The Molecular Pathology of Pre-Eclamptic Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Angiotensinogen and Renin
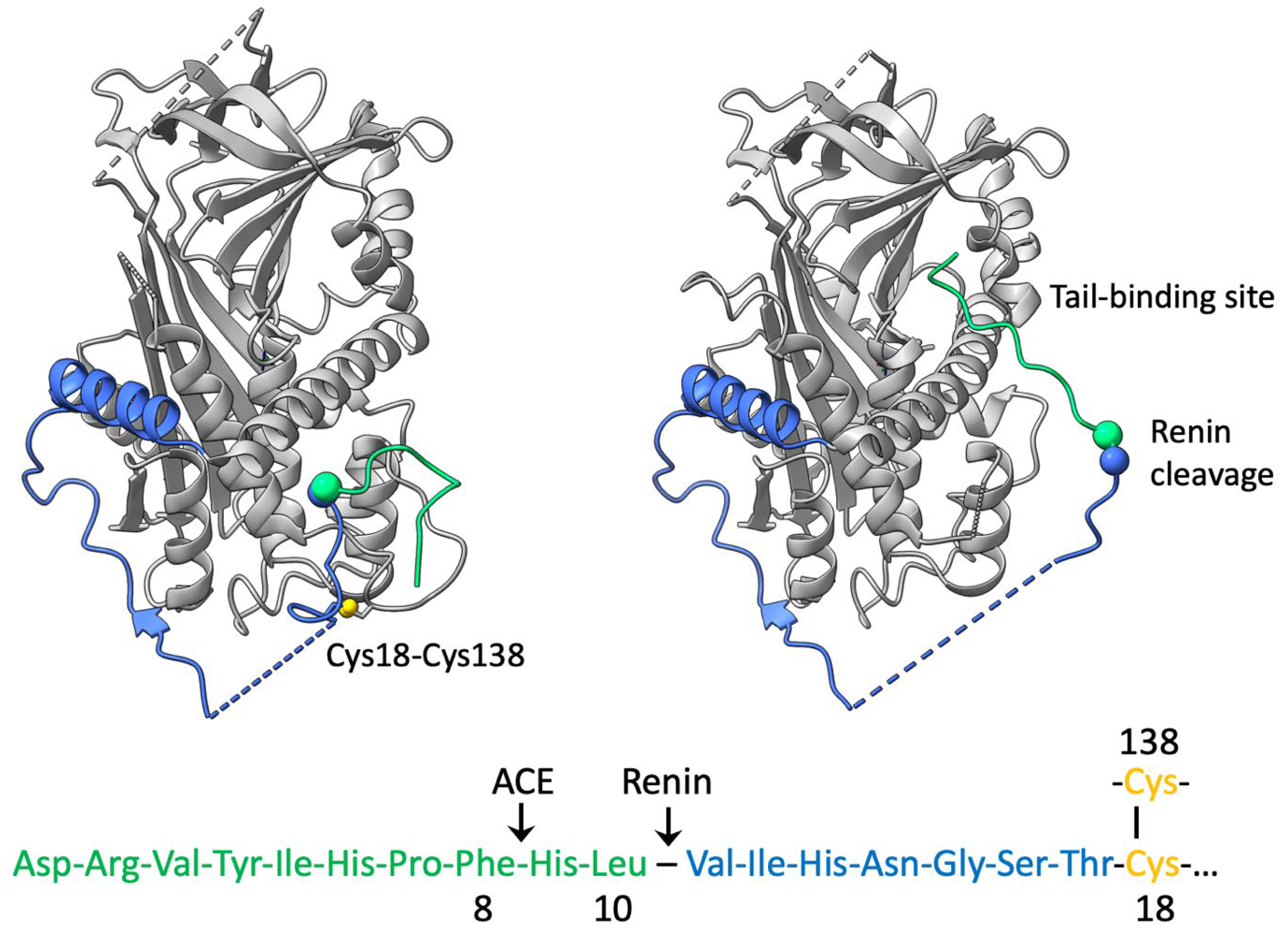
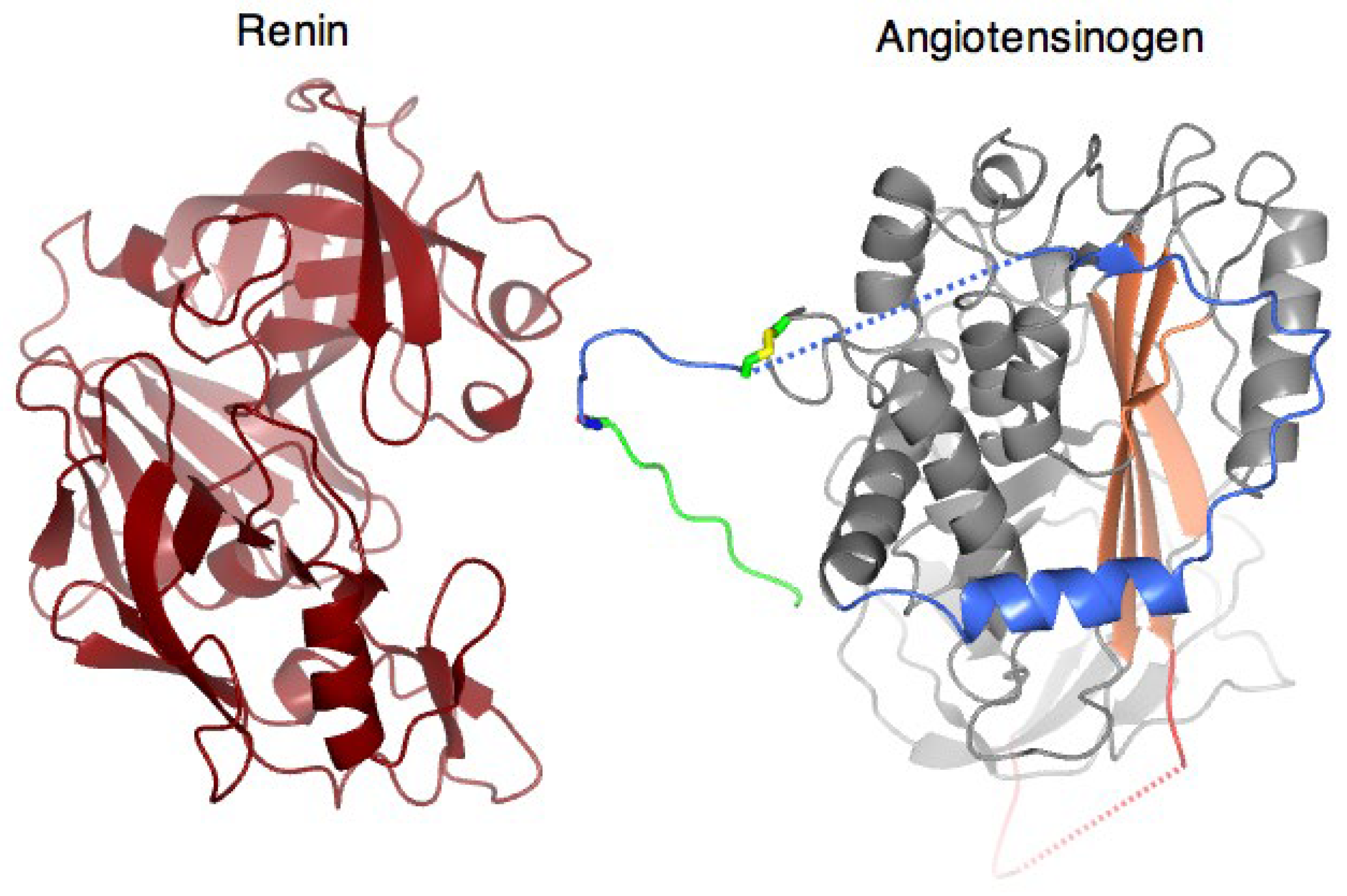
3. Structural Mechanism of Cleavage and Angiotensin Release
4. Disulphide Modulation
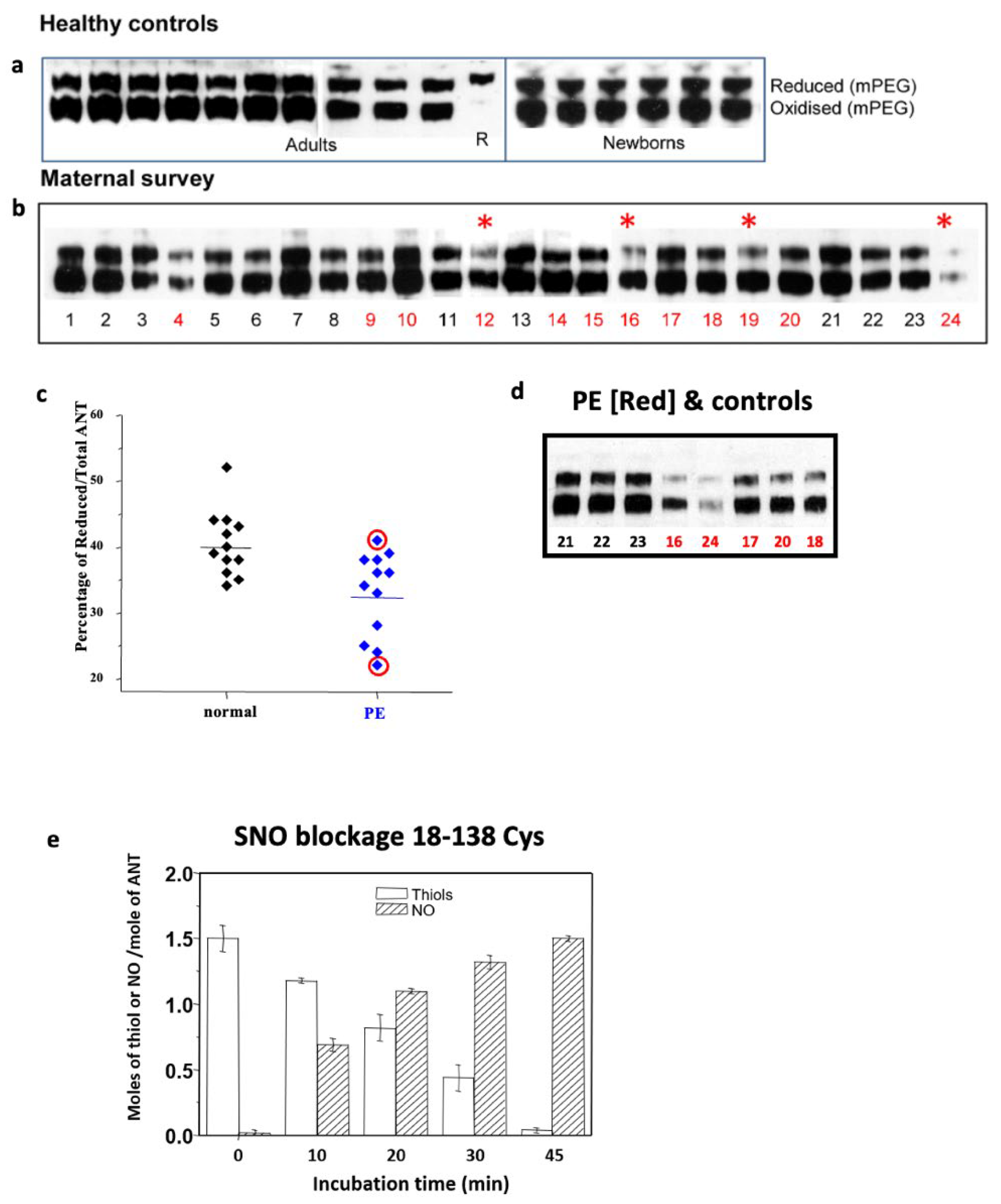
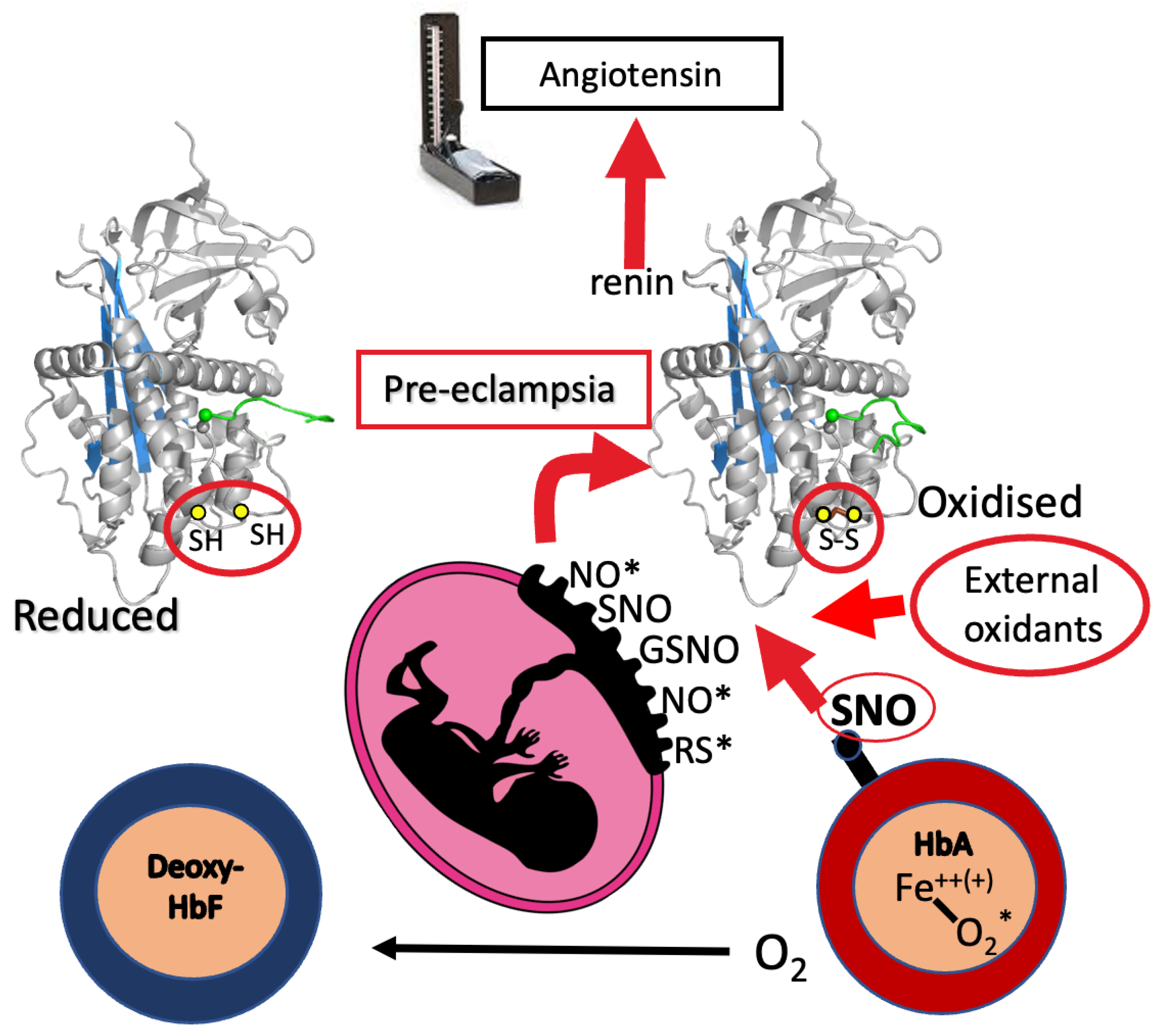
5. Pre-Eclampsia
6. Circulatory Milieu: Haemoglobin a Redox Agent?
7. Placental Oxidative Stress
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doolittle, R.F. Angiotensinogen is related to the antitrypsin-antithrombin-ovalbumin family. Science 1983, 222, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, R.; Carrell, R.W. Implications of the three-dimensional structure of alpha 1-antitrypsin for structure and function of serpins. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 8951–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, P.E.; Tewkesbury, D.A.; Carrell, R.W. Ovalbumin and angiotensinogen lack serpin S-R conformational change. Biochem. J. 1989, 262, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cleland, S.J.; Reid, J.L. The renin-angiotensin system and the heart: A historical review. Heart 1996, 76, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, C.; Lu, H.; Cassis, L.A.; Daugherty, A. Molecular and Pathophysiological Features of Angiotensinogen: A Mini Review. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 4, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, H.S.; Krege, J.H.; Kluckman, K.D.; Hagaman, J.R.; Hodgin, J.B.; Best, C.F.; Jennette, J.C.; Coffman, T.M.; Maeda, N.; Smithies, O. Genetic control of blood pressure and the angiotensinogen locus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2735–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Uijl, E.; Mirabito Colafella, K.M.; Sun, Y.; Ren, L.; van Veghel, R.; Garrelds, I.M.; de