Short-Term Functional and Morphological Changes in the Primary Cultures of Trigeminal Ganglion Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
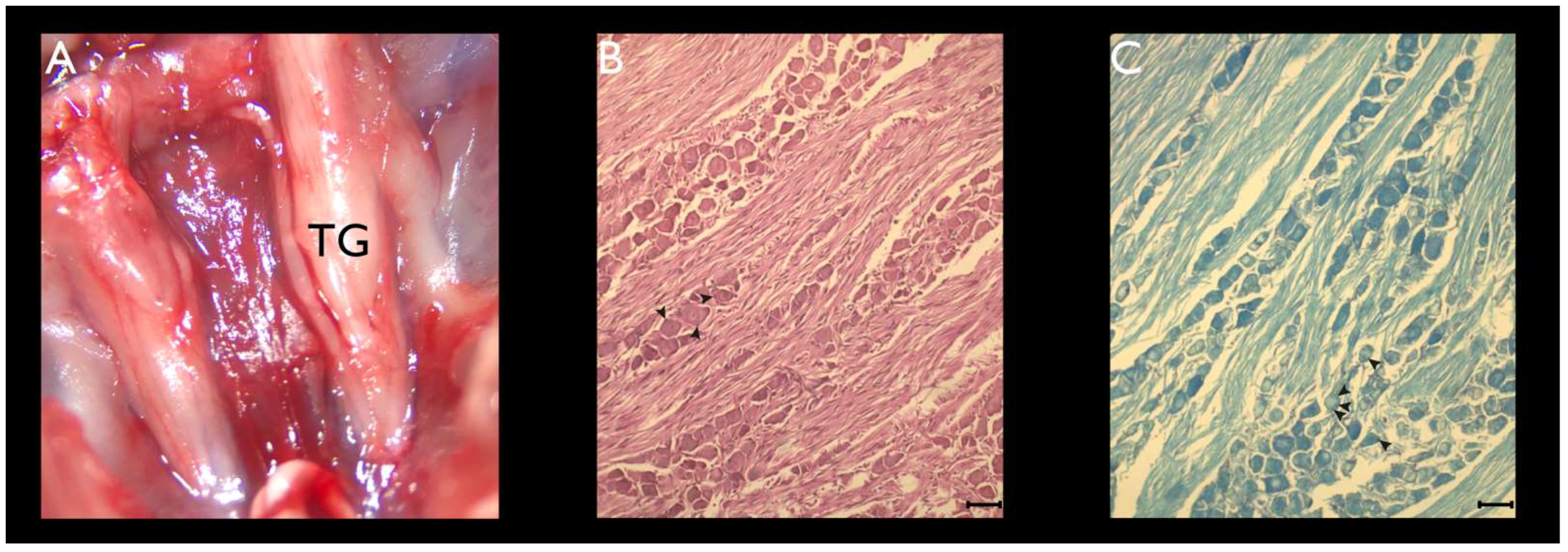
2.2. TG Dissection
2.3. Primary Culture of TG Cells
2.4. Histochemistry
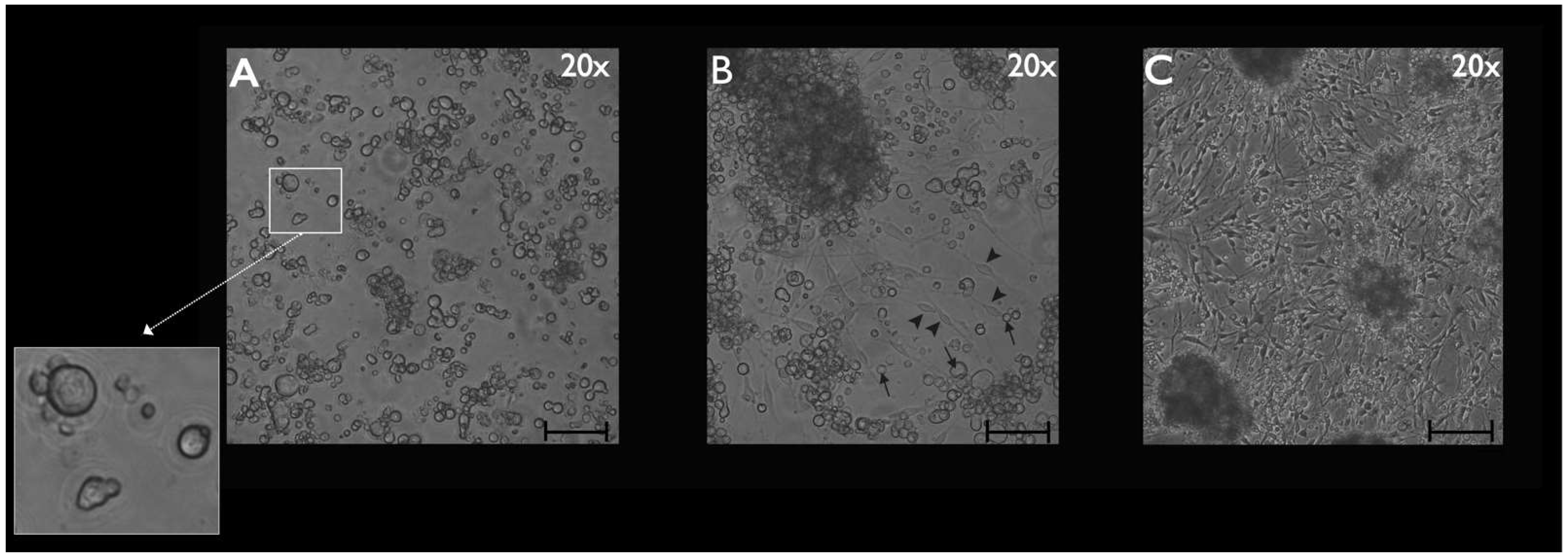
2.5. Phase-Contrast Microscopy
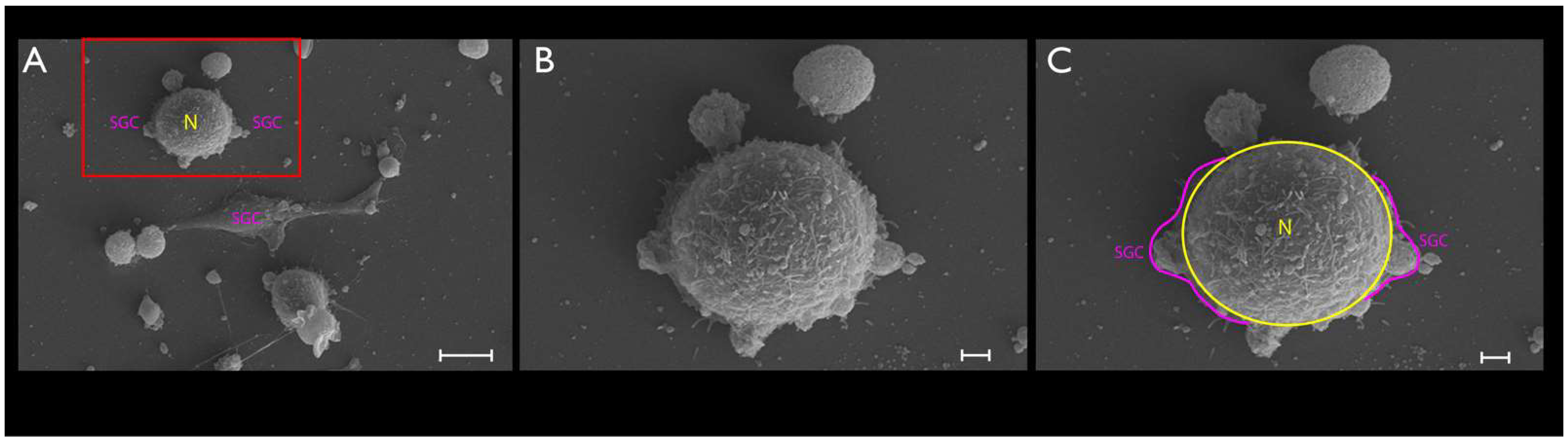
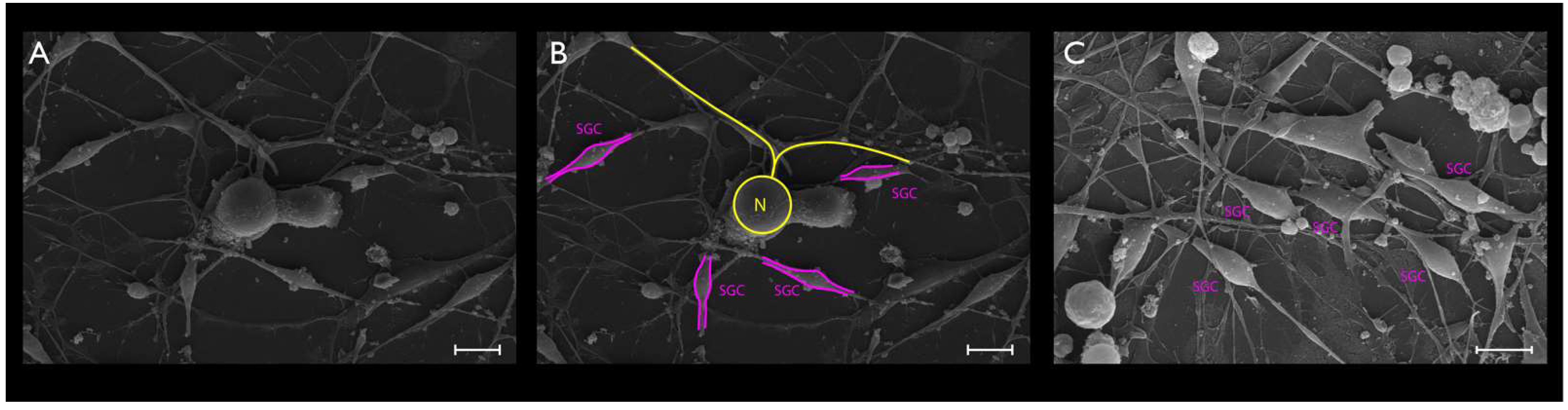
2.6. SEM
2.7. Time-Lapse Photography and Analysis
2.8. Immunocytochemistry
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Histochemistry
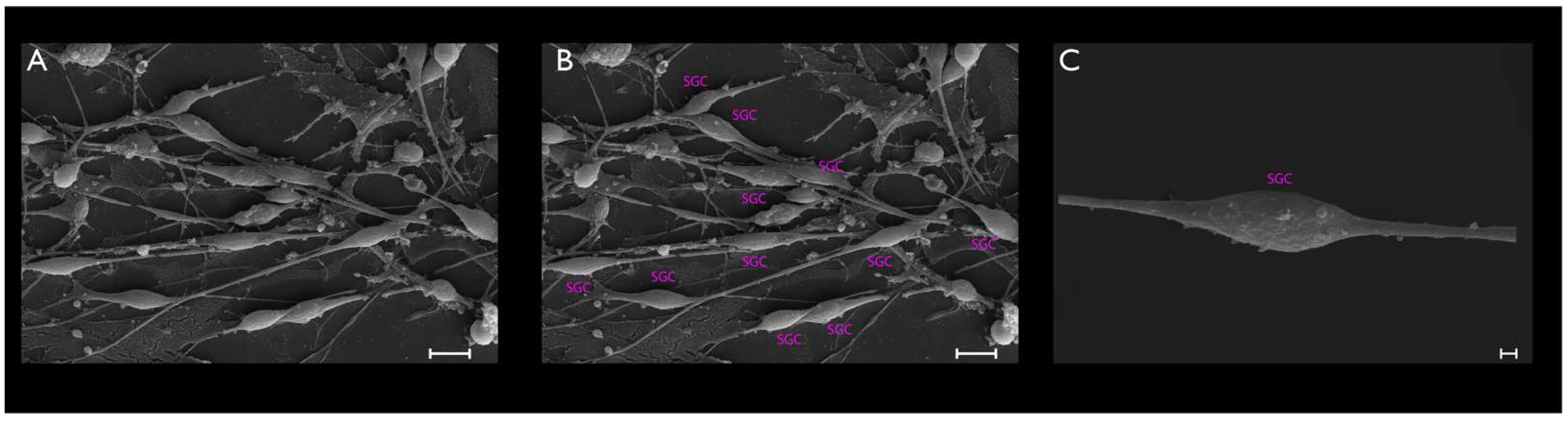
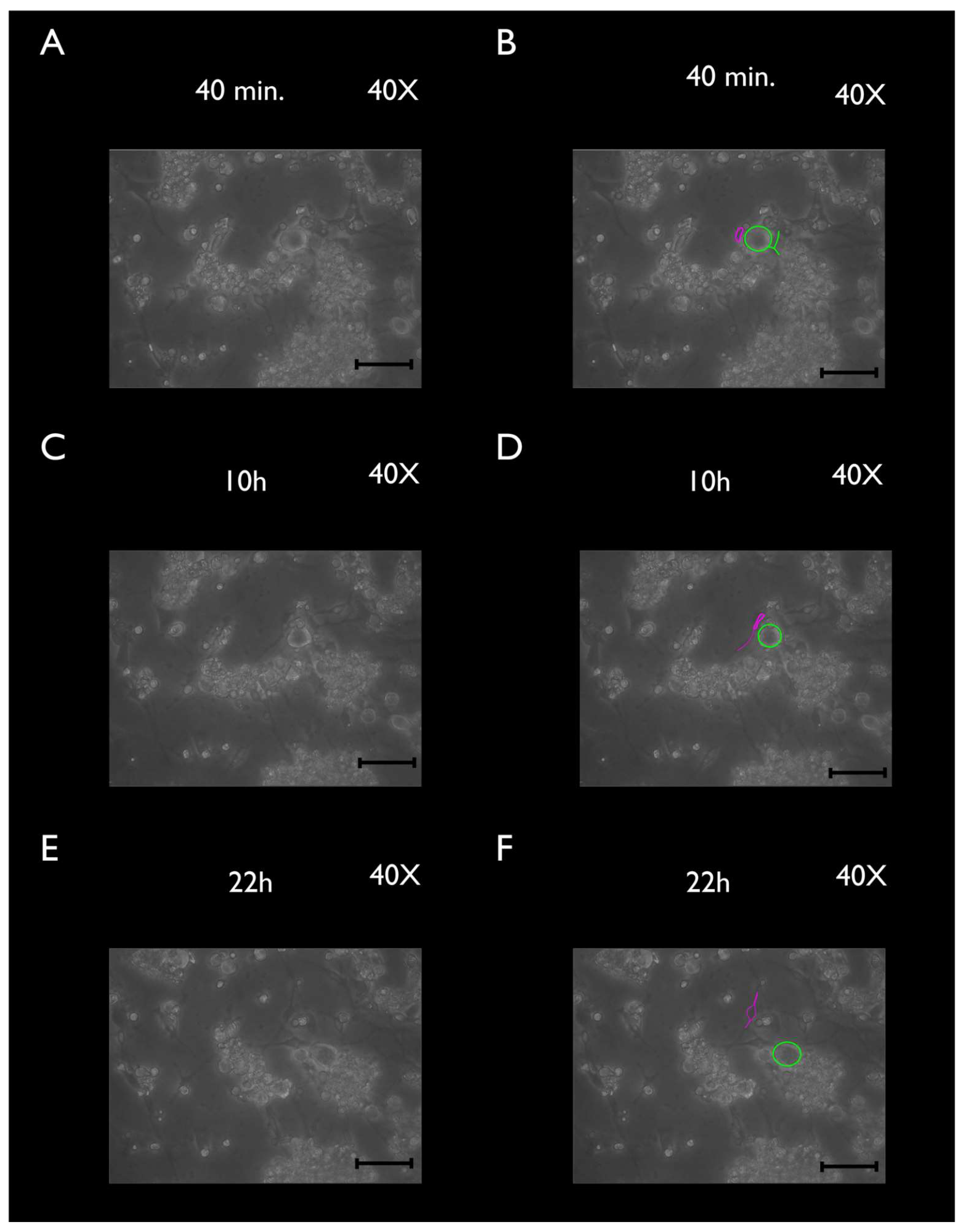
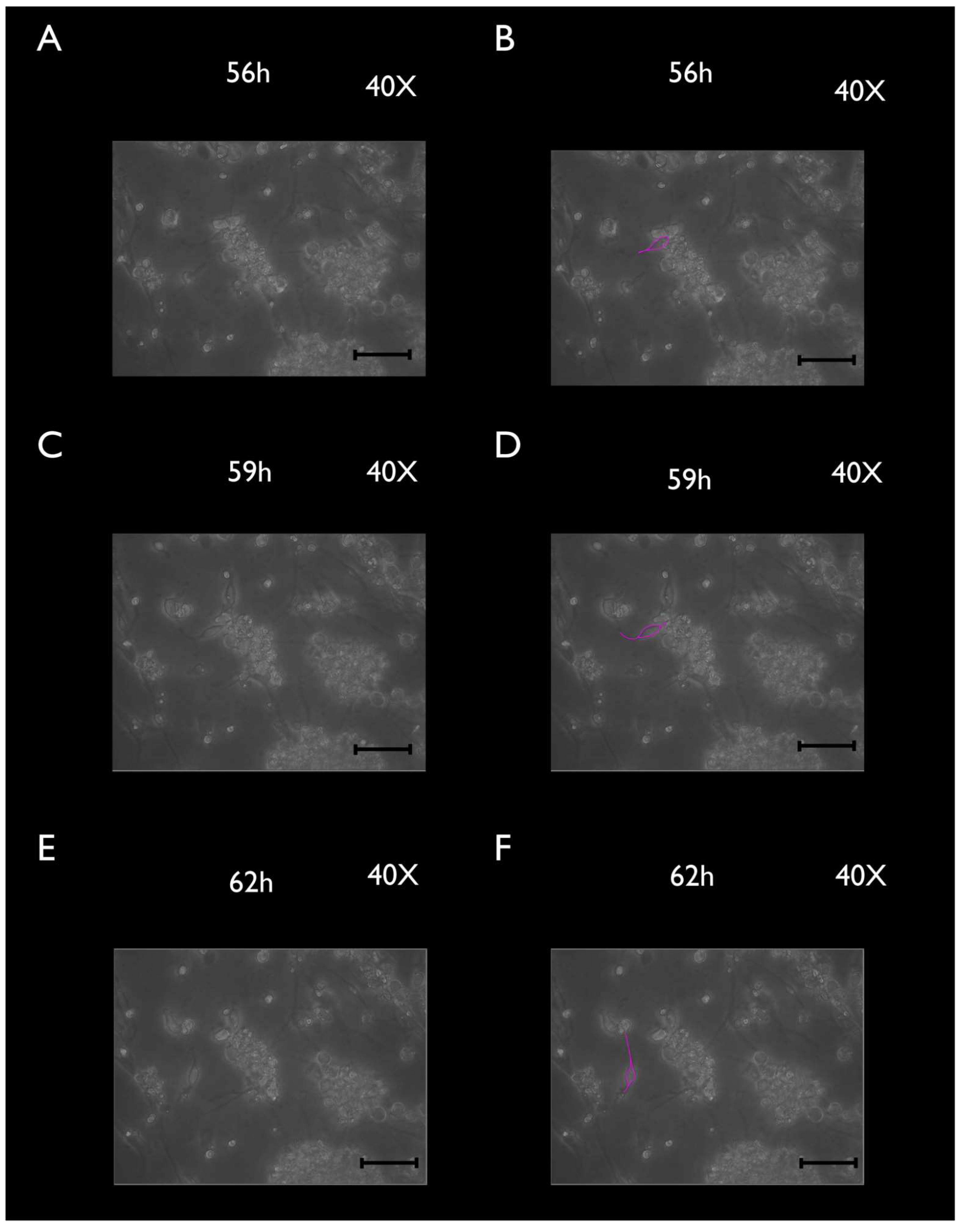
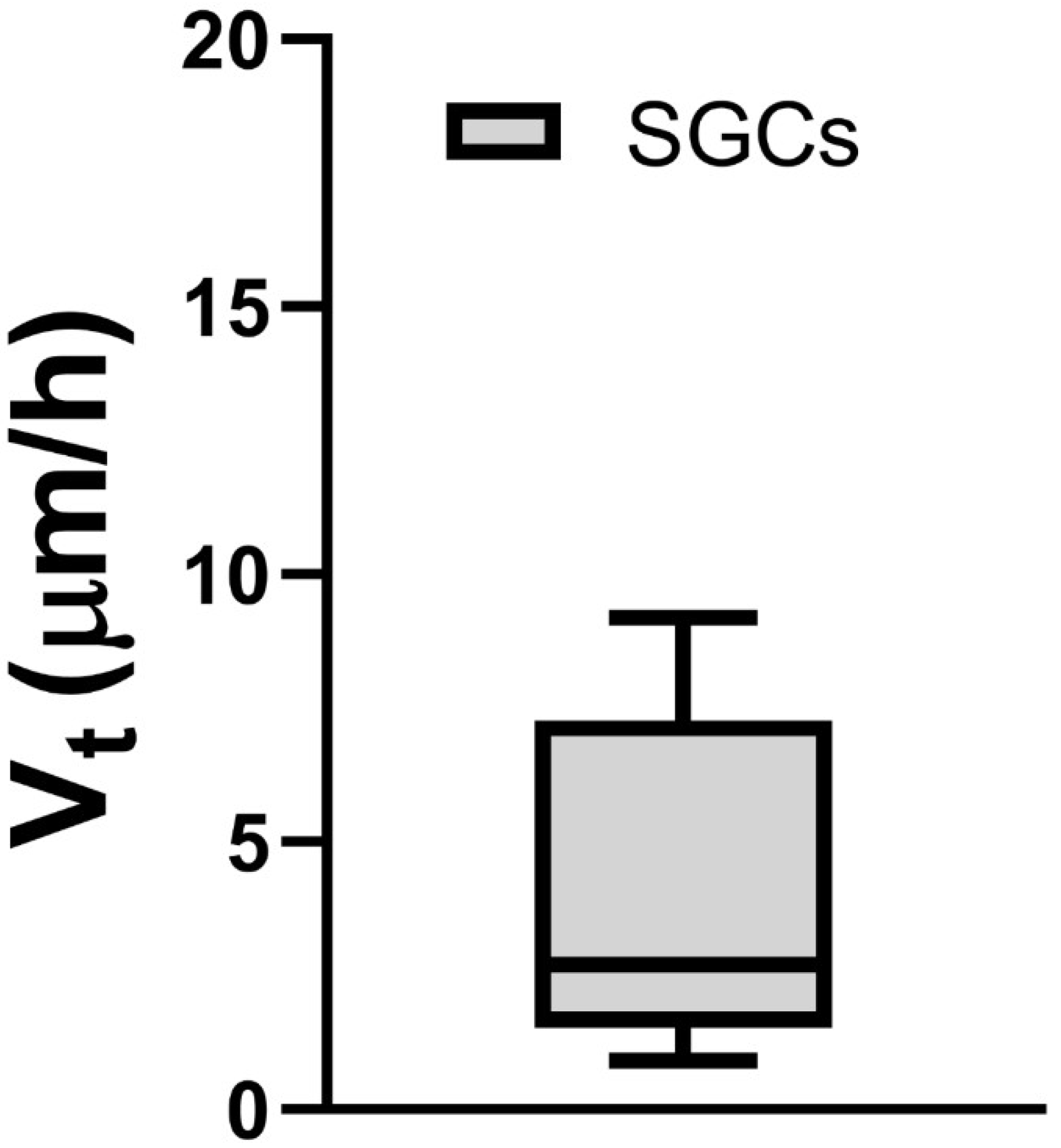
3.2. Phase-Contrast Microscopy, SEM, and Time-Lapse Photography Analyses
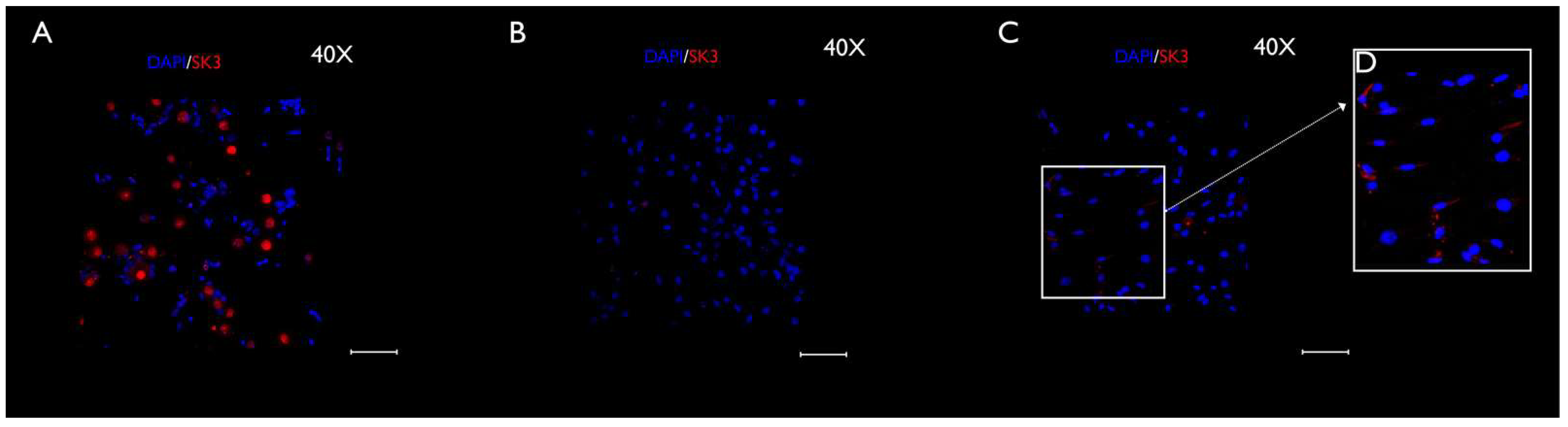
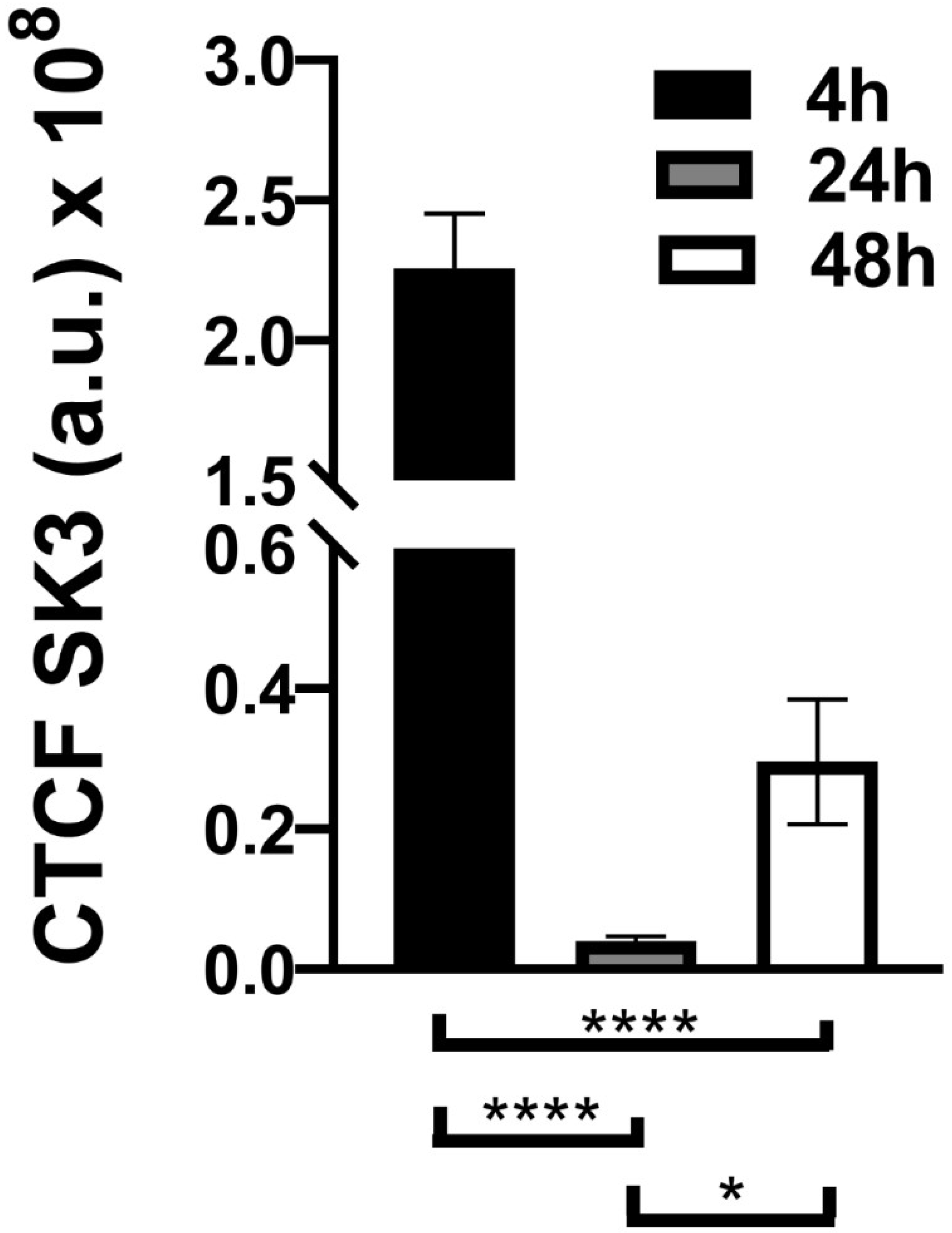
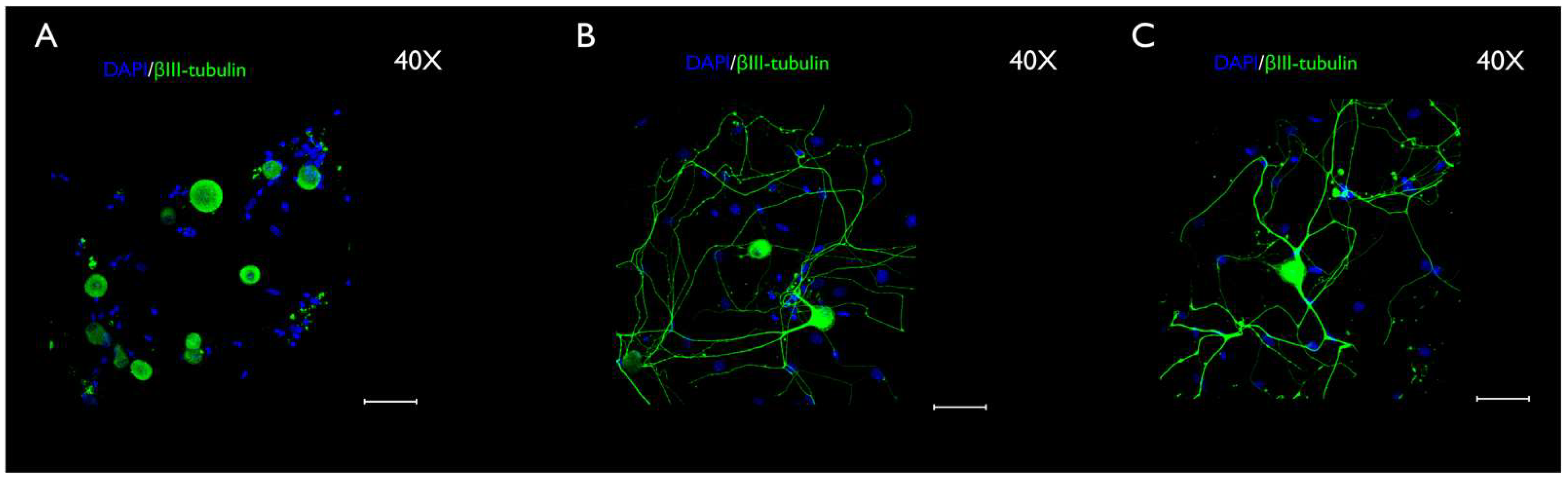
3.3. Immunocytochemistry Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macfarlane, T.V.; Blinkhorn, A.S.; Davies, R.M.; Kincey, J.; Worthington, H.V. Oro-facial pain in the community: Prevalence and associated impact. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2002, 30, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, J.L., 3rd; Gilbert, G.H. Orofacial pain symptoms: An interaction between age and sex. Pain 2001, 90, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häggman-Henrikson, B.; Alstergren, P.; Davidson, T.; Högestätt, E.D.; Östlund, P.; Tranaeus, S.; Vitols, S.; List, T. Pharmacological treatment of oro-facial pain-health technology assessment including a systematic review with network meta-analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2017, 44, 800–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, L.L.; Siegel, M.A.; Benoliel, R.; De Laat, A. Management of burning mouth syndrome: Systematic review and management recommendations. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2007, 103, S39.e1–S39.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, L.; Zakrzewska, J.M.; Abbott, J.; Braschinsky, M.; Di Stefano, G.; Donnet, A.; Eide, P.K.; Leal, P.R.L.; Maarbjerg, S.; May, A.; et al. European Academy of Neurology guideline on trigeminal neuralgia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.P.; Mao, J. Neuropathic pain: Mechanisms and their clinical implications. BMJ 2014, 348, f7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J. Current challenges in translational pain research. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, B.E. Pathophysiology of TMD pain—Basic mechanisms and their implications for pharmacotherapy. J. Oral Rehabil. 2010, 37, 391–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye Larsen, D.; Ingemann Kristensen, G.; Panchalingam, V.; Laursen, J.C.; Nørgaard Poulsen, J.; Skallerup Andersen, M.; Kandiah, A.; Gazerani, P. Investigating the expression of metabotropic glutamate receptors in trigeminal ganglion neurons and satellite glial cells: Implications for craniofacial pain. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2014, 34, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceruti, S.; Fumagalli, M.; Villa, G.; Verderio, C.; Abbracchio, M.P. Purinoceptor-mediated calcium signaling in primary neuron-glia trigeminal cultures. Cell Calcium 2008, 43, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceruti, S.; Villa, G.; Fumagalli, M.; Colombo, L.; Magni, G.; Zanardelli, M.; Fabbretti, E.; Verderio, C.