Gene Co-Expression Analysis Reveals Functional Differences Between Early- and Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
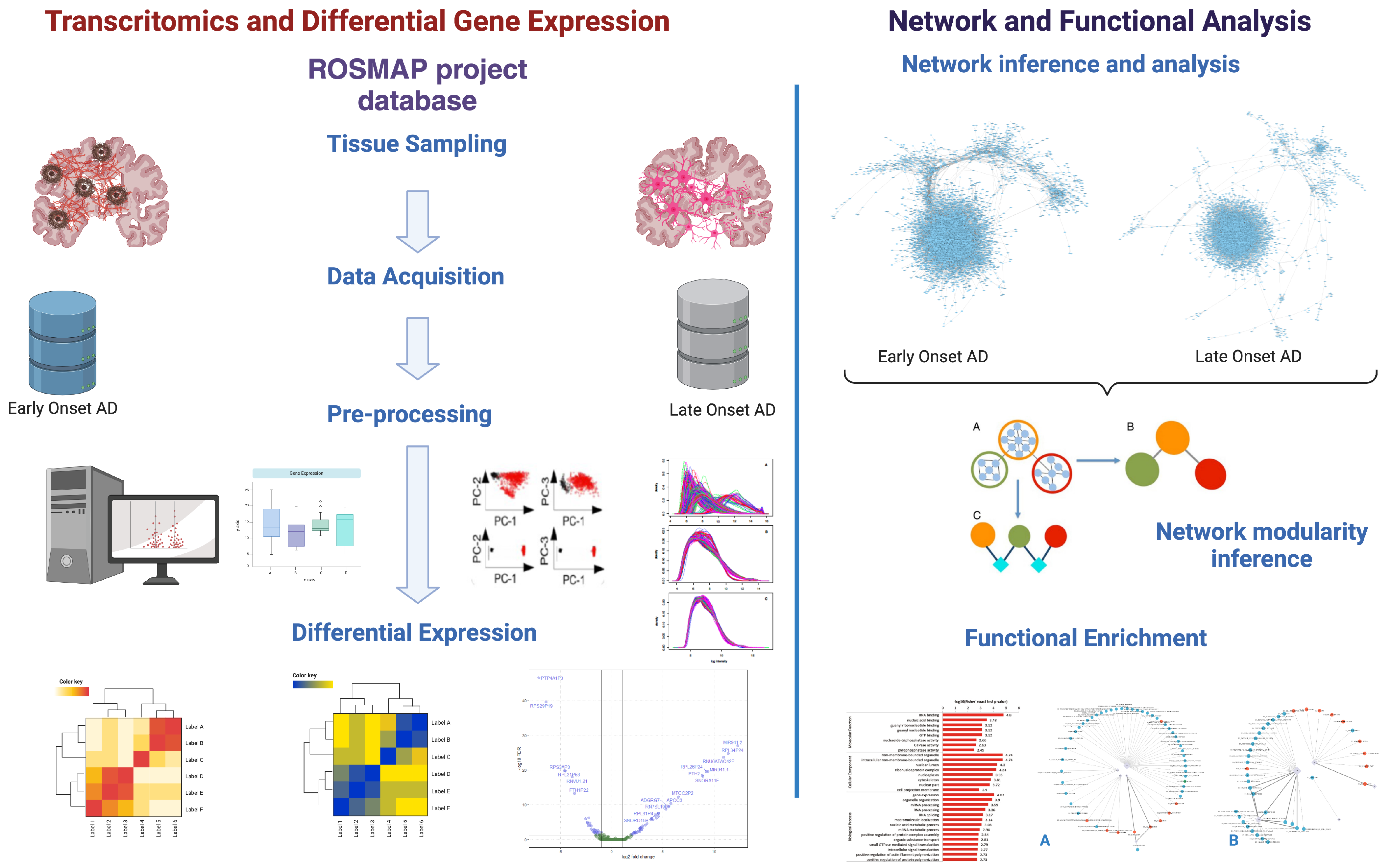
2. Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition, Preprocessing, and Differential Expression
2.2. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.3. Reconstruction of Gene Co-Expression Networks
2.4. Inference of Modular Structure and Functional Analysis in Alzheimer’s Disease Co-Expression Networks
3. Results
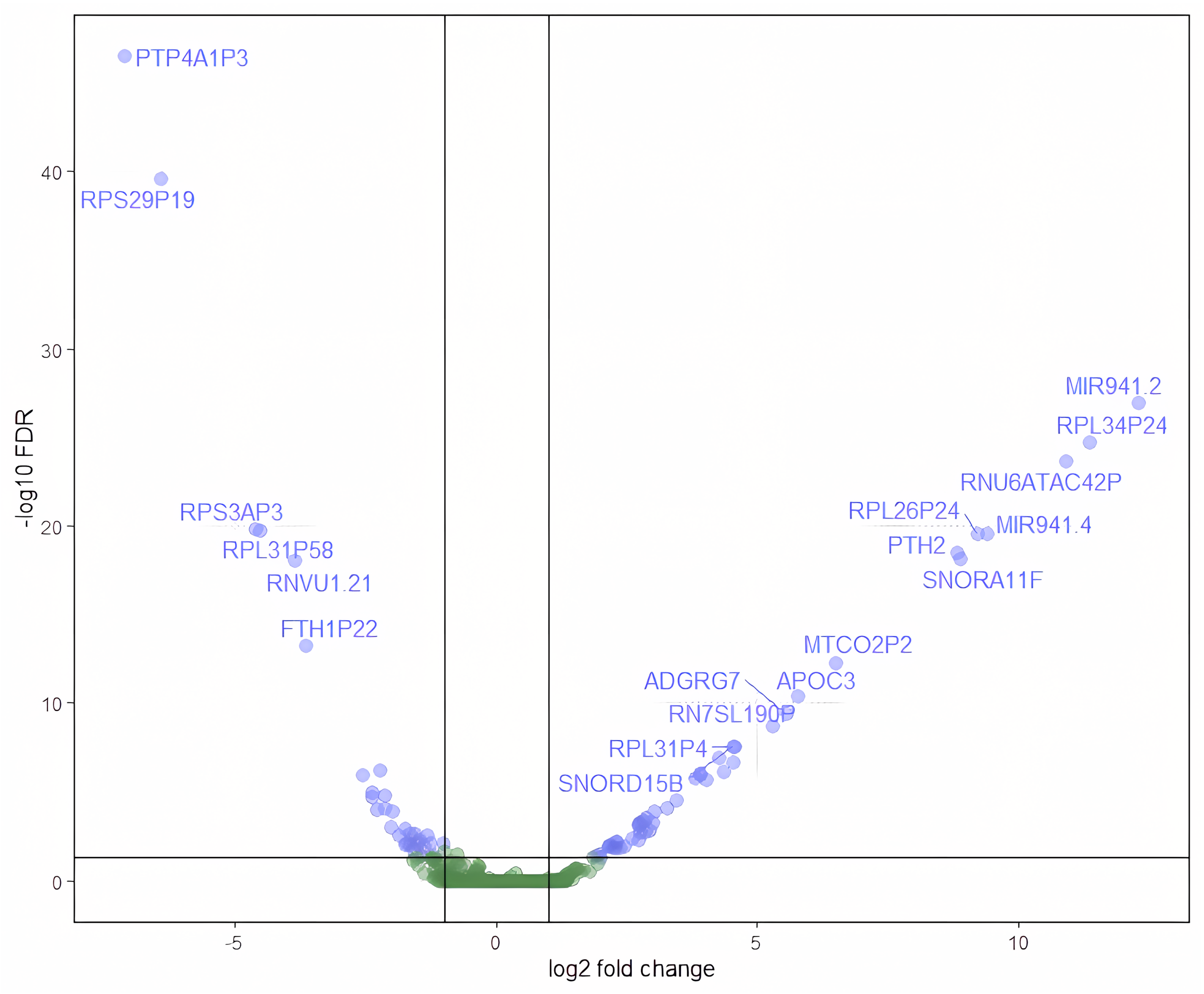
3.1. Differential Gene Expression and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
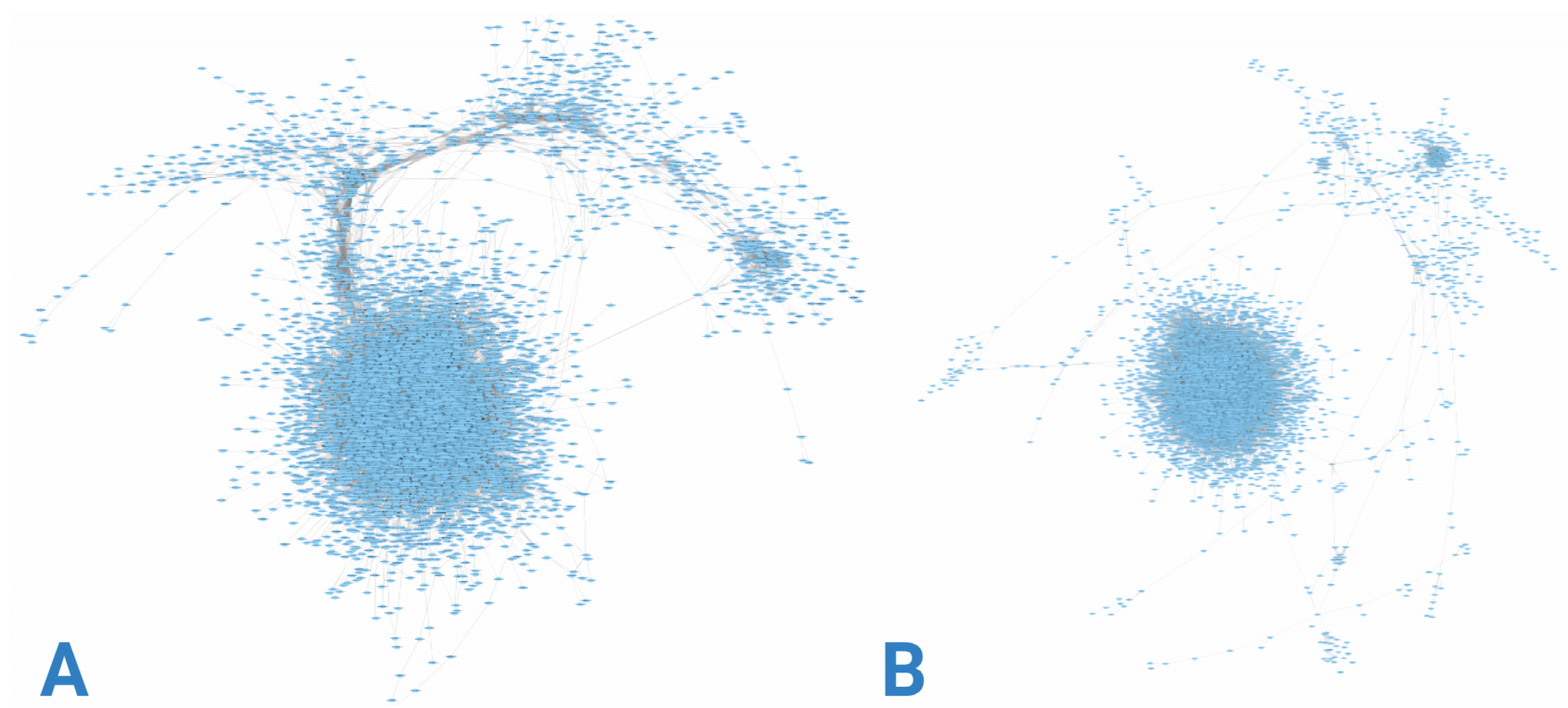
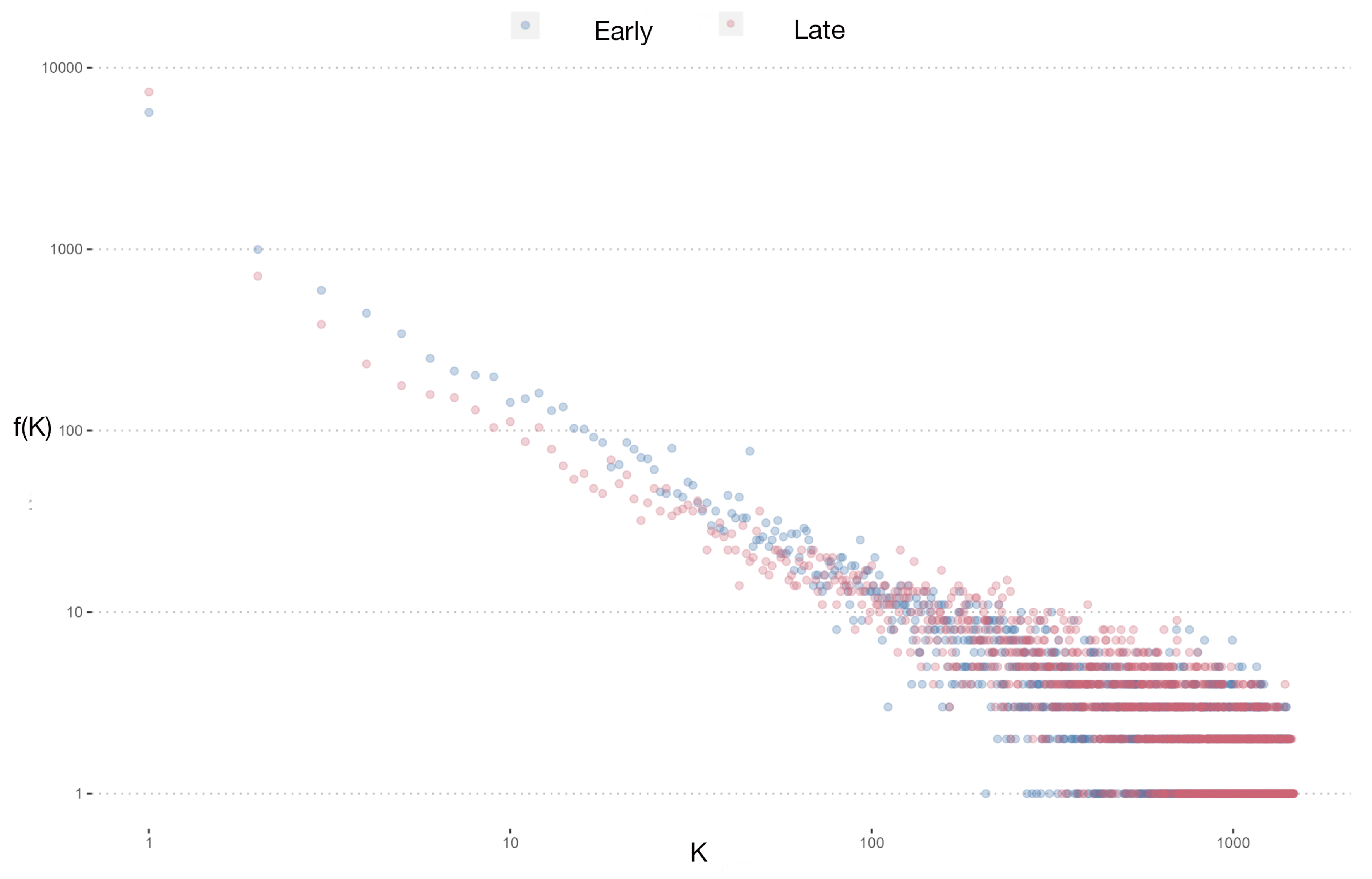
3.2. Gene Co-Expression Networks
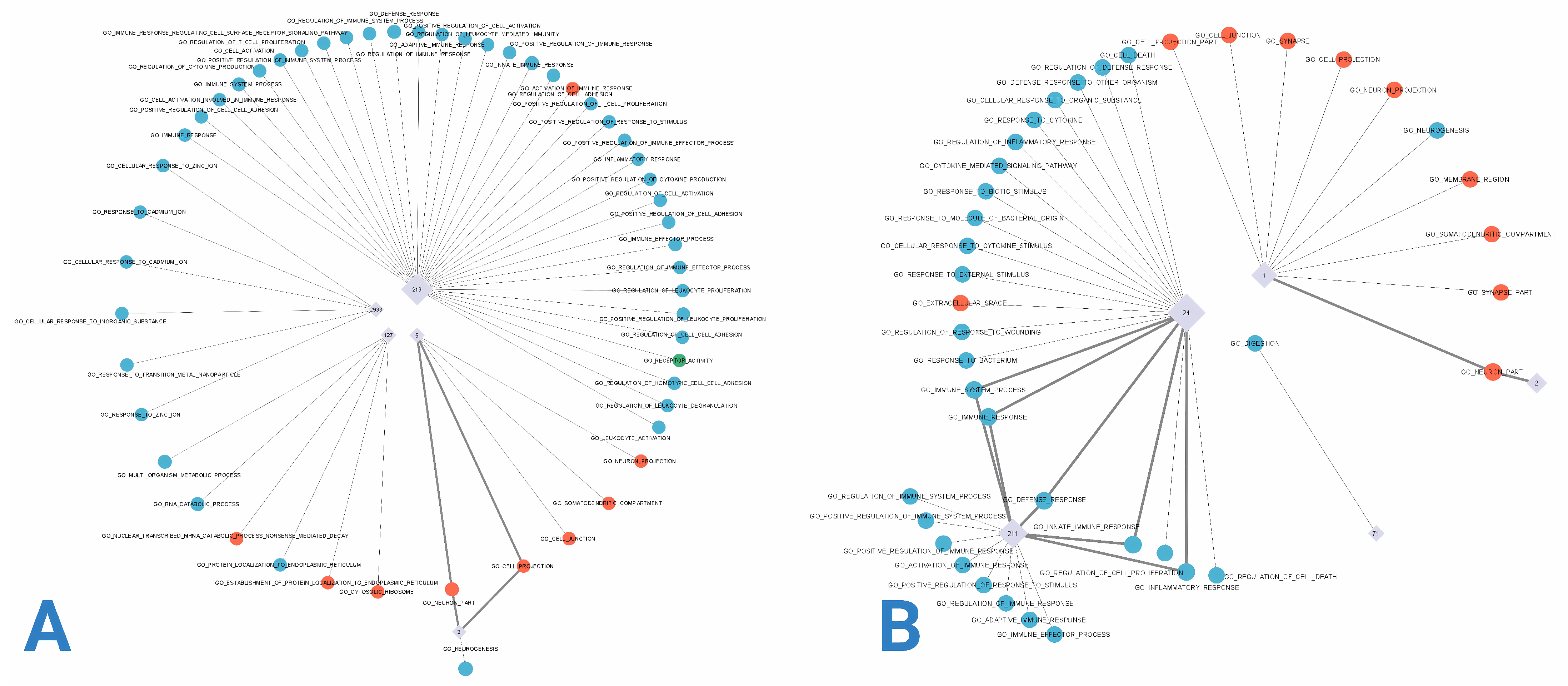
3.3. Network Modularity and Functional Enrichment
4. Discussion
Scope and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lanctôt, K.L.; Hahn-Pedersen, J.H.; Eichinger, C.; Freeman, C.; Clark, A.; Tarazona, L.; Cummings, J. Burden of illness in people with Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review of epidemiology, comorbidities and mortality. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 11, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, R.K.; Mateti, U.V.; Khanal, P.; Rawal, K.B.; Jain, P.; Patil, V.S.; Shrivastava, A.K.; Patil, B. Alzheimer’s Disease: Epidemiology, Neuropathology, and Neurochemistry. In Computational and Experimental Studies in Alzheimer’s Disease; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Better, M.A. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 1598–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Kamble, S.M.; Patil, K.R.; Upaganlawar, A.B. Etiology, pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and amyloid beta hypothesis. In Alzheimer’s Disease and Advanced Drug Delivery Strategies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, J.D.; Truong, V.; Kumar, R.; Venkatesan, M.; Graham, B.E.; Hao, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Ritchie, M.D.; et al. The Alzheimer’s Knowledge Base: A Knowledge Graph for Alzheimer Disease Research. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e46777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimzadeh, N.; Srinivasan, S.S.; Zhang, J.; Swarup, V. Gene networks and systems biology in Alzheimer’s disease: Insights from multi-omics approaches. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 3587–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharo, C.; Zhai, T.; Huang, Z. Investigation of Potential Drug Targets Involved in Inflammation Contributing to Alzheimer’s Disease Progression. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, A.P.; García-Kroepfly, A.L.; Pérez-Fuentes, K.A.; García-Reyes, R.I.; Solis-Roldan, F.F.; Alba-González, J.A.; Hernández-Lemus, E.; de Anda-Jáuregui, G. The ROSMAP project: Aging and neurodegenerative diseases through omic sciences. Front. Neuroinform. 2024, 18, 1443865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniri, A.; Hosseini, M.M.; Akhavan-Niaki, H. Alzheimer’s disease-related epigenetic changes: Novel therapeutic targets. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 1282–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Kim, B.M.; Lee, T.H. Death-associated protein kinase 1 as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyubova, G. Apoe4 is A risk factor and potential therapeutic target for alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets (Former. Curr. Drug Targets-CNS Neurol. Disord.) 2024, 23, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinetti-Luque, M.; Trujillo-Estrada, L.; Garcia-Fuentes, E.; Andreo-Lopez, J.; Sanchez-Varo, R.; Garrido-Sánchez, L.; Gómez-Mediavilla, Á.; Lopez, M.G.; Garcia-Caballero, M.; Gutierrez, A.; et al. Adipose tissue as a therapeutic target for vascular