Deciphering the Anti-Cancer Efficacy of the Combination of Small-Molecule Inhibitor KAN0438757 and Curcumin in Lung Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture Conditions
2.3. Cell Viability Test
2.4. Evaluation of Real-Time Cell Proliferation
2.5. In Vitro Scratch Assay
2.6. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) Assay
2.7. Acridine Orange and Ethidium Bromide Double Staining
2.8. Single Cell Gel Electrophoresis (Comet Assay)
2.9. Cell Lysate Preparation and Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
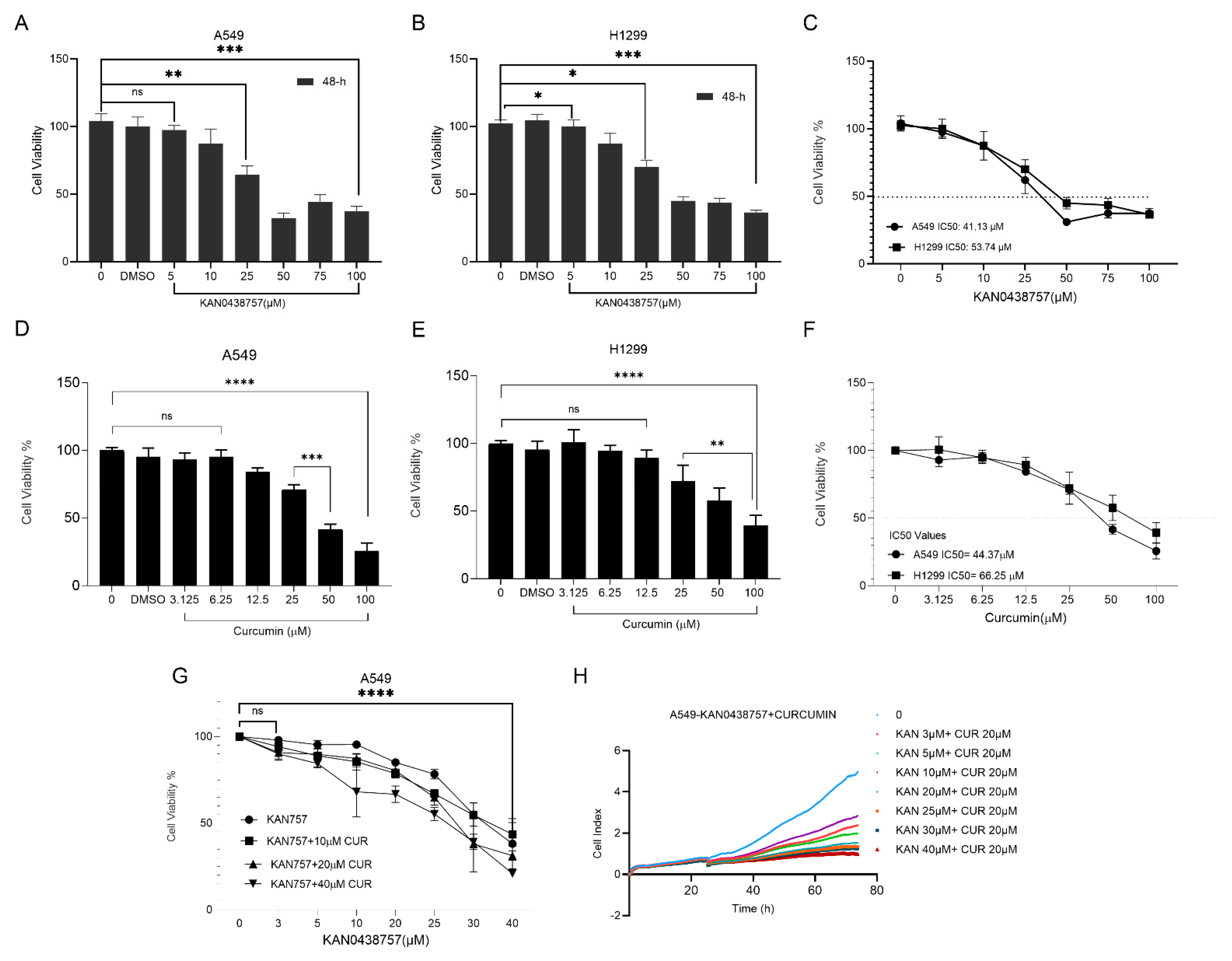
3.1. Antiproliferative Effects of KAN0438757, Curcumin, and Their Combination in A549 and H1299 Cells
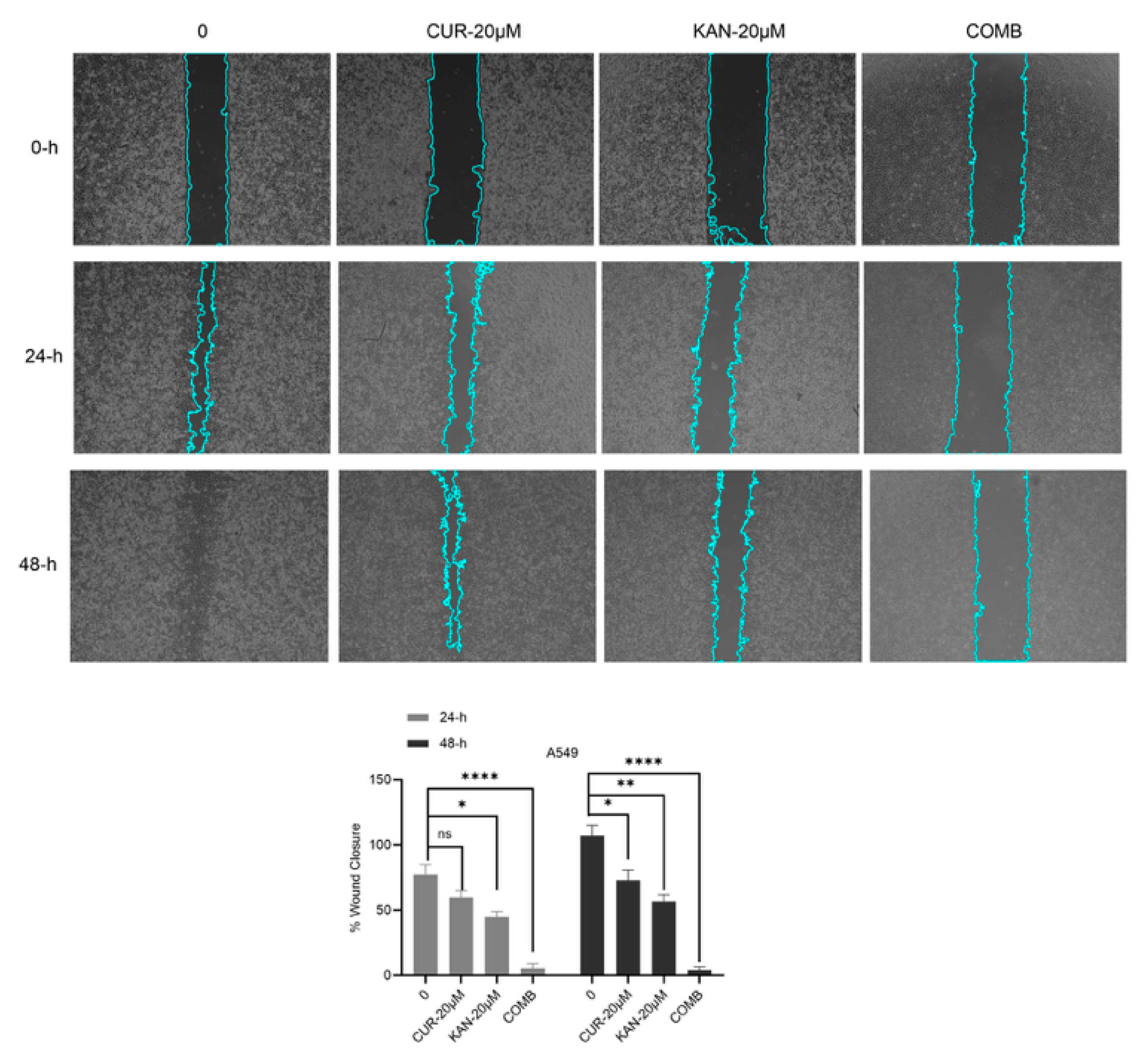
3.2. Cell Migration Findings of KAN0438757 and Curcumin Combinations in A549 Cell Line
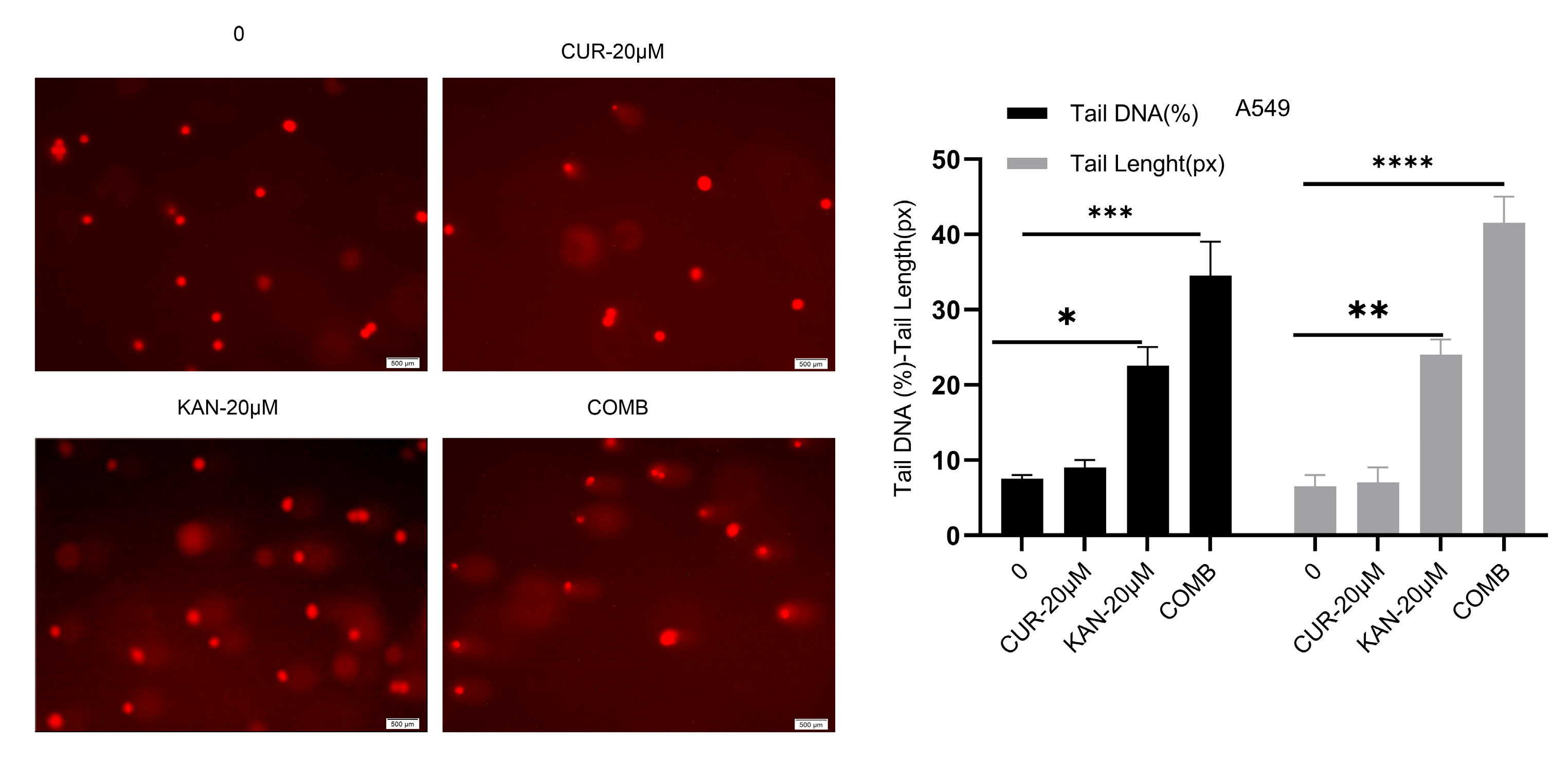
3.3. DNA Damage in A549 Cells Induced by KAN0438757–Curcumin Combination
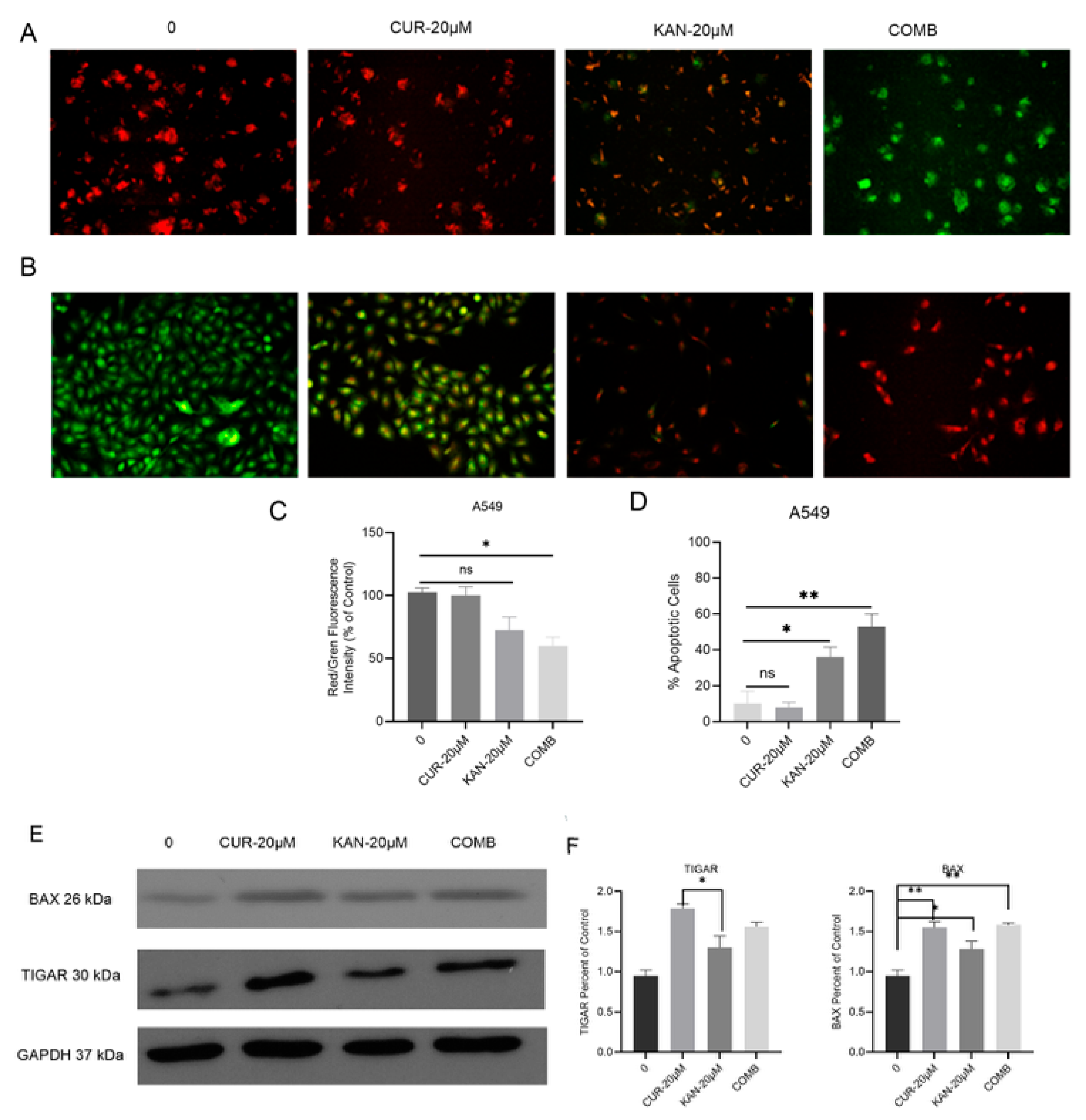
3.4. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Cell Death in A549 Cells Treated with KAN0438757–Curcumin Combination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PFKFB | 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6 bisphosphatase |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| MMP | Mitochondrial membrane potential |
| PFKFB3 | 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 3 |
| Curcumin | Diferuloylmethane; Cur |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| RTCA | Real-Time Cell Analyzer |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| CI | Cell Index |
| NMA | Normal-Melting-Point Agarose |
| LMA | Low-Melting-Point Agarose |
| AO/EtBr | Acridine Orange and Ethidium Bromide |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Difluoride |
| IC50 | Half-Maximal Inhibitory Concentration |
References
