Network Pharmacology and In Vitro Experimental Validation Reveal the Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Lotus Leaf Extract in Treating Inflammatory Diarrhea in Pigs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Lotus Leaf Extract (LLE)
2.2. Determination of Components in LLE by LC-MS
2.3. Screening of Active Components and Targets of Lotus Leaf
2.4. Screening of Disease Targets for Inflammatory Diarrhea
2.5. Diseases and Drugs Share Target Gene Acquisition
2.6. Lotus Leaf Component—Construction of Target Network of Porcine Inflammatory Diarrhea Disease
2.7. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network and Core Target Screening
2.8. Gene Ontology (GO) Function and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.9. Molecular Docking
2.10. In Vitro Experiments
2.10.1. Cell Maintenance and Cell Viability Assay
2.10.2. Flow Cytometry Assay
2.10.3. Western Blot Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The LC-MS Detection Results of the LLE
3.2. Active Components and Targets of Lotus Leaf
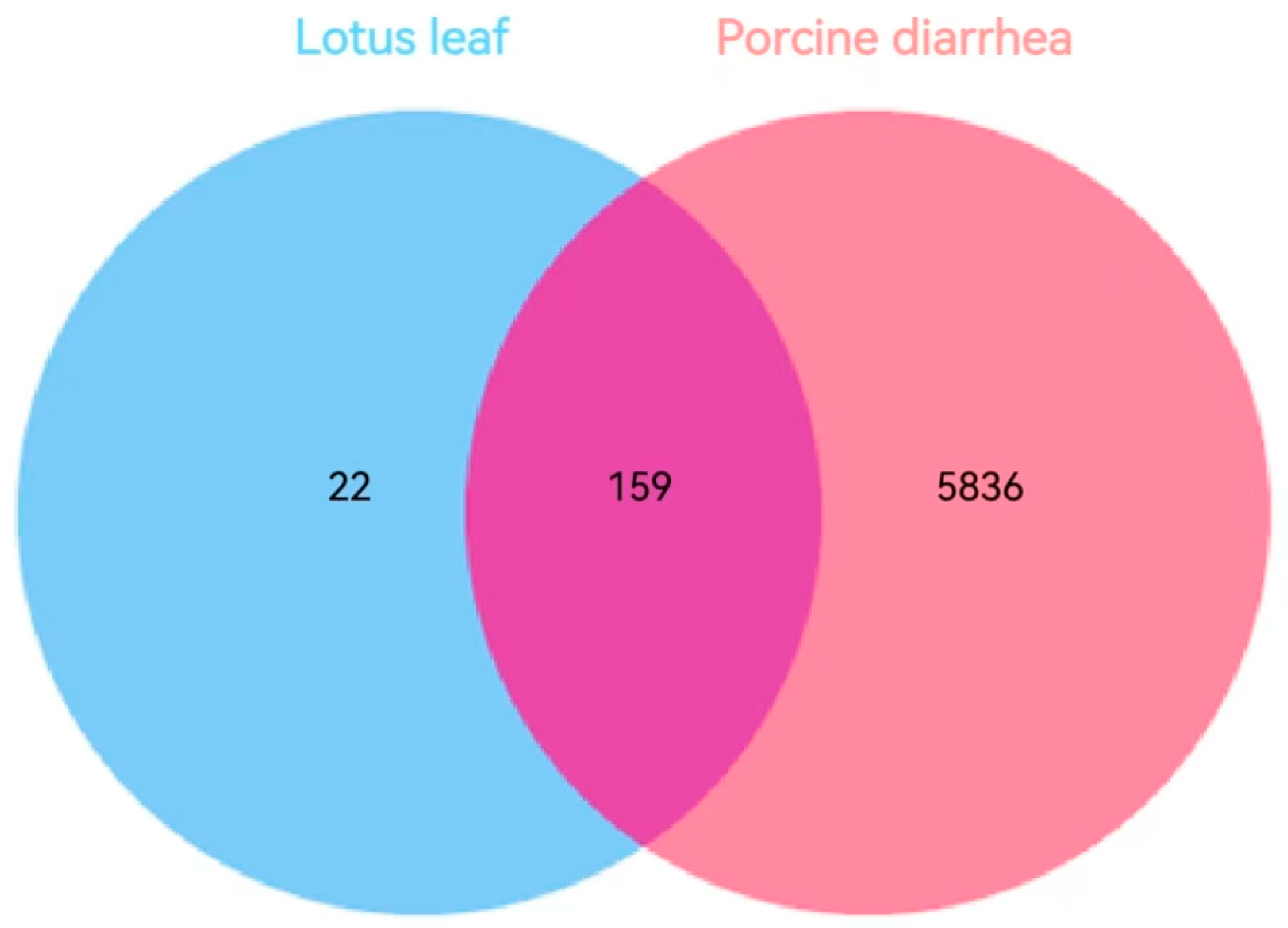
3.3. Targets of Lotus Leaf Active Components for Inflammatory Diarrhea in Pigs
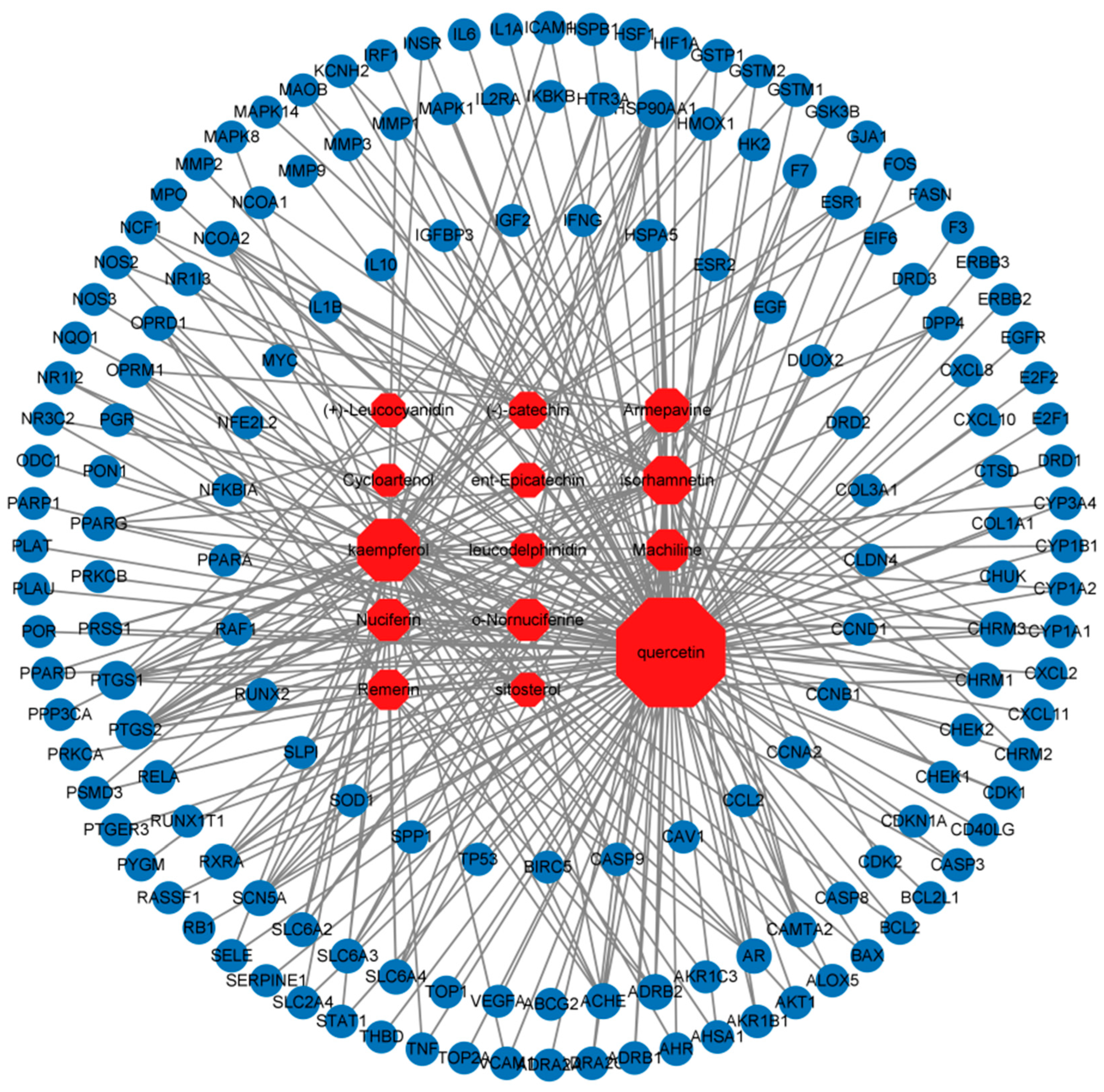
3.4. Component–Disease Target Network
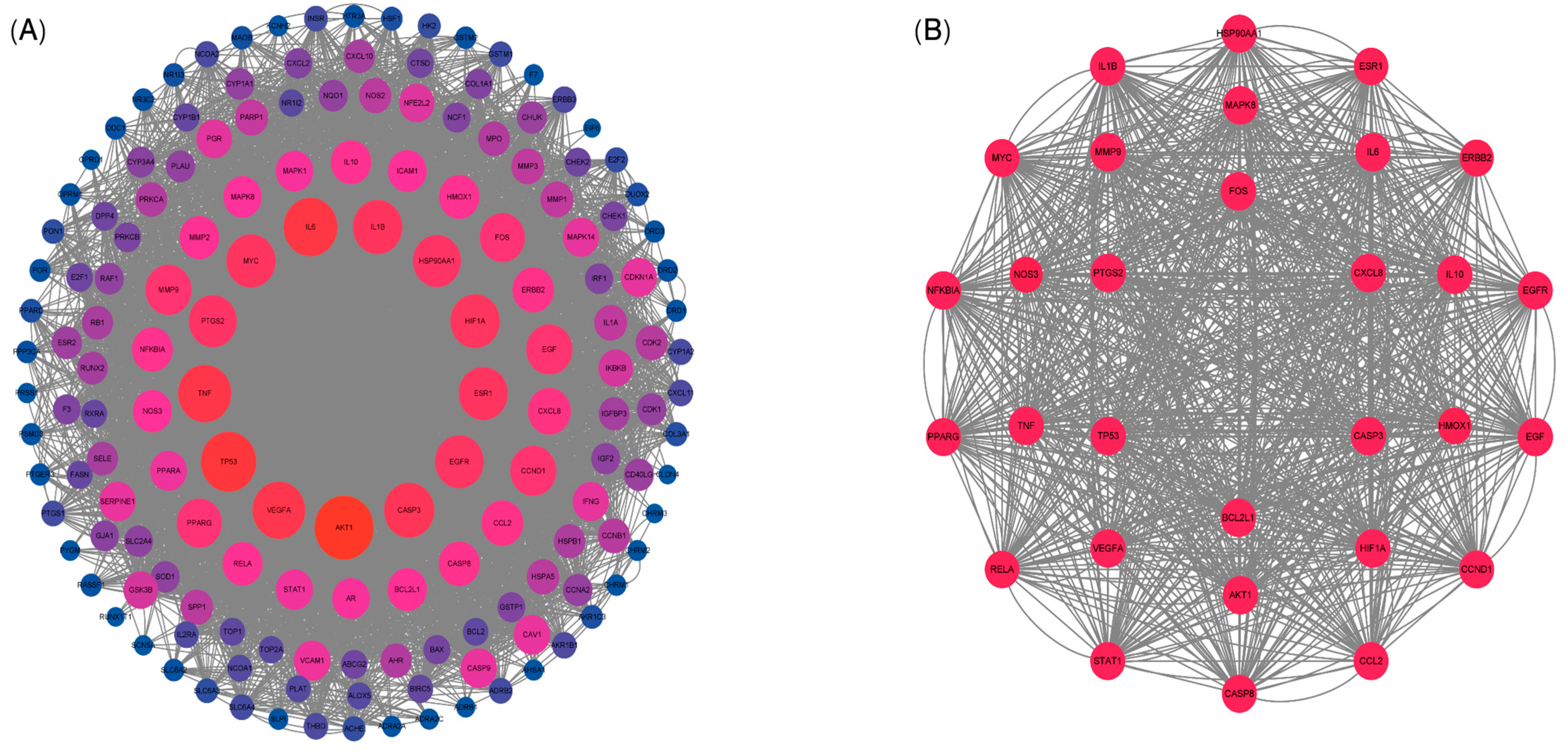
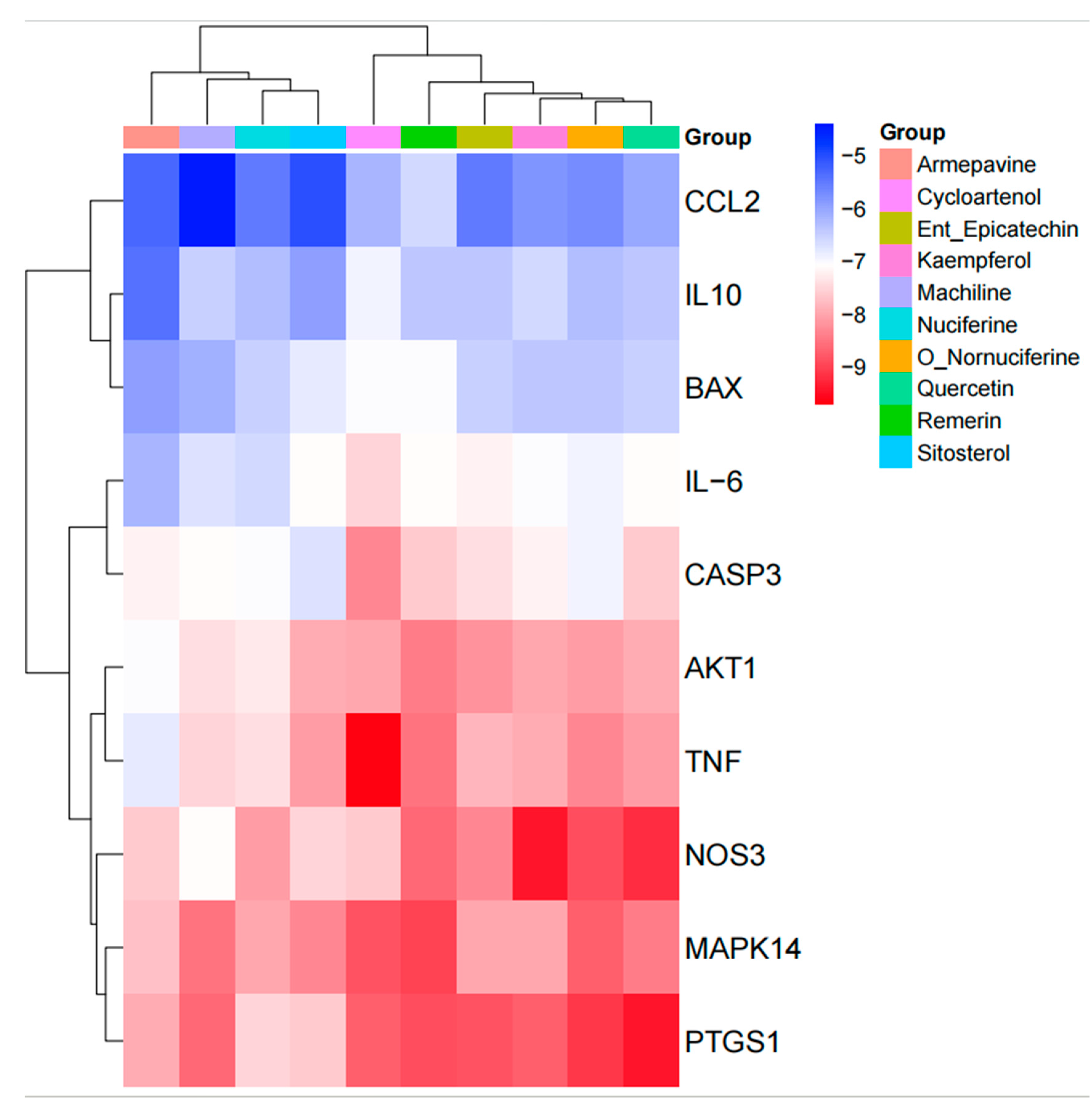
3.5. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis
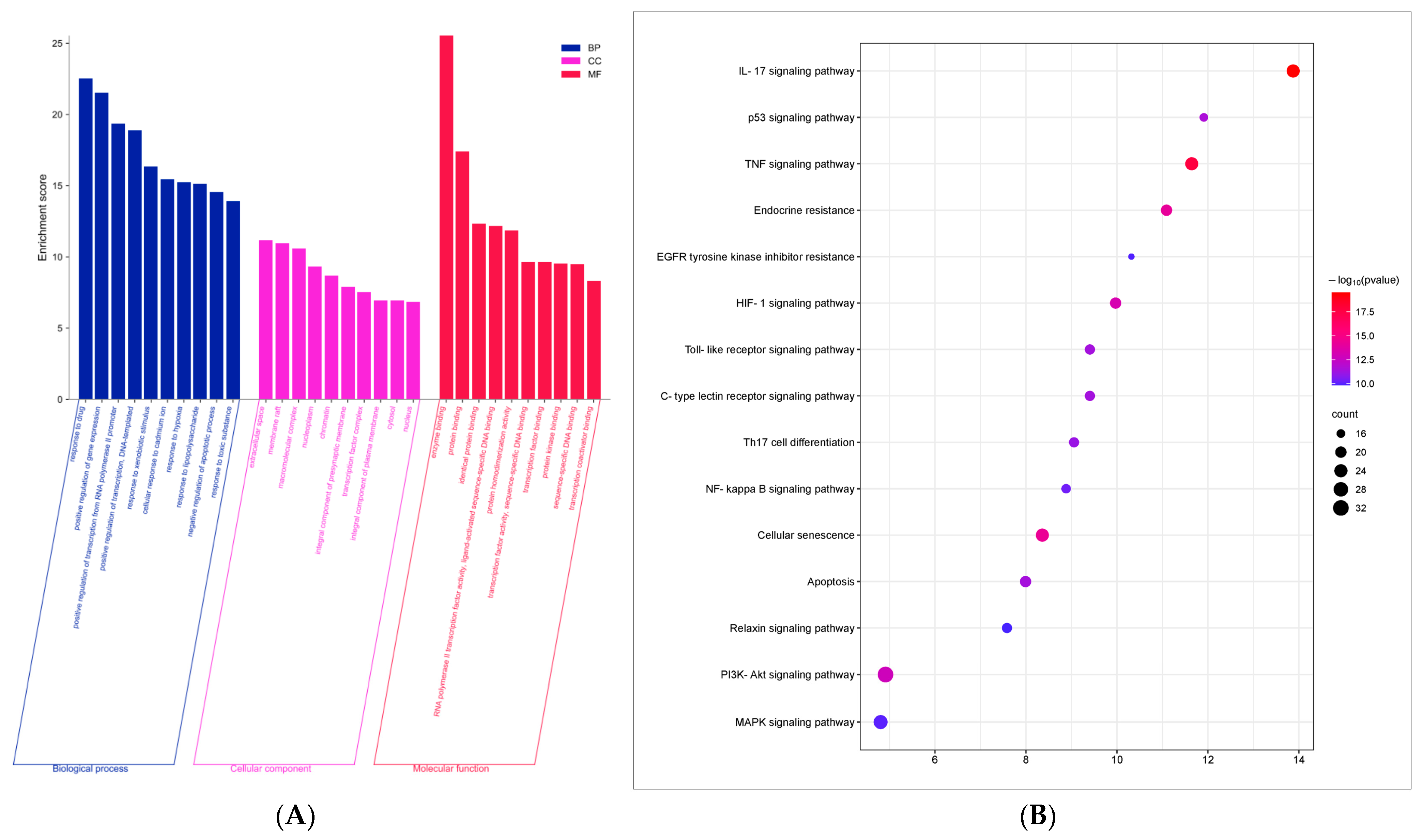
3.6. GO Function and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
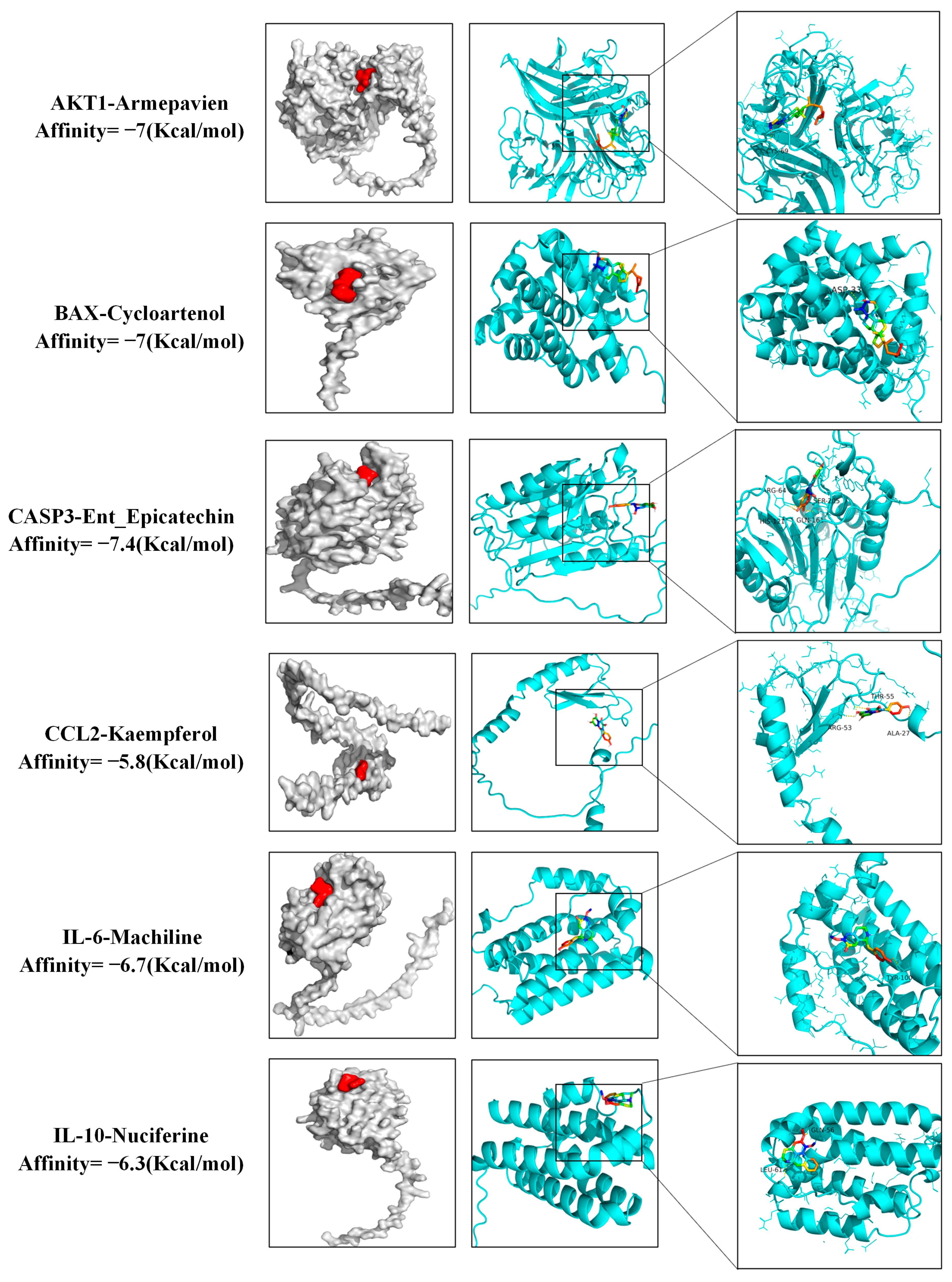
3.7. Molecular Docking Results
3.8. In Vitro Experiment Results
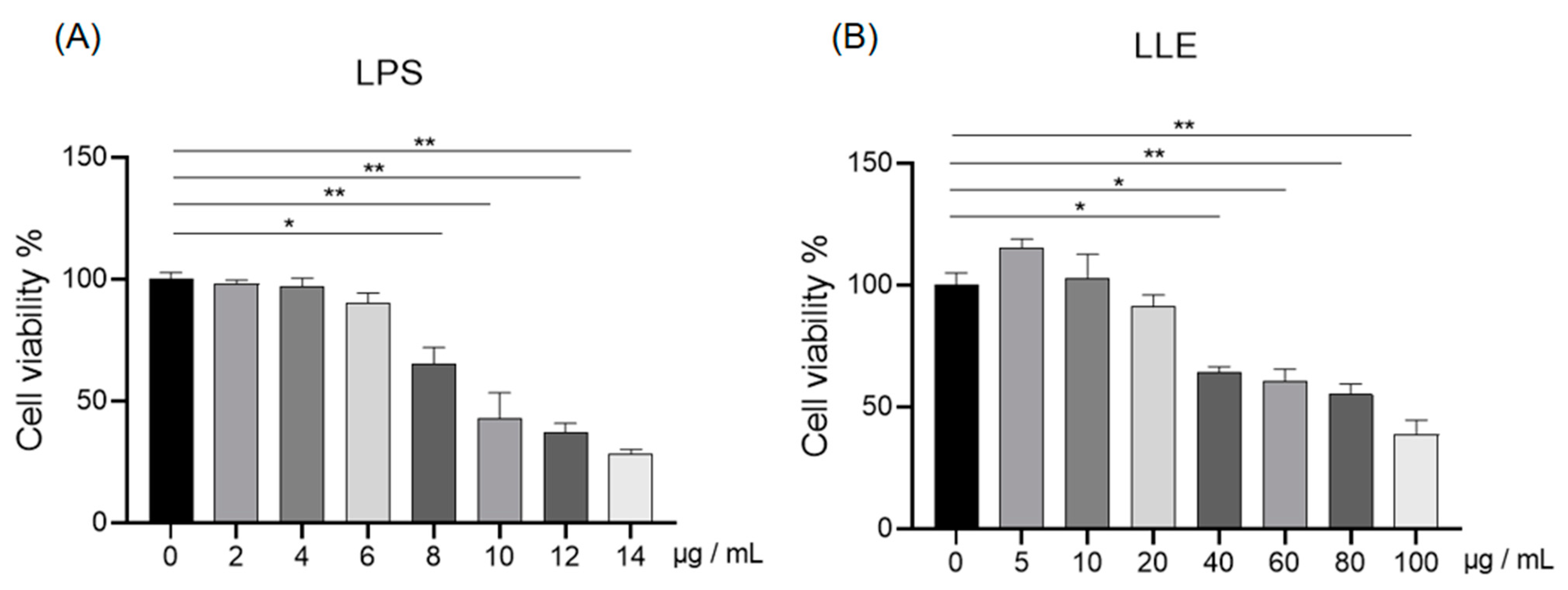
3.8.1. Effects of LLE and LPS on IPEC-J2 Cell Viability
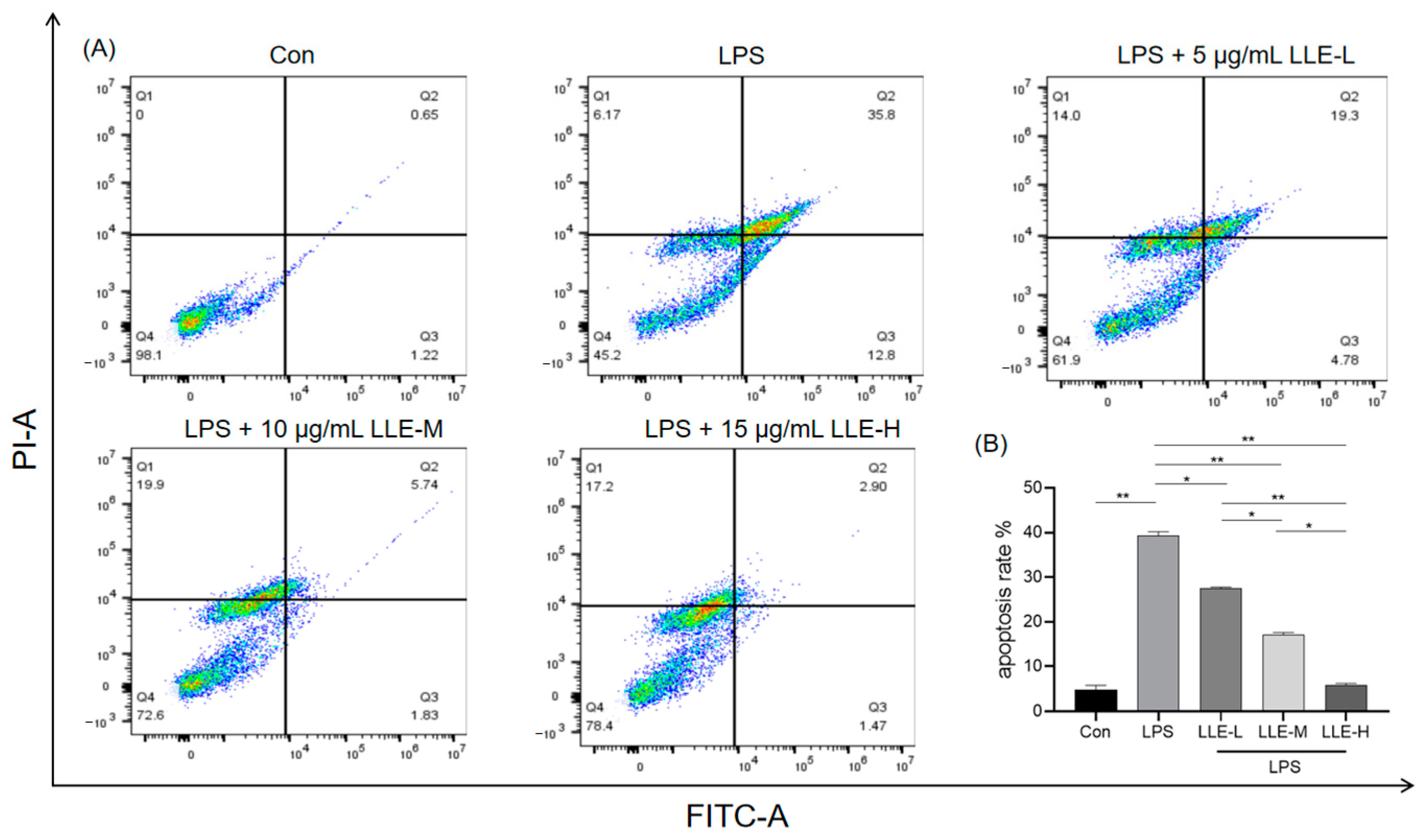
3.8.2. LLE Mitigated LPS-Induced IPEC-J2 Cell Apoptosis
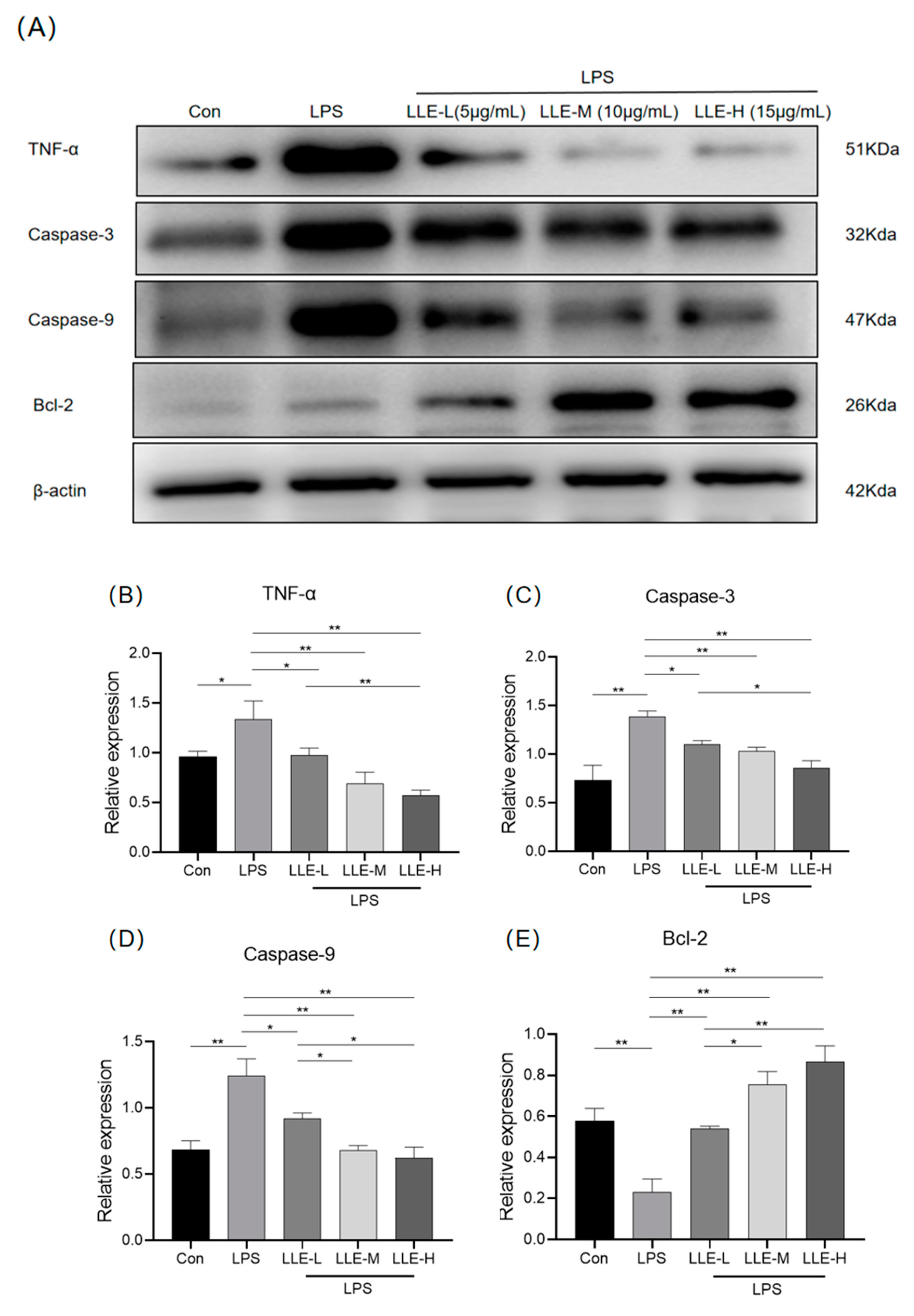
