Role of Diuretics and Ultrafiltration in Congestive Heart Failure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
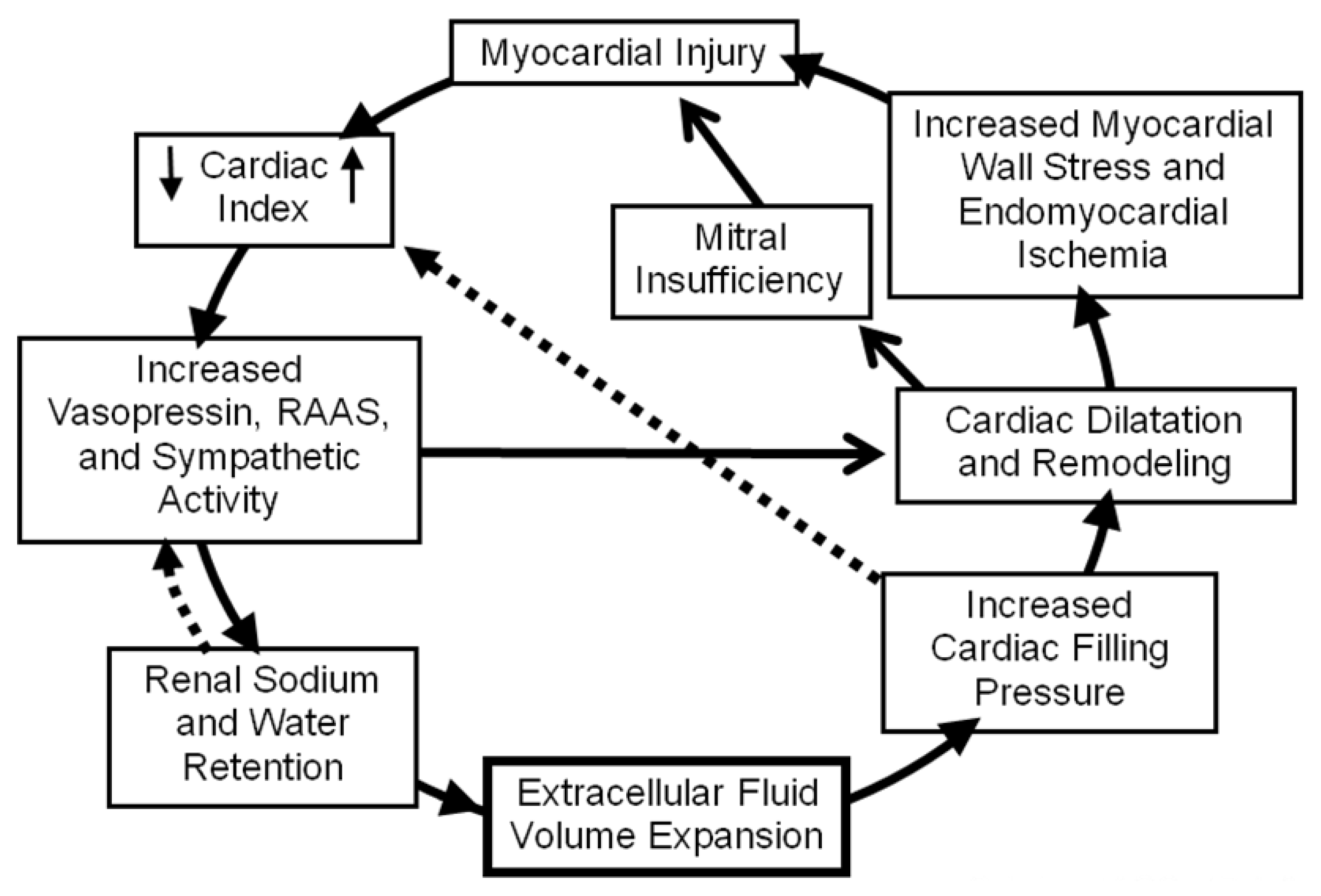
2. Pathophysiology of Sodium and Water Retention in Heart Failure
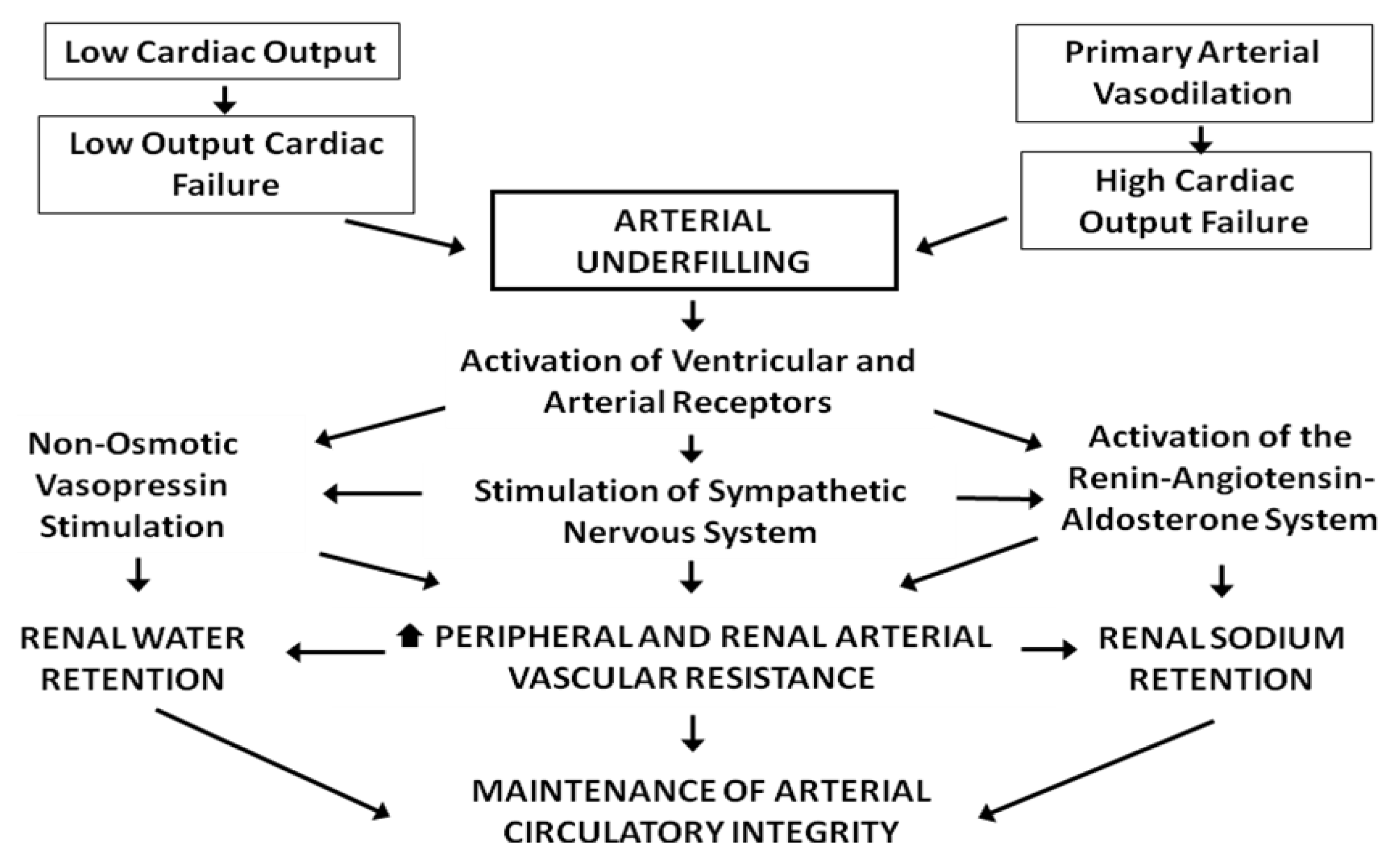
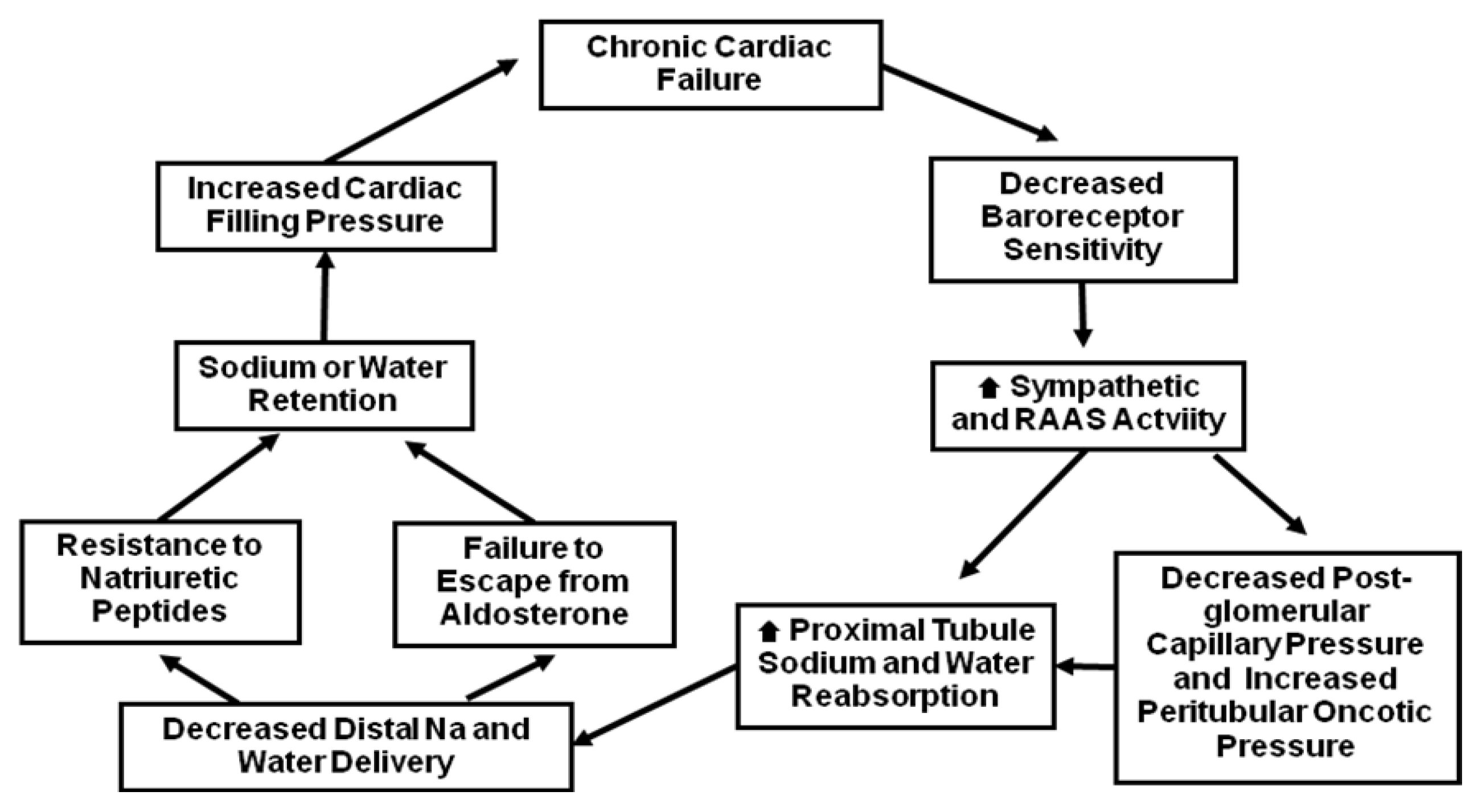
3. Use of Loop Diuretics to Treat HF
| Furosemide | Bumetamide | Torsemide | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relative IV patency (mg) | 40 | 1 | 20 |
| Bioavailability (%) | 10-100 (50) | 80-100 | 80-100 |
| Average effect duration (h) | 6–8 | 4–6 | 6–8 |
| Oral to IV conversion | 2:1 | 1:1 | 1:1 |
| 30 day cost ($) | 4 | 4 | 19–23 |
4. Use of Thiazide Diuretics to Treat HF
5. Use of Acetazolamide to Treat HF
6. Use of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) to treat HF
7. Use of V2-Vasopressin Receptor Blockers (Vaptans) To Treat HF
8. Consequences of Diuretic Treatment
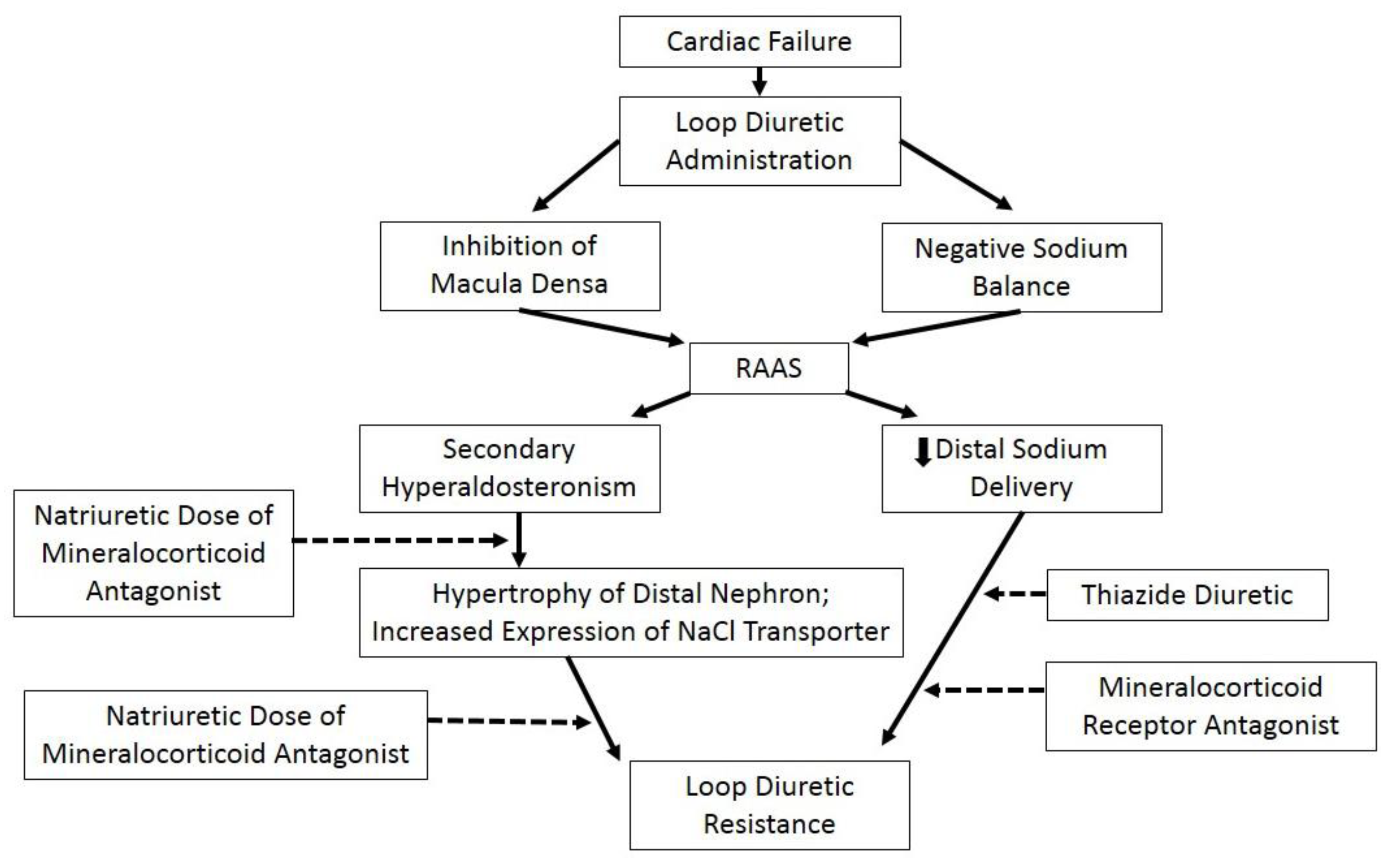
9. Diuretic Resistance
10. Ultrafiltration
11. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest
References
- Lloyd-Jones, D.; Adams, R.J.; Brown, T.M.; Carnethon, M.; Dai, S.; De Simone, G.; Ferguson, T.B,; Ford, E.; Furie, K.; Gillespie, C.; Go, A.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2009 update: A report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 2009, 119, 480–486. [Google Scholar]
- Jencks, S.F.; Williams, M.V.; Coleman, E.A. Rehospitalizations among patients in the Medicare fee-for-service program. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1418–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.A.; Abraham, W.T.; Chin, M.H.; Feldman, A.M.; Francis, G.S.; Ganiats, T.G.; Jessup, M.; Konstam, M.A.; Mancini, D.M.; Michl, K.; et al. 2009 focused update incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2005 guidelines for the diagnosis and management of heart failure in adults: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, e1–e90. