NMDA Receptor Antagonists for Treatment of Depression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. NMDA Receptor and Subunits
3. NMDA Receptor Antagonists
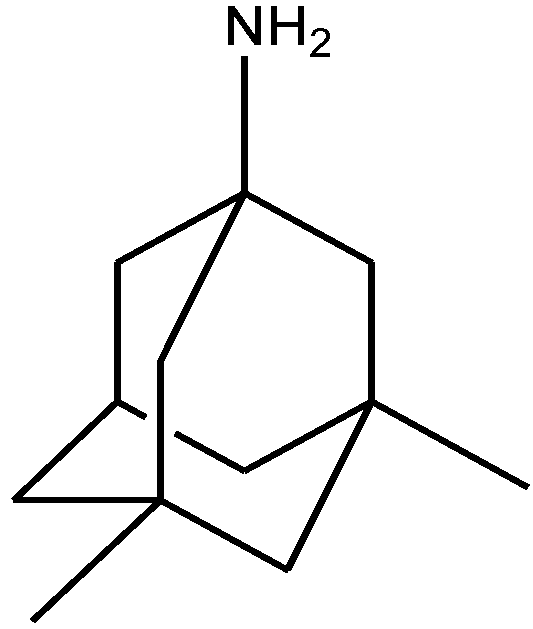
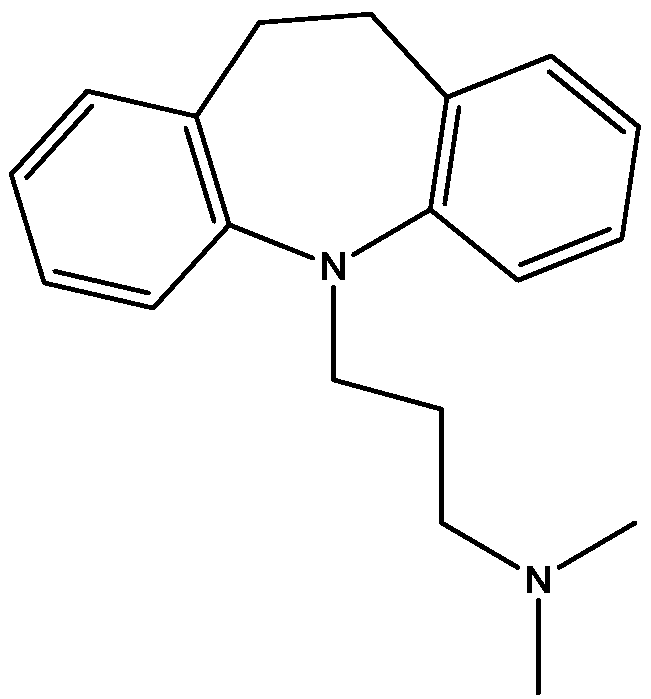
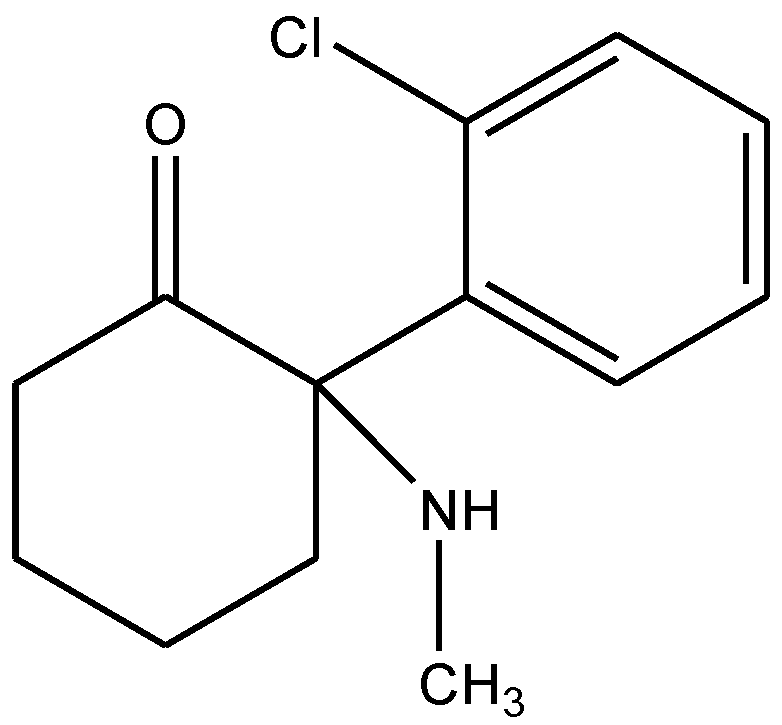
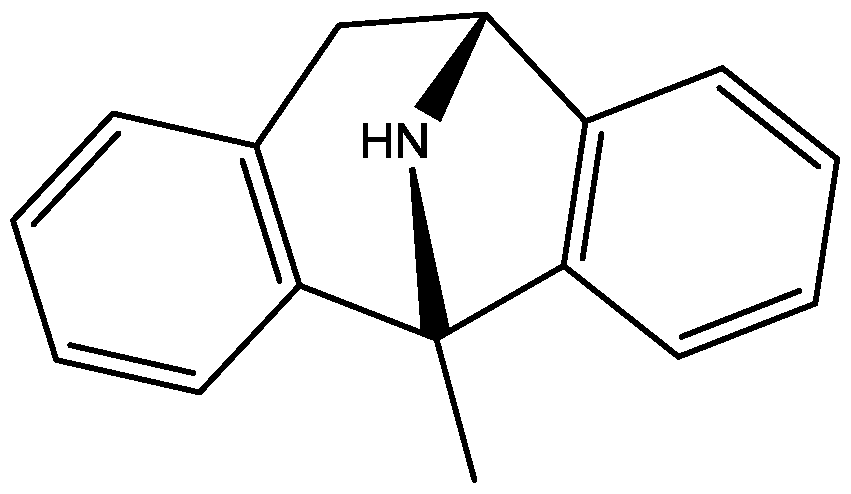
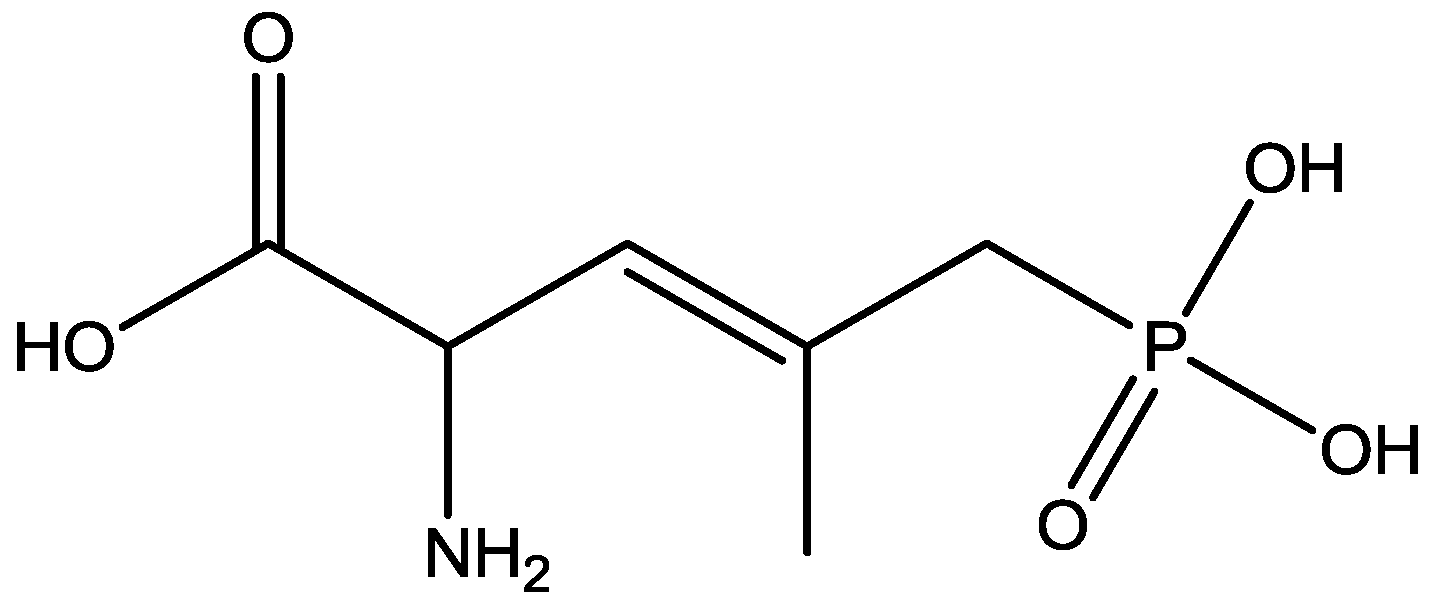
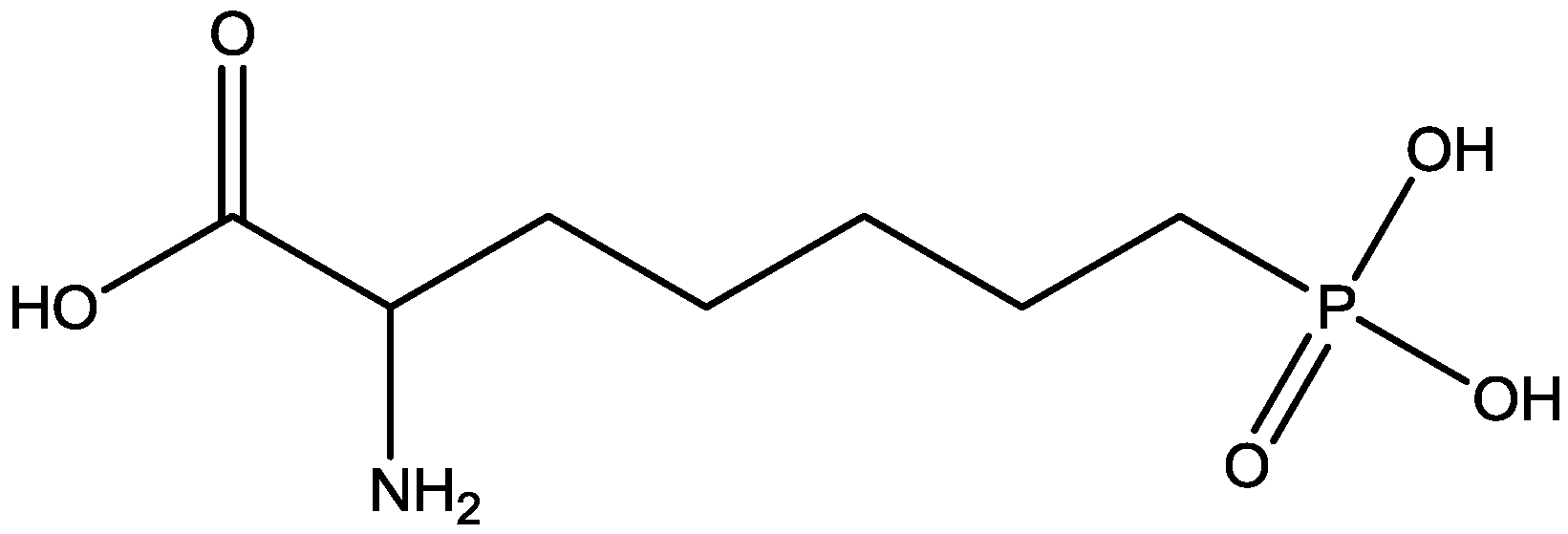
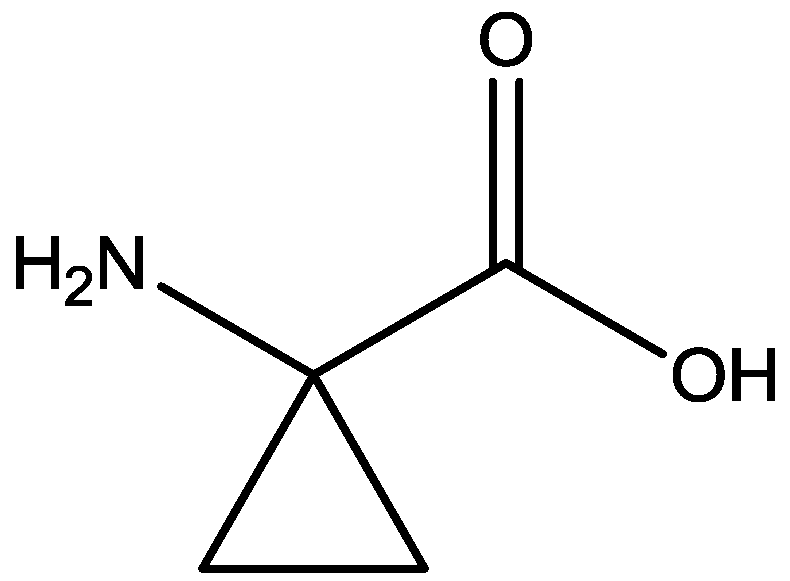

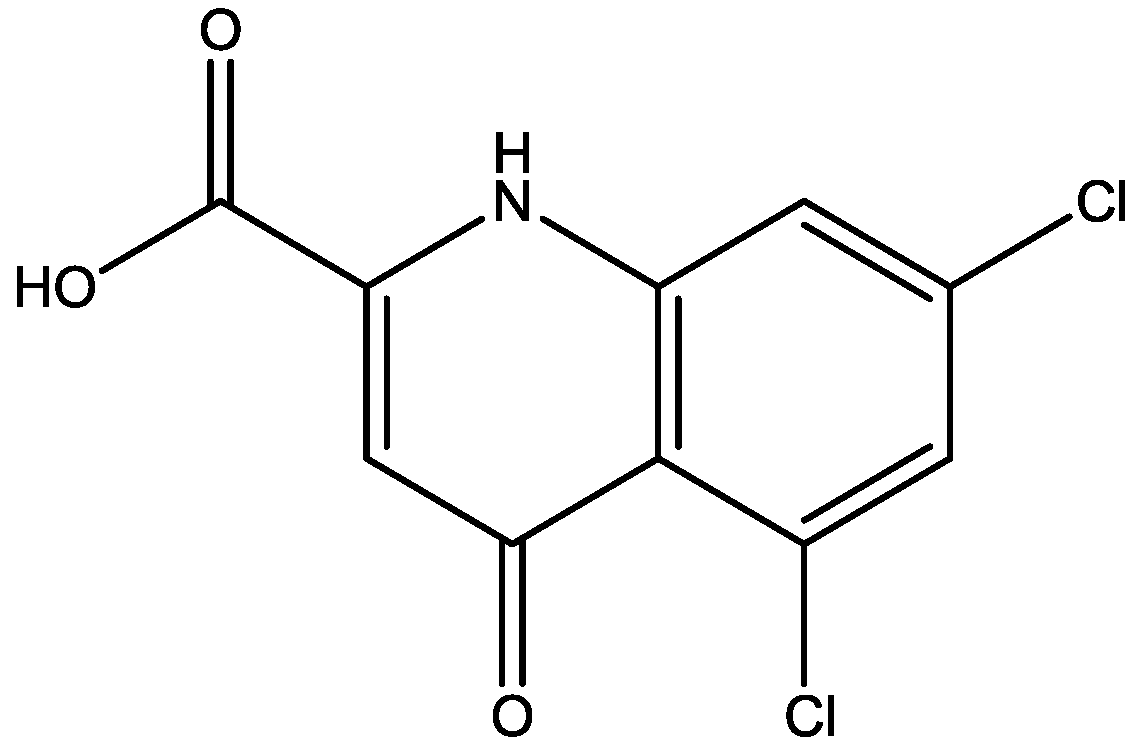
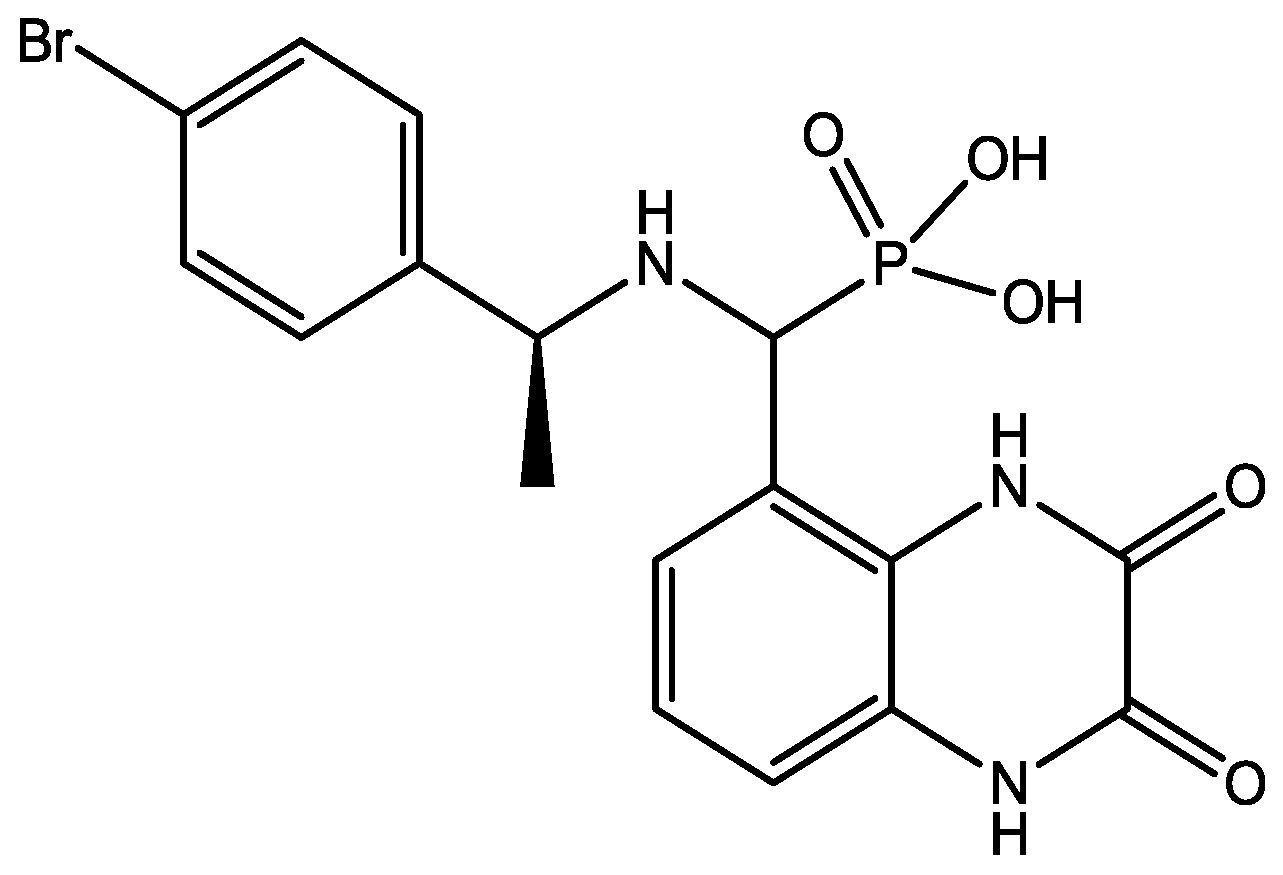
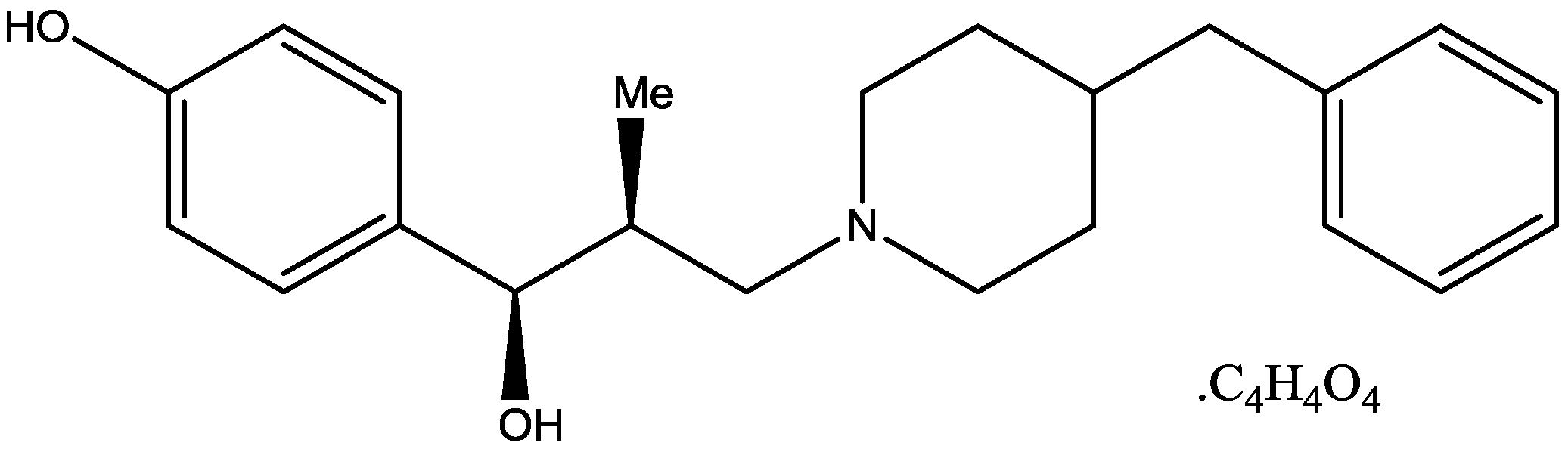
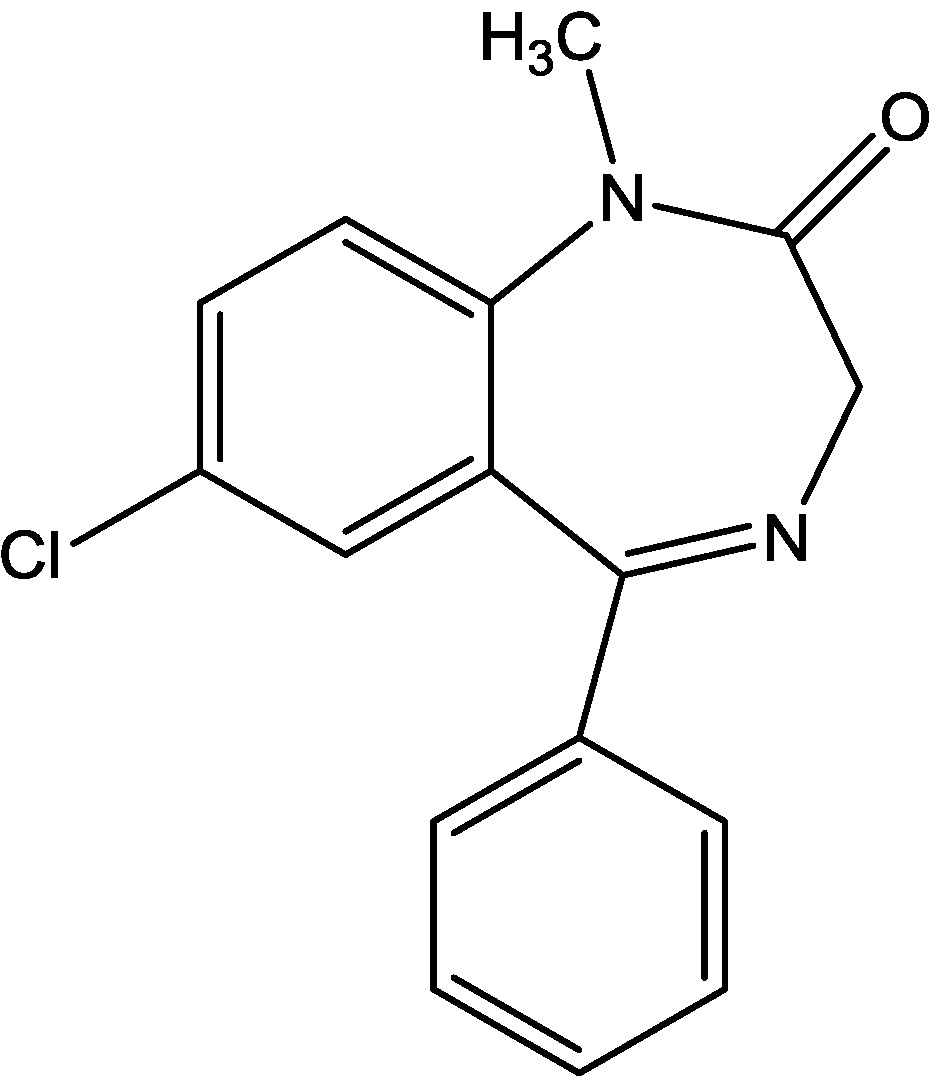
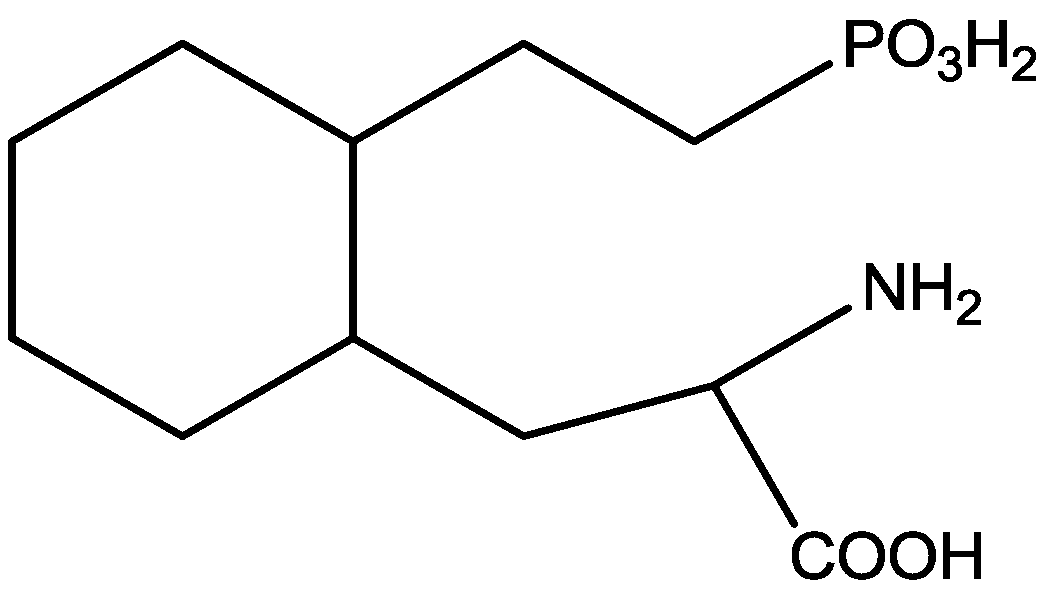

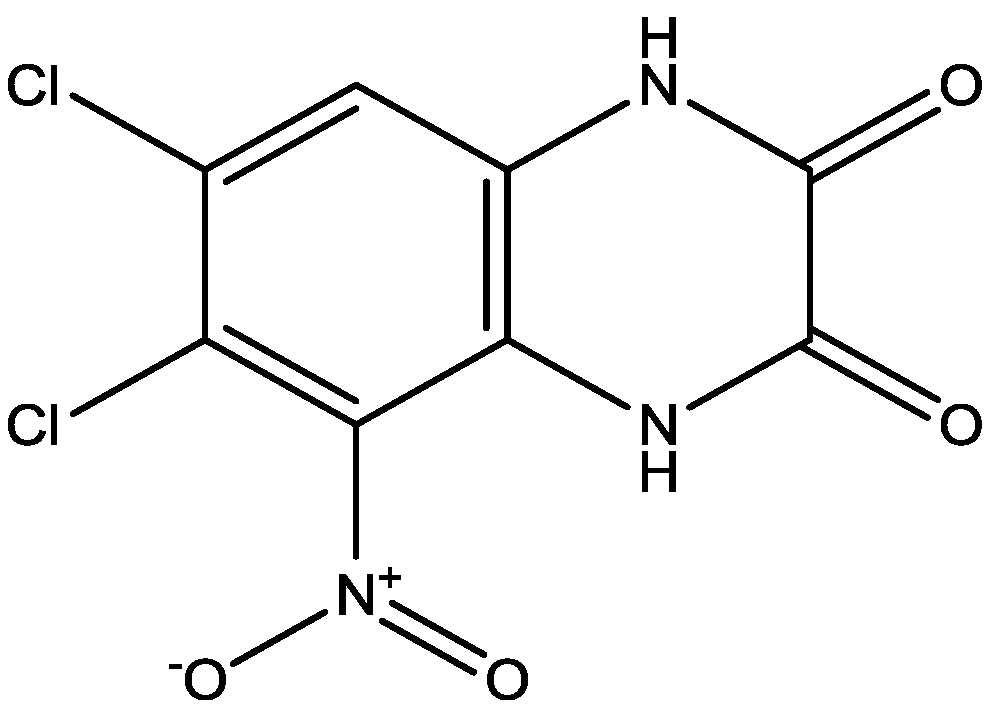
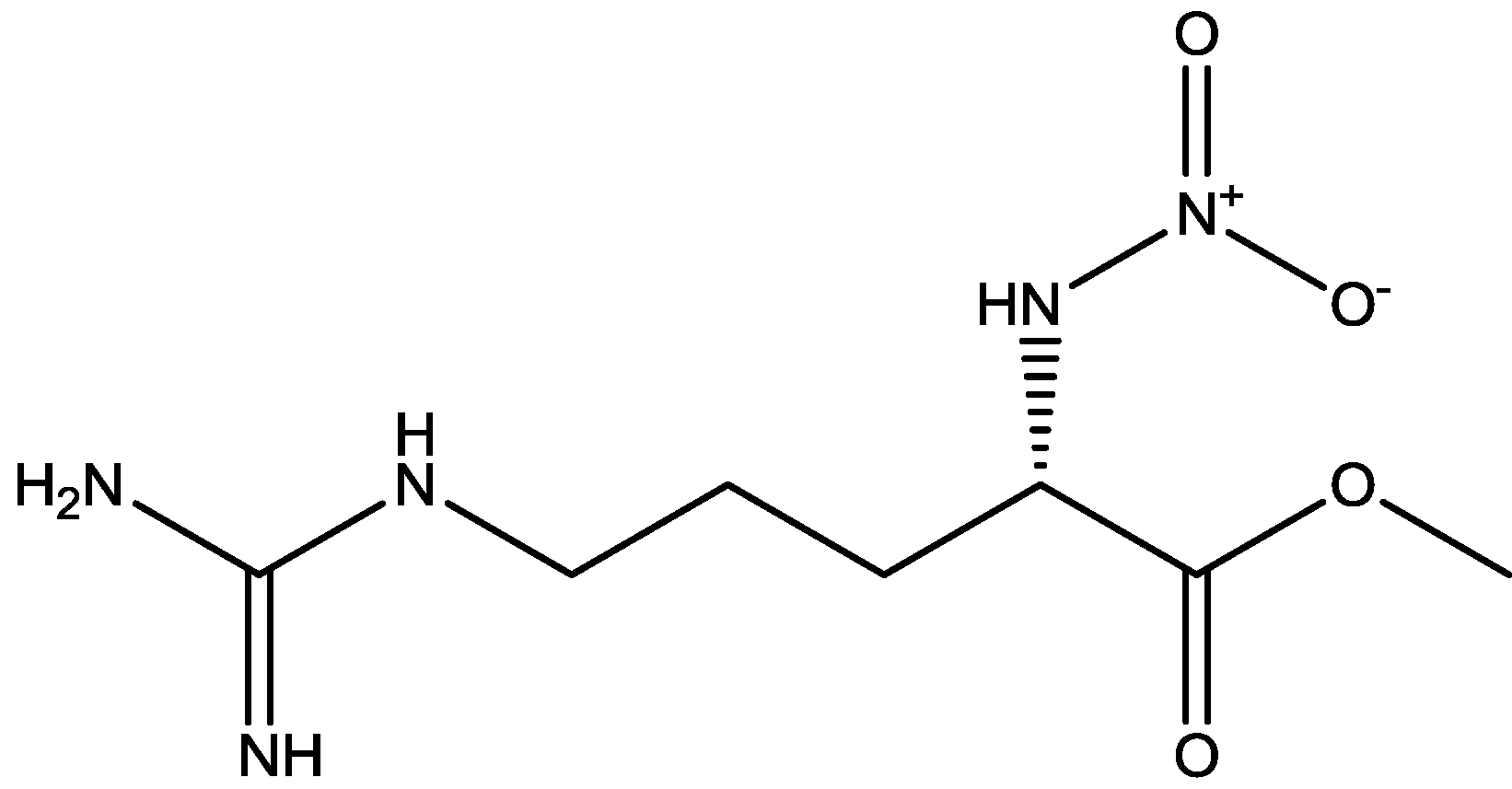
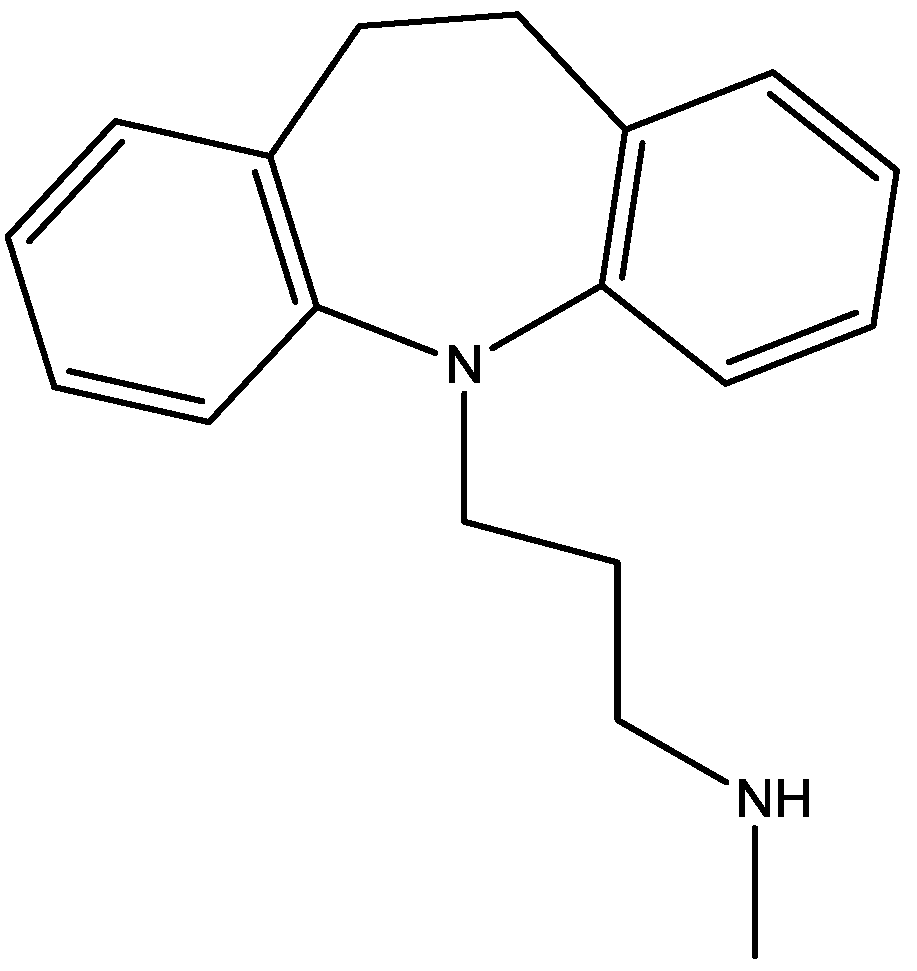
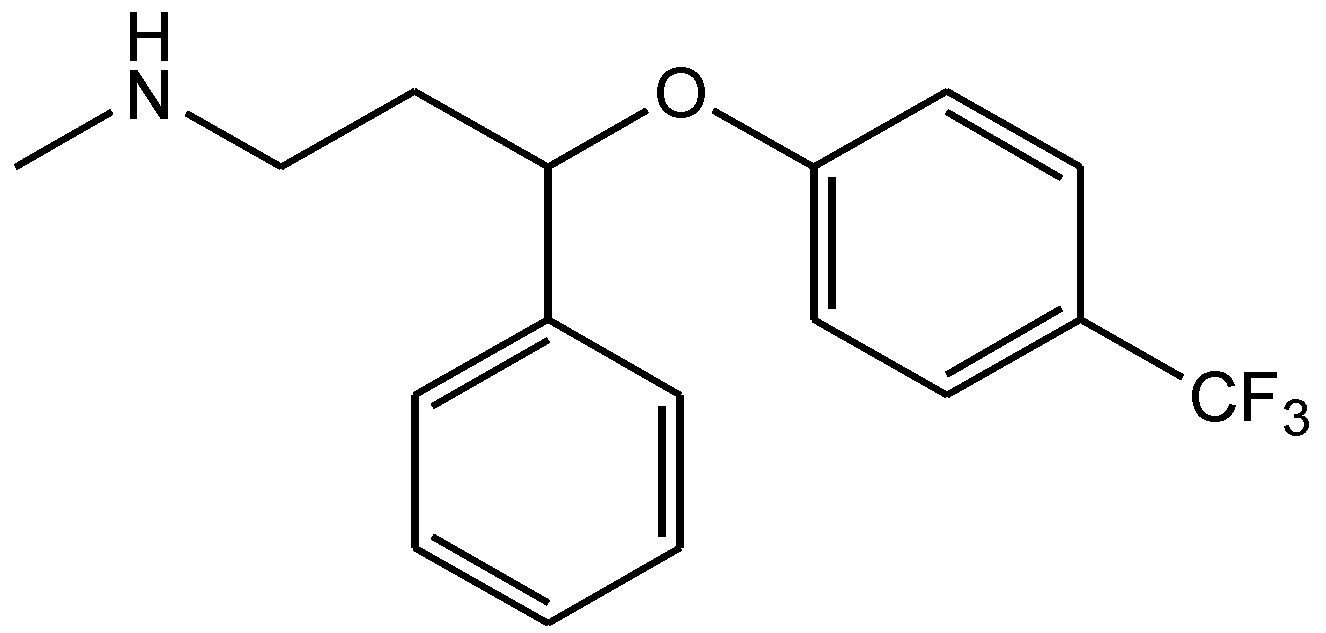
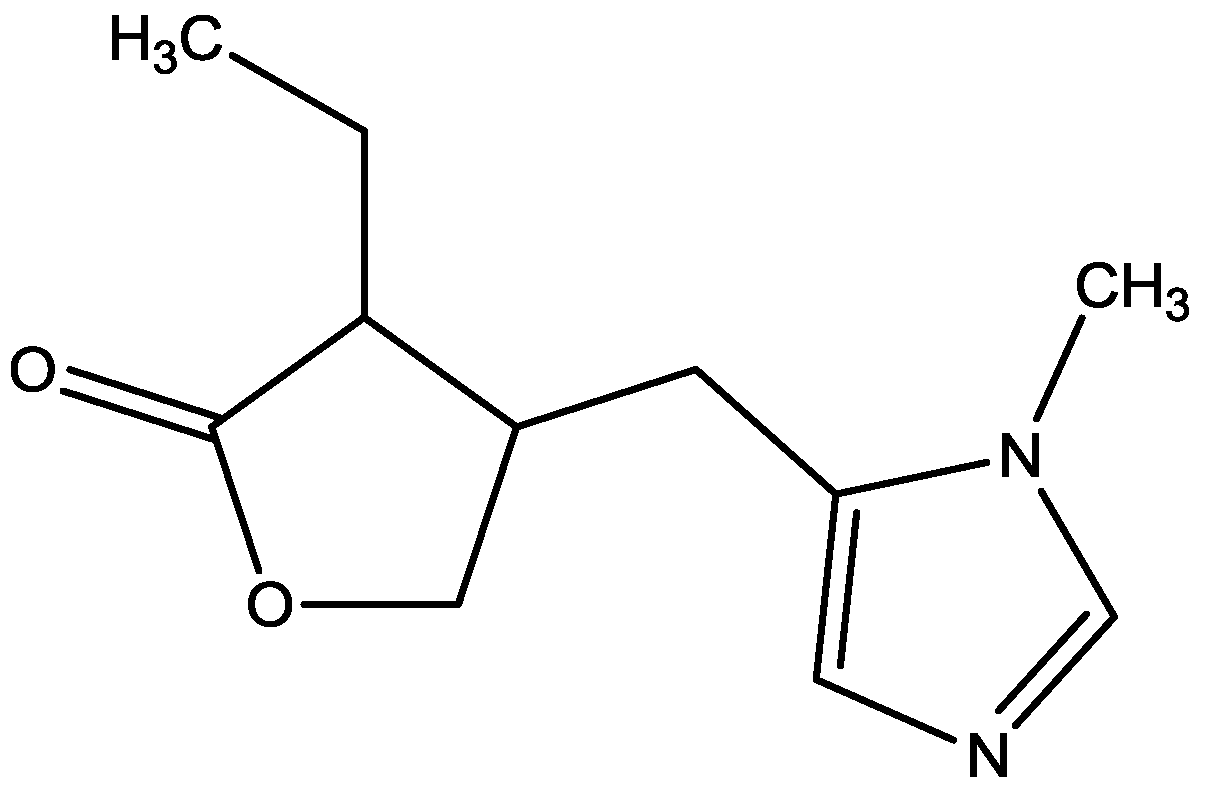
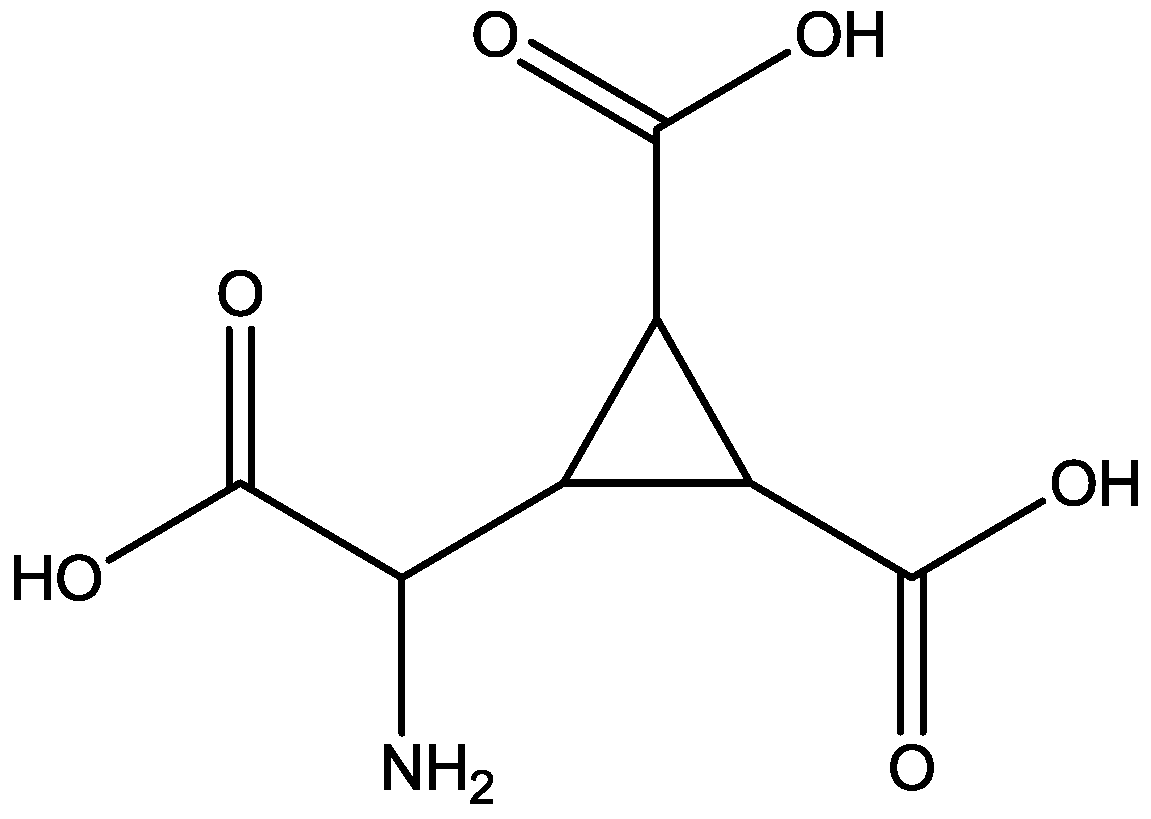
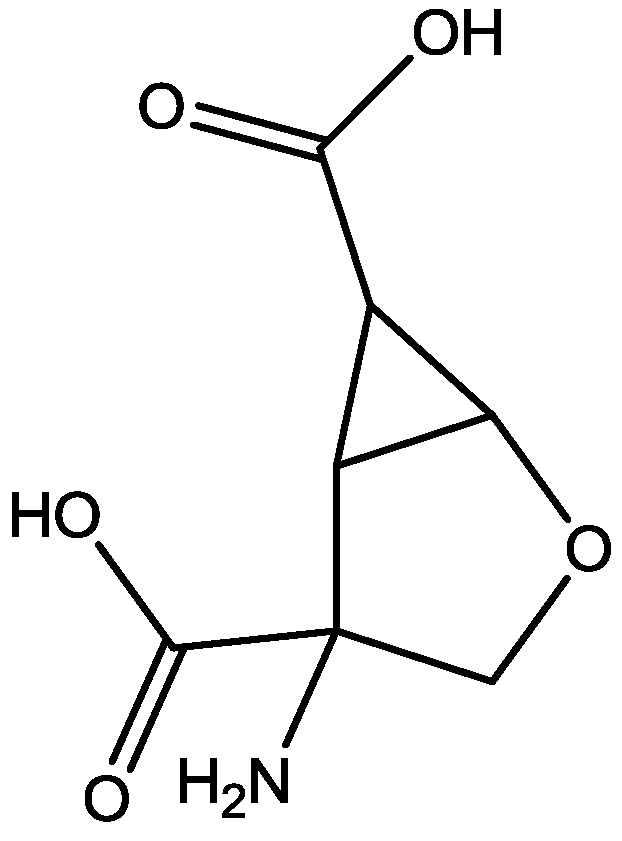
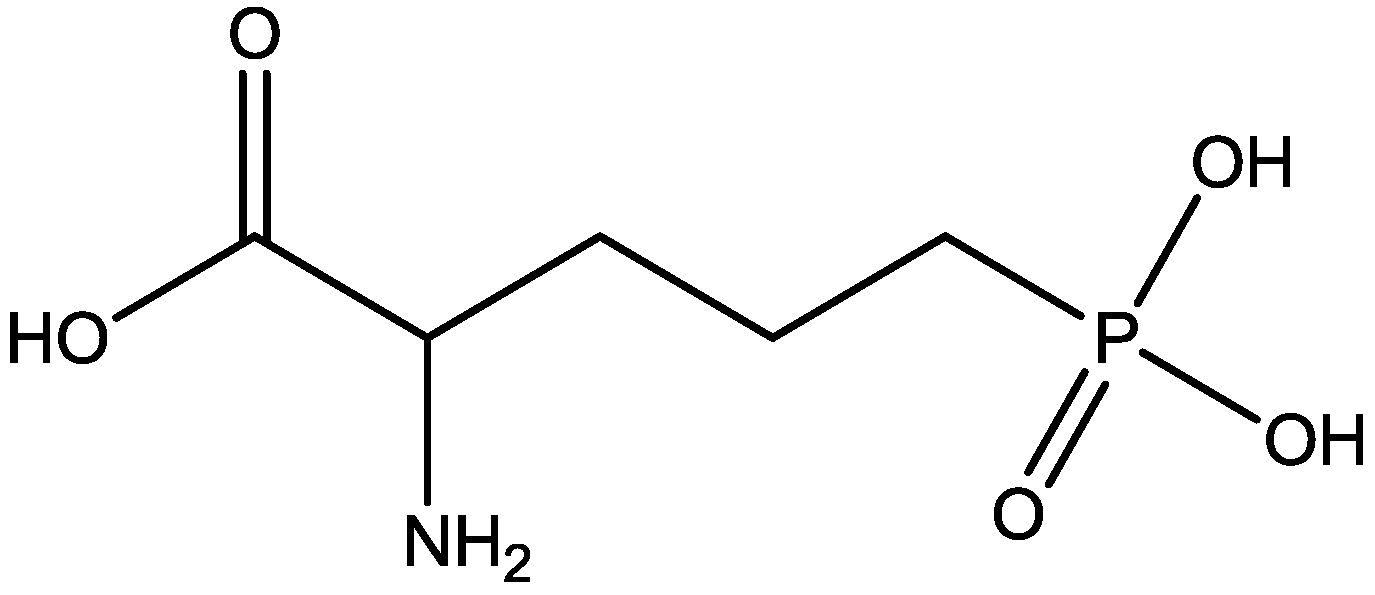
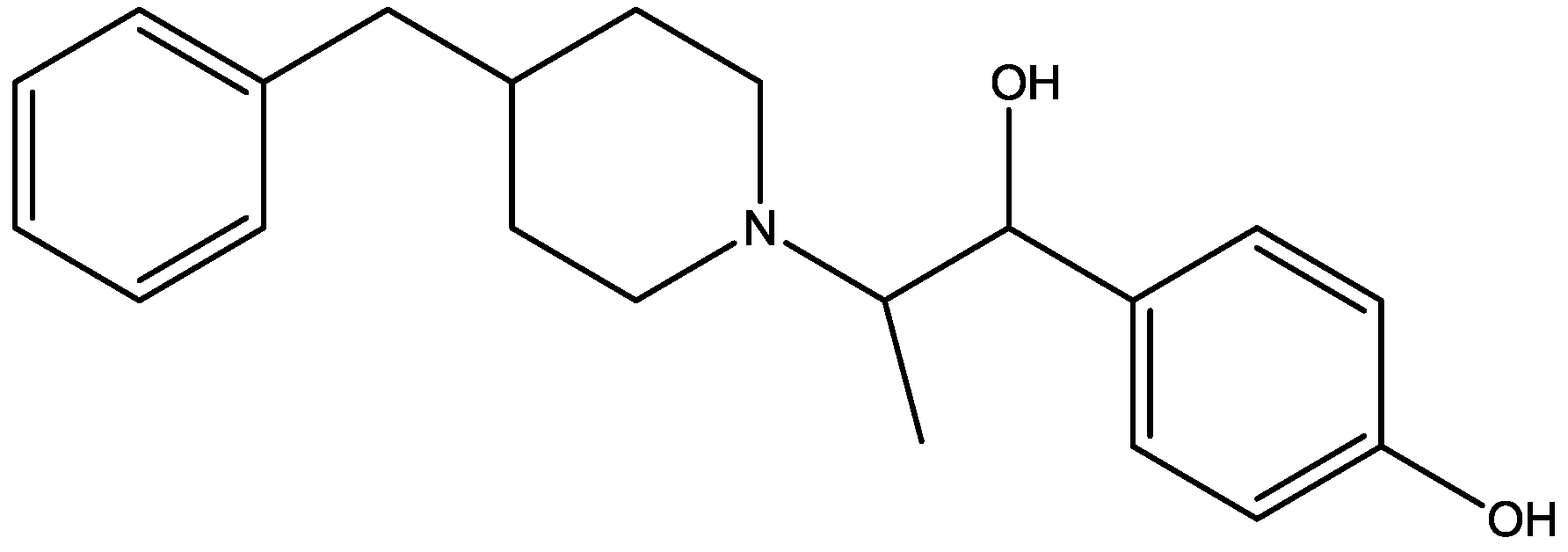
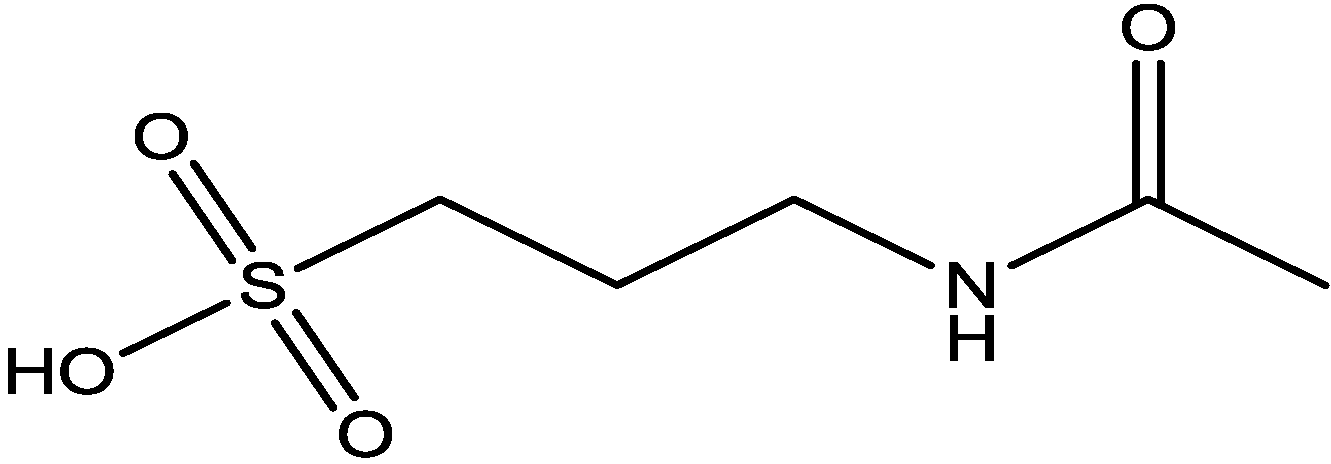
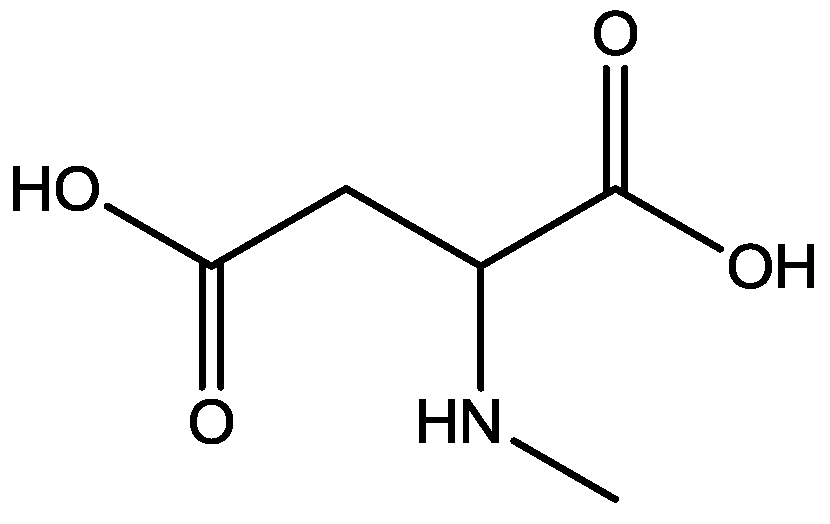
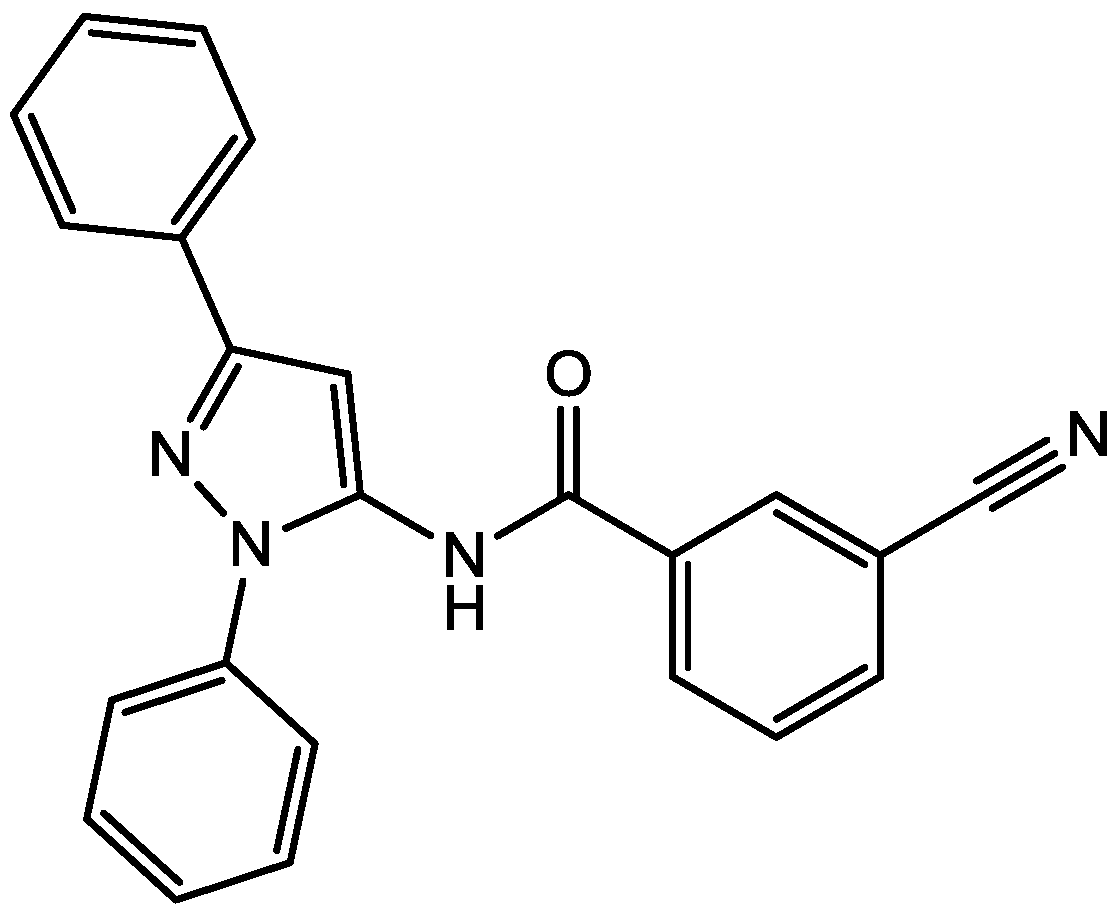
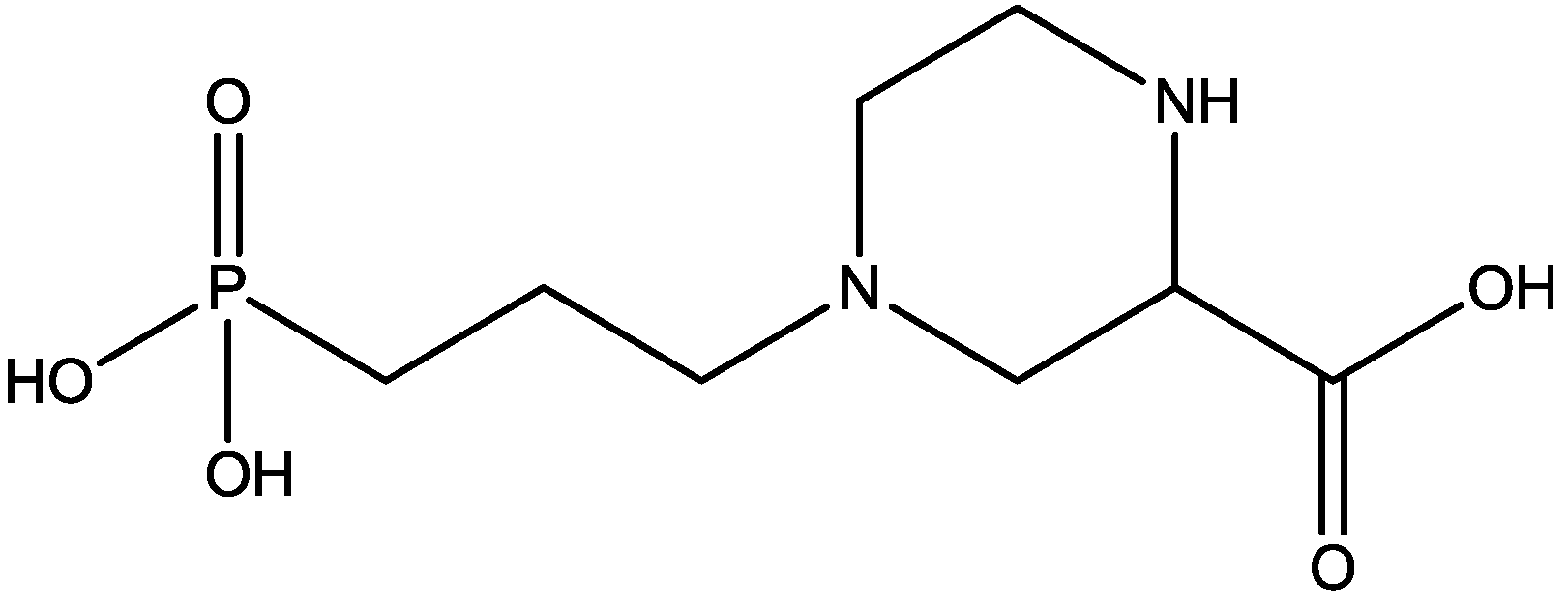
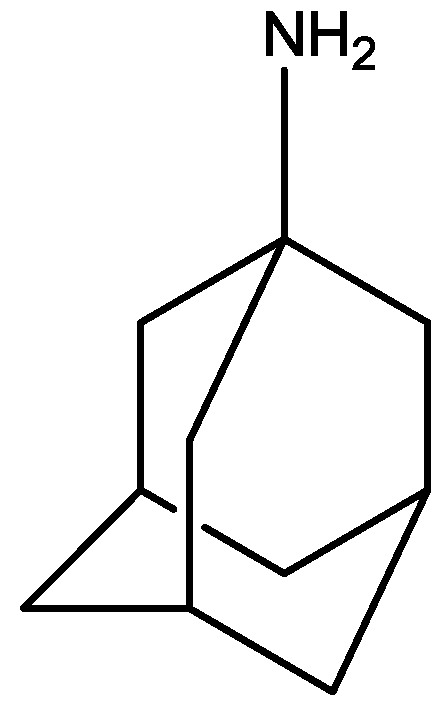
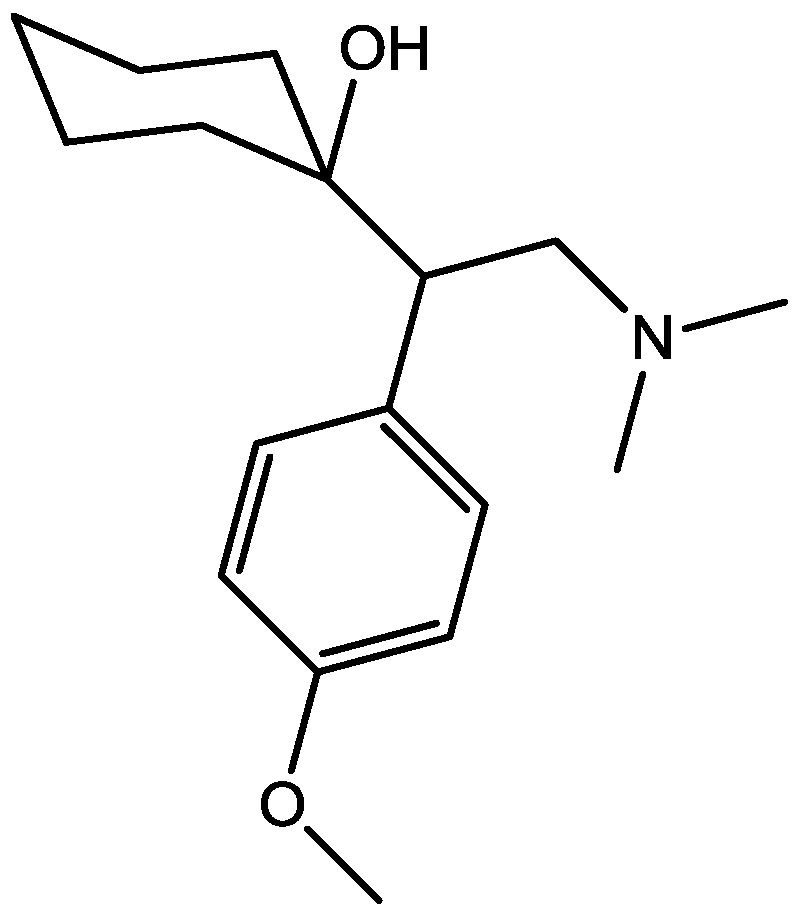
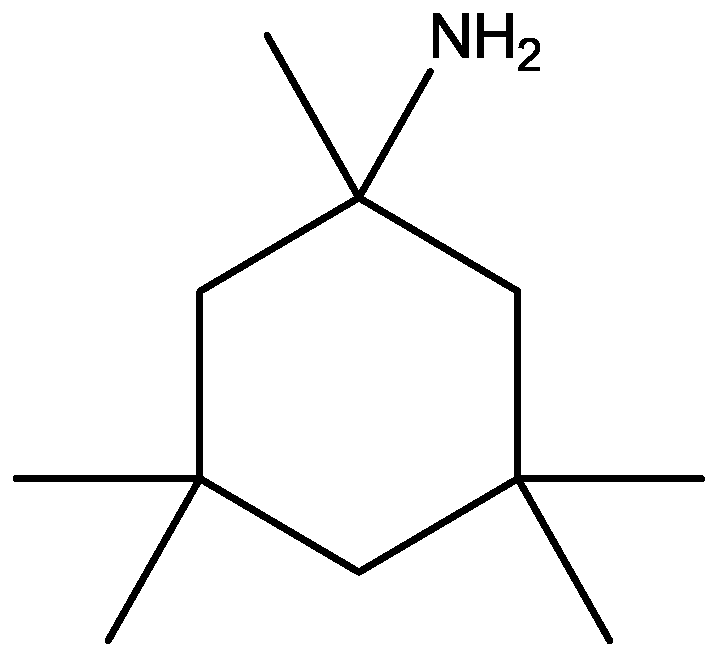
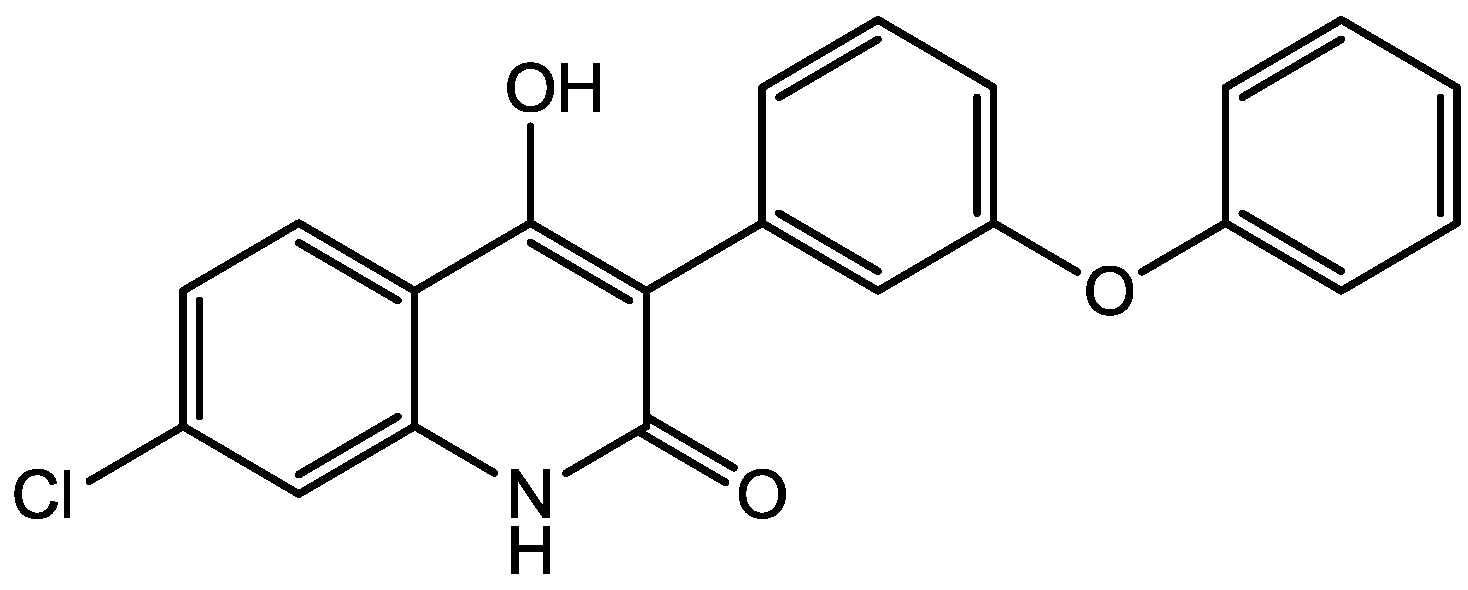
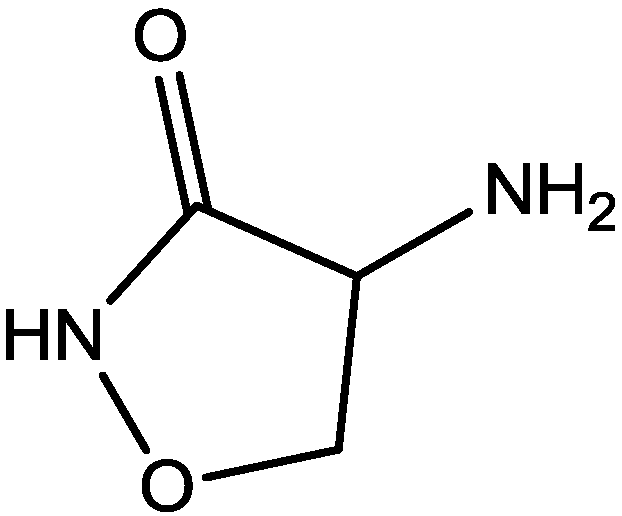
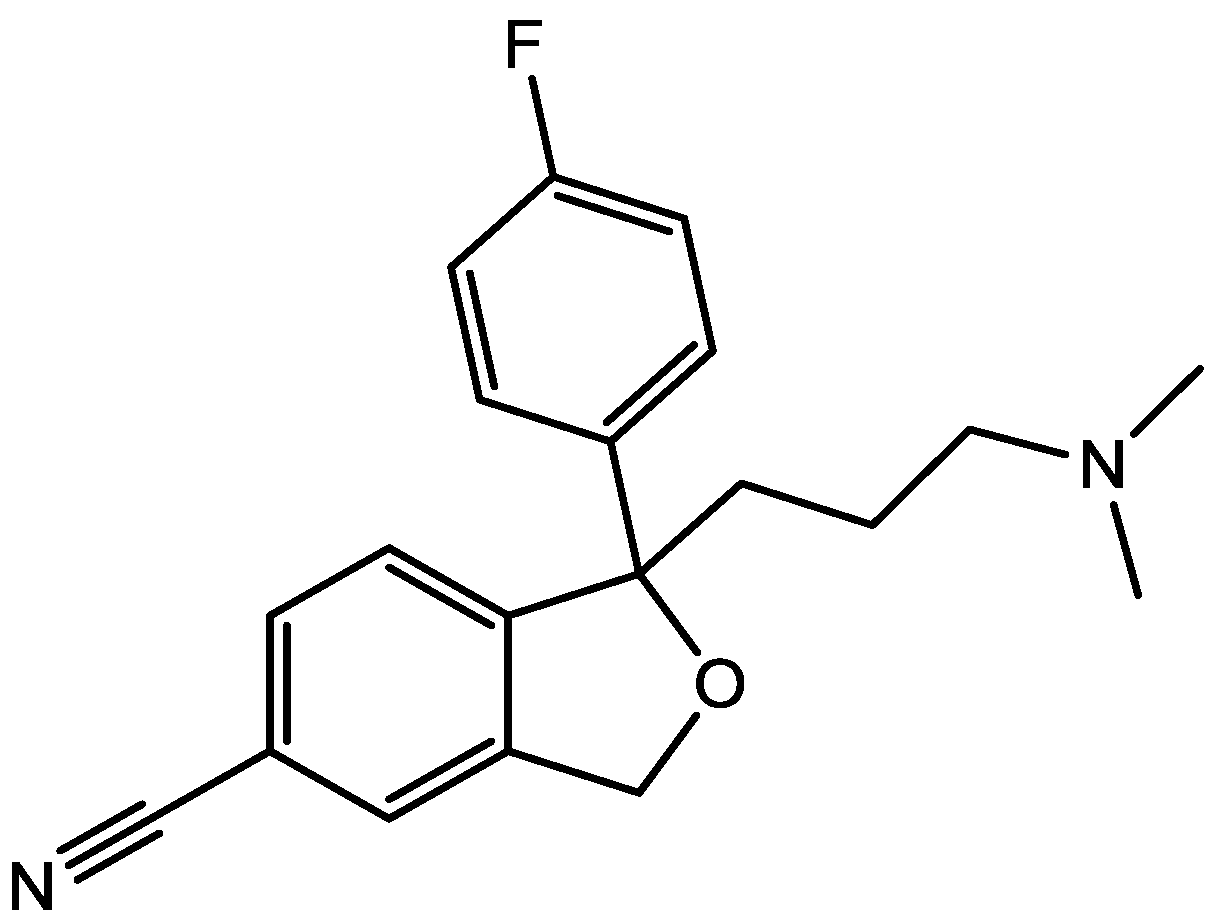
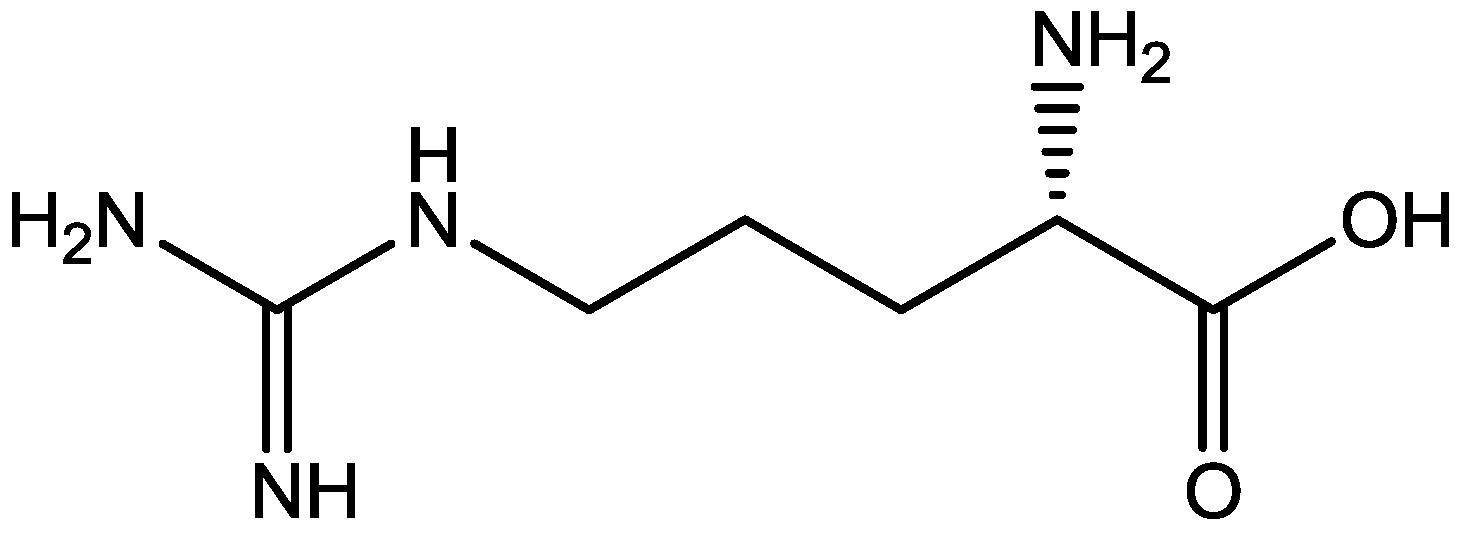
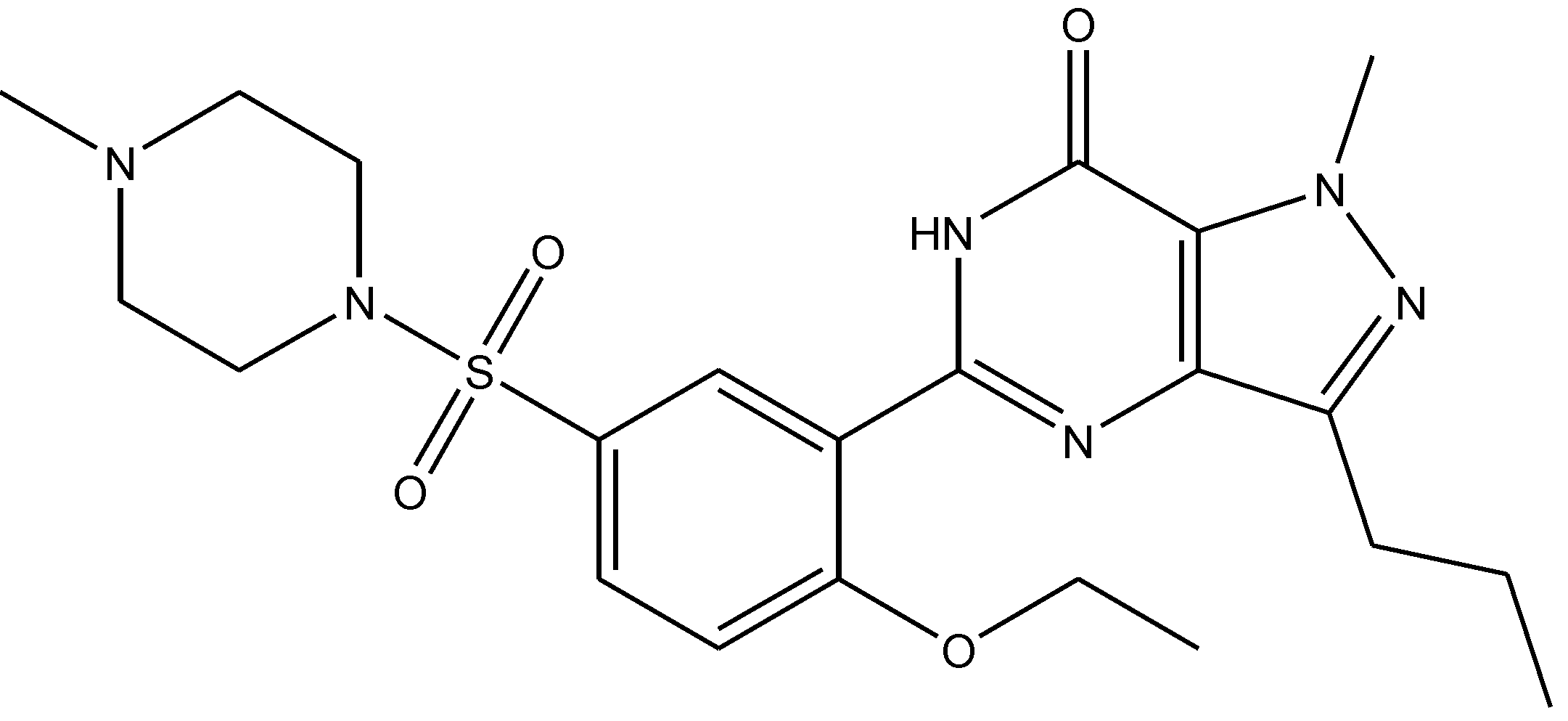
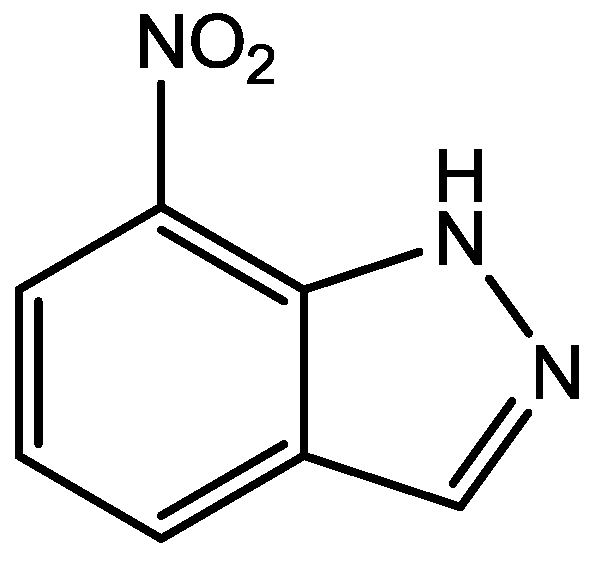
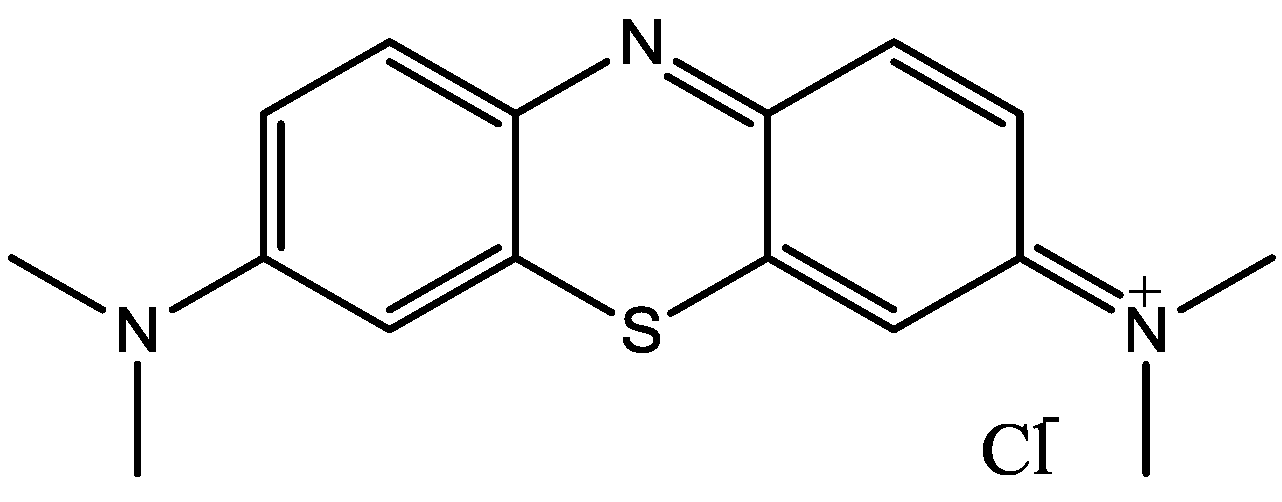
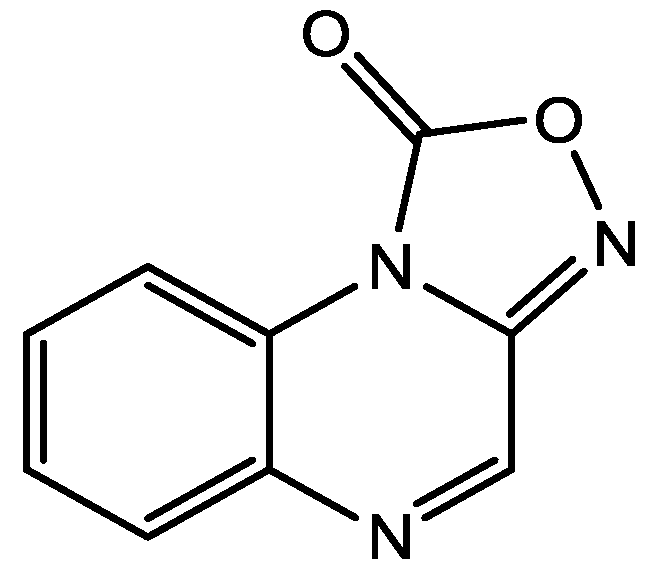
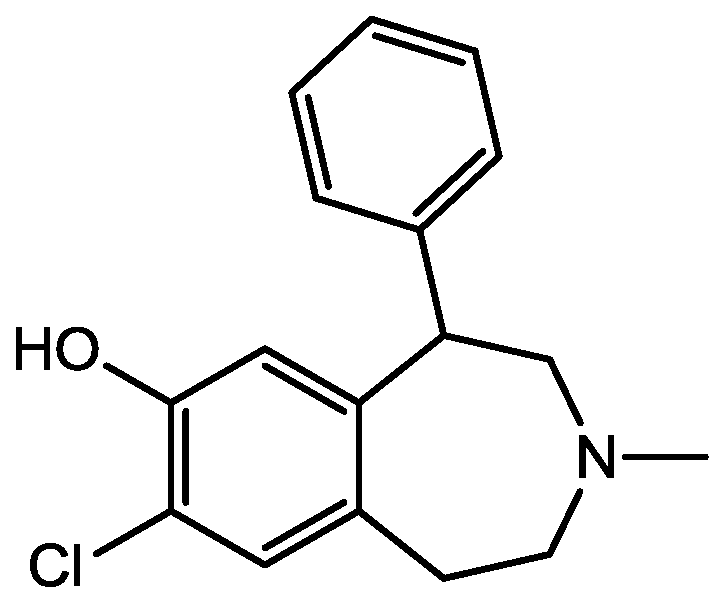

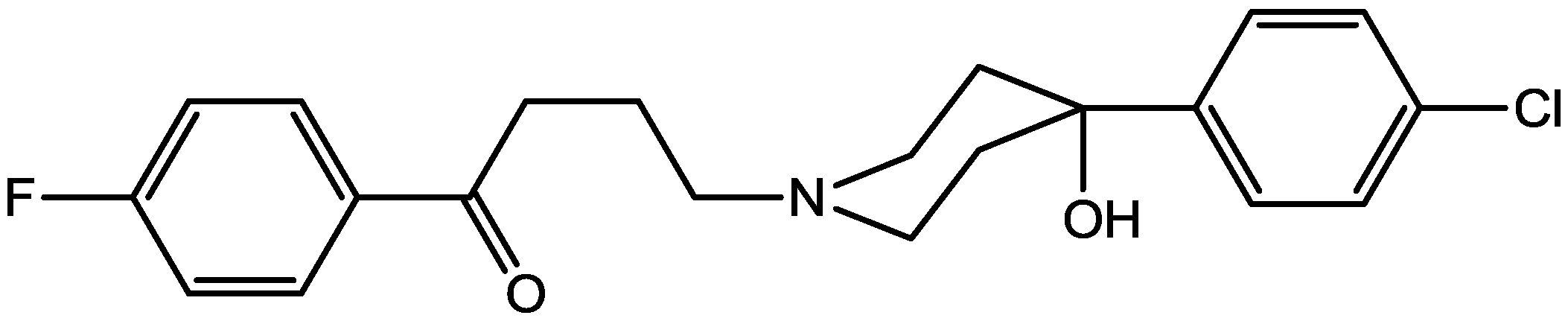
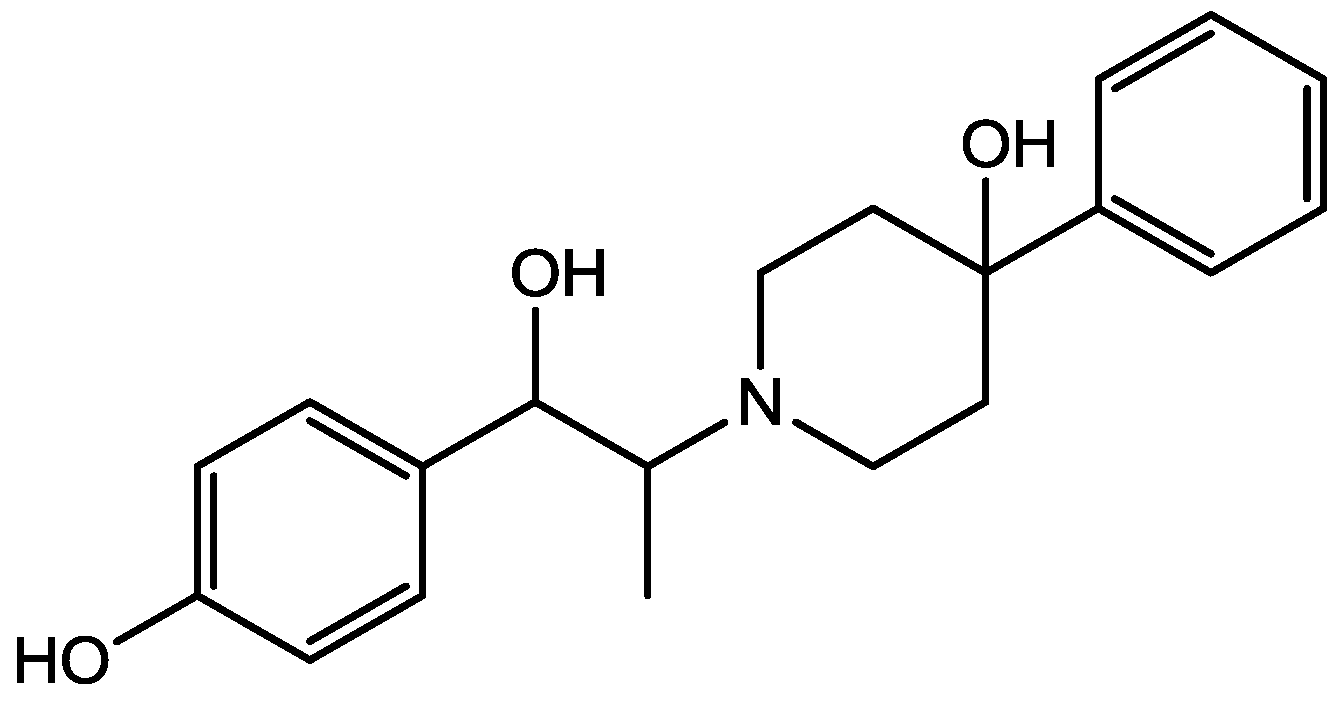
4. Conclusions
References
- Rosenzweig-Lipson, S.; Beyer, C.E.; Hughes, Z.A.; Khawaja, X.; Rajarao, S.J.; Malberg, J.E.; Rahman, Z.; Ring, R.H.; Lee, E.; Schechter, L.E. Differentiating antidepressants of the future: Efficacy and safety. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2007, 113, 134–153. [Google Scholar]