Vries, R.; Poglitsch, M.; Zlatev, I.; Kim, J.B.; et al. Strong and Sustained Antihypertensive Effect of Small Interfering RNA Targeting Liver Angiotensinogen. Hypertension 2019, 73, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, I.; Rohrwasser, A.; Helin, C.; Jeunemaitre, X.; Crain, P.; Bohlender, J.; Lifton, R.P.; Corvol, P.; Ward, K.; Lalouel, J.M. A mutation of angiotensinogen in a patient with preeclampsia leads to altered kinetics of the renin-angiotensin system. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 11430–11436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, A.; Carrell, R.W.; Murphy, M.P.; Wei, Z.; Yan, Y.; Stanley, P.L.; Stein, P.E.; Broughton Pipkin, F.; Read, R.J. A redox switch in angiotensinogen modulates angiotensin release. Nature 2010, 468, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shu, Z.; Wan, J.; Read, R.J.; Carrell, R.W.; Zhou, A. Angiotensinogen and the Modulation of Blood Pressure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 645123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yan, Y.; Zhou, A.; Carrell, R.W.; Read, R.J. Structural basis for the specificity of renin-mediated angiotensinogen cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 2353–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Web Reference to Video (from Nature [9] 2010). Available online: https://static-content.springer.com/esm/art%3A10.1038%2Fnature09505/MediaObjects/41586_2010_BFnature09505_MOESM78_ESM.mov (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Streatfeild-James, R.M.; Williamson, D.; Pike, R.N.; Tewksbury, D.; Carrell, R.W.; Coughlin, P.B. Angiotensinogen cleavage by renin: Importance of a structurally constrained N-terminus. FEBS Lett. 1998, 436, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimenez-Roqueplo, A.P.; Célérier, J.; Schmid, G.; Corvol, P.; Jeunemaitre, X. Role of cysteine residues in human angiotensinogen. Cys232 is required for angiotensinogen-pro major basic protein complex formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 34480–34487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubel, C.A. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1999, 222, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.J.; Jauniaux, E. Placental oxidative stress: From miscarriage to preeclampsia. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 2004, 11, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.G.; Gongora, M.C. Oxidative stress and hypertension. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 93, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, H.D.; Kurlak, L.O.; Broughton Pipkin, F. The placental renin-angiotensin system and oxidative stress in pre-eclampsia. Placenta 2013, 34, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premont, R.T.; Singel, D.J.; Stamler, J.S. The enzymatic function of the honorary enzyme: S-nitrosylation of hemoglobin in physiology and medicine. Mol. Asp. Med. 2022, 84, 101056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sibai, B.; Dekker, G.; Kupferminc, M. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 2005, 365, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahgozar, S.; Amirian, T.; Qi, M.; Shahshahan, Z.; Entezar-E-Ghaem, M.; Ghasemi, H.; Miroliaei, M.; Krilis, S.A.; Giannakopoulos, B. Improved Assay for Quantifying a Redox Form of Angiotensinogen as a Biomarker for Pre-Eclampsia: A Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qi, M.; Weaver, J.C.; Rahgozar, S.; Giannakopoulos, B.; Krilis, S.A. Quantitation of Total and Free Thiol Angiotensinogen as a Prognostic Marker for Preeclampsia. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1967, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahabiyeh, L.A.; Tooth, D.; Kurlak, L.O.; Mistry, H.D.; Pipkin, F.B.; Barrett, D.A. A pilot study of alterations in oxidized angiotensinogen and antioxidants in pre-eclamptic pregnancyu. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lehmann, H.; Carrell, R.W. Variations in the structure of human haemoglobin. With particular reference to the unstable haemoglobins. Br. Med. Bull. 1969, 25, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterbourn, C.C.; McGrath, B.M.; Carrell, R.W. Reactions involving superoxide and normal and unstable haemoglobins. Biochem. J. 1976, 155, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carrell, R.W.; Winterbourn, C.C.; Rachmilewitz, E.A. Activated oxygen and haemolysis. Br. J. Haematol. 1975, 30, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterbourn, C.C. Free-radical production and oxidative reactions of hemoglobin. Environ. Health Perspect. 1985, 64, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrell, R.W. The Unstable Haemoglobins. Ph.D. Dissertation, University Library, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 1967; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Nobbs, C.; Watson, H.; Kendrew, J. Structure of Deoxymyoglobin: A Crystallographic Study. Nature 1966, 209, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, H.P.; Fridovich, I. The generation of superoxide radical during the autoxidation of hemoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 6960–6962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrell, R.W.; Winterbourn, C.C.; French, J.K. Haemoglobin—A frustrated oxidase? Implications for red cell metabolism. Hemoglobin 1977, 1, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterbourn, C.C.; Carrell, R.W. Oxidation of human haemoglobin by copper. Mechanism and suggested role of the thiol group of residue beta-93. Biochem. J. 1977, 165, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ladner, R.C.; Heidner, E.J.; Perutz, M.F. The