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, K.F., Jr; Fonarow, G.C.; Emerman, C.L.; LeJemtel, T.H.; Costanzo, M.R.; Abraham, W.T.; Berkowitz, R.L.; Galvao, M.; Horton, D.P.; ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee and Investigators. Characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized for heart failure in the United States: Rationale, design, and preliminary observations from the first 100,000 cases in the Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry (ADHERE). Am. Heart J. 2005, 149, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghiade, M.; Filippatos, G.L.; Burnett, J. Congestion in acute heart failure syndromes: An essential target of evaluation and treatment. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zile, M.R.; Bennett, T.D.; St John Sutton, M.; Cho, Y.K.; Adamson, P.B.; Aaron, M.F.; Aranda, J.M., Jr; Abraham, W.T.; Smart, F.W.; Stevenson, L.W.; et al. Transition from chronic compensated to acute decompensated heart failure: Pathophysiological insights obtained from continuous monitoring of intracardiac pressures. Circulation 2008, 118, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Gaasch, W.H.; Zile, M.R. Left ventricular structural remodeling in health and disease: With special emphasis on volume, mass, and geometry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, R.W. Role of diminished renal function in cardiovascular mortality: Marker or pathogenetic factor? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, R.J.; Kappagoda, C.T. Atrial receptors and renal blood flow. In Atrial Receptors; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Packer, M. Neurohormone interaction and adaptations in congestive HF. Circulation 1988, 77, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarraf, M.; Masoumi, A.; Schrier, R.W. CRS in Acute Decompensated HF. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 2013–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, R.W. Body fluid volume regulation in health and disease: A unifying hypothesis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1990, 113, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, R.W.; Abraham, W.T. Hormones and hemodynamics in HF. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankstein, R.; Bakris, G.L. Renal hemodynamic changes in HF. Heart. Fail. Clin. 2008, 4, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K. Mechanisms of disease: Aldosterone in chronic HF. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, J.N.; Levine, T.V.; Olivari, M.T.; Garberg, V.; Lura, D.; Francis, G.S.; Simon, A.B.; Rector, T. Plasma norepinephrine as a guide to prognosis in patients with chronic congestive HF. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 311, 819–823. [Google Scholar]
- Schrier, R.W.; Berl, T.; Anderson, R.J. Osmotic and nonosmotic control of vasopressin release. Am. J. Physiol. 1979, 236, F321–F332. [Google Scholar]
- Brater, D.C. Update in diuretic therapy: Clinical pharmacology. Semin. Nephrol. 2011, 31, 483–494. [Google Scholar]
- Chennavasin, P.; Seiwell, R.; Brater, D.C.; Liang, W.M.M. Pharmacodynamic analysis of the furosemide-probenecid interaction in man. Kidney Int. 1979, 6, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Odlind, B.; Beerman, B. Renal tubular secretion and effects of furosemide. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1980, 27, 784–790. [Google Scholar]
- Brater, D.C. Diuretic pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. In The in vivo Study of Drug Action (Principles and Applications of Kinetic-Dynamic Modelling); van Boxtel, C.J., Holford, N.H.G., Danhof, M., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, M.D.; Haag, K.M.; Black, P.K.; Hall, S.D.; Brater, D.C. Variable furosemide absorption and poor predictability of response in elderly patients. Pharmacotherapy 1997, 17, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, C.S.; Mitch, W.E.; Kelly, R.A.; Skorecki, K.; Meyer, T.W.; Friedman, P.A.; Souney, P.F. Response of the kidney to furosemide (I. Effects of salt intake and renal compensation). J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1983, 102, 450–458. [Google Scholar]
