Systematic Review: Exosomes as Molecular Messengers in the Development of Obesity-Related Complications in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
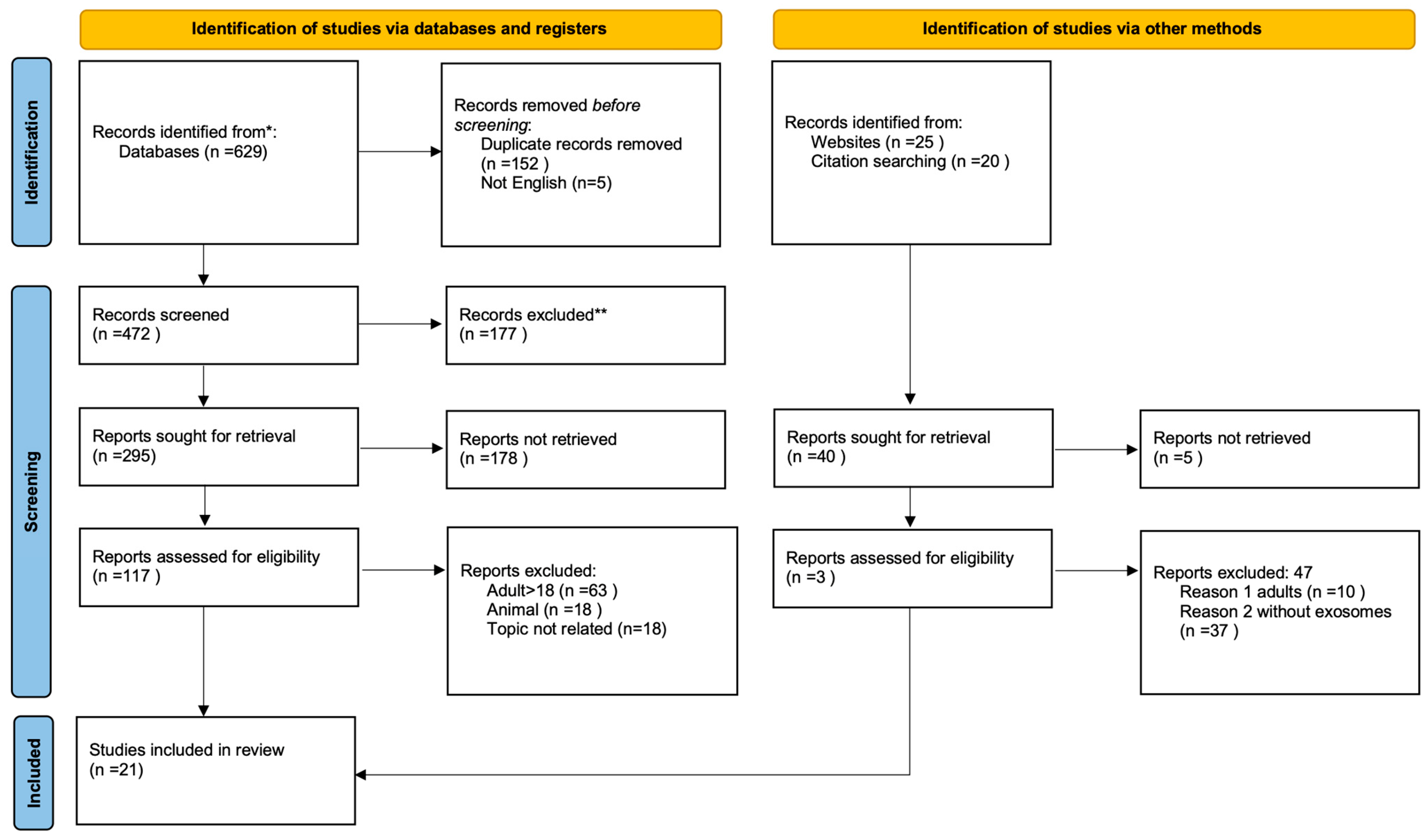
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
- -
- Study characteristics (authors, year of publication).
- -
- Participant demographics (age, sex, BMI, comorbidities).
- -
- EV source and type (e.g., plasma, urine, breast milk, adipose tissue).
- -
- Molecular cargo analyzed (miRNAs, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids).
- -
- Main outcomes and clinical correlations (insulin resistance, MAFLD, endothelial dysfunction, renal injury, etc.).
- -
- Studies involving participants aged 0–18 years.
