Key Roles of Brown, Subcutaneous, and Visceral Adipose Tissues in Obesity and Insulin Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Obesity and Insulin Resistance as a Disease
1.2. Key Contributing Factors to Obesity and Insulin Resistance
1.3. Outline of the Review Themes
2. Overview of BAT, BeAT, sWAT, and vWAT
2.1. Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT)
2.2. Beige Adipose Tissue (BeAT)
2.3. Subcutaneous White Adipose Tissue (sWAT)
2.4. Visceral White Adipose Tissue (vWAT)
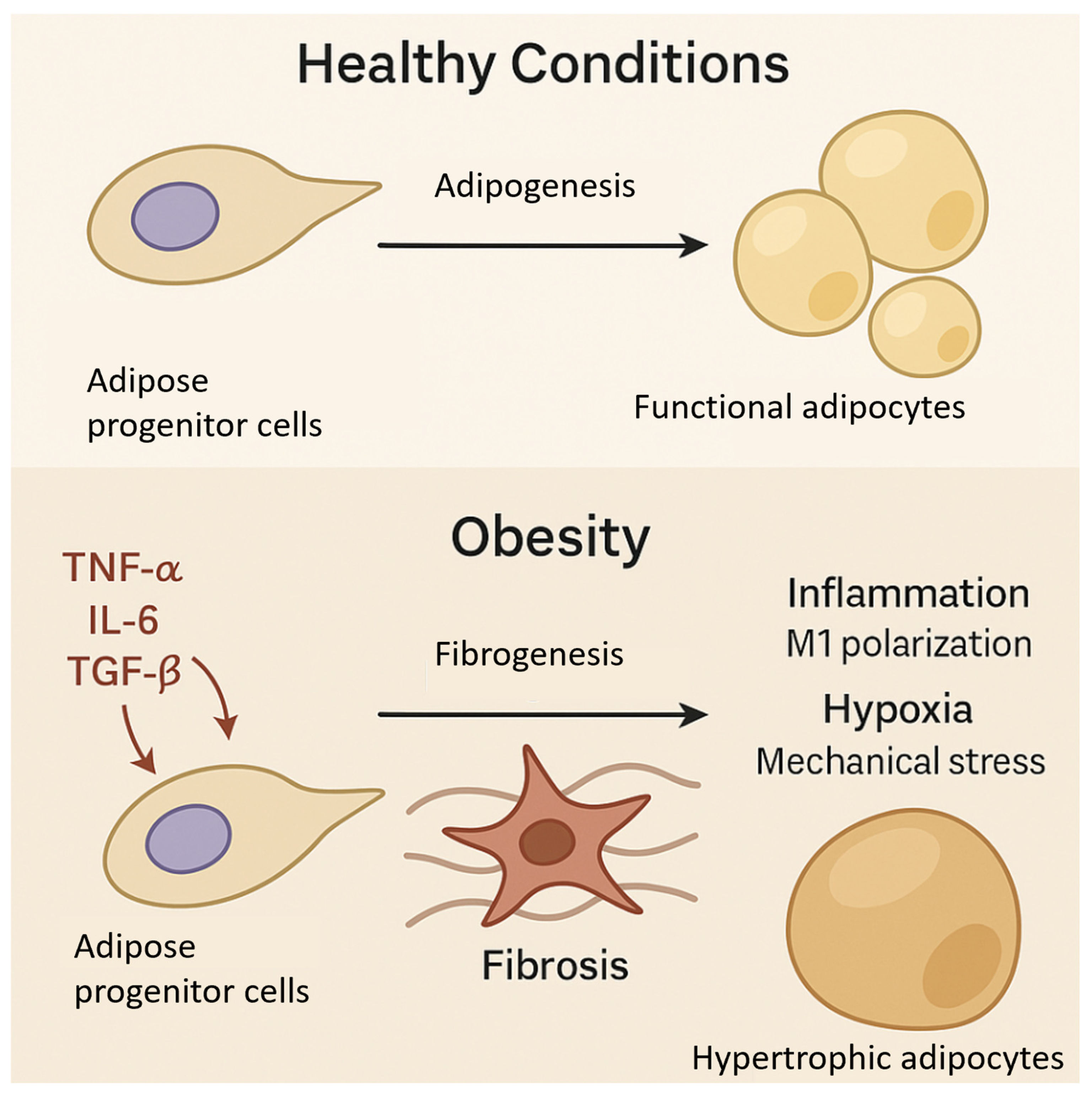
3. Adipose Progenitor Cells and Fibrosis in Obesity
3.1. Therapeutic Potential of Targeting APCs to Modulate Adipose Tissue Function
3.2. Modulating ECM Remodeling to Reduce Fibrosis
3.3. Targeting Inflammatory Pathways to Promote Healthy APC Function
3.4. Pharmacological Activation of Adipogenesis
3.5. Cell-Based Therapies for Adipose Tissue Restoration
3.6. Challenges and Future Directions
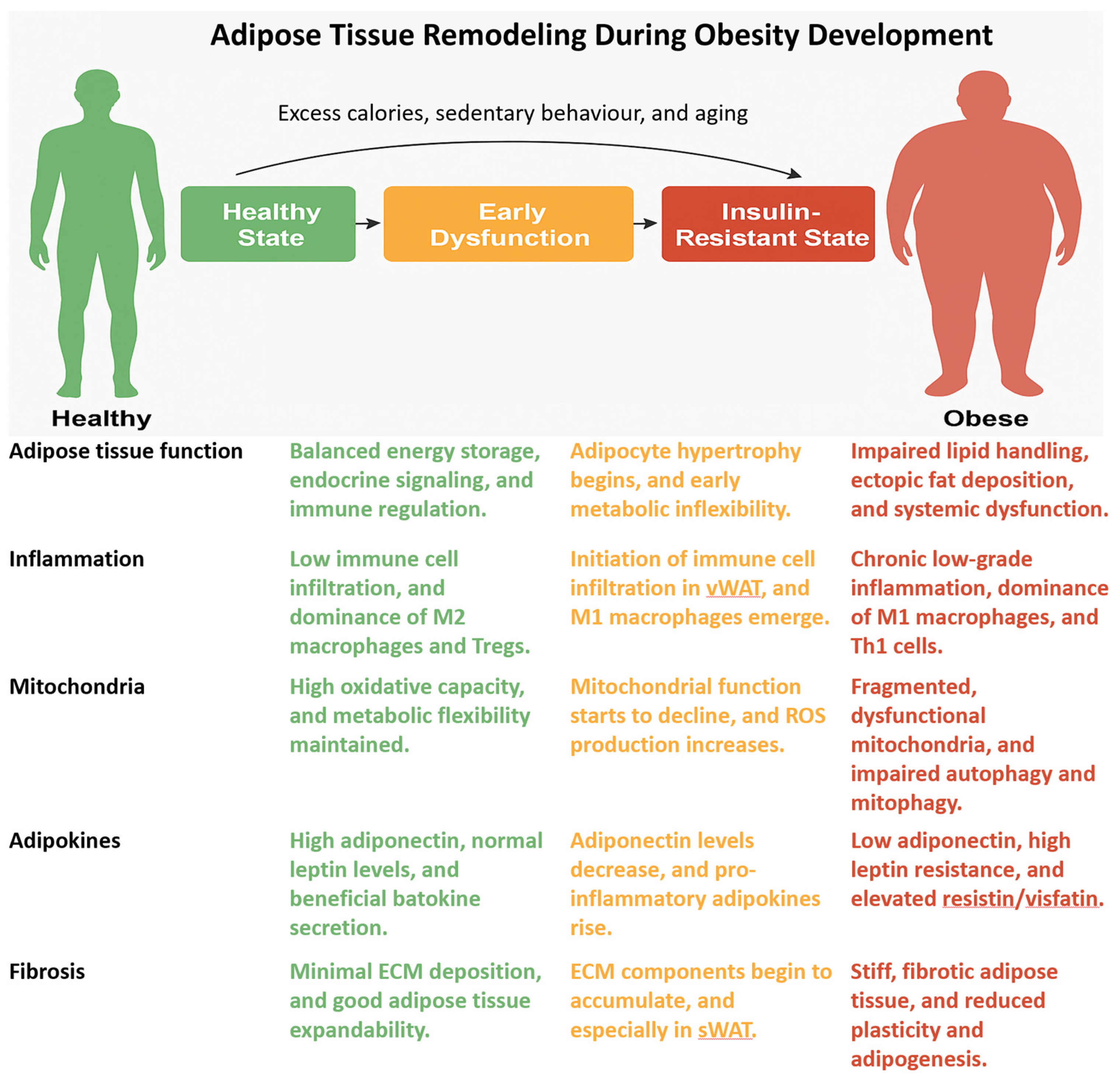
4. Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Insulin Resistance
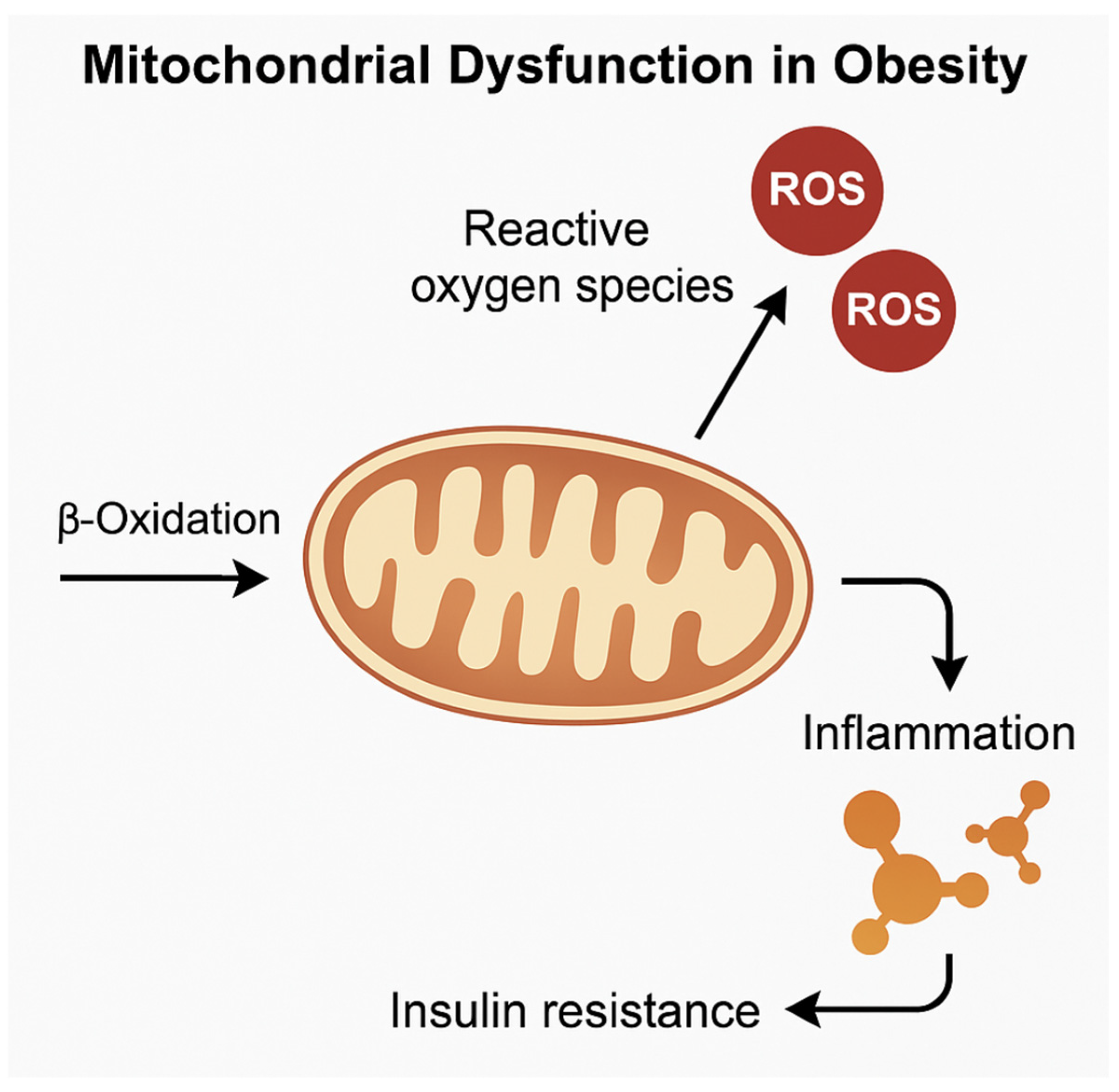
5. Mitochondrial Function and Metabolic Flexibility in Adipose Depots
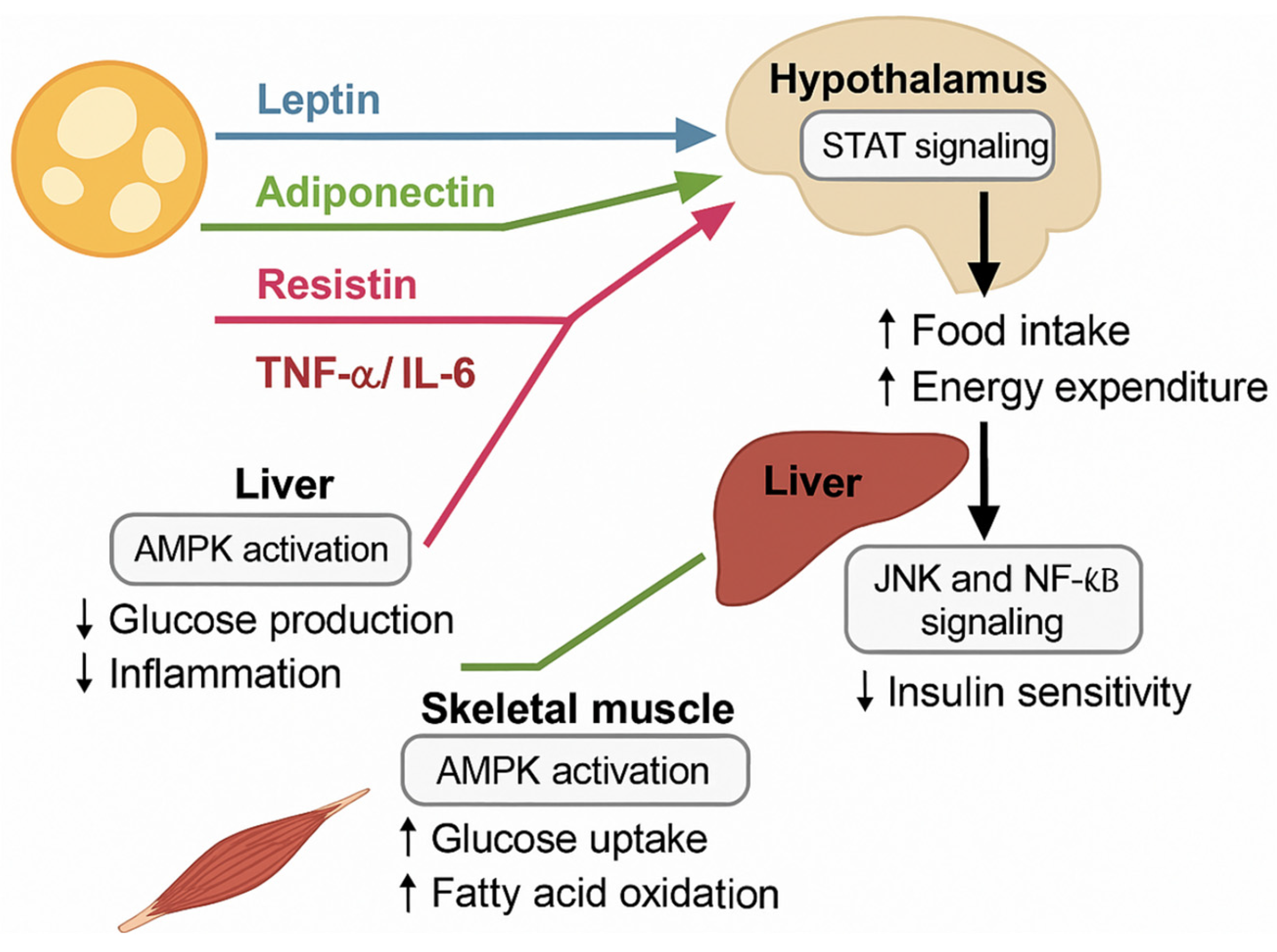
6. Adipokines and Systemic Metabolic Regulation
7. Therapeutic Implications and Future Directions
Clinical Applications and Translational Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| vWAT | Visceral white adipose tissue |
| sWAT | Subcutaneous white adipose tissue |
| BAT | Brown adipose tissue |
| APCs | Adipose progenitor cells |
| BeAT | Beige adipose tissue |
| scRNA-seq | Single-cell RNA sequencing |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| ILCs | Innate lymphoid cells |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| ADSCs | Adipose-derived stem cells |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-beta |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| IL | Interleukin |
| Tregs | Regulatory T cells |
| PPARγ | Proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| BMP4 | Bone morphogenetic protein 4 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| UCP1 | Uncoupling protein 1 |
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Halder, S.K.; Melkani, G.C. The Interplay of Genetic Predisposition, Circadian Misalignment, and Metabolic Regulation in Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2025, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Bayardo, T.I.; Román-Rojas, D.; García-Sánchez, A.; Cardona-Muñoz, E.G.; Sánchez-Lozano, D.I.; Totsuka-Sutto, S.; Gómez-Hermosillo, L.F.; Casillas-Moreno, J.; Andrade-Sierra, J.; Pazarín-Villaseñor, L.; et al. The Role of TLRs in Obesity and Its Related Metabolic Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rocco, G.; Trivisonno, A.; Trivisonno, G.; Toietta, G. Dissecting human adipose tissue heterogeneity using single-cell omics technologies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Dai, H.; Duan, Y.; An, Y.; Shi, L.; Lv, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Ma, Q.; et al. Brown and beige adipose tissue: A novel therapeutic strategy for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J. Plasticity of adipose tissues: Interconversion among white, Brown, and beige fat and its role in energy homeostasis. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fano, M.; Bartolini, D.; Tortoioli, C.; Vermigli, C.; Malara, M.; Galli, F.; Murdolo, G. Adipose tissue plasticity in response to pathophysiological cues: A connecting link between obesity and its associated comorbidities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilano, K.; Zhou, B.; Brestoff, J.R.; Lettieri-Barbato, D. Multifaceted mitochondrial quality control in brown adipose tissue. Trends Cell Biol. 2023, 33, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J.A. Brown adipose tissue: Function and physiological significance. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 277–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, K.A.; Lidell, M.E.; Orava, J.; Heglind, M.; Westergren, R.; Niemi, T.; Taittonen, M.; Laine, J.; Savisto, N.J.; Enerbäck, S.; et al. Functional brown adipose tissue in healthy adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyad-ul-Ferdous, M.; Gul, I.; Raheem, M.A.; Pandey, V. Mitochondrial UCP1: Potential thermogenic mechanistic switch against obesity and neurodegenerative diseases using natural and epigenetic drugs. Phytomedicine 2024, 130, 55672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cypess, A.M.; Lehman, S.; Williams, G.; Tal, I.; Rodman, D.; Goldfine, A.B.; Kuo, F.C.; Palmer, E.L.; Tseng, Y.H.; Doria, A.; et al. Identification and importance of brown adipose tissue in adult humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Marken Lichtenbelt, W.D.; Vanhommerig, J.W.; Smulders, N.M.; Drossaerts, J.M.A.F.L.; Kemerink, G.J.; Bouvy, N.D.; Schrauwen, P.; Schrauwen, P.; Teule, G.J.J. Cold-activated brown adipose tissue in healthy men. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanford, K.I.; Middelbeek, R.J.; Townsend, K.L.; An, D.; Nygaard, E.B.; Hitchcox, K.M.; Markan, K.R.; Nakano, K.; Hirshman, M.F.; Tseng, Y.H.; et al. Brown adipose tissue regulates glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, F.; Wang, C.H.; Tseng, Y.H. The evolving view of thermogenic adipocytes—Ontogeny, niche and function. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 726–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, T.; Palanisamy, S.; Kramer, D.J.; Eljalby, M.; Marx, S.J.; Wibmer, A.G.; Butler, S.D.; Jiang, C.S.; Vaughan, R.; Schöder, H.; et al. Brown adipose tissue is associated with cardiometabolic health. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya, F.; Cereijo, R.; Gavaldà-Navarro, A.; Villarroya, J.; Giralt, M. Inflammation of brown/beige adipose tissues in obesity and metabolic disease. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, R.; Ganbold, K.; Sparman, N.Z.; Rajbhandari, P. Immune Regulatory Crosstalk in Adipose Tissue Thermogenesis. Compr. Physiol. 2025, 15, e70001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Quan, Y.; Zhu, S.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Liang, Z.; Liao, Y.; Jiang, W.; He, Y.; et al. The browning and mobilization of subcutaneous white adipose tissue supports efficient skin repair. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1287–1301.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononova, Y.A.; Tuchina, T.P.; Babenko, A.Y. Brown and beige adipose tissue: One or different targets for treatment of obesity and obesity-related metabolic disorders? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Hernández, A.; de Las Heras, N.; Gálvez, B.G.; Fernández-Marcelo, T.; Fernández-Millán, E.; Escribano, Ó. New mediators in the crosstalk between different adipose tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emont, M.P.; Jacobs, C.; Essene, A.L.; Pant, D.; Tenen, D.; Colleluori, G.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Jørgensen, A.M.; Dashti, H.; Stefek, A.; et al. A single-cell atlas of human and mouse white adipose tissue. Nature 2022, 603, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massier, L.; Jalkanen, J.; Elmastas, M.; Zhong, J.; Wang, T.; Nono Nankam, P.A.; Frendo-Cumbo, S.; Bäckdahl, J.; Subramanian, N.; Sekine, T.; et al. An integrated single cell and spatial transcriptomic map of human white adipose tissue. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckdahl, J.; Franzén, L.; Massier, L.; Li, Q.; Jalkanen, J.; Gao, H.; Andersson, A.; Bhalla, N.; Thorell, A.; Rydén, M.; et al. Spatial mapping reveals human adipocyte subpopulations with distinct sensitivities to insulin. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1869–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Shamsi, F.; Altemose, N.; Dorlhiac, G.F.; Cypess, A.M.; White, A.P.; Yosef, N.; Patti, M.E.; Tseng, Y.H.; Streets, A. Characterization of transcript enrichment and detection bias in single-nucleus RNA-seq for mapping of distinct human adipocyte lineages. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobini, C.; Vitale, M.; Haxhi, J.; Menini, S.; Pugliese, G. Impaired remodeling of white adipose tissue in obesity and aging: From defective adipogenesis to adipose organ dysfunction. Cells 2024, 13, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.Y.; Han, Y.X.; Xu, S.N.; Jiang, H.L.; Wu, H.X.; Cai, J.M.; Li, L.; Bu, Y.H.; Xiao, F.; Liang, H.D.; et al. Adipose Tissue Plasticity: A Comprehensive Definition and Multidimensional Insight. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerre, D.J.; Galmozzi, A. Deconstructing adipose tissue heterogeneity one cell at a time. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 847291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Li, X.; Scherer, P.E. Extracellular matrix (ECM) and fibrosis in adipose tissue: Overview and perspectives. Compr. Physiol. 2023, 13, 4387–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecoutre, S.; Rebière, C.; Maqdasy, S.; Lambert, M.; Dussaud, S.; Abatan, J.B.; Dugail, I.; Gautier, E.L.; Clément, K.; Marcelin, G. Enhancing adipose tissue plasticity: Progenitor cell roles in metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2025, 21, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelin, G.; Gautier, E.L.; Clément, K. Adipose tissue fibrosis in obesity: Etiology and challenges. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2022, 84, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Du, Y.; Huang, S.; Sun, X.; Ye, Y.; Sun, H.; Chu, X.; Shan, X.; Yuan, Y.; Shen, L.; et al. Single-cell analysis reveals a subpopulation of adipose progenitor cells that impairs glucose homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrina, I.; Chung, K.J.; Michailidou, Z.; Koutsilieris, M.; Chavakis, T.; Chatzigeorgiou, A. Fate of adipose progenitor cells in obesity-related chronic inflammation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Tordjman, J.; Clément, K.; Scherer, P.E. Fibrosis and adipose tissue dysfunction. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaben, A.L.; Scherer, P.E. Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchkonia, T.; Thomou, T.; Zhu, Y.I.; Karagiannides, I.; Pothoulakis, C.; Jensen, M.D.; Kirkland, J.L. Mechanisms and metabolic implications of regional differences among fat depots. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eirin, A.; Thaler, R.; Glasstetter, L.M.; Xing, L.; Zhu, X.Y.; Osborne, A.C.; Mondesir, R.; Bhagwate, A.V.; Lerman, A.; van Wijnen, A.J.; et al. Obesity-driven mitochondrial dysfunction in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells involves epigenetic changes. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, G.; Hu, Y.; Mohsin, A.; Chen, Z.; Hao, W.; Li, Z.; Gao, W.Q.; Guo, M.; Xu, H. Uncovering impaired mitochondrial and lysosomal function in adipose-derived stem cells from obese individuals with altered biological activity. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Hao, H.; Yue, H. Inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) promotes the proangiogenic ability of adipose stem cells from obese subjects via the IL-6 signaling pathway. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 18, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, A. Adipose Tissue Hypoxia in Obesity: Clinical Reappraisal of Hypoxia Hypothesis. Obes. Lipotoxicity 2024, 1460, 329–356. [Google Scholar]
