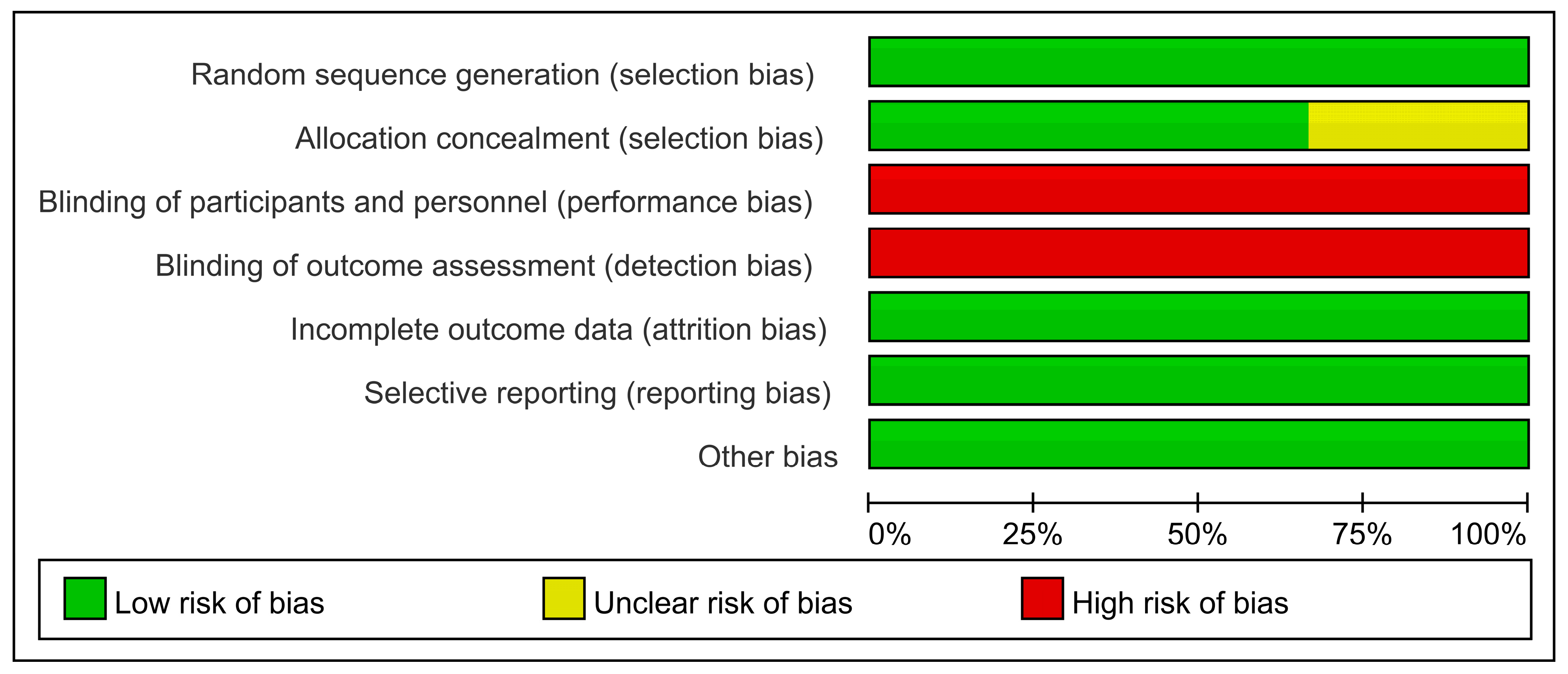
2.7.4. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.7.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Retrieval Results of Active Ingredients of Astragalus
3.2. Acquisition of Ap Targets
3.3. Validation of Therapeutic Targets
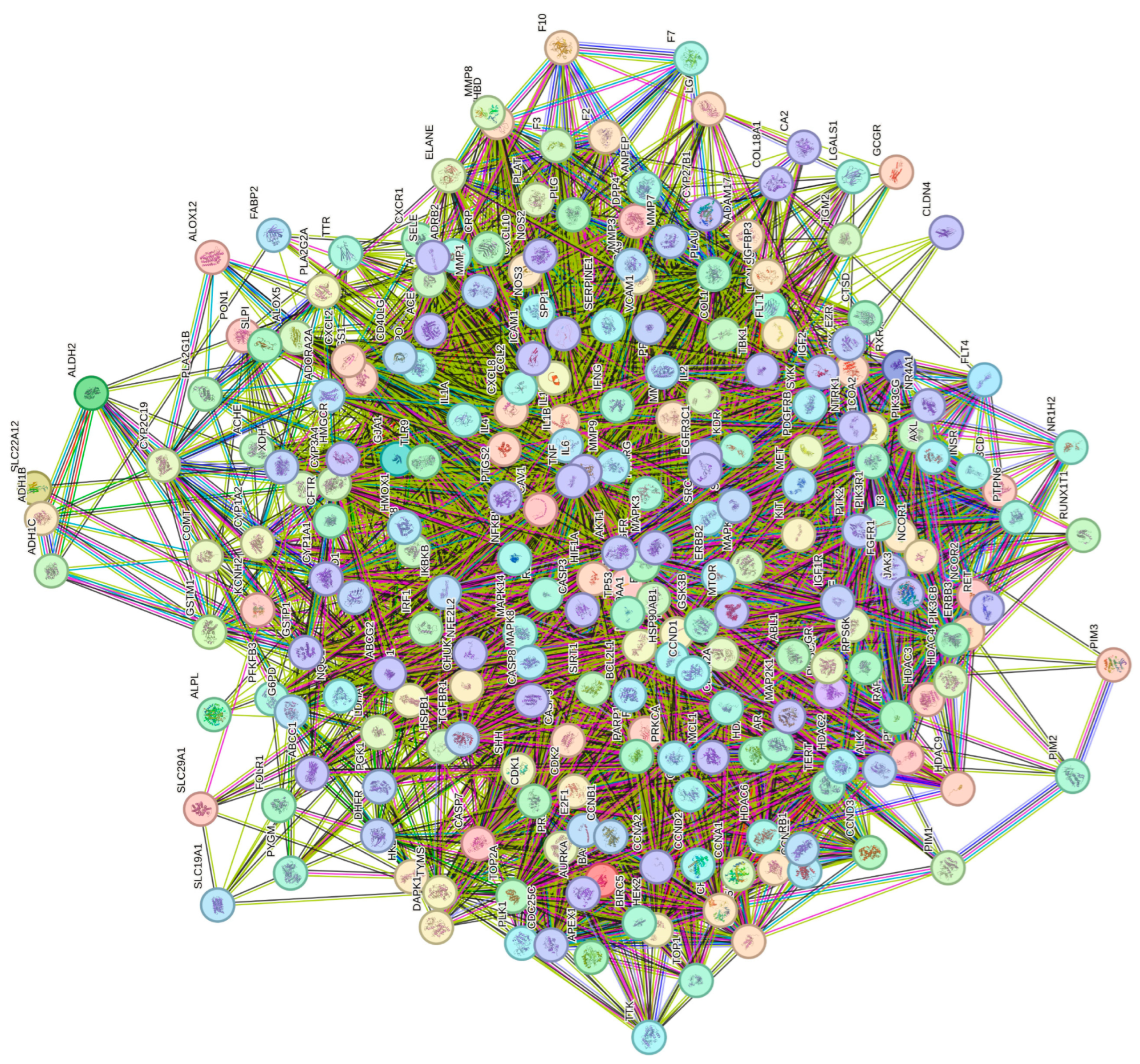
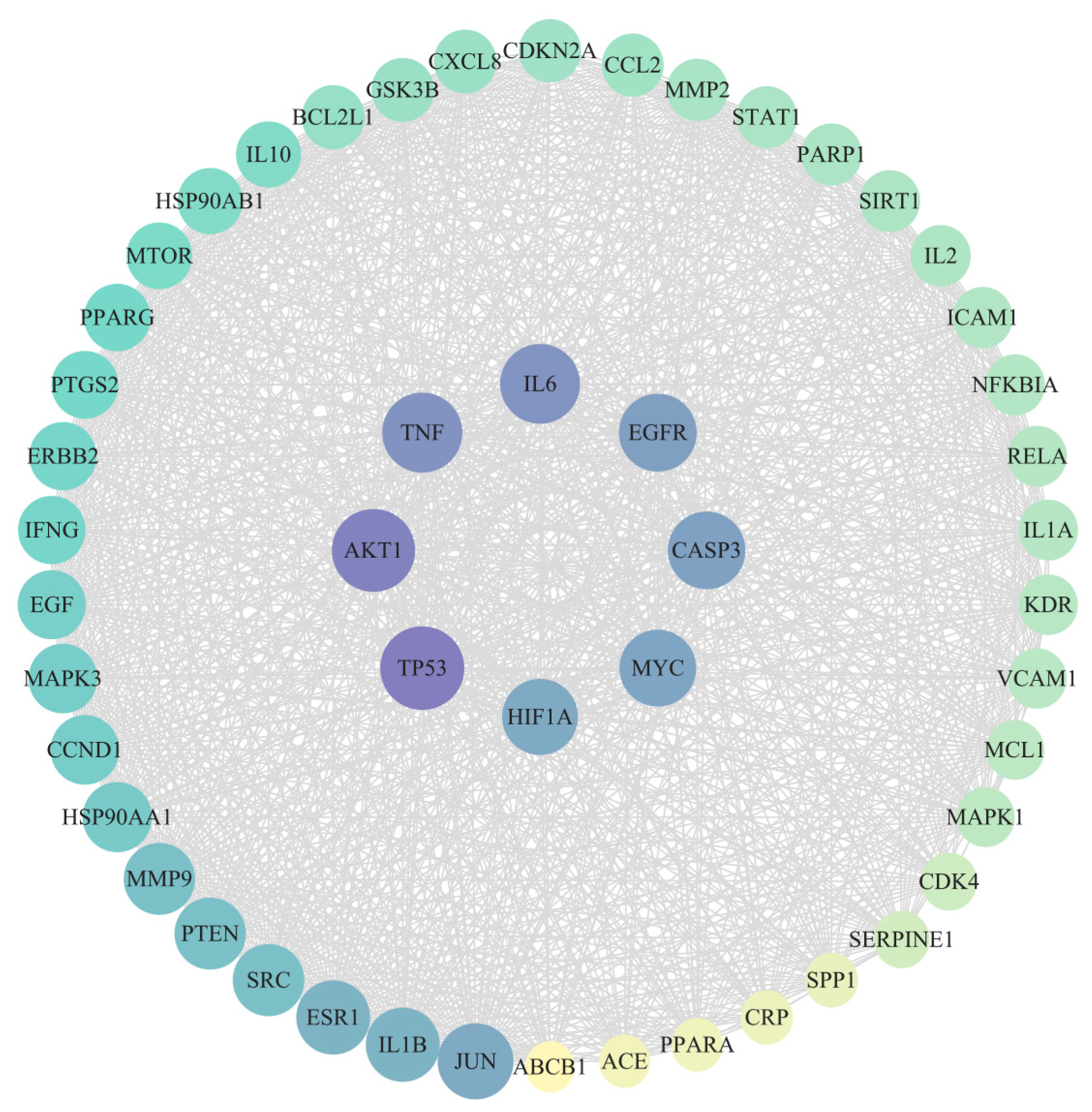
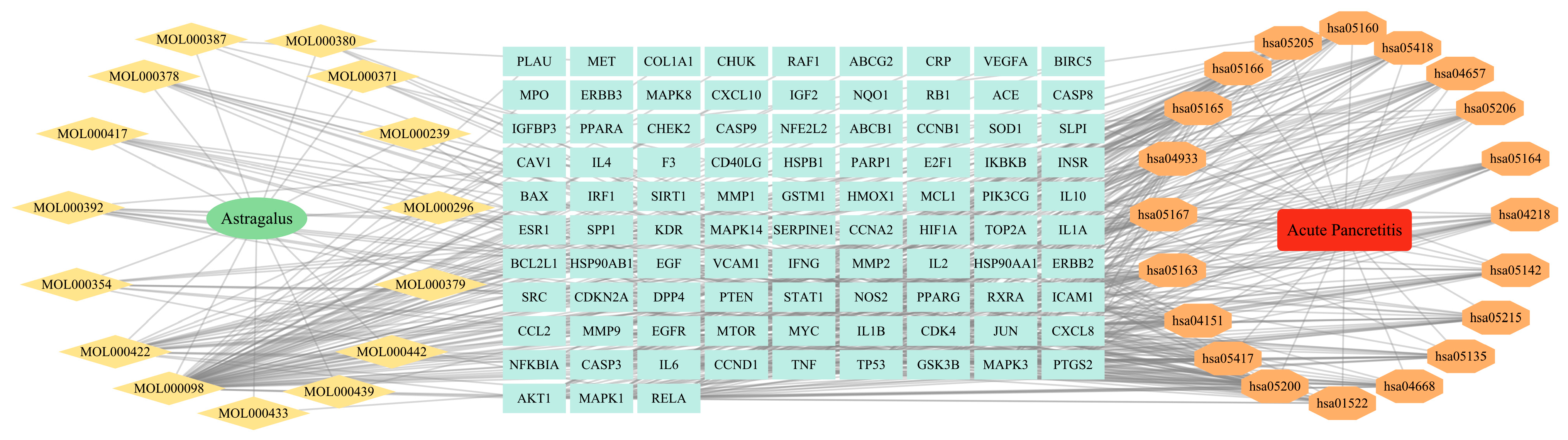
3.4. Construction of PPI Network
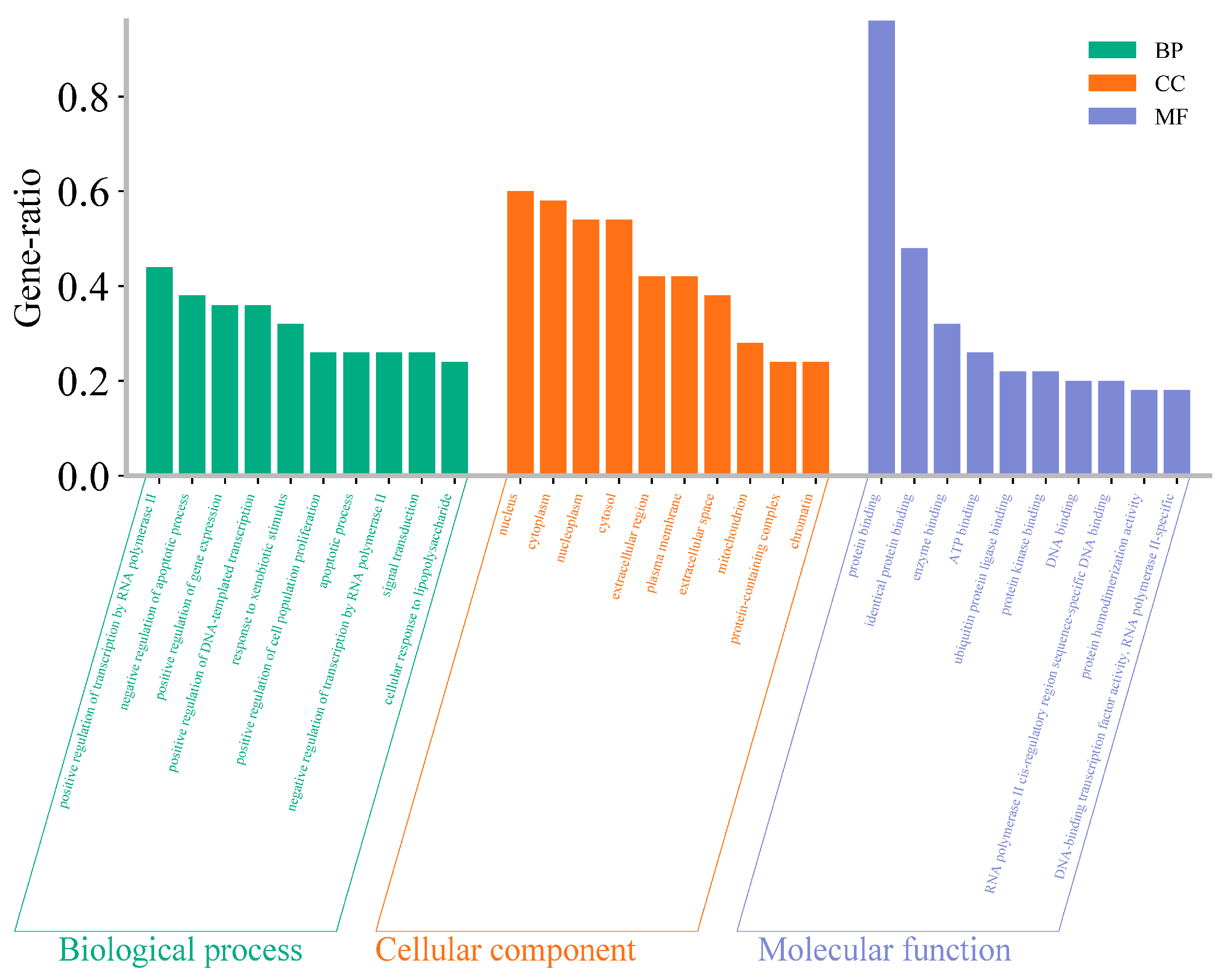
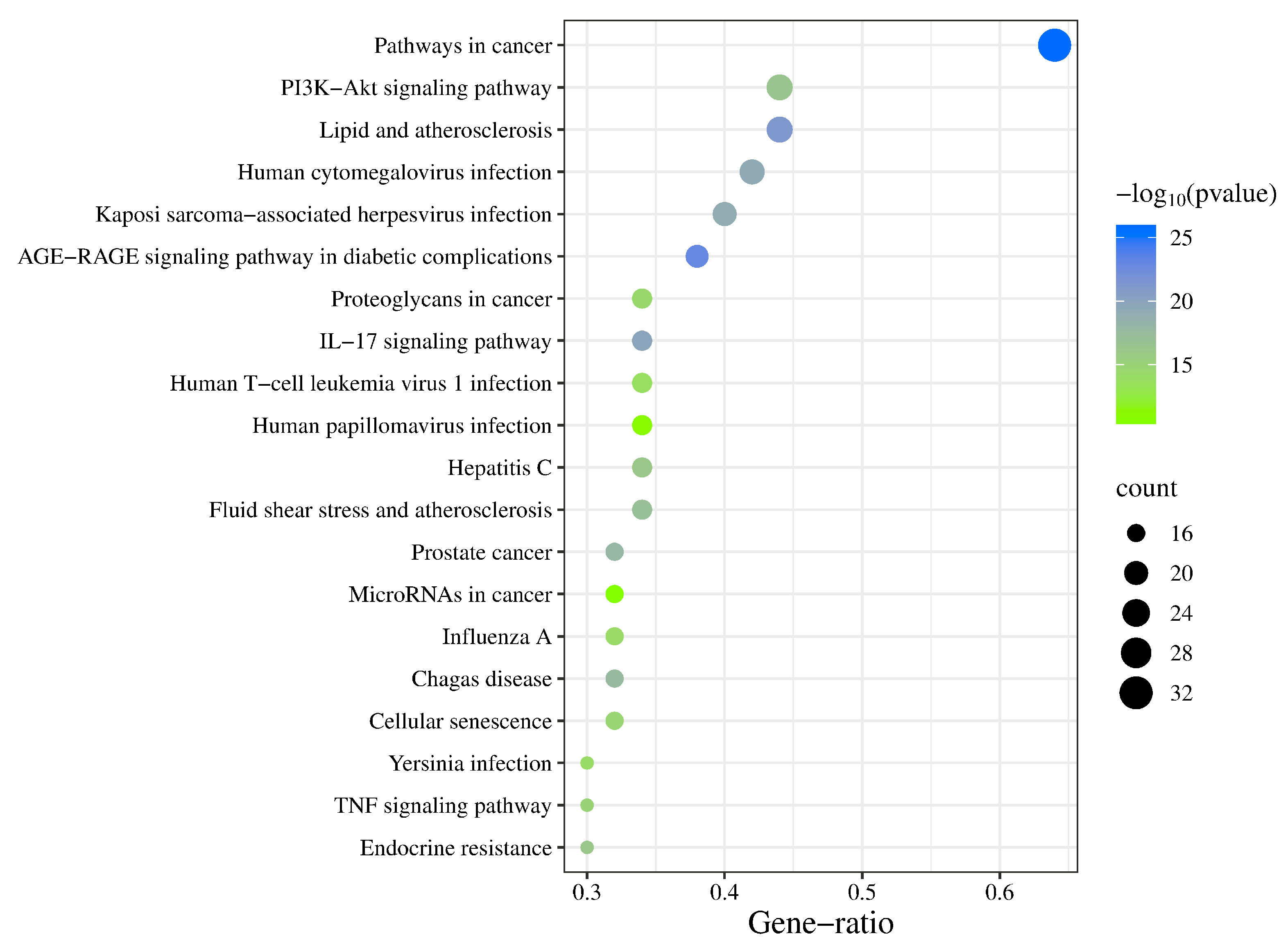
3.5. GO Enrichment Analysis and KEGG Pathway Analysis
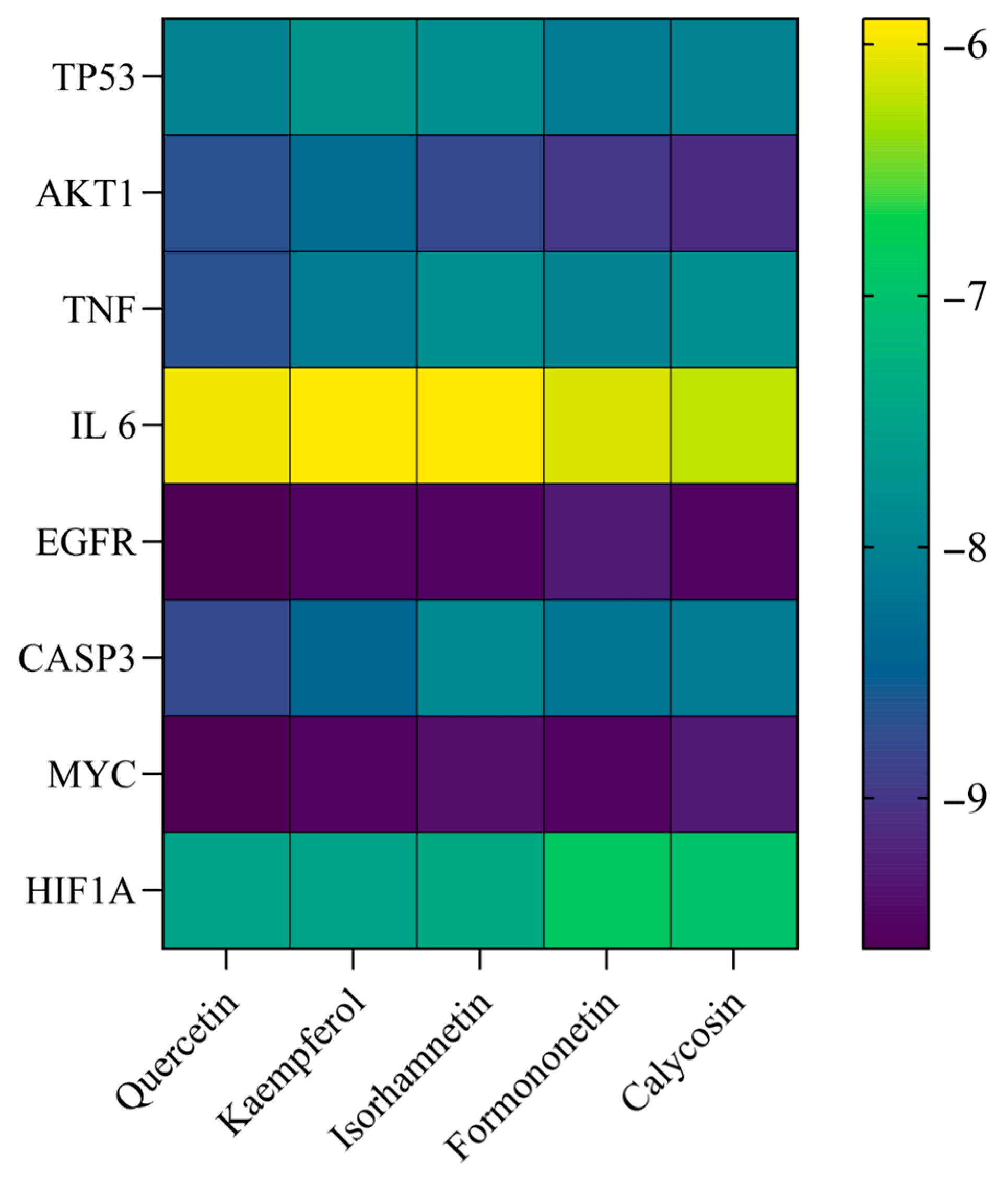
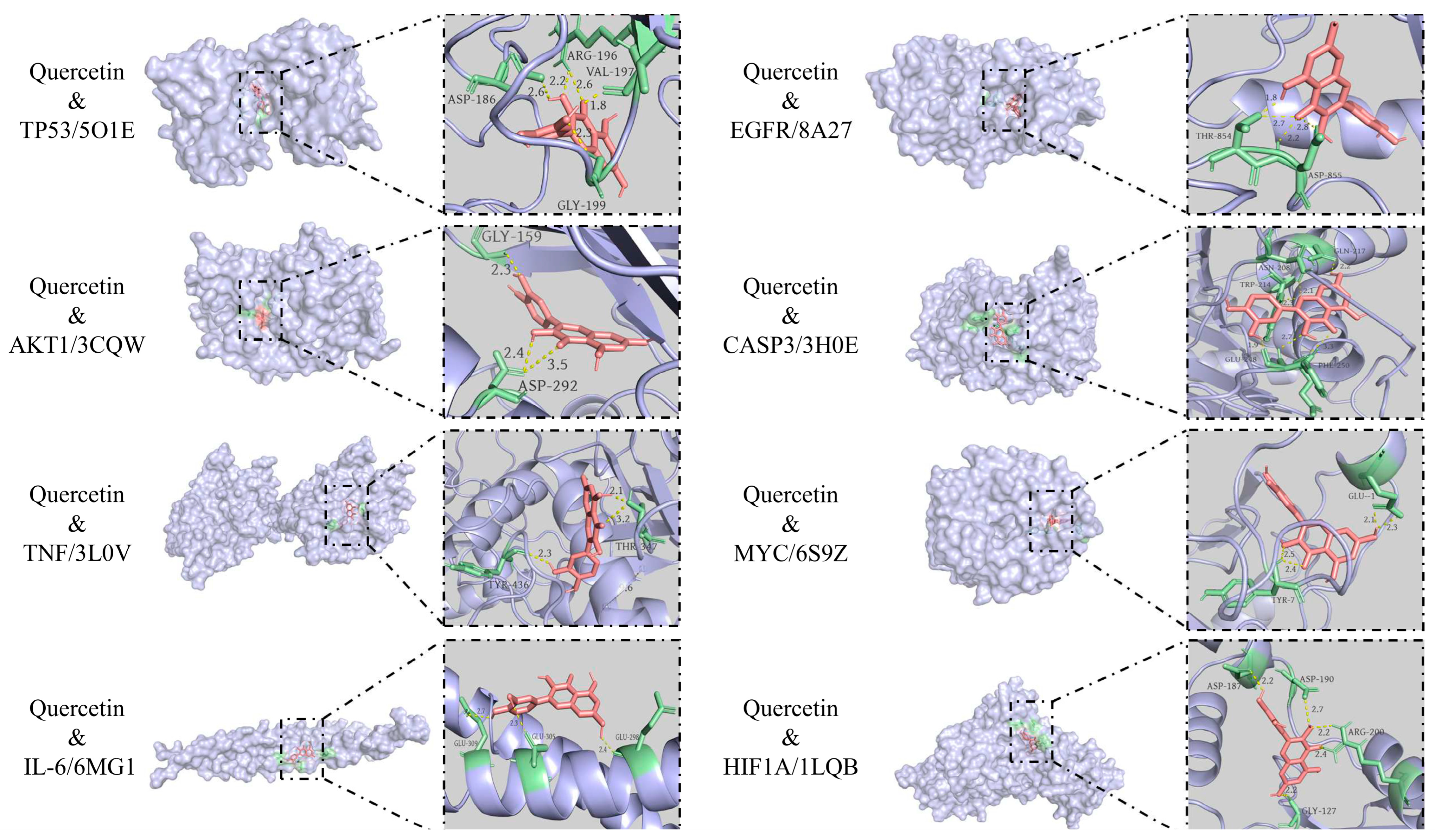
3.6. Molecular Docking Results
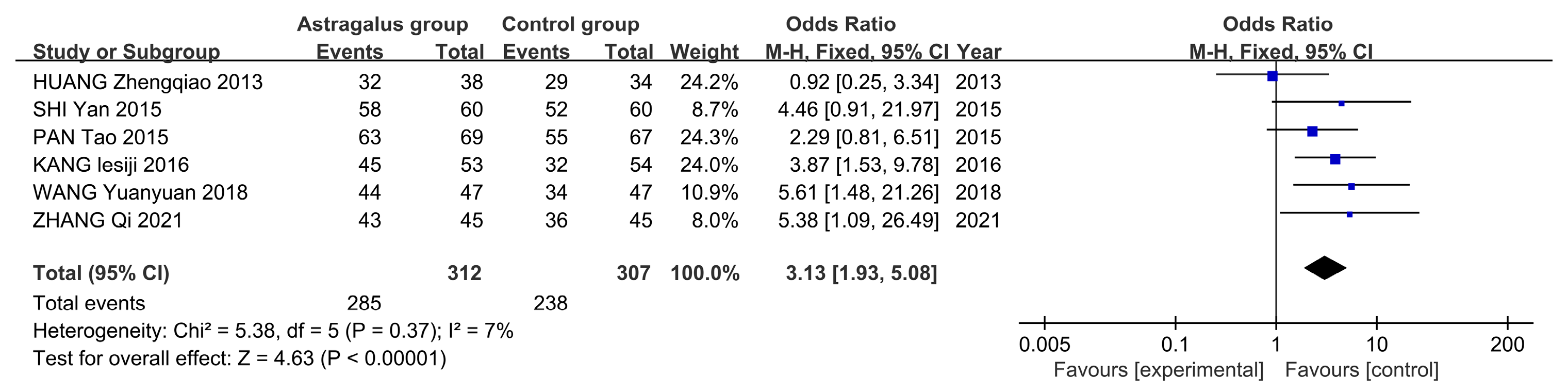
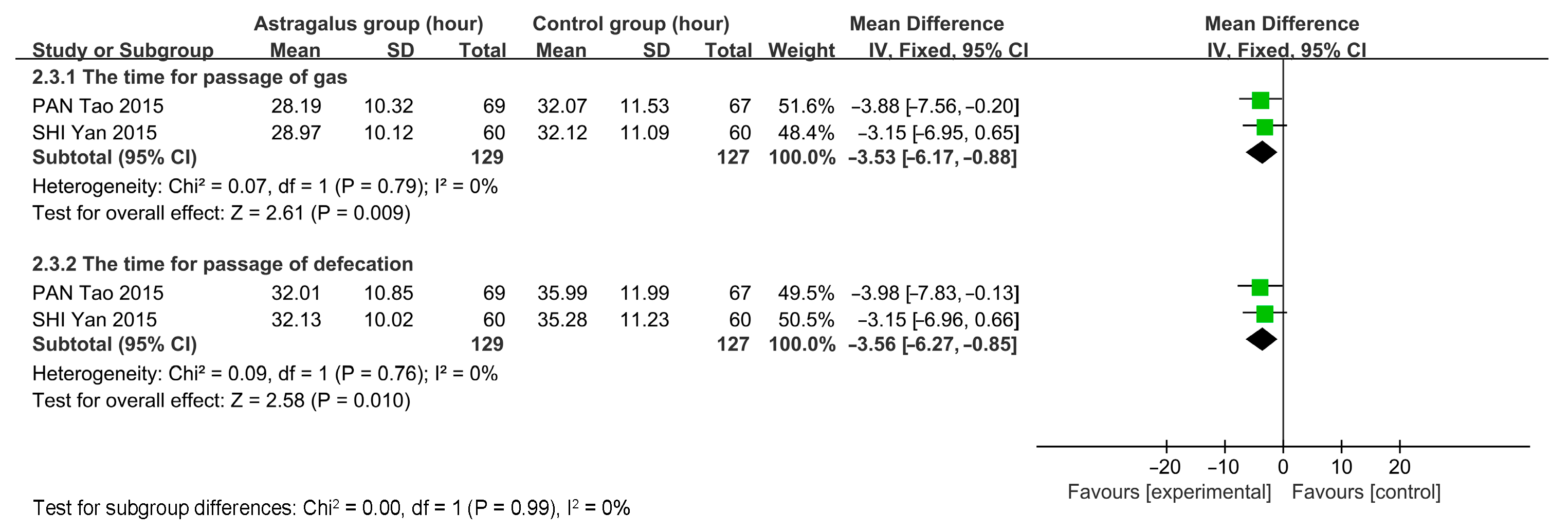
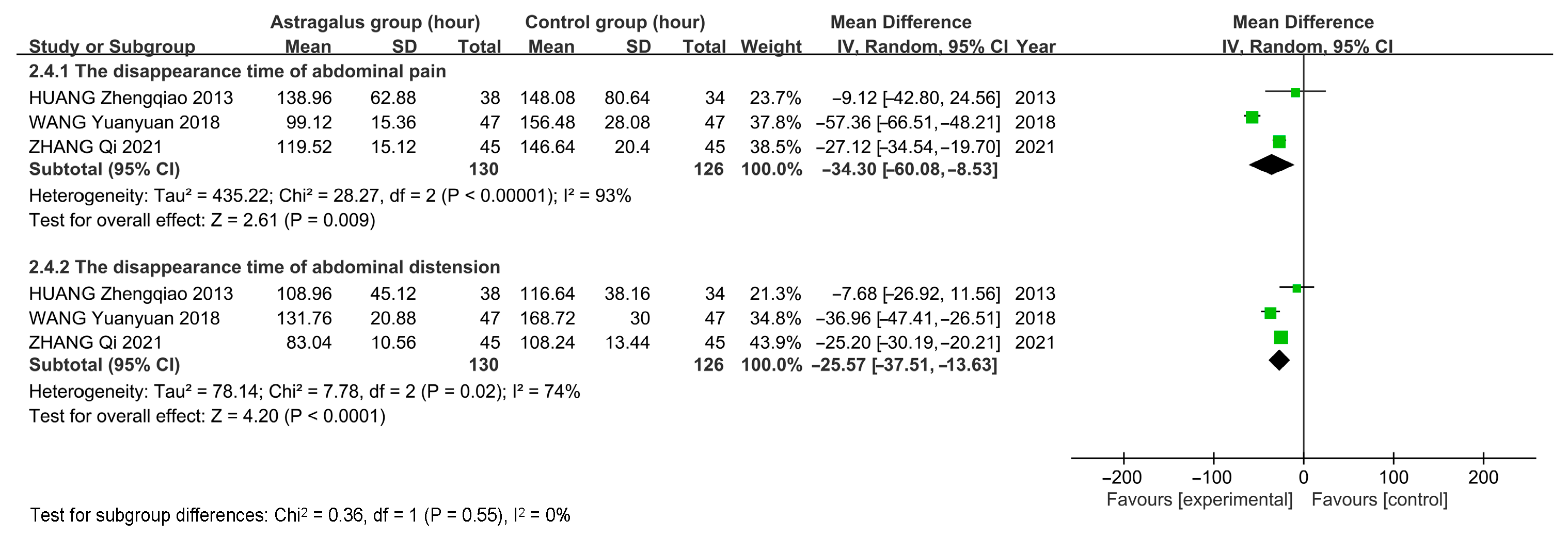
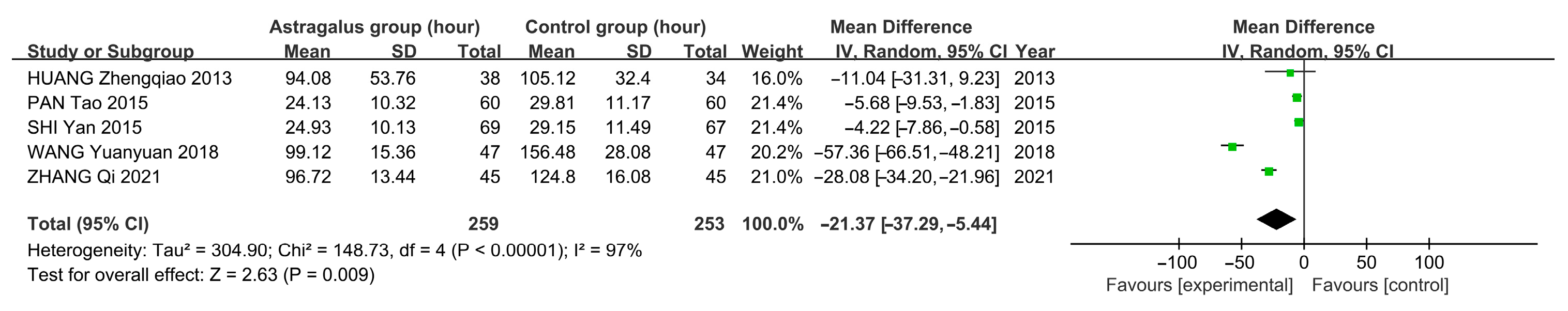
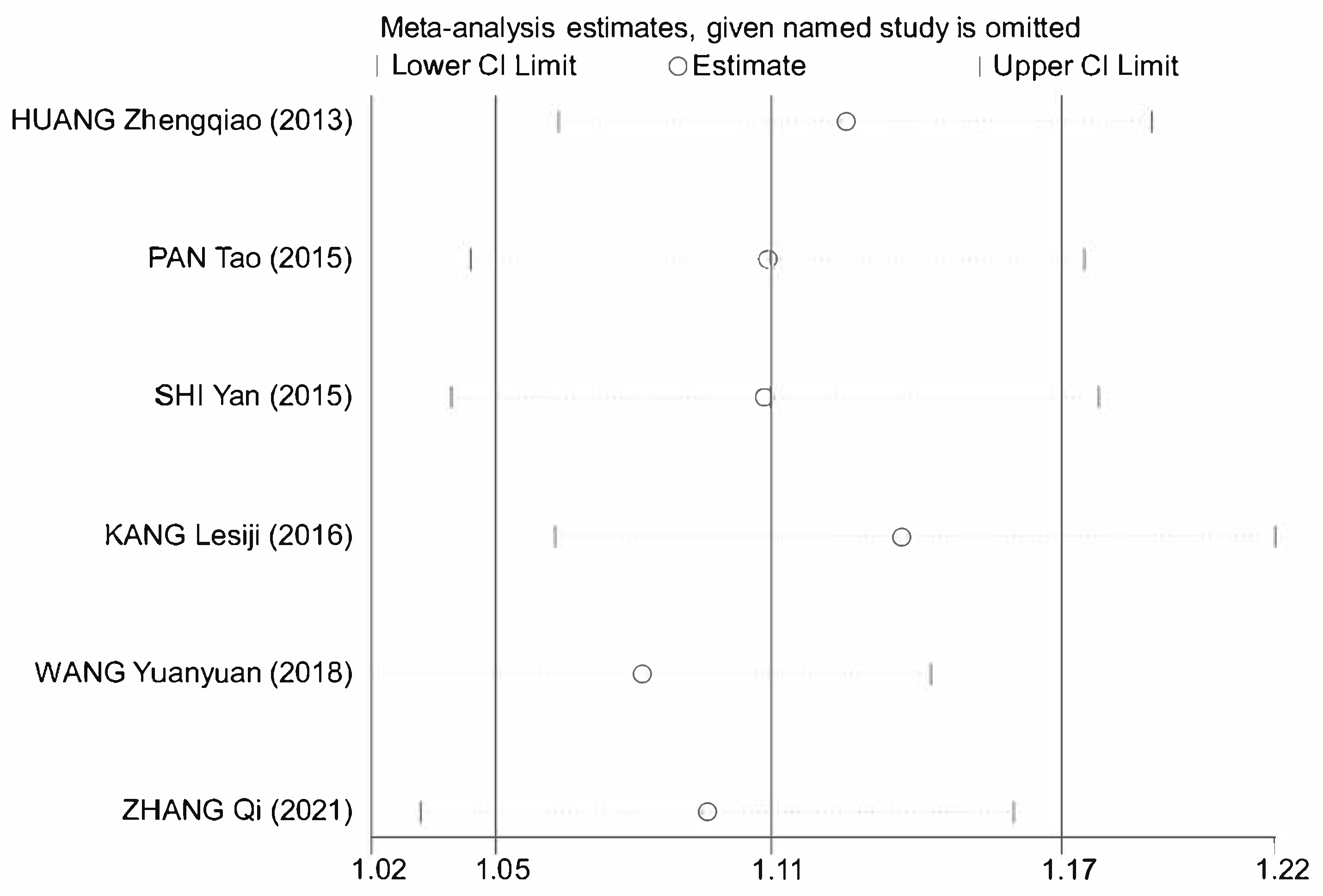
3.7. Meta-Analysis
3.7.1. Literature Retrieval
3.7.2. Data Extraction and Methodological Assessment
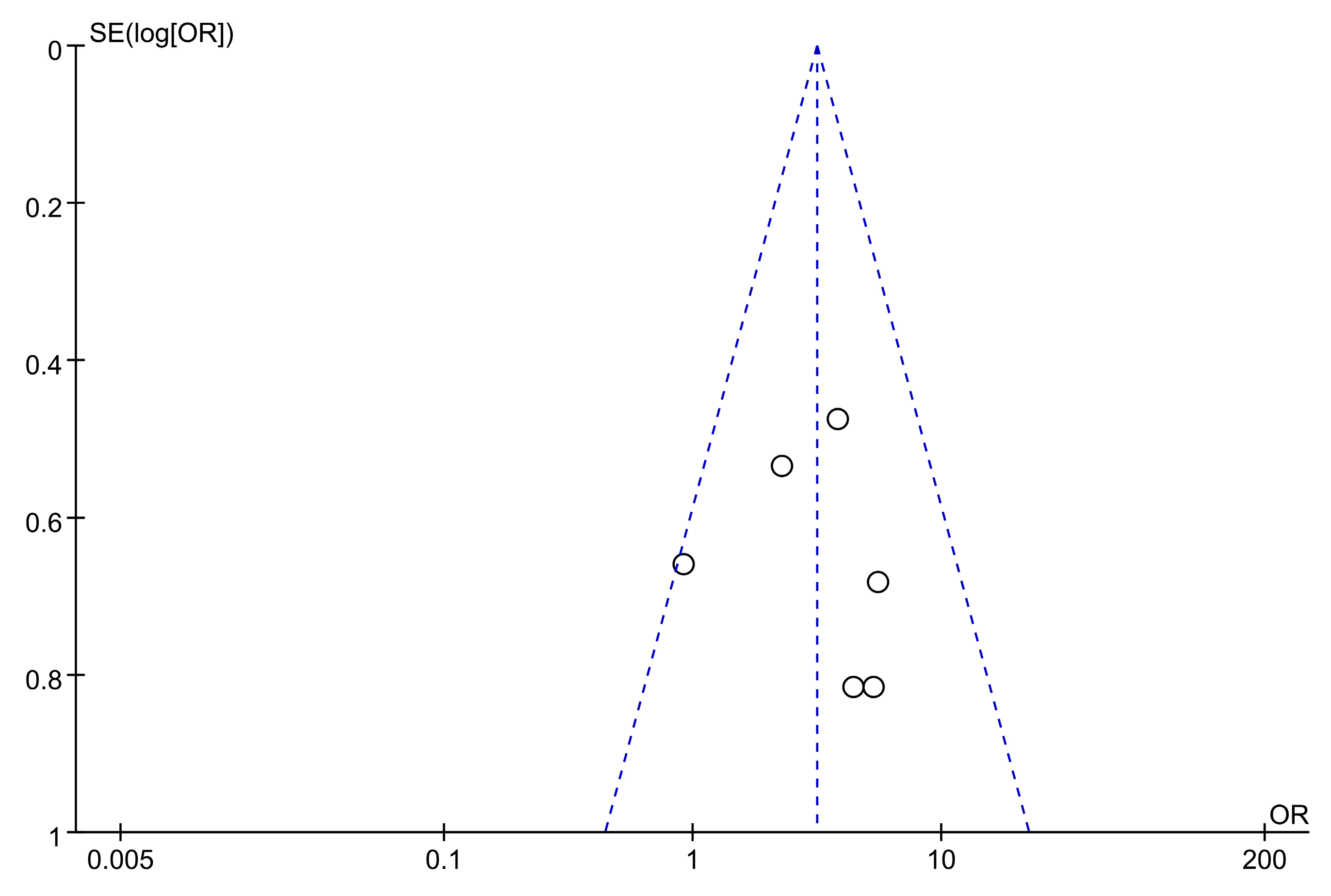
3.7.3. Meta-Analysis Results of Astragalus for AP
4. Discussions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sellers, Z.M.; MacIsaac, D.; Yu, H.; Dehghan, M.; Zhang, K.-Y.; Bensen, R.; Wong, J.J.; Kin, C.; Park, K. Nationwide Trends in Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis among Privately Insured Children and Non-Elderly Adults in the United States, 2007–2014. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S.K.; Sarvepalli, S.; Campbell, J.P.; Obaitan, I.; Singh, D.; Bazerbachi, F.; Singh, R.; Sanaka, M.R.M. Incidence, Admission Rates, and Predictors, and Economic Burden of Adult Emergency Visits for Acute Pancreatitis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, M.S.; Yadav, D. Global Epidemiology and Holistic Prevention of Pancreatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, T.B. Acute