Adipocytokine Protein Expression from Visceral Fat Differs Significantly Based on Diet, Sex, and Age in C3H/HeJ Mice Fed Long-Term, High-Fat Diets, ± Ammonium-Hydroxide-Supplemented Dietary Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Study Design
2.2. WAT Extraction
2.3. Protein Extraction from Adipose Tissue
2.4. Protein Quantification
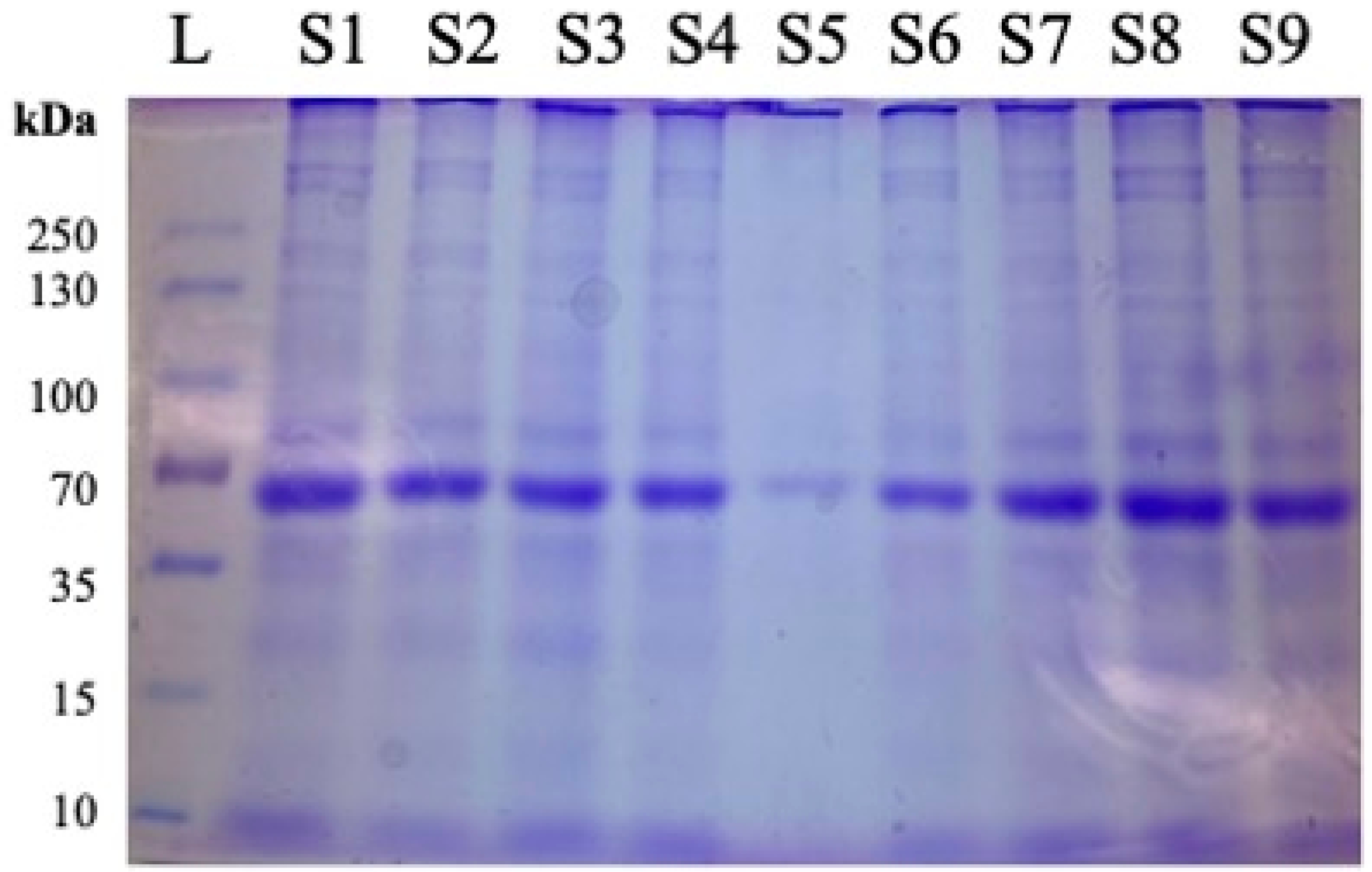
2.5. SDS-PAGE with Coomassie Brilliant Blue Staining
2.6. ELISA
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
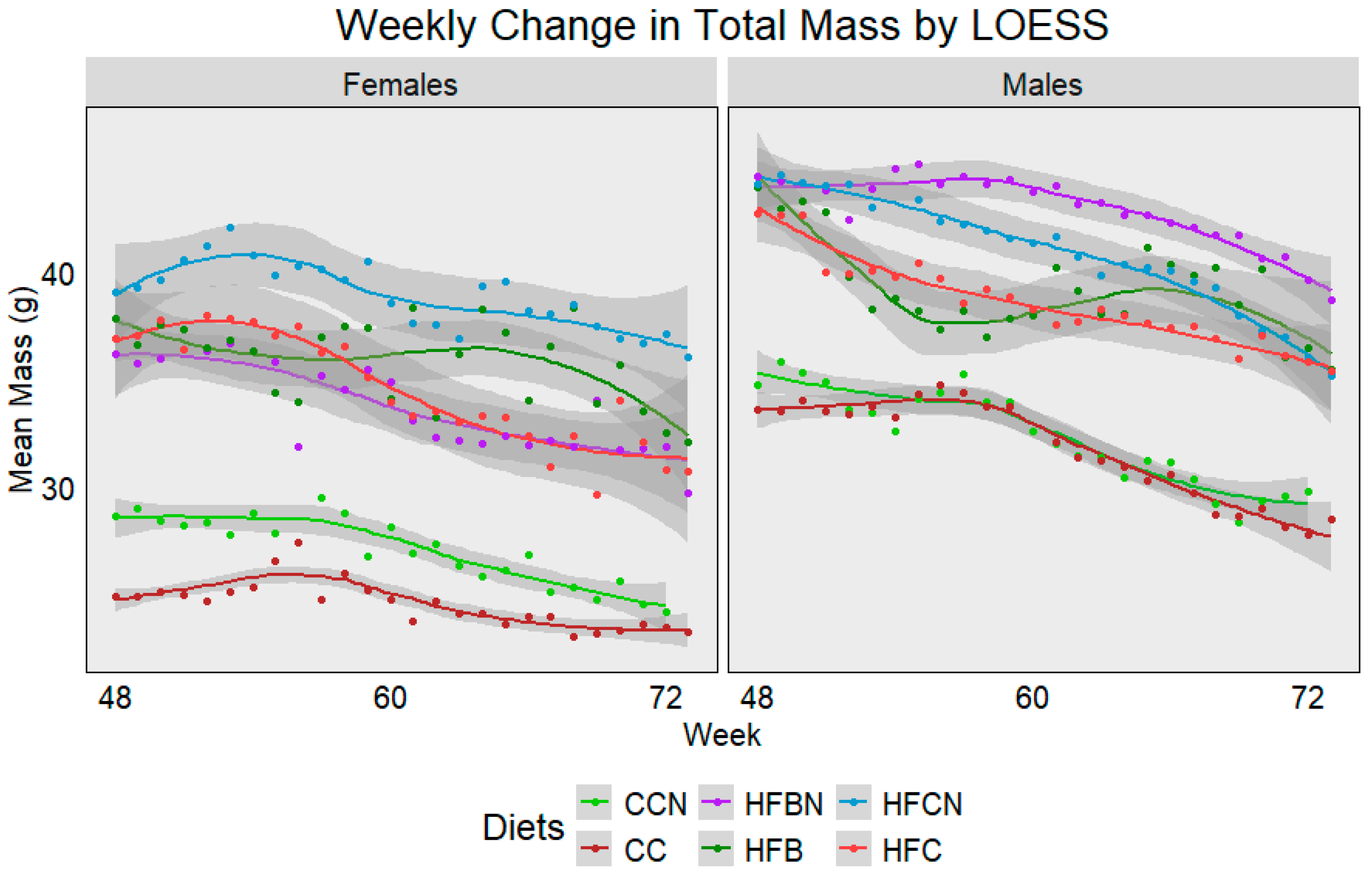
3.1. Trends in Total Mass from 12 to 18 Months
3.2. Adipocytokine Expression Levels
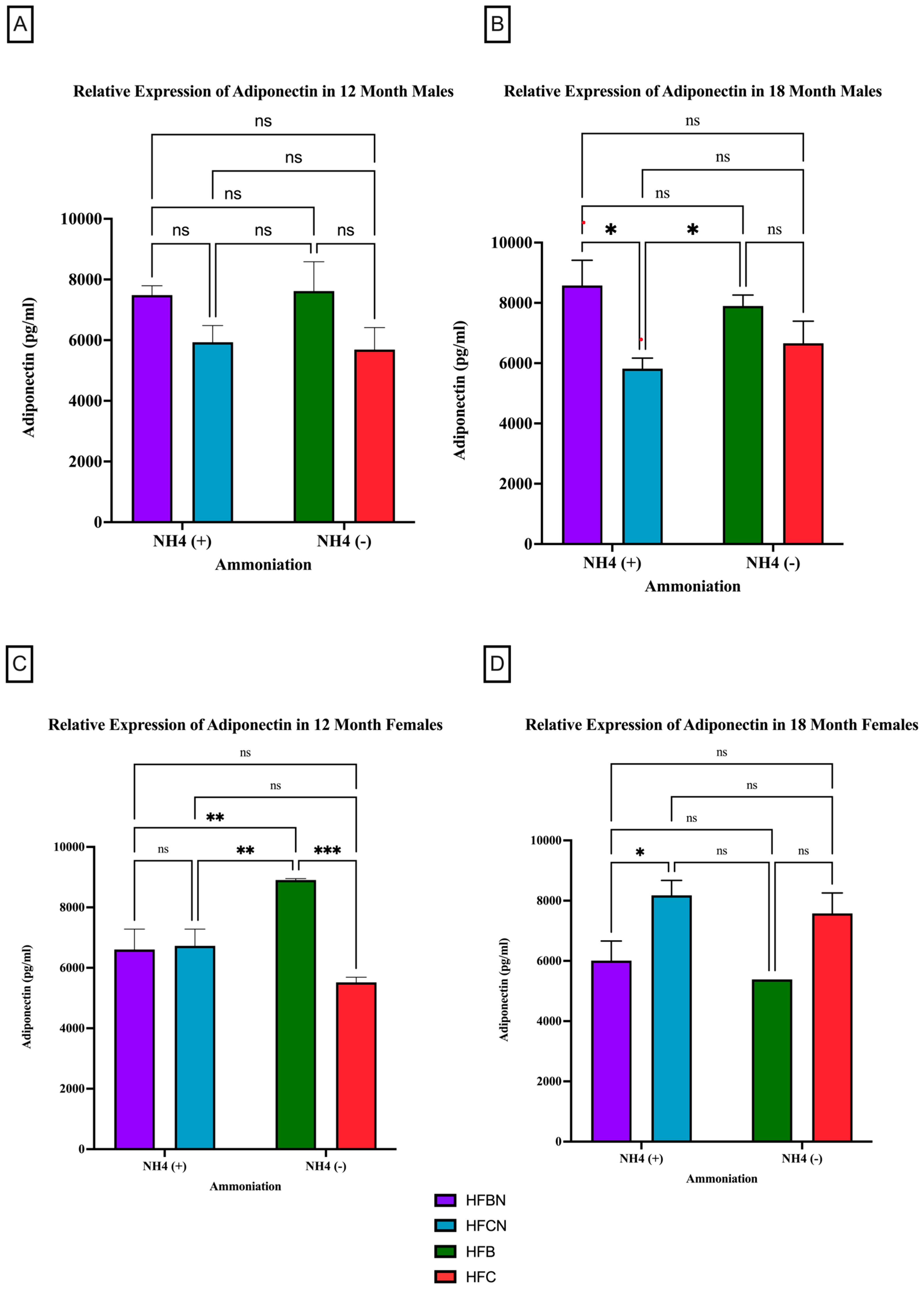
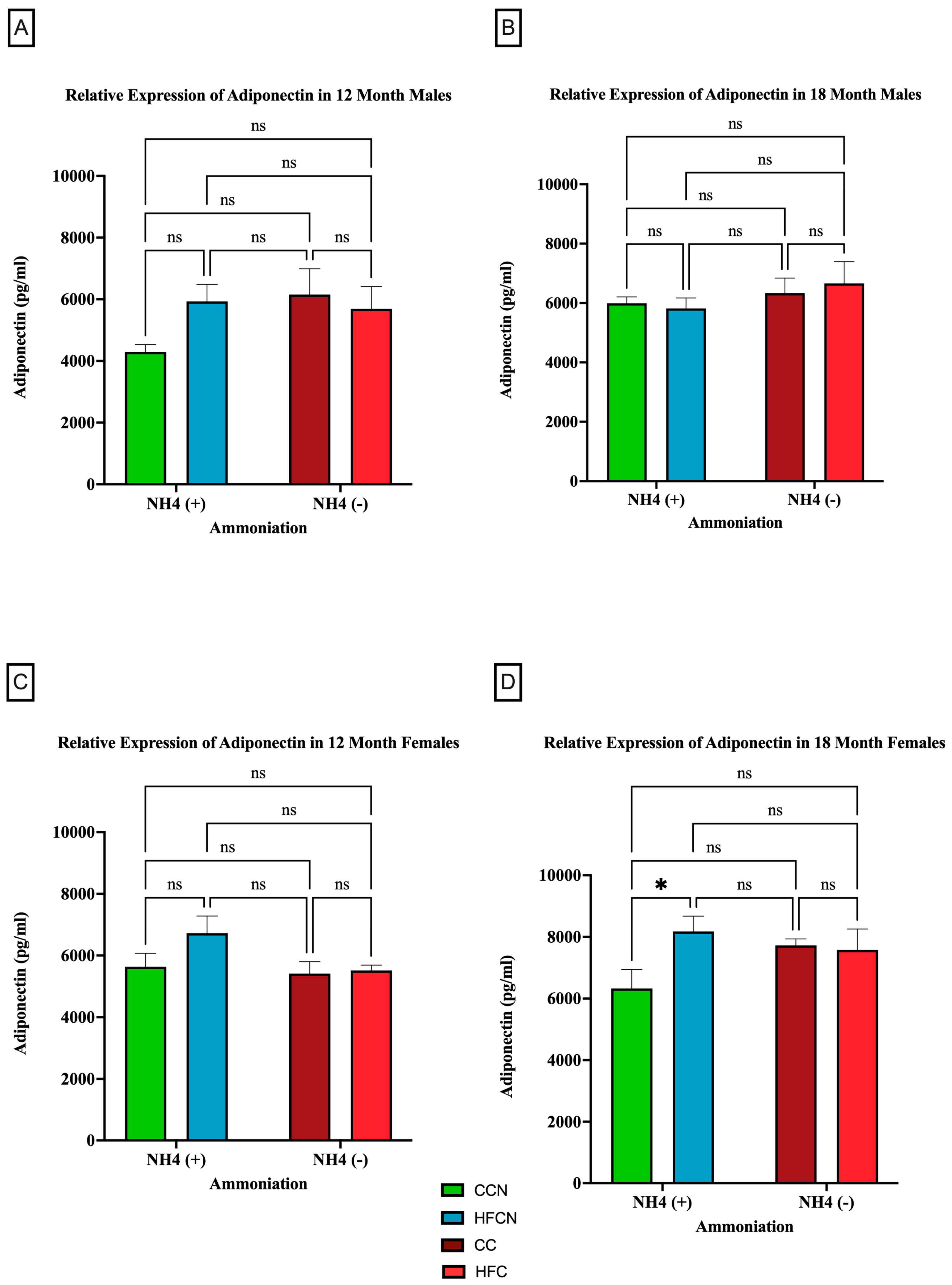
3.2.1. Adiponectin
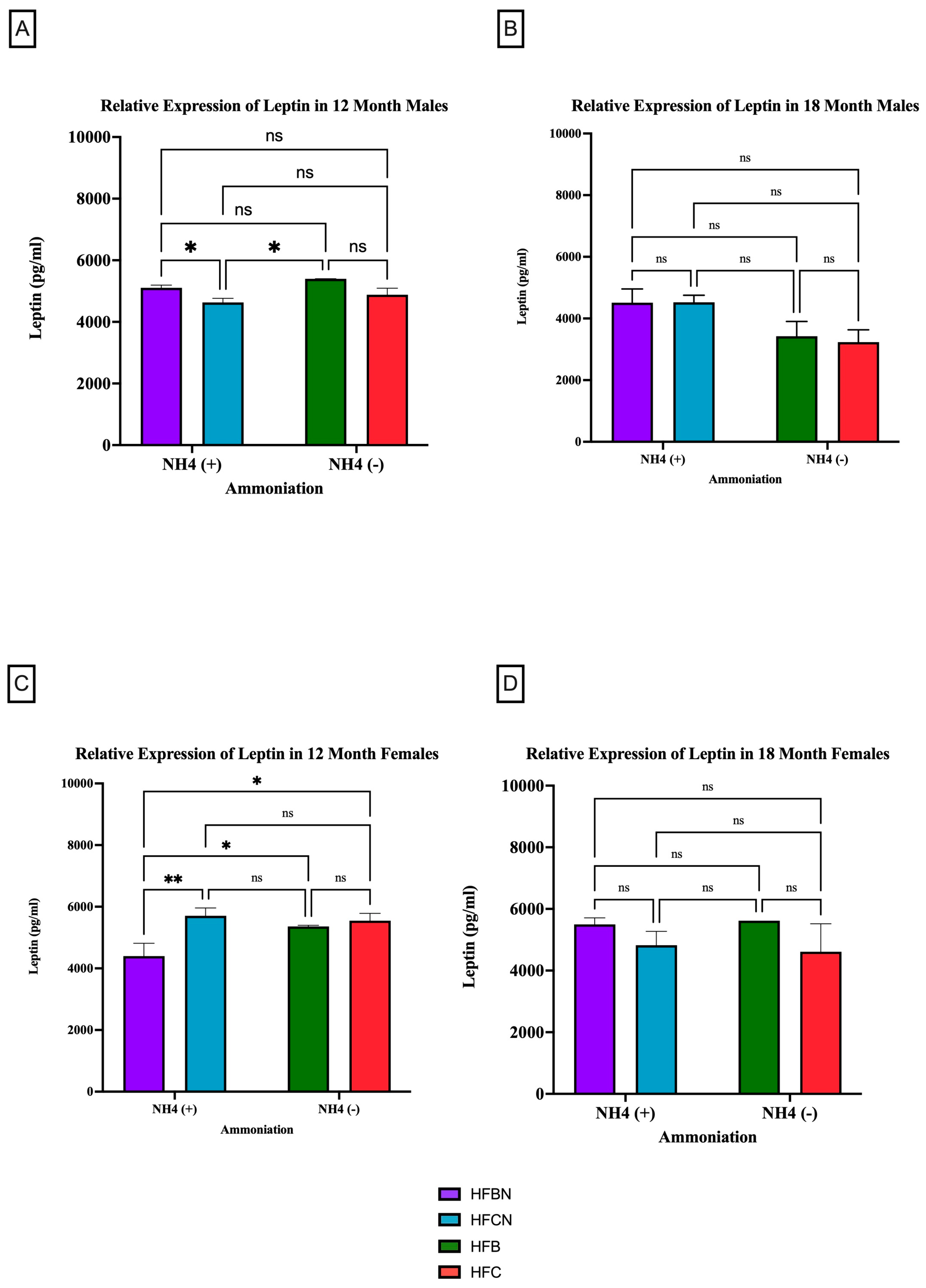
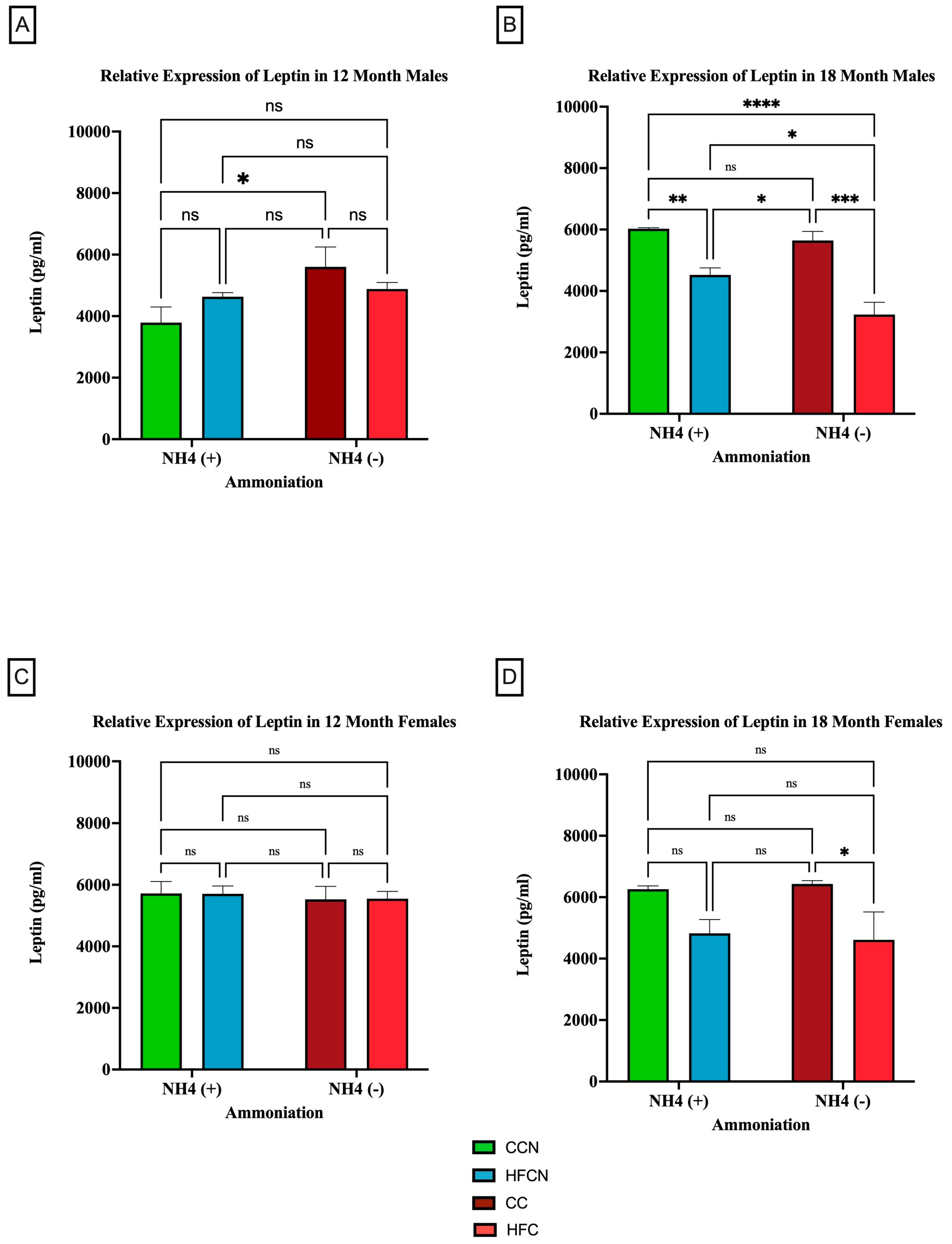
3.2.2. Leptin
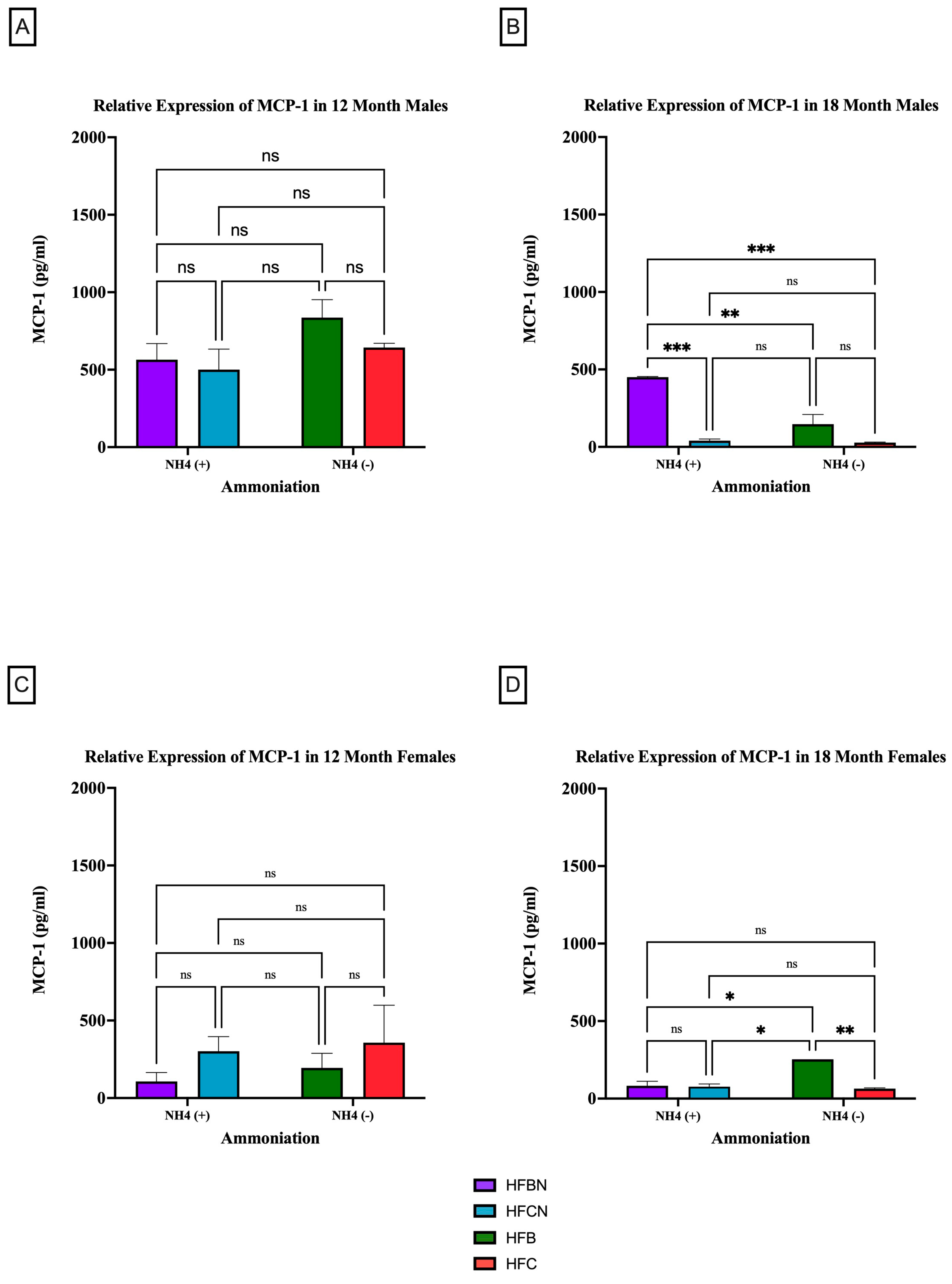
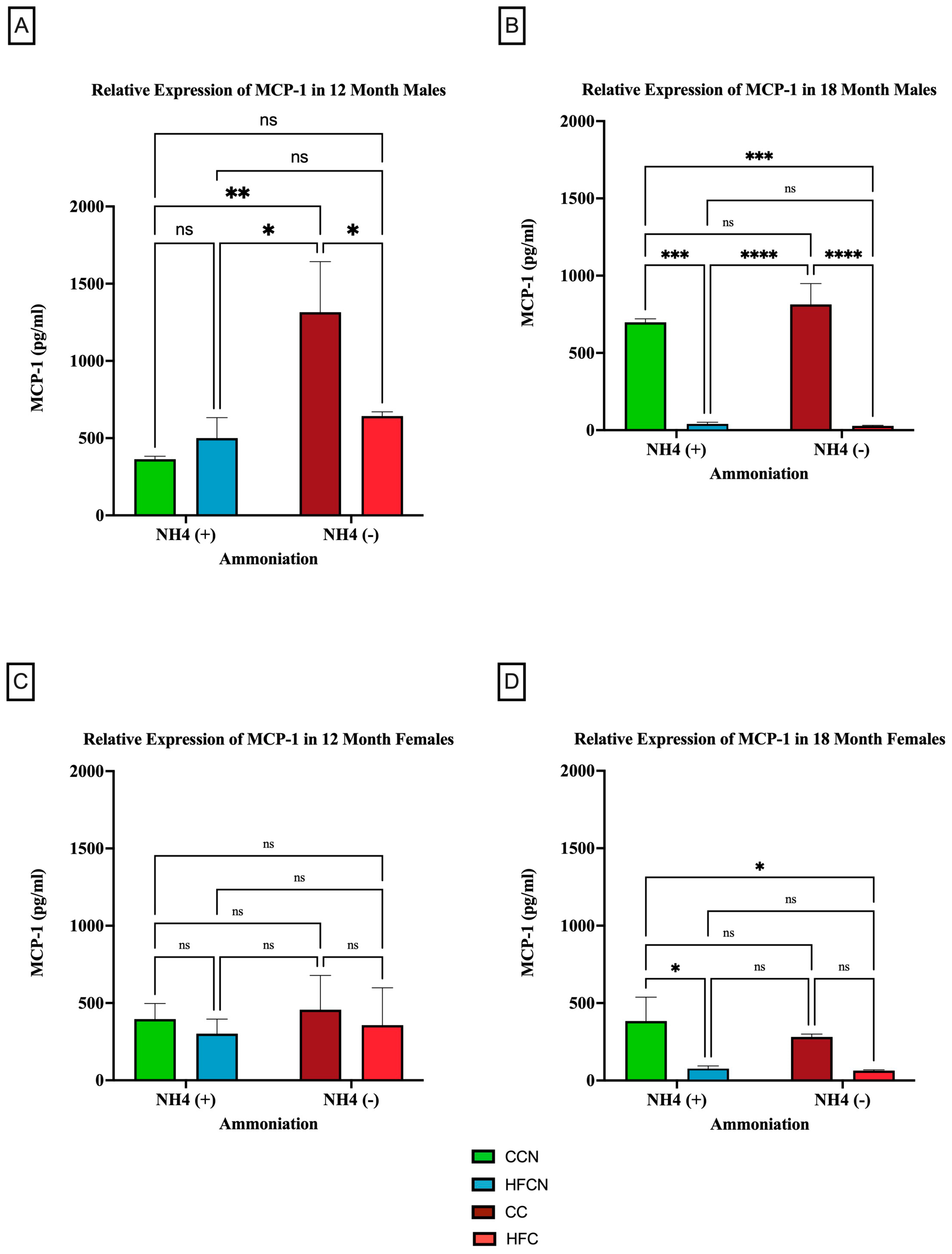
3.2.3. MCP-1
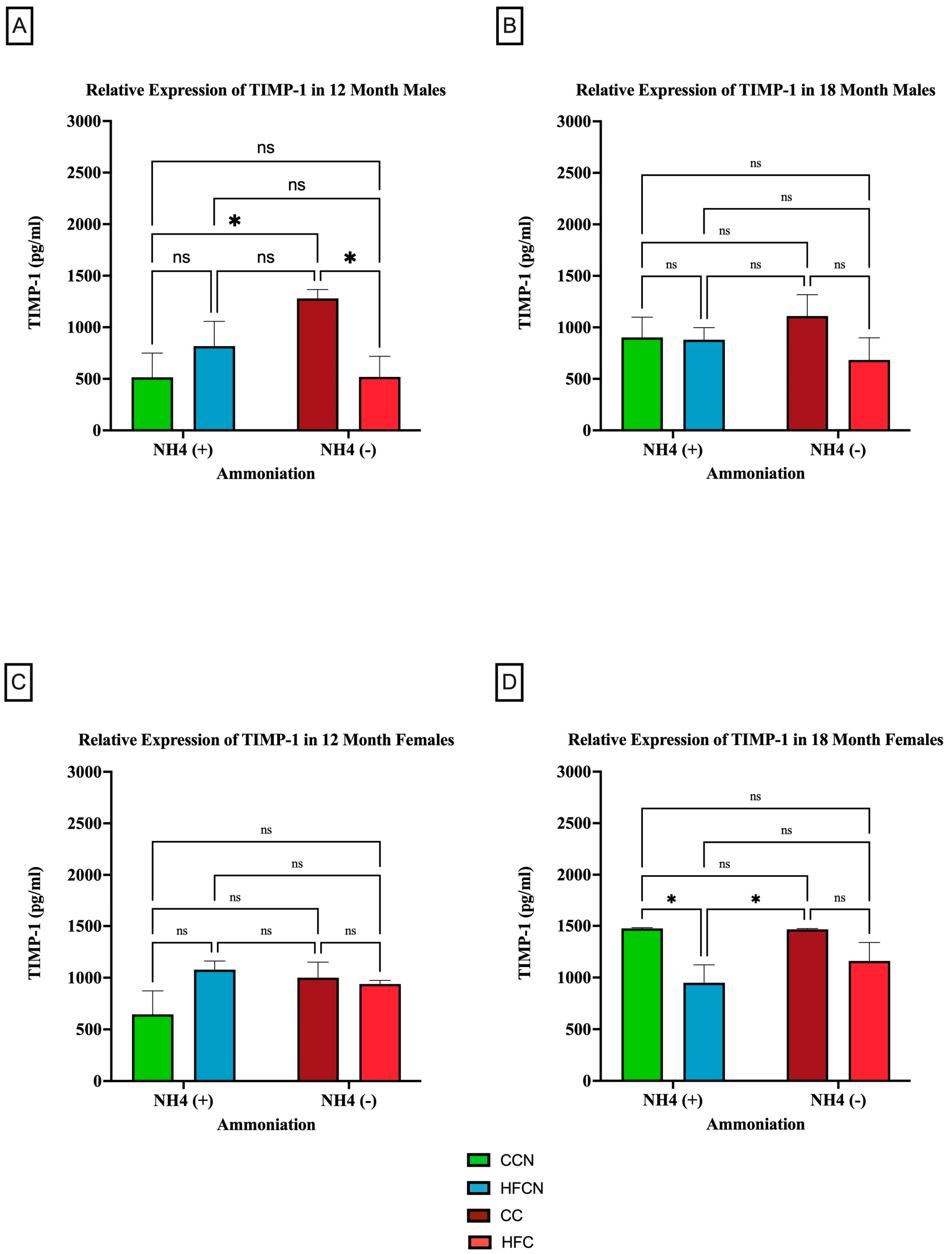
3.2.4. TIMP-1
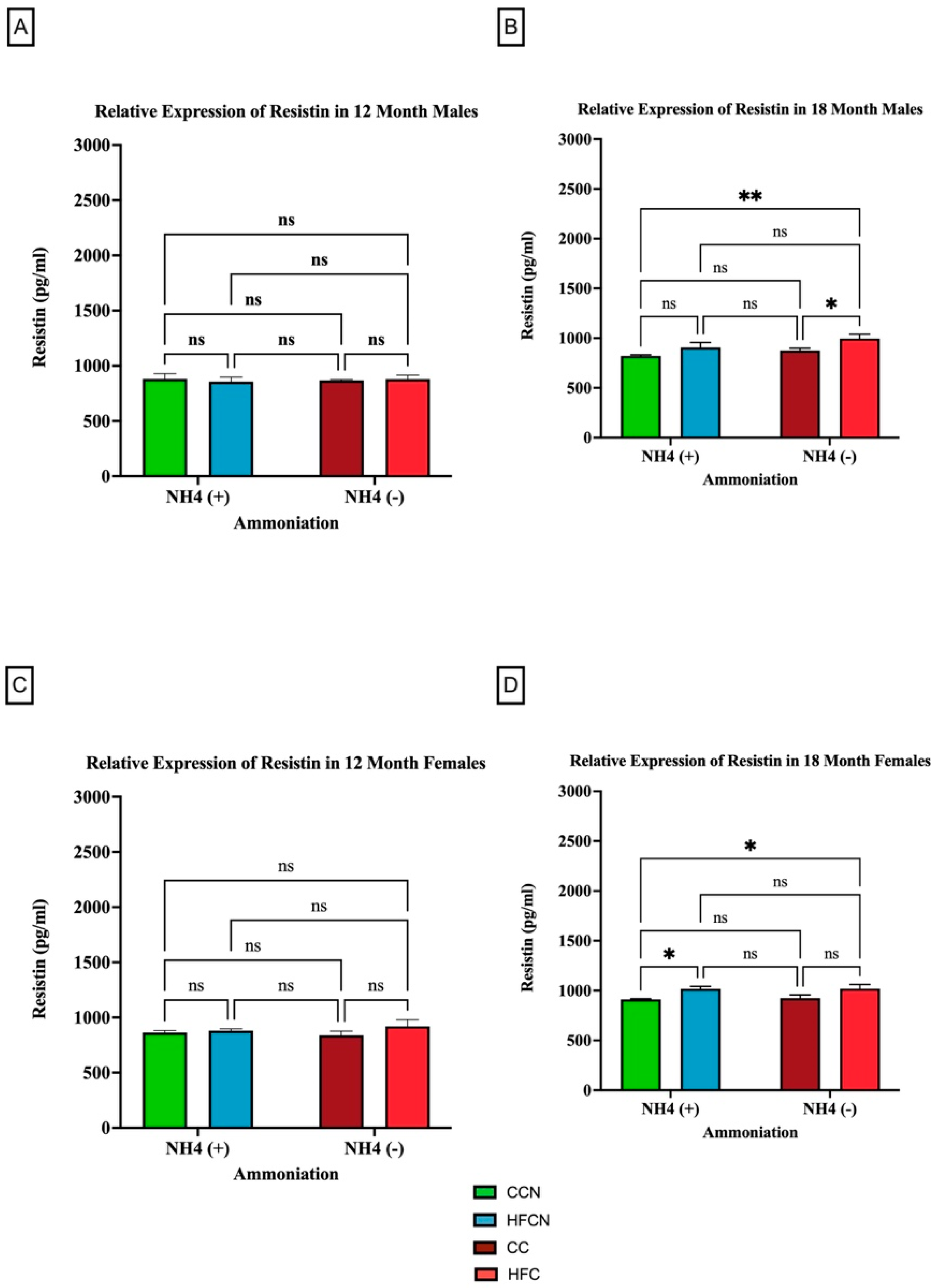
3.2.5. Resistin
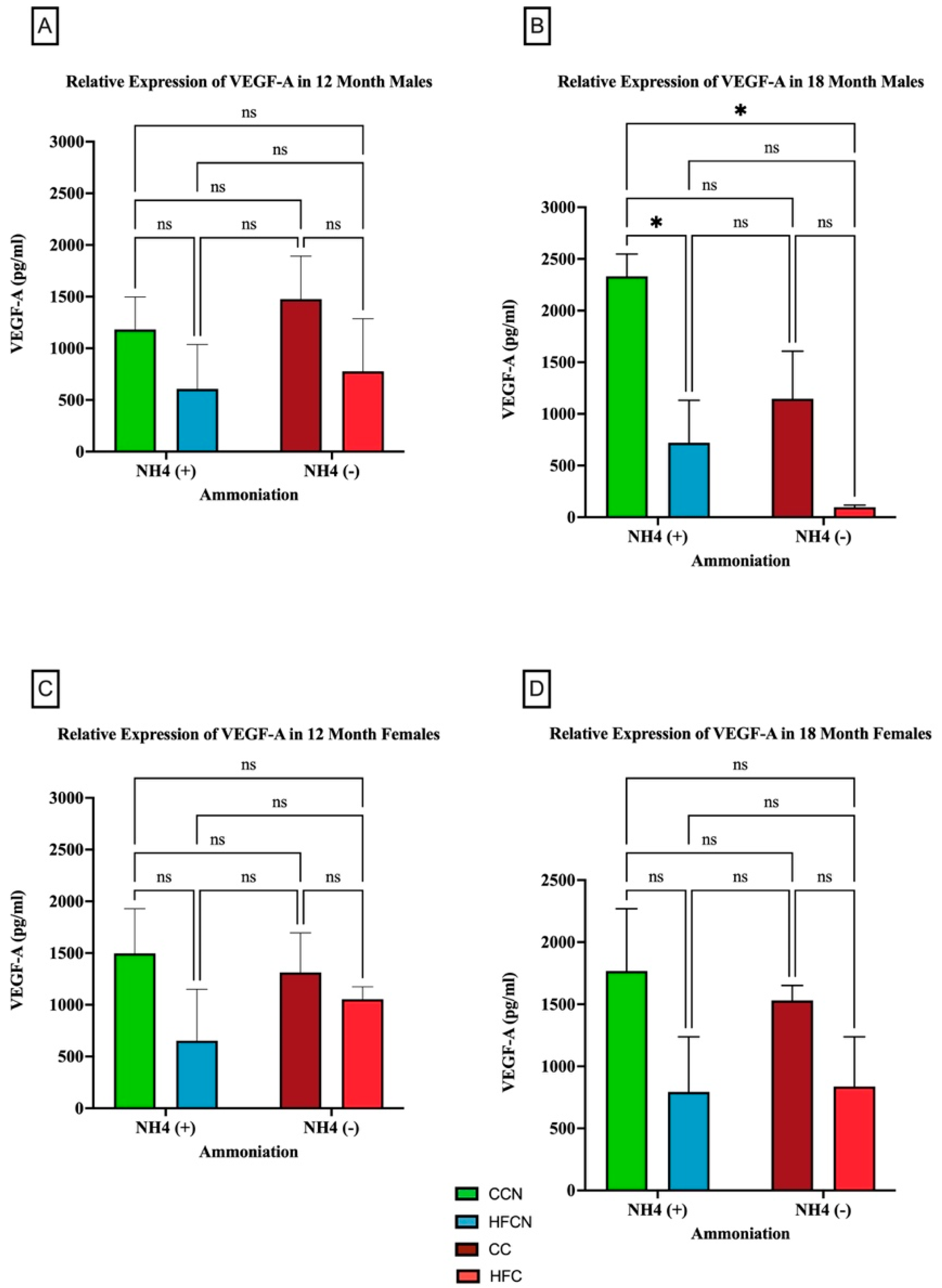
3.2.6. VEGF-A
4. Discussion
4.1. Adiponectin
4.2. Leptin
4.3. MCP-1
4.4. TIMP-1
4.5. Resistin
4.6. VEGF-A
4.7. Microbiome Changes and High-Fat Diets ± AHE
4.8. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ansah, J.P.; Chiu, C.T. Projecting the chronic disease burden among the adult population in the United States using a multi-state population model. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1082183. [Google Scholar]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fagherazzi, G.; Vilier, A.; Bonnet, F.; Lajous, M.; Balkau, B.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Clavel-Chapelon, F. Dietary acid load and risk of type 2 diabetes: The E3N-EPIC cohort study. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Uenishi, K. Association between dietary acid-base load and cardiometabolic risk factors in young Japanese women. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 642–651. [Google Scholar]
- Buclin, T.; Cosma, M.; Appenzeller, M.; Jacquet, A.F.; Decosterd, L.A.; Biollaz, J.; Burckhardt, P. Diet acids and alkalis influence calcium retention in bone. Osteoporos. Int. 2001, 12, 493–499. [Google Scholar]
- Carnauba, R.A.; Baptistella, A.B.; Paschoal, V.; Hübscher, G.H. Diet-Induced Low-Grade Metabolic Acidosis and Clinical Outcomes: A Review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, I.; Maher, T.; Hulter, H.N.; Schambelan, M.; Sebastian, A. Effect of diet on plasma acid-base composition in normal humans. Kidney Int. 1983, 24, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Tomás, T.; Rueda-Robles, A.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Álvarez-Mercado, A.I. Nutrition and cellular senescence in obesity-related disorders. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 99, 108861. [Google Scholar]
- Menikdiwela, K.R.; Guimarães, J.P.T.; Scoggin, S.; Gollahon, L.S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Dietary pH Enhancement Improves Metabolic Outcomes in Diet-Induced Obese Male and Female Mice: Effects of Beef vs. Casein Proteins. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (US); Institute of Medicine (US). The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health. In U.S. Health in International Perspective: Shorter Lives, Poorer Health; Woolf, S.H., Aron, L., Eds.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara, C.M.; Flint, A.J.; de Gonzalez, A.B.; Bernstein, L.; Brotzman, M.; MacInnis, R.J.; Moore, S.C.; Robien, K.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Singh, P.N.; et al. Association between class III obesity (BMI of 40–59 kg/m2) and mortality: A pooled analysis of 20 prospective studies. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001673. [Google Scholar]