- -
- Participants classified as overweight or obese according to standardized BMI criteria.
- -
- Studies investigating extracellular vesicles (EVs), particularly exosomes, in the context of obesity or obesity-related complications.
- -
- Articles assessing molecular cargo of EVs (e.g., microRNAs, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids) and their associations with metabolic, cardiovascular, hepatic or renal outcomes.
- -
- Original peer-reviewed research (cohort, case–control, cross-sectional, or interventional designs).
- -
- Publications in English between 2020–2025.
- -
- Animal or in vitro studies without validation in pediatric human populations.
- -
- Studies not focusing on obesity or obesity-related complications (e.g., general growth, normal-weight controls without an obesity subgroup).
- -
- Papers investigating EVs but without specific analysis of exosomal content or functions.
- -
- Editorials, conference abstracts, and case reports.
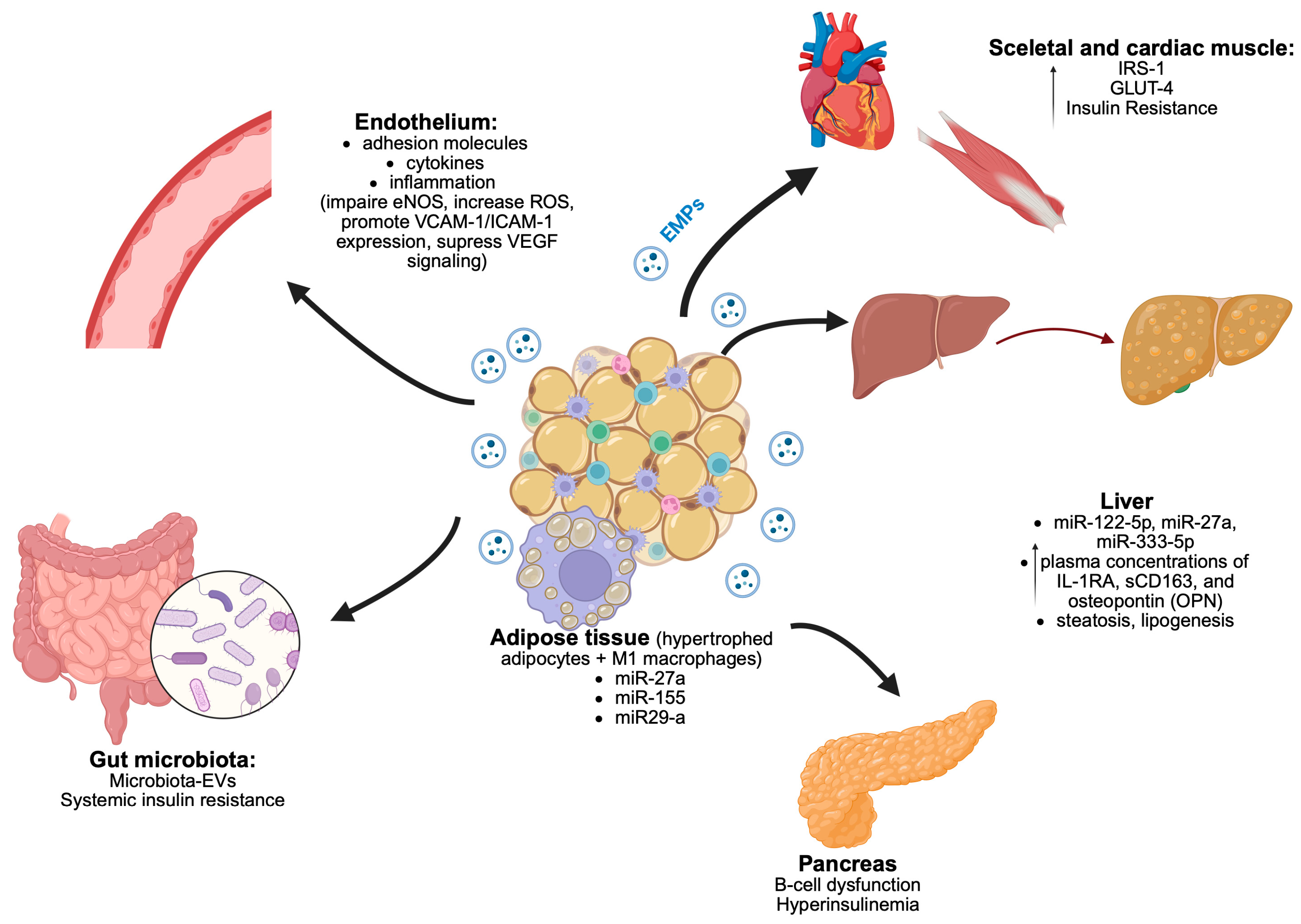
3.1. Adipose Tissue and Its Role in Pathophysiology of Obesity-Related Comorbidities
3.2. Endothelial Dysfunction in Obesity and the Role of Exosomes
3.3. Extracellular Vesicles in Maternal—Fetal Communication
3.4. Extracellular Vesicles in Pathogenesis of Glucose Disturbances, Insulin Resistance and Diabetes
3.5. Extracellular Vesicles and Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)
3.6. Extracellular Vesicles in Obesity-Related Kidney Disease
3.7. Extracellular Vesicles in Cardiovascular Complications in Children with Obesity
3.8. Exercise-Induced Extracellular Vesicles and Metabolic Adaptation in Pediatric Obesity
3.9. Extracellular Vesicles in the Context of Bariatric Surgery and Metabolic Improvement
4. Discussion
- -
- Molecular messengers for early detection of complications such as metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), endothelial dysfunction, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, kidney dysfunction.