- Maeng, S.; Zarate, C.A. The Role of Glutamate in Mood Disorders: Results from the Ketamine in Major Depression Study and the Presumed Cellular Mechanism Underlying its Antidepressant Effects. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2007, 9, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagiolini, A.; Kupfer, D.J.; Masalehdan, A.; Scott, J.A.; Houck, P.R.; Frank, E. Functional impairment in the remission phase of bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2005, 7, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxley, N.; Baldessarini, R.J. Disability and its treatment in bipolar disorder patients. Bipolar Disord. 2007, 9, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richelson, E. Synaptic pharmacology of antidepressants: An update. McLean Hosp. J. 1988, 13, 67–88. [Google Scholar]
- Tizabi, Y.; Bhatti, B.H.; Manaye, K.F.; Da Sa, J.R.; Akinfiresoye, L. Antidepressant-like effects of low ketamine dose is associated with increased hippocampal AMPA/NMDA receptor density ratio in female wistar-kyoto rats. Neuroscience 2012, 213, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Stewart, J.W.; Warden, D.; Niederehe, G.; Thase, M.E.; Lavori, P.W.; Lebowitz, B.D.; et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: A STAR*D report. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, M.H.; Rush, A.J.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Warden, D.; Ritz, L.; Norquist, G.; Howland, R.H.; Lebowitz, B.D.; McGrath, P.J.; et al. STAR*D Study Team. Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR*D: Implications for clinical practice. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacabelos, R.; Takeda, M.; Winblad, B. The glutamatergic system and neurodegeneration in dementia: preventive strategies in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Geriatr Psychiatry 1999, 14, 3–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, L.A. Excitotoxicity in Huntington disease. Clin. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 3, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.M.Y.; Raymond, L.A. N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor function and excitotoxicity in Huntington’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 272–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.G.; Danysz, W.; Quack, G. Glutamate in CNS disorders as a target for drug development: an update. Drug News Perspect. 1998, 11, 523–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, I.; MacDonald, J.F. NMDA receptor-dependent excitotoxicity: The role of intracellular Ca2+ release. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1995, 16, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, R.; Tymianski, M. Molecular mechanisms of calcium-dependent excitotoxicity. J. Mol. Med. 2000, 78, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, D.T.; Irvine, M.W.; Costa, B.M.; Fang, G.; Jane, D.E. Pharmacological modulation of NMDA receptor activity and the advent of negative and positive allosteric modulators. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collingridge, G. Synaptic plasticity. The role of NMDA receptors in learning and memory. Nature 1987, 330, 604–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotman, C.W.; Monaghan, D.T.; Ganong, A.H. Excitatory amino acid neurotransmission: NMDA receptors and Hebb-type synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1988, 11, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.W. Excitotoxic cell death. J. Neurobiol. 1992, 23, 1261–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, L.V.; Kalia, S.K.; Salter, M.W. NMDA receptors in clinical neurology: Excitatory times ahead. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przegalýnský, E.; Ttatarczynska, E.; Deren-Wesolek, A.; Chojnacka-Wojcýk, E. Antidepressant-like effects of a partial agonist at strychnine-insensitive glycine receptors and a competitive NMDA receptor antagonist. Neuropharmacology 1997, 36, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maj, J.; Rogoz, Z.; Skuza, G.; Kolodziejczyk, K. Some central effects of kynurenicacid, 7-chlorokynurenicacid and 5,7-dichlorokynurenicacid, glycine site antagonists. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Layer, R.T.; Popik, P.; Olds, T.; Skolnick, P. Antidepressant-like actions of the polyamine site NMDA antagonist, eliprodil (SL-82.0715). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1995, 52, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, I.A.; Trullas, R.; Skolnick, P.; Nowak, G. Downregulation of cortical/3-adrenoceptorsby chronic treatment with functional NMDA antagonists. Psychopharmacology 1992, 106, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trullas, R.; Folio, T.; Young, A.; Miller, R.; Boje, K.; Skolnick, P. l-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylates exhibit antidepressant and anxiolytic actions in animal models. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 203, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, J.P.; Szasz, B.K.; Fodor, L.; Mike, A.; Lenkey, N.; Kurkó, D.; Nagy, J.; Vizi, E.S. GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors as possible targets for the neuroprotective and antidepressant effects of fluoxetine. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maj, J.; Rogoz, Z.; Skuza, G.; Sowinska, H. The effect of antidepressant drugs on the locomotor hyperactivity induced by MK-801, a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist. Neuropharmacology 1992, 31, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, D.; Gambarana, C.; De Montis, M.G.; Dal Prá, P.; Taddei, I.; Tagliamonte, A. Dizocilpine antagonizes the effect of chronic imipramine on learned helplessness in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1993, 46, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, M.; Moryl, E. New evidence for the antidepressant activity of MK-801, a non-competitive antagonist of NMDA receptors. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 45, 549–553. [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick, P.; Miller, R.; Young, A.; Boje, K.; Trullas, R. Chronic treatment with 1-aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid desensitizes behavioral responses to compounds acting at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 1992, 107, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trullas, R.; Skolnick, P. Functional