Emerging Tumor Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer and Their Clinical Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Biomarker | Type | Function/Mechanism | Diagnostic/Prognostic Value | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MicroRNA | Non-coding RNA | Regulates gene expression and impacts cell growth, apoptosis, and chemoresistance | High expression levels of some miRNAs and/or low expression levels of others are linked with poor prognosis and chemoresistance | [16,17,18,19] |
| GATA6 | Transcription Factor | Regulates differentiation and growth, and is involved in Wnt signaling pathway | Low GATA6 expression is associated with poor differentiation and survival | [20,21] |
| L1CAM | Cell Adhesion Molecule | Enhances cell migration, invasion, and immune evasion | High expression correlates with advanced stages and poor prognosis | [22,23,24] |
| MUC1 | Glycoprotein | Aids in chemoresistance, immune evasion, and metastasis | Overexpression is linked to poor prognosis and treatment resistance | [25,26,27,28] |
2. Emerging Tumor Markers in Pancreatic Cancer
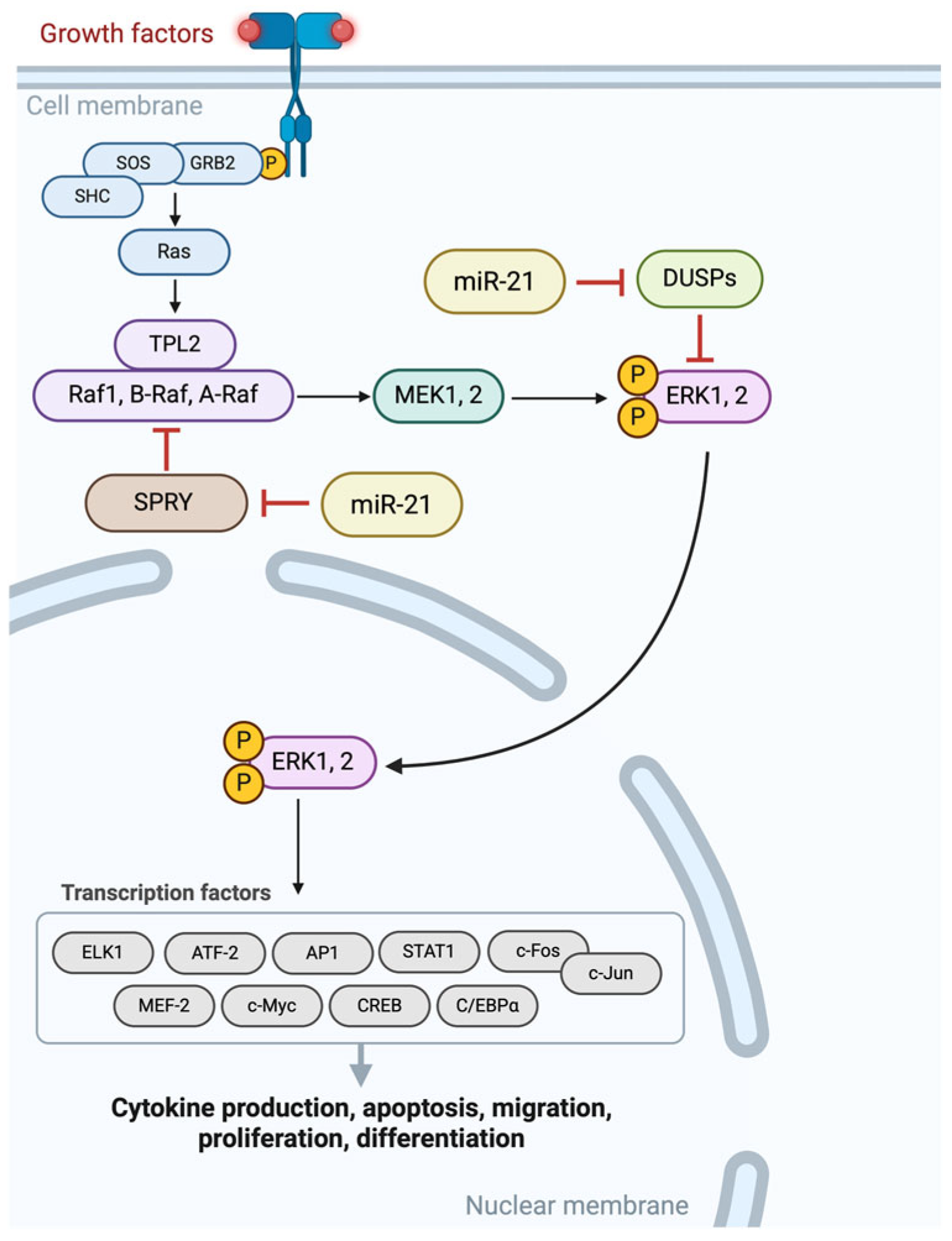
2.1. MicroRNA Signatures
2.2. Role of MicroRNA in Diagnosis
2.3. Role of MicroRNA in Prognosis
2.4. Therapeutic Potential of MicroRNA and Its Limitations
2.5. GATA Family
2.6. Diagnostic Value of GATA6
2.7. GATA6 and Its Contribution in Prognosis
2.8. Therapeutic Potential of GATA6
2.9. L1CAM (L1 Cell Adhesion Molecule)
2.10. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of L1CAM
2.11. L1CAM’s Therapeutic Potential
2.12. MUC1 (Mucin 1)
2.13. MUC1 as a Potential Diagnostic Marker
2.14. Prognostic and Therapeutic Significance of MUC1
3. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pancreaswho.html (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Gurbuz, N.; Ozpolat, B. MicroRNA-based Targeted Therapeutics in Pancreatic Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Chang, P.; LeBlanc, A.; Li, D.; Abbruzzesse, J.L.; Frazier, M.L.; Killary, A.M.; Sen, S. MicroRNAs in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolarz, B.; Durczyński, A.; Romanowicz, H.; Hogendorf, P. The Role of microRNA in Pancreatic Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Zubair, H.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.P. Insights into the Role of microRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer Pathogenesis: Potential for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 889, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo-Sastre, A.; Lubeseder-Martellato, C.; Engleitner, T.; Steiger, K.; Zhong, S.; Desztics, J.; Öllinger, R.; Rad, R.; Schmid, R.M.; Hermeking, H.; et al. Mir34a constrains pancreatic carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Blood-Derived microRNAs for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis: A Narrative Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, M.; Kadian, K.; Gupta, Y.; Kumar, A.; Chain, P.S.G.; Kovbasnjuk, O.; Kumar, S.; Parasher, G. MicroRNA in Pancreatic Cancer: From Biology to Therapeutic Potential. Genes 2019, 10, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koustas, E.; Trifylli, E.M.; Sarantis, P.; Papadopoulos, N.; Papanikolopoulos, K.; Aloizos, G.; Damaskos, C.; Garmpis, N.; Garmpi, A.; Karamouzis, M.V. The Emerging Role of MicroRNAs and Autophagy Mechanism in Pancreatic Cancer Progression: Future Therapeutic Approaches. Genes 2022, 13, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, E.; Chitty, J.; Cox, T. miRNAs in pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2024, 41, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo-Vázquez, L.A.; Frías-Reid, N.; Ramos-Delgado, A.G.; Osorio-Pérez, S.M.; Zlotnik-Chávez, H.R.; Pathak, S.; Banerjee, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Paul, S. MicroRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in pancreatic cancer: From epigenetics to potential clinical applications. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 27, 101579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Wang, Z.; Lv, J.; Fan, C. MicroRNA-1469-5p promotes the invasion and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells via direct regulating the NDRG1/NF-κB/E-cadherin axis. Hum. Cell 2020, 33, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, L.-A.; R Murphy, P. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Taheri, M. Emerging roles of miRNAs in the development of pancreatic cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.; Wei, D.; Liu, X.; Long, D.; Tian, X.; Yang, Y. MicroRNAs as potential therapeutic targets for pancreatic cancer. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, A.A. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer—Advances and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yan, B. Multiple roles and regulatory mechanisms of the transcription factor GATA6 in human cancers. Clin. Genet. 2020, 97, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cheng, K.; Lin, H.; Han, W.; He, T.; Nie, X.; Sun, Y.; Qiuman, S.; Reheman, Y.; Chen, Q. Characterization of the GATA Transcription Factor Family and Exploration of Their Relevance to Immune Infiltration and Tumor Microenvironment in Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 9083–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na’ara, S.; Amit, M.; Gil, Z. L1CAM induces perineural invasion of pancreas cancer cells by upregulation of metalloproteinase expression. Oncogene 2019, 38, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grage-Griebenow, E.; Jerg, E.; Gorys, A.; Wicklein, D.; Wesch, D.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Goebel, L.; Vogel, I.; Becker, T.; Ebsen, M.; et al. L1CAM promotes enrichment of immunosuppressive T cells in human pancreatic cancer correlating with malignant progression. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 982–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, M.; Cavallaro, U. Different Shades of L1CAM in the Pathophysiology of Cancer Stem Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; You, L.; Dai, M.; Zhao, Y. Mucins in pancreatic cancer: A well-established but promising family for diagnosis, prognosis and therapy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 10279–10289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachagani, S.; Torres, M.P.; Kumar, S.; Haridas, D.; Baine, M.; Macha, M.A.; Kaur, S.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; Dey, P.; Seshacharyulu, P.; et al. Mucin (Muc) expression during pancreatic cancer progression in spontaneous mouse model: Potential implications for diagnosis and therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Mukherjee, P. MUC1: A multifaceted oncoprotein with a key role in cancer progression. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, P.; Ko, J.K.; Yung, K.K. MUC1: Structure, Function, and Clinic Application in Epithelial Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Cheng, H.H.; Tewari, M. MicroRNA profiling: Approaches and considerations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, G. Argonaute proteins: Functional insights and emerging roles. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Carmell, M.A.; Rivas, F.V.; Marsden, C.G.; Thomson, J.M.; Song, J.-J.; Hammond, S.M.; Joshua-Tor, L.; Hannon, G.J. Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science 2004, 305, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagoni, M.; Cava, C.; Sideris, D.C.; Avgeris, M.; Zoumpourlis, V.; Michalopoulos, I.; Drakoulis, N. miRNA-Based Technologies in Cancer Therapy. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, K.; Bayraktar, R.; Ferracin, M.; Calin, G.A. Non-coding RNAs in disease: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2024, 25, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, A.Z.; Mulholland, E.J.; Cole, G.; McCarthy, H.O. MicroRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer: Biomarkers, prognostic, and therapeutic modulators. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Hu, D.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Z.; He, L.; Zhu, J. The Serum MicroRNA Signatures for Pancreatic Cancer Detection and Operability Evaluation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemori, K.; Kurahara, H.; Maemura, K.; Natsugoe, S. MicroRNA in pancreatic cancer. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 62, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, R.S.; Stoita, A. Biomarkers in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: Are we closer to finding the golden ticket? World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 4045–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemar, B.; Izetti, P.; Gregorio, C.; Macedo, G.S.; Castro, M.A.A.; Osvaldt, A.B.; Matte, U.; Ashton-Prolla, P. miRNA-21 and miRNA-34a are potential minimally invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2016, 45, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abue, M.; Yokoyama, M.; Shibuya, R.; Tamai, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sato, I.; Tanaka, N.; Hamada, S.; Shimosegawa, T.; Sugamura, K. Circulating miR-483-3p and miR-21 is highly expressed in plasma of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 46, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhong, A.; Wang, Y.; Lu, R.; Guo, L. Identification of Serum microRNA-25 as a novel biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Medicine 2020, 99, e23863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guz, M.; Jeleniewicz, W.; Cybulski, M.; Kozicka, J.; Kurzepa, J.; Mądro, A. Serum miR-210-3p can be used to differentiate between patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis. Biomed. Rep. 2021, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.S.; Huang, X.; Cao, H.; Christman-Skieller, C.; Bennewith, K.; Le, Q.-T.; Koong, A.C. Circulating miR-210 as a novel hypoxia marker in pancreatic cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2010, 3, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Du, Y.; Yao, W.; Shen, L.; Wang, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhuang, R.; Ning, G.; Zhang, C. Serum microRNA expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Fujiya, M.; Konishi, H.; Sasajima, J.; Fujibayashi, S.; Hayashi, A.; Utsumi, T.; Sato, H.; Iwama, T.; Ijiri, M. An elevated expression of serum exosomal microRNA-191,− 21,− 451a of pancreatic neoplasm is considered to be efficient diagnostic marker. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, G.A.; Gore, J.A.; McElyea, S.D.; Heathers, L.E.; Xu, H.; Sherman, S.; Korc, M. A pilot study to develop a diagnostic test for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on differential expression of select miRNA in plasma and bile. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2014, 109, 1942–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganepola, G.A.; Rutledge, J.R.; Suman, P.; Yiengpruksawan, A.; Chang, D.H. Novel blood-based microRNA biomarker panel for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2014, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Yu, J.; Kim, H.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Canto, M.I.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. MicroRNA array analysis finds elevated serum miR-1290 accurately distinguishes patients with low-stage pancreatic cancer from healthy and disease controls. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3600–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y.-n.; Xu, J. Serum miR-1290 and miR-1246 as potential diagnostic biomarkers of human pancreatic cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Wang, M.; McElyea, S.D.; Sherman, S.; House, M.; Korc, M. A microRNA signature in circulating exosomes is superior to exosomal glypican-1 levels for diagnosing pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 393, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, R.; Ding, G.; Chen, J.; Cao, L. Analysis of serum exosomal microRNAs and clinicopathologic features of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavan, B.; Yue, S.; Galli, U.; Rana, S.; Gross, W.; Müller, M.; Giese, N.A.; Kalthoff, H.; Becker, T.; Büchler, M.W. Combined evaluation of a panel of protein and miRNA serum-exosome biomarkers for pancreatic cancer diagnosis increases sensitivity and specificity. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 2616–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debernardi, S.; Massat, N.J.; Radon, T.P.; Sangaralingam, A.; Banissi, A.; Ennis, D.P.; Dowe, T.; Chelala, C.; Pereira, S.P.; Kocher, H.M. Noninvasive urinary miRNA biomarkers for early detection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 3455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishige, F.; Hoshino, I.; Iwatate, Y.; Chiba, S.; Arimitsu, H.; Yanagibashi, H.; Nagase, H.; Takayama, W. MIR1246 in body fluids as a biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadakari, Y.; Ohtsuka, T.; Ohuchida, K.; Tsutsumi, K.; Takahata, S.; Nakamura, M.; Mizumoto, K.; Tanaka, M. MicroRNA expression analyses in preoperative pancreatic juice samples of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Pancreas 2010, 11, 587–592. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, J.J.; Toste, P.; Wu, N.; Li, L.; Wong, J.; Malkhassian, D.; Tran, L.M.