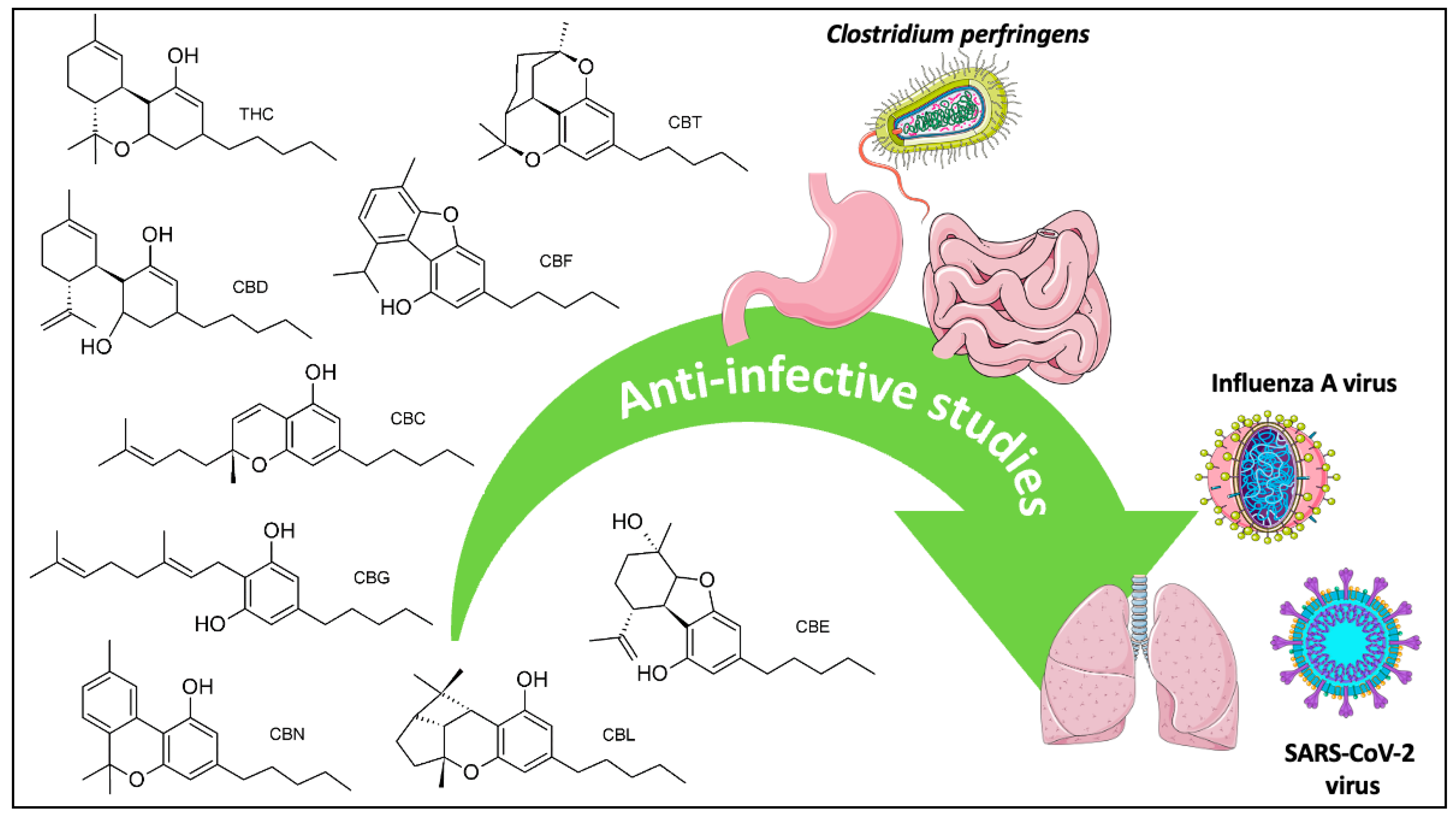
Anti-Infective Screening of Selected Nine Cannabinoids Against Clostridium perfringens and Influenza A (H5N1) Neuraminidases, and SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease and Spike Protein Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Anti-C. perfringens Neuraminidase Assay
2.3. Anti-Influenza A Viral Neuraminidase Assay
2.4. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Activity Assay
2.5. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein–Human ACE2 Interaction Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
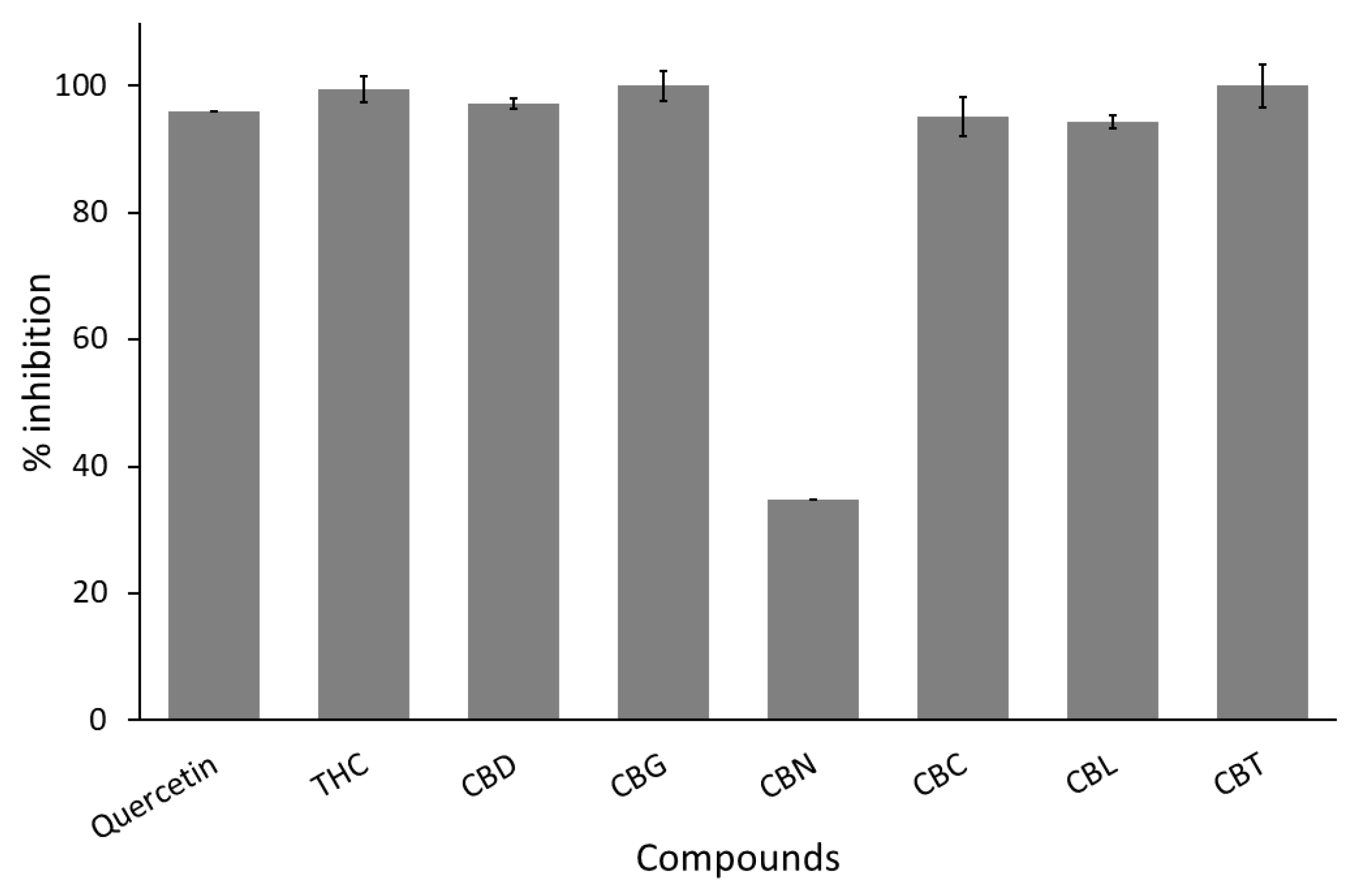
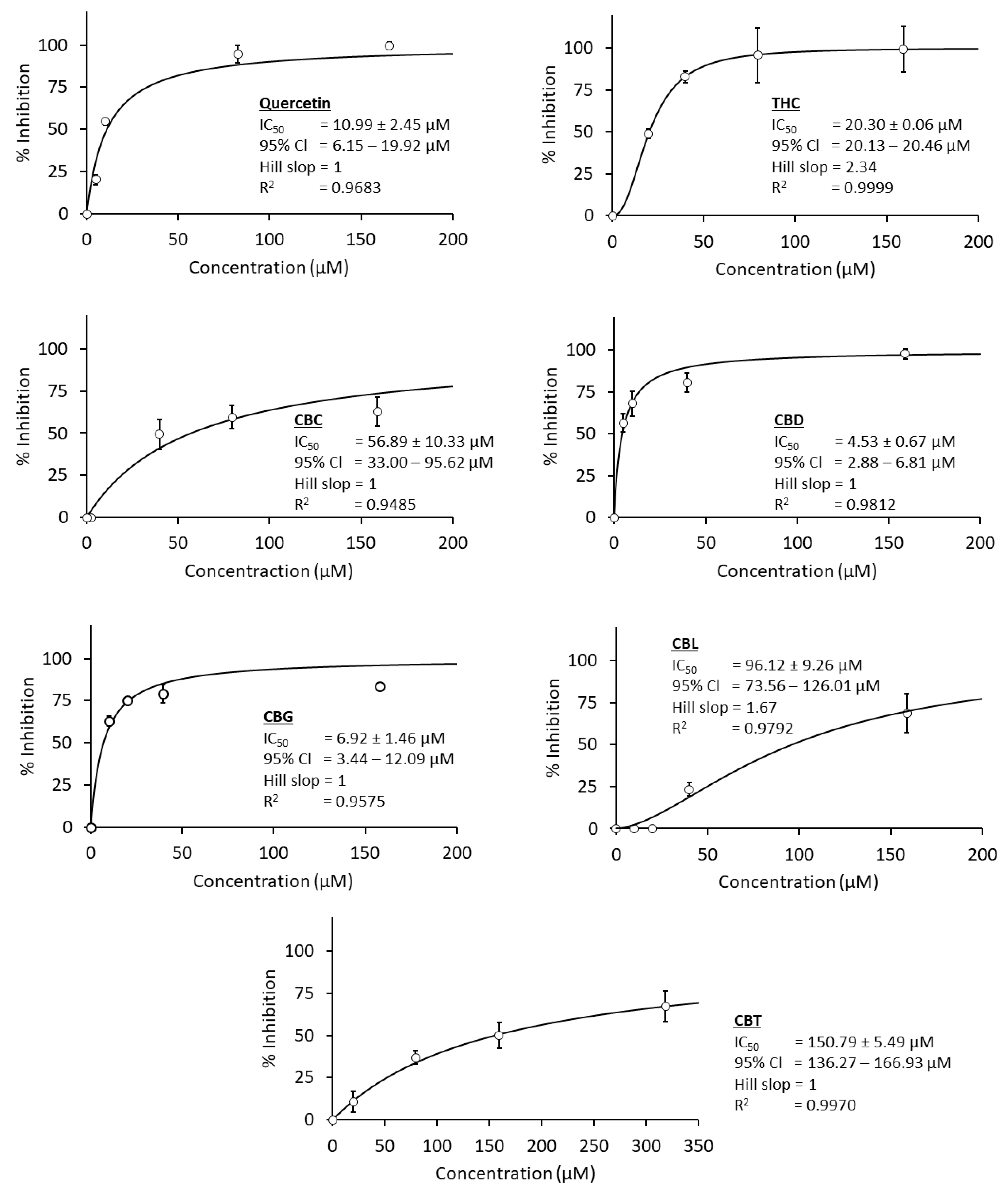
3.1. Anti-C. perfringens Neuraminidase Activity
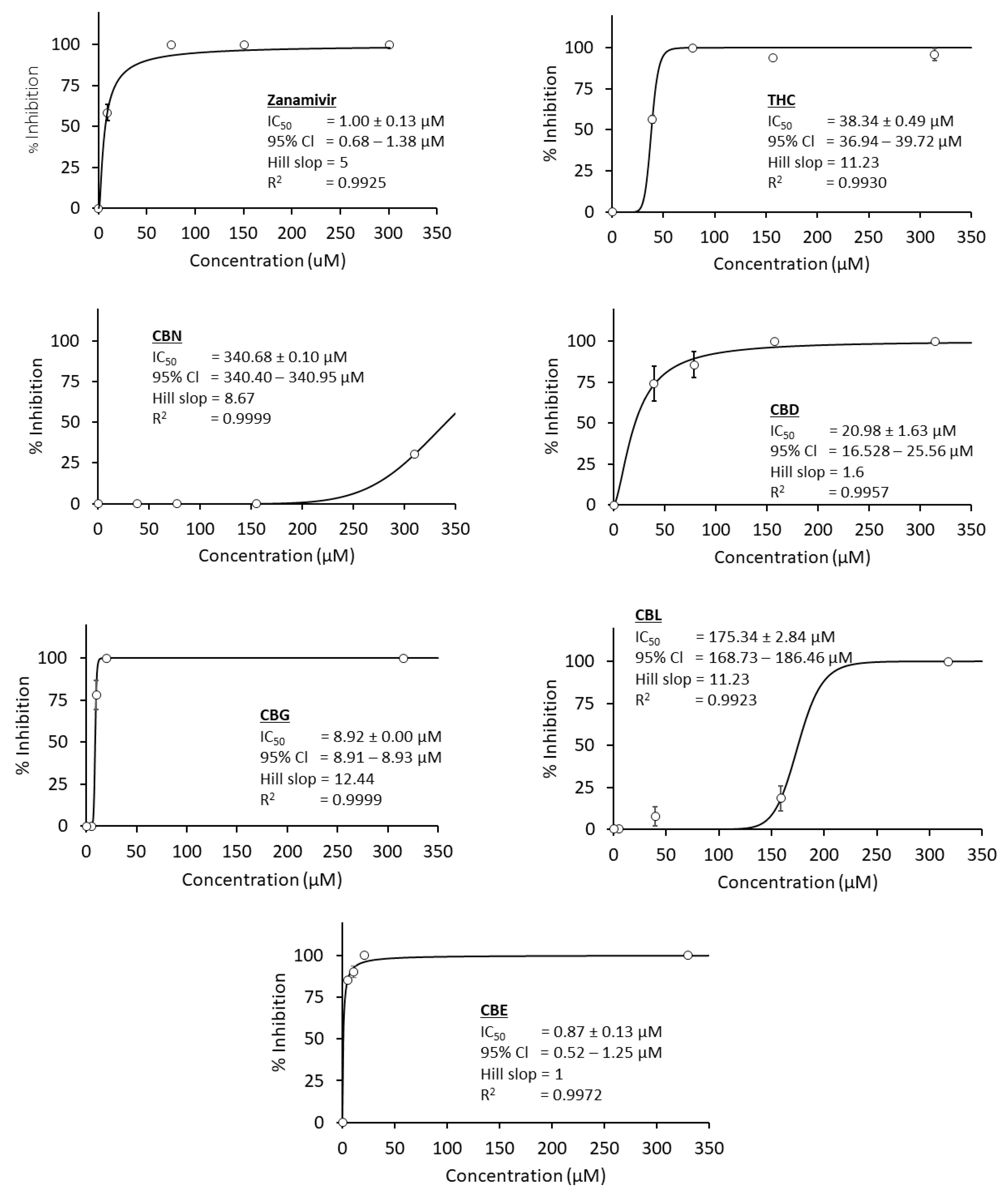
3.2. Anti-Influenza A Virus Neuraminidase Activity
3.3. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activities
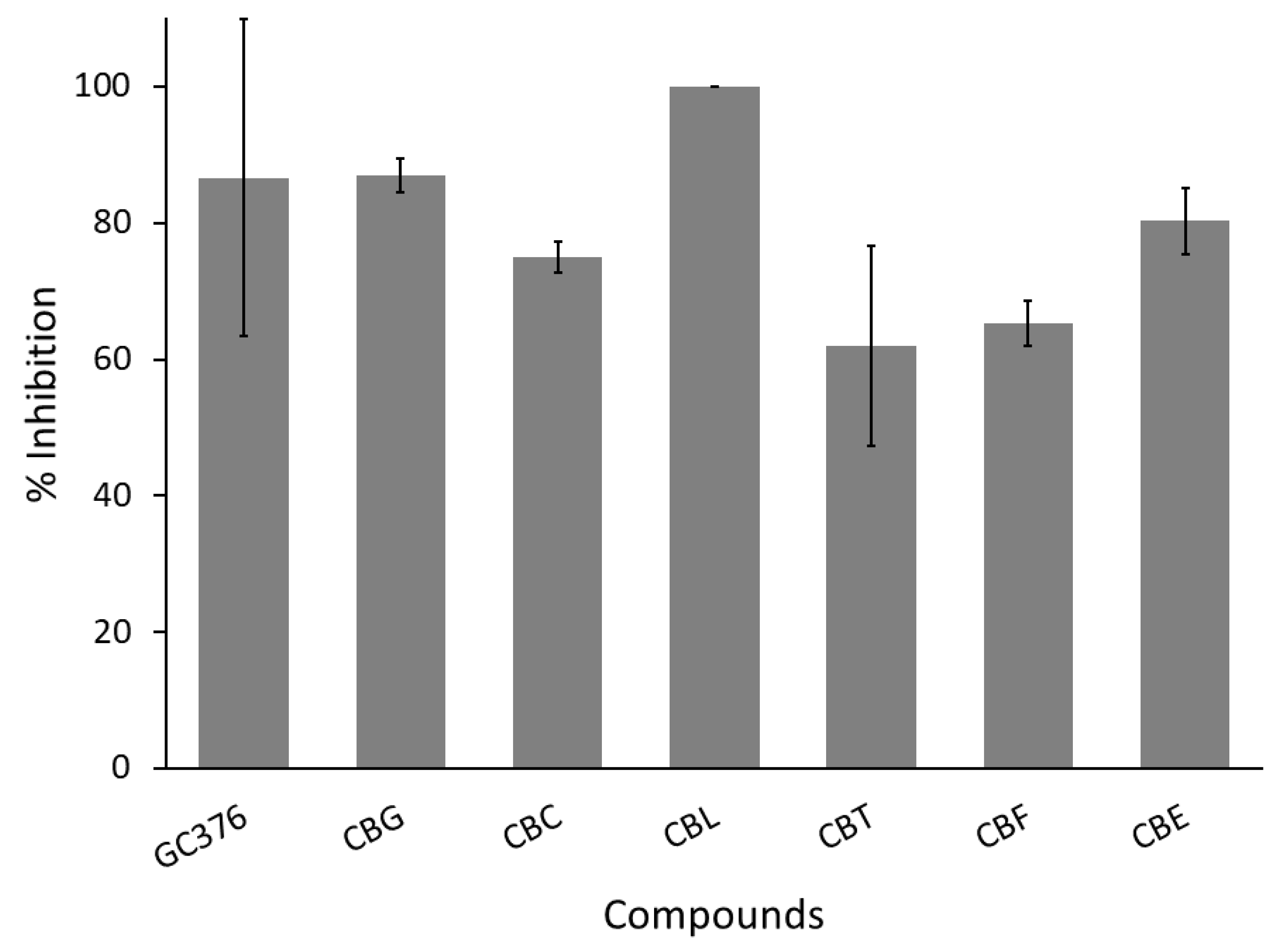
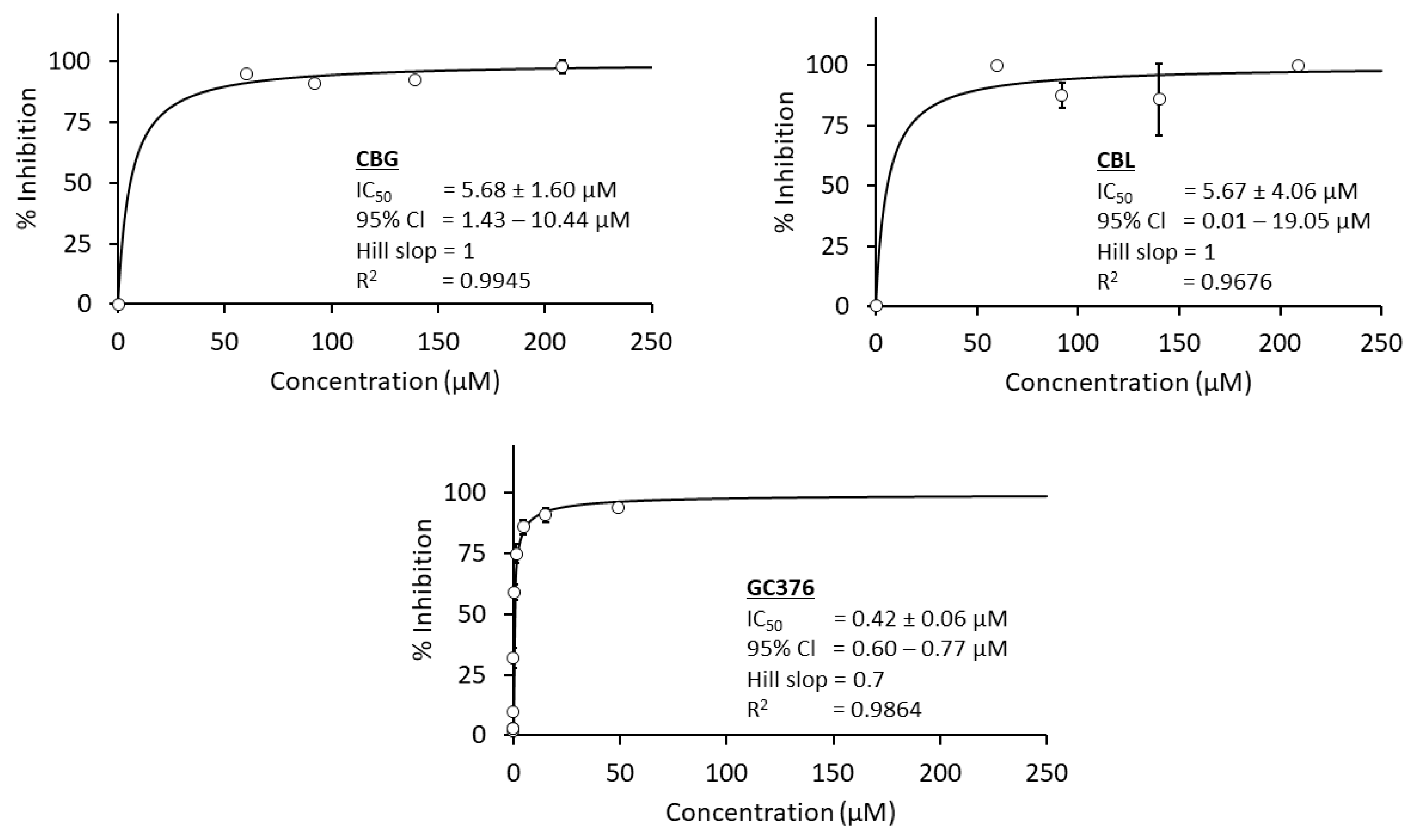
3.3.1. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease
3.3.2. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein–Human ACE2 Interaction
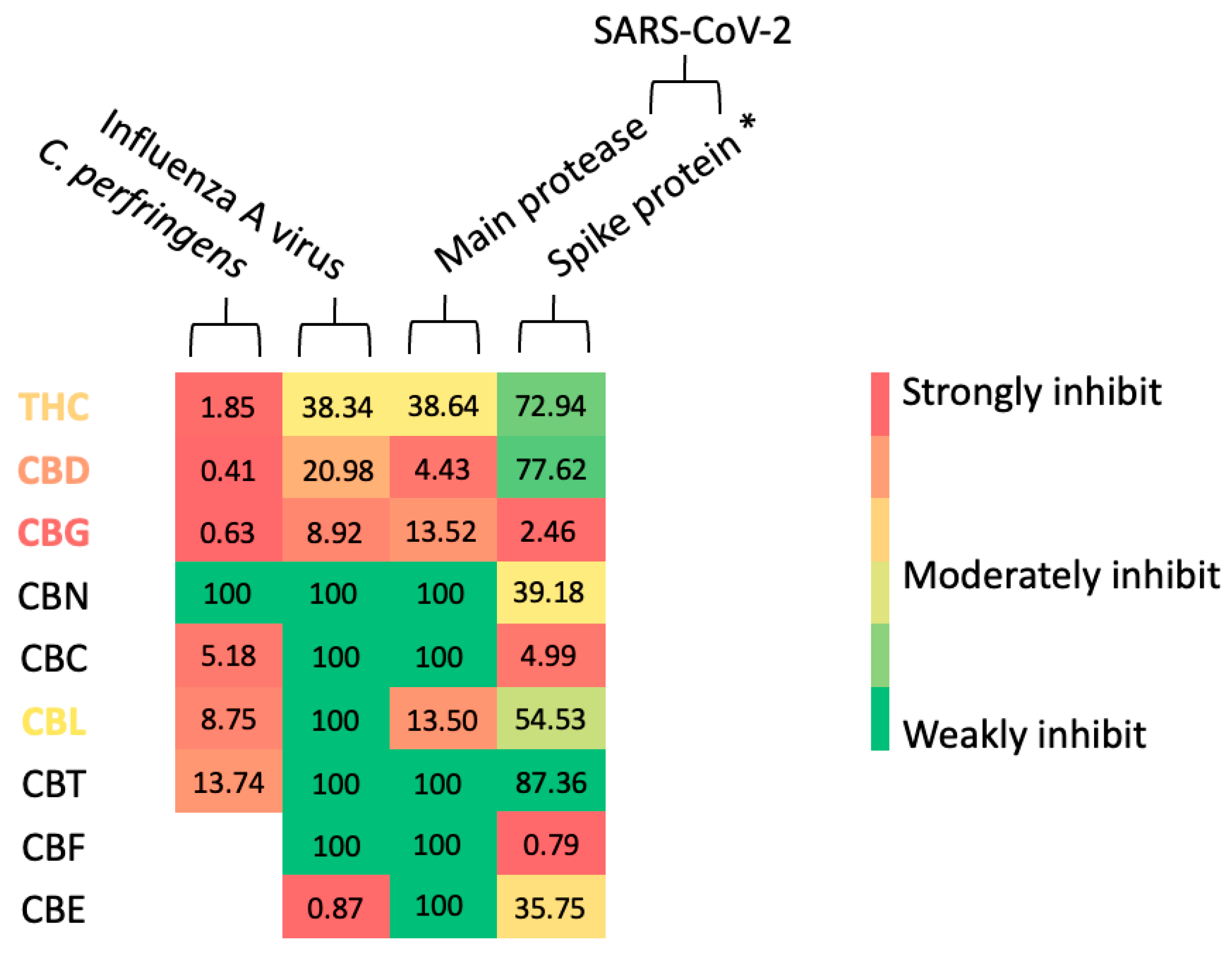
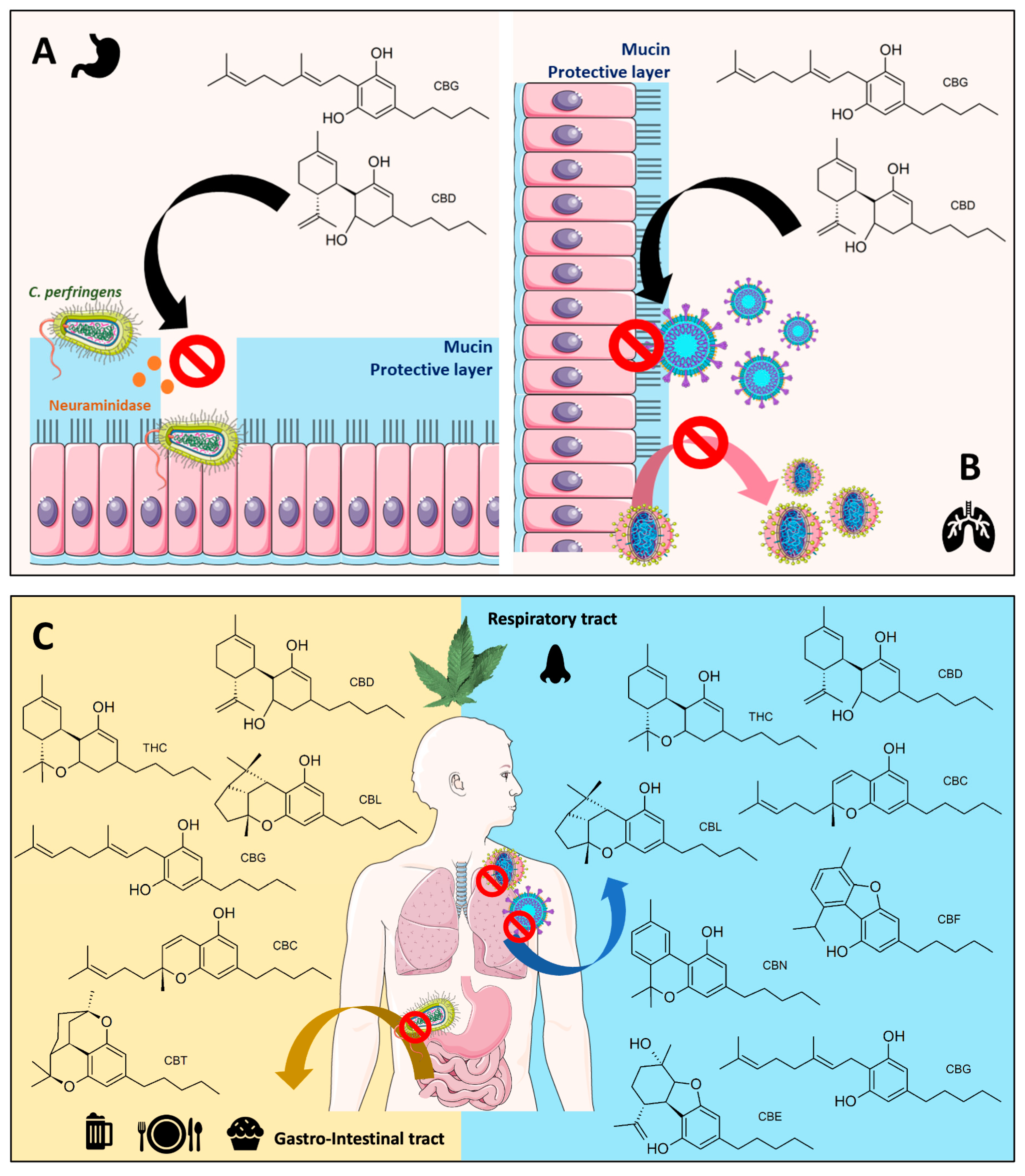
4. Discussion
4.1. Cannabinoids in Bacterial and Viral Neuraminidases
4.2. Cannabinoids in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Their Possible Correlation to Neuraminidase Inhibitions
4.3. Limitation
4.4. Projection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorensen, M.D.B.B.; Hayat, S.Y.; Wellner, N.; Bjarnholt, N.; Janfelt, C. Leaves of Cannabis Sativa and Their Trichomes Studied by DESI and MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging for Their Contents of Cannabinoids and Flavonoids. Phytochem. Anal. 2023, 34, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Qian, P.; Hao, J.; Li, L. Analytical Characterization of Hempseed (Seed of Cannabis Sativa L.) Oil from Eight Regions in China. J. Diet. Suppl. 2010, 7, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balant, M.; Gras, A.; Ruz, M.; Vallès, J.; Vitales, D.; Garnatje, T. Traditional Uses of Cannabis: An Analysis of the CANNUSE Database. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korus, J.; Witczak, M.; Ziobro, R.; Juszczak, L. Hemp (Cannabis Sativa Subsp. Sativa) Flour and Protein Preparation as Natural Nutrients and Structure Forming Agents in Starch Based Gluten-Free Bread. LWT 2017, 84, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelczyk, M.; Gimbut, M.; Łochyńska, M. Nuts of Fibrous Hemp Cannabis Sativa L.