Pancreatitis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, ITC17–ITC32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatmary, P.; Grammatikopoulos, T.; Cai, W.; Huang, W.; Mukherjee, R.; Halloran, C.; Beyer, G.; Sutton, R. Acute Pancreatitis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Drugs 2022, 82, 1251–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, M.M.; Yao, Q.Q.; Li, Y.J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.R. Clinical Study of Dachengqi Decoction Combined with Octreotide in Treatment of Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 41, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.J.; Chen, Y.F.; Gao, L.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Feng, D.X. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Chinese Medicine in Treating Acute Pancreatitis. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2019, 41, 1932–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.G.W.; Duan, R.; Wang, H.Y.; Kong, X.P.; Dong, T.T.X.; Tsim, K.W.K.; Chan, K. Evaluation of the Pharmaceutical Properties and Value of Astragali Radix. Medicines 2018, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y. Effects of Huangqi Injection on the Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Jilin J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 41, 1616–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.Q. Acupoint Injection of Astragalus Injection in the Treatment of 38 Cases of Acute Pancreatitis. Jiangxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 44, 54–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.S.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Jin, Z.H. Effect of Astragalus Injection on Acute Edematous Pancreatiti. Chin. J. Drug Eval. 2016, 33, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Fu, G.C.; Liu, F.C. Randomised Control Study of the Effect of Membranaceous Zusanli Acupoint Injection on Acute Pancreatitis with Intestinal Paralysis. J. Chengdu Med. Coll. 2015, 10, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Shen, H.L. Randomized