TNF Signaling Pathway Is the Key Pathway Regulated by Disitamab Vedotin in Bladder Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acquisition of Transcriptome Sequencing Data
2.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.3. Gene Enrichment Analysis
2.4. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis and Identification of Hub Genes
2.5. Correlation Analysis of Hub Gene Expression
2.6. Identification of Signaling Pathways for Hub Genes
2.7. Cell Culture
2.8. Main Reagents and Instruments
2.9. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. DEGs Regulated by Disitamab Vedotin in Bladder Cancer Cells
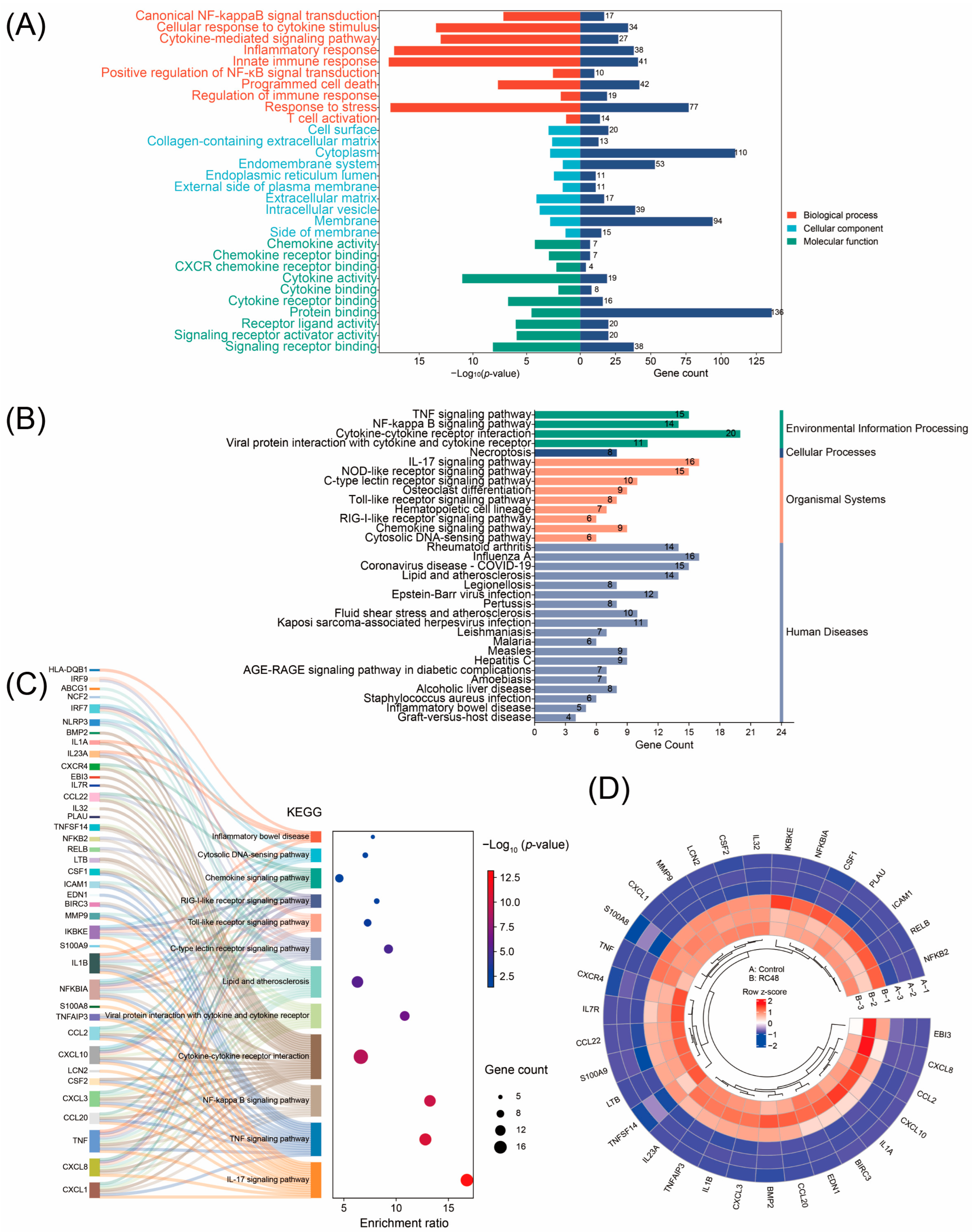
3.2. GO Function and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analyses of DEGs
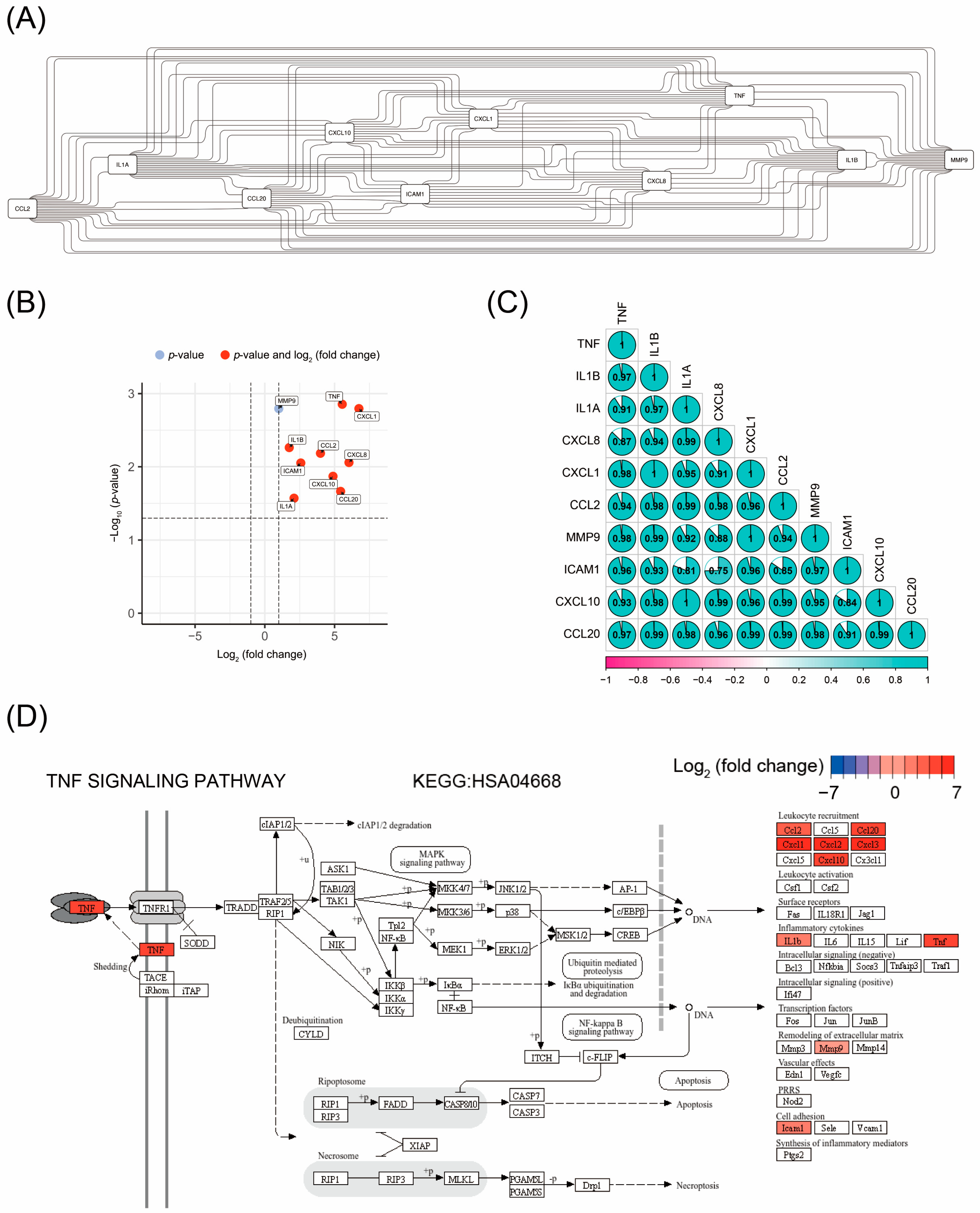
3.3. Identification of Hub Genes Through PPI Network Analysis
3.4. Correlation Analysis of the Expression Levels of Hub Gene
3.5. TNF Signaling Pathway as the Key Pathway Regulated by Disitamab Vedotin in Bladder Cancer Cells
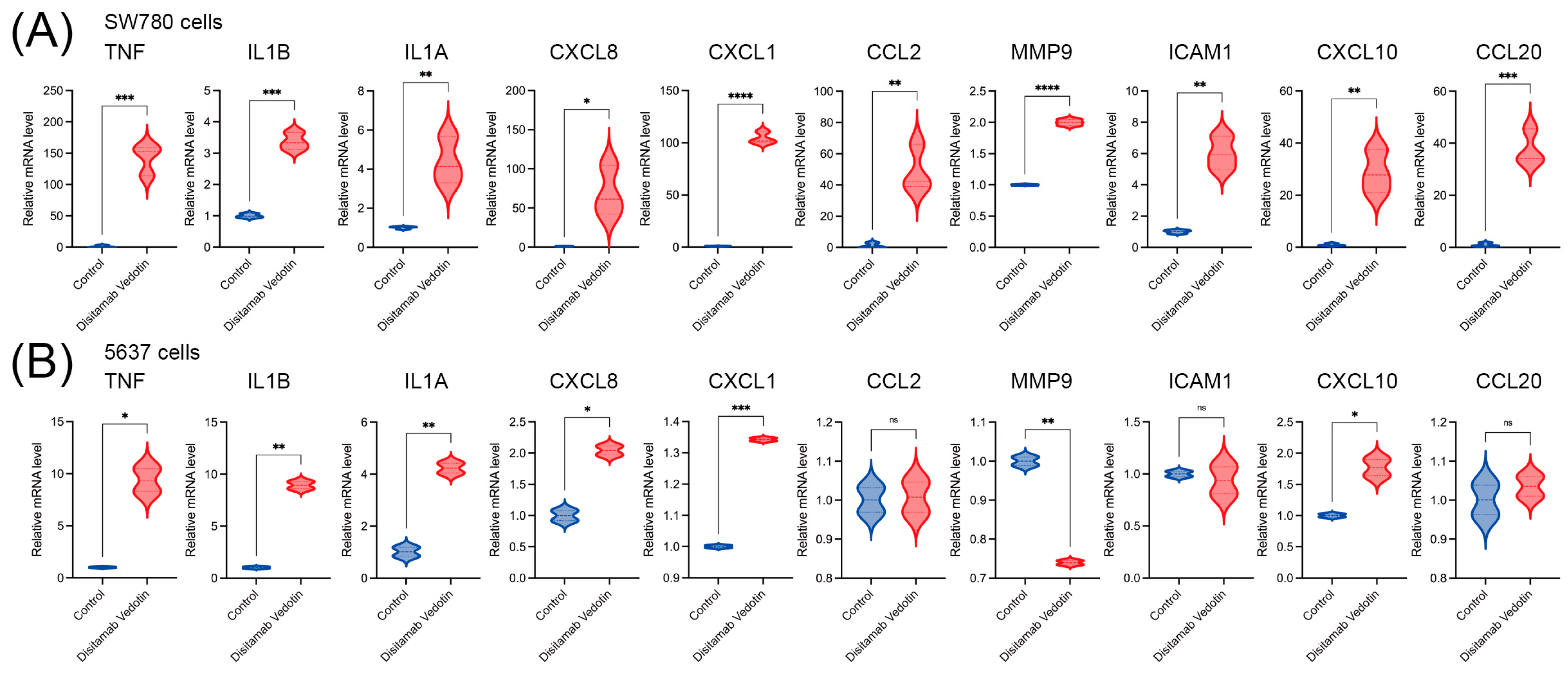
3.6. TNF Signaling Pathway Genes Are Upregulated in Bladder Cancer Cells Treated with Disitamab Vedotin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deeks, E.D. Disitamab Vedotin: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Li, G.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; An, R.; Miao, J.; Zhang, K.; Yang, H.; Huang, Y.; Guo, R.; et al. Evaluation of the Effectiveness and Safety of Disitamab Vedotin in HER2-Expressing 2L Recurrent or Metastatic Cervical Cancer (r/mCC): Interim Results of RC48-C018. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Feng, J.; Wang, X.; Fang, J.; Han, Y.; Xu, B. Disitamab Vedotin, a HER2-Directed Antibody-Drug Conjugate, in Patients with HER2-Overexpression and HER2-Low Advanced Breast Cancer: A Phase I/Ib Study. Cancer Commun. Lond. Engl. 2024, 44, 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, J.; Wang, A.; Wei, J.; Peng, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Qi, C.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; et al. Disitamab Vedotin (RC48) plus Toripalimab for HER2-Expressing Advanced Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction and Other Solid Tumours: A Multicentre, Open Label, Dose Escalation and Expansion Phase 1 Trial. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 68, 102415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Yan, X.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Yao, X.; Luo, H.; Shi, B.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Yu, G.; et al. Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase II Study of RC48-ADC, a HER2-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate, in Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Wang, L.; He, Z.; Shi, Y.; Luo, H.; Han, W.; Yao, X.; Shi, B.; Liu, J.; Hu, C.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Disitamab Vedotin in Patients With Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Combined Analysis of Two Phase II Clinical Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Qi, X.; Long, H.; Qi, N.; Wu, L.; Ke, M.; Shao, S.; Li, P.; Chen, Y.; et al. RC48-Antibody-Drug Conjugate in Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Multicenter Real-World Study in China. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2024, 22, 102093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, Z.; Luo, C.; Wu, Y.; Lei, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, J. 2009P PUNCH02: Primary Results from a Phase II Study of Tislelizumab Combined with Disitamab Vedotin as a Bladder Preservation Therapy for Urine Tumor DNA (utDNA)-Defined Clinical Complete Response (cCR) MIBC Patients. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, S1159–S1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Shen, P.; Xue, R.; Zhang, M. Disitamab Vedotin: A Novel Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Cancer Therapy. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A Free Online Platform for Data Visualization and Graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the Unification of Biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolberg, L.; Raudvere, U.; Kuzmin, I.; Vilo, J.; Peterson, H. Gprofiler2—An R Package for Gene List Functional Enrichment Analysis and Namespace Conversion Toolset g:Profiler. F1000Research 2020, 9, ELIXIR-709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING Database in 2023: Protein-Protein Association Networks and Functional Enrichment Analyses for Any Sequenced Genome of Interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, S.; Shan, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Huang, M.; Dong, L.; Chen, F. Preclinical Safety Profile of Disitamab Vedotin: A Novel Anti-HER2 Antibody Conjugated with MMAE. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 324, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X. Proteolytic Signaling by TNFalpha: Caspase Activation and IkappaB Degradation. Cytokine 2003, 21, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Sudandiradoss, C. Andrographolide-Based Potential Anti-Inflammatory Transcription Inhibitors against Nuclear Factor NF-Kappa-B P50 Subunit (NF-κB P50): An Integrated Molecular and Quantum Mechanical Approach. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-κB Pathway for the Therapy of Diseases: Mechanism and Clinical Study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Ren, R.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Z.; et al. Human Amniotic Epithelial Stem Cells Promote Colonic Recovery in Experimental Colitis via Exosomal MiR-23a-TNFR1-NF-κB Signaling. Adv. Sci. Weinh. Baden-Wurtt. Ger. 2024, 11, e2401429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.; Debnath, B.; Neamati, N. Role of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 Axis in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1543–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, S.J.; Lu, D.; Sparer, T.E.; Masi, T.; Goff, M.R.; Karlstad, M.D.; Collier, J.J. NF-κB and STAT1 Control CXCL1 and CXCL2 Gene Transcription. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E131–E149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-J.; Lim, J.-H.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, W.-J.; Moon, S.-K. Interleukin-28A Triggers Wound Healing Migration of Bladder Cancer Cells via NF-κB-Mediated MMP-9 Expression Inducing the MAPK Pathway. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astarci, E.; Sade, A.; Cimen, I.; Savaş, B.; Banerjee, S. The NF-κB Target Genes ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 Are Differentially Regulated during Spontaneous Differentiation of Caco-2 Cells. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 2966–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