—Concentrated Power of Nutrients. J. Nat. Fibers 2023, 20, 2128967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Luckett, T.; Amgarth-Duff, I.; Agar, M.R. Efficacy of Medicinal Cannabis for Appetite-Related Symptoms in People with Cancer: A Systematic Review. Palliat. Med. 2022, 36, 912–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Jeena, G.; Pitakbut, T.; Vasilev, N.; Kayser, O. Cannabis sativa Research Trends, Challenges, and New-Age Perspectives. iScience 2021, 24, 10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitakbut, T.; Nguyen, G.-N.; Kayser, O. Activity of THC, CBD, and CBN on Human ACE2 and SARS-CoV1/2 Main Protease to Understand Antiviral Defense Mechanism. Planta Med. 2022, 88, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen, N.; Pitakbut, T.; Schöfbänker, M.; Kühn, J.; Hrincius, E.R.; Ludwig, S.; Hensel, A.; Kayser, O. Cannabigerol and Cannabicyclol Block SARS-CoV-2 Cell Fusion. Planta Med. 2024, 90, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroński, A.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Stasiewicz, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Phytocannabinoids in the Pharmacotherapy of Psoriasis. Molecules 2023, 28, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.J.H.; Lim, Y.P.; Hartono, Y.D.; Go, M.K.; Fan, H.; Yew, W.S. Biosynthesis of Nature-Inspired Unnatural Cannabinoids. Molecules 2021, 26, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, V.; Park, J.G.; Cho, K.-H.; Choi, P.; Kim, T.; Ham, J.; Lee, J. Assessment of Antiviral Potencies of Cannabinoids against SARS-CoV-2 Using Computational and in Vitro Approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Puopolo, T.; Li, H.; Cai, A.; Seeram, N.P.; Ma, H. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors from a Library of Minor Cannabinoids by Biochemical Inhibition Assay and Surface Plasmon Resonance Characterized Binding Affinity. Molecules 2022, 27, 6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.C.; Yang, D.; Nicolaescu, V.; Best, T.J.; Gula, H.; Saxena, D.; Gabbard, J.D.; Chen, S.-N.; Ohtsuki, T.; Friesen, J.B.; et al. Cannabidiol Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication through Induction of the Host ER Stress and Innate Immune Responses. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabi6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Kavanagh, A.M.; Elliott, A.G.; Zhang, B.; Ramu, S.; Amado, M.; Lowe, G.J.; Hinton, A.O.; Pham, D.M.T.; Zuegg, J.; et al. The Antimicrobial Potential of Cannabidiol. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abichabki, N.; Zacharias, L.V.; Moreira, N.C.; Bellissimo-Rodrigues, F.; Moreira, F.L.; Benzi, J.R.L.; Ogasawara, T.M.C.; Ferreira, J.C.; Ribeiro, C.M.; Pavan, F.R.; et al. Potential Cannabidiol (CBD) Repurposing as Antibacterial and Promising Therapy of CBD plus Polymyxin B (PB) against PB-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, C.S.; Højrup, P.; Klitgaard, J.K. Cannabidiol Is an Effective Helper Compound in Combination with Bacitracin to Kill Gram-Positive Bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchweitz, J.P.; Karmaus, P.W.F.; Williams, K.J.; Harkema, J.R.; Kaminski, N.E. Targeted Deletion of Cannabinoid Receptors CB1 and CB2 Produced Enhanced Inflammatory Responses to Influenza A/PR/8/34 in the Absence and Presence of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaus, P.W.F.; Chen, W.; Crawford, R.B.; Harkema, J.R.; Kaplan, B.L.F.; Kaminski, N.E. Deletion of Cannabinoid Receptors 1 and 2 Exacerbates APC Function to Increase Inflammation and Cellular Immunity during Influenza Infection. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaus, P.W.F.; Chen, W.; Crawford, R.; Kaplan, B.L.F.; Kaminski, N.E. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Impairs the Inflammatory Response to Influenza Infection: Role of Antigen-Presenting Cells and the Cannabinoid Receptors 1 and 2. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 131, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudanski, K.; Wain, J. Considerations for Cannabinoids in Perioperative Care by Anesthesiologists. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Talukder, M. A Cannabinoid Hairy-Tale: Hair Loss or Hair Gain? J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 6653–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klahn, P. Cannabinoids-Promising Antimicrobial Drugs or Intoxicants with Benefits? Antibiotics 2020, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofs, L.; Sparo, M.D.; Sánchez Bruni, S.F. The Antimicrobial Effect behind Cannabis sativa. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2021, 9, e00761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, G.-N.; Jordan, E.N.; Kayser, O. Synthetic Strategies for Rare Cannabinoids Derived from Cannabis Sativa. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Ryu, Y.B.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, H.-J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, K.H.; Rho, M.-C.; Lee, W.S. Neuraminidase Inhibitory Activities of Flavonols Isolated from Rhodiola Rosea Roots and Their in Vitro Anti-Influenza Viral Activities. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6816–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, S.-J.; Cho, J.K.; Park, K.H.; Ryu, Y.B.; Lee, W.S. Selective and Slow-Binding Inhibition of Shikonin Derivatives Isolated from Lithospermum Erythrorhizon on Glycosyl Hydrolase 33 and 34 Sialidases. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 1740–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, J.-H.; Lee, I.-K.; Ki, D.-W.; Lee, M.-S.; Seok, S.-J.; Yun, B.-S. Neuraminidase Inhibitors from the Culture Broth of Phellinus Linteus. Mycobiology 2012, 40, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Dhanabalan, K.; Scalise, M.; Friemann, R.; Indiveri, C.; Dobson, R.C.; Vinothkumar, K.R.; Ramaswamy, S. Molecular Determinants of Neu5Ac Binding to a Tripartite ATP Independent Periplasmic (TRAP) Transporter. eLife 2025, 13, RP98158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Uddin, Z.; Song, Y.H.; Li, Z.P.; Kim, J.Y.; Ban, Y.J.; Park, K.H. Bacterial Neuraminidase Inhibition by Phenolic Compounds from Usnea Longissima. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 120, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, M.G.E.; Matei, M.-F.; Jaiswal, R.; Illenberger, S.; Kuhnert, N. Neuraminidase Inhibition of Dietary Chlorogenic Acids and Derivatives—Potential Antivirals from Dietary Sources. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frimayanti, N.; Yaeghoobi, M.; Namavar, H.; Ikhtiarudin, I.; Afzali, M. In Silico Studies and Biological Evaluation of Chalcone-Based 1,5-Benzothiazepines as New Potential H1N1 Neuraminidase Inhibitors. J. App Pharm. Sci. 2020, 10, 086–094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, H.; Şal, F.; Can, Z.; Kara, Y.; Yildiz, O.; Beldüz, A.; Çanakçi, S.; Kolayli, S. Targeting CoV-2 Spike RBD and ACE-2 Interaction with Flavonoids of Anatolian Propolis by in Silico and in Vitro Studies in Terms of Possible COVID-19 Therapeutics. Turk. J. Biol. 2021, 45, 530–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yao, L.; Chen, R.; He, J.; Lin, T.; Qiu, S.