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; Nistri, A.; et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide-mediated enhancement of purinergic neuron/glia communication by the algogenic factor bradykinin in mouse trigeminal ganglia from wild-type and R192Q Cav2.1 Knock-in mice: Implications for basic mechanisms of migraine pain. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 3638–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubový, P.; Klusáková, I.; Svízenská, I.; Brázda, V. Satellite glial cells express IL-6 and corresponding signal-transducing receptors in the dorsal root ganglia of rat neuropathic pain model. Neuron. Glia Biol. 2010, 6, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; McLachlan, E.M. Macrophage and lymphocyte invasion of dorsal root ganglia after peripheral nerve lesions in the rat. Neuroscience 2002, 112, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Y.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Y. Communication between neuronal somata and satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia. Glia 2013, 61, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanani, M. Satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia: From form to function. Brain Res. Rev. 2005, 48, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maro, G.S.; Vermeren, M.; Voiculescu, O.; Melton, L.; Cohen, J.; Charnay, P.; Topilko, P. Neural crest boundary cap cells constitute a source of neuronal and glial cells of the PNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho-Aguiar, J.e.M.; Bon-Frauches, A.C.; Gomes, A.L.; Veríssimo, C.P.; Aguiar, D.P.; Matias, D.; Thomasi, B.B.; Gomes, A.S.; Brito, G.A.; Moura-Neto, V. The enteric glia: Identity and functions. Glia 2015, 63, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.R.; Berta, T.; Nedergaard, M. Glia and pain: Is chronic pain a gliopathy? Pain 2013, 154, S10–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannese, E.; Ledda, M.; Cherkas, P.S.; Huang, T.Y.; Hanani, M. Satellite cell reactions to axon injury of sensory ganglion neurons: Increase in number of gap junctions and formation of bridges connecting previously separate perineuronal sheaths. Anat. Embryol. 2003, 206, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanani, M.; Spray, D.C. Emerging importance of satellite glia in nervous system function and dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannese, E. The Satellite Cells of the Sensory Ganglia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; Volume 65, 111p. [Google Scholar]
- Basbaum, A.I.; Bautista, D.M.; Scherrer, G.; Julius, D. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pain. Cell 2009, 139, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, S.; Ballantyne, J.; Rathmell, J.P.; Bonica, J.J. Bonica’s Management of Pain; Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, S.L.; Gustin, S.M.; Eykman, E.N.; Fowler, G.; Peck, C.C.; Murray, G.M.; Henderson, L.A. Trigeminal nerve anatomy in neuropathic and non-neuropathic orofacial pain patients. J. Pain 2013, 14, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standring, S. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 40th ed.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, B.P.; Strassman, A.M.; Maciewicz, R.J. Behavioral evidence of trigeminal neuropathic pain following chronic constriction injury to the rat’s infraorbital nerve. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 2708–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Rao, Y.; Fu, J.; Hua, L.; Ou, C. Activation of SK3 channel plays a pivotal role in modulation of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurol. Res. 2021, 43, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, M.; Hirschberg, B.; Bond, C.T.; Kinzie, J.M.; Marrion, N.V.; Maylie, J.; Adelman, J.P. Small-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels from mammalian brain. Science 1996, 273, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.; Pedarzani, P. Differential distribution of three Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel subunits, SK1, SK2, and SK3, in the adult rat central nervous system. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2000, 15, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahia, P.K.; Suzuki, R.; Benton, D.C.; Jowett, A.J.; Chen, M.X.; Trezise, D.J.; Dickenson, A.H.; Moss, G.W. A functional role for small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in sensory pathways including nociceptive processes. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3489–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mongan, L.C.; Hill, M.J.; Chen, M.X.; Tate, S.N.; Collins, S.D.; Buckby, L.; Grubb, B.D. The distribution of small and intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in the rat sensory nervous system. Neuroscience 2005, 131, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vit, J.P.; Jasmin, L.; Bhargava, A.; Ohara, P.T. Satellite glial cells in the trigeminal ganglion as a determinant of orofacial neuropathic pain. Neuron. Glia Biol. 2006, 2, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, J.N.; Larsen, F.; Duroux, M.; Gazerani, P. Primary culture of trigeminal satellite glial cells: A cell-based platform to study morphology and function of peripheral glia. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Erzurumlu, R.S.; Jhaveri, S.; Takahashi, H.; McKay, R.D. Target-derived influences on axon growth modes in cultures of trigeminal neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7235–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belzer, V.; Shraer, N.; Hanani, M. Phenotypic changes in satellite glial cells in cultured trigeminal ganglia. Neuron. Glia Biol. 2010, 6, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jager, S.B.; Pallesen, L.T.; Vaegter, C.B. Isolation of satellite glial cells for high-quality RNA purification. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 297, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jager, S. Satellite Glial Cell Involvement in Neuropathic Pain; Aarhus University: Aarhus, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jager, S.E.; Pallesen, L.T.; Richner, M.; Harley, P.; Hore, Z.; McMahon, S.; Denk, F.; Vaegter, C.B. Changes in the transcriptional fingerprint of satellite glial cells following peripheral nerve injury. Glia 2020, 68, 1375–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weick, M.; Cherkas, P.S.; Hartig, W.; Pannicke, T.; Uckermann, O.; Bringmann, A.; Tal, M.; Reichenbach, A.; Hanani, M. P2 receptors in satellite glial cells in trigeminal ganglia of mice. Neuroscience 2003, 120, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The arrive guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Unno, S.; Ando, H.; Masuda, Y.; Kitagawa, J. Neuron-Glia Crosstalk and Neuropathic Pain: Involvement in the Modulation of Motor Activity in the Orofacial Region. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljevic, A.; Jancic, J.; Mircic, A.; Dozic, A.; Boljanovic, J.; Milisavljevic, M.; Cetkovic, M. Morphological and functional characteristics of satellite glial cells in the peripheral nervous system. Folia Morphol. 2021, 80, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Ahrens, P.; Lambert, S. Satellite glial cells represent a population of developmentally arrested Schwann cells. Glia 2018, 66, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessen, K.R.; Mirsky, R. The origin and development of glial cells in peripheral nerves. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fex Svenningsen, A.; Colman, D.R.; Pedraza, L. Satellite cells of dorsal root ganglia are multipotential glial precursors. Neuron. Glia Biol. 2004, 1, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Say, E.H.; Zhou, X.F. Isolation and characterization of neural crest progenitors from adult dorsal root ganglia. Stem. Cells 2007, 25, 2053–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capuano, A.; De Corato, A.; Lisi, L.; Tringali, G.; Navarra, P.; Dello Russo, C. Proinflammatory-activated trigeminal satellite cells promote neuronal sensitization: Relevance for migraine pathology. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiansen, K.A.; Edvinsson, L. Neurogenic inflammation: A study of rat trigeminal ganglion. J. Headache Pain 2010, 11, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, M.; Fabbro, A.; D’Arco, M.; Zweyer, M.; Nistri, A.; Giniatullin, R.; Fabbretti, E. Comparison of P2X and TRPV1 receptors in ganglia or primary culture of trigeminal neurons and their modulation by NGF or serotonin. Mol. Pain 2006, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, H.Z.; Moules, E.; Burnstock, G. Changes in P2X3 purinoceptors in sensory ganglia of the mouse during embryonic and postnatal development. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 122, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Veríssimo, C.P.; Acosta Filha, L.G.; Moreira da Silva, F.J.; Westgarth, H.; Coelho Aguiar, J.D.M.; Pontes, B.; Moura-Neto, V.; Gazerani, P.; DosSantos, M.F. Short-Term Functional and Morphological Changes in the Primary Cultures of Trigeminal Ganglion Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 1257-1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44030084
Veríssimo CP, Acosta Filha LG, Moreira da Silva FJ, Westgarth H, Coelho Aguiar JDM, Pontes B, Moura-Neto V, Gazerani P, DosSantos MF. Short-Term Functional and Morphological Changes in the Primary Cultures of Trigeminal Ganglion Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2022; 44(3):1257-1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44030084
Chicago/Turabian StyleVeríssimo, Carla Pires, Lionete Gall Acosta Filha, Fábio Jorge Moreira da Silva, Harrison Westgarth, Juliana De Mattos Coelho Aguiar, Bruno Pontes, Vivaldo Moura-Neto, Parisa Gazerani, and Marcos F. DosSantos. 2022. "Short-Term Functional and Morphological Changes in the Primary Cultures of Trigeminal Ganglion Cells" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 44, no. 3: 1257-1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44030084
APA StyleVeríssimo, C. P., Acosta Filha, L. G., Moreira da Silva, F. J., Westgarth, H., Coelho Aguiar, J. D. M., Pontes, B., Moura-Neto, V., Gazerani, P., & DosSantos, M. F. (2022). Short-Term Functional and Morphological Changes in the Primary Cultures of Trigeminal Ganglion Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(3), 1257-1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44030084