- Salvador, D.R.; Rey, N.R.; Ramos, G.C.; Punzalan, F.E. Continuous infusion versus bolus injection of loop diuretics in congestive heart failure. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005, 20, CD003178. [Google Scholar]
- Felker, G.M.; Lee, K.L.; Bull, D.A.; Redfield, M.M.; Stevenson, L.W.; Goldsmith, S.R.; LeWinter, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Rouleau, J.L.; Ofili, E.O.; et al. Diuretic strategies in patients with acute decompensated HF. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 797–805. [Google Scholar]
- Heart Failure Society of America; Lindenfeld, J.; Albert, N.M.; Boehmer, J.P.; Collins, S.P.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Givertz, M.M.; Katz, S.D.; Klapholz, M.; Moser, D.K.; et al. Executive summary: HFSA 2010 comprehensive HF practice guidelines. J. Card Fail. 2010, 16, 475–539. [Google Scholar]
- Jentzer, J.C.; DeWald, T.A.; Hernandez, A.F. Combination of loop diuretics with thiazide-type diuretics in heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.H. Long-term adaptation of renal ion transporters to chronic diuretic treatment. Am. J. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 595–605. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, D.H. The physiologic basis of diuretic synergism: Its role in treating diuretic resistance. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991, 114, 886–894. [Google Scholar]
- Sica, D.A.; Gehr, T.W. Diuretic combinations in refractory oedema states: Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1996, 30, 229–249. [Google Scholar]