- The Global BMI Mortality Collaboration; Di Angelantonio, E.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Wormser, D.; Gao, P.; Kaptoge, S.; de Gonzalez, A.B.; Cairns, B.J.; Huxley, R.; Jackson, C.L.; et al. Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: Individual-participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. Lancet 2016, 388, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, B.T.; Morais, J.A.; Santosa, S. Obesity and ageing: Two sides of the same coin. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, J.K.; Raghunath, M. ’Obesageing’: Linking obesity & ageing. Indian. J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salvestrini, V.; Sell, C.; Lorenzini, A. Obesity May Accelerate the Aging Process. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.C.; Kane, J.; Slaton, A.; Abramowitz, M.K. Associations of Metabolic Syndrome and Abdominal Obesity with Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis among US Adults. Kidney360 2022, 3, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; O’Keefe, J. Low-grade metabolic acidosis as a driver of chronic disease: A 21st century public health crisis. Open Heart 2021, 8, e001730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeva, M.M.; Souto, G. Diet-induced metabolic acidosis. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, B.; Gollahon, L. The Effects of Obesity on Sex, Aging, and Cancer Development in a Longitudinal Study of High-Fat-Diet-Fed C3H/HeJ Mice. Obesities 2024, 4, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, B.; Gollahon, L. The Modification of Dietary Protein with Ammonium Hydroxide Enhancement Improves Longevity and Metabolic Outcomes in a Sex-Dependent Manner. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, E.C.; Brown, A.M.V.; Salazar, M.M.; Barr, B.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Gollahon, L.S. Microbiome Taxonomic and Functional Differences in C3H/HeJ Mice Fed a Long-Term High-Fat Diet with Beef Protein ± Ammonium Hydroxide Supplementation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.-L.; Gong, Y.; Qi, Y.-J.; Shao, Z.-M.; Jiang, Y.-Z. Effects of dietary intervention on human diseases: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubtasim, N.; Gollahon, L. Characterizing 3T3-L1 MBX Adipocyte Cell Differentiation Maintained with Fatty Acids as an In Vitro Model to Study the Effects of Obesity. Life 2023, 13, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjære, E.; Andersen, C.; Myrmel, L.S.; Petersen, R.K.; Hansen, J.B.; Tastesen, H.S.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Brünner, N.; Kristiansen, K.; Madsen, L.; et al. Tissue Inhibitor Of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 Is Required for High-Fat Diet-Induced Glucose Intolerance and Hepatic Steatosis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.K.; Doh, K.-O.; Son, J.E.; Park, J.G.; Bae, Y.; Choi, S.; Nelson, S.M.L.; Cowling, R.; Nagy, K.; Michael, I.P.; et al. Adipose vascular endothelial growth factor regulates metabolic homeostasis through angiogenesis. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlsten, D.; Metten, P.; Crabbe, J.C. A rating scale for wildness and ease of handling laboratory mice: Results for 21 inbred strains tested in two laboratories. Genes Brain Behav. 2003, 2, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carswell, K.A.; Lee, M.J.; Fried, S.K. Culture of isolated human adipocytes and isolated adipose tissue. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 806, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.A.; Scherer, P.E. Mouse Adipose Tissue Protein Extraction. Bio Protoc. 2020, 10, e3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, R.A.M.; Chen, Z.J. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Measurement: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 17, pp. 160–167. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, J.K. A mouse model of diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Mtor Methods Protoc. 2012, 821, 421–433. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.M.; Doss, H.M.; Kim, K.S. Multifaceted Physiological Roles of Adiponectin in Inflammation and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.P. The association of serum leptin levels with metabolic diseases. Ci Ji Yi Xue Za Zhi 2017, 29, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadge, A.A.; Khaire, A.A. Leptin as a predictive marker for metabolic syndrome. Cytokine 2019, 121, 154735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Anshita, D.; Ravichandiran, V. MCP-1: Function, regulation, and involvement in disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101 Pt B, 107598. [Google Scholar]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar]
