Simvastatin Attenuates Areca Nut Extract-Induced Subdermal Fibrosis in Mice by Targeting TGF-β Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals
- (1)
- Group A: Simvastatin 0.05 mL + PBS 0.05 mL
- (2)
- Group B: ANE 0.05 mL + PBS 0.05 mL
- (3)
- Group C: Simvastatin 0.01 mL + ANE 0.05 mL + PBS 0.04 mL
- (4)
- Group D: Simvastatin 0.05 mL + ANE 0.05 mL+ PBS 0.04 mL
2.3. Western Blot (WB) Analysis
2.4. Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) Stain
2.5. Masson’s Trichrome Stain (MT)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Inhibitory Effect of Simvastatin on ANE-Induced Subdermal Thickening
3.2. The Therapeutic Potential of Simvastatin on ANE-Induced Subdermal Fibrosis
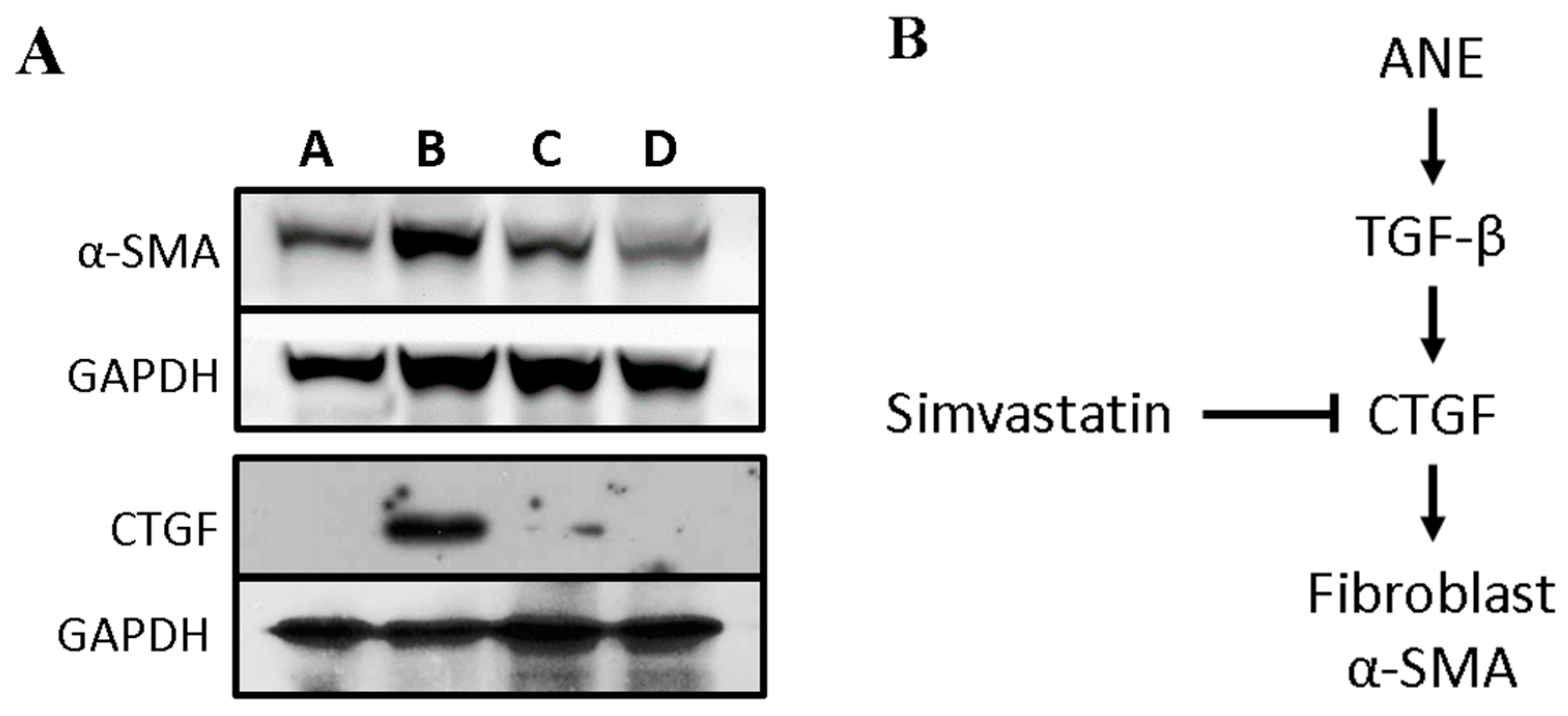
3.3. Simvastatin Attenuates the Expression of Fibrosis-Related Factors Induced by ANE
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shih, Y.H.; Wang, T.H.; Shieh, T.M.; Tseng, Y.H. Oral submucous fibrosis: A review on etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierly, G.; Celentano, A.; Breik, O.; Moslemivayeghan, E.; Patini, R.; McCullough, M.; Yap, T. Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwini Rani, S.; Suragimath, G.; Rajmane, V.; Rajmane, Y. Prevalence of recurrent herpes labialis in Western Maharashtr. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2021, 25, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-H.; Lee, H.-Y.; Tung, S.; Shieh, T.-Y. Epidemiological survey of oral submucous fibrosis and leukoplakia in aborigines of Taiwan. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2001, 30, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakeri, G.; Brennan, P.A. Oral submucous fibrosis: An overview of the aetiology, pathogenesis, classification, and principles of management. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 51, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkuru, S.; Muniraj, G.; Sudhaharan, T.; Chiam, K.H.; Wright, G.D.; Sriram, G. Cellular ageing of oral fibroblasts differentially modulates extracellular matrix organization. J. Periodontal Res. 2021, 56, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budi, E.H.; Schaub, J.R.; Decaris, M.; Turner, S.; Derynck, R. TGF-β as a driver of fibrosis: Physiological roles and therapeutic opportunities. J. Pathol. 2021, 254, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihn, H. Pathogenesis of fibrosis: Role of TGF-β and CTGF. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2002, 14, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambal, A.M.; Bhambal, A.; Shukla, U.S.; Dhingra, A. Effectiveness of Pentoxifylline in the treatment of oral submucous fibrosis patients: A case-control study. Appl. Cancer Res. 2019, 39, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S. Areca nut chewing and esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma risk in Asians: A meta-analysis of case-control studies. Cancer Causes Control 2013, 24, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.; Ali, S.; Lone, M.A.; Atif, M.; Hassona, Y.; Prime, S.S.; Pitiyage, G.N.; James, E.L.N.; Parkinson, E.K. Areca nut alkaloids induce irreparable DNA damage and senescence in fibroblasts and may create a favourable environment for tumour progression. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.T.; Chen, H.M.; Cheng, S.J.; Chiang, C.P.; Kuo, M.Y.P. Arecoline-stimulated connective tissue growth factor production in human buccal mucosal fibroblasts: Modulation by curcumin. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, e99–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, J.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Chiang, B.L.; Lee, P.H.; Chan, C.P.; Ho, Y.S.; Wang, T.M.; Lee, J.J.; Hahn, L.J.; Chang, M.C. Roles of keratinocyte inflammation in oral cancer: Regulating the prostaglandin E2, interleukin-6 and TNF-α production of oral epithelial cells by areca nut extract and arecoline. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, I.; Kumar, N.; Khan, I.; Rao, S.G.; Kondaiah, P. Role of areca nut induced TGF-β and epithelial-mesenchymal interaction in the pathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e129252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Chang, K.W.; Liu, C.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Yang, S.C.; Lin, S.C. Areca nut extract represses migration and differentiation while activating matrix metalloproteinase-9 of normal gingival epithelial cells. J. Periodontal Res. 2008, 43, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnus, M.; Ohannesson, J.; Önsson, J.; Ohn, J.; Jekshus, K.; Lsson, N.G.O.; Edersen, E.R.P.; Ans, H.; Edel, W. Cost effectiveness of simvastatin treatment to lower cholesterol levels in patients with coronary heart disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L. Hepatic Stellate Cells: Protean, Multifunctional, and Enigmatic Cells of the Liver. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 125–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, C.B.; Das, S.; Patel, H.; Adalja, C.; Kamatchi, V.; Venkatesh, R. Proposed clinical classification for oral submucous fibrosis. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chade, A.R.; Zhu, X.Y.; Grande, J.P.; Krier, J.D.; Lerman, A.; Lerman, L.O. Simvastatin abates development of renal fibrosis in experimental renovascular disease. J. Hypertens. 