Association between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Hearing Impairment: A Nested Case-Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
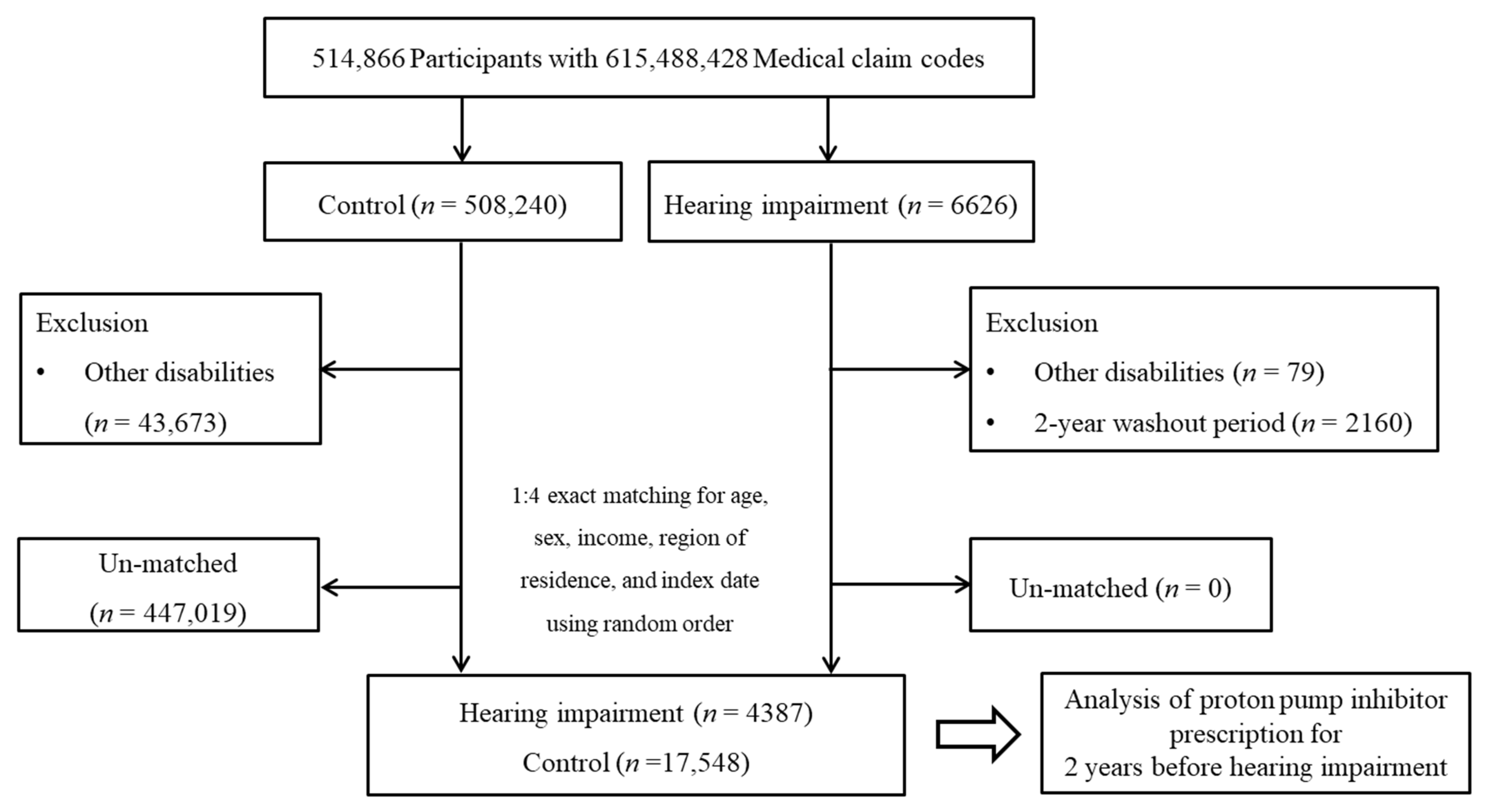
2.2. Study Population and Participant Selection
2.3. Exposure (Days of Proton Pump Inhibitor Prescription)
2.4. Outcome (Hearing Impairment)
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, H.; Liu, H. Proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux disease: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e23297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, V.; Marabotto, E.; Zentilin, P.; Furnari, M.; Bodini, G.; de Maria, C.; Pellegatta, G.; Coppo, C.; Savarino, E. Proton pump inhibitors: Use and misuse in the clinical setting. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clissold, S.P.; Campoli-Richards, D.M. Omeprazole. A preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in peptic ulcer disease and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Drugs 1986, 32, 15–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walan, A.; Bader, J.P.; Classen, M.; Lamers, C.B.; Piper, D.W.; Rutgersson, K.; Eriksson, S. Effect of omeprazole and ranitidine on ulcer healing and relapse rates in patients with benign gastric ulcer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makunts, T.; Alpatty, S.; Lee, K.C.; Atayee, R.S.; Abagyan, R. Proton-pump inhibitor use is associated with a broad spectrum of neurological adverse events including impaired hearing, vision, and memory. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makunts, T.; Cohen, I.V.; Awdishu, L.; Abagyan, R. Analysis of postmarketing safety data for proton-pump inhibitors reveals increased propensity for renal injury, electrolyte abnormalities, and nephrolithiasis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, B.; Chen, Y.; Wilson, F.P.; Sang, Y.; Chang, A.R.; Coresh, J.; Grams, M.E. Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and the Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomm, W.; von Holt, K.; Thome, F.; Broich, K.; Maier, W.; Fink, A.; Doblhammer, G.; Haenisch, B. Association of Proton Pump Inhibitors With Risk of Dementia: A Pharmacoepidemiological Claims Data Analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusanya, B.O.; Davis, A.C.; Hoffman, H.J. Hearing loss: Rising prevalence and impact. Bull. World Health Organ. 2019, 97, 646-646A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, B.; Winter, E.; Fuchs, J.; Haupt, H.; Gross, J. Susceptibility of the hair cells of the newborn rat cochlea to hypoxia and ischemia. Heart Res. 2003, 182, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirodda, A.; Brandolini, C.; Borghi, C. The influence of systemic circulation on hearing: The reliability of a different impact of microcirculatory defects and atherosclerosis. Med. Hypotheses 2016, 91, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.H.; Chung, J.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Cochlear Damage Caused by the Striking Noise of Titanium Head Golf Driver. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 12, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patuzzi, R. Ion flow in stria vascularis and the production and regulation of cochlear endolymph and the endolymphatic potential. Heart Res. 2011, 277, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhovershin, R.A.; Cooke, J.P. How May Proton Pump Inhibitors Impair Cardiovascular Health? Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2016, 16, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Min, C.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Tobacco Smoking and Alcohol Consumption Are Related to Benign Parotid Tumor: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 12, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lim, J.S.; Kong, I.G.; Choi, H.G. Hearing impairment and the risk of neurodegenerative dementia: A longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Min, C.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Bidirectional Association Between GERD and Asthma: Two Longitudinal Follow-Up Studies Using a National Sample Cohort. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Oh, D.J.; Park, B.; Choi, H.G. Bell’s palsy and obesity, alcohol consumption and smoking: A nested case-control study using a national health screening cohort. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Li, B.; Couris, C.M.; Fushimi, K.; Graham, P.; Hider, P.; Januel, J.M.; Sundararajan, V. Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.M.; Curhan, S.G.; Wang, M.; Jacobson, B.C.; Eavey, R.; Stankovic, K.M.; Curhan, G.C. Prospective Study of Gastroesophageal Reflux, Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors and H2-Receptor Antagonists, and Risk of Hearing Loss. Ear Heart 2017, 38, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eusebi, L.H.; Rabitti, S.; Artesiani, M.L.; Gelli, D.; Montagnani, M.; Zagari, R.M.; Bazzoli, F. Proton pump inhibitors: Risks of long-term use. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobanoglu, H.B.; Vuralkan, E.; Arslan, A.; Mirasoglu, B.; Toklu, A.S. Is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Effective in Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Rats? Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 12, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhovershin, R.A.; Yepuri, G.; Ghebremariam, Y.T. Endothelium-Derived Nitric Oxide as an Antiatherogenic Mechanism: Implications for Therapy. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2015, 11, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Cryer, B.L.; Contant, C.F.; Cohen, M.; Lanas, A.; Schnitzer, T.J.; Shook, T.L.; Lapuerta, P.; Goldsmith, M.A.; Laine, L.; et al. Clopidogrel with or without omeprazole in coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, P.M.; Maddox, T.M.; Wang, L.; Fihn, S.D.; Jesse, R.L.; Peterson, E.D.; Rumsfeld, J.S. Risk of adverse outcomes associated with concomitant use of clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitors following acute coronary syndrome. JAMA 2009, 301, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.M.E.; Drinkwater, J.; Davis, W.A. Proton Pump Inhibitors, Nephropathy, and Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: The Fremantle Diabetes Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 2985–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Eltriki, M.; Green, C.J.; Maclure, M.; Musini, V.; Bassett, K.L.; Wright, J.M. Do proton pump inhibitors increase mortality? A systematic review and in-depth analysis of the evidence. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2020, 8, e00651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijarnpreecha, K.; Thongprayoon, C.; Panjawatanan, P.; Ungprasert, P. Proton pump inhibitors and risk of dementia. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiola, N.; Alcalde, V.; Pujol, A.; Munter, L.M.; Multhaup, G.; Lleo, A.; Coma, M.; Soler-Lopez, M.; Aloy, P. The proton-pump inhibitor lansoprazole enhances amyloid beta production. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicinski, M.; Malinowski, B.; Puk, O.; Gorski, K.; Adamkiewicz, D.; Chojnacki, G.; Walczak, M.; Wodkiewicz, E.; Szambelan, M.; Adamska, P.; et al. Possible Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors on Hearing Loss Development. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4853695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, M.F.; Yang, Y.X.; Howden, C.W. Complications of Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, D.B.; Rees, C.J.; Lippert, D.; Sataloff, R.T.; Wright, S.C., Jr. Adverse effects of long-term proton pump inhibitor use: A review for the otolaryngologist. J. Voice 2011, 25, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecain, E.; Robert, J.C.; Thomas, A.; Tran Ba Huy, P. Gastric proton pump is expressed in the inner ear and choroid plexus of the rat. Heart Res. 2000, 149, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Hibino, H.; Doi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Hisa, Y.; Kurachi, Y. Gastric type H+,K+-ATPase in the cochlear lateral wall is critically involved in formation of the endocochlear potential. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C1038–C1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Total Participants | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hearing Impairment (n, %) | Control (n, %) | p-Value | |
| Age (years old) | 1.000 | ||
| 40–44 | 42 (1.0) | 168 (1.0) | |
| 45–49 | 144 (3.3) | 576 (3.3) | |
| 50–54 | 302 (6.9) | 1208 (6.9) | |
| 55–59 | 485 (11.1) | 1940 (11.1) | |
| 60–64 | 621 (14.2) | 2484 (14.2) | |
| 65–69 | 788 (18.0) | 3152 (18.0) | |
| 70–74 | 851 (19.4) | 3404 (19.4) | |
| 75–79 | 715 (16.3) | 2860 (16.3) | |
| 80–84 | 356 (8.1) | 1424 (8.1) | |
| 85+ | 83 (1.9) | 332 (1.9) | |
| Sex | 1.000 | ||
| Male | 2651 (60.4) | 10,604 (60.4) | |
| Female | 1736 (39.6) | 6944 (39.6) | |
| Income | 1.000 | ||
| 1 (lowest) | 829 (18.9) | 3316 (18.9) | |
| 2 | 612 (14.0) | 2448 (14.0) | |
| 3 | 693 (15.8) | 2772 (15.8) | |
| 4 | 809 (18.4) | 3236 (18.4) | |
| 5 (highest) | 1444 (32.9) | 5776 (32.9) | |
| Region of residence | 1.000 | ||
| Urban | 1807 (41.2) | 7228 (41.2) | |
| Rural | 2580 (58.8) | 10,320 (58.8) | |
| Obesity ‡ | 0.457 | ||
| Underweight | 141 (3.2) | 623 (3.6) | |
| Normal | 1611 (36.7) | 6399 (36.5) | |
| Overweight | 1145 (26.1) | 4735 (27.0) | |
| Obese I | 1382 (31.5) | 5342 (30.4) | |
| Obese II | 108 (2.5) | 449 (2.6) | |
| Smoking status | 0.097 | ||
| Nonsmoker | 3182 (72.5) | 12,439 (70.9) | |
| Past smoker | 477 (10.9) | 2031 (11.6) | |
| Current smoker | 728 (16.6) | 3078 (17.5) | |
| Alcohol consumption | |||
| <1 time a week | 3234 (73.7) | 12,640 (72.0) | 0.025 * |
| ≥1 time a week | 1153 (26.3) | 4908 (28.0) | |
| Systolic blood pressure | <0.001 * | ||
