Unexploited Antineoplastic Effects of Commercially Available Anti-Diabetic Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Metformin and Pioglitazone: Overview of Current Clinical Use and Molecular Targets
2.1. Pre-Clinical Data Suggesting Possible Repurposing
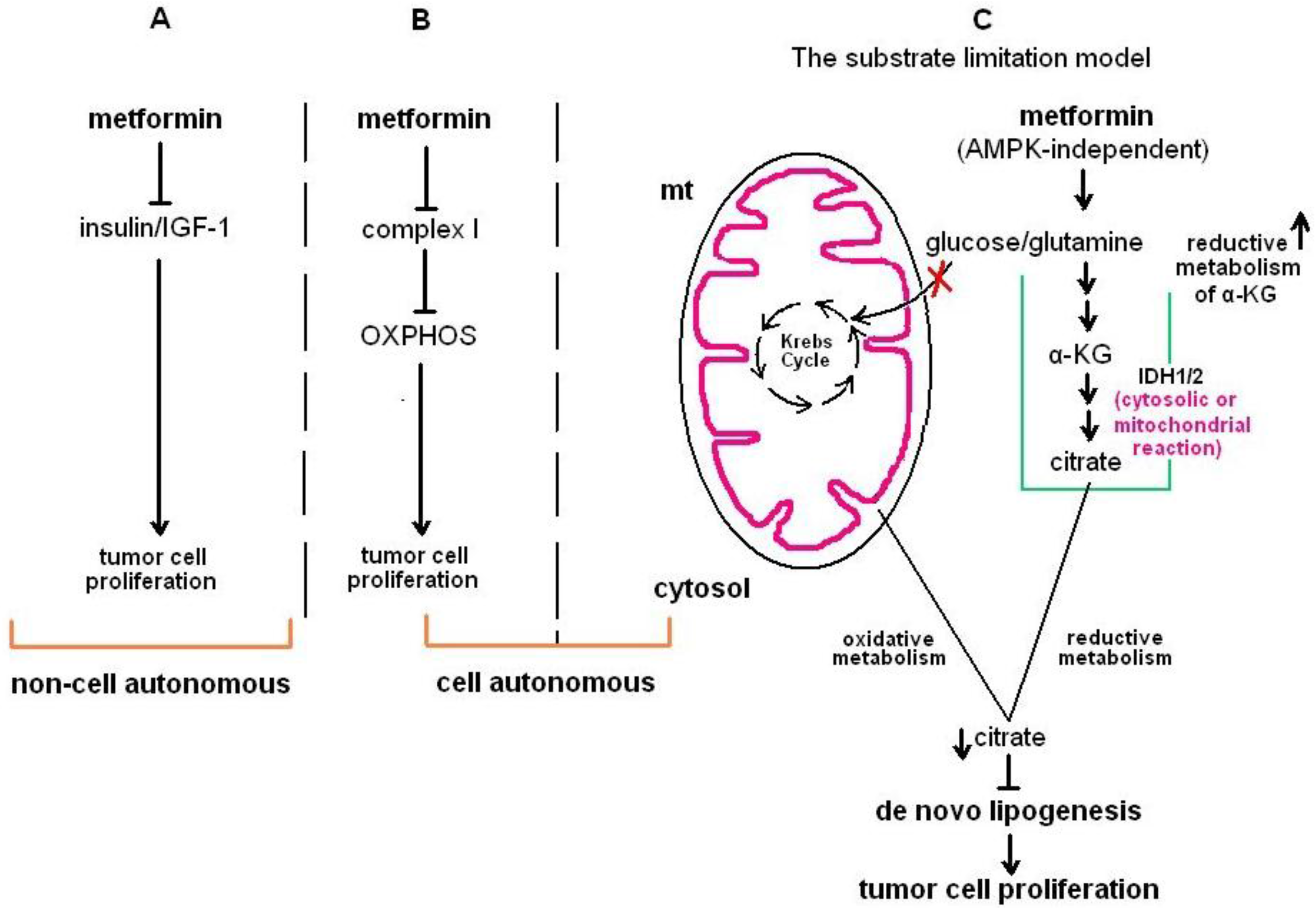
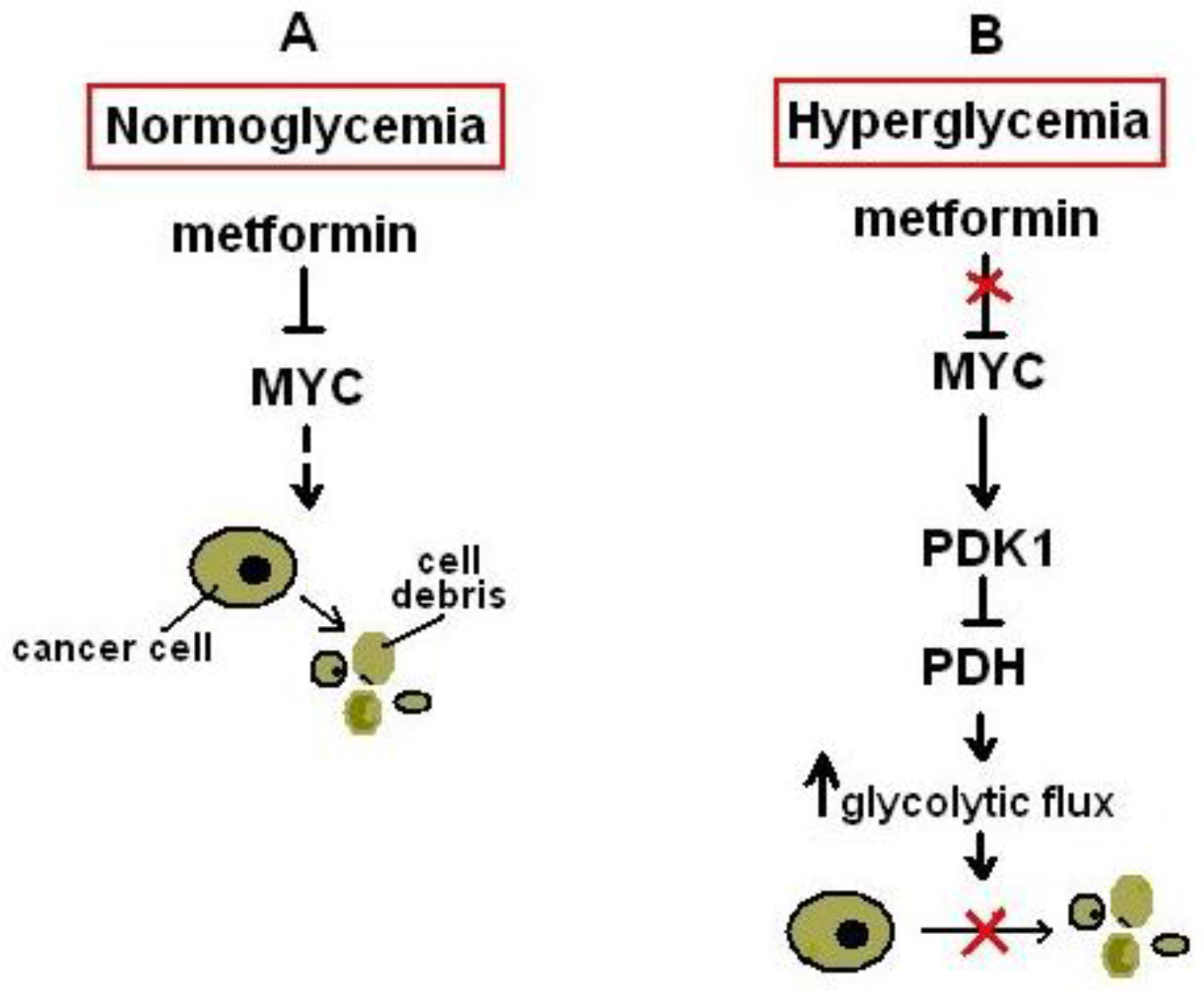
2.1.1. In Vitro Evidence for the Antineoplastic Effects of Metformin
2.1.2. Pre-Clinical In Vivo Evidence for the Antineoplastic Effects of Metformin
2.1.3. In Vitro Evidence for the Antineoplastic Effects of Pioglitazone
2.1.4. Pre-Clinical In Vivo Evidence for the Antineoplastic Effects of Pioglitazone
2.2. Clinical Data Suggesting Possible Repurposing
2.2.1. Metformin
2.2.2. Pioglitazone
2.3. Considerations for Using and Repurposing Metformin and Pioglitazone
2.4. Pitfalls and Limitations Stemming from the Use of Mouse Models to Study the Effects of Anti-Diabetic Drugs on Human Cancer Biology
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
References
- Duda, D.G.; Jain, R.K. Pleiotropy of tissue-specific growth factors: From neurons to vessels via the bone marrow. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 596–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tyler, A.L.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Williams, S.M.; Moore, J.H. Shadows of complexity: What biological networks reveal about epistasis and pleiotropy. Bioessays 2009, 31, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darabos, C.; Moore, J.H. Genome-Wide epistasis and pleiotropy characterized by the bipartite human phenotype network. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1253, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wathieu, H.; Issa, N.T.; Byers, S.W.; Dakshanamurthy, S. Harnessing polypharmacology with computer-aided drug design and systems biology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, P.M.; Cifkova, R. Blood pressure-lowering aspects of lipid-lowering and anti-diabetic drugs. Pharmaceuticals 2011, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, A.; Williams, G.; Ballard, C. Drug repositioning in Alzheimer‘s disease. Front. Biosci. 2015, 7, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Nemeno, J.G.; Lee, J.I. Repositioning bevacizumab: A promising therapeutic strategy for cartilage regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kast, R.E.; Boockvar, J.A.; Bruning, A.; Cappello, F.; Chang, W.W.; Cvek, B.; Dou, Q.P.; Duenas-Gonzalez, A.; Efferth, T.; Focosi, D.; et al. A conceptually new treatment approach for relapsed glioblastoma: Coordinated undermining of survival paths with nine repurposed drugs (cusp9) by the international initiative for accelerated improvement of glioblastoma care. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 502–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Febbraro, T.; Lengyel, E.; Romero, I.L. Old drug, new trick: Repurposing metformin for gynecologic cancers? Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 135, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchfield, L.M.; Mukherjee, A.; Eckert, M.A.; Johnson, A.; Mills, K.A.; Pan, S.; Shridhar, V.; Lengyel, E.; Romero, I.L. Hyperglycemia-induced metabolic compensation inhibits metformin sensitivity in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23548–23560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kast, R.E. The role of interleukin-18 in glioblastoma pathology implies therapeutic potential of two old drugs-disulfiram and ritonavir. Chin. J. Cancer 2015, 34, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Changou, C.A.; Chen, C.H.; Liu, Y.R.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Luh, F.; Yen, Y. Integrin beta3 and lkb1 are independently involved in the inhibition of proliferation by lovastatin in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, A.J.; Villani, L.A.; Broadfield, L.A.; Houde, V.P.; Galic, S.; Blandino, G.; Kemp, B.E.; Tsakiridis, T.; Muti, P.; Steinberg, G.R. Salicylate activates ampk and synergizes with metformin to reduce the survival of prostate and lung cancer cells ex vivo through inhibition of de novo lipogenesis. Biochem. J. 2015, 469, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanagnou, P.; Baltopoulos, P.; Tsironi, M. Marketed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, antihypertensives, and human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors: As-yet-unused weapons of the oncologists’ arsenal. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adekola, K.U.; Dalva Aydemir, S.; Ma, S.; Zhou, Z.; Rosen, S.T.; Shanmugam, M. Investigating and targeting chronic lymphocytic leukemia metabolism with the human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitor ritonavir and metformin. Leuk Lymphoma 2015, 56, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadon, V.; Balbi, M.; Ghersetti, M.; Grazioli, S.; Perciaccante, A.; Della Valentina, G.; Gardenal, R.; Dal Mas, M.; Casarin, P.; Zanette, G.; et al. Antidiabetic therapy and increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2506–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.M.; Curley, S.A.; Li, D.; Kaseb, A.; Davila, M.; Abdalla, E.K.; Javle, M.; Moghazy, D.M.; Lozano, R.D.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; et al. Association of diabetes duration and diabetes treatment with the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2010, 116, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodmer, M.; Becker, C.; Meier, C.; Jick, S.S.; Meier, C.R. Use of antidiabetic agents and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A case-control analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Friedrich, N. Do GLP-1-based therapies increase cancer risk? Diabetes Care 2013, 36, S245–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.W.; Tseng, C.H. A review on the relationship between SGLT2 inhibitors and cancer. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 719578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.W.; Liao, K.F.; Chen, P.C.; Tsai, P.Y.; Hsieh, D.P.; Chen, C.C. Antidiabetes drugs correlate with decreased risk of lung cancer: A population-based observation in taiwan. Clin. Lung Cancer 2012, 13, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sharkawi, F.Z.; El Shemy, H.A.; Khaled, H.M. Possible anticancer activity of rosuvastatine, doxazosin, repaglinide and oxcarbazepin. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Bai, P. Troglitazone induces apoptosis in gastric cancer cells through the NAG-1 pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2011, 4, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Chu, E.S.; Zhao, G.; Man, K.; Wu, C.W.; Cheng, J.T.; Li, G.; Nie, Y.; Lo, C.M.; Teoh, N.; et al. Ppargamma inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastases in vitro and in mice. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pon, C.K.; Firth, S.M.; Baxter, R.C. Involvement of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated inhibition of breast cancer cell growth. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 399, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.Q.; Shao, Z.L.; Liang, H.H.; Zhang, D.W.; Yang, X.W.; Jiang, X.F.; Xue, P. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) inhibits hepatoma cell growth via downregulation of sept2 expression. Cancer Lett. 2015, 359, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, L.H.; Hsu, S.P.; Zhong, W.B.; Liang, Y.C. Combined treatment with troglitazone and lovastatin inhibited epidermal growth factor-induced migration through the downregulation of cysteine-rich protein 61 in human anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostapanos, M.S.; Elisaf, M.S.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Pioglitazone and cancer: Angel or demon? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 4913–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orecchioni, S.; Reggiani, F.; Talarico, G.; Mancuso, P.; Calleri, A.; Gregato, G.; Labanca, V.; Noonan, D.M.; Dallaglio, K.; Albini, A.; et al. The biguanides metformin and phenformin inhibit angiogenesis, local and metastatic growth of breast cancer by targeting both neoplastic and microenvironment cells. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E534–E544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, L.; Liu, C.; Xia, T.; Zha, X.; Wang, S. Phenformin induces cell cycle change, apoptosis, and mesenchymal-epithelial transition and regulates the AMPK/mTOR/p70s6k and MAPK/ERK pathways in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.D.; Wei, S.Q.; Wang, Q.Y. Targeting oncogenic kras in non-small cell lung cancer cells by phenformin inhibits growth and angiogenesis. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 3339–3349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wheaton, W.W.; Weinberg, S.E.; Hamanaka, R.B.; Soberanes, S.; Sullivan, L.B.; Anso, E.; Glasauer, A.; Dufour, E.; Mutlu, G.M.; Budigner, G.S.; et al. Metformin inhibits mitochondrial complex I of cancer cells to reduce tumorigenesis. Elife 2014, 3, e02242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Hirsch, H.A.; Struhl, K. Metformin decreases the dose of chemotherapy for prolonging tumor remission in mouse xenografts involving multiple cancer cell types. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3196–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lily, M.; Godwin, M. Treating prediabetes with metformin: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. Fam. Physician 2009, 55, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maruthur, N.M.; Joy, S.M.; Dolan, J.G.; Shihab, H.M.; Singh, S. Use of the analytic hierarchy process for medication decision-making in type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyzyk, A.; Szczepanik, Z. Diabetes mellitus and cancer. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2000, 11, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Krishnaswamy, G.; Karnad, A.; Peiris, A.N. Insulin: A novel factor in carcinogenesis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2002, 323, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.J.; Lu, L.J.; Jin, L.B.; Li, H.Y.; Ren, G.S.; Wu, K.N.; Liu, S.C.; Kong, L.Q. Clinicopathologic features of breast cancer patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in southwest of china. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onitilo, A.A.; Stankowski, R.V.; Berg, R.L.; Engel, J.M.; Glurich, I.; Williams, G.M.; Doi, S.A. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, glycemic control, and cancer risk. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 23, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjartaker, A.; Langseth, H.; Weiderpass, E. Obesity and diabetes epidemics: Cancer repercussions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 630, 72–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stoll, B.A. Nutrition and breast cancer risk: Can an effect via insulin resistance be demonstrated? Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1996, 38, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, I.; Sadetzki, S.; Catane, R.; Karasik, A.; Kaufman, B. Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, I.; Sadetzki, S.; Gluck, I.; Oberman, B.; Ben-David, M.; Papa, M.Z.; Catane, R.; Kaufman, B. Association between diabetes mellitus and adverse characteristics of breast cancer at presentation. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draznin, B. Mechanism of the mitogenic influence of hyperinsulinemia. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2011, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, R.J. Lkb1 and AMP-activated protein kinase control of mtor signalling and growth. Acta Physiol. (Oxf) 2009, 196, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoncu, R.; Efeyan, A.; Sabatini, D.M. Mtor: From growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzai, M.; Jones, R.G.; Amaravadi, R.K.; Lum, J.J.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Zhao, F.; Viollet, B.; Thompson, C.B. Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6745–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wullschleger, S.; Shpiro, N.; McGuire, V.A.; Sakamoto, K.; Woods, Y.L.; McBurnie, W.; Fleming, S.; Alessi, D.R. Important role of the lkb1-AMPK pathway in suppressing tumorigenesis in PTEN-deficient mice. Biochem. J. 2008, 412, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Sahra, I.; Regazzetti, C.; Robert, G.; Laurent, K.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y.; Auberger, P.; Tanti, J.F.; Giorgetti-Peraldi, S.; Bost, F. Metformin, independent of AMPK, induces mTOR inhibition and cell-cycle arrest through REDD1. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4366–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.; Gigoni, A.; Wurth, R.; Cancedda, R.; Florio, T.; Pagano, A. Metformin inhibition of neuroblastoma cell proliferation is differently modulated by cell differentiation induced by retinoic acid or overexpression of NDM29 non-coding RNA. Cancer Cell Int. 2014, 14, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, M.; Ma, J.; Yang, C.; Han, L.; Nan, K.; Liang, X. Metformin inhibits growth of human non-small cell lung cancer cells via liver kinase B-1-independent activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2590–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollak, M.N. Investigating metformin for cancer prevention and treatment: The end of the beginning. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, B.J.; Kitagawa, H.; Memmott, R.M.; Gills, J.J.; Dennis, P.A. Repositioning metformin for cancer prevention and treatment. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griss, T.; Vincent, E.E.; Egnatchik, R.; Chen, J.; Ma, E.H.; Faubert, B.; Viollet, B.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Jones, R.G. Metformin antagonizes cancer cell proliferation by suppressing mitochondrial-dependent biosynthesis. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. Ppargamma: A nuclear regulator of metabolism, differentiation, and cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 37731–37734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotland, S.; Saland, E.; Skuli, N.; de Toni, F.; Boutzen, H.; Micklow, E.; Senegas, I.; Peyraud, R.; Peyriga, L.; Theodoro, F.; et al. Mitochondrial energetic and AKT status mediate metabolic effects and apoptosis of metformin in human leukemic cells. Leukemia 2013, 27, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, N.; Kollipara, R.K.; Singh, D.K.; Sudderth, J.; Hu, Z.; Nguyen, H.; Wang, S.; Humphries, C.G.; Carstens, R.; Huffman, K.E.; et al. Inhibition of cancer cell proliferation by PPARγ is mediated by a metabolic switch that increases reactive oxygen species levels. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babcook, M.A.; Sramkoski, R.M.; Fujioka, H.; Daneshgari, F.; Almasan, A. Combination simvastatin and metformin induces G1-phase cell cycle arrest and Ripk1- and Ripk3-dependent necrosis in C4–2B osseous metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, P.S.; Thompson, C.B. Metabolic reprogramming: A cancer hallmark even warburg did not anticipate. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boland, M.L.; Chourasia, A.H.; Macleod, K.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction in cancer. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verduzco, D.; Flaherty, K.T.; Smalley, K.S. Feeling energetic? New strategies to prevent metabolic reprogramming in melanoma. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 657–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimova, I.N.; Liu, B.; Fan, Z.; Edgerton, S.M.; Dillon, T.; Lind, S.E.; Thor, A.D. Metformin inhibits breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces cell cycle arrest in vitro. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.A.; Iliopoulos, D.; Tsichlis, P.N.; Struhl, K. Metformin selectively targets cancer stem cells, and acts together with chemotherapy to block tumor growth and prolong remission. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7507–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, S.; Pellat, L.; Ahmetaga, A.; Bano, G.; Mason, H.D.; Whitehead, S.A. Dual effect of metformin on growth inhibition and oestradiol production in breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.A.; Hunger, N.I.; Docanto, M.; Simpson, E.R. Metformin inhibits aromatase expression in human breast adipose stromal cells via stimulation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 123, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, F.; Petit, J.Y.; Kolonin, M.G. Stem cells from adipose tissue and breast cancer: Hype, risks and hope. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherbakov, A.M.; Sorokin, D.V.; Tatarskiy, V.V., Jr.; Prokhorov, N.S.; Semina, S.E.; Berstein, L.M.; Krasil’nikov, M.A. The phenomenon of acquired resistance to metformin in breast cancer cells: The interaction of growth pathways and estrogen receptor signaling. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lengyel, E.; Litchfield, L.M.; Mitra, A.K.; Nieman, K.M.; Mukherjee, A.; Zhang, Y.; Johnson, A.; Bradaric, M.; Lee, W.; Romero, I.L. Metformin inhibits ovarian cancer growth and increases sensitivity to paclitaxel in mouse models. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 212, 479.e1–479.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shank, J.J.; Yang, K.; Ghannam, J.; Cabrera, L.; Johnston, C.J.; Reynolds, R.K.; Buckanovich, R.J. Metformin targets ovarian cancer stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 127, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, P.; Wang, H.; Hou, D.; Li, W.; Xiao, G.; Li, C. Inhibitory effects of metformin at low concentration on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of CD44+ CD117+ ovarian cancer stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Ding, S.; Lu, J.; Zhang, H. Metformin inhibits 17β-estradiol-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via βKlotho-related ERK1/2 signaling and AMPKα signaling in endometrial adenocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 21315–21331. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, K.; Iwama, H.; Yamashita, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Fujihara, S.; Fujimori, T.; Kamada, H.; Kobara, H.; Masaki, T. The anti-diabetic drug metformin inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo: Study of the micrornas associated with the antitumor effect of metformin. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwei, D.; Liang, Z.; Zhimin, L.; Ruilei, L.; Yingying, Z.; Zhen, L.; Chunlei, G.; Zhangchao, L.; Yuanbo, X.; Jinyan, Y.; et al. NLK functions to maintain proliferation and stemness of nsclc and is a target of metformin. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Chuang, H.C.; Guo, C.S.; Lin, Y.T.; Luo, S.D.; Fang, F.M.; Chien, C.Y. Effect of routine esophageal screening in patients with head and neck cancer. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 139, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madera, D.; Vitale-Cross, L.; Martin, D.; Schneider, A.; Molinolo, A.A.; Gangane, N.; Carey, T.E.; McHugh, J.B.; Komarck, C.M.; Walline, H.M.; et al. Prevention of tumor growth driven by PIK3CA and HPV oncogenes by targeting mtor signaling with metformin in oral squamous carcinomas expressing OCT3. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2015, 8, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujihara, S.; Kato, K.; Morishita, A.; Iwama, H.; Nishioka, T.; Chiyo, T.; Nishiyama, N.; Miyoshi, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Kobara, H.; et al. Antidiabetic drug metformin inhibits esophageal adenocarcinoma cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, D.; Hu, S.; Xiang, M.; Xu, Z.; et al. Metformin inhibits the growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and sensitizes the cells to radiation via inhibition of the DNA damage repair pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2596–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Hu, X.; Tan, X.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Guan, Y.; Chen, C.; Jing, X. Metformin induced ampk activation, g0/g1 phase cell cycle arrest and the inhibition of growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinomas in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Feng, W.; Zhang, S.; Bian, K.; Yang, Y.; Fang, C.; Chen, M.; Yang, J.; Zou, X. Metformin inhibits gastric cancer via the inhibition of HIF1α/PKM2 signaling. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.W.; Li, Z.S.; Zou, D.W.; Jin, Z.D.; Gao, J.; Xu, G.M. Metformin induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 7192–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; He, F.; Kurago, Z.; Myssiorek, D.; Wu, Y.; Lee, P.; et al. Metformin inhibits salivary adenocarcinoma growth through cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 3600–3611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ben Sahra, I.; Laurent, K.; Giuliano, S.; Larbret, F.; Ponzio, G.; Gounon, P.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y.; Giorgetti-Peraldi, S.; Cormont, M.; Bertolotto, C.; et al. Targeting cancer cell metabolism: The combination of metformin and 2-deoxyglucose induces p53-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikas, A.; Jensen, K.; Patel, A.; Costello, J., Jr.; McDaniel, D.; Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, J.; Larin, O.; Hoperia, V.; Burman, K.D.; Boyle, L.; et al. Glucose-deprivation increases thyroid cancer cells sensitivity to metformin. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loubiere, C.; Goiran, T.; Laurent, K.; Djabari, Z.; Tanti, J.F.; Bost, F. Metformin-induced energy deficiency leads to the inhibition of lipogenesis in prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15652–15661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, S.; Ledda, B.; Tenca, C.; Ravera, S.; Orengo, A.M.; Mazzarello, A.N.; Pesenti, E.; Casciaro, S.; Racchi, O.; Ghiotto, F.; et al. Metformin inhibits cell cycle progression of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22624–22640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.H.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, C.K.; Jung, W.G.; Jeong, Y.K.; Jeong, J.H. Low and high linear energy transfer radiation sensitization of HCC cells by metformin. J. Radiat. Res. 2014, 55, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrini, I.; Conti, A.; Pazzaglia, L.; Novello, C.; Ferrari, S.; Picci, P.; Benassi, M.S. Metformin inhibits growth and sensitizes osteosarcoma cell lines to cisplatin through cell cycle modulation. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, Q.; Xia, P.; Qi, M.; Yang, M.; Han, B. Metformin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells: Involvement of the tumor suppressor MIR30A and its target gene SOX4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 452, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Sekine, Y.; Furuya, Y.; Miyazawa, Y.; Koike, H.; Suzuki, K. Metformin inhibits the proliferation of human prostate cancer pc-3 cells via the downregulation of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 461, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Cui, H.; Kang, L.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Z.; Lu, L.; Fan, Z. Metformin inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth, migration, and emt through the mtor pathway. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 6295–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, F.; Yu, P. Metformin inhibits the proliferation, metastasis, and cancer stem-like sphere formation in osteosarcoma mg63 cells in vitro. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 9873–9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Ding, M.; Lu, H.; Cao, N.A.; Niu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Lu, J. Metformin upregulates e-cadherin and inhibits b16f10 cell motility, invasion and migration. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Davis, M.; Blackwelder, A.J.; Bachman, N.; Liu, B.; Edgerton, S.; Williams, L.L.; Thor, A.D.; Yang, X. Metformin selectively targets tumor-initiating cells in ERBB2-overexpressing breast cancer models. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2014, 7, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cufi, S.; Corominas-Faja, B.; Vazquez-Martin, A.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Dorca, J.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Menendez, J.A. Metformin-induced preferential killing of breast cancer initiating CD44+CD24−/low cells is sufficient to overcome primary resistance to trastuzumab in HER2+ human breast cancer xenografts. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimov, V.N.; Egormin, P.A.; Piskunova, T.S.; Popovich, I.G.; Tyndyk, M.L.; Yurova, M.N.; Zabezhinski, M.A.; Anikin, I.V.; Karkach, A.S.; Romanyukha, A.A. Metformin extends life span of HER-2/neu transgenic mice and in combination with melatonin inhibits growth of transplantable tumors in vivo. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Li, L.; Fan, C.; Sun, Y. Combined use of metformin and everolimus is synergistic in the treatment of breast cancer cells. Oncol. Res. 2015, 22, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesen, J.; Dahan, P.; Scotland, S.J.; Saland, E.; Dang, V.T.; Lemarie, A.; Tyler, B.M.; Brem, H.; Toulas, C.; Cohen-Jonathan Moyal, E.; et al. Metformin inhibits growth of human glioblastoma cells and enhances therapeutic response. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honjo, S.; Ajani, J.A.; Scott, A.W.; Chen, Q.; Skinner, H.D.; Stroehlein, J.; Johnson, R.L.; Song, S. Metformin sensitizes chemotherapy by targeting cancer stem cells and the mTOR pathway in esophageal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisfalvi, K.; Eibl, G.; Sinnett-Smith, J.; Rozengurt, E. Metformin disrupts crosstalk between G protein-coupled receptor and insulin receptor signaling systems and inhibits pancreatic cancer growth. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6539–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, K.; Endo, H.; Takahashi, H.; Sugiyama, M.; Uchiyama, T.; Suzuki, K.; Nozaki, Y.; Yoneda, K.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; et al. Metformin suppresses azoxymethane-induced colorectal aberrant crypt foci by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Mol. Carcinog. 2010, 49, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, R.; Li, L.; Xiang, T.; He, L.; Long, H.; Zhu, B.; He, Y. Metformin inhibits the IL-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lung adenocarcinoma growth and metastasis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, C.; Capristo, M.; Manara, M.C.; Mancarella, C.; Landuzzi, L.; Belfiore, A.; Lollini, P.L.; Picci, P.; Scotlandi, K. Metformin as an adjuvant drug against pediatric sarcomas: Hypoxia limits therapeutic effects of the drug. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Settleman, J. Emt, cancer stem cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4741–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Cao, M.; You, A.; Gao, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Fang, F.; Zhang, W.; Song, T.; et al. Metformin inhibits the pro-metastatic effect of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma by upregulating the expression of tip30. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, I.; Yamazaki, K.; Oyama, K.; Hayashi, H.; Tajima, H.; Kitagawa, H.; Fushida, S.; Fujimura, T.; Ohta, T. Pioglitazone inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of human pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 2709–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.H.; Huang, B.; Wang, R.Y.; Yuan, S.X.; Tao, Q.F.; Xu, Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Lin, C.; Zhou, W.P. Pioglitazone, a PPARγ agonist, inhibits growth and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma via blockade of the rage signaling. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalit, O.; Wang, D.; Dubois, R.N. PPARγ agonists target aromatase via both PGE2 and BRCA1. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2012, 5, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadarajan, K.; Balaram, P.; Khoo, B.Y. Mk886 inhibits the pioglitazone-induced anti-invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells is associated with PPARα/γ, FGF4 and 5LOX. Cytotechnology 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehrer, J.P.; Biswal, S.S.; La, E.; Thuillier, P.; Datta, K.; Fischer, S.M.; Vanden Heuvel, J.P. Inhibition of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)α by MK886. Biochem. J. 2001, 356, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Shi, W.; Shao, B.; Shi, J.; Shen, A.; Ma, Y.; Chen, J.; Lan, Q. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ agonist pioglitazone inhibits β-catenin-mediated glioma cell growth and invasion. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 349, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiki, M.; Hatta, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Itoh, T.; Enomoto, Y.; Takeuchi, J.; Sawada, U.; Aizawa, S.; Horie, T. Pioglitazone inhibits the growth of human leukemia cell lines and primary leukemia cells while sparing normal hematopoietic stem cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2006, 29, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annicotte, J.S.; Iankova, I.; Miard, S.; Fritz, V.; Sarruf, D.; Abella, A.; Berthe, M.L.; Noel, D.; Pillon, A.; Iborra, F.; et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma regulates e-cadherin expression and inhibits growth and invasion of prostate cancer. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 7561–7574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borbath, I.; Leclercq, I.; Moulin, P.; Sempoux, C.; Horsmans, Y. The PPARγ agonist pioglitazone inhibits early neoplastic occurrence in the rat liver. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshamouni, V.G.; Arenberg, D.A.; Reddy, R.C.; Newstead, M.J.; Anthwal, S.; Standiford, T.J. PPAR-γ activation inhibits angiogenesis by blocking ELR+CXC chemokine production in non-small cell lung cancer. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, T.; Teraoka, N.; Takasu, S.; Nakano, K.; Takahashi, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Fujii, G.; Komiya, M.; Yanaka, A.; Wakabayashi, K.; et al. Suppressive effect of pioglitazone, a PPAR γ ligand, on azoxymethane-induced colon aberrant crypt foci in KK-AY mice. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 4067–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, S.; Kubota, T.; Nishibori, H.; Hasegawa, H.; Ishii, Y.; Nitori, N.; Ochiai, H.; Okabayashi, K.; Kitagawa, Y.; Watanabe, M.; et al. Pioglitazone, a ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma acts as an inhibitor of colon cancer liver metastasis. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, P.J.; Ligibel, J.A.; Stambolic, V. Metformin in breast cancer: Time for action. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3271–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.L.; Stanford, J.L. Metformin use and prostate cancer in caucasian men: Results from a population-based case-control study. Cancer Causes Control. 2009, 20, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, G.; Donnelly, L.A.; Donnan, P.T.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D.; Evans, J.M. New users of metformin are at low risk of incident cancer: A cohort study among people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Diaz, S.; Adami, H.O. Diabetes therapy and cancer risk: Causal effects and other plausible explanations. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodmer, M.; Meier, C.; Krahenbuhl, S.; Jick, S.S.; Meier, C.R. Long-term metformin use is associated with decreased risk of breast cancer. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1304–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadon, V.; Balbi, M.; Mas, M.D.; Casarin, P.; Zanette, G. Metformin and reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in diabetic patients with chronic liver disease. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodmer, M.; Becker, C.; Meier, C.; Jick, S.S.; Meier, C.R. Use of metformin and the risk of ovarian cancer: A case-control analysis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 123, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monami, M.; Colombi, C.; Balzi, D.; Dicembrini, I.; Giannini, S.; Melani, C.; Vitale, V.; Romano, D.; Barchielli, A.; Marchionni, N.; et al. Metformin and cancer occurrence in insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraldine, N.; Marc, A.; Carla, T.; Chantal, M.; Stefaan, B.; Welcome, W.; Frank, B. Relation between diabetes, metformin treatment and the occurrence of malignancies in a Belgian primary care setting. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 97, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landman, G.W.; Kleefstra, N.; van Hateren, K.J.; Groenier, K.H.; Gans, R.O.; Bilo, H.J. Metformin associated with lower cancer mortality in type 2 diabetes: Zodiac-16. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, S.; Benso, A.; Durazzo, M.; Ghigo, E. Does use of metformin protect against cancer in type 2 diabetes mellitus? J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2012, 35, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, S.; Ciccone, G.; Rosato, R.; Villois, P.; Appendino, G.; Ghigo, E.; Grassi, G. Cancer mortality reduction and metformin: A retrospective cohort study in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vissers, P.A.; Cardwell, C.R.; van de Poll-Franse, L.V.; Young, I.S.; Pouwer, F.; Murray, L.J. The association between glucose-lowering drug use and mortality among breast cancer patients with type 2 diabetes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 150, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, K.; Endo, H.; Takahashi, H.; Sugiyama, M.; Sakai, E.; Uchiyama, T.; Suzuki, K.; Iida, H.; Sakamoto, Y.; Yoneda, K.; et al. Metformin suppresses colorectal aberrant crypt foci in a short-term clinical trial. Cancer Prev Res. (Phila) 2010, 3, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, J.L.; Antonsen, S.; Sorensen, H.T.; Pedersen, L.; Lash, T.L. Metformin and incident breast cancer among diabetic women: A population-based case-control study in denmark. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.X.; Tu, S.M.; Lee, M.H.; Yeung, S.C. Thiazolidinediones and metformin associated with improved survival of diabetic prostate cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 2640–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiter, R.; Visser, L.E.; van Herk-Sukel, M.P.; Coebergh, J.W.; Haak, H.R.; Geelhoed-Duijvestijn, P.H.; Straus, S.M.; Herings, R.M.; Stricker, B.H. Lower risk of cancer in patients on metformin in comparison with those on sulfonylurea derivatives: Results from a large population-based follow-up study. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, C.J.; Poole, C.D.; Jenkins-Jones, S.; Gale, E.A.; Johnson, J.A.; Morgan, C.L. Mortality after incident cancer in people with and without type 2 diabetes: Impact of metformin on survival. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Esteva, F.J.; Ensor, J.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Lee, M.H.; Yeung, S.C. Metformin and thiazolidinediones are associated with improved breast cancer-specific survival of diabetic women with HER2+ breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Benhawy, S.A.; El-Sheredy, H.G. Metformin and survival in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J. Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2014, 89, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktar, S.; Hernadez-Aya, L.F.; Lei, X.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Litton, J.K.; Hsu, L.