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Dawson, D. Endoscopically acquired pancreatic cyst fluid microRNA 21 and 221 are associated with invasive cancer. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2013, 108, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthaei, H.; Wylie, D.; Lloyd, M.B.; Dal Molin, M.; Kemppainen, J.; Mayo, S.C.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Schulick, R.D.; Langfield, L.; Andruss, B.F. miRNA biomarkers in cyst fluid augment the diagnosis and management of pancreatic cysts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4713–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utomo, W.; Looijenga, L.; Bruno, M.; Hansen, B.; Gillis, A.; Biermann, K.; Peppelenbosch, M.; Fuhler, G.; Braat, H. A microRNA panel in pancreatic cyst fluid for the risk stratification of pancreatic cysts in a prospective cohort. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeau, M.; Vignolle-Vidoni, A.; Sicard, F.; Martins, F.; Bournet, B.; Buscail, L.; Torrisani, J.; Cordelier, P. Salivary microRNA in pancreatic cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, J.; Emparan, C.; Hernandez, C.A.; Sulkowski, U.; Dietl, K.; Menzel, J.; Wolters, H.; Glodny, B.; Senninger, N. Gallbladder bile tumor marker quantification for detection of pancreato-biliary malignancies. Anticancer Res. 2000, 20, 4941–4947. [Google Scholar]
- Machida, T.; Tomofuji, T.; Maruyama, T.; Yoneda, T.; Ekuni, D.; Azuma, T.; Miyai, H.; Mizuno, H.; Kato, H.; Tsutsumi, K. miR-1246 and miR-4644 in salivary exosome as potential biomarkers for pancreatobiliary tract cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2375–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, L.-Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, L.-M.; Chen, Z. MicroRNA expression in salivary supernatant of patients with pancreatic cancer and its relationship with ZHENG. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 756347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Z.; Liu, S.-M.; Huang, J.-T.; Zhang, X.; Yan, D.; Xia, Q.; Ji, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J. Clinically relevant circulating microRNA profiling studies in pancreatic cancer using meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsubo, K.; Miyake, K.; Arai, S.; Fukuda, K.; Yanagimura, N.; Suzuki, C.; Otani, S.; Adachi, Y.; Tanimoto, A.; Nishiyama, A. Aberrant methylation of tumor suppressive miRNAs in bile from patients with pancreaticobiliary diseases. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 5449–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, J.-Q.; Wang, X.-W.; Gu, J.-J.; Huang, H.-J.; Gong, Y.-F.; Li, Z.-S. Differential signature of fecal microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Link, A.; Becker, V.; Goel, A.; Wex, T.; Malfertheiner, P. Feasibility of Fecal MicroRNAs as Novel Biomarkers for Pancreatic Cancer; Public Library of Science: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, N.A.; Dehlendorff, C.; Jensen, B.V.; Bjerregaard, J.K.; Nielsen, K.R.; Bojesen, S.E.; Calatayud, D.; Nielsen, S.E.; Yilmaz, M.; Holländer, N.H.; et al. MicroRNA Biomarkers in Whole Blood for Detection of Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA 2014, 311, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, N.F.; Serafini, L.N.; Novais, P.C.; Neto, F.S.L.; Cirino, M.L.d.A.; Kemp, R.; Ardengh, J.C.; Saggioro, F.P.; Gaspar, A.F.; Sankarankutty, A.K.; et al. The role of circulating miRNAs and CA19-9 in pancreatic cancer diagnosis. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 1638–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, R.; Saberi, S.; Zali, M.; Sadeghi, A.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Aghdaei, H.A. Identification of potential microRNA panels for pancreatic cancer diagnosis using microarray datasets and bioinformatics methods. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Demirkhanyan, L.; Gondi, C. The Multifaceted Role of miR-21 in Pancreatic Cancers. Cells 2024, 13, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Mirdamadi, M.S.A.; Talebi, Y.; Khaniabad, N.; Banaei, G.; Daneii, P.; Gholami, S.; Ghorbani, A.; Tavakolpournegari, A.; Farsani, Z.M.; et al. Pre-clinical and clinical importance of miR-21 in human cancers: Tumorigenesis, therapy response, delivery approaches and targeting agents. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 187, 106568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Bian, C.; Li, J.; Du, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, R.C. miR-21 modulates the ERK-MAPK signaling pathway by regulating SPRY2 expression during human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. J. Cell Biochem. 2013, 114, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, L.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, M.; Weng, J.; Li, B. miR-21 promotes EGF-induced pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by targeting Spry2. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Imani, S.; Wu, M.-Y.; Wu, R.-C. MicroRNA-34 Family in Cancers: Role, Mechanism, and Therapeutic Potential. Cancers 2023, 15, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misso, G.; Di Martino, M.T.; De Rosa, G.; Farooqi, A.A.; Lombardi, A.; Campani, V.; Zarone, M.R.; Gullà, A.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P. Mir-34: A new weapon against cancer? Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Hao, X.; Zhang, M.; Tang, W.; Yang, M.; Li, L.; Xiang, D.; DeSano, J.T.; Bommer, G.T.; Fan, D.; et al. MicroRNA miR-34 Inhibits Human Pancreatic Cancer Tumor-Initiating Cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Tao, H.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; Qiao, G.; Guo, M.; Cao, S.; Liu, M.; Lin, X. Exosomes-Coated miR-34a Displays Potent Antitumor Activity in Pancreatic Cancer Both in vitro and in vivo. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3495–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, Y.S. miR-34a inhibits pancreatic cancer progression through Snail1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the Notch signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 38232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.-K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Brenner, A.J.; Park, K.; Lee, J.-L.; Kim, T.-Y.; et al. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA: Trends in clinical trials of cancer diagnosis and therapy strategies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.J.; Javed, Z.; Sadia, H.; Mehmood, S.; Akbar, A.; Zahid, B.; Nadeem, T.; Roshan, S.; Varoni, E.M.; Iriti, M.; et al. Targeted therapy using nanocomposite delivery systems in cancer treatment: Highlighting miR34a regulation for clinical applications. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y. Anti-tumor effects of miR-34a by regulating immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 11602–11610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, S.; Borok, M.J.; Decker, K.J.; Battle, M.A.; Duncan, S.A.; Hale, M.A.; Macdonald, R.J.; Sussel, L. Pancreas-specific deletion of mouse Gata4 and Gata6 causes pancreatic agenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3516–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, A.; Chen, X.; Gao, P.; Zeng, Q. GATA4 inhibits cell differentiation and proliferation in pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Harmston, N.; Wood, K.C.; Madan, B.; Virshup, D.M. A p300/GATA6 axis determines differentiation and Wnt dependency in pancreatic cancer models. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e156305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, P.; Madriles, F.; Cañamero, M.; Pau, E.C.-d.S.; Pozo, N.d.; Guerra, C.; Real, F.X. The acinar regulator Gata6 suppresses KrasG12V driven pancreatic tumorigenesis in mice. Gut 2016, 65, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, P.C.; Sancho, P.; Cañamero, M.; Martinelli, P.; Madriles, F.; Michl, P.; Gress, T.; de Pascual, R.; Gandia, L.; Guerra, C.; et al. Nicotine Promotes Initiation and Progression of KRAS-Induced Pancreatic Cancer via Gata6-Dependent Dedifferentiation of Acinar Cells in Mice. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1119–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokumai, T.; Omori, Y.; Ishida, M.; Ohtsuka, H.; Mizuma, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Maeda, C.; Ono, Y.; Mizukami, Y.; Miura, S.; et al. GATA6 and CK5 Stratify the Survival of Patients With Pancreatic Cancer Undergoing Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Mod. Pathol. 2023, 36, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Jang, G.