antagonists at the NMDA receptor complex exhibit antidepressant actions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 185, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovan, C.M.; Guimaraes, F.S. Antidepressant-like effects of NMDA-receptor antagonist injected into the dorsal hippocampus of rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2004, 77, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.T. Glutamatergic approaches in major depressive disorder: Focus on ketamine, memantine and riluzole. Drugs Today (Barc.) 2012, 48, 469–478. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, R.; Kong, X.; Han, J.; Zhao, G. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists for migraine: a potential therapeutic approach. Med. Hypotheses 2009, 72, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P.; Neyton, J. NMDA receptor subunits: function and pharmacology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine, R.; Borges, K.; Bowie, D.; Traynelis, S.F. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 7–61. [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy, S.G.; Leszkiewicz, D.N. Role of distinct NMDA receptor subtypes at central synapses. Sci. STKE 2004, 255, re16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakura, T.; Shimoji, K. Subunit- and site-specific pharmacology of the NMDA receptor channel. Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 59, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.J.; Zhuo, M. Targeting the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Neurotherapeutics 2009, 6, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.F.; Rothe, T.; Premkumar, L.S.; Das, S.; Cui, J.; Talantova, M.V.; Wong, H.K.; Gong, X.; Chan, S.F.; Zhang, D.; et al. Characterization and comparison of the NR3A subunit of the NMDA receptor in recombinant systems and primary cortical neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 87, 2052–2063. [Google Scholar]
