Development of Digital Droplet PCR Targeting the Influenza H3N2 Oseltamivir-Resistant E119V Mutation and Its Performance through the Use of Reverse Genetics Mutants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses, Cells, and Chemicals
2.2. Mutagenesis and Reverse Genetics
2.3. Wild-Type and E119V Mutant Virus Mixes
2.4. NA Activity and Inhibition Assays
2.5. ddPCR Protocol

3. Results
3.1. Generation of the Wild Type and E119V-NA Mutant
3.2. Adaptation of RT-qPCR to Obtain a Specific RT-ddPCR to Detect the Polymorphism at Position 119-NA of Influenza A(H3N2) Viruses
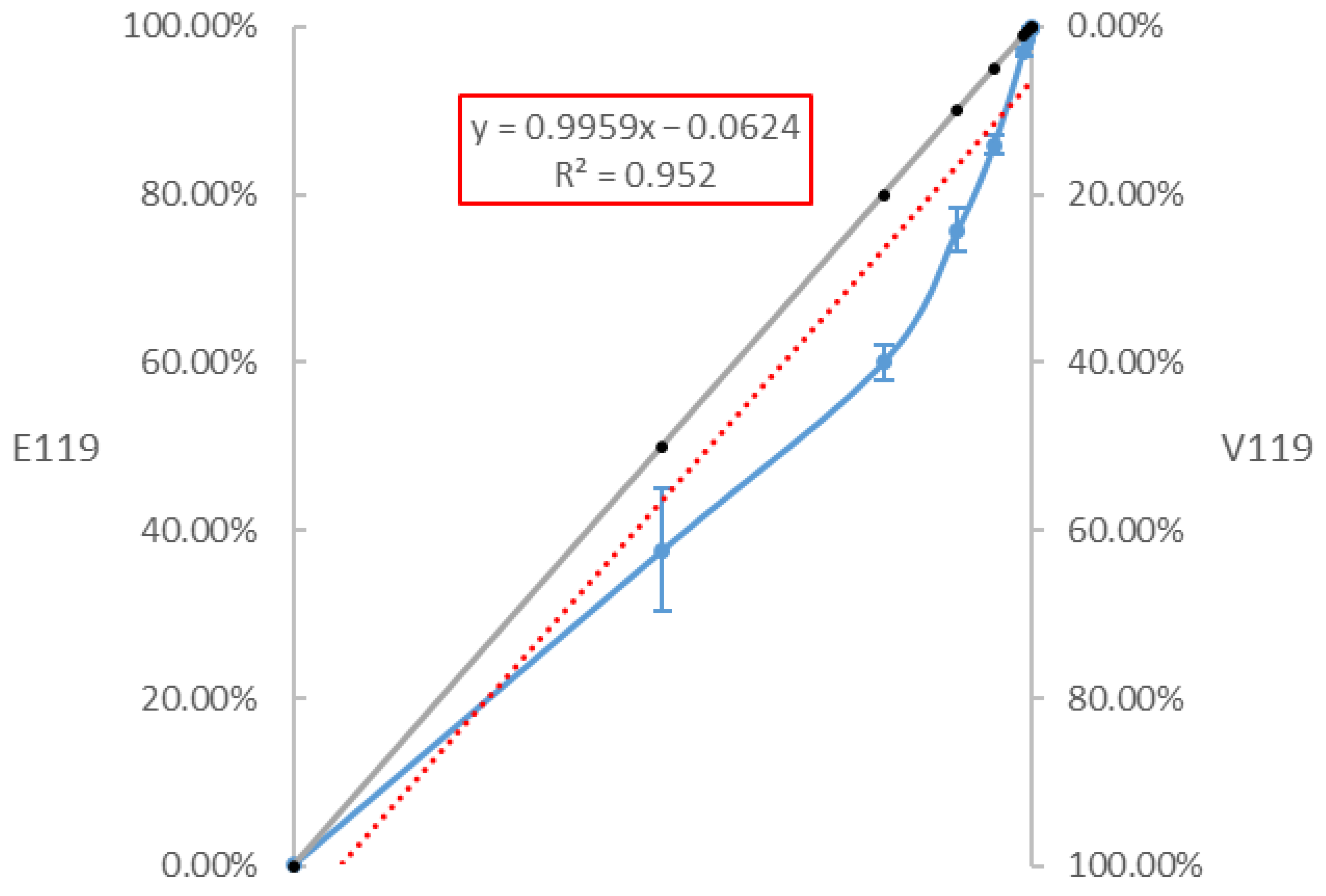
3.3. Sensitivity of the RT-ddPCR to Quantify the Proportion of the E119V-NA Mutation
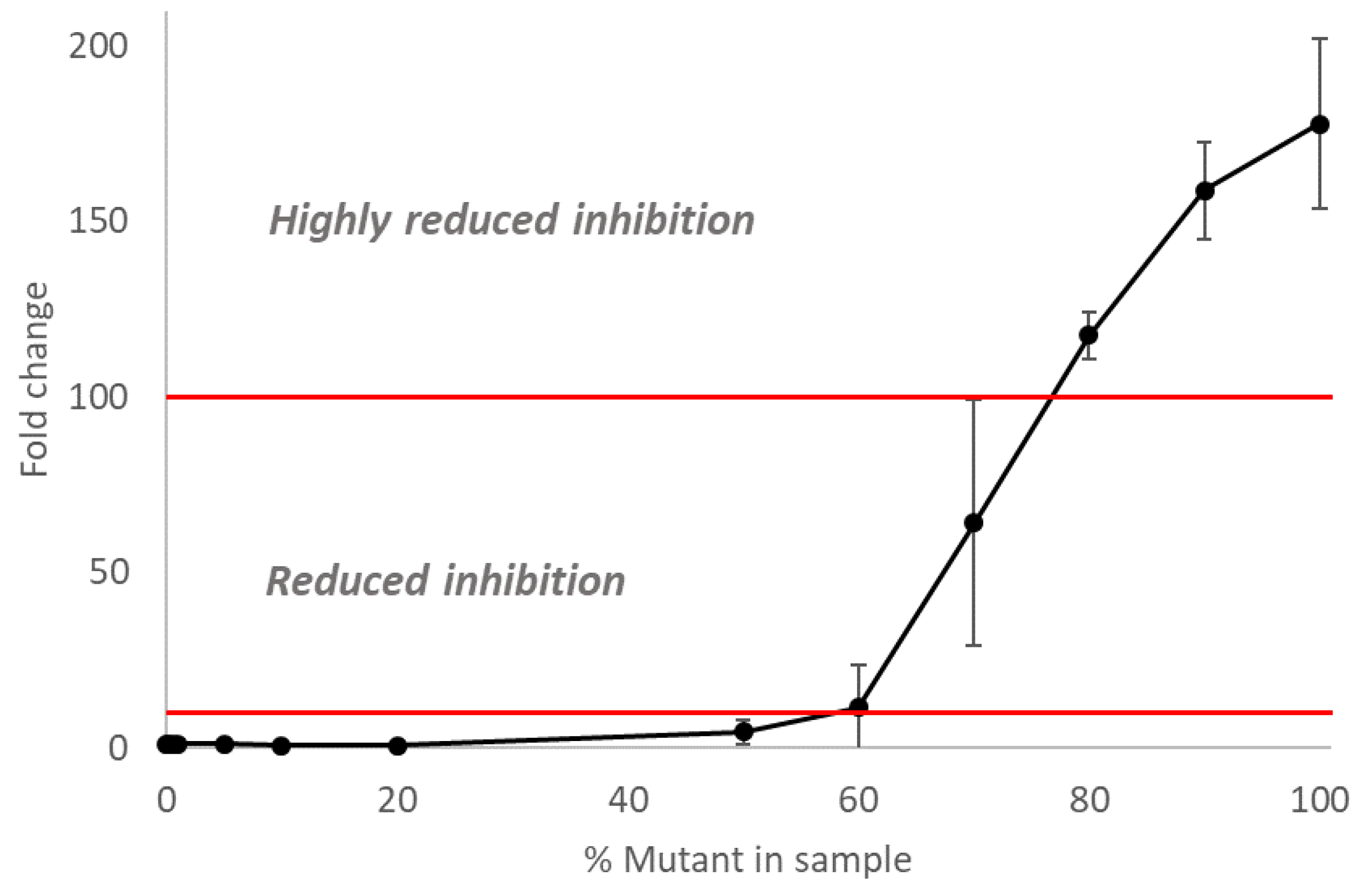
3.4. The Inhibitory Activity of Oseltamivir on Mixed Populations of NAI-Susceptible and -Resistant Influenza A(H3N2) Viruses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van der Vries, E.; Anber, J.; Van Der Linden, A.; Wu, Y.; Maaskant, J.; Stadhouders, R.; Van Beek, R.; Rimmelzwaan, G.; Osterhaus, A.; Boucher, C.; et al. Molecular Assays for Quantitative and Qualitative Detection of Influenza Virus and Oseltamivir Resistance Mutations. J. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 15, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Vries, E.; Schutten, M.; Fraaij, P.; Boucher, C.; Osterhaus, A. Influenza Virus Resistance to Antiviral Therapy. Adv. Pharmacol. 2013, 67, 217–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Strategy for Containment of Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kosik, I.; Yewdell, J.W. Influenza Hemagglutinin and Neuraminidase: Yin–Yang Proteins Coevolving to Thwart Immunity. Viruses 2019, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, R.G.; Bean, W.J.; Gorman, O.T.; Chambers, T.M. Evolution and Ecology of Influenza A Viruses. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 152–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosnier, A.; Caini, S.; Daviaud, I.; Nauleau, E.; Bui, T.T.; Debost, E.; Bedouret, B.; Agius, G.; van der Werf, S.; Lina, B.; et al. Clinical Characteristics Are Similar across Type A and B Influenza Virus Infections. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monto, A.S.; McKimm-Breschkin, J.L.; Macken, C.; Hampson, A.W.; Hay, A.; Klimov, A.; Tashiro, M.; Webster, R.G.; Aymard, M.; Hayden, F.G.; et al. Detection of Influenza Viruses Resistant to Neuraminidase Inhibitors in Global Surveillance during the First 3 Years of Their Use. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Chung, J.; Palese, P. Alterations of the Stalk of the Influenza Virus Neuraminidase: Deletions and Insertions. Virus Res. 1993, 29, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palese, P.; Tobita, K.; Ueda, M.; Compans, R.W. Characterization of Temperature Sensitive Influenza Virus Mutants Defective in Neuraminidase. Virology 1974, 61, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demicheli, V.; Jefferson, T.; Pietrantonj, C.; Ferroni, E.; Thorning, R.E.; Rivette, A. Vaccines for Preventing Influenza in the Elderly. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, F.Y.; Boivin, G.; Roberts, N. Influenza Virus Susceptibility and Resistance to Oseltamivir. Antivir. Ther. 2007, 12, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, I.; Democratis, J.; Lackenby, A.; McNally, T.; Smith, J.; Pareek, M.; Ellis, J.; Bermingham, A.; Nicholson, K.; Zambon, M. Neuraminidase Inhibitor Resistance after Oseltamivir Treatment of Acute Influenza A and B in Children. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2009, 48, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiso, M.; Mitamura, K.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; Shiraishi, K.; Kawakami, C.; Kimura, K.; Hayden, F.G.; Sugaya, N.; Kawaoka, Y. Resistant Influenza A Viruses in Children Treated with Oseltarnivir: Descriptive Study. Lancet 2004, 364, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, M.; Abed, Y.; McDonald, J.; Boivin, G. Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Influenza A/H3N2 Viruses Shed during 1 Year by an Immunocompromised Child. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2006, 43, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, D.; Sugaya, N.; Ozawa, M.; Takano, R.; Ichikawa, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Kawakami, C.; Shimizu, H.; Uehara, R.; Kiso, M.; et al. Frequency of Drug-Resistant Viruses and Virus Shedding in Pediatric Influenza Patients Treated with Neuraminidase Inhibitors. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, M.G.; Gubareva, L.V.; Atmar, R.L.; Treanor, J.; Hayden, F.G. Recovery of Drug-Resistant Influenza Virus from Immunocompromised Patients: A Case Series. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuret, V.; Ferraris, O.; Lina, B. The Antiviral Resistance of Influenza Virus. Therapy 2011, 8, 741–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Poelvoorde, L.A.E.; Saelens, X.; Thomas, I.; Roosens, N.H. Next-Generation Sequencing: An Eye-Opener for the Surveillance of Antiviral Resistance in Influenza. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 38, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Laboratory Methodologies for Testing the Antiviral Susceptibility of Influenza Viruses: Neuraminidase Inhibitor (NAI). Available online: https://www.who.int/influenza/gisrs_laboratory/antiviral_susceptibility/nai_overview/en/ (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Meijer, A.; Rebelo-De-Andrade, H.; Correia, V.; Besselaar, T.; Drager-Dayal, R.; Fry, A.; Gregory, V.; Gubareva, L.; Kageyama, T.; Lackenby, A.; et al. Global Update on the Susceptibility of Human Influenza Viruses to Neuraminidase Inhibitors, 2012–2013. Antivir. Res. 2014, 110, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.I.; Lackenby, A.; Daniels, R.S.; McCauley, J.W.; Pereyaslov, D.; Broberg, E.K.; Meijer, A.; Zambon, M.C. Evaluation of Influenza Virus Antiviral Susceptibility Testing in Europe: Results from the First External Quality Assessment Exercise. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2013, 56, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okomo-Adhiambo, M.; Mishin, V.P.; Sleeman, K.; Saguar, E.; Guevara, H.; Reisdorf, E.; Griesser, R.H.; Spackman, K.J.; Mendenhall, M.; Carlos, M.P.; et al. Standardizing the Influenza Neuraminidase Inhibition Assay among United States Public Health Laboratories Conducting Virological Surveillance. Antivir. Res. 2016, 128, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Vries, E.; Stittelaar, K.J.; van Amerongen, G.; Veldhuis Kroeze, E.J.B.; de Waal, L.; Fraaij, P.L.A.; Meesters, R.J.; Luider, T.M.; van der Nagel, B.; Koch, B.; et al. Prolonged Influenza Virus Shedding and Emergence of Antiviral Resistance in Immunocompromised Patients and Ferrets. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Honzumi, K.; Sato, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Watanabe, M.; Miyazaki, K.; Kawasaki, Y.; Hosoya, M. Quantitative Analysis of Influenza A (H3N2) E119V and R292K Variants in Clinical Specimens by Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 68, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindson, B.J.; Ness, K.D.; Masquelier, D.A.; Belgrader, P.; Heredia, N.J.; Makarewicz, A.J.; Bright, I.J.; Lucero, M.Y.; Hiddessen, A.L.; Legler, T.C.; et al. High-Throughput Droplet Digital PCR System for Absolute Quantitation of DNA Copy Number. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8604–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, R.; Huggett, J.F.; Bushell, C.A.; Cowen, S.; Scott, D.J.; Foy, C.A. Evaluation of Digital PCR for Absolute DNA Quantification. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6474–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whale, A.S.; Huggett, J.F.; Cowen, S.; Speirs, V.; Shaw, J.; Ellison, S.; Foy, C.A.; Scott, D.J. Comparison of Microfluidic Digital PCR and Conventional Quantitative PCR for Measuring Copy Number Variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R.; Mason, D.J.; Foy, C.A.; Huggett, J.F. Evaluation of Digital PCR for Absolute RNA Quantification. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindson, C.M.; Chevillet, J.R.; Briggs, H.A.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Ruf, I.K.; Hindson, B.J.; Vessella, R.L.; Tewari, M. Absolute Quantification by Droplet Digital PCR versus Analog Real-Time PCR. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeke, T.; Dobnik, D. Critical Assessment of Digital PCR for the Detection and Quantification of Genetically Modified Organisms. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4039–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Poelvoorde, L.A.E.; Gand, M.; Fraiture, M.