3.8.3. LLE Inhibited the Expression Levels of Apoptosis-Related Proteins Induced by LPS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, M.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Huangfu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ali, Q.; Liu, B.; Li, D.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation alleviates intestinal inflammatory diarrhea caused by oxidative stress and pyroptosis via reducing gut microbiota-derived lipopolysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, P.; Yang, Q.; Gao, X.; Gun, S.; Huang, X. Change in Long Non-Coding RNA Expression Profile Related to the Antagonistic Effect of Clostridium perfringens Type C on Piglet Spleen. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 2309–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Gao, X.; Huang, X.; Luo, R.; Yang, Q.; Yan, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Xie, K.; et al. METTL3 Regulates the Inflammatory Response in CPB2 Toxin-Exposed IPEC-J2 Cells through the TLR2/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, H.B.; Gonzalez, S.; Gustafson, M.E.; Dickenson, N.E. Differential regulation of Shigella Spa47 ATPase activity by a native C-terminal product of Spa33. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1183211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, H.; Qiu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, M.; Xiang, H.; Bo, Z.; Shen, H.; Sun, P. PA-824 inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection in vivo and in vitro by inhibiting p53 activation. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0041323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, H.M.; Fanelli, N.S.; Campbell, J.M.; Stein, H.H. Addition of Spray-Dried Plasma in Phase 2 Diets for Weanling Pigs Improves Growth Performance, Reduces Diarrhea Incidence, and Decreases Mucosal Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines. Animals 2024, 14, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Lan, T.; Zhou, C.; Gao, J.; Wu, L.; Wei, H.; Li, W.; Tang, Z.; Tang, W.; Diao, H.; et al. Nutrition strategies to control post-weaning diarrhea of piglets: From the perspective of feeds. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 17, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trung, H.D.; Hoang, H.V.; Thong, N.T.; Chitana, K.; Hoai, D.T.T.; Linh, N.Q. Antibiotics and lectin C for diarrhea control intervention in piglets and influences. AMB Express 2024, 14, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, S.; Calderón-Franco, D.; Urhan, A.; Abeel, T. Metagenomic-based surveillance systems for antibiotic resistance in non-clinical settings. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1066995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Yang, Y.; Bai, Z.; Si, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Xiao, X.; Liu, Y.; Ren, Z. The role of Traditional Chinese medicine in anti-HBV: Background, progress, and challenges. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.T.; Yao, X.; Lu, W.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Malhi, K.K.; Li, H.X.; Li, J.L. Matrine exhibits antiviral activities against PEDV by directly targeting Spike protein of the virus and inducing apoptosis via the MAPK signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Xia, J.; Xu, J.F.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J.J.; Tang, F.; Ao, H.; Peng, C. Nuciferine, an active ingredient derived from lotus leaf, lights up the way for the potential treatment of obesity and obesity-related diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, P.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Xia, J.; Liu, M.; Bai, R.; Wang, N.; Guo, L.; et al. Lotus leaf extract can attenuate salpingitis in laying hens by inhibiting apoptosis. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Lu, K.; He, Z. Lotus leaf extract inhibits ER(−) breast cancer cell migration and metastasis. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Tao, Y.; Qiu, L.; Xu, W.; Huang, X.; Wei, H.; Tao, X. Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) Leaf-Fermentation Supernatant Inhibits Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes and Suppresses Obesity in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, C.; Mamdouh, Z.M.; List, M.; Kiel, C.; Casas, A.I.; Schmidt, H. Network pharmacology: Curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xu, Y.; An, W.; Bi, S.; Xu, S.; Zhang, R.; Cong, M.; Chen, S. Mining Important Herb Combinations of Traditional Chinese Medicine against Hypertension Based on the Symptom-Herb Network Combined with Network Pharmacology. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. eCAM 2022, 2022, 5850899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, X.; Kang, Y.; Li, P.; Guo, X.; Zhao, W.; Yang, L.; Yang, Q.; Li, R.; Liu, X.; et al. Integrating network pharmacology with pharmacological research to elucidate the mechanism of modified Gegen Qinlian Decoction in treating porcine epidemic diarrhea. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, K.; Liu, Z.; Lü, Y.; Wang, C.; Yi, X.; Guo, J. Compound Kushen injection inhibits EMT of gastric cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 20, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, D.; Tian, G.; Mao, X.; He, J.; Zheng, P.; Yu, J.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; Huang, Z.; et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3) Negatively Regulates the Inflammatory Response to Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection by Inhibiting NF-κB and JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in IPEC-J2 Porcine Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, L.A.; Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. Lantibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2015, 79, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, I.C.; Alonzo, F., 3rd. Antibiotic treatment ignites a fire that lasts. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbein, S.R.S.; Mahmud, B.; Dantas, G. Antibiotic perturbations to the gut microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 772–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngogang, M.P.; Ernest, T.; Kariuki, J.; Mouliom Mouiche, M.M.; Ngogang, J.; Wade, A.; van der Sande, M.A.B. Microbial Contamination of Chicken Litter Manure and Antimicrobial Resistance Threat in an Urban Area Setting in Cameroon. Antibiotics 2020, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, H.Y.; Qin, M.; Dai, X.Y.; Yan, B.B.; Guo, X.Z.; Zhou, L.; Lin, H.B.; et al. Application of tissue culture technology of medicinal plants in sustainable development of Chinese medicinal resources. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi = China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2023, 48, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Li, H.; Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, W.; Ma, L.; Fan, Y. The effects of Fraxini cortex and Andrographis herba on Escherichia coli-induced diarrhea in chicken. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Yan, P.; Xia, J.; Guo, L.; et al. Nuciferine Regulates Immune Function and Gut Microbiota in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 939377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulhari, U.; Kundu, S.; Mugale, M.N.; Sahu, B.D. Nuciferine alleviates intestinal inflammation by inhibiting MAPK/NF-κB and NLRP3/Caspase 1 pathways in vivo and in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 115, 109613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, J.; Muhammad, I.; Cao, C.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Li, C.; Liu, F. Dihydromyricetin attenuates Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide-induced ileum injury in chickens by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and TLR4/NF-κB signalling pathway. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fu, R.; Meng, Y.; Liang, J.; Xue, W.; Hu, H.; Meng, J.; Zhang, M. pH Sensitive Quercetin Nanoparticles Ameliorate DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Colon-Specific Delivery. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2300051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ai, X.; Duan, Y.; Xue, M.; He, W.; Wang, C.; Xu, T.; Xu, M.; Liu, B.; Li, C.; et al. Kaempferol ameliorates H9N2 swine influenza virus-induced acute lung injury by inactivation of TLR4/MyD88-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, T.; Liu, P.; Li, H.; Bian, Y.; Liu, Z. Kaempferol relieves the DSS-induced chronic colitis in C57BL/6J mice, alleviates intestinal angiogenesis, and regulates colonic microflora structure. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 107, 105646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetsko, T. Bacterial Intestinal Infections of Swine. Sci. Tech. Bull. State Sci. Res. Control Inst. Vet. Med. Prod. Fodd. Addit. Inst. Anim. Biol. 2022, 23, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhal, R.; Kataria, R. Biofilm patterns in gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 251, 126829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Luo, D.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Cen, S.; Huang, M.; Jiang, X.; Zhong, G.; Zeng, W. The roles and potential mechanisms of plant polysaccharides in liver diseases: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1400958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Yeh, W.C.; Ohashi, P.S. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 2008, 42, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.H.; Zhao, X.P.; Wang, B.J.; Yang, D.L.; Hao, L.J. FADD and TRADD expression and apoptosis in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 6, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, N.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Tam, S.; Xiao, D.; Liu, S.; Wen, F.; et al. A Nuclear Long Non-Coding RNA LINC00618 Accelerates Ferroptosis in a Manner Dependent upon Apoptosis. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2021, 29, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Li, H.; Ren, T.; Kim, I.H. Protective effects of methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) on barrier function injury of porcine intestinal epithelial cells (IPEC-J2) induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 103, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Bastin, A.R.; Ghahremani, H.; Doustimotlagh, A.H. The effects of rosmarinic acid on oxidative stress parameters and inflammatory cytokines