| <120 mmHg | 938 (21.4) | 4159 (23.7) | |
| 120–139 mmHg | 1935 (44.1) | 8187 (46.7) | |
| ≥140 mmHg | 1514 (34.5) | 5202 (29.6) | |
| Diastolic blood pressure | <0.001 * | ||
| <80 mmHg | 1592 (36.3) | 7213 (41.1) | |
| 80–89 mmHg | 1566 (35.7) | 6407 (36.5) | |
| ≥90 mmHg | 1229 (28.0) | 3928 (22.4) | |
| Fasting blood glucose | <0.001 * | ||
| <100 mg/dL | 2824 (64.4) | 10,604 (60.4) | |
| 100–125 mg/dL | 1140 (26.0) | 5126 (29.2) | |
| ≥126 mg/dL | 423 (9.6) | 1818 (10.4) | |
| Total cholesterol | 0.889 | ||
| <200 mg/dL | 2366 (53.9) | 9535 (54.3) | |
| 200–239 mg/dL | 1433 (32.7) | 5676 (32.4) | |
| ≥240 mg/dL | 588 (13.4) | 2337 (13.3) | |
| CCI score | <0.001 * | ||
| 0 | 2385 (54.4) | 10,115 (57.6) | |
| 1 | 854 (19.5) | 3057 (17.4) | |
| 2 | 536 (12.2) | 1813 (10.3) | |
| 3 | 298 (6.8) | 1119 (6.4) | |
| ≥4 | 314 (7.2) | 1444 (8.2) | |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | <0.001 * | ||
| Yes | 962 (21.9) | 3046 (17.4) | |
| No | 3425 (78.1) | 14,502 (82.6) | |
| H2 blocker | 63.03 (123.0) | 54.16 (119.9) | <0.001 † |
| Prescription dates of proton pump inhibitor | <0.001 * | ||
| <30 days | 451 (10.3) | 2679 (15.3) | |
| ≥30 to <365 days | 1647 (37.5) | 5972 (34.0) | |
| ≥365 days | 2289 (52.2) | 8897 (50.7) | |
| Characteristics | N of Hearing Impairment | N of Control | ORs of Hearing Impairment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Exposure/Total, %) | (Exposure/Total, %) | Crude † | p-Value | Model 1 †,‡ | p-Value | Model 2 †,§ | p-Value | Model 3 † | p-Value | |
| Total participants (n =21,935) | ||||||||||
| ≥0 to <30 days | 451/4387 (10.3%) | 2679/17,548 (15.3%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| ≥30 to <365 days | 1647/4387 (37.5%) | 5972/17,548 (34.0%) | 1.67 (1.49–1.88) | <0.001 * | 1.68 (1.50–1.89) | <0.001 * | 1.69 (1.50–1.89) | <0.001 * | 1.65 (1.47–1.86) | <0.001 * |
| ≥365 days | 2289/4387 (52.2%) | 8897/17,548 (50.7%) | 1.59 (1.42–1.78) | <0.001 * | 1.61 (1.43–1.81) | <0.001 * | 1.62 (1.44–1.82) | <0.001 * | 1.52 (1.35–1.72) | <0.001 * |
| Age <70 years old (n = 11,910) | ||||||||||
| ≥0 to <30 days | 343/2382 (14.4%) | 2073/9528 (21.8%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| ≥30 to <365 days | 1049/2382 (44.0%) | 3752/9528 (39.4%) | 1.72 (1.51–1.97) | <0.001 * | 1.74 (1.52−1.99) | <0.001 * | 1.74 (1.52−1.99) | <0.001 * | 1.70 (1.49−1.95) | <0.001 * |
| ≥365 days | 990/2382 (41.6%) | 3703/9528 (38.9%) | 1.67 (1.46−1.93) | <0.001 * | 1.70 (1.47−1.95) | <0.001 * | 1.70 (1.47−1.96) | <0.001 * | 1.60 (1.38−1.86) | <0.001 * |
| Age ≥70 years old (n = 10,025) | ||||||||||
| ≥0 to <30 days | 108/2005 (5.4%) | 606/8020 (7.6%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| ≥30 to <365 days | 598/2005 (29.8%) | 2220/8020 (27.7%) | 1.51 (1.21–1.90) | <0.001 * | 1.51 (1.21–1.89) | <0.001 * | 1.52 (1.22–1.91) | <0.001 * | 1.49 (1.19–1.87) | <0.001 * |
| ≥365 days | 1299/2005 (64.8%) | 5194/8020 (64.8%) | 1.41 (1.14–1.74) | 0.001 * | 1.42 (1.15–1.77) | 0.001 * | 1.43 (1.15–1.78) | 0.001 * | 1.34 (1.07–1.67) | 0.010 * |
| Men (n = 13,255) | ||||||||||
| ≥0 to <30 days | 321/2651 (12.1%) | 1964/10,604 (18.5%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| ≥30 to <365 days | 1058/2651 (39.9%) | 3594/10,604 (33.9%) | 1.83 (1.60–2.10) | <0.001 * | 1.84 (1.60–2.11) | <0.001 * | 1.85 (1.61–2.13) | <0.001 * | 1.80 (1.57–2.07) | <0.001 * |