Controlled Clinical Study on the Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Intestinal Paralysis by Acupoint Injection of Astragalus at Zusanli. Med. Inf. 2015, 42, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Dong, H.X. Clinical Study on Huangqi Injection on Intestinal Barrier Function and Micro Inflammatory State in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. World Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 818–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, L. The Effects of Chaiqin Chengqi Decoction Combined with Ulinastatin on Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Clin. Res. 2025, 33, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, R.S.J.; Steiger, K. A Critical Role for Akt1 Signaling in Acute Pancreatitis Progression. J. Pathol. 2020, 251, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Zhao, L.; Zang, X.; Zhen, J.; Liu, Y.; Bian, W.; Chen, W. Quercetin Inhibits Caerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis through Regulating Mir-216b by Targeting Map2k6 and Neat1. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 29, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yin, D.H.; Xu, W.M. Experimental Study of Hesperidin on Reducing Lung Injury in Rats with Severe Acute Pancreatitis by Regulating Pi3k/Akt/Nf-Κb Signaling Pathway. J. Logist. Univ. PAP (Med. Sci.) 2019, 28, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.J.; Papachristou, G.I.; Speake, C.; Lacy-Hulbert, A. Immune Markers of Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2024, 40, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.T.; Zhou, Y.; Han, P.Y.; Ren, H.B. Ferroptosis Inhibition Attenuates Inflammatory Response in Mice with Acute Hypertriglyceridemic Pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol 2023, 29, 2294–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mititelu, A.; Grama, A.; Colceriu, M.-C.; Benţa, G.; Popoviciu, M.