-H.; Grant, R.C.; Wilson, J.M.; Notta, F.; O’Kane, G.M.; Knox, J.J.; Gallinger, S.; Fischer, S. The value of GATA6 immunohistochemistry and computer-assisted diagnosis to predict clinical outcome in advanced pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloesch, B.; Ionasz, V.; Paliwal, S.; Hruschka, N.; Martinez de Villarreal, J.; Öllinger, R.; Mueller, S.; Dienes, H.P.; Schindl, M.; Gruber, E.S.; et al. A GATA6-centred gene regulatory network involving HNFs and ΔNp63 controls plasticity and immune escape in pancreatic cancer. Gut 2022, 71, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatani, P.; August, D.; Eskander, M.; Grandhi, M.; In, H.; Kennedy, T.; Maggi, J.; Pitt, H.; Wei, A.; Langan, R. Association between SMAD4 mutations and GATA6 expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma specimens. HPB 2023, 25, S127–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia-Soto, V.; Gutiérrez-Sainz, L.; Ghanem, I.; Guerra, L.; Palacios, E.; de Uribe, M.; Trilla-Fuertes, L.; de Miguel, M.; Cejas, P.; Medina, L.; et al. The Relationship between the Expression of GATA4 and GATA6 with the Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis of Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.C.; Duan, K.; Jackson, R.; Greenhalf, W.; Costello-Goldring, E.; Ghaneh, P.; Halloran, C.; Palmer, D.; Hackert, T.; Buchler, M.; et al. Abstract PO-005: GATA6 expression is prognostic after surgical resection of pancreatic cancer: Results from the ESPAC trials. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, PO-005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, P.; Carrillo-de Santa Pau, E.; Cox, T.; Sainz, B.; Dusetti, N.; Greenhalf, W.; Rinaldi, L.; Costello, E.; Ghaneh, P.; Malats, N.; et al. GATA6 regulates EMT and tumour dissemination, and is a marker of response to adjuvant chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Gut 2017, 66, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, Q.-W.; Wang, J.-C.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, F.; Yao, W.-Y.; Yuan, Y.-Z. Positive Expression of L1-CAM is Associated with Perineural Invasion and Poor Outcome in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Kane, G.M.; Grünwald, B.T.; Jang, G.-H.; Masoomian, M.; Picardo, S.; Grant, R.C.; Denroche, R.E.; Zhang, A.; Wang, Y.; Miller, J.K.; et al. GATA6 Expression Distinguishes Classical and Basal-like Subtypes in Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4901–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Roberts, C.W.M. Targeting EZH2 in cancer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Steuber, B.; Kopp, W.; Kari, V.; Urbach, L.; Wang, X.; Küffer, S.; Bohnenberger, H.; Spyropoulou, D.; Zhang, Z.; et al. EZH2 Regulates Pancreatic Cancer Subtype Identity and Tumor Progression via Transcriptional Repression of GATA6. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 4620–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunton, H.; Caligiuri, G.; Cunningham, R.; Upstill-Goddard, R.; Bailey, U.-M.; Garner, I.M.; Nourse, C.; Dreyer, S.; Jones, M.; Moran-Jones, K. HNF4A and GATA6 loss reveals therapeutically actionable subtypes in pancreatic cancer. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Gong, W. GATA6 impairs pancreatic cancer cells stemness by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Q.; Kong, F.; Kong, X.; Jiang, T.; Ma, M.; Zheng, S.; Guo, J.; Xie, K. Loss of GATA6-mediated up-regulation of UTX promotes pancreatic tumorigenesis and progression. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, T. GATA6: A Molecular Regulator of Pancreatic Tumour Growth and Phenotype. Master’s Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ben, Q.; Liu, N.; Wang, J.; Zhai, Y.; Bao, Y.; Zhou, L. GATA6-AS1 suppresses epithelial–mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer under hypoxia through regulating SNAI1 mRNA stability. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Xie, K. Crosstalk of Sp1 and Stat3 signaling in pancreatic cancer pathogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012, 23, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geismann, C.; Morscheck, M.; Koch, D.; Bergmann, F.; Ungefroren, H.; Arlt, A.; Tsao, M.-S.; Bachem, M.G.; Altevogt, P.; Sipos, B.; et al. Up-regulation of L1CAM in Pancreatic Duct Cells Is Transforming Growth Factor β1– and Slug-Dependent: Role in Malignant Transformation of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4517–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grage-Griebenow, E.; Schäfer, H.; Sebens, S. The fatal alliance of cancer and T cells: How pancreatic tumor cells gather immunosuppressive T cells. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e29382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Morohashi, S.; Kudo, Y.; Akasaka, H.; Ogasawara, H.; Ono, M.; Takasugi, K.; Ishido, K.; Hakamada, K.; Kijima, H. L1 Cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM) expression at the cancer invasive front is a novel prognostic marker of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 103, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maten, M.V.; Reijnen, C.; Pijnenborg, J.M.A.; Zegers, M.M. L1 Cell Adhesion Molecule in Cancer, a Systematic Review on Domain-Specific Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefel, H.; Bondong, S.; Erbe-Hoffmann, N.; Hazin, J.; Riedle, S.; Wolf, J.; Pfeifer, M.; Arlt, A.; Schäfer, H.; Müerköster, S.S.; et al. L1CAM–integrin interaction induces constitutive NF-κB activation in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells by enhancing IL-1β expression. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4766–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanisha, S.S.; Guruvayoorappan, C.; Drishya, S.; Abeesh, P. Mucins: Structural diversity, biosynthesis, its role in pathogenesis and as possible therapeutic targets. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2018, 122, 98–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altevogt, P.; Ben-Ze’ev, A.; Gavert, N.; Schumacher, U.; Schäfer, H.; Sebens, S. Recent insights into the role of L1CAM in cancer initiation and progression. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 3292–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-L.; Zeng, Z.-L.; Yang, J.; Ren, C.; Wang, D.-S.; Wu, W.-J.; Xu, R.-H. L1cam promotes tumor progression and metastasis and is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in gastric cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, Q.; An, W.; Fei, J.; Xu, M.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Y. Downregulation of L1CAM inhibits proliferation, invasion and arrests cell cycle progression in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 7, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, K.; Dembinski, J.L.; Solberg, N.; Urbanucci, A.; Mills, I.G.; Krauss, S. Slug-Dependent Upregulation of L1CAM Is Responsible for the Increased Invasion Potential of Pancreatic Cancer Cells following Long-Term 5-FU Treatment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, O.; Mennrich, R.; Petrick, D.; Goebel, L.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Röder, C.; Kalthoff, H.; Röcken, C.; Sipos, B.; Kabelitz, D.; et al. Comparative Characterization of Stroma Cells and Ductal Epithelium in Chronic Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Huang, S. The immunoregulation effect of tumor microenvironment in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 951019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonckheere, N.; Skrypek, N.; Van Seuningen, I. Mucins and Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2010, 2, 1794–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.; Ni, W.; Tai, G. Expression of MUC1 in different tumours and its clinical significance (Review). Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 17, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.F.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.J.; Rizvi, S.M.A.; Raja, C.; Zhang, D.; Samra, J.; Smith, R.; Perkins, A.C.; Apostolidis, C.; et al. MUC1 expression in primary and metastatic pancreatic cancer cells for in vitro treatment by 213Bi-C595 radioimmunoconjugate. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 91, 2086–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucan-Karnak, F.; Akgöl, S. A New Nanomaterial Based Biosensor for MUC1 Biomarker Detection in Early Diagnosis, Tumor Progression and Treatment of Cancer. Nanomanufacturing 2021, 1, 14–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Fang, X.