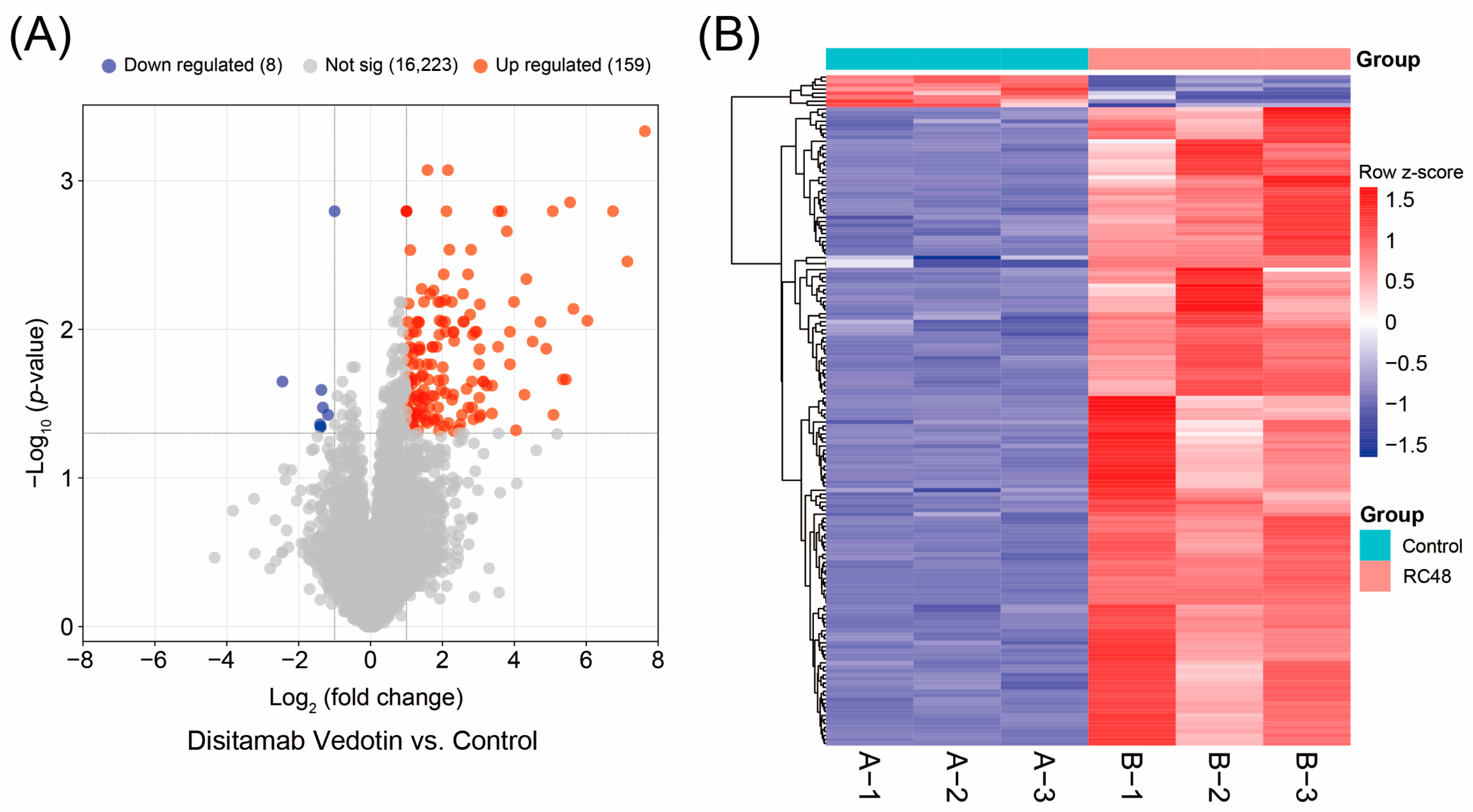
| Top 15 Upregulated DEGs * | ||||
| Gene Symbol | Log2 (Fold Change) | Adjusted p-Value | t | B |
| UBD | 8.974 | 0.010 | 14.425 | 3.185 |
| LTB | 7.633 | 0.000 | 65.409 | 7.323 |
| ERCC5 | 7.143 | 0.003 | 22.952 | 5.079 |
| CXCL1 | 6.744 | 0.002 | 28.700 | 5.801 |
| CXCL8 | 6.032 | 0.009 | 16.185 | 3.696 |
| IL32 | 5.643 | 0.007 | 17.179 | 3.951 |
| TNF | 5.549 | 0.001 | 38.924 | 6.560 |
| CCL20 | 5.434 | 0.022 | 10.857 | 1.843 |
| CXCL3 | 5.349 | 0.022 | 10.923 | 1.873 |
| CSF2 | 5.087 | 0.038 | 8.334 | 0.535 |
| LCN2 | 5.068 | 0.002 | 28.913 | 5.822 |
| CXCL10 | 4.887 | 0.014 | 12.956 | 2.690 |
| KLHDC7B | 4.725 | 0.009 | 15.411 | 3.481 |
| SAA1 | 4.508 | 0.012 | 13.646 | 2.931 |
| C3 | 4.334 | 0.005 | 21.047 | 4.763 |
| Top 8 Downregulated DEGs | ||||
| Gene Symbol | Log2 (Fold Change) | Adjusted p-Value | t | B |
| HOTS | −2.451 | 0.022 | −10.652 | 1.750 |
| FAM81A | −1.408 | 0.044 | −7.787 | 0.196 |
| ZNF334 | −1.390 | 0.045 | −7.669 | 0.120 |
| MEGF10 | −1.390 | 0.045 | −7.669 | 0.120 |
| CLCA2 | −1.368 | 0.026 | −10.030 | 1.455 |
| RGS16 | −1.327 | 0.034 | −8.814 | 0.814 |
| GJA1 | −1.184 | 0.038 | −8.320 | 0.527 |
| UGT2B28 | −1.000 | 0.002 | −28.944 | 5.826 |
| Source | Term Name | FDR * | Count | Intersections |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG | IL-17 signaling pathway | <0.001 | 16 | CXCL1, CXCL8, TNF, CCL20, CXCL3, CSF2, LCN2, CXCL10, CCL2, TNFAIP3, S100A8, NFKBIA, IL1B, S100A9, IKBKE, MMP9 |