- Sica, D.A. Metolazone and its role in edema management. Congest. Heart Fail. 2003, 9, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Channer, K.S.; McLean, K.A.; Lawson-Matthews, P.; Richardson, M. Combination diuretic treatment in severe heart failure: A randomized controlled trial. Br. Heart J. 1994, 71, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Asscher, A.W. Treatment of frusemide resistant edema with metolazone. Clin. Trials J. 1974, 4, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.I. Treatment of refractory congestive heart failure and normokalemic hypochloremic alkalosis with acetazolamide and spironolactone. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1980, 123, 883–887. [Google Scholar]
- Javaheri, S. Acetazolamide improves central sleep apnea in heart failure: A double-blind, prospective study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 234–237. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, B.; Zannad, F.; Remme, W.J.; Cody, R.; Castaigne, A.; Perez, A.; Palensky, J.; Wittes, J. For the Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 709–717. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, B.; Remme, W.; Zannad, F.; Neaton, J.; Martinez, F.; Roniker, B.; Bittman, R.; Hurley, S.; Kleiman, J.; Gatlin, M. Eplerenone Post-Acute Myocardial Infarction Heart Failure Efficacy and Survival Study Investigators. Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Zannad, F.; McMurray, J.J.; Krum, H.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Swedberg, K.; Shi, H.; Vincent, J.; Pocock, S.J.; Pitt, B. EMPHASIS-HF Study Group Eplerenone in patients with systolic heart failure and mild symptoms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- The RALES Investigators. Effectiveness of spironolactone added to an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and a loop diuretic for severe chronic congestive heart failure (The Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study [RALES]). Am. J. Cardiol. 1996, 78, 902–907.