- Ries, C. Cytokine functions of TIMP-1. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 659–672. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, E.; Dassé, E.; Haye, B.; Petitfrère, E. TIMPs as multifacial proteins. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2004, 49, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassina, G.; Ferrari, N.; Brigati, C.; Benelli, R.; Santi, L.; Noonan, D.M.; Albini, A. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases: Regulation and biological activities. Clin. Exp. Metast. 2000, 18, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Chavey, C.; Mari, B.; Monthouel, M.-N.; Bonnafous, S.; Anglard, P.; Van Obberghen, E.; Tartare-Deckert, S. Matrix metalloproteinases are differentially expressed in adipose tissue during obesity and modulate adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11888–11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steppan, C.M.; Bailey, S.T.; Bhat, S.; Brown, E.J.; Banerjee, R.R.; Wright, C.M.; Patel, H.R.; Ahima, R.S.; Lazar, M.A. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 2001, 409, 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Jamaluddin, M.S.; Weakley, S.M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Resistin: Functional roles and therapeutic considerations for cardiovascular disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 622–632. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor system: Physiological functions in angiogenesis and pathological roles in various diseases. J. Biochem. 2012, 153, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yancy, W.S., Jr.; Olsen, M.K.; Dudley, T.; Westmaln, E.C. Acid-base analysis of individuals following two weight loss diets. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues Neto Angéloco, L.; Arces de Souza, G.C.; Almeida Romão, E.; Garcia Chiarello, P. Alkaline Diet and Metabolic Acidosis: Practical Approaches to the Nutritional Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, E.; Engberink, M.F.; Brink, E.J.; van Baak, M.A.; Joosten, M.M.; Gans, R.O.B.; Navis, G.; Bakker, S.J.L. Dietary acid load and metabolic acidosis in renal transplant recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1811–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Wang, Q.; Yi, S.; Liu, X.; Jin, H.; Xu, J.; Wen, G.; Zhu, J.; Tuo, B. The source of the fat significantly affects the results of high-fat diet intervention. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Laborde-Cárdenas, C.C.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The Role of Adipokines in Health and Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, P.; Bouchard, B. The Impact of Aging on Adipose Function and Adipokine Synthesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefzadeh, M.J.; Schafer, M.J.; Hooten, N.N.; Atkinson, E.J.; Evans, M.K.; Baker, D.J.; Quarles, E.K.; Robbins, P.D.; Ladiges, W.C.; LeBrasseur, N.K.; et al. Circulating levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 as a potential measure of biological age in mice and frailty in humans. Aging Cell 2018, 17, e12706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, J.; Hirose, H.; Ishikawa, S. Tissue Inhibitor of Matrix Metalloproteinase 1 Increases With Ageing and Can Be Associated With Stroke—Nested Case-Control Study. Circ. Rep. 2019, 1, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunewald, M.; Kumar, S.; Sharife, H.; Volinsky, E.; Gileles-Hillel, A.; Licht, T.; Permyakova, A.; Hinden, L.; Azar, S.; Friedmann, Y.; et al. Counteracting age-related VEGF signaling insufficiency promotes healthy aging and extends life span. Science 2021, 373, eabc8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquarone, E.; Monacelli, F.; Borghi, R.; Nencioni, A.; Odetti, P. Resistin: A reappraisal. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2019, 178, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Memili, A.; Chen, H.-H.; Highland, H.M.; Polikowsky, H.G.; Anwar, M.Y.; Laing, S.T.; Lee, M.; McCormick, J.B.; Fisher-Hoch, S.P.; et al. Sex-specific associations between adipokine profiles and carotid-intima media thickness in the Cameron County Hispanic Cohort (CCHC). Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cossins, B.C.; Munckhof, I.v.D.; Rutten, J.H.W.; van der Graaf, M.; Stienstra, R.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Netea, M.G.; Li, Y.; Riksen, N.P. Sex-specific Association Between Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Vascular and Metabolic Complications of Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 2537–2549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kirichenko, T.V.; Markina, Y.V.; Bogatyreva, A.I.; Tolstik, T.V.; Varaeva, Y.R.; Starodubova, A.V. The Role of Adipokines in Inflammatory Mechanisms of Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, V.; Azadbakht, L. Specific dietary patterns and concentrations of adiponectin. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2015, 20, 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Tobe, K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, R.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, driver or passenger on the road to insulin sensitivity? Mol. Metab. 2013, 2, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnard, C.; Durand, A.; Vidal, H.; Rieusset, J. Changes in adiponectin, its receptors and AMPK activity in tissues of diet-induced diabetic mice. Diabetes Metab. 2008, 34, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Barnea, M.; Shamay, A.; Stark, A.H.; Madar, Z. A high-fat diet has a tissue-specific effect on adiponectin and related enzyme expression. Obesity 2006, 14, 2145–2153. [Google Scholar]
- Yagi, T.; Toyoshima, Y.; Tokita, R.; Taguchi, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Takahashi, S.-I.; Kato, H.; Minami, S. Low-protein diet enhances adiponectin secretion in rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-Y.; van de Wall, E.; Laplante, M.; Azzara, A.; Trujillo, M.E.; Hofmann, S.M.; Schraw, T.; Durand, J.L.; Li, H.; Li, G.; et al. Obesity-associated improvements in metabolic profile through expansion of adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2621–2637. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chai, W.; Morimoto, Y.; Cooney, R.V.; Franke, A.A.; Shvetsov, Y.B.; Le Marchand, L.; Haiman, C.A.; Kolonel, L.N.; Goodman, M.T.; Maskarinec, G. Dietary Red and Processed Meat Intake and Markers of Adiposity and Inflammation: The Multiethnic Cohort Study. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2017, 36, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ley, S.H.; Sun, Q.; Willett, W.C.; Eliassen, A.H.; Wu, K.; Pan, A.; Grodstein, F.; Hu, F.B. Associations between red meat intake and biomarkers of inflammation and glucose metabolism in women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, A.T.; ElZalabany, M.; Salama, M.; Ansari, B. Serum leptin concentrations during severe protein-energy malnutrition: Correlation with growth parameters and endocrine function. Metabolism 2000, 49, 819–825. [Google Scholar]
- Aisike, G.; Kuerbanjiang, M.; Muheyati, D.; Zaibibuli, K.; Lv, M.-X.; Han, J. Correlation analysis of obesity phenotypes with leptin and adiponectin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17718. [Google Scholar]
- Esin, K.; Batirel, S.; Ülfer, G.; Yigit, P.; Sanlier, N. Association of Serum Irisin Levels with Body Composition, Metabolic Profile, Leptin, and Adiponectin Levels in Lean and Obese Children. Medicina 2023, 59, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Considine, R.V.; Sinha, M.K.; Heiman, M.L.; Kriauciunas, A.; Stephens, T.W.; Nyce, M.R.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Marco, C.C.; McKee, L.J.; Bauer, T.L.; et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 292–295. [Google Scholar]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Tchernova, J.; Whincup, P.; Lowe, G.D.O.; Kelly, A.; Rumley, A.; Wallace, A.M.; Sattar, N. Plasma leptin: Associations with metabolic, inflammatory and haemostatic risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2007, 191, 418–426. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, A.A.; Do Carmo, J.; Dubinion, J.; Hall, J.E. The role of the sympathetic nervous system in obesity-related hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2009, 11, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Chiriacò, M.; Nesti, L.