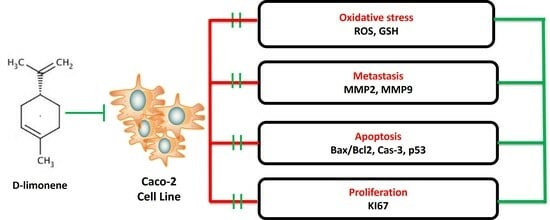
D-Limonene Exhibits Antiproliferative Activity Against Human Colorectal Adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) Cells via Regulation of Inflammatory and Apoptotic Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. D-Limonene Preparation
2.2. Caco-2 Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Reactive Oxygen Species Exploration
2.5. Reduced Glutathione (GSH) Detection
2.6. Assessment of Pro-Inflammatory Markers
2.7. Estimation of Apoptotic/Anti-Apoptotic Markers
2.8. Gene Expression Analysis
2.9. Valuation of Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
2.10. Estimation of Cellular Proliferation Marker (Ki67)
2.11. Assessment of Matrix Metalloproteinases
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
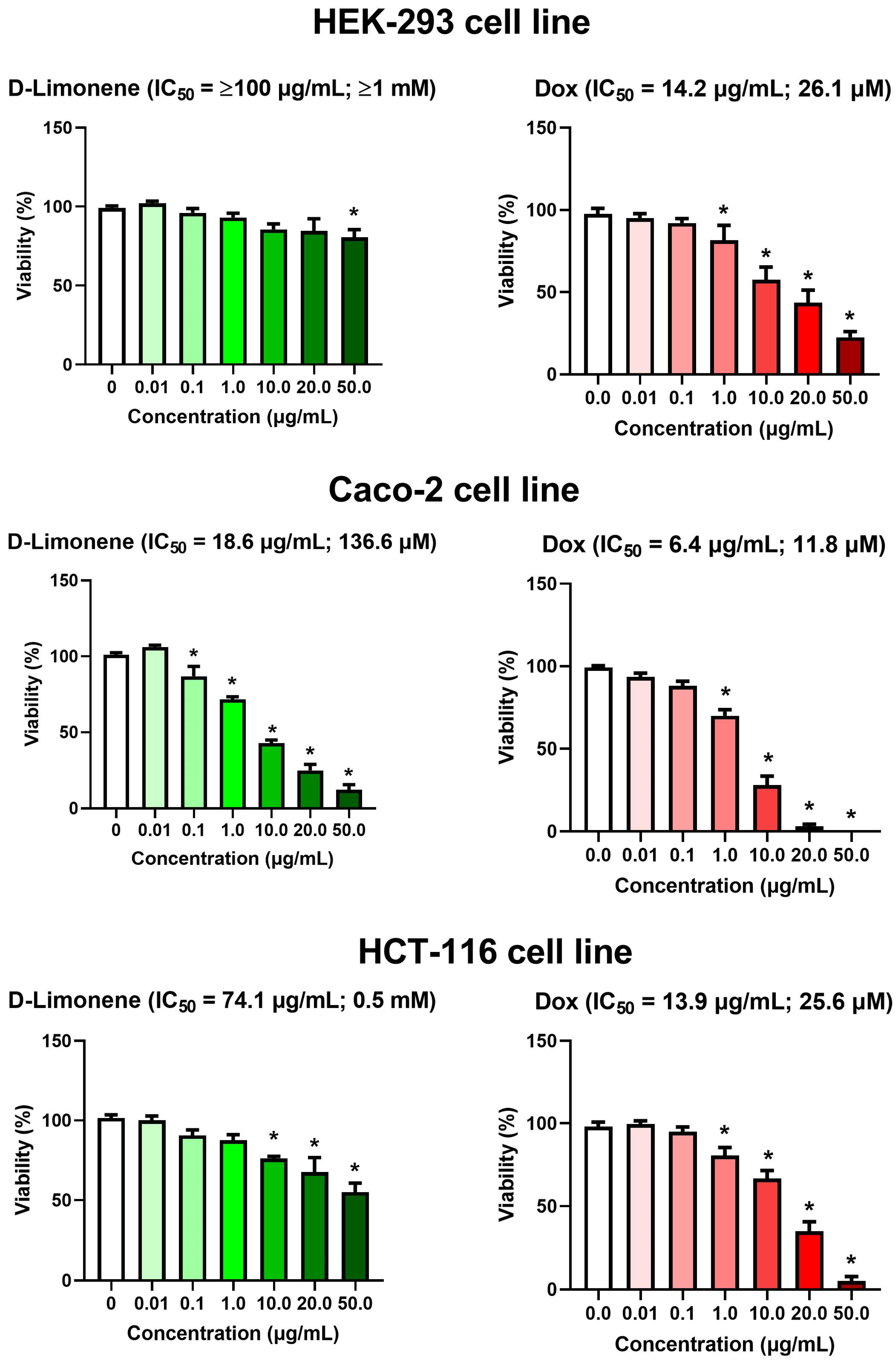
3.1. Cytotoxic Activity of D-Limonene
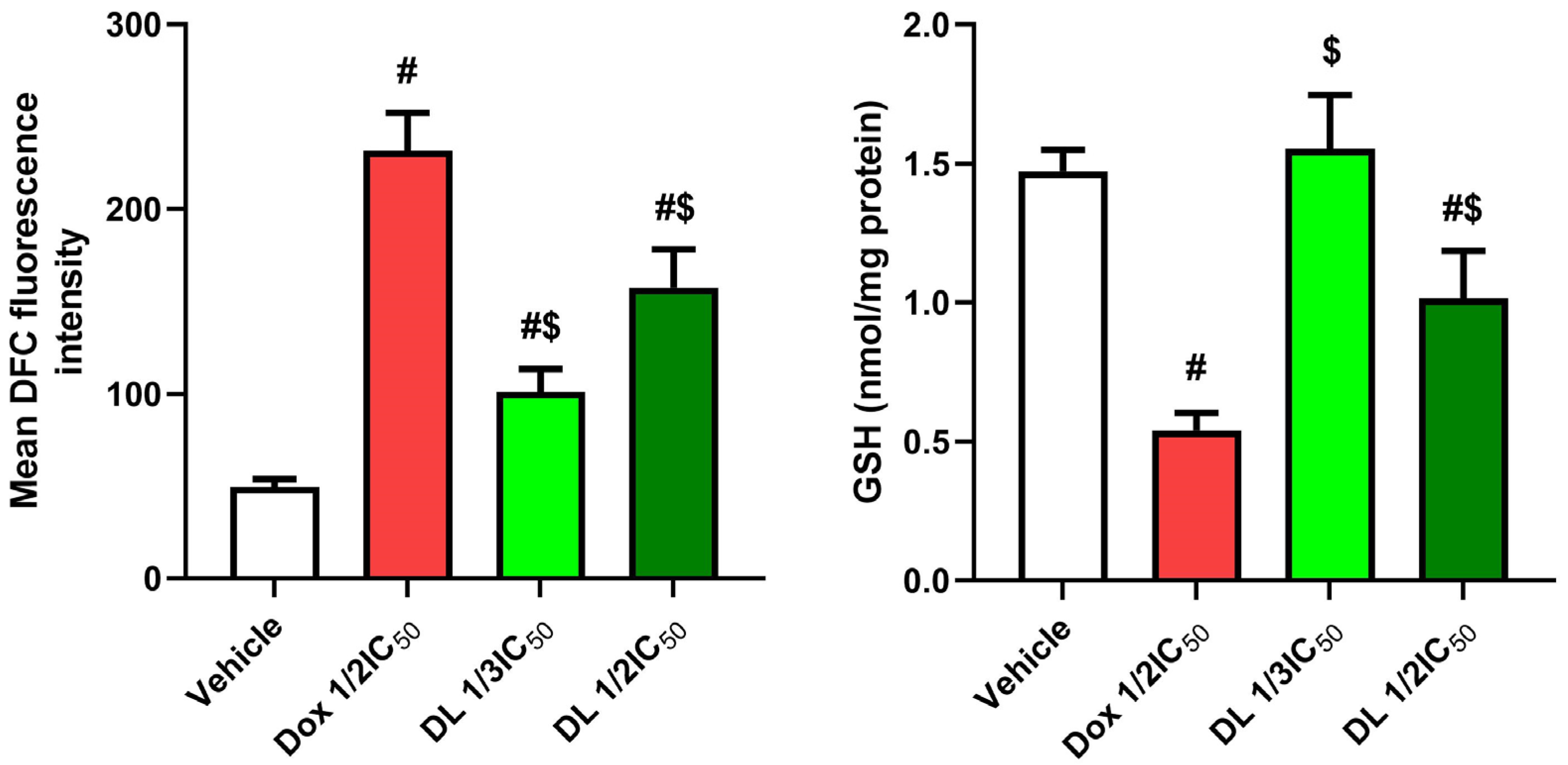
3.2. Effects of D-Limonene on Oxidant–Antioxidant Balance
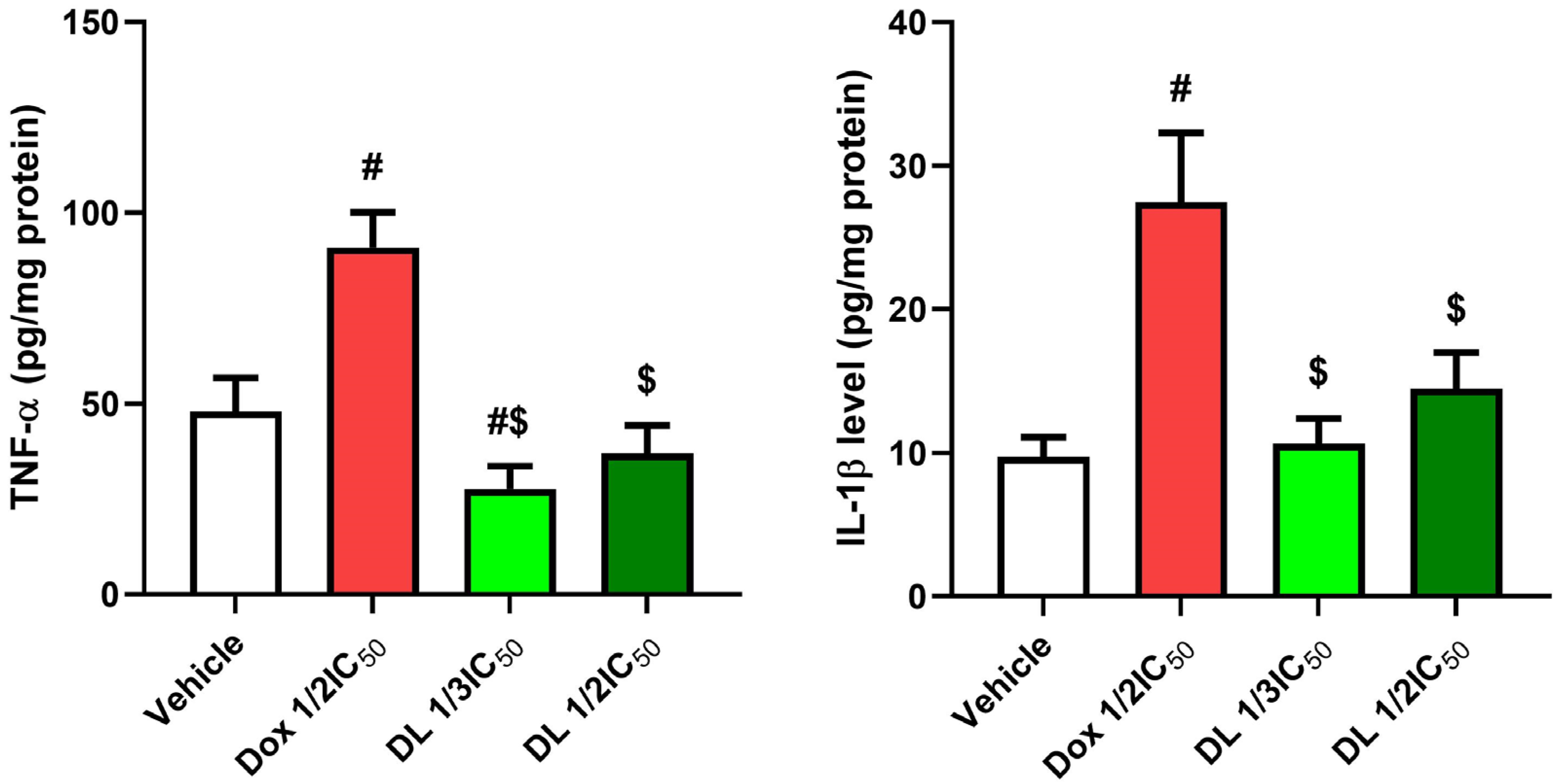
3.3. Impact of D-Limonene on Pro-Inflammatory Biomarkers
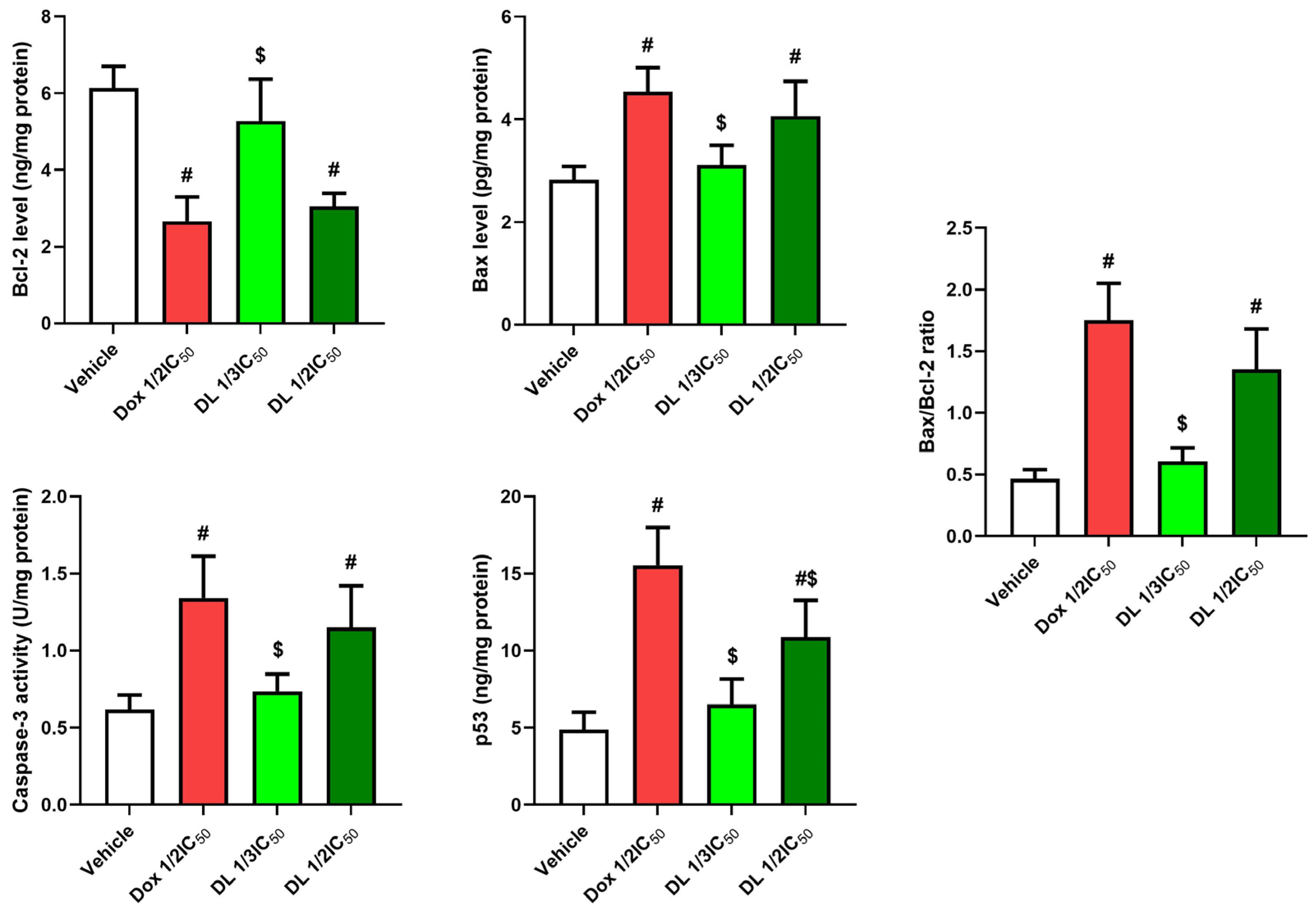
3.4. D-Limonene’s Effect on Apoptotic Markers
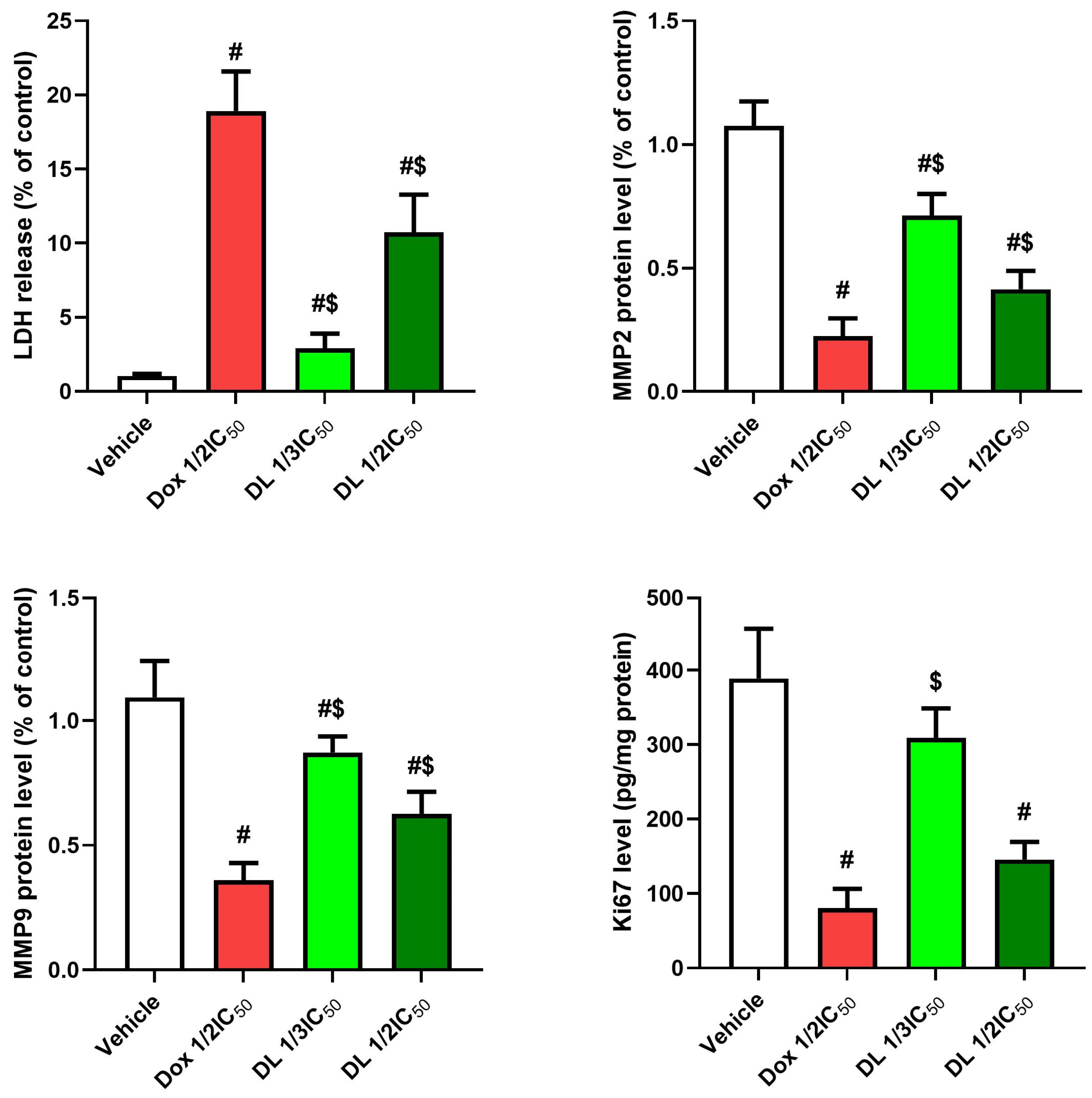
3.5. Effects on LDH, Matrix Metalloproteinases, and Ki67
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morgan, E.; Arnold, M.; Gini, A.; Lorenzoni, V.; Cabasag, C.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Murphy, N.; Bray, F. Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut 2023, 72, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almatroudi, A. The incidence rate of colorectal cancer in Saudi Arabia: An observational descriptive epidemiological analysis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2020, 13, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Garawani, I.M.; Elkhateeb, W.A.; Zaghlol, G.M.; Almeer, R.S.; Ahmed, E.F.; Rateb, M.E.; Moneim, A.E.A. Candelariella vitellina extract triggers in vitro and in vivo cell death through induction of apoptosis: A novel anticancer agent. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 127, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.S.; Al-Bagawi, A.H.; Obeidat, S.T.; Fareid, M.A.; Habotta, O.A.; Moneim, A.E.A. Antitumor activity of zinc nanoparticles synthesized with berberine on human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) cells through acting on Cox-2/NF-kB and p53 pathways. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. (Former. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Cancer Agents) 2022, 22, 2002–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadid, M.F.S.; Aghaei, E.; Taheri, E.; Seyyedsani, N.; Chavoshi, R.; Abbasi, S.; Khorrami, A.; Goleij, P.; Hajazimian, S.; Taefehshokr, S. Melatonin increases the anticancer potential of doxorubicin in Caco-2 colorectal cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokman, M.S.; Althagafi, H.A.; Alharthi, F.; Habotta, O.A.; Hassan, A.A.; Elhefny, M.A.; Al Sberi, H.; Theyab, A.; Mufti, A.H.; Alhazmi, A. Protective effect of quercetin against 5-fluorouracil-induced cardiac impairments through activating Nrf2 and inhibiting NF-κB and caspase-3 activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 17657–17669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor Antony Santiago, J.; Jayachitra, J.; Shenbagam, M.; Nalini, N. Dietary d-limonene alleviates insulin resistance and oxidative stress–induced liver injury in high-fat diet and L-NAME-treated rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yan, J.; Sun, Z. D-limonene exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in an ulcerative colitis rat model via regulation of iNOS, COX-2, PGE2 and ERK signaling pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, D.; Micucci, P.; Sebastian, T.; Graciela, F.; Anesini, C. Antioxidant activity of limonene on normal murine lymphocytes: Relation to H2O2 modulation and cell proliferation. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 106, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chen, R.; Li, W.-y.; Zhu, H.-y.; Chen, X.-x.; Hou, Z.-f.; Cao, R.-s.; Zang, G.; Li, Y.-x.; Zhang, W. D-limonene is a potential monoterpene to inhibit PI3K/Akt/IKK-α/NF-κB p65 signaling pathway in coronavirus disease 2019 pulmonary fibrosis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 591830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Alessio, P.A.; Mirshahi, M.; Bisson, J.-F.; Bene, M.C. Skin repair properties of d-Limonene and perillyl alcohol in murine models. Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents Med. Chem. (Former. Curr. Med. Chem.-Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents) 2014, 13, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummer, R.; Fachini-Queiroz, F.C.; Estevão-Silva, C.F.; Grespan, R.; Silva, E.L.; Bersani-Amado, C.A.; Cuman, R.K.N. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity of Citrus latifolia Tanaka essential oil and limonene in experimental mouse models. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 859083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinelli, A.C.; Santos, J.A.; Konkiewitz, E.C.; Oesterreich, S.A.; Formagio, A.S.N.; Croda, J.; Ziff, E.B.; Kassuya, C.A.L. Antihyperalgesic and antidepressive actions of (R)-(+)-limonene, α-phellandrene, and essential oil from Schinus terebinthifolius fruits in a neuropathic pain model. Nutr. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaeenezhad, E.; Hadipour Moradi, F.; Rahimi Monfared, S.; Fattahi, M.D.; Nasri, M.; Amini, A.; Dezfoulian, O.; Ahmadvand, H. D-limonene alleviates acute kidney injury following gentamicin administration in rats: Role of NF-κB pathway, mitochondrial apoptosis, oxidative stress, and PCNA. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6670007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacanlı, M.; Anlar, H.G.; Aydın, S.; Çal, T.; Arı, N.; Bucurgat, Ü.Ü.; Başaran, A.A.; Başaran, N. D-limonene ameliorates diabetes and its complications in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 110, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.G.; Zhan, L.B.; Feng, B.A.; Qu, M.Y.; Yu, L.H.; Xie, J.H. Inhibition of growth and metastasis of human gastric cancer implanted in nude mice by d-limonene. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2004, 10, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh, M.R.; Maleki, H.; Barani, M.; Fahmidehkar, M.A.; Mahmoodi, M.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M. In vitro cytotoxicity assay of D-limonene niosomes: An efficient nano-carrier for enhancing solubility of plant-extracted agents. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 448–458. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Liang, Z.; Mi, Q.; Guo, Y. Limonene terpenoid obstructs human bladder cancer cell (T24 cell line) growth by inducing cellular apoptosis, caspase activation, G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and stops cancer metastasis. J. BUON 2020, 25, 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Motie, F.M.; Howyzeh, M.S.; Ghanbariasad, A. Synergic effects of DL-limonene, R-limonene, and cisplatin on AKT, PI3K, and mTOR gene expression in MDA-MB-231 and 5637 cell lines. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 136216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Roper, M.G. Measurement of DCF fluorescence as a measure of reactive oxygen species in murine islets of Langerhans. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, J.S.; Perestrelo, R.; Ferreira, R.; Berenguer, C.V.; Pereira, J.A.; Castilho, P.C. Plant-derived terpenoids: A plethora of bioactive compounds with several health functions and industrial applications—A comprehensive overview. Molecules 2024, 29, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.; Obeidat, S.; Al-Bagawi, A.; Fareid, M.; El-Borady, O.; Kassab, R.; Moneim, A.A. Evaluation of the potential role of silver nanoparticles loaded with berberine in improving anti-tumor efficiency. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 28, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassab, R.B.; Vasicek, O.; Ciz, M.; Lojek, A.; Perecko, T. The effects of berberine on reactive oxygen species production in human neutrophils and in cell-free assays. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2017, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Lv, W.; Zhang, S.; Qian, Y.; Deng, X.; Feng, N.; Yu, H.; Qian, B. D-limonene exhibits antitumor activity by inducing autophagy and apoptosis in lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 1833–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.-S.; Xi, G.-P.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.-B.; Lei, B.; Dong, X.-S.; Yang, Y.-M. Induction of apoptosis by D-limonene is mediated by inactivation of Akt in LS174T human colon cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, D.-W.; Tang, G.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Y. Synergistic inhibitory effect of berberine and d-limonene on human gastric carcinoma cell line MGC803. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigushin, D.M.; Poon, G.K.; Boddy, A.; English, J.; Halbert, G.W.; Pagonis, C.; Jarman, M.; Coombes, R.C.; Committee, C.R.C.P.I.I.C.T. Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of D-limonene in patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1998, 42, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ping Dou, Q. Targeting apoptosis pathway with natural terpenoids: Implications for treatment of breast and prostate cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2010, 11, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.; Shaikh, M.V.; Chaudagar, K.; Nivsarkar, M.; Mehta, A. D-limonene possesses cytotoxicity to tumor cells but not to hepatocytes. Pol. Ann. Med. 2018, 26, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Li, Y.; Feng, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Gao, J.; Quan, X.; Qian, Y.; Yu, H.; Qian, B. d-Limonene inhibits the occurrence and progression of LUAD through suppressing lipid droplet accumulation induced by PM2.5 exposure in vivo and in vitro. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukiatsiri, S.; Siriwong, S.; Thumanu, K. Pupae protein extracts exert anticancer effects by downregulating the expression of IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α through biomolecular changes in human breast cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rébé, C.; Ghiringhelli, F. Interleukin-1β and cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeer, R.S.; Hammad, S.F.; Leheta, O.F.; Abdel Moneim, A.E.; Amin, H.K. Anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperuricemic functions of two synthetic hybrid drugs with dual biological active sites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Baruch, A. Host microenvironment in breast cancer development: Inflammatory cells, cytokines and chemokines in breast cancer progression: Reciprocal tumor–microenvironment interactions. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.; Lee, O.-Y.; Park, Y.; Seo, M.W.; Lee, D.-S. IL-1β induces IL-6 production and increases invasiveness and estrogen-independent growth in a TG2-dependent manner in human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holen, I.; Lefley, D.V.; Francis, S.E.; Rennicks, S.; Bradbury, S.; Coleman, R.E.; Ottewell, P. IL-1 drives breast cancer growth and bone metastasis in vivo. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.M.; Ma, T.Y. IL-1β causes an increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 4641–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.Y.; Iwamoto, G.K.; Hoa, N.T.; Akotia, V.; Pedram, A.; Boivin, M.A.; Said, H.M. TNF-α-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability requires NF-κB activation. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 286, G367–G376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Capoulade, C.; Moyret-Lalle, C.; Amor-Gueret, M.; Feunteun, J.; Larsen, A.K.; Paillerets, B.B.-d.; Chouaib, S. Resistance of MCF7 human breast carcinoma cells to TNF-induced cell death is associated with loss of p53 function. Oncogene 1997, 15, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolczyk, D.; Zaremba-Czogalla, M.; Hryniewicz-Jankowska, A.; Tabola, R.; Grabowski, K.; Sikorski, A.F.; Augoff, K. TNF-α promotes breast cancer cell migration and enhances the concentration of membrane-associated proteases in lipid rafts. Cell. Oncol. 2016, 39, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnier, D.I.; Bailey, S.R.; Schuster, R.M.; Lentsch, A.B.; Pritts, T.A. TNF-α induces vectorial secretion of IL-8 in Caco-2 cells. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2010, 14, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augoff, K.; Hryniewicz-Jankowska, A.; Tabola, R.; Stach, K. MMP9: A tough target for targeted therapy for cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Youssef, M.; Rawat, M.; Guo, S.; Dokladny, K.; Haque, M.; Watterson, M.D.; Ma, T.Y. MMP-9-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight permeability is mediated by p38 kinase signaling pathway activation of MLCK gene. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 316, G278–G290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, S.A.; Elsaed, W.M.; Eladl, M.A.