-S.; Pop, T.L. Role of Interleukin 6 in Acute Pancreatitis: A Possible Marker for Disease Prognosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.G.; Kong, D.S.; Li, W.K. Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharides on Acute Pancreatitis in Rats and Its Mechanism. Hainan Med. J. 2024, 35, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, D.D.; Tiriac, H.; Rivera, K.D.; Pommier, A.; Whalen, S.; Oni, T.E.; Alagesan, B.; Lee, E.J.; Yao, M.A.; Lucito, M.S.; et al. The Glycan Ca19-9 Promotes Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer in Mice. Science 2019, 364, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Meng, Z.; Pang, Y.; Li, W. Study on the Mechanism of Dachaihu Decoction in the Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis Based on Artificial Intelligence Combined with in Vivo Experiments. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2023, 26, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, K.; Tan, J.; Tian, H.; Xu, T.; Liu, F.; Peng, N.; Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; et al. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Attenuates Coxsackievirus B3-Induced Pancreatitis through the Bax/Bcl2/Casp3 Signaling Pathway. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 4129–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Han, Z. Mir-339-3p Regulated Acute Pancreatitis Induced by Caerulein through Targeting Tnf Receptor-Associated Factor 3 in Ar42j Cells. Open Life Sci. 2020, 15, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Lin, K.T.; Rahman, M.A.; Ishigami, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jensen, M.A.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Park, Y.; Tuveson, D.A.; Krainer, A.R. Splicing Factor Srsf1 Promotes Pancreatitis and Krasg12d-Mediated Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 1678–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Iyer, S.; Xue, X.; Bragazzi Cunha, J.; Gu, S.; Moons, D.; Pipe, S.W.; Williams, J.A.; Simeone, D.M.; Shah, Y.M.; et al. Hif1-Alpha Regulates Acinar Cell Function and Response to Injury in Mouse Pancreas. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1630–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Zhu, X.; Li, D.Y. Effects of Huangqin Decoction Combined with Sequential Hepatic Arterial Chemoembolization on the Serum Levels of Nf-Κb, Hif-1α and Afp and the Liver Function in Patients with Primary Hepatic Carcinoma. J. Chang. Univ. Chin. Med. 2022, 38, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, E.; Cao, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; You, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; He, J.; Feng, Y. The Mitochondria-Targeted Kaempferol Nanoparticle Ameliorates Severe Acute Pancreatitis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y.; Pandey, R.P.; Lee, J.; Sohng, J.K.; Namkung, W.; Park, Y.I. Quercetin 3-O-Xyloside Ameliorates Acute Pancreatitis in Vitro Via the Reduction of Er Stress and Enhancement of Apoptosis. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Tan, J.-H.; Zhou, W.-Y.; Xu, J.; Ren, S.-J.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Chen, X.-M.; Zhang, G.-W. P53 Activated by Er Stress Aggravates Caerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis Progression by Inducing Acinar Cell Apoptosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 3211–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Yuan, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Fan, T.; Wang, F. Calycosin Alleviates Cerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis by Inhibiting the Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress Via the P38 Mapk and Nf-Κb Signal Pathways in Mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, F.; Liu, T.; Zhang, K.; Wen, A.; Feng, L.; Shu, X.; Tian, S.; et al. Isorhamnetin Alleviates Mitochondrial Injury in Severe Acute Pancreatitis Via Modulation of Kdm5b/Htra2 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Duan, J.; Sun, Y.; Yang, R.; Yang, H.; Li, W. Phillygenin rescues impaired autophagy flux by modulating the PI3K/Akt/mToR signaling pathway in a rat model of severe acute pancreatitis. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2024, 38, 3946320241309260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.Y.; Fu, L.Y.; Hu, C.L.; Chen, D.X.; Gan, T.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhao, X.Y. H2S mitigates severe acute pancreatitis through the PI3K/AKT-NF-κB pathway in vivo. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 4555–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankisch, P.G.; Apte, M.; Banks, P.A. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet 2015, 386, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capner, P.; Lendrum, R.; Jeffries, D.J.; Walker, G. Viral antibody studies in pancreatic disease. Gut 1975, 16, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Code | Ingredient | OB (Oral Bioavailability) (%) | DL (Drug-Likeness) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000392 | Formononetin | 69.67 | 0.21 |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 |
| MOL000417 | Calycosin | 47.75 | 0.24 |
| MOL000438 | (3R)-3-(2-hydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)chroman-7-ol | 67.67 | 0.26 |
| MOL000098 | Quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| MOL000239 | Jaranol | 50.83 | 0.29 |
| MOL000398 | Isoflavanone | 109.99 | 0.3 |
| MOL000378 | 7-O-methylisomucronulatol | 74.69 | 0.3 |
| MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | 49.6 | 0.31 |
| MOL000380 | (6aR,11aR)-9,10-dimethoxy-6a,11a-dihydro-6H-benzofurano[3,2-c]chromen-3-ol | 64.26 | 0.42 |
| MOL000371 | 3,9-Di-O-methylnissolin | 53.74 | 0.48 |
| MOL000442 | 1,7-Dihydroxy-3,9-dimethoxy pterocarpene | 39.05 | 0.48 |
| MOL000439 | Isomucronulatol-7,2′-di-O-glucosiole | 49.28 | 0.62 |