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Golay, A.; Nazare, J.-A.; Anderwald, C.-H.; Mitrakou, A.; Bizzotto, R.; Mari, A.; Natali, A. At any Level of Adiposity, Relatively Elevated Leptin Concentrations Are Associated With Decreased Insulin Sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Puurunen, V.P.; Lepojärvi, E.; Piira, O.; Hedberg, P.; Junttila, M.; Ukkola, O.; Huikuri, H. High plasma leptin levels are associated with impaired diastolic function in patients with coronary artery disease. Peptides 2016, 84, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.E.; Won, S.; Mok, Y.; Cui, W.; Kimm, H.; Jee, S.H. Association of the leptin to high-molecular-weight adiponectin ratio with metabolic syndrome. Endocr. J. 2011, 58, 807–815. [Google Scholar]
- Kolaczynski, J.W. Response of leptin to short-term and prolonged overfeeding in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 4162–4165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García-Jiménez, S.; Fernández, G.B.; Salazar, M.F.M.; Noyola, A.M.; Jaimes, C.T.; Acosta, A.M.; Maya, L.G.; Ojeda, E.A.; Meraz, M.A.T.; Marie-Catherine, B.; et al. Serum leptin is associated with metabolic syndrome in obese Mexican subjects. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2015, 29, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lazo-de-la-Vega-Monroy, M.L.; Preciado-Puga, M.-D.; Ruiz-Noa, Y.; Salum-Zertuche, M.; Ibarra-Reynoso, L.-D. Correlation of the pediatric metabolic index with NAFLD or MAFLD diagnosis, and serum adipokine levels in children. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2023, 47, 102137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haschimi, K.; Pierroz, D.D.; Hileman, S.M.; Bjørbæk, C.; Flier, J.S. Two defects contribute to hypothalamic leptin resistance in mice with diet-induced obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Martin, R.; Schaffhauser, A.O.; York, D.A. Acute changes in the response to peripheral leptin with alteration in the diet composition. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 280, R504–R509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Beyec, J.; Pelletier, A.-L.; Arapis, K.; Hourseau, M.; Cluzeaud, F.; Descatoire, V.; Ducroc, R.; Aparicio, T.; Joly, F.; Couvelard, A.; et al. Overexpression of gastric leptin precedes adipocyte leptin during high-fat diet and is linked to 5HT-containing enterochromaffin cells. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Dirlewanger, M.; di Vetta, V.; Guenat, E.; Battilana, P.; Seematter, G.; Schneiter, P.; Jéquier, E.; Tappy, L. Effects of short-term carbohydrate or fat overfeeding on energy expenditure and plasma leptin concentrations in healthy female subjects. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Romon, M.; Lebel, P.; Velly, C.; Marecaux, N.; Fruchart, J.C.; Dallongeville, J. Leptin response to carbohydrate or fat meal and association with subsequent satiety and energy intake. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, E855–E861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.; Tümer, N.; Galo, Y.; Cheng, K.-Y.; Scarpace, P.J. Prevention and reversal of diet-induced leptin resistance with a sugar-free diet despite high fat content. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aparecida de França, S.; Dos Santos, M.P.; Garófalo MA, R.; Navegantes, L.C.; do Carmo Kettelhut, I.; Lopes, C.F.; Kawashita, N.H. Low protein diet changes the energetic balance and sympathetic activity in brown adipose tissue of growing rats. Nutrition 2009, 25, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Du, F.; Higginbotham, D.A.; White, B.D. Food intake, energy balance and serum leptin concentrations in rats fed low-protein diets. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 514–521. [Google Scholar]
- Weigle, D.S.; Breen, P.A.; Matthys, C.C.; Callahan, H.S.; Meeuws, K.E.; Burden, V.R.; Purnell, J.Q. A high-protein diet induces sustained reductions in appetite, ad libitum caloric intake, and body weight despite compensatory changes in diurnal plasma leptin and ghrelin concentrations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Herrera, K.; Florio, A.A.; Moore, M.; Marrero, A.; Tamez, M.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Mattei, J. The Leptin System and Diet: A Mini Review of the Current Evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 749050. [Google Scholar]