in lipopolysaccharide-induced peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 3557–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrache, A.; Micheau, O. TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand: Non-Apoptotic Signalling. Cells 2024, 13, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.X.; Lu, C.; Wang, B.; Ren, X.Y.; Xu, K. Effects of rapamycin on osteosarcoma cell proliferation and apoptosis by inducing autophagy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Zhu, H.; Huang, R.; Yan, B.; Xu, B.; Shi, Y.; Mao, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Roles of Cyt-c/Caspase-9/Caspase-3/Bax/Bcl-2 pathway in Cd-induced testicular injury in rats and the protective effect of quercetin. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2024, 237, 107561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Wu, F.; Zheng, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X. Kaempferol attenuates retinal ganglion cell death by suppressing NLRP1/NLRP3 inflammasomes and caspase-8 via JNK and NF-κB pathways in acute glaucoma. Eye 2019, 33, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model | Component Name | Component Type | Expected RT | Area | Retention Time | Adduct/Charge | Precursor Mass | Found At Mass | Mass Error (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| positive | Catechin | Quantifiers | 3.44 | 3.15 × 105 | 3.69 | [M + H]+ | 113.963 | 113.963 | 3.3 |
| positive | Kaempferol | Quantifiers | 5.36 | 1.99 × 105 | 5.35 | [M + H]+ | 476.305 | 476.3042 | 2.5 |
| positive | Nuciferine | Quantifiers | 6.94 | 8.43 × 104 | 6.95 | [M + H]+ | 296.163 | 296.1633 | 1 |
| positive | Quercetin | Quantifiers | 13.99 | 4.17 × 105 | 14 | [M + H]+ | 496.337 | 496.3376 | 2.6 |
| negative | Leucodelphinidin | Quantifiers | 4.15 | 7.07 × 105 | 4.13 | [M − H]− | 121.029 | 121.0292 | 7.1 |
| MOL ID | Molecule Name | Oral Bioavailability (%) | Drug-Likeness |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000098 | Quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | 49.60 | 0.31 |
