Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal Key Responses of Cotton to Salt Stress Post-Germination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Experimental Design
2.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.3. Metabolomic Analysis
2.4. RNA-Seq Analysis
2.5. Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis
2.6. qRT-PCR Validation
2.7. Data Processing, Visualization, and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
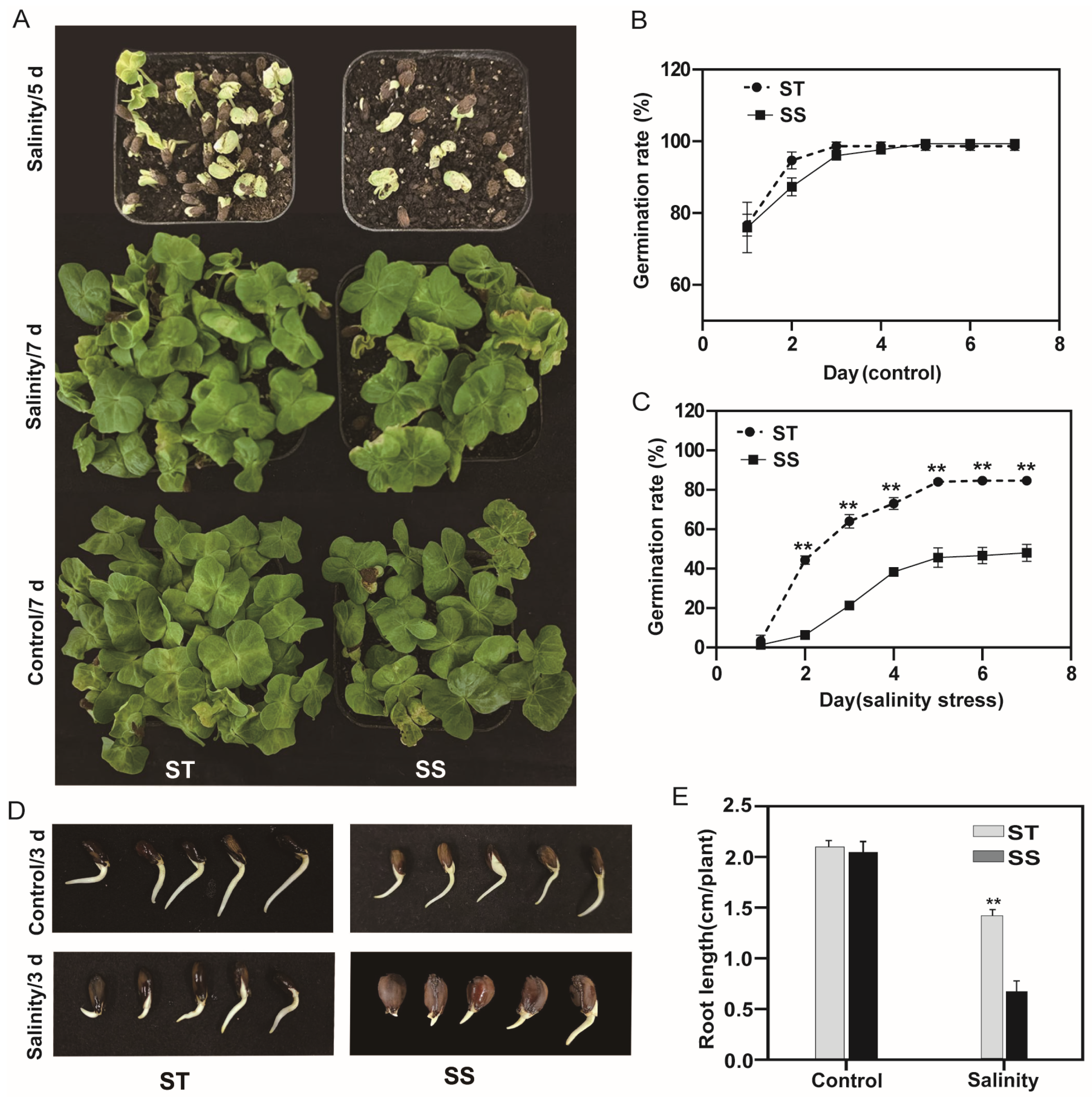
3.1. Salt Tolerance Assay of Cotton Cultivars During Germination and Post-Germination Stages
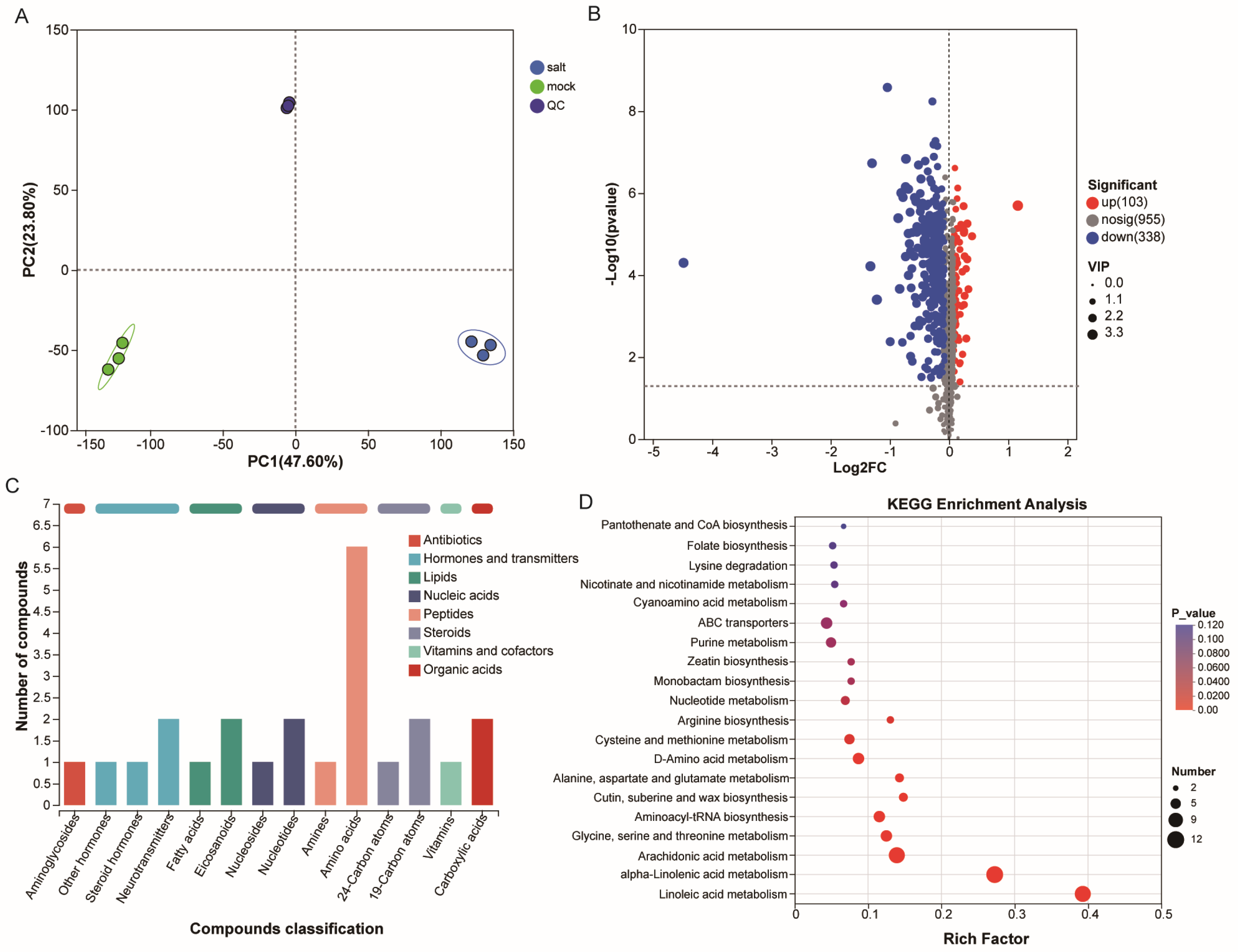
3.2. Metabolomic Characteristics of ST in the Post-Germination Stage Under Salt Stress
3.3. Identification of Salt Stress-Responsive Genes in ST Post-Germination Stage by Transcriptome Analysis
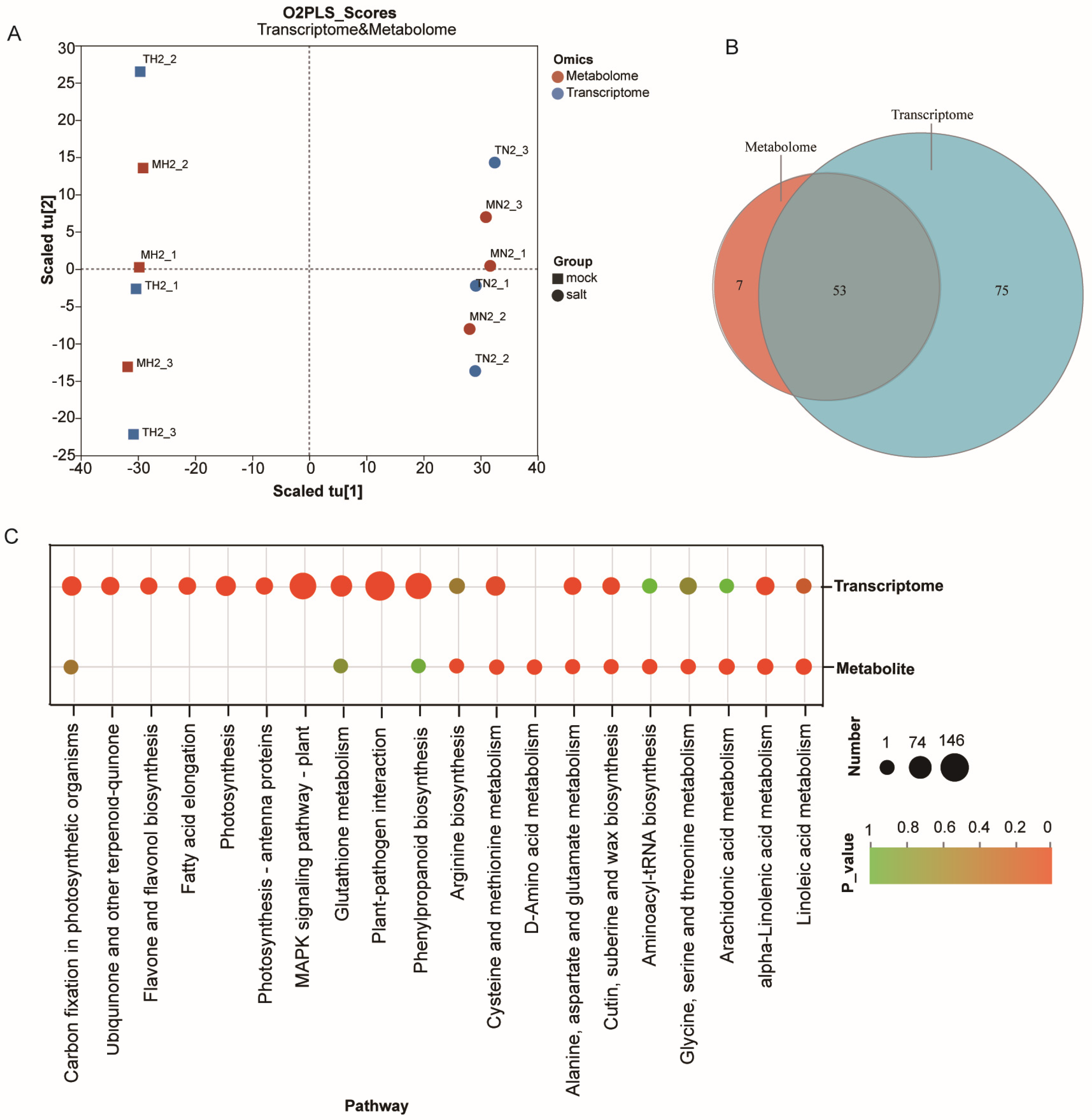
3.4. Integrated Metabolome–Transcriptome Analysis
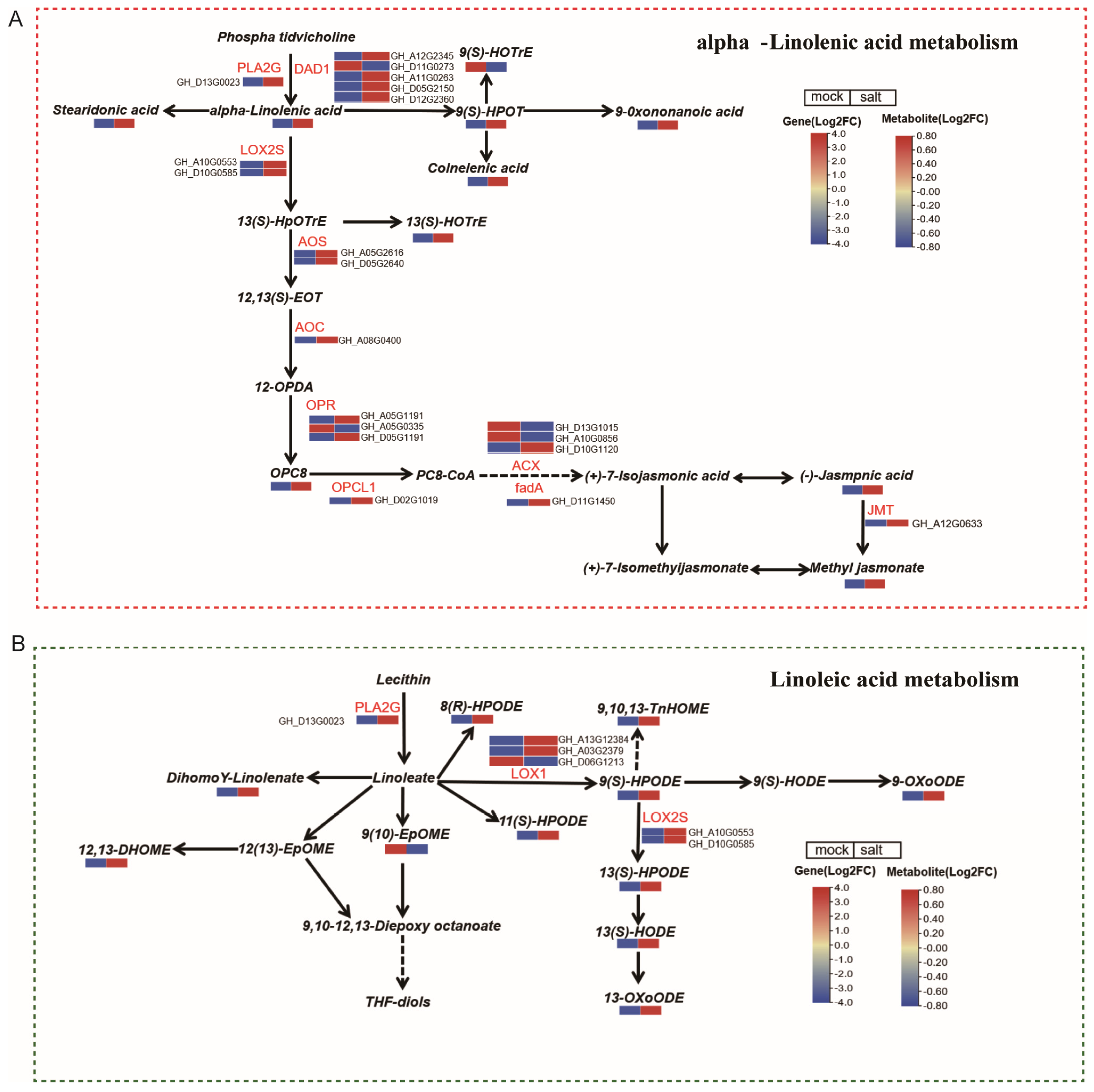
3.5. Integrated Analysis of Genes and Metabolites Related to Alpha-Linolenic Acid and Linoleic Acid Metabolism in ST in the Post-Germination Stage Under Salt Stress
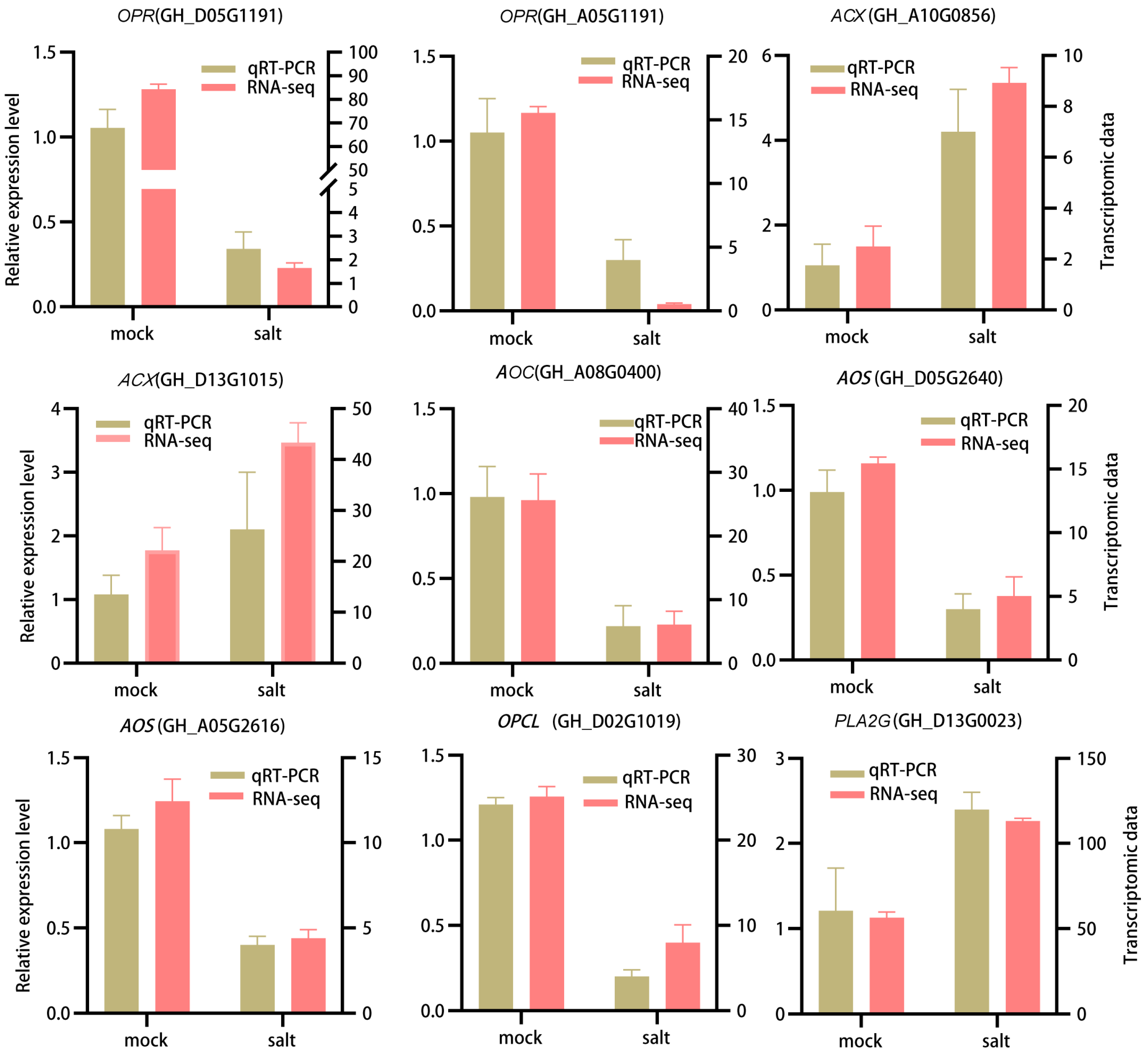
3.6. qRT-PCR Validation of DEGs in ST in the Post-Germination Stage Under Salt Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.; Tian, Z.; Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Roberts, J.A.; Zhang, X.; Miao, Y. Genome-wide analysis and characterization of F-box gene family in Gossypium hirsutum L. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; Lu, B.; Liu, L.; Meng, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H.; et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on root physiology, transcriptome and metabolome of cotton seedlings under salt stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zheng, H.; Wu, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Jia, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Lei, L.; Zou, D.; et al. QTL Mapping and Candidate Gene Analysis for Alkali Tolerance in Japonica Rice at the bud Stage Based on Linkage Mapping and Genome-Wide Association Study. Rice 2020, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Li, X.Z.; Lin, S.W.; Ma, Y.X. Economic evaluation and systematic review of salt marsh restoration projects at a global scale. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 865516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaygan, M.; Baumgartl, T. Reclamation of salt-affected land: A review. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Yang, T.; Pang, B.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Liang, W.; Rui, C.; Gao, W. Response of different cotton genotypes to salt stress and re-watering. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, I.; Aleem, S.; Farooq, J.; Rizwan, M.; Younas, A.; Sarwar, G.; Chohan, S. Salinity stress in cotton: Effects, mechanism of tolerance and its management strategies. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2019, 25, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.X.; Zhao, H.X.; Cui, J.L. Endophyte is an effective supplement to traditional factors affecting plant seed germination and its mechanism research progress. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2025, 72, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yoshida, H.; Chu, C.; Matsuoka, M.; Sun, J. Seed dormancy and germination in rice: Molecular regulatory mechanisms and breeding. Mol. Plant 2025, 18, 960–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, N.; Lounifi, I.; Cueff, G.; Collet, B.; Clément, G.; Balzergue, S.; Huguet, S.; Valot, B.; Galland, M.; Rajjou, L. Multi-omics approaches unravel specific features of embryo and endosperm in rice seed germination. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 867263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolikova, G.; Krylova, E.; Petrik, I.; Vilis, P.; Vikhorev, A.; Strygina, K.; Strnad, M.; Frolov, A.; Khlestkina, E.; Medvedev, S. Involvement of Abscisic Acid in Transition of Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Seeds from Germination to Post-Germination Stages. Plants 2024, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolikova, G.; Medvedev, S. Seed-to-seedling transition: Novel aspects. Plants 2022, 11, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Luo, P.; Wang, Z.; Shi, S.; Gao, W.; Li, S. RNA-seq and WGCNA analyses reveal key regulatory modules and genes for salt tolerance in cotton. Genes 2024, 15, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.; Wijewardene, I.; Cai, Y.; Esmaeili, N.; Shen, G.; Hequet, E.; Ritchie, G.; Payton, P.; Zhang, H. Co-overexpression of RCA and AVP1 in Cotton Substantially Improves Fiber Yield for Cotton Under Drought, Moderate Heat, and Salt Stress Conditions. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2023, 5, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Rehman, A.