damage in Alzheimer’s disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 840–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola-Sevilla, N.; Puerta, E. SIRT2 as a potential new therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, I.W.; Lin, Y.; Granholm, E.L.; Singh, F. A Focused Review of Gamma Neuromodulation as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer’s Spectrum Disorders. J. Psychiatry Brain Sci. 2024, 9, e240001. [Google Scholar]
- Prabha, S.; Sajad, M.; Hasan, G.M.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I.; Thakur, S.C. Recent advancement in understanding of Alzheimer’s disease: Risk factors, subtypes, and drug targets and potential therapeutics. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 101, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaisa-Aad, M.; Muñoz-Castro, C.; Serrano-Pozo, A. Update on modifiable risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Curr. Opin. Neuro 2024, 37, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Bi, D.; Shen, Y. Complement-mediated synapse loss in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms and involvement of risk factors. Trends Neurosci. 2024, 47, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobaderi, T.; Kazemnejad, A.; Salehi, M. Exploring the impacts of risk factors on mortality patterns of global Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias from 1990 to 2021. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gracely, E.J.; Zhao, X.; Gliebus, G.P.; May, N.S.; Volpe, S.L.; Shi, J.; DiMaria-Ghalili, R.A.; Eisen, H.J. Association of multiple metabolic and cardiovascular markers with the risk of cognitive decline and mortality in adults with Alzheimer’s disease and AD-related dementia or cognitive decline: A prospective cohort study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1361772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmaksoud, N.M.; Sallam, A.A.M.; Abulsoud, A.I.; El-Dakroury, W.A.; Mageed, S.S.A.; Al-Noshokaty, T.M.; Elrebehy, M.A.; Elshaer, S.S.; Mahmoud, N.A.; Fathi, D.; et al. Unraveling the role of miRNAs in the diagnosis, progression, and therapeutic intervention of Alzheimer’s disease. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 253, 155007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, J.; Xiong, W.; Luo, Y.; Feng, H.; Zhou, H.; Peng, Y.; He, Y.; Ye, Q. The oral-brain axis: Can periodontal pathogens trigger the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s disease? Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1358179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Cuesta, P.; Marcos, A.; Montenegro-Peña, M.; Yus, M.; Rodríguez-Rojo, I.C.; Bruña, R.; Maestú, F.; López, M.E. Sex differences in the progression to Alzheimer’s disease: A combination of functional and structural markers. GeroScience 2024, 46, 2619–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.A.; Buchman, A.S.; Boyle, P.A.; Barnes, L.L.; Wilson, R.S.; Schneider, J.A. Religious Orders Study and Rush Memory and Aging Project. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 64, S161–S189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarazona, S.; Furió-Tarí, P.; Turrà, D.; Pietro, A.D.; Nueda, M.J.; Ferrer, A.; Conesa, A. Data quality aware analysis of differential expression in RNA-seq with NOISeq R/Bioc package. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, A.; Madrigal, P.; Tarazona, S.; Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Cervera, A.; McPherson, A.; Szcześniak, M.W.; Gaffney, D.J.; Elo, L.L.; Zhang, X.; et al. A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis. Genom. Biol. 2016, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Kirtipal, N.; Song, B.; Lee, S. Normalization of RNA-Seq data using adaptive trimmed mean with multi-reference. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Lun, A.T.L.; Baldoni, P.L.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR 4.0: Powerful differential analysis of sequencing data with expanded functionality and improved support for small counts and larger datasets. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Friedman, M.S.; Shedden, K.; Hankenson, K.D.; Woolf, P.J. GAGE: Generally applicable gene set enrichment for pathway analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, P.E.; Lafitte, F.; Bontempi, G. minet: A R/Bioconductor Package for Inferring Large Transcriptional Networks Using Mutual Information. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csárdi, G.; Nepusz, T.; Traag, V.; Horvát, S.; Zanini, F.; Noom, D.; Müller, K. igraph: Network Analysis and Visualization in R. R package version 2.0.3. Zenodo 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genom. Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edler, D.; Holmgren, A.; Rosvall, M. The MapEquation Software Package. 2024. Available online: https://mapequation.org (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Lancichinetti, A.; Fortunato, S.; Radicchi, F. Benchmark graphs for testing community detection algorithms. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 046110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Terfve, C.; Rose, J.C.; Markowetz, F. HTSanalyzeR: An R/Bioconductor package for integrated network analysis of high-throughput screens. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 879–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, R.J.; Hyman, B.T.; Serrano-Pozo, A. Multifaceted roles of APOE in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Strickland, M.R.; Soranno, A.; Holtzman, D.M. Apolipoprotein E: Structural insights and links to Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. Neuron 2021, 109, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, S.; Ratna, S.; Yamamoto, H.A.; Ebenezer, A.T.; Ferguson, D.S.; Kaur, A.; McIntyre, B.C.; Snow, R.; Solesio, M.E. ATP synthase and mitochondrial bioenergetics dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furcila, D.; Domínguez-Álvaro, M.; DeFelipe, J.; Alonso-Nanclares, L. Subregional Density of Neurons, Neurofibrillary Tangles and Amyloid Plaques in the Hippocampus of Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neuroanat. 2019, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, M.C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Knopman, D.S.; Ndumele, C.; Mosley, T.H.; Selvin, E.; Shah, A.M.; Solomon, S.D.; Gottesman, R.F.; et al. Risk of Dementia Associated with Atrial Cardiopathy: The ARIC Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, 025646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncone, L.; Luciani, M.; Coggins, M.; Wilker, E.H.; Ho, C.Y.; Codispoti, K.E.; Frosch, M.P.; Kayed, R.; del Monte, F. Aβ Amyloid Pathology Affects the Hearts of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Entropy, relative entropy and mutual information. Elem. Inf. Theory 1991, 2, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, C.A.; Perdigao, R.A. Minimum mutual information and non-Gaussianity through the maximum entropy method: Theory and properties. Entropy 2012, 14, 1103–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussler, D.; Opper, M. Mutual information, metric entropy and cumulative relative entropy risk. Ann. Stat. 1997, 25, 2451–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakopoulos, P.; Mertikopoulos, P.; Moustakas, A.L.; Caire, G. Distribution of MIMO mutual information: A large deviations approach. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Information Theory Workshop on Networking and Information Theory, Volos, Greece, 10–12 June 2009; pp. 306–310. [Google Scholar]