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M. Effect of metformin on survival outcomes in diabetic patients with triple receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer 2012, 118, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiralerspong, S.; Palla, S.L.; Giordano, S.H.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Liedtke, C.; Barnett, C.M.; Hsu, L.; Hung, M.C.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M. Metformin and pathologic complete responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3297–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppong, B.A.; Pharmer, L.A.; Oskar, S.; Eaton, A.; Stempel, M.; Patil, S.; King, T.A. The effect of metformin on breast cancer outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cancer Med. 2014, 3, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuhashi, A.; Kiyokawa, T.; Sato, Y.; Shozu, M. Effects of metformin on endometrial cancer cell growth in vivo: A preoperative prospective trial. Cancer 2014, 120, 2986–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, M.J.; Ernst, S.; Johnson, C.; Winquist, E. A phase I study of temsirolimus and metformin in advanced solid tumours. Invest. New Drugs 2012, 30, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordes, S.; Pollak, M.N.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Mathot, R.A.; Weterman, M.J.; Beeker, A.; Punt, C.J.; Richel, D.J.; Wilmink, J.W. Metformin in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatoum, D.; McGowan, E.M. Recent advances in the use of metformin: Can treating diabetes prevent breast cancer? Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 548436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasznicki, J.; Sliwinska, A.; Drzewoski, J. Metformin in cancer prevention and therapy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reichle, A.; Bross, K.; Vogt, T.; Bataille, F.; Wild, P.; Berand, A.; Krause, S.W.; Andreesen, R. Pioglitazone and rofecoxib combined with angiostatically scheduled trofosfamide in the treatment of far-advanced melanoma and soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer 2004, 101, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, T.; Hafner, C.; Bross, K.; Bataille, F.; Jauch, K.W.; Berand, A.; Landthaler, M.; Andreesen, R.; Reichle, A. Antiangiogenetic therapy with pioglitazone, rofecoxib, and metronomic trofosfamide in patients with advanced malignant vascular tumors. Cancer 2003, 98, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.M.; Song, S.O.; Jung, C.H.; Chang, J.S.; Suh, S.; Kang, S.M.; Jung, I.; Park, C.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.H.; et al. Risk of bladder cancer among patients with diabetes treated with a 15 mg pioglitazone dose in korea: A multi-center retrospective cohort study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azoulay, L.; Yin, H.; Filion, K.B.; Assayag, J.; Majdan, A.; Pollak, M.N.; Suissa, S. The use of pioglitazone and the risk of bladder cancer in people with type 2 diabetes: Nested case-control study. BMJ 2012, 344, e3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Shen, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhong, S.; Xu, C. Increased risk of bladder cancer with pioglitazone therapy in patients with diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 98, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.D.; Habel, L.A.; Quesenberry, C.P.; Strom, B.L.; Peng, T.; Hedderson, M.M.; Ehrlich, S.F.; Mamtani, R.; Bilker, W.; Vaughn, D.J.; et al. Pioglitazone use and risk of bladder cancer and other common cancers in persons with diabetes. Jama 2015, 314, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monami, M.; Dicembrini, I.; Mannucci, E. Thiazolidinediones and cancer: Results of a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.D.; Ferrara, A.; Peng, T.; Hedderson, M.; Bilker, W.B.; Quesenberry, C.P., Jr.; Vaughn, D.J.; Nessel, L.; Selby, J.; Strom, B.L. Risk of bladder cancer among diabetic patients treated with pioglitazone: Interim report of a longitudinal cohort study. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krentz, A.J.; Ferner, R.E.; Bailey, C.J. Comparative tolerability profiles of oral antidiabetic agents. Drug Saf. 1994, 11, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schraml, E.; Grillari, J. From cellular senescence to age-associated diseases: The mirna connection. Longev. Healthspan 2012, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Espin, D.; Serrano, M. Cellular senescence: From physiology to pathology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, E.L.; Michalek, R.D.; Pitiyage, G.N.; de Castro, A.M.; Vignola, K.S.; Jones, J.; Mohney, R.P.; Karoly, E.D.; Prime, S.S.; Parkinson, E.K. Senescent human fibroblasts show increased glycolysis and redox homeostasis with extracellular metabolomes that overlap with those of irreparable DNA damage, aging, and disease. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1854–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sorenson, A.L.; Poczobutt, J.; Amin, J.; Joyal, T.; Sullivan, T.; Crossno, J.T., Jr.; Weiser-Evans, M.C.; Nemenoff, R.A. Activation of ppargamma in myeloid cells promotes lung cancer progression and metastasis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28133. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Bonifati, S.; Hristov, G.; Marttila, T.; Valmary-Degano, S.; Stanzel, S.; Schnolzer, M.; Mougin, C.; Aprahamian, M.; Grekova, S.P.; et al. Synergistic combination of valproic acid and oncolytic parvovirus H-1PV as a potential therapy against cervical and pancreatic carcinomas. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1537–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.C.; Johnstone, R.W. New and emerging HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, J.J.; Kenyani, J.; Butt, Z.; Carter, R.; Chew, H.Y.; Cheeseman, L.P.; Darling, S.; Denny, M.; Urbe, S.; Clague, M.J.; et al. Loss of the deubiquitylase Bap1 alters class I histone deacetylase expression and sensitivity of mesothelioma cells to hdac inhibitors. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13757–13771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursini-Siegel, J.; Schade, B.; Cardiff, R.D.; Muller, W.J. Insights from transgenic mouse models of ERBB2-induced breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, P.; Frazier, D.P.; Kendig, R.D.; Maglic, D.; Sugiyama, T.; Kai, F.; Taneja, N.K.; Inoue, K. MMTV mouse models and the diagnostic values of MMTV-like sequences in human breast cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2009, 9, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetrius, L. Of mice and men. When it comes to studying ageing and the means to slow it down, mice are not just small humans. EMBO Rep. 2005, 6, S39–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himms-Hagen, J. Physiological roles of the leptin endocrine system: Differences between mice and humans. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1999, 36, 575–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneeberger, M.; Claret, M. Recent insights into the role of hypothalamic AMPK signaling cascade upon metabolic control. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrero, A.; Cubero, M.; Llaverias, G.; Alegret, M.; Sanchez, R.; Laguna, J.C.; Vazquez-Carrera, M. Leptin down-regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPAR-γ) MRNA levels in primary human monocyte-derived macrophages. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 275, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shao, Y.Y.; Ballock, R.T. Leptin antagonizes peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ signaling in growth plate chondrocytes. PPAR Res. 2012, 2012, 756198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Setting | Anti-diabetic Intervention | Other Intervention | Phase | Status | ClinicalTrials. Gov Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metastatic or unresectable solid tumor or lymphoma | Metformin | Temsirolimus | I | Completed § | NCT00659568 |
| Li Fraumeni Syndrome | Metformin | - | I | Recruiting | NCT01981525 |
| Advanced cancers | Metformin | Temsirolimus | I | Recruiting | NCT01529593 |
| Hormone-resistant prostate cancer | Metformin | Enzalutamide/Laboratory biomarker analysis | I | Not yet recruiting | NCT02339168 |
| Locally advanced or metastatic prostate cancer | Metformin | - | II | Active, not recruiting | NCT01243385 |
| Breast cancer prevention in obese /overweight premenopausal women with metabolic syndrome | Metformin | Placebo | II | Recruiting | NCT02028221 |
| Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | Metformin | Placebo/Stereotactic body Radiotherapy (SBRT) | II | Recruiting | NCT02285855 |
| Colorectal and breast cancer | Metformin | Exercise training/Exercise training plus metformin | II | Active, not recruiting | NCT01340300 |
| Bladder cancer | Metformin | Simvastatin | II | Not yet recruiting | NCT02360618 |
| Advanced stage ovarian, fallopian tube and primary peritoneal cancer | Metformin | Combination chemotherapy/Laboratory biomarker analysis | II | Recruiting | NCT02122185 |
| Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin plus chemo-radiotherapy | Chemo-radiotherapy | II | Recruiting | NCT02115464 |
| Metastatic pancreatic cancer | Metformin | Modified FOLFOX 6/ Laboratory biomarker analysis | II | Recruiting | NCT01666730 |
| Hormone-dependent prostate cancer | Metformin | Aspirin/Placebo/ Laboratory biomarker analysis | II | Recruiting | NCT02420652 |
| Metastatic breast cancer | Metformin | Placebo | II | Recruiting | NCT01310231 |
| Castration resistant prostate cancer | Metformin | Enzalutamide | II | Not yet recruiting | NCT02640534 |
| Hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women | Metformin | Everolimus/Exemestane | II | Active, not recruiting | NCT01627067 |
| Locally advanced rectal cancer | Metformin | - | II | Recruiting | NCT02437656 |
| Breast cancer prevention | Metformin | Placebo | II | Recruiting | NCT02028221 |
| Prostate cancer | Metformin plus bicalutamide | Bicalutamide | II | Recruiting | NCT02614859 |
| Prostate cancer, Prostate cancer recurrent | Metformin | - | II | Recruiting | NCT02176161 |
| Ovarian, Fallopian tube, and Primary peritoneal cancer | Metformin | - | II | Recruiting | NCT01579812 |
| Refractory colorectal cancer | Metformin | Irinotecan | II | Not yet recruiting | NCT01930864 |
| Early stage breast cancer | Metformin | Placebo | III | Active, not recruiting | NCT01101438 |
| Prostate cancer | Metformin | Placebo | III | Recruiting | NCT01864096 |
| Advanced solid tumors | Pioglitazone | Carboplatin | I | Active, not recruiting | NCT02133625 |
| PAX8-PPARγ fusion gene-positive thyroid cancer | Pioglitazone | - | II | Recruiting | NCT01655719 |
| Pancreatic cancer | Pioglitazone | - | II | Recruiting | NCT01838317 |
| Oral leukoplakia | Pioglitazone | Placebo/Laboratory biomarker analysis | II | Completed§ | NCT00951379 |
| Lung cancer chemoprevention | Pioglitazone | Placebo/fluorescence bronchoscopy/quantitative high resolution computerized tomography (CT) scan | II | Active, not recruiting | NCT00780234 |
| Squamous cell cancer chemoprevention | Pioglitazone | - | II | Enrolling by invitation | NCT02347813 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papanagnou, P.; Stivarou, T.; Tsironi, M. Unexploited Antineoplastic Effects of Commercially Available Anti-Diabetic Drugs. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9020024
Papanagnou P, Stivarou T, Tsironi M. Unexploited Antineoplastic Effects of Commercially Available Anti-Diabetic Drugs. Pharmaceuticals. 2016; 9(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9020024
Chicago/Turabian StylePapanagnou, Panagiota, Theodora Stivarou, and Maria Tsironi. 2016. "Unexploited Antineoplastic Effects of Commercially Available Anti-Diabetic Drugs" Pharmaceuticals 9, no. 2: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9020024
APA StylePapanagnou, P., Stivarou, T., & Tsironi, M. (2016). Unexploited Antineoplastic Effects of Commercially Available Anti-Diabetic Drugs. Pharmaceuticals, 9(2), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9020024