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Du, X.; Peng, Z.; He, S. Late embryogenesis abundant gene GhLEA-5 of semi-wild cotton positively regulates salinity tolerance in upland cotton. Gene 2025, 949, 149372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zong, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, S.; Duan, M.; Lu, R.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z. Integrated analysis of transcriptome and metabolome reveals molecular mechanisms of salt tolerance in seedlings of upland rice landrace 17SM-19. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 961445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; An, W.; He, X.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Z.; He, J.; Wan, R. Widely-Targeted Metabolic Profiling in Lycium barbarum Fruits under Salt-alkaline Stress Uncovers Mechanism of Salinity Tolerance. Molecules 2022, 27, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, D.; Ma, Z.; Yan, F.; Liu, Y. Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Role of phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis Pathway in the Salt Tolerance Process of Sophora alopecuroides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, B.; Li, C.; Yang, Z.; Ni, R.; Chen, L.; Liu, N.; Mao, P.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X. Synergistic responses of physiological, transcriptomic, and metabolomic levels in soybean (Glycine max (Linn.) Merr.) under combined salt-alkali stress. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 234, 121499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reta, K.; Lazarovitch, N.; Fait, A. Metabolic and physiological analysis reveals distinct salinity tipping point in Vitis vinifera cv. Syrah to enter a stress response mode. Plant Stress 2025, 16, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Chen, L. Unravelling the Dynamic Physiological and metabolome Responses of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Saline-alkaline Stress at the Seedling Stage. Metabolites 2025, 15, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackey, O.K.; Feng, N.; Mohammed, Y.Z.; Dzou, C.F.; Zheng, D.; Zhao, L.; Shen, X. A comprehensive review on rice responses and tolerance to salt stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1561280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Meng, W.; Sun, Z.; Tan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, B.; Yang, J. Integrated analysis of transcriptome and metabolome reveals molecular mechanisms of rice with different salinity tolerances. Plants 2023, 12, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Li, Y.; Feng, N.