| ≥365 days | 1272/2651 (48.0%) | 5046/10,604 (47.6%) | 1.59 (1.39–1.83) | <0.001 * | 1.63 (1.41–1.87) | <0.001 * | 1.65 (1.43–1.90) | <0.001 * | 1.50 (1.30–1.74) | <0.001* |
| Women (n = 8680) | ||||||||||
| ≥0 to <30 days | 130/1736 (7.5%) | 715/6944 (10.3%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| ≥30 to <365 days | 589/1736 (33.9%) | 2378/6944 (34.2%) | 1.38 (1.12–1.71) | 0.002 * | 1.39 (1.13–1.71) | 0.002 * | 1.39 (1.13–1.71) | 0.002 * | 1.38 (1.12–1.70) | 0.003 * |
| ≥365 days | 1017/1736 (58.6%) | 3851/6944 (55.5%) | 1.50 (1.22–1.85) | <0.001 * | 1.52 (1.23–1.87) | <0.001 * | 1.51 (1.23–1.86) | <0.001 * | 1.48 (1.20–1.83) | <0.001 * |
| Characteristics | N of Hearing Impairment | N of Control | ORs of Hearing Impairment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Exposure/Total, %) | (Exposure/Total, %) | Crude † | p-Value | Model 1 †,‡ | p-Value | Model 2 †,§ | p-Value | Model 3 † | p-Value | |
| Severe hearing loss (n = 4075 for hearing impairment, n = 16,300 for control) | ||||||||||
| ≥0 to <30 days | 409/4075 (10.0%) | 2457/16,300 (15.1%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| ≥30 to <365 days | 1528/4075 (37.5%) | 5502/16,300 (33.8%) | 1.70 (1.51–1.92) | <0.001 * | 1.71 (1.52–1.93) | <0.001 * | 1.72 (1.52–1.94) | <0.001 * | 1.69 (1.49–1.90) | <0.001 * |
| ≥365 days | 2138/4075 (52.5%) | 8341/16,300 (51.2%) | 1.60 (1.42–1.81) | <0.001 * | 1.63 (1.45–1.84) | <0.001 * | 1.64 (1.45–1.86) | <0.001 * | 1.55 (1.37–1.76) | <0.001 * |
| Profound hearing loss (n = 312 for hearing impairment, n = 1248 for control) | ||||||||||
| ≥0 to <30 days | 42/312 (13.5%) | 222/1248 (17.8%) | ||||||||
| ≥30 to <365 days | 119/312 (38.1%) | 470/1248 (37.7%) | 1.36 (0.92–2.02) | 0.122 | 1.34 (0.91–1.99) | 0.155 | 1.33 (0.90–1.98) | 0.140 | 1.30 (0.87–1.94) | 0.196 |
| ≥365 days | 151/312 (48.4%) | 556/1248 (44.6%) | 1.49 (1.00–2.20) | 0.048 * | 1.39 (0.94–2.08) | 0.143 | 1.35 (0.90–2.03) | 0.102 | 1.26 (0.83–1.91) | 0.288 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Min, C.; Yoo, D.M.; Choi, H.G. Association between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Hearing Impairment: A Nested Case-Control Study. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 142-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43010012
Kim SY, Lee CH, Min C, Yoo DM, Choi HG. Association between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Hearing Impairment: A Nested Case-Control Study. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2021; 43(1):142-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, So Young, Chang Ho Lee, Chanyang Min, Dae Myoung Yoo, and Hyo Geun Choi. 2021. "Association between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Hearing Impairment: A Nested Case-Control Study" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 43, no. 1: 142-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43010012
APA StyleKim, S. Y., Lee, C. H., Min, C., Yoo, D. M., & Choi, H. G. (2021). Association between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Hearing Impairment: A Nested Case-Control Study. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 43(1), 142-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43010012