- Juurlink, D.; Mamdani, M.; Lee, D.S.; Kopp, A.; Austin, P.C.; Laupacis, A; Redelmeier, D.A. Rates of hyperkalemia after publication of the Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 543–551. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Struthers, A.D.; Fahey, T.; Watson, A.D.; MacDonald, T.M. Spironolactone use and renal toxicity: Population based longitudinal analysis. BMJ 2010, 340, c1768. [Google Scholar]
- Shchekochikhin, D.; Lindenfeld, J.; Schrier, R.W. Increased Spironolactone in Advanced HF: Effect of Doses Greater Than 25 mg/day on Plasma Potassium Concentration. Cardiorenal. Med. 2013, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Udelson, J.E.; Smith, W.B.; Hendrix, G.H.; Painchaud, C.A.; Ghazzi, M.; Thomas, I.; Ghali, J.K.; Selaru, P.; Chanoine, F.; Pressler, M.L.; Konstam, M.A. Acute hemodynamic effects of conivaptan, a dual V(1A) and V(2) vasopressin receptor antagonist, in patients with advanced heart failure. Circulation 2001, 104, 2417–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, R.W.; Gross, P.; Gheorghiade, M.; Berl, T.; Verbalis, J.G.; Czerwiec, F.S.; Orlandi, C. For the SALT Investigators: Tolvaptan, a selective oral vasopressin V2-receptor antagonist, for hyponatremia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghiade, M.; Niazi, I.; Ouyang, J.; Czerwiec, F.; Kambayashi, J.; Zampino, M.; Orlandi, C.; Tolvaptan Investigators. Vasopressin V2-receptor blockade with tolvaptan in patients with chronic heart failure: Results from a double-blind, randomized trial. Circulation 2003, 107, 2690–2696. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghiade, M.; Gattis, W.A.; O’Connor, C.M.; Adams, K.F., Jr.; Elkayam, U.; Barbagelata, A.; Ghali, J.K.; Benza, R.L.; McGrew, F.A.; Klapholz, M.; et al. Acute and chronic therapeutic impact of a vasopressin antagonist in congestive heart failue (ACTIV in CHF) Investigators. Effects of tolvaptan, a vasopressin antagonist, in patients hospitalized with worsening heart failure: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2004, 291, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar]
- Udelson, J.E.; McGrew, F.A.; Flores, E.; Ibrahim, H.; Katz, S.; Koshkarian, G.; O'Brien, T.; Kronenberg, M.W.; Zimmer, C.; Orlandi, C.; Konstam, M.A. Multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study on the effect of oral tolvaptan on left ventricular dilation and function in patients with heart failure and systolic dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar]
- Udelson, J.E.; Orlandi, C; Ouyang, J.; Krasa, H.; Zimmer, C.A.; Frivold, G.; Haught, W.H.; Meymandi, S.; Macarie, C.; Raef, D.; et al. Acute hemodynamic effects of tolvaptan, a vasopressin V2 receptor blocker, in patients with symptomatic heart failure and systolic dysfunction: An international, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1540–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Konstam, M.A.; Gheorghiade, M.; Burnett, J.C., Jr.; Grinfeld, L.; Maggioni, A.P.; Swedberg, K.; Udelson, J.E.; Zannad, F.; Cook, T.; Ouyang, J.; et al. Efficacy of Vasopressin Antagonism in Heart Failure Outcome Study With Tolvaptan (EVEREST) Investigators. Effects of oral tolvaptan in patients hospitalized for worsening heart failure: The EVEREST Outcome Trial. JAMA 2007, 297, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Schrier, R.W. Use of diuretics in heart failure and cirrhosis. Semin. Nephrol. 2011, 31, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.H. Diuretic therapy and resistance in congestive heart failure. Cardiology 2001, 96, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quamme, G.A. Effect of furosemide on calcium and magnesium transport in the rat nephron. Am. J. Physiol. 1981, 241, F340–F347. [Google Scholar]
- Publication Committee for the VMAC Investigators (Vasodilatation in the Management of Acute CHF). Intravenous nesiritide vs. nitroglycerin for treatment of decompensated congestiveheart failure: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2002, 287, 1531–1540.