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.; Qiu, S.-X. Pinostrobin from Plants and Propolis against Human Coronavirus HCoV-OC43 by Modulating Host AHR/CYP1A1 Pathway and Lipid Metabolism. Antivir. Res. 2023, 212, 105570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, R.C. COVID-19 and Its Sequelae: A Platform for Optimal Patient Care, Discovery and Training. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis. 2021, 51, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasper, E.E.; Ajibola, V.O.; Onwuka, J.C. Nonlinear Regression Analysis of the Sorption of Crystal Violet and Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions onto an Agro-Waste Derived Activated Carbon. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Baty, F.; Ritz, C.; Charles, S.; Brutsche, M.; Flandrois, J.-P.; Delignette-Muller, M.-L. A Toolbox for Nonlinear Regression in R: The Package Nlstools. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 66, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeviani, W.M. wzRfun: Walmes Zeviani’s Collection of Functions; Paraná, Brazil, 2019. Available online: https://github.com/walmes/wzRfun (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Nishikawa, T.; Shimizu, K.; Tanaka, T.; Kuroda, K.; Takayama, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Hanada, N.; Hamada, Y. Bacterial Neuraminidase Rescues Influenza Virus Replication from Inhibition by a Neuraminidase Inhibitor. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quosdorf, S.; Schuetz, A.; Kolodziej, H. Different Inhibitory Potencies of Oseltamivir Carboxylate, Zanamivir, and Several Tannins on Bacterial and Viral Neuraminidases as Assessed in a Cell-Free Fluorescence-Based Enzyme Inhibition Assay. Molecules 2017, 22, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summary of Neuraminidase (NA) Amino Acid Substitutions Associated with Reduced Inhibition by Neuraminidase Inhibitors (NAIs) Among Avian Influenza Viruses of Group 1 and Group 2 Nas. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/summary-of-neuraminidase-(na)-amino-acid-substitutions-associated-with-reduced-inhibition-by-neuraminidase-inhibitors-(nais)-among-avian-influenza-viruses-of-group-1-and-group-2-nas (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Gesztelyi, R.; Zsuga, J.; Kemeny-Beke, A.; Varga, B.; Juhasz, B.; Tosaki, A. The Hill Equation and the Origin of Quantitative Pharmacology. Arch. Hist. Exact. Sci. 2012, 66, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, M.J.; Kotwal, S.S.; Bassi, A.; Hockham, C.; Jones, M.; Wilcox, A.; Pollock, C.; Burrell, L.M.; McGree, J.; Rathore, V.; et al. Angiotensin Receptor Blockers for the Treatment of COVID-19: Pragmatic, Adaptive, Multicentre, Phase 3, Randomised Controlled Trial. BMJ 2022, 379, e072175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, R.D.; Macedo, A.V.S.; de Barros E Silva, P.G.M.; Moll-Bernardes, R.J.; dos Santos, T.M.; Mazza, L.; Feldman, A.; D’Andréa Saba Arruda, G.; de Albuquerque, D.C.; Camiletti, A.S.; et al. Effect of Discontinuing vs Continuing Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers on Days Alive and Out of the Hospital in Patients Admitted with COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kwon, E.-B.; Kim, B.; Chung, H.-S.; Choi, G.; Kim, Y.-H.; Choi, J.-G. Mulberry Component Kuwanon C Exerts Potent Therapeutic Efficacy In Vitro against COVID-19 by Blocking the SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 RBD:ACE2 Receptor Interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Gutiérrez, G.; Elste, J.E.; Cabello-Gutiérrez, C.; Millán-Pacheco, C.; Martínez-Gómez, M.H.; Mejía-Alvarez, R.; Tiwari, V.; Mejía, A. A Potent Virucidal Activity of Functionalized TiO2 Nanoparticles Adsorbed with Flavonoids against SARS-CoV-2. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 5987–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupasinghe, H.P.V.; Davis, A.; Kumar, S.K.; Murray, B.; Zheljazkov, V.D. Industrial Hemp (Cannabis Sativa Subsp. Sativa) as an Emerging Source for Value-Added Functional Food Ingredients and Nutraceuticals. Molecules 2020, 25, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, A.H.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Derefinko, K. A Critical Review of Cannabis in Medicine and Dentistry: A Look Back and the Path Forward. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2022, 8, 613–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werlang, C.; Cárcarmo-Oyarce, G.; Ribbeck, K. Engineering Mucus to Study and Influence the Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurgea, L.T.; Morens, D.M.