-J.; Zheng, D.-F.; Khan, A.; Du, Y.-W.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Sun, Z.-Y.; Wu, J.-S.; Xue, Y.-B.; et al. Integrative analysis of transcriptome and metabolome reveal molecular mechanism of tolerance to salt stress in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, R.; Ahmad, F.; Kaya, C.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Muneer, S.; Kumar, V.; Meena, M.; Liu, H.; Upadhyaya, H.; Seth, C.S. Decrypting proteomics, transcriptomics, genomics, and integrated omics for augmenting the abiotic, biotic, and climate change stress resilience in plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2025, 305, 154430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Si, L.; Zhang, L.; Guo, R.; Wang, R.; Dong, H.; Guo, C. Metabolomics and transcriptomics analysis revealed the response mechanism of alfalfa to combined cold and saline-alkali stress. Plant J. 2024, 119, 1900–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Lian, Y.; Li, S.; Fahim, A.M.; Hou, X.; Liu, L.; Pu, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.; et al. Integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis revealed molecular regulatory mechanism of saline-alkali stress tolerance and identified bHLH142 in winter rapeseed (Brassica rapa). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 295, 139542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Huo, X.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. Comparative phenotypic and transcriptomic analysis reveals key responses of upland cotton to salinity stress during postgermination. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 639104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Tao, M.; Lv, T.; Li, F.; Yu, D.; Liu, C. Mechanistic insight into the impact of polystyrene microparticle on submerged plant during asexual propagules germination to seedling: Internalization in functional organs and alterations of physiological phenotypes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.; Masson, P. Processing and analysis of GC/LC-MS-based metabolomics data. In Metabolic Profiling: Methods and Protocols; Metz, T.O., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 708, pp. 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Tian, X.; Lin, X.; Han, Y.; Han, Z.; Sha, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. A transposon insertion in the promoter of OsUBC12 enhances cold tolerance during japonica rice germination. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Kong, X.; Wang, X.; Si, A.; Zhao, F.; Huang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Z. Time-course transcriptomics analysis reveals molecular mechanisms of salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive cotton cultivars in response to salt stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Yamada, T.; Kanehisa, M.; Bork, P. IPath: Interactive exploration of biochemical pathways and networks. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Tian, L.; Zhi, Z.; Wang, X.; Jia, W.; Zhou, R.; Chen, H.; Zhu, G.P.; Chen, X.; et al. Integrated transcriptome and chromatin accessibility dynamics in developing walnut kernels reveal regulators of oil accumulation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 233, 121380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Zhou, L.; Shan, L.; Li, F.; Li, Z. Phosphatase GhDs PTP3a interacts with annexin protein GhANN8b to reversely regulate salt tolerance in cotton (Gossypium spp.). New Phytol. 2019, 223, 1856–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Geilfus, C.M.; Dietz, K.J. Salinity and crop yield. Plant Biol. 2019, 21, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.; Ren, Y. Transcriptome and metabolome Analysis of Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) Seed Pretreatment with MgSO4 in Response to Salinity Stress. Life 2022, 12, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Fu, Q.; Huang, J.; Qi, T.; Fu, Y.; Kaisaier, K. Analysis of salt tolerance capacity of Xinjiang Cotton Guring germination. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2025, 27, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Xu, F.; Fu, Q.; Huang, J.; Qi, T.; Meng, A.; Fu, Y.; Kaisaier, K. Effects of different types of salt and alkali stress on cotton seed germination. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2024, 61, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Cao, P.; Luo, M.; Wang, F. Unraveling wheat’s response to salt stress during early growth stages through transcriptomic analysis and co-expression network profiling. BMC Genom. Data 2024, 25, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Liu, A.