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Ebrahim, H.A.; Asseri, S.M.; Eltahir, Y.A.; Elsherbiny, N.; Eldesoqui, M. Curcumin modulates oxidative stress, fibrosis, and apoptosis in drug-resistant cancer cell lines. Life 2022, 12, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Accession No. | Sense (5′–3′) | Antisense (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P53 | NM_000546.6 | GACACGCTTCCCTGGATTGG | GCTCGACGCTAGGATCTGAC |
| Bcl2 | NM_000633.3 | AAAAATACAACATCACAGAGGAAGT | GTTTCCCCCTTGGCATGAGA |
| Casp3 | NM_001354777.2 | GCGGATGGGTGCTATTGTGA | ACACAGCCACAGGTATGAGC |
| Bax | NM_001291428.2 | ATGGACGGGTCCGGGG | GGAAAAAGACCTCTCGGGGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alghamdi, A.A.A. D-Limonene Exhibits Antiproliferative Activity Against Human Colorectal Adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) Cells via Regulation of Inflammatory and Apoptotic Pathways. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050370
Alghamdi AAA. D-Limonene Exhibits Antiproliferative Activity Against Human Colorectal Adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) Cells via Regulation of Inflammatory and Apoptotic Pathways. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050370
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlghamdi, Abdullah A. A. 2025. "D-Limonene Exhibits Antiproliferative Activity Against Human Colorectal Adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) Cells via Regulation of Inflammatory and Apoptotic Pathways" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050370
APA StyleAlghamdi, A. A. A. (2025). D-Limonene Exhibits Antiproliferative Activity Against Human Colorectal Adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) Cells via Regulation of Inflammatory and Apoptotic Pathways. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050370