- Arner, P.; Spalding, K.L. Fat cell turnover in humans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, K.M.; Bessesen, D.H. Sex Differences in Adipose Tissue Function. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 49, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syarif; Aman, M.; Lawrence, G.S. High-fat diet increases the level of circulating Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 in Wistar rats, independent of obesity. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 65, 102266. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, J.; Kim, K. Effects of exercise and diet composition on expression of MCP-1 and oxidative stress-related mRNA of adipose tissue in diet-induced obese mice. J. Exerc. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 17, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.L.; Norhaizan, M.E. Effect of High-Fat Diets on Oxidative Stress, Cellular Inflammatory Response and Cognitive Function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, M.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Gollahon, L. The Molecular Effects of Dietary Acid Load on Metabolic Disease (The Cellular PasaDoble: The Fast-Paced Dance of pH Regulation). Front. Mol. Med. 2021, 1, 777088. [Google Scholar]
- Akhter, N.; Wilson, A.; Thomas, R.; Al-Rashed, F.; Kochumon, S.; Al-Roub, A.; Arefanian, H.; Al-Madhoun, A.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R.; et al. ROS/TNF-α Crosstalk Triggers the Expression of IL-8 and MCP-1 in Human Monocytic THP-1 Cells via the NF-κB and ERK1/2 Mediated Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeps, B.; Frädrich, J.; Krüger, A. Cut loose TIMP-1: An emerging cytokine in inflammation. Trends Cell Biol. 2023, 33, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meissburger, B.; Stachorski, L.; Röder, E.; Rudofsky, G.; Wolfrum, C. Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP1) controls adipogenesis in obesity in mice and in humans. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1468–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Codoñer-Franch, P.; Alonso-Iglesias, E. Resistin: Insulin resistance to malignancy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 438, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Taouis, M.; Benomar, Y. Is resistin the master link between inflammation and inflammation-related chronic diseases? Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2021, 533, 111341. [Google Scholar]
- Filková, M.; Haluzík, M.; Gay, S.; Šenolt, L. The role of resistin as a regulator of inflammation: Implications for various human pathologies. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 133, 157–170. [Google Scholar]
- Christou, K.A.; Christou, G.A.; Karamoutsios, A.; Vartholomatos, G.; Gartzonika, K.; Tsatsoulis, A.; Tigas, S. The regulation of serum resistin levels in metabolically healthy and unhealthy obese individuals. Hormones 2020, 19, 523–529. [Google Scholar]
- Owecki, M.; Miczke, A.; Nikisch, E.; Pupek-Musialik, D.; Sowiński, J. Serum resistin concentrations are higher in human obesity but independent from insulin resistance. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2011, 119, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Takata, Y.; Osawa, H.; Kurata, M.; Kurokalwa, M.; Yamauchi, J.; Ochi, M.; Nishida, W.; Okura, T.; Higaki, J.; Makino, H. Hyperresistinemia Is Associated With Coexistence of Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes. Hypertension 2008, 51, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.; Hindle, A.K.; Fu, S.; Brody, F. Downregulation of leptin and resistin expression in blood following bariatric surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2011, 25, 1962–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koebnick, C.; Wagner, K.; Garcia, A.L.; Gruendel, S.; Lahmann, P.H.; O Weickert, M.; Möhlig, M.; A Harsch, I.; Einig, C.; Speth, M.; et al. Increase in serum resistin during weight loss in overweight subjects is related to lipid metabolism. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzaghi, C.; Salvemini, L.; Fini, G.; Thompson, R.; Mangiacotti, D.; Di Paola, R.; Morini, E.; Giorelli, M.; De Bonis, C.; De Cosmo, S.; et al. Serum resistin and kidney function: A family-based study in non-diabetic, untreated individuals. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marouga, A.; Dalamaga, M.; Kastania, A.N.; Kroupis, C.; Lagiou, M.; Saounatsou, K.; Dimas, K.; Vlahakos, D.V. Circulating resistin is a significant predictor of mortality independently from cardiovascular comorbidities in elderly, non-diabetic subjects with chronic kidney disease. Biomarkers 2016, 21, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouga, A.; Dalamaga, M.; Kastania, A.N.; Antonakos, G.; Thrasyvoulides, A.; Kontelia, G.; Dimas, C.; Vlahakos, D.V. Correlates of serum resistin in elderly, non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. Lab. 2013, 59, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhao, C.-Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.-D.; Sun, H.; Cao, W.; Yu, W.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Ji, R.; Li, M.; et al. The relationship between hepatic resistin overexpression and inflammation in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruszyńska-Oszmałek, E.; Wojciechowska, M.; Sassek, M.; Krauss, H.; Leciejewska, N.; Szczepankiewicz, D.; Ślósarz, P.; Nogowski, L.; Kołodziejski, P.A. The Long-Term Effects of High-Fat and High-Protein Diets on the Metabolic and Endocrine Activity of Adipocytes in Rats. Biology 2021, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, M.W.; Qi, Y.; Patel, H.R.; Takahashi, N.; Banerjee, R.; Pajvani, U.B.; Sinha, M.K.; Gingerich, R.L.; Scherer, P.E.; Ahima, R.S. Regulation of resistin expression and circulating levels in obesity, diabetes, and fasting. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggi, M.; Bastelica, D.; Gual, P.; Iglesias, M.A.; Gremeaux, T.; Knauf, C.; Peiretti, F.; Verdier, M.; Juhan-Vague, I.; Tanti, J.F.; et al. C3H/HeJ mice carrying a toll-like receptor 4 mutation are protected against the development of insulin resistance in white adipose tissue in response to a high-fat diet. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkowski, A.; Bjersing, J.; Shestakov, A.; Bokarewa, M.I. Resistin competes with lipopolysaccharide for binding to toll-like receptor 4. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miyazawa-Hoshimoto, S.; Takahashi, K.; Bujo, H.; Hashimoto, N.; Saito, Y. Elevated serum vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with visceral fat accumulation in human obese subjects. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García de la Torre, N.; Rubio, M.A.; Bordiu, E.; Cabrerizo, L.; Aparicio, E.; Hernández, C.; Sánchez-Pernaute, A.; Di, L.; Torres, A.J.; Puente, M.; et al. Effects of weight loss after bariatric surgery for morbid obesity on vascular endothelial growth factor-A, adipocytokines, and insulin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4276–4281. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, I.; Franckhauser, S.; Ferré, T.; Vilà, L.; Tafuro, S.; Muñoz, S.; Roca, C.; Ramos, D.; Pujol, A.; Riu, E.; et al. Adipose tissue overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor protects against diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1801–1813. [Google Scholar]
- Tinahones, F.J.; Coín-Aragüez, L.; Mayas, M.D.; Garcia-Fuentes, E.; Hurtado-Del-Pozo, C.; Vendrell, J.; Cardona, F.; Calvo, R.-M.; Obregon, M.-J.; El Bekay, R. Obesity-associated insulin resistance is correlated to adipose tissue vascular endothelial growth factors and metalloproteinase levels. BMC Physiol. 2012, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidou, Z.; Turban, S.; Miller, E.; Zou, X.; Schrader, J.; Ratcliffe, P.J.; Hadoke, P.W.F.; Walker, B.R.; Iredale, J.P.; Morton, N.M.; et al. Increased angiogenesis protects against adipose hypoxia and fibrosis in metabolic disease-resistant 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (HSD1)-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4188–4197. [Google Scholar]