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Jin, Y. Mechanism of salt-inhibited early seed germination analysed by transcriptomic sequencing. Seed Sci. Res. 2019, 29, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Ha, Y.; Lee, M.M.; Nam, K.H. Salt overly sensitive components differentially regulate seed germination and seedling growth under saline conditions in Arabidopsis. J. Plant Biol. 2025, 68, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Molecular insights into salinity responsiveness in contrasting genotypes of rice at the seedling stage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Ren, Y. Transcriptome and metabolome Analyses of Salt Stress Response in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) Seed pretreated with NaCl. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xing, H.; Zeng, W.; Xu, J.; Mao, L.; Wang, L.; Feng, W.; Tao, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Genome-wide association and differential expression analysis of salt tolerance in Gossypium hirsutum L. at the germination stage. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Du, S.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, J. Analysis of the Antioxidant Mechanism of Tamarix ramosissima Roots under NaCl Stress Based on Physiology, transcriptomic and metabolomic. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, M.; Zhao, X.; Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Wu, X.; Lu, Z.; Han, Z. Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis revealed the salt tolerance mechanism of Populus talassica × Populus euphratica. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, G.; Li, W.; Xie, L.; Zhan, S.; Yao, X.; Zuo, Z.; Tian, D. Analysis of volatile metabolome and transcriptome in sweet basil under drought stress. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Duan, L. Combining Physiological and metabolomic Analysis to Unravel the Regulations of coronatine Alleviating water Stress in Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Biomolecules 2020, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Bian, X.; Yu, J.; Xiao, X.; Duan, B.; Huang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Ma, N. Comparative metabolomics analysis of tolerant and sensitive genotypes of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) seedlings under drought stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 296, 108797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, N.; Li, Y.; Tang, H.; Huang, X.; Yang, T.; Xu, J. Integrated Ultrastructural, Physiological, Transcriptomic, and Metabolomic Analysis Uncovers the Mechanisms by Which Nicotinamide Alleviates Cadmium Toxicity In Pistia stratiotes L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 467, 133702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Shin, S.; Choi, S.; Choi, G.J.; Son, H. A mitochondrial NAD/NADH kinase governs fungal virulence through an oxidative stress response and arginine biosynthesis in Fusarium graminearum. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 283, 127692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, M.; Turkyilmaz Unal, B.; García-Caparrós, P.; Khursheed, A.; Gul, A.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Osmoregulation and its actions during the drought stress in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mostafa, S.; Zeng, W.; Jin, B. Function and mechanism of jasmonic acid in plant responses to abiotic and biotic stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhang, N.; Ai, X.; Wang, M.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, L.; Xia, G. A wheat allene oxide cyclase gene enhances salinity tolerance via jasmonate signaling. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lou, S.; Gong, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Zhai, M.; Duan, L.; et al. Coronatine-treated seedlings increase the tolerance of cotton to low-temperature stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 213, 108832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.I.; Pandian, S.; Rakkammal, K.; Largia, M.J.V.; Thamilarasan, S.K.; Balaji, S.; Zoclanclounon, Y.A.B.; Shilpha, J.; Ramesh, M. Jasmonates in plant growth and development and elicitation of secondary metabolites: An updated overview. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 942789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Viswanathan P, A.; Bari, V.K. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing of jasmonic acid pathways to enhance biotic & abiotic stress tolerance: An overview & prospects. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2025, 25, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, H.; Xiong, L. Endogenous auxin and jasmonic acid levels are differentially modulated by abiotic stresses in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraku, M.L.; Magwanga, R.O.; Cai, X.; Kirungu, J.N.; Xu, Y.; Mehari, T.G.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Agong, S.G.; Peng, R.; et al. Functional characterization of GhACX3 gene reveals its significant role in enhancing drought and salt stress tolerance in cotton. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 658755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yao, Z.; Ruan, M.; Wang, R.; Ye, Q.; Wan, H.; Zhou, G.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, C.; et al. The PLA gene family in tomato: Identification, phylogeny, and functional characterization. Genes 2025, 16, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.X.; Song, J.K.; Zhang, M.; Shahzad, K.; Zhang, X.X.; Guo, L.P.; Qi, T.X.; Tang, H.N.; Shi, L.P.; Qiao, X.Q.; et al. Integrated multiple environmental tests and QTL mapping uncover novel candidate genes for seed oil content in upland cotton. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 220, 119193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Ding, N.Z. Plant unsaturated fatty acids: Multiple roles in stress response. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 562785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.W.; Cao, X.Y.; Jiang, W.H.; Xu, G.Z.; Liang, Q.Z.; Yang, Z.Y. Cryoprotectant-mediated cold stress mitigation in litchi flower development: Transcriptomic and metabolomic perspectives. Metabolites 2024, 14, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Bu, Y.; Li, L. Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Rice Leaves Response to High Saline–Alkali Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Xiang, R.; Bai, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal Key Responses of Cotton to Salt Stress Post-Germination. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110951
Liu Y, Shi Y, Xiang R, Bai J, Wang J, Zhang X. Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal Key Responses of Cotton to Salt Stress Post-Germination. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(11):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110951
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanzhen, Yaxin Shi, Ren Xiang, Jianduo Bai, Jingshun Wang, and Xianliang Zhang. 2025. "Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal Key Responses of Cotton to Salt Stress Post-Germination" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 11: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110951
APA StyleLiu, Y., Shi, Y., Xiang, R., Bai, J., Wang, J., & Zhang, X. (2025). Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal Key Responses of Cotton to Salt Stress Post-Germination. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(11), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110951