- Bansal, S.; Lindenfeld, J.A.; Schrier, R.W. Sodium retention in heart failure and cirrhosis: Potential role of natriuretic doses of mineralocorticoid antagonist? Circ. Heart Fail. 2009, 2, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauf, H.; Mutschler, E. Sequential Nephron Blockade Breaks Resistance to Diuretics in Edematous States. J. Cardiovasc. Pharm. 1997, 29, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brater, D.C. Diuretic Resistance: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Cardiology 1994, 84 (suppl. 2), 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, K.A. Mechanisms of diuretic resistance in nephrotic syndrome. In Diuretics IV, Chemistry, Pharmacology and Clinical Applictions; Puschett, J.B., Greenberg, A., Eds.; Excerpta Medica pupl.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 435–443. [Google Scholar]
- Voelker, J.R.; Brater, D.C. Diuretics: Applied pharmacokinetics and drug resistance. In The Regulation of Sodium and Chloride Balance; Seldin, D.W., Giebisch, G., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 503–524. [Google Scholar]
- Knauf, H.; Mutschler, E. The Na+ load in the nephron segment determines the ceiling quality of a diuretic. In Diuretics III, Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Clinical Applications; Puschett, J.B., Greenberg, A., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 359–362. [Google Scholar]
- Schrier, R.W. Pathogenesis of sodium and water retention in high and low output cardiac failure, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, and pregnancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.H.; Velazquez, H.; Wright, F.S. Adaption of the distal convoluted tubule of the rat. Structural and functional effects of dietary salt intake and chronic diuretic infusion. J. Clin. Invest. 1989, 83, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielsen, A.; Bie, P.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H.; Christensen, N.J.; Warberg, J.; Dige-Petersen, H.; Frandsen, E.; Galatius, S.; Pump, B.; Sørensen, V.B.; et al. Neuroendocrine and renal effects of intravascular volume expansion in compensated heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 281, R459–R467. [Google Scholar]
- Spahr, L.; Villeneuve, J.P.; Tran, H.K.; Pomier-Layrargues, G. Furosemide-Induced Natriuresis as a Test To Identify Cirrhotic Patients With Refractory Ascites. Hepatology 2001, 33, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.S.; Sirota, R.A.; Ebert, T.H.; Lichtenstein, N.S. Low fractional excretion of sodium with contrast media-induced acute renal failure. Arch. Intern. Med. 1980, 140, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, M.E.; Ford, C.A.; Lysaght, M.J.; Henderson, L.W. Treatment of severe fluid overload by ultrafiltration. N. Engl. J. Med. 1974, 291, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bart, B.A.; Boyle, A.; Bank, A.J.; Anand, I.; Olivari, M.T.; Kraemer, M.; Mackedanz, S.; Sobotka, P.A.; Schollmeyer, M.; Goldsmith, S.R. Ultrafiltration versus usual care for hospitalized patients with heart failure: The Relief for Acutely Fluid-Overloaded Patients With Decompensated Congestive Heart Failure (RAPID-CHF) trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 2043–2046. [Google Scholar]
- Pepi, M.; Marenzi, G.C.; Agostoni, P.G.; Doria, E.; Barbier, P.; Muratori, M.; Celeste, F.; Guazzi, M.D. Sustained cardiac diastolic changes elicited by ultrafiltration in patients with moderate congestive heart failure: Pathophysiological correlates. Br. Heart J. 1993, 70, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Jaski, B.E.; Ha, J.; Denys, B.G.; Trupp, R.J.; Abraham, W.T. Peripherally inserted veno-venous ultrafiltration for rapid treatment of volume overloaded patients. J. Card. Fail. 2003, 9, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Agostoni, P.G.; Marenzi, G.C.; Pepi, M.; Doria, E.; Salvioni, A.; Perego, G.; Lauri, G.; Giraldi, F.; Grazi, S.; Guazzi, M.D. Isolated ultrafiltration in moderate congestive heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1993, 21, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.R.; Saltzberg, M.; O'Sullivan, J.; Sobotka, P. Early ultrafiltration in patients with decompensated heart