- Corvera, S.; Gealekman, O. Adipose tissue angiogenesis: Impact on obesity and type-2 diabetes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 463–472. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Asterholm, I.W.; Kusminski, C.M.; Bueno, A.C.; Wang, Z.V.; Pollard, J.W.; Brekken, R.A.; Scherer, P.E. Dichotomous effects of VEGF-A on adipose tissue dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5874–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, M.; Sun, K.; An, Y.A.; Gu, X.; Scherer, P.E. VEGF-A-Expressing Adipose Tissue Shows Rapid Beiging and Enhanced Survival After Transplantation and Confers IL-4-Independent Metabolic Improvements. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, I.; Franckhauser, S.; Bosch, F. New insights into adipose tissue VEGF-A actions in the control of obesity and insulin resistance. Adipocyte 2013, 2, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalehbandi, S.; Yuzugulen, J.; Pranjol, Z.I.; Pourgholami, M.H. The role of VEGF in cancer-induced angiogenesis and research progress of drugs targeting VEGF. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 949, 175586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weddell, J.C.; Chen, S.; Imoukhuede, P.I. VEGFR1 promotes cell migration and proliferation through PLCγ and PI3K pathways. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2018, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.C.; Chang, Y.-W.; Hong, C.-C.; Yu, Y.-H.; Su, J.-L. The role of the VEGF-C/VEGFRs axis in tumor progression and therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 14, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieran, M.W.; Kalluri, R.; Cho, Y.J. The VEGF pathway in cancer and disease: Responses, resistance, and the path forward. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006593. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.A.; Nilsson, M.B.; Le, X.; Cascone, T.; Jain, R.K.; Heymach, J.V. Molecular Mechanisms and Future Implications of VEGF/VEGFR in Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
| Assay Kits Applied | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kit Type | Species | Protein | Company | Catalog Number | Location | |
| 1 * | Adipokine Array | Mouse | 38 Common Adipokines | R&D Systems | ARY013 | Minneapolis, MN, USA |
| 2 | ELISA | Mouse | Adiponectin | Invitrogen | KMP0041 | Waltham, MA, USA |
| 3 | ELISA | Mouse | Leptin | Invitrogen | KMC2281 | Waltham, MA, USA |
| 4 | ELISA | Mouse | MCP-1 | Invitrogen | BMS6005 | Waltham, MA, USA |
| 5 | ELISA | Mouse | Resistin | Invitrogen | EMRETN | Waltham, MA, USA |
| 6 | ELISA | Mouse | TIMP-1 | Proteintech | KE10039 | Rosemont, IL, USA |
| 7 | ELISA | Mouse | VEGF-A | Invitrogen | BMS619-2 | Waltham, MA, USA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boren, C.; Barr, B.; Mubtasim, N.; Gollahon, L. Adipocytokine Protein Expression from Visceral Fat Differs Significantly Based on Diet, Sex, and Age in C3H/HeJ Mice Fed Long-Term, High-Fat Diets, ± Ammonium-Hydroxide-Supplemented Dietary Protein. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040218
Boren C, Barr B, Mubtasim N, Gollahon L. Adipocytokine Protein Expression from Visceral Fat Differs Significantly Based on Diet, Sex, and Age in C3H/HeJ Mice Fed Long-Term, High-Fat Diets, ± Ammonium-Hydroxide-Supplemented Dietary Protein. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(4):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040218
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoren, Caleb, Benjamin Barr, Noshin Mubtasim, and Lauren Gollahon. 2025. "Adipocytokine Protein Expression from Visceral Fat Differs Significantly Based on Diet, Sex, and Age in C3H/HeJ Mice Fed Long-Term, High-Fat Diets, ± Ammonium-Hydroxide-Supplemented Dietary Protein" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 4: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040218
APA StyleBoren, C., Barr, B., Mubtasim, N., & Gollahon, L. (2025). Adipocytokine Protein Expression from Visceral Fat Differs Significantly Based on Diet, Sex, and Age in C3H/HeJ Mice Fed Long-Term, High-Fat Diets, ± Ammonium-Hydroxide-Supplemented Dietary Protein. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(4), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040218