- -
- Therapeutic targets, since modulation of EV release or uptake may attenuate inflammation and vascular damage.
- -
- Dynamic indicators of intervention efficacy, given that EV signatures have been shown to change following lifestyle modifications, structured exercise programs, or bariatric surgery.
5. Clinical Significance and Innovation
- -
- Early detection of complications: EV-derived miRNAs and proteins may act as sensitive, non-invasive biomarkers for the early identification of MAFLD, vascular dysfunction, or insulin resistance, before irreversible damage occurs.
- -
- Therapeutic targeting: Modulation of exosome biogenesis, release, or uptake represents a novel therapeutic approach. Moreover, exosomes may serve as natural carriers for drugs or RNA-based therapies, enabling targeted delivery with reduced systemic toxicity.
- -
- Monitoring interventions: EV profiles respond dynamically to lifestyle modifications, physical activity, and bariatric surgery, making them valuable biomarkers to track treatment efficacy and therapeutic “windows of opportunity.”
6. Limitations
- -
- Timeframe restriction: Our systematic search covered studies published within the last 5 years. While this was a deliberate decision to capture the most up-to-date and methodologically relevant data in this rapidly evolving field, it may have led to omission of earlier but still valuable publications,
- -
- Heterogeneity of methodologies: The included studies used diverse techniques for EVs isolation, characterization, and biomarker profiling. This heterogeneity limits the possibility of direct comparison and prevents formal meta-analysis
- -
- Small number of pediatric studies: Compared to adults, studies focusing specifically on extracellular vesicles in children remain scarce. This limits the strength of conclusions directly applicable to the pediatric population and underscores the need for large-scale, longitudinal pediatric studies.
- -
- Narrative synthesis: Owing to the diversity of study designs and outcome measures, we performed a narrative rather than quantitative synthesis. Although this allowed us to summarize key findings, it reduces the ability to assess pooled effect sizes,
- -
- Potential publication bias: As in most systematic reviews, there is a possibility that negative or null findings remain unpublished, which may lead to an overestimation of positive associations.
7. Future Perspectives
- -
- Elucidating the longitudinal dynamics of EVs during the progression of pediatric obesity and its treatment.
- -
- Developing EV-based risk stratification tools to personalize prevention and therapy.
- -
- Advancing EV engineering approaches, e.g., loading exosomes with insulin-sensitizing or anti-inflammatory molecules to enhance therapeutic precision.