- Serafini, G.; Pompili, M.; Innamorati, M.; Dwivedi, Y.; Brahmachari, G. Girardi PPharmacological properties of glutamatergic drugs targeting NMDA receptors and their application in major depression. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 1898–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musazzi, L.; Treccani, G.; Mallei, A.; Popoli, M. The action of antidepressants on the glutamate system: Regulation of glutamate release and glutamate receptors. Biol. Psychiatry. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réus, G.Z.; Stringari, R.B.; Kirsch, T.R.; Fries, G.R.; Kapczinski, F.; Roesler, R.; Quevedo, J. Neurochemical and behavioural effects of acute and chronic memantine administration in rats: Further support for NMDA as a new pharmacological target for the treatment of depression? Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 81, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autry, A.E.; Adachi, M.; Nosyreva, E.; Na, E.S.; Los, M.F.; Cheng, P.F.; Kavalali, E.T.; Monteggia, L.M. NMDA receptor blockade at rest triggers rapid behavioural antidepressant responses. Nature 2011, 475, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Papp, M.; Moryl, E. Antidepressant activity of non-competitive and competitive NMDA receptor antagonists in a chronic mild stress model of depression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 263, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, T.E.; Bannister, N.J.; Collett, V.J.; Dargan, S.L.; Massey, P.V.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Fitzjohn, S.M.; Bashir, Z.I.; Collingridge, G.L.; Lodge, D. Differential roles of NR2A and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in LTP and LTD in the CA1 region of two-week old rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, J.L.; Cristello, A.F.; Balster, R.L. Effects of site-selective NMDA receptor antagonists in an elevated plus-maze model of anxiety in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 294, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes-Aguiar, C.; Bueno-Junior, L.S.; Ruggiero, R.N.; Romcy-Pereira, R.N.; Leite, J.P. NMDA receptor blockade impairs the muscarinic conversion of sub-threshold transient depression into long-lasting LTD in the hippocampuseprefrontal cortex pathway in vivo: Correlation with gamma oscillations. Neuropharmacology 2013, 65, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Hsu, K.