- Yu, X.; Jia, L.; Tang, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, S. Regulation of cisplatin resistance in lung cancer by epigenetic mechanisms. Clin. Epigenetics 2025, 17, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kwon, R.; Curran, W.J., Jr.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L. Lung cancer: Current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiseo, M.; Bartolotti, M.; Gelsomino, F.; Ardizzoni, A. First-line treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: The emerging role of the histologic subtype. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2009, 9, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Pan, H.; Liu, Z.; Xie, J.; Han, W. Roles of PFKFB3 in cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, J.; Qian, L.; Ke, H.; Yao, C.; Tian, W.; Zhang, J. Expression of PFKFB3 and Ki67 in lung adenocarcinomas and targeting PFKFB3 as a therapeutic strategy. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 445, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, B.; Telang, S.; Clem, A.; Yalcin, A.; Meier, J.; Simmons, A.; Chesney, J. Small-molecule inhibition of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase activity suppresses glycolytic flux and tumor growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lypova, N.; Telang, S.; Chesney, J.; Imbert-Fernandez, Y. Increased 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2, 6-bisphosphatase-3 activity in response to EGFR signaling contributes to non–small cell lung cancer cell survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10530–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, L.; Yan, H.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, J. Non-canonical roles of PFKFB3 in regulation of cell cycle through binding to CDK4. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, N.M.; Färnegårdh, K.; Bonagas, N.; Ninou, A.H.; Groth, P.; Wiita, E.; Helleday, T. Targeting PFKFB3 radiosensitizes cancer cells and suppresses homologous recombination. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantelmo, A.R.; Conradi, L.C.; Brajic, A.; Goveia, J.; Kalucka, J.; Pircher, A.; Carmeliet, P. Inhibition of the glycolytic activator PFKFB3 in endothelium induces tumor vessel normalization, impairs metastasis, and improves chemotherapy. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, T.; Goldhardt, T.; Edelmann, M.; Rogge, T.; Rauch, K.; Kyuchukov, N.D.; Conradi, L.C. Effects of the novel pfkfb3 inhibitor kan0438757 on colorectal cancer cells and its systemic toxicity evaluation in vivo. Cancers 2021, 13, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsamydai, A.; Jaber, N. Pharmacological aspects of curcumin: Review article. Int. J. Pharmacogn. 2018, 5, 313–326. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Gao, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Fan, Y.; Ma, W.; Yu, Y. Antitumor activity of curcumin by modulation of apoptosis and autophagy in human lung cancer A549 cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzarini, E.; Mariano, S.; Tacconi, S.; Carata, E.; Tata, A.M.; Dini, L. Novel therapeutic delivery of nanocurcumin in central nervous system related disorders. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Kumar, A.; Bharti, A.C. Anticancer potential of curcumin: Preclinical and clinical studies. Anticancer Res. 2003, 23, 363–398. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, H.J.; Patel, V.; Sadikot, R.T. Curcumin and lung cancer—A review. Target. Oncol. 2014, 9, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Mohd Tajuddin, W.N.B.; Lajis, N.H.; Abas, F.; Othman, I.; Naidu, R. Mechanistic Understanding of Curcumin’s Therapeutic Effects in Lung Cancer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, Ö.; Saruhan, S.; Ağca, C.A. Kan0438757: A Novel Pfkfb3 Inhibitor That Induces