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AT | Adipose Tissue |
| BCAAs | branched-chain amino acids |
| VAT | Visceral Adipose Tissue |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| DM2 | type 2 diabates |
| MMP2 | metaloproteinase 2 |
| PVAT | Perivascular adipose tissue |
| (ADMA) | L-arginine/asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) |
| eNOS | endothelial NO synthase |
| VSG | Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy |
| MAFLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease |
References
- Zhao, H.; Shang, Q.; Pan, Z.; Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q. Exosomes from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Attenuate Adipose Inflammation and Obesity Through Polarizing M2 Macrophages and Beiging in White Adipose Tissue. Diabetes 2018, 67, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, H.; Huang, X.; Miao, R.; Yin, R.; Tian, J. Endothelial Extracellular Vesicles: Their Possible Function and Clinical Significance in Diabetic Vascular Complications. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Tian, W. Physiological and Pathological Impact of Exosomes of Adipose Tissue. Cell Prolif. 2016, 49, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Eley, J.; Mahmood, N.; Bhandary, B.; Dukic, T.; Tu, K.J.; Polf, J.; Lamichhane, N.; Mahmood, J.; Vujaskovic, Z.; et al. Therapeutic Efficacy of Variable Biological Effectiveness of Proton Therapy in U-CH2 and MUG-Chor1 Human Chordoma Cell Death. Cancers 2021, 13, 6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.A.; Patton, G.C.; Cini, K.I.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbas, N.; Abd Al Magied, A.H.A.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Abdollahi, A.; Abdoun, M.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Prevalence of Child and Adolescent Overweight and Obesity, 1990–2021, with Forecasts to 2050: A Forecasting Study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 785–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, J.Y.L.; Poon, G.W.K.; Du, J.; Wong, K.K.Y. Obesity in Children and Adolescents: Overview of the Diagnosis and Management. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2023, 9, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, M.; Llewellyn, A.; Owen, C.G.; Woolacott, N. Predicting Adult Obesity from Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaratnam, R.; Svenningsen, P. Adipocyte-Endothelium Crosstalk in Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 681290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chait, A.; Den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ye, S.; Liu, B. Roles of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Healthy and Obese Adipose Tissue in Inter-Organ Crosstalk and Potential Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1409000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gao, Y.; Cui, F.; Zhang, N. Exosomes from High Glucose-Treated Glomerular Endothelial Cells Activate Mesangial Cells to Promote Renal Fibrosis. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Shah, A.S.; Nakamura, T. Extracellular Vesicles: A Potential Novel Regulator of Obesity and Its Associated Complications. Children 2018, 5, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maligianni, I.; Yapijakis, C.; Bacopoulou, F.; Chrousos, G. The Potential Role of Exosomes in Child and Adolescent Obesity. Children 2021, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camino, T.; Lago-Baameiro, N.; Pardo, M. Extracellular Vesicles as Carriers of Adipokines and Their Role in Obesity. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Kaushal, D.; Wilson, R.B. Cellular Senescence and Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Obesity—A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzi, B.; Urciuoli, E.; Mariani, M.; Chioma, L.; Tomao, L.; Montano, I.; Algeri, M.; Luciano, R.; Fintini, D.; Manco, M. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles Impair Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Differentiation Favoring Adipogenic Rather than Osteogenic Differentiation in Adolescents with Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korecka, K.; Gawin, M.; Pastuszka, A.; Partyka, M.; Koszutski, T.; Pietrowska, M.; Hyla-Klekot, L. Proteomics of Urinary Small Extracellular Vesicles in Early Diagnosis of Kidney Diseases in Children—Expectations and Limitations. Proteomics 2024, 24, 2300168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, S.C.; Nadler, E.P.; Pillai, D.K.; Hubal, M.J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.M.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; Koeck, E.; Sevilla, S.; Wiles, A.A.; et al. Adipocyte-Derived Exosomal miRNAs: A Novel Mechanism for Obesity-Related Disease. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghesmati, Z.; Rashid, M.; Fayezi, S.; Gieseler, F.; Alizadeh, E.; Darabi, M. An Update on the Secretory Functions of Brown, White, and Beige Adipose Tissue: Towards Therapeutic Applications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2024, 25, 279–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elmoniem, K.Z.; Edwan, J.H.; Dietsche, K.B.; Villalobos-Perez, A.; Shams, N.; Matta, J.; Baumgarten, L.; Qaddumi, W.N.; Dixon, S.A.; Chowdhury, A.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction in Youth-Onset Type 2 Diabetes: A Clinical Translational Study. Circ. Res. 2024, 135, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicle 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV2023): From Basic to Advanced Approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicle 2024, 13, e12404, Correction in J. Extracell. Vesicle 2024, 13, e12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Gao, H.; Dos Reis, F.C.G.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Luo, Z.; Ji, Y.; Jin, Z.; Ly, C.; Olefsky, J.M. MiR-690, an Exosomal-Derived miRNA from M2-Polarized Macrophages, Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Mice. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 781–790.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engin, A. Endothelial Dysfunction in Obesity. In Obesity and Lipotoxicity; Engin, A.B., Engin, A., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 960, pp. 345–379. ISBN 978-3-319-48380-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Ye, R. Adipose-derived Exosomes: A Novel Adipokine in Obesity-associated Diabetes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 16692–16702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gündüz, Z.; Dursun, İ.; Tülpar, S.; Baştuğ, F.; Baykan, A.; Yıkılmaz, A.; Patıroğlu, T.; Poyrazoglu, H.M.; Akın, L.; Yel, S.; et al. Increased Endothelial Microparticles in Obese and Overweight Children. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 25, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, A.; Lazic, M.; Armando, A.M.; Phillips, S.A.; Katebian, R.; Maraka, S.; Quehenberger, O.; Sears, D.D.; Feldstein, A.E. Circulating Adipocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Are Novel Markers of Metabolic Stress. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Blanco, C.; Iglesias-Fortes, S.; Lockwood, Á.C.; Figaredo, C.; Vitulli, D.; Guillén, C. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolic Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Huo, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Human Breast Milk Exosomal miRNAs Are Influenced by Premature Delivery and Affect Neurodevelopment. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, 2300113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.B.; Chernausek, S.D.; Garman, L.D.; Pezant, N.P.; Plows, J.F.; Kharoud, H.K.; Demerath, E.W.; Fields, D.A. Human Milk Exosomal MicroRNA: Associations with Maternal Overweight/Obesity and Infant Body Composition at 1 Month of Life. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.E.; Vorn, R.; Chimenti, M.; Crouch, K.; Shaoshuai, C.; Narayanaswamy, J.; Harken, A.; Schmidt, R.; Gill, J.; Lee, H. Extracellular Vesicle miRNAs in Breast Milk of Obese Mothers. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 976886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunte, P.; Barberio, M.; Tiwari, P.; Sukla, K.; Harmon, B.; Epstein, S.; Bhat, D.; Authelet, K.; Goldberg, M.; Rao, S.; et al. Neonatal Adiposity Is Associated with microRNAs in Adipocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Maternal and Cord Blood, a Discovery Analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.; Quesada-López, T.; Villarroya, F.; Casano, P.; López-Bermejo, A.; De Zegher, F.; Ibáñez, L. The Proteome of Exosomes at Birth Predicts Insulin Resistance, Adrenarche and Liver Fat in Childhood. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, E.; Cemali, Ö.; Şahin, T.Ö.; Deveci, G.; Biçer, N.Ç.; Hirfanoğlu, İ.M.; Ağagündüz, D.; Budán, F. Human Breast Milk Exosomes: Affecting Factors, Their Possible Health Outcomes, and Future Directions in Dietetics. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaya, J.; Tanabe, Y.; Kaneko, K. Sonic Hedgehog N-Terminal Level Correlates with Adiponectin Level and Insulin Resistance in Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 36, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Eguchi, A.; Imami, K.; Tempaku, M.; Izuoka, K.; Takase, T.; Kainuma, K.; Nagao, M.; Furuta, N.; Iwasa, M.; et al. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles Are Associated with Pathophysiological Condition Including Metabolic Syndrome-Related Dysmetabolism in Children and Adolescents with Obesity. J. Mol. Med. 2024, 102, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Alkhouri, N.; Vajro, P.; Baumann, U.; Weiss, R.; Socha, P.; Marcus, C.; Lee, W.S.; Kelly, D.; Porta, G.; et al. Defining Paediatric Metabolic (Dysfunction)-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: An International Expert Consensus Statement. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa, M.; Malczyk, Ż.; Bik-Multanowski, M.; Brandt-Heunemann, S.; Flehmig, B.; Małecka-Tendera, E.; Mazur, A.; Petriczko, E.; Ranke, M.B.; Wabitsch, M.; et al. High Prevalence of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) in Children and Adolescents with Severe Obesity. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago-Baameiro, N.; Camino, T.; Vazquez-Durán, A.; Sueiro, A.; Couto, I.; Santos, F.; Baltar, J.; Falcón-Pérez, J.M.; Pardo, M. Intra and Inter-Organ Communication through Extracellular Vesicles in Obesity: Functional Role of Obesesomes and Steatosomes. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiStefano, J.K.; Piras, I.S.; Wu, X.; Sharma, R.; Garcia-Mansfield, K.; Willey, M.; Lovell, B.; Pirrotte, P.; Olson, M.L.; Shaibi, G.Q. Changes in Proteomic Cargo of Circulating Extracellular Vesicles in Response to Lifestyle Intervention in Adolescents with Hepatic Steatosis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 60, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-W.; Pan, H.-T. microRNA Profiles of Serum Exosomes Derived from Children with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver. Genes Genom. 2022, 44, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YiRan Li, V.; Rosas, N.; Fleischer, S.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Cheng, K. MicroRNAs Won the Nobel Prize. Now, Can Extracellular Vesicles Help Them Become Drugs? Extracell. Vesicle 2025, 5, 100080, Erratum in Extracell. Vesicle 2025, 6, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lischka, J.; Schanzer, A.; De Gier, C.; Greber-Platzer, S.; Zeyda, M. Macrophage-Associated Markers of Metaflammation Are Linked to Metabolic Dysfunction in Pediatric Obesity. Cytokine 2023, 171, 156372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangat, G.; Nair, N.; Barat, O.; Abboud, B.; Pais, P.; Bagga, S.; Raina, R. Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy in Children: Connecting Pathophysiology to Clinical Care. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin-Schwartz, Y.; Curtin, P.; Flores, D.; Aushev, V.N.; Tamayo-Ortiz, M.; Svensson, K.; Pantic, I.; Estrada-Gutierrez, G.; Pizano-Zárate, M.L.; Gennings, C.; et al. Exosomal miRNAs in Urine Associated with Children’s Cardiorenal Parameters: A Cross-Sectional Study. Epigenomics 2021, 13, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Lewis, C.E.; Schreiner, P.J.; Shikany, J.M.; Sidney, S.; Reis, J.P. The Coronary Artery Risk Development In Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyer, X.; Boulanger, C.M.; Le Lay, S. Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicles: Rescuers of Cardiac Mitochondrial Stress. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltero, E.G.; Solovey, A.N.; Hebbel, R.P.; Palzer, E.F.; Ryder, J.R.; Shaibi, G.Q.; Olson, M.; Fox, C.K.; Rudser, K.D.; Dengel, D.R.; et al. Relationship of Circulating Endothelial Cells with Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e018092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Palzer, E.F.; Rudser, K.D.; Fox, C.K.; Hebbel, R.P.; Dengel, D.R.; Milbauer, L.; Kelly, A.S.; Ryder, J.R. Relationship of Endothelial Microparticles to Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Children and Adolescents. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e026430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierdona, T.M.; Martin, A.; Obi, P.O.; Seif, S.; Bydak, B.; Labouta, H.I.; Eadie, A.L.; Brunt, K.R.; McGavock, J.M.; Sénéchal, M.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles as Predictors of Individual Response to Exercise Training in Youth Living with Obesity. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2022, 27, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, B.P.; Nie, Y.; Evans, S.; Kargl, C.K.; Hettinger, Z.R.; Garner, R.T.; Hubal, M.J.; Kuang, S.; Stout, J.; Gavin, T.P. Obesity and Exercise Training Alter Inflammatory Pathway Skeletal Muscle Small Extracellular Vesicle microRNAs. Exp. Physiol. 2022, 107, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigamonti, A.E.; Bollati, V.; Pergoli, L.; Iodice, S.; De Col, A.; Tamini, S.; Cicolini, S.; Tringali, G.; De Micheli, R.; Cella, S.G.; et al. Effects of an Acute Bout of Exercise on Circulating Extracellular Vesicles: Tissue-, Sex-, and BMI-Related Differences. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Kim, S.; Woo, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Jeon, J.S.; Noh, H.; Han, D.C.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, H.C.; et al. Weight Change Alters the Small RNA Profile of Urinary Extracellular Vesicles in Obesity. Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Okura, T.; Choi, K.; Gill, R.; Borra, V.J.; Murakami, K.; Poulos, A.; Zhang, X.; Jenkins, T.; Shah, A.S.; et al. Exploring Organ-Specific Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolic Improvements Following Bariatric Surgery in Adolescents with Obesity. Obesity 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Clinical Context | Role of EVs | Key References |