| MOL000359 | Sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 |
| MOL006405 | (1S)-1-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-2-methyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinoline-6,7-diol | 67.14 | 0.23 |
| MOL003578 | Cycloartenol | 38.69 | 0.78 |
| MOL007206 | Armepavine | 69.31 | 0.29 |
| MOL007207 | Machiline | 79.64 | 0.24 |
| MOL007210 | o-Nornuciferine | 33.52 | 0.36 |
| MOL007213 | Nuciferine | 34.43 | 0.40 |
| MOL007214 | (+)-Leucocyanidin | 37.61 | 0.27 |
| MOL007217 | Leucodelphinidin | 30.02 | 0.31 |
| MOL007218 | Remerin | 40.75 | 0.52 |
| MOL000073 | ent-Epicatechin | 48.96 | 0.24 |
| MOL000096 | (-)-Catechin | 49.68 | 0.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, B.; Li, Q.; Huang, X.; Lin, Z. Network Pharmacology and In Vitro Experimental Validation Reveal the Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Lotus Leaf Extract in Treating Inflammatory Diarrhea in Pigs. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050314
Zheng Y, Zheng J, Wang J, Li J, Liu J, Zheng B, Li Q, Huang X, Lin Z. Network Pharmacology and In Vitro Experimental Validation Reveal the Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Lotus Leaf Extract in Treating Inflammatory Diarrhea in Pigs. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050314
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yu, Jiana Zheng, Jiao Wang, Junxin Li, Jiali Liu, Bohan Zheng, Qinjin Li, Xiaohong Huang, and Zhaoyan Lin. 2025. "Network Pharmacology and In Vitro Experimental Validation Reveal the Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Lotus Leaf Extract in Treating Inflammatory Diarrhea in Pigs" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050314
APA StyleZheng, Y., Zheng, J., Wang, J., Li, J., Liu, J., Zheng, B., Li, Q., Huang, X., & Lin, Z. (2025). Network Pharmacology and In Vitro Experimental Validation Reveal the Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Lotus Leaf Extract in Treating Inflammatory Diarrhea in Pigs. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050314