Programmed Cell Death and Suppresses Cell Migration in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cells. Biotechnol. Acta 2023, 16, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çağlar, H.O.; Süslüer, S.Y.; Kavaklı, Ş.; Gündüz, C.; Ertürk, B.; Özkınay, F.; Haydaroğlu, A. Meme kanseri kök hücrelerinde elajik asit ile indüklenmiş miRNA’ların ifadesi ve elajik asidin apoptoz üzerine etkisi. Ege Tıp Derg. 2017, 56, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, H.; Lilja, J.; Ivaska, J. Using xCELLigence RTCA Instrument to Measure Cell Adhesion. Bio-Protoc. 2017, 7, e2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cory, G. Scratch-wound assay. In Cell Migration: Developmental methods and protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 769, pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kasibhatla, S.; Amarante-Mendes, G.P.; Finucane, D.; Brunner, T.; Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Green, D.R. Acridine orange/ethidium bromide (AO/EB) staining to detect apoptosis. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2006, 2006, pdb-prot4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, D.; Ağca, C.A. AZD1390, an Ataxia telangiectasia mutated inhibitor, enhances cisplatin mediated apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2025, 444, 114382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, C.A.; Kırıcı, M.; Nedzvetsky, V.S.; Gundogdu, R.; Tykhomyrov, A.A. The Effect of TIGAR Knockdown on Apoptotic and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Markers Expression in Doxorubicin-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer A549 Cell Lines. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Report on Trends in Prevalence of Tobacco Smoking 2000–2025; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pendharkar, D.; Ausekar, B.V.; Gupta, S. Molecular Biology of Lung Cancer-A Review. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 4, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburg, O.; Wind, F.; Negelein, E. The Metabolism of Tumors in the Bod. J. Gen. Physiol. 1927, 8, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Xu, J.; Huo, Y. PFKFB3-mediated endothelial glycolysis promotes pulmonary hypertension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13394–13403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Thompson, C.B. The emerging hallmarks of cancer metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, S.; Schulze, A. Balancing glycolytic flux: The role of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose 2, 6-bisphosphatases in cancer metabolism. Cancer Metab. 2013, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Gupta, R.K.; Srivastava, R. Curcumin-the yellow magic. Asian J. Appl. Sci. 2011, 4, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Jin, L.; Deng, C.; Guan, Y.; Kalogera, E.; Ray, U.; Shridhar, V. Inhibition of PFKFB3 induces cell death and synergistically enhances chemosensitivity in endometrial cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1409–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lypova, N.; Dougherty, S.M.; Lanceta, L.; Chesney, J.; Imbert-Fernandez, Y. PFKFB3 Inhibition Impairs Erlotinib-Induced Autophagy in NSCLCs. Cells 2021, 10, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharuddin, P.; Satar, N.; Fakiruddin, K.S.; Zakaria, N.; Lim, M.N.; Yusoff, N.M.; Yahaya, B.H. Curcumin improves the efficacy of cisplatin by targeting cancer stem-like cells through p21 and cyclin D1-mediated tumour cell inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, G.R.; Srivastava, A.S.; Hassanein, T.I.; Chauhan, D.P.; Carrier, E. Induction of apoptosis in human lung cancer cells by curcumin. Cancer Lett. 2004, 208, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorova, L.D.; Popkov, V.A.