|---|---|---|
| Adipose tissue dysfunction | Adipocyte-derived EVs carry miRNAs (miR-27a, miR-155, miR-29a) affecting insulin signaling, glucose uptake, and inflammation; macrophage-derived EVs modulate PI3K-Akt pathway; M2-derived EVs with miR-690 improve insulin sensitivity. | Kobayashi et al., 2024 [37]; Ying et al., 2021 [24] |
| Endothelial dysfunction | Adipocyte- and macrophage-derived EVs impair eNOS, increase ROS, promote VCAM-1/ICAM-1 expression; suppress VEGF signaling; link adipose inflammation with vascular dysfunction. | Engin 2017 [25]; Fang et al., 2024 [2] |
| Maternal-fetal communication | Breast milk and placental EVs convey miRNAs (miR-148a, miR-30b, miR-575, miR-630, miR-642a-3p) affecting infant adiposity, neurodevelopment, and immune maturation; cord blood EV proteome predicts later hepatic fat fraction. | Shah et al., 2021 [31]; Cho et al., 2022 [54]; Kunte et al., 2023 [33]; Díaz et al., 2025 [34] |
| Glucose disturbances/T2DM | Circulating EVs elevated in adolescents with obesity/T2D; markers (CD9/CD63, Shh-N) predict insulin resistance; patient-derived EVs induce endothelial dysfunction; EV proteome remodeling reflects metabolic derangement. | Takaya 2023 [36]; Abd-Elmoniem et al., 2024 [20]; Kobayashi et al., 2024 [37] |
| MAFLD (Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease) | Adipocyte/hepatocyte-derived EVs (‘obesesomes’ and ‘steatosomes’) modulate inflammation and lipid metabolism; exosomal miRNAs (miR-122-5p, miR-27a, miR-335-5p) linked to MAFLD progression; EV proteins (sCD163, IL-1RA) correlate with liver fat and ALT. | Lago-Baameiro et al., 2025 [40]; Zhang et al., 2022 [42]; Lischka et al., 2023 [44]; DiStefano et al., 2024 [41] |
| Kidney disease: Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy (ORG) | Urinary EV miRNAs proposed as early biomarkers; AGP and podocyte injury markers potentially superior to albuminuria; need for pediatric validation studies. | Mangat et al., 2023 [45]; Levin-Schwartz et al., 2021 [46] |
| Cardiovascular complications | Endothelial-derived EVs, circulating endothelial cells (CECs), and microparticles (EMPs) reflect early vascular injury. Severe obesity is linked with greater CEC activation, while higher CEC number correlates with adiposity and blood pressure. EMPs and activated EMPs increase with adiposity and are associated with arterial stiffness and subclinical atherosclerosis. | Soltero et al.; 2021 [49]; Jang et al., 2022 [50] |
| Exercise-induced adaptations | Exercise-induced EVs enriched in specific miRNAs regulating insulin sensitivity, inflammation, Wnt/IGF-1/PI3K pathways; distinct EV size/protein content predicts exercise responsiveness. | Pierdona et al., 2022 [51]; Sullivan et al., 2022 [52]; Rigamonti et al., 2022 [53] |
| Bariatric surgery & metabolic improvement | Bariatric surgery alters EV cargo (RNAs, proteins) reflecting improved metabolic state; liver/adipose EVs correlate with insulin resistance, hepatic biomarkers, leptin, BCAA levels; urinary EV RNAs proposed as biomarkers of weight-loss benefits. | Choi et al., 2022 [54]; Kim et al., 2024 [55] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szeliga, K.; Krakowczyk, D.; Chyra, M.; Pietrowska, M.; Koszutski, T.; Gawlik-Starzyk, A.M.; Hyla-Klekot, L. Systematic Review: Exosomes as Molecular Messengers in the Development of Obesity-Related Complications in Children. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100865
Szeliga K, Krakowczyk D, Chyra M, Pietrowska M, Koszutski T, Gawlik-Starzyk AM, Hyla-Klekot L. Systematic Review: Exosomes as Molecular Messengers in the Development of Obesity-Related Complications in Children. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(10):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100865
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzeliga, Kamila, Dominika Krakowczyk, Marcin Chyra, Monika Pietrowska, Tomasz Koszutski, Aneta Monika Gawlik-Starzyk, and Lidia Hyla-Klekot. 2025. "Systematic Review: Exosomes as Molecular Messengers in the Development of Obesity-Related Complications in Children" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 10: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100865
APA StyleSzeliga, K., Krakowczyk, D., Chyra, M., Pietrowska, M., Koszutski, T., Gawlik-Starzyk, A. M., & Hyla-Klekot, L. (2025). Systematic Review: Exosomes as Molecular Messengers in the Development of Obesity-Related Complications in Children. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(10), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100865