| KEGG | TNF signaling pathway | <0.001 | 15 | CXCL1, TNF, CCL20, CXCL3, CSF2, CXCL10, CCL2, TNFAIP3, BIRC3, EDN1, ICAM1, NFKBIA, IL1B, CSF1, MMP9 |
| KEGG | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | <0.001 | 14 | LTB, CXCL1, CXCL8, TNF, CXCL3, TNFAIP3, BIRC3, RELB, ICAM1, NFKB2, TNFSF14, NFKBIA, IL1B, PLAU |
| KEGG | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | <0.001 | 20 | LTB, CXCL1, CXCL8, IL32, TNF, CCL20, CXCL3, CSF2, CXCL10, CCL2, CCL22, IL7R, EBI3, CXCR4, IL23A, IL1A, TNFSF14, IL1B, BMP2, CSF1 |
| KEGG | Viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor | <0.001 | 11 | CXCL1, CXCL8, TNF, CCL20, CXCL3, CXCL10, CCL2, CCL22, CXCR4, TNFSF14, CSF1 |
| KEGG | Lipid and atherosclerosis | <0.001 | 14 | CXCL1, CXCL8, TNF, CXCL3, CCL2, ICAM1, NFKBIA, NLRP3, IL1B, IRF7, IKBKE, NCF2, ABCG1, MMP9 |
| KEGG | C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | <0.001 | 10 | TNF, CCL22, RELB, IL23A, NFKB2, NFKBIA, NLRP3, IL1B, IRF9, IKBKE |
| KEGG | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.001 | 8 | CXCL8, TNF, CXCL10, NFKBIA, IL1B, IRF9, IRF7, IKBKE |
| KEGG | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.008 | 6 | CXCL8, TNF, CXCL10, NFKBIA, IRF7, IKBKE |
| KEGG | Chemokine signaling pathway | 0.013 | 9 | CXCL1, CXCL8, CCL20, CXCL3, CXCL10, CCL2, CCL22, CXCR4, NFKBIA |
| KEGG | Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | 0.018 | 6 | CXCL10, NFKBIA, NLRP3, IL1B, IRF7, IKBKE |
| KEGG | Inflammatory bowel disease | 0.040 | 5 | TNF, IL23A, IL1A, IL1B, HLA-DQB1 |
| Rank | Gene Symbol | Gene Description | Degree | Log2 (Fold Change) | Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor | 62 | 5.549 | 0.001 |