- Marcelin, G.; Silveira, A.L.; Martins, L.B.; Ferreira, A.V.; Clément, K. Deciphering the cellular interplays underlying obesity-induced adipose tissue fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4032–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gao, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Lu, X. Fight against fibrosis in adipose tissue remodeling. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 321, E169–E175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahn, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Dagur, P.; Scott, N.; Cero, C.; Long, K.T.; Nguyen, N.; Cypess, A.M.; Rane, S.G. TGF-β antagonism synergizes with PPARγ agonism to reduce fibrosis and enhance beige adipogenesis. Mol. Metab. 2024, 90, 102054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asthana, P.; Wong, H.L. Preventing obesity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes by targeting MT1-MMP. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Sun, S.; Li, J.J.; Yuan, J.P.; Sun, S.R.; Wu, Q. Adipose tissue macrophages: Implications for obesity-associated cancer. Mil. Med. Res. 2023, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Li, Q.; Ryu, M.O.; Nam, A.; An, J.H.; Yang, J.I.; Kim, S.M.; Song, W.J.; Youn, H.Y. Preconditioning of canine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells with deferoxamine potentiates anti-inflammatory effects by directing/reprogramming M2 macrophage polarization. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2020, 219, 109973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, E.H.; Wang, X.; Balaji, S.; Butte, M.J.; Bollyky, P.L.; Keswani, S.G. The role of the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 in tissue fibrosis. Adv. Wound Care 2020, 9, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. What we talk about when we talk about fat. Cell 2014, 156, 20–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Siqueira, M.K.; Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Ahn, I.S.; Tamboline, M.; Hildreth, A.D.; Larios, J.; Schcolnik-Cabrera, A.; Nouhi, Z.; et al. PPARγ-dependent remodeling of translational machinery in adipose progenitors is impaired in obesity. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, S.; Wolfrum, C. The dual role of BMP4 in adipogenesis and metabolism. Adipocyte 2017, 6, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, N.; Combellack, E.J.; Griffin, M.; Sedaghati, T.; Javed, M.; Findlay, M.W.; Wallace, C.G.; Mosahebi, A.; Butler, P.E.; Seifalian, A.M.; et al. The regenerative role of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSC) in plastic and reconstructive surgery. Int. Wound J. 2017, 14, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, H.; Issa, K.; Eid, A.; Saleh, F.A. The therapeutic effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on obesity and its associated diseases in diet-induced obese mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Regaiey, K. Crosstalk between adipogenesis and aging: Role of polyphenols in combating adipogenic-associated aging. Immun. Ageing 2024, 21, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Pan, A.; Liao, Y. Adipose tissue senescence: Biological changes, hallmarks and therapeutic approaches. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2024, 222, 111988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vratarić, M.; Teofilović, A.; Milutinović, D.V.; Veličković, N.; Vučićević, L.; Đmura, G.; Djordjevic, A. Changes in lipid metabolism in visceral rather than the subcutaneous adipose tissue depot attenuate metabolic disturbances in obesity-resistant mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2025, 141, 109912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexaki, V.I. Adipose tissue-derived mediators of systemic inflammation and metabolic control. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 2024, 37, 100560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; You, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, F. Relationship between macrophage subtypes in obese adipose tissue and metabolic diseases. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 2025, 29, 2832. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, H. T cells in adipose tissue: Critical players in immunometabolism. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Xu, L.; Zhuang, Q. Mitochondrial dysfunction in fibrotic diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya, J.; Cereijo, R.; Gavaldà-Navarro, A.; Peyrou, M.; Giralt, M.; Villarroya, F. New insights into the secretory functions of brown adipose tissue. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 243, R19–R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.d.N.; Amato, A.A. Thermogenic adipose tissue aging: Mechanisms and implications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 955612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohm, T.V.; Meier, D.T.; Olefsky, J.M.; Donath, M.Y. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity 2022, 55, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michurina, S.; Stafeev, I.; Podkuychenko, N.; Sklyanik, I.; Shestakova, E.; Yah’yaev, K.; Yurasov, A.; Ratner, E.; Menshikov, M.; Parfyonova, Y.; et al. Decreased UCP-1 expression in beige adipocytes from adipose-derived stem cells of type 2 diabetes patients associates with mitochondrial ROS accumulation during obesity. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 169, 108410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mello, A.H.; Costa, A.B.; Engel, J.D.; Rezin, G.T. Mitochondrial dysfunction in obesity. Life Sci. 2018, 192, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilingiris, D.; Tzeravini, E.; Koliaki, C.; Dalamaga, M.; Kokkinos, A. The role of mitochondrial adaptation and metabolic flexibility in the pathophysiology of obesity and insulin resistance: An updated overview. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 10, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Veeragandham, P.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Rhyne, T.E.; Qian, J.; Hung, C.W.; Zhao, P.; Jones, Y.; Gao, H.; et al. Obesity causes mitochondrial fragmentation and dysfunction in white adipocytes due to RalA activation. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissanka, N.; Moraes, C.T. Mitochondrial DNA damage and reactive oxygen species in neurodegenerative disease. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Huang, Y.; Song, Z.; Zhou, H.J.; Zhang, H.; Perry, R.J.; Shulman, G.I.; Min, W. Mitophagy-mediated adipose inflammation contributes to type 2 diabetes with hepatic insulin resistance. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 218, e20201416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickles, S.; Vigié, P.; Youle, R.J. Mitophagy and quality control mechanisms in mitochondrial maintenance. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R170–R185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimura, S.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Seale, P. Brown and beige fat: Physiological roles beyond heat generation. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consitt, L.A.; Bell, J.A.; Koves, T.R.; Muoio, D.M.; Hulver, M.W.; Haynie, K.R.; Dohm, G.L.; Houmard, J.A. Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α overexpression increases lipid oxidation in myocytes from extremely obese individuals. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, M.E.; Gillen, Z.M.; Fukuda, D.H.; Cramer, J.T. Metabolic Flexibility and Inflexibility: Pathology Underlying Metabolism Dysfunction. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paglialunga, S.; Ludzki, A.; Root-McCaig, J.; Holloway, G.P. In adipose tissue, increased mitochondrial emission of reactive oxygen species is important for short-term high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pafili, K.; Kahl, S.; Mastrototaro, L.; Strassburger, K.; Pesta, D.; Herder, C.; Pützer, J.; Dewidar, B.; Hendlinger, M.; Granata, C.; et al. Mitochondrial respiration is decreased in visceral but not subcutaneous adipose tissue in obese individuals with fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarparanta, J.; Garcia-Macia, M.; Singh, R. Autophagy and mitochondria in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2017, 13, 352–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Min, M.; Duan, H.; Mai, J.; Liu, X. The role of macrophage and adipocyte mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of obesity. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1481312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Suhaimi, E.A. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ and a glance on local hormones. In Emerging Concepts in Endocrine Structure and Functions; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 349–392. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.M.; Halaas, J.L. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 1998, 395, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, P.E.; Williams, S.; Fogliano, M.; Baldini, G.; Lodish, H.F. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26746–26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Muruzábal, F.J.; Burrell, M.A. The adipocyte: A model for integration of endocrine and metabolic signaling in energy metabolism regulation. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E827–E847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chait, A.; Den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose tissue distribution, inflammation and its metabolic consequences, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 522637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Terauchi, Y.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Mori, Y.; Ide, T.; Murakami, K.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N.; et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.; Vohra, M.S.; Saleemi, M.A.; Serpell, C.J.; Fong, I.L.; Wong, E.H. Brown/Beige adipose tissues and the emerging role of their secretory factors in improving metabolic health: The batokines. Biochimie 2021, 184, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, F.M.; Maratos-Flier, E. Understanding the physiology of FGF21. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, F.; Wang, P.; Xie, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, B. Neuregulin-4 attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy by regulating autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR signalling pathway. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, A.J.; Carobbio, S.; Martins, L.; Slawik, M.; Hondares, E.; Vázquez, M.J.; Morgan, D.; Csikasz, R.I.; Gallego, R.; Rodriguez-Cuenca, S.; et al. BMP8B increases brown adipose tissue thermogenesis through both central and peripheral actions. Cell 2012, 149, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Shan, T. Adipose tissue adipokines and lipokines: Functions and regulatory mechanism in skeletal muscle development and homeostasis. Metabolism 2023, 139, 155379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.; Szerenos, E.; Lewandowski, D.; Toczylowski, K.; Sulik, A. The role of adipokines in the pathologies of the central nervous system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, M.Y.; Shoelson, S.E. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmi, V.; Sbraccia, P. Obesity phenotypes: Depot-differences in adipose tissue and their clinical implications. Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2018, 23, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada-Iwabu, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Honma, T.; Hamagami, K.I.; Matsuda, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tanabe, H.; Kimura-Someya, T.; Shirouzu, M.; et al. A small-molecule AdipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity. Nature 2013, 503, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asterholm, I.W.; Tao, C.; Morley, T.S.; Wang, Q.A.; Delgado-Lopez, F.; Wang, Z.V.; Scherer, P.E. Adipocyte inflammation is essential for healthy adipose tissue expansion and remodeling. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 103–118. [Google Scholar]
- Markan, K.R.; Potthoff, M.J. Metabolic fibroblast growth factors (FGFs): Mediators of energy homeostasis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 53, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, E.D.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Pablo Frias, J.; Kundu, S.; Luo, Y.; Tirucherai, G.S.; Christian, R. Pegbelfermin (BMS-986036), PEGylated FGF21, in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes: Results from a randomized phase 2 study. Obesity 2019, 27, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.X.; Zhao, X.Y.; Meng, Z.X.; Kern, M.; Dietrich, A.; Chen, Z.; Cozacov, Z.; Zhou, D.; Okunade, A.L.; Su, X.; et al. The brown fat–enriched secreted factor Nrg4 preserves metabolic homeostasis through attenuation of hepatic lipogenesis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, C.; Álvarez-Indo, J.; Cifuentes, M.; Morselli, E.; Kerr, B.; Burgos, P.V. Enhancing adipose tissue functionality in obesity: Senotherapeutics, autophagy and cellular senescence as a target. Biol. Res. 2024, 57, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.L.; Tan, B.K.; Barber, T.M.; Randeva, H.S. Brown adipose tissue: Endocrine determinants of function and therapeutic manipulation as a novel treatment strategy for obesity. BMC Obes. 2014, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; de Jonge, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Rensen, P.C.; Kooijman, S. Electrical neurostimulation promotes brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 567545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z. Non-shivering thermogenesis and its current advances in clinical trials targeting obesity. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2022, 8, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelin, G.; Ferreira, A.; Liu, Y.; Atlan, M.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Pelloux, V.; Botbol, Y.; Ambrosini, M.; Fradet, M.; Rouault, C.; et al. A PDGFRα-mediated switch toward CD9high adipocyte progenitors controls obesity-induced adipose tissue fibrosis. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, T.; Pošćić, N.; Colitti, M. Factors involved in white-to-brown adipose tissue conversion and in thermogenesis: A review. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikiy, S.; Rudensky, A.Y. Principles of regulatory T cell function. Immunity 2023, 56, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahdah, N.; Tercero-Alcázar, C.; Malagón, M.M.; Garcia-Roves, P.M.; Guzmán-Ruiz, R. Interrelation of adipose tissue macrophages and fibrosis in obesity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 225, 116324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Meng, Y.; He, S.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W. Macrophages, chronic inflammation, and insulin resistance. Cells 2022, 11, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, A.M.; Kamarudin, T.A.; Abd Ghafar, N. The role of BMP4 in adipose-derived stem cell differentiation: A minireview. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1045103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, L.; Lin, T.; Pei, X.; Gao, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z. C/EBPZ modulates the differentiation and proliferation of preadipocytes. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. The sexual dimorphism of obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 402, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevener, A.L.; Zhou, Z.; Moore, T.M.; Drew, B.G.; Ribas, V. The impact of ERα action on muscle metabolism and insulin sensitivity–strong enough for a man, made for a woman. Mol. Metab. 2018, 15, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.M.; Moore, L.B.; Smith-Oliver, T.A.; Wilkison, W.O.; Willson, T.M.; Kliewer, S.A. An antidiabetic Thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor Γ (PPARγ). J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 12953–12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhurst, R.J.; Hata, A. Targeting the TGFβ signalling pathway in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 790–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubert, M.A.; Yow, E.; Dunn, G.; Marchev, S.; Barnhart, H.; Douglas, P.S.; O’Connor, C.; Goldstein, S.; Udelson, J.E.; Sabbah, H.N. Novel mitochondria-targeting peptide in heart failure treatment: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of elamipretide. Circ. Heart Fail. 2017, 10, e004389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT) | Beige Adipose Tissue (BeAT) | Subcutaneous White Adipose Tissue (sWAT) | Visceral White Adipose Tissue (vWAT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| High mitochondria density, UCP1+ | Induced in sWAT (transdifferentiation) | Metabolically protective (lean) | Pro-inflammatory (M1 macrophages) |
| Thermogenesis | Variable thermogenic capacity | Fibrosis under metabolic stress | High lipolytic activity |
| Improves glucose metabolism | Plasticity | APC-mediated adipogenesis | APC heterogeneity affects remodeling |
| Sensitive to aging/obesity | Sensitive to inflammatory signals | Single-nucleus RNA-seq data advances | Associated with insulin resistance |
| APC role emerging | May become pro-inflammatory |
| Molecule/Therapy | Target Pathway | Clinical Status | Main Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pioglitazone | PPARγ activation | Approved | Improves insulin sensitivity |
| Pegbelfermin | FGF21 analog | Phase II trials | Enhances lipid and glucose metabolism |
| AdipoRon | Adiponectin receptor agonist | Preclinical | Mimics adiponectin’s insulin-sensitizing effects |
| Fresolimumab | TGF-β neutralization | Phase II trials | Reduces fibrosis and inflammation |
| Elamipretide | Mitochondrial membrane stabilization | Phase II trials | Restores mitochondrial function |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobre, M.-Z.; Virgolici, B.; Timnea, O. Key Roles of Brown, Subcutaneous, and Visceral Adipose Tissues in Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050343
Dobre M-Z, Virgolici B, Timnea O. Key Roles of Brown, Subcutaneous, and Visceral Adipose Tissues in Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050343
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobre, Maria-Zinaida, Bogdana Virgolici, and Olivia Timnea. 2025. "Key Roles of Brown, Subcutaneous, and Visceral Adipose Tissues in Obesity and Insulin Resistance" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050343
APA StyleDobre, M.-Z., Virgolici, B., & Timnea, O. (2025). Key Roles of Brown, Subcutaneous, and Visceral Adipose Tissues in Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050343