-S. The role of NMDA receptors in regulating group II metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated long-term depression in rat medial prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, W.; Lu, W.; Smith, G.B.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bea, M.F.; Malenka, R.C. Activation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors is not required for NMDA receptor-dependent long-term depression. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałucha-Poniewiera, A.; Pilc, A. Involvement of mGlu5 and NMDA receptors in the antidepressant-like effect of acamprosate in the tail suspension test. Prog. Neuro Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 39, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, N.I.; Povpov, V.I.; Dallerac, G.; Davies, H.A.; Laroche, S.; Kraev, I.V.; Rodriguez Arellano, J.J.; Doyere, V.; Stewart, M.G. Alterations in synaptic curvature in the dentate gyrus following induction of long-term potentiation, long-term depression, and treatment with the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist CPP. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabetova, S.; Sacktor, T.C. Long-term potentiation and long-term depression are induced through pharmacologically distinct NMDA receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 226, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogóz, Z.; Skuza, G.; Maj, J.; Danysz, W. Synergistic effect of uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists and antidepressant drugs in the forced swimming test in rats. Neuropharmacology 2002, 42, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poleszak, E.; Wlaź, P.; Kedzierska, E.; Nieoczym, D.; Wróbel, A.; Fidecka, S.; Pilc, A.; Nowak, G. NMDA/glutamate mechanism of antidepressant-like action of magnesium in forced swim test in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2007, 88, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomkowski, A.D.; Engel, D.; Gabilan, N.H.; Rodrigues, A.L. Involvement of NMDA receptors and L-arginine-nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway in the antidepressant-like effects of escitalopram in the forced swimming test. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 20, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Otani, S.; Kimura, S.I.; Shimamura, K.I.; Ishikawa, S.; Yanagawa, Y.; Togashi, H. Mechanisms underlying ketamine-induced synaptic depression in rat hippocampus-medial prefrontal cortex pathway. Neuroscience 2011, 177, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preskorn, S.H.; Baker, B.R.N.; Kolluri, S.; Menniti, F.S.; Krams, M.; Landen, J.W. An ınnovative design to establish proof of concept of the antidepressant effects of the NR2B subunit selective N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist, CP-101,606, in patients with treatment-refractory major depressive disorder. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2008, 28, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atez-Alagoz, Z.; Sun, S.; Wallach, J.; Adejare, A. Syntheses and pharmacological evaluationof novel N-substituted bicycloheptane-2-amines at N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2011, 78, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ates-Alagoz, Z.; Adejare, A. NMDA Receptor Antagonists for Treatment of Depression. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 480-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6040480
Ates-Alagoz Z, Adejare A. NMDA Receptor Antagonists for Treatment of Depression. Pharmaceuticals. 2013; 6(4):480-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6040480
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtes-Alagoz, Zeynep, and Adeboye Adejare. 2013. "NMDA Receptor Antagonists for Treatment of Depression" Pharmaceuticals 6, no. 4: 480-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6040480
APA StyleAtes-Alagoz, Z., & Adejare, A. (2013). NMDA Receptor Antagonists for Treatment of Depression. Pharmaceuticals, 6(4), 480-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6040480