| 2 | IL1B | Interleukin 1 Beta | 60 | 1.752 | 0.005 |
| 3 | IL1A | Interleukin 1 Alpha | 58 | 2.094 | 0.027 |
| 4 | CXCL8 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 8 | 58 | 6.032 | 0.009 |
| 5 | CXCL1 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 1 | 54 | 6.744 | 0.002 |
| 6 | CCL2 | C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2 | 50 | 3.989 | 0.007 |
| 7 | MMP9 | Matrix Metallopeptidase 9 | 50 | 1.000 | 0.002 |
| 8 | ICAM1 | Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 | 50 | 2.580 | 0.009 |
| 9 | CXCL10 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 10 | 50 | 4.887 | 0.014 |
| 10 | CCL20 | C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 20 | 48 | 5.434 | 0.022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, Y.; Yang, X.; Du, P.; Yang, Y. TNF Signaling Pathway Is the Key Pathway Regulated by Disitamab Vedotin in Bladder Cancer Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050369
Tang X, Liu J, Zhao Q, Cao Y, Yang X, Du P, Yang Y. TNF Signaling Pathway Is the Key Pathway Regulated by Disitamab Vedotin in Bladder Cancer Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050369
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xingxing, Jia Liu, Qiang Zhao, Yudong Cao, Xiao Yang, Peng Du, and Yong Yang. 2025. "TNF Signaling Pathway Is the Key Pathway Regulated by Disitamab Vedotin in Bladder Cancer Cells" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050369
APA StyleTang, X., Liu, J., Zhao, Q., Cao, Y., Yang, X., Du, P., & Yang, Y. (2025). TNF Signaling Pathway Is the Key Pathway Regulated by Disitamab Vedotin in Bladder Cancer Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050369



_Kim.png)