2008, 26, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Yim, H.J.; Hwang, J.W.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Jung, Y.K.; Yim, H.; Kim, B.H.; Park, H.C.; Seo, Y.S.; et al. Improved anti-fibrotic effects by combined treatments of simvastatin and NS-398 in experimental liver fibrosis models. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2022, 37, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.F.; Hsieh, C.C.; Wang, S.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Hung, C.H.; Kuo, P.L.; Liu, Y.R.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, P.L. Simvastatin attenuates cardiac fibrosis via regulation of cardiomyocyte-derived exosome secretion. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroll, S.; Lange, T.J.; Arzt, M.; Sebah, D.; Nowrotek, A.; Lehmann, H.; Wensel, R.; Pfeifer, M.; Blumberg, F.C. Effects of simvastatin on pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension and exercise capacity in bleomycin-treated rats. Acta Physiol. 2013, 208, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.H.; Lee, K.T.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, K.K.; Wang, Y.H. Photobiomodulation therapy inhibits oral submucous fibrosis in mice. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, M.H.; Chen, P.H.; Chen, Y.K.; Chen, C.H.; Ho, M.L.; Wang, Y.H. Characterization of a novel dermal fibrosis model induced by areca nut extract that mimics oral submucous fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.J.; Park, K.R.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.G.; Kim, Y.H. Simvastatin reduces capsular fibrosis around silicone implants. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, M.J.; Keating, N.M.; Elderiny, S.; Cerda, S.; Keaveny, A.P.; Afdhal, N.H.; Nunes, D.P. An Assessment of Digital Image Analysis to Measure Fibrosis in Liver Biopsy Specimens of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 114, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtman, M.K.; Otero-Vinas, M.; Falanga, V. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) isoforms in wound healing and fibrosis. Wound Repair Regen. 2016, 24, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulek, B.; Kiyan, E.; Kiyici, A.; Toy, H.; Bariskaner, H.; Suerdem, M. Effects of simvastatin on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fi brosis in female rats. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motawi, T.M.K.; Atta, H.M.; Sadik, N.A.H.; Azzam, M. The Therapeutic Effects of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Simvastatin in a Rat Model of Liver Fibrosis. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 68, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.L.; Chen, D.Q.; Vaziri, N.D.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.Y. Small molecule inhibitors of epithelial-mesenchymal transition for the treatment of cancer and fibrosis. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 54–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovadya, Y.; Krizhanovsky, V. A new Twist in kidney fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 975–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandi, S.; Alkahtani, A.; Mashyakhy, M.; Abumelha, A.S.; Albar, N.H.M.; Renugalakshmi, A.; Patil, V.R. Effect of ascorbic acid on differentiation, secretome and stemness of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous tooth (SHEDs). J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, M.K.; Huang, B.; Lu, M.; Mani, S.A.; Levine, H.; Ben-Jacob, E. Towards elucidating the connection between epithelial–mesenchymal transitions and stemness. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, Y.; Maeda, M.; Chaika, N.; Johnson, K.R.; Wheelock, M.J. Collagen I promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells via transforming growth factor–β signaling. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.S.; Carter, A.J.; Dixit, M.; Arany, I. Simvastatin inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through induction of HO-1 in cultured renal proximal tubule cells. In Vivo 2016, 30, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mullen, L.; Ferdjani, J.; Sacre, S. Simvastatin inhibits toll-like receptor 8 (TLR8) signaling in primary human monocytes and spontaneous tumor necrosis factor production from rheumatoid synovial membrane cultures. Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Song, Y.; Kang, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, K.; Li, S.; Hua, W.; et al. Simvastatin Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis and Extracellular Matrix Degradation by Suppressing the NF-kB and MAPK Pathways in Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Inflammation 2017, 40, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, F.; Siddiqui, R.; DeFranco, A.; Homar, P.; Emelyanova, L.; Holmuhamedov, E.; Ross, G.; Tajik, A.J.; Jahangir, A. Simvastatin reduces TGF-β1-induced SMAD2/3-dependent human ventricular fibroblasts differentiation: Role of protein phosphatase activation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 270, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; He, D.E. Simvastatin treatment promotes proliferation of human dental pulp stem cells via modulating PI3K/AKT/miR-9/KLF5 signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 10892–10901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, N.; Chu, H.Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.K.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.T. Connective Tissue Growth Factor: From Molecular Understandings to Drug Discovery. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 593269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
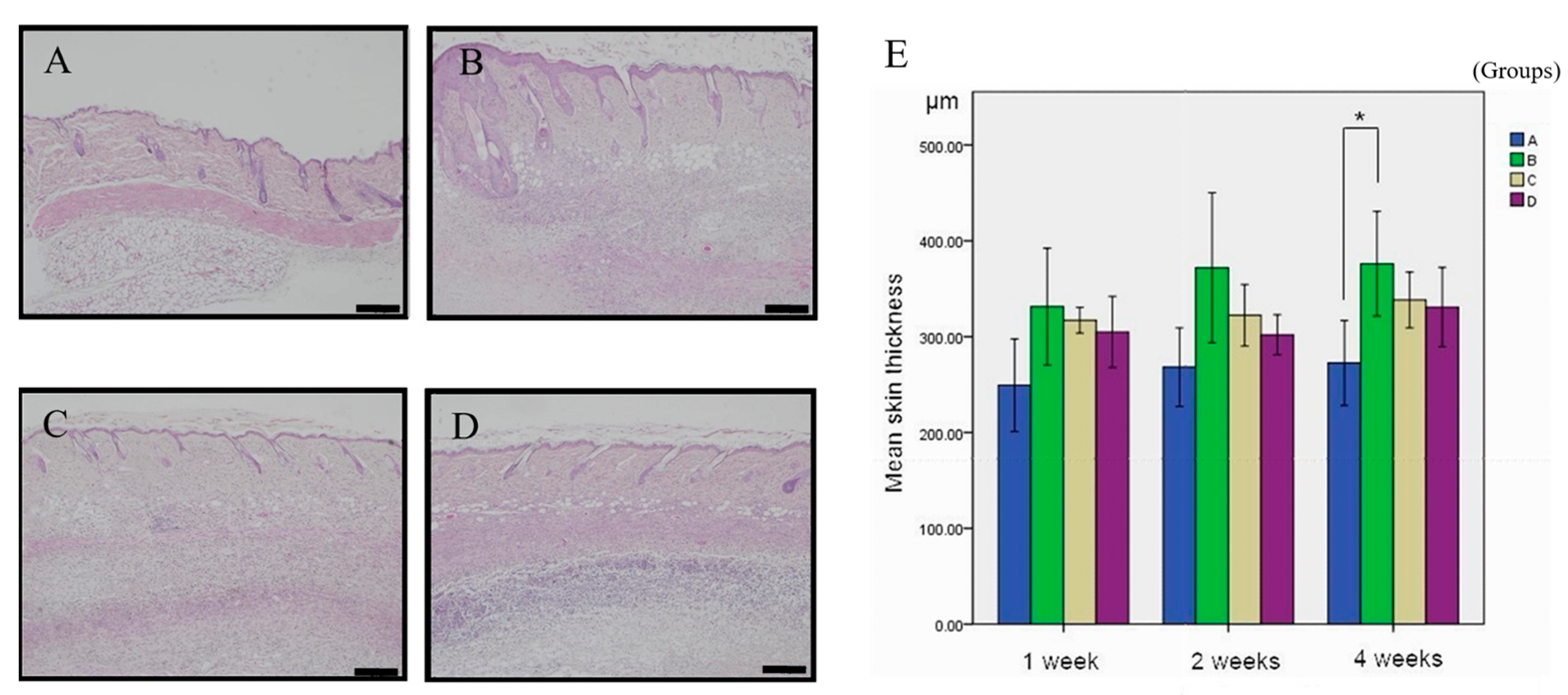
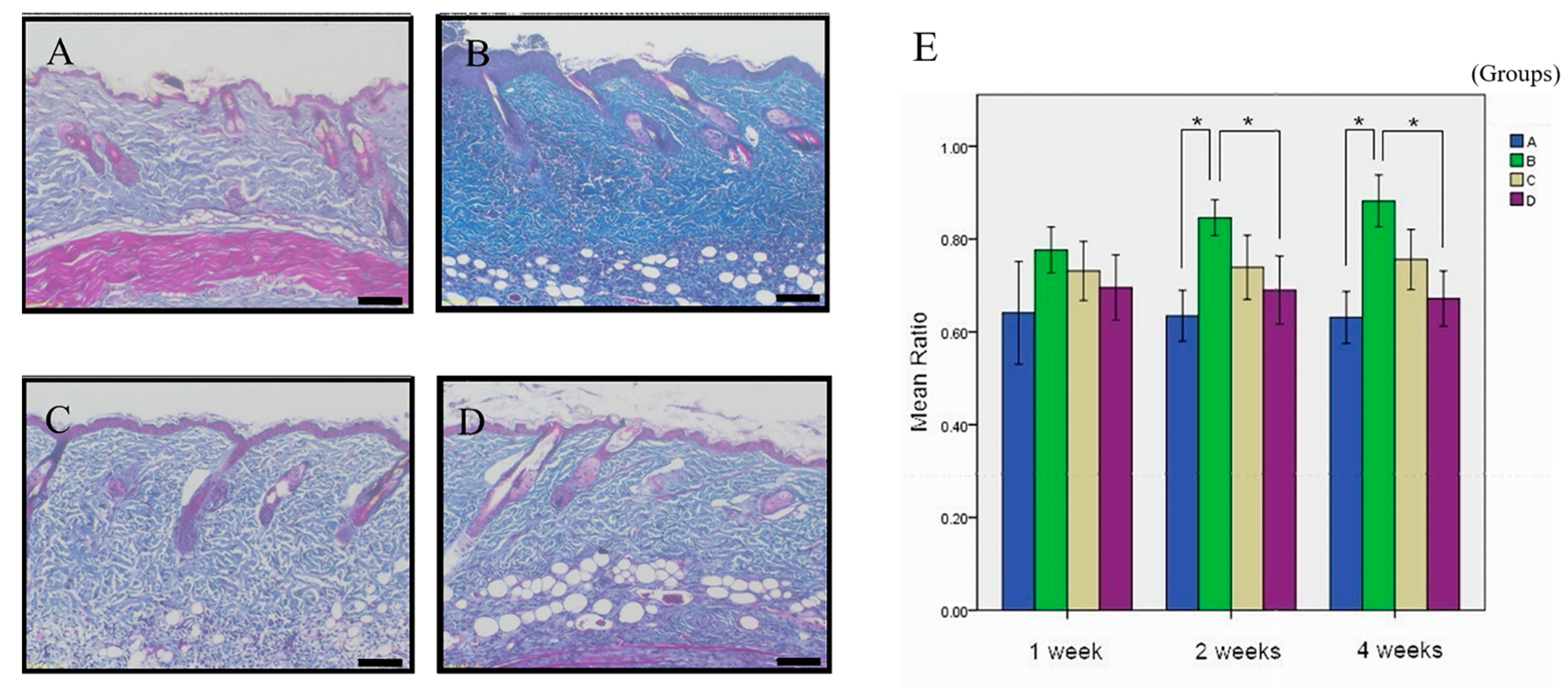
| Formula | 1-Week (n = 6) | 2-Week (n = 6) | 4-Week (n = 7) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 249.28 ± 48.34 μm | 268.21 ± 41.00 μm | 272.57 ± 44.41 μm a |
| B | 331.33 ± 60.99 μm | 371.92 ± 78.00 μm | 376.20 ± 54.66 μm a |
| C | 317.17 ± 13.53 μm | 322.37 ± 32.04 μm | 338.23 ± 29.06 μm ab |
| D | 304.96 ± 37.12 μm | 302.03 ± 20.93 μm | 297.52 ± 36.37 μm ab |
| Formula | 1-Week (n = 6) | 2-Week (n = 6) | 4-Week (n = 7) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 64.10% ± 11.07% | 64.47% ± 5.5% ac | 63.11% ± 5.61% ac |
| B | 77.64% ± 4.93% | 84.59% ± 3.89% b | 88.21% ± 5.60% |
| C | 73.12% ± 6.35% | 73.92% ± 6.92% abc | 75.59% ± 6.48% abc |
| D | 69.55% ± 7.03% | 68.99% ± 7.32% | 67.18% ± 5.96% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.-H.; Lin, C.-P.; Chen, Y.-K.; Hsiao, Y.-F.; Wang, Y.-H. Simvastatin Attenuates Areca Nut Extract-Induced Subdermal Fibrosis in Mice by Targeting TGF-β Signaling Pathways. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 8622-8632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45110542
Chang C-H, Lin C-P, Chen Y-K, Hsiao Y-F, Wang Y-H. Simvastatin Attenuates Areca Nut Extract-Induced Subdermal Fibrosis in Mice by Targeting TGF-β Signaling Pathways. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2023; 45(11):8622-8632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45110542
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Chi-Hua, Ching-Ping Lin, Yuk-Kwan Chen, Yu-Fang Hsiao, and Yan-Hsiung Wang. 2023. "Simvastatin Attenuates Areca Nut Extract-Induced Subdermal Fibrosis in Mice by Targeting TGF-β Signaling Pathways" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45, no. 11: 8622-8632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45110542
APA StyleChang, C.-H., Lin, C.-P., Chen, Y.-K., Hsiao, Y.-F., & Wang, Y.-H. (2023). Simvastatin Attenuates Areca Nut Extract-Induced Subdermal Fibrosis in Mice by Targeting TGF-β Signaling Pathways. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(11), 8622-8632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45110542