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Memoli, M.J. Influenza Neuraminidase: A Neglected Protein and Its Potential for a Better Influenza Vaccine. Vaccines 2020, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Haymour, H.S.; Zhang, F.; Xu, L.; Srinivasarao, M.; Low, P.S. A Universal Dual Mechanism Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Influenza Virus Infections. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Yap, Y.L. The 3D Structure Analysis of SARS-CoV S1 Protein Reveals a Link to Influenza Virus Neuraminidase and Implications for Drug and Antibody Discovery. J. Mol. Struct. Theochem. 2004, 681, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, B. Bioinformatics Studies on a Function of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein as the Binding of Host Sialic Acid Glycans. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 122, 103849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheau, C.; Caruntu, C.; Badarau, I.A.; Scheau, A.-E.; Docea, A.O.; Calina, D.; Caruntu, A. Cannabinoids and Inflammations of the Gut-Lung-Skin Barrier. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, M.; Wilson, K.; Abdulla, O.A.; Busbee, P.B.; Hall, A.; Carter, T.; Singh, N.; Chatterjee, S.; Nagarkatti, P.; Nagarkatti, M. Endocannabinoid Anandamide Attenuates Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome through Modulation of Microbiome in the Gut-Lung Axis. Cells 2021, 10, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| No. | Compound Names | % Inhibition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. perfringen Neuraminidase | Influenza A Viral Neuraminidase | SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease | SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein–Human ACE2 Interaction | ||
| 1 | THC | 99.53 (± 0.81) * | 100.00 (± 0.00) * | - | 57.82 (± 2.88) |
| 2 | CBD | 97.24 (± 2.41) * | 100.00 (± 0.00) * | - | 56.30 (± 2.54) |
| 3 | CBG | 100.00 (± 0.00) * | 100.00 (± 0.00) * | 86.99 (± 2.44) * | 97.60 (± 4.16) * |
| 4 | CBN | 34.87 (± 3.08) | 100.00 (± 0.00) * | - | 71.35 (± 8.21) |
| 5 | CBC | 95.05 (± 1.04) * | ND | 74.96 (± 2.25) | 95.25 (± 4.54) * |
| 6 | CBL | 94.25 (± 3.45) * | 100.00 (± 0.00) * | 100.00 (± 0.00) * | 64.71 (± 4.64) |