| MOL000387 | Bifendate | 31.1 | 0.67 |
| MOL000374 | 5′-Hydroxyiso-muronulatol-2′,5′-di-O-glucoside | 41.72 | 0.69 |
| MOL000433 | FA | 68.96 | 0.71 |
| MOL000296 | Hederagenin | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| MOL000211 | Mairin | 55.38 | 0.78 |
| MOL000033 | (3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-Dimethyl-17-[(2R,5S)-5-propan-2-yloctan-2-yl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-Dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol | 36.23 | 0.78 |
| MOL000379 | 9,10-Dimethoxypterocarpan-3-O-β-D-glucoside | 36.74 | 0.92 |
| Gene Name | Degree | Betweenness | Closeness |
|---|---|---|---|
| TP53 | 185 | 2422.629693 | 0.003610108 |
| AKT1 | 182 | 1795.229331 | 0.003571429 |
| TNF | 171 | 1963.275514 | 0.003436426 |
| IL6 | 170 | 1653.318961 | 0.003424658 |
| EGFR | 163 | 1693.215029 | 0.003344482 |
| CASP3 | 162 | 994.273886 | 0.003322259 |
| MYC | 159 | 1536.505978 | 0.00330033 |
| HIF1A | 156 | 1012.411402 | 0.003267974 |
| Ligand Compound | Receptor Protein | PUB (ID) | Binding Energy (KJ/mol) | Positive Control Ligand | Binding Energy (KJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | TP53 | 5O1E | −8.0 | 5o1e_D_9GT | −7.1 |
| Quercetin | AKT1 | 3CQW | −8.6 | 3cqw_D_CQW | −8.9 |
| Quercetin | TNF | 3L0V | −8.7 | 3l0v_D_724 | −8.6 |
| Quercetin | IL-6 | 6MG1 | −6.0 | 6mg1_I_GOL | −2.9 |
| Quercetin | EGFR | 8A27 | −9.6 | 8a27_C_KY9 | −10.4 |
| Quercetin | CASP3 | 3H0E | −8.8 | 3h0e_C_H0E | −8.6 |
| Quercetin | MYC | 6S9Z | −9.6 | 6s9z_H_VKL | −8.7 |
| Quercetin | HIF1A | 1LQB | −7.5 | 1lqb_E_SO4 | −3.4 |
| First Author and Publication Year | Number of Participants Astragalus and Control | Intervention | Frequency and Treatment Duration (d) | Jadad Score | Research Indicators | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astragalus Group | Control Group | |||||
| HUANG Zhengqiao 2013 [10] | 38 & 34 | General Treatment and Astragalus | General Treatment and Metoclopramide Injection Subcutaneous 2 mL | 1–2 treatments per day for 2 days | 2 | ①④⑤⑥ |