failure and diuretic resistance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 2047–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, H.L.; Marshall, J.; Bock, J.; Dowling, T.C.; Feller, E.; Robinson, S.; Gottlieb, S.S. A randomized, controlled trial of the renal effects of ultrafiltration as compared to furosemide in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. J. Card. Fail. 2008, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Constanzo, M.R.; Guglin, M.E.; Saltzberg, M.T.; Jessup, M.L.; Bart, B.A.; Teerlink, J.R.; Jaski, B.E.; Fang, J.C.; Feller, E.D.; Haas, G.J.; et al. Ultrafiltration versus intravenous diuretics for patients hospitalized for acute decompensated HF. J. Am. Coll. Card. 2007, 49, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.R.; Saltzberg, M.T.; Jessup, M.; Teerlink, J.R.; Sobotka, P.A.; Ultrafiltration Versus Intravenous Diuretics for Patients Hospitalized for Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (UNLOAD) Investigators. Ultrafiltration is associated with fewer rehospitalizations than continuous diuretic infusion in patients with decompensated heart failure: Results from UNLOAD. J. Card. Fail. 2010, 16, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Marenzi, G.; Grazi, S.; Giraldi, F.; Lauri, G.; Perego, G.; Guazzi, M.; Salvioni, A.; Guazzi, M.D. Interrelation of humoral factors, hemodynamics, and fluid and salt metabolism in congestive HF: Effects of extracorporeal ultrafiltration. Am. J. Med. 1993, 94, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Patarroyo, M.; Wehbe, E.; Hanna, M.; Taylor, D.O.; Starling, R.C.; Demirjian, S.; Tang, W.H. Cardiorenal outcomes after slow continuous ultrafiltration therapy in refractory patients with advanced decompensated heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1906–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bart, B.A.; Goldsmith, S.R.; Lee, K.L.; Givertz, M.M.; O'Connor, C.M.; Bull, D.A.; Redfield, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Rouleau, J.L.; LeWinter, M.M.; et al. Ultrafiltration in decompensated HF with CRS. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2296–2304. [Google Scholar]
- Aronson, D.; Burger, A.J. The relationship between transient and persistent worsening renal function and mortality in patients with acute decompensated HF. J. Card. Fail. 2010, 16, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauchauld, P. Effects of ultrafiltration of body fluid and transcapillary colloid osmotic gradient in hemodialysis patients, improvements in dialysis therapy. Contrib. Nephr. 1989, 74, 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Fiaccadori, E.; Regolisti, G.; Maggiore, U.; Parenti, E.; Cremaschi, E.; Detrenis, S.; Caiazza, A.; Cabassi, A. Ultrafiltration in heart failure. Am. Heart J. 2011, 161, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M. Nonuremic indication for peritoneal dialysis for refractory heart failure in cardiorenal syndrome type II: Review and perspective. Perit. Dial. Int. 2013, 33, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regolisti, G.; Fiaccadori, E. Ultrafiltration in acute decompensated heart failure: Friend or foe for the kidney? J. Nephrol. 2013, 26, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Shchekochikhin, D.; Al Ammary, F.; Lindenfeld, J.A.; Schrier, R. Role of Diuretics and Ultrafiltration in Congestive Heart Failure. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 851-866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6070851
Shchekochikhin D, Al Ammary F, Lindenfeld JA, Schrier R. Role of Diuretics and Ultrafiltration in Congestive Heart Failure. Pharmaceuticals. 2013; 6(7):851-866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6070851
Chicago/Turabian StyleShchekochikhin, Dmitry, Fawaz Al Ammary, Jo Ann Lindenfeld, and Robert Schrier. 2013. "Role of Diuretics and Ultrafiltration in Congestive Heart Failure" Pharmaceuticals 6, no. 7: 851-866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6070851
APA StyleShchekochikhin, D., Al Ammary, F., Lindenfeld, J. A., & Schrier, R. (2013). Role of Diuretics and Ultrafiltration in Congestive Heart Failure. Pharmaceuticals, 6(7), 851-866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6070851