| 7 | CBT | 100.00 (± 0.00) * | 27.10 (± 0.77) | 62.00 (± 14.60) | 53.37 (± 5.99) |
| 8 | CBF | - | 13.86 (± 1.85) | 65.29 (± 3.28) | 99.22 (± 1.36) * |
| 9 | CBE | - | 100.00 (± 0.00) * | 80.26 (± 4.87) | 73.66 (± 0.50) |
| 10 | Positive control | 96.07 (± 2.06) | 100.00 (± 0.00) | 86.60 (± 23.20) | 100.00 (± 0.00) |
| No. | Compound Names | IC50 Value (µM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. perfringen Neuraminidase | Influenza A Viral Neuraminidase | SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease | ||
| 1 | THC | 20.3 | 38.34 | 16.23 |
| 2 | CBD | 4.53 * | 20.9 | 1.86 * |
| 3 | CBG | 6.92 * | 8.92 * | 5.68 * |
| 4 | CBN | - | 340.68 | - |
| 5 | CBC | 56.89 | - | - |
| 6 | CBL | 96.12 | 175.34 | 5.67 * |
| 7 | CBT | 150.97 | - | - |
| 8 | CBF | - | - | - |
| 9 | CBE | - | 0.87 ** | - |
| 10 | Positive control | 10.99 | 1.00 | 0.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pitakbut, T.; Kayser, O. Anti-Infective Screening of Selected Nine Cannabinoids Against Clostridium perfringens and Influenza A (H5N1) Neuraminidases, and SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease and Spike Protein Interactions. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030185
Pitakbut T, Kayser O. Anti-Infective Screening of Selected Nine Cannabinoids Against Clostridium perfringens and Influenza A (H5N1) Neuraminidases, and SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease and Spike Protein Interactions. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(3):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030185
Chicago/Turabian StylePitakbut, Thanet, and Oliver Kayser. 2025. "Anti-Infective Screening of Selected Nine Cannabinoids Against Clostridium perfringens and Influenza A (H5N1) Neuraminidases, and SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease and Spike Protein Interactions" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 3: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030185
APA StylePitakbut, T., & Kayser, O. (2025). Anti-Infective Screening of Selected Nine Cannabinoids Against Clostridium perfringens and Influenza A (H5N1) Neuraminidases, and SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease and Spike Protein Interactions. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(3), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030185