structure of horse methaemoglobin at 2-0 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 114, 385–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamler, J.S.; Jia, L.; Eu, J.P.; McMahon, T.J.; Demchenko, I.T.; Bonaventura, J.; Gernert, K.; Piantadosi, C.A. Blood flow regulation by S-nitrosohemoglobin in the physiological oxygen gradient. Science 1997, 276, 2034–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawloski, J.R.; Hess, D.T.; Stamler, J.S. Export by red blood cells of nitric oxide bioactivity. Nature 2001, 409, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premont, R.T.; Stamler, J.S. Essential Role of Hemoglobin βCys93 in Cardiovascular Physiology. Physiology 2020, 35, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kalinina, E.; Novichkova, M. Glutathione in Protein Redox Modulation through S-Glutathionylation and S-Nitrosylation. Molecules 2021, 26, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Robaczewska, J.; Kedziora-Kornatowska, K.; Kozakiewicz, M.; Zary-Sikorska, E.; Pawluk, H.; Pawliszak, W.; Kedziora, J. Role of glutathione metabolism and glutathione-related antioxidant defense systems in hypertension. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 67, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hill, B.G.; Bhatnagar, A. Protein S-glutathiolation: Redox-sensitive regulation of protein function. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2012, 52, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Amoroso, E.C. Placentation. In Marshall’s Physiology of Reproduction, 3rd ed.; Parkes, A.S., Ed.; Longmans: London, UK, 1952; Volume 2, pp. 127–311. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J.M.; Gammill, H.S. Preeclampsia: Recent insights. Hypertension 2005, 46, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, U.D.; Gram, M.; Ranstam, J.; Thilaganathan, B.; Kerström, B.; Hansson, S.R. Fetal hemoglobin, α1-microglobulin and hemopexin are potential predictive first trimester biomarkers for preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2016, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, S.R.; Nääv, Å.; Erlandsson, L. Oxidative stress in preeclampsia and the role of free fetal hemoglobin. Front. Physiol. 2015, 5, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Elrefaei, A.M.; Zakarya, A.M.; Motaal, A.; Assem, A. Fetal hemoglobln as a predictor in cases of pre-eclampsia. Al Azhar Med. J. 2022, 23, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabacco, S.; Ambrosii, S.; Polsinelli, V.; Fantasia, I.; D’Alfonso, A.; Ludovisi, M.; Cecconi, S.; Guido, M. Pre-Eclampsia: From Etiology and Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Tools-A Review of the Literature. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 6202–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ives, C.W.; Sinkey, R.; Rajapreyar, I.; Tita, A.T.N.; Oparil, S. Preeclampsia-Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentations: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1690–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carrell, R.W.; Read, R.J.; Zhou, A. The Molecular Pathology of Pre-Eclamptic Hypertension. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050375
Carrell RW, Read RJ, Zhou A. The Molecular Pathology of Pre-Eclamptic Hypertension. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050375
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarrell, Robin W., Randy J. Read, and Aiwu Zhou. 2025. "The Molecular Pathology of Pre-Eclamptic Hypertension" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050375
APA StyleCarrell, R. W., Read, R. J., & Zhou, A. (2025). The Molecular Pathology of Pre-Eclamptic Hypertension. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050375