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Kong, J. Ultrasensitive detection of mucin 1 biomarker by immuno-loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Talanta 2017, 164, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Sharma, S.; Rana, S.; Rohilla, R.; Prabhakar, N. Ag-CuO integrated polyaniline based impedimetric detection of cancer biomarker MUC1. Microchem. J. 2023, 194, 109266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.K.; Khan, P.; Natarajan, G.; Atri, P.; Aithal, A.; Ganti, A.K.; Batra, S.K.; Nasser, M.W.; Jain, M. Mucins as Potential Biomarkers for Early Detection of Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; You, L.; Dai, M.; Zhao, Y. Quantitative assessment of the diagnostic role of mucin family members in pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striefler, J.K.; Riess, H.; Lohneis, P.; Bischoff, S.; Kurreck, A.; Modest, D.P.; Bahra, M.; Oettle, H.; Sinn, M.; Bläker, H.; et al. Mucin-1 Protein Is a Prognostic Marker for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Results From the CONKO-001 Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 670396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tréhoux, S.; Duchêne, B.; Jonckheere, N.; Van Seuningen, I. The MUC1 oncomucin regulates pancreatic cancer cell biological properties and chemoresistance. Implication of p42–44 MAPK, Akt, Bcl-2 and MMP13 pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 456, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Daneshvar, K.; Roy, L.D.; Grover, P.; Kidiyoor, A.; Mosley, L.; Sahraei, M.; Mukherjee, P. MUC1 induces drug resistance in pancreatic cancer cells via upregulation of multidrug resistance genes. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Liao, X.; Lv, Y.; Pang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liao, Y.; Ye, Q.; Chen, G.; Zhao, K.; et al. MUC1 induces acquired chemoresistance by upregulating ABCB1 in EGFR-dependent manner. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, L.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; Wang, G.; Jiang, Z.; Qin, Y.; He, L.; Li, H.; Cao, J.; et al. Therapeutic effect of a MUC1-specific monoclonal antibody-drug conjugates against pancreatic cancer model. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Fan, D. Advances in MUC1 resistance to chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer. J. Chemother. 2024, 36, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Tissue/Fluid Source | Potential miRNA Biomarker |
|---|---|
| Serum | miR-21 [4,40,41,42,43], miR-210-3p [43], miR-210 [4,44], miR-196a [4,45], miR-451a [46], miR-155 [4,47], miR-1469 [37], miR-125a-3p [37], miR-642b-3p [48], miR-34a [40], miR-1290 [49,50], miR-1246 [50] |
| Liquid biopsy | miR-10b [51], miR-21 [52], miR-181a [51], miR-1246 [53] |
| Urinary biomarkers | miR-143 [54], miR-1246 [55] |
| Pancreatic juice biomarkers | miR-21 [56], miR-155 [56] |
| Pancreatic cyst fluid | miR-21 [57], miR-221 [57], miR-142-3p [58,59] |
| Salivary fluid | miR-23a [60], miR-21 [40,60,61], miR-1246 [62], miR-34a [40], miR-155 [40], miR-200b [40], miR-196a [63] |
| Biliary fluid | miR-10b [47,64], miR-155 [47,64], miR-212 [47,64], miR-200a [65], miR-200b [65] |
| Feces | miR-181b [66], miR-210 [66], miR-155 [67], miR-196a [66,67], miR143 [67] |
| Clinical Study | Nonclinical Study | |
|---|---|---|
| miRNAs | [4,15,31,37,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,65,66,67,68,69,76,82] | [7,8,9,10,13,14,16,17,18,29,30,34,35,36,38,39,64,70,71,72,73,74,75,77,78,79,80,81,83,84,85] |
| GATA | [91,92,95,96,98,99,101] | [20,21,86,87,88,89,90,93,94,97,100,102,103,104,105,106] |
| L1CAM | [23,108,110,118] | [22,24,107,109,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,119] |
| MUC1 | [122,128] | [25,26,27,28,120,121,123,124,125,126,127,129,130,131,132,133] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefanoudakis, D.; Frountzas, M.; Michalopoulos, N.V.; Schizas, D.; Theodorou, D.; Toutouzas, K.G. Emerging Tumor Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer and Their Clinical Implications. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050347
Stefanoudakis D, Frountzas M, Michalopoulos NV, Schizas D, Theodorou D, Toutouzas KG. Emerging Tumor Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer and Their Clinical Implications. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050347
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefanoudakis, Dimitrios, Maximos Frountzas, Nikolaos V. Michalopoulos, Dimitrios Schizas, Dimitrios Theodorou, and Konstantinos G. Toutouzas. 2025. "Emerging Tumor Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer and Their Clinical Implications" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050347
APA StyleStefanoudakis, D., Frountzas, M., Michalopoulos, N. V., Schizas, D., Theodorou, D., & Toutouzas, K. G. (2025). Emerging Tumor Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer and Their Clinical Implications. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050347