| PAN Tao 2015 [11] | 69 & 67 | General treatment and astragalus injection subcutaneous 2 mL | General treatment and saline (medicine) subcutaneous 2 mL | 2 treatments per day for 7 days | 3 | ①②③⑥ |
| SHI Yan 2015 [12] | 60 & 60 | General treatment and astragalus injection subcutaneous 0.5~1 mL | General treatment and saline (medicine) subcutaneous 0.5~1 mL | 1–2 times daily for 20 treatments | 3 | ①②③⑥ |
| KANG Lesiji 2016 [13] | 53 & 54 | General treatment and astragalus injection IV 20 mL | General treatment | 1 treatment per day for 7 days | 2 | ① |
| WANG Yuanyuan 2018 [14] | 47 & 47 | General treatment and astragalus injection IV 60 mL | General treatment | 1 treatment per day for 10 days | 4 | ①④⑤⑥ |
| ZHANG Qi 2021 [15] | 45 & 45 | General treatment and astragalus injection IV 20 mL | General treatment | 1 treatment per day for 10 days | 3 | ①④⑤⑥ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, X.; Duan, S.; Li, A.; He, Z. Astragalus in Acute Pancreatitis: Insights from Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Meta-Analysis Validation. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050379
Cao X, Duan S, Li A, He Z. Astragalus in Acute Pancreatitis: Insights from Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Meta-Analysis Validation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050379
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Xingxin, Suqin Duan, Aiyi Li, and Zhanlong He. 2025. "Astragalus in Acute Pancreatitis: Insights from Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Meta-Analysis Validation" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050379
APA StyleCao, X., Duan, S., Li, A., & He, Z. (2025). Astragalus in Acute Pancreatitis: Insights from Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Meta-Analysis Validation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050379