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; Silachev, D.N.; Pevzner, I.B.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Zorov, D.B. Mitochondrial membrane potential. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 552, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klarer, A.C.; O’Neal, J.; Imbert-Fernandez, Y.; Clem, A.; Ellis, S.R.; Clark, J.; Telang, S. Inhibition of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (PFKFB3) induces autophagy as a survival mechanism. Cancer Metab. 2014, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Ye, L.; Zhang, J.; Yu, P.; Wang, H.; Ye, Z.; Tian, J. PFK15, a small molecule inhibitor of PFKFB3, induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and inhibits invasion in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özdemir, D.; Ağca, C.A. Deciphering the Anti-Cancer Efficacy of the Combination of Small-Molecule Inhibitor KAN0438757 and Curcumin in Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110892
Özdemir D, Ağca CA. Deciphering the Anti-Cancer Efficacy of the Combination of Small-Molecule Inhibitor KAN0438757 and Curcumin in Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(11):892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110892
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzdemir, Deniz, and Can Ali Ağca. 2025. "Deciphering the Anti-Cancer Efficacy of the Combination of Small-Molecule Inhibitor KAN0438757 and Curcumin in Lung Cancer Cell Lines" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 11: 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110892
APA StyleÖzdemir, D., & Ağca, C. A. (2025). Deciphering the Anti-Cancer Efficacy of the Combination of Small-Molecule Inhibitor KAN0438757 and Curcumin in Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(11), 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110892