- Rosvall, M.; Axelsson, D.; Bergstrom, C.T. The map equation. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2009, 178, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosvall, M.; Bergstrom, C.T. Maps of random walks on complex networks reveal community structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá-Corona, S.A.; Sandoval-Motta, S.; Espinal-Enriquez, J.; Hernandez-Lemus, E. Modularity in biological networks. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 701331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wool, I.G. Extraribosomal functions of ribosomal proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996, 21, 164–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastroeni, D.; Khdour, O.M.; Delvaux, E.; Nolz, J.; Olsen, G.; Berchtold, N.; Cotman, C.; Hecht, S.M.; Coleman, P.D. Nuclear but not mitochondrial-encoded oxidative phosphorylation genes are altered in aging, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 13, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, T.; Ohnishi, S.T.; Salerno, J.C. Five decades of research on mitochondrial NADH-quinone oxidoreductase (complex I). Biol. Chem. 2018, 399, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, G.; Gentile, F.; Pizzimenti, S.; Canuto, R.; Daga, M.; Arcaro, A.; Cetrangolo, G.; Lepore, A.; Ferretti, C.; Dianzani, C.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Cancer and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Spotlight on Fatty Acid Oxidation and Lipoperoxidation Products. Antioxidants 2016, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodeiri Farshbaf, M.; Kiani-Esfahani, A. Succinate dehydrogenase: Prospect for neurodegenerative diseases. Mitochondrion 2018, 42, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravasz, E.; Somera, A.L.; Mongru, D.A.; Oltvai, Z.N.; Barabási, A.L. Hierarchical Organization of Modularity in Metabolic Networks. Science 2002, 297, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paparazzo, E.; Lagani, V.; Geracitano, S.; Citrigno, L.; Aceto, M.A.; Malvaso, A.; Bruno, F.; Passarino, G.; Montesanto, A. An ELOVL2-based epigenetic clock for forensic age prediction: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvaso, A.; Gatti, A.; Negro, G.; Calatozzolo, C.; Medici, V.; Poloni, T.E. Microglial senescence and activation in healthy aging and Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and neuropathological scoring. Cells 2023, 12, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amore, F.M.; Moscatelli, M.; Malvaso, A.; D’Antonio, F.; Rodini, M.; Panigutti, M.; Mirino, P.; Carlesimo, G.A.; Guariglia, C.; Caligiore, D. Explainable machine learning on clinical features to predict and differentiate Alzheimer’s progression by sex: Toward a clinician-tailored web interface. J. Neurol. Sci. 2025, 468, 123361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez Cruz, A.I.; de Anda-Jáuregui, G.; Hernández-Lemus, E. Gene Co-Expression Analysis Reveals Functional Differences Between Early- and Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030200
Gutiérrez Cruz AI, de Anda-Jáuregui G, Hernández-Lemus E. Gene Co-Expression Analysis Reveals Functional Differences Between Early- and Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(3):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030200
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez Cruz, Abel Isaías, Guillermo de Anda-Jáuregui, and Enrique Hernández-Lemus. 2025. "Gene Co-Expression Analysis Reveals Functional Differences Between Early- and Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 3: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030200
APA StyleGutiérrez Cruz, A. I., de Anda-Jáuregui, G., & Hernández-Lemus, E. (2025). Gene Co-Expression Analysis Reveals Functional Differences Between Early- and Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(3), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030200