-A.; De Keersmaecker, S.C.J.; Verhaegen, B.; Van Hoorde, K.; Cay, A.B.; Balmelle, N.; Herman, P.; Roosens, N. Strategy to Develop and Evaluate a Multiplex RT-DdPCR in Response to SARS-CoV-2 Genomic Evolution. CIMB 2021, 43, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devonshire, A.S.; O’Sullivan, D.M.; Honeyborne, I.; Jones, G.; Karczmarczyk, M.; Pavšič, J.; Gutteridge, A.; Milavec, M.; Mendoza, P.; Schimmel, H.; et al. The Use of Digital PCR to Improve the Application of Quantitative Molecular Diagnostic Methods for Tuberculosis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, G.P.; Do, D.; Litterst, C.M.; Maar, D.; Hindson, C.M.; Steenblock, E.R.; Legler, T.C.; Jouvenot, Y.; Marrs, S.H.; Bemis, A.; et al. Multiplexed Target Detection Using DNA-Binding Dye Chemistry in Droplet Digital PCR. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11619–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.C.; Carbonneau, J.; Shelton, D.N.; Boivin, G. Optimization of Droplet Digital PCR from RNA and DNA Extracts with Direct Comparison to RT-QPCR: Clinical Implications for Quantification of Oseltamivir-Resistant Subpopulations. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 224, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, T.; Liu, X.; Feng, J.; Guo, M.; Hu, W.; Guo, D.; Ullah, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; et al. DdPCR: A More Accurate Tool for SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Low Viral Load Specimens. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whale, A.S.; Bushell, C.A.; Grant, P.R.; Cowen, S.; Gutierrez-Aguirre, I.; O’Sullivan, D.M.; Žel, J.; Milavec, M.; Foy, C.A.; Nastouli, E.; et al. Detection of Rare Drug Resistance Mutations by Digital PCR in a Human Influenza A Virus Model System and Clinical Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, M.; Gaymard, A.; Josset, L.; Valette, M.; Millat, G.; Lina, B.; Escuret, V. Characterization of Oseltamivir-Resistant Influenza Virus Populations in Immunosuppressed Patients Using Digital-Droplet PCR: Comparison with QPCR and next Generation Sequencing Analysis. Antivir. Res. 2017, 145, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. CDC Protocol of Realtime RTPCR for Influenza A(H1N1); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, D.V.; Nordholm, J.; Madjo, U.; Pfeiffer, A.; Daniels, R. Assembly of Subtype 1 Influenza Neuraminidase Is Driven by Both the Transmembrane and Head Domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dohna, H.Z.; Cardona, C.J.; Miller, J.; Carpenter, T.E. Emergence and Genetic Variation of Neuraminidase Stalk Deletions in Avian Influenza Viruses. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claas, E.C.; Osterhaus, A.D.; van Beek, R.; De Jong, J.C.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Senne, D.A.; Krauss, S.; Shortridge, K.F.; Webster, R.G. Human Influenza A H5N1 Virus Related to a Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus. Lancet 1998, 351, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrucci, M.R.; Kawaoka, Y. Biologic Importance of Neuraminidase Stalk Length in Influenza A Virus. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosovich, M.; Zhou, N.; Kawaoka, Y.; Webster, R. The Surface Glycoproteins of H5 Influenza Viruses Isolated from Humans, Chickens, and Wild Aquatic Birds Have Distinguishable Properties. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.W.; Munier, S.; Larcher, T.; Soubieux, D.; Ledevin, M.; Esnault, E.; Tourdes, A.; Croville, G.; Guerin, J.-L.; Quere, P.; et al. Length Variations in the NA Stalk of an H7N1 Influenza Virus Have Opposite Effects on Viral Excretion in Chickens and Ducks. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhirnov, O.P.; Vorobjeva, I.V.; Saphonova, O.A.; Poyarkov, S.V.; Ovcharenko, A.V.; Anhlan, D.; Malyshev, N.A. Structural and Evolutionary Characteristics of HA, NA, NS and M Genes of Clinical Influenza A/H3N2 Viruses Passaged in Human and Canine Cells. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 45, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrell, E.M.; Song, H.; Pena, L.; Perez, D.R. A 27-Amino-Acid Deletion in the Neuraminidase Stalk Supports Replication of an Avian H2N2 Influenza A Virus in the Respiratory Tract of Chickens. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11831–11840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirst, G.K. Adsorption of Influenza Hemagglutinins and Virus by Red Blood Cells. J. Exp. Med. 1942, 76, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, A. Neuraminidase: The Specific Enzyme of Influenza Virus and Vibrio Cholerae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1957, 23, 645–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palese, P.; Compans, R.W. Inhibition of Influenza Virus Replication in Tissue Culture by 2-Deoxy-2,3-Dehydro-N-Trifluoroacetylneuraminic Acid (FANA): Mechanism of Action. J. Gen. Virol. 1976, 33, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.J.; Haire, L.F.; Stevens, D.J.; Collins, P.J.; Lin, Y.P.; Blackburn, G.M.; Hay, A.J.; Gamblin, S.J.; Skehel, J.J. The Structure of H5N1 Avian Influenza Neuraminidase Suggests New Opportunities for Drug Design. Nature 2006, 443, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.G.; Laver, W.G. Preparation and Properties of Antibody Directed Specifically against the Neuraminidase of Influenza Virus. J. Immunol. 1967, 99, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, J.N.; Laver, W.G.; Colman, P.M. Structure of the Influenza Virus Glycoprotein Antigen Neuraminidase at 2.9 Å Resolution. Nature 1983, 303, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugbaja, S.C.; Mtambo, S.E.; Mushebenge, A.G.; Appiah-Kubi, P.; Abubakar, B.H.; Ntuli, M.L.; Kumalo, H.M. Structural Investigations and Binding Mechanisms of Oseltamivir Drug Resistance Conferred by the E119V Mutation in Influenza H7N9 Virus. Molecules 2022, 27, 4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutyavin, I.V.; Afonina, I.A.; Mills, A.; Gorn, V.V.; Lukhtanov, E.A.; Belousov, E.S.; Singer, M.J.; Walburger, D.K.; Lokhov, S.G.; Gall, A.A.; et al. 3’-Minor Groove Binder-DNA Probes Increase Sequence Specificity at PCR Extension Temperatures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampejo, T. Influenza and Antiviral Resistance: An Overview. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.M.; Caldwell, N.; Hurt, A.; Shaw, T.; Kelso, A.; Chidlow, G.; Williams, S.; Smith, D.; Barr, I. A Comparison of Pyrosequencing and Neuraminidase Inhibition Assays for the Detection of Oseltamivir-Resistant Pandemic Influenza A(H1N1) 2009 Viruses. Antivir. Res. 2011, 90, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, A.J.; Armstrong, J.; Lowen, A.C.; Webster, R.G.; Govorkova, E.A. Competitive Fitness of Influenza B Viruses with Neuraminidase Inhibitor-Resistant Substitutions in a Coinfection Model of the Human Airway Epithelium. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4575–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, L.; Elsinga, G.; de Graaf, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Medema, G. Droplet Digital RT-PCR to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern in Wastewater. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xagoraraki, I.; O’Brien, E. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology for Early Detection of Viral Outbreaks. In Women in Engineering and Science; O’Bannon, D.J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 75–97. ISBN 978-3-030-17818-5. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, W.; Hayman, A.; Lackenby, A.; Whiteley, A.; Londt, B.; Banks, J.; McCauley, J.; Barclay, W. The Development of a Reverse Genetics System Enabling the Rescue of Recombinant Avian Influenza Virus, A/Turkey/England/50-92/91 (H5N1). Avian Dis. 2007, 2, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Poelvoorde, L.A.E.; Dufrasne, F.E.; Van Gucht, S.; Saelens, X.; Roosens, N.H.C. Development of Digital Droplet PCR Targeting the Influenza H3N2 Oseltamivir-Resistant E119V Mutation and Its Performance through the Use of Reverse Genetics Mutants. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 2521-2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45030165
Van Poelvoorde LAE, Dufrasne FE, Van Gucht S, Saelens X, Roosens NHC. Development of Digital Droplet PCR Targeting the Influenza H3N2 Oseltamivir-Resistant E119V Mutation and Its Performance through the Use of Reverse Genetics Mutants. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2023; 45(3):2521-2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45030165
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Poelvoorde, Laura A. E., François E. Dufrasne, Steven Van Gucht, Xavier Saelens, and Nancy H. C. Roosens. 2023. "Development of Digital Droplet PCR Targeting the Influenza H3N2 Oseltamivir-Resistant E119V Mutation and Its Performance through the Use of Reverse Genetics Mutants" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45, no. 3: 2521-2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45030165
APA StyleVan Poelvoorde, L. A. E., Dufrasne, F. E., Van Gucht, S., Saelens, X., & Roosens, N. H. C. (2023). Development of Digital Droplet PCR Targeting the Influenza H3N2 Oseltamivir-Resistant E119V Mutation and Its Performance through the Use of Reverse Genetics Mutants. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(3), 2521-2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45030165





