Abstract
Although previously thought of as the peripheral cannabinoid receptor, it is now accepted that the CB2 receptor is expressed in the central nervous system on microglia, astrocytes and subpopulations of neurons. Expression of the CB2 receptor in the brain is significantly lower than that of the CB1 receptor. Conflicting findings have been reported on the neurological effects of pharmacological agents targeting the CB2 receptor under normal conditions. Under inflammatory conditions, CB2 receptor expression in the brain is enhanced and CB2 receptor agonists exhibit potent anti-inflammatory effects. These findings have prompted research into the CB2 receptor as a possible target for the treatment of neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders. Neuroinflammatory alterations are also associated with neuropsychiatric disorders and polymorphisms in the CB2 gene have been reported in depression, eating disorders and schizophrenia. This review will examine the evidence to date for a role of brain CB2 receptors in neuropsychiatric disorders.
1. Introduction
The endogenous cannabinoid (endocannabinoid) system is an important lipid signalling system playing a key role in mediating and modulating physiological responses including central nervous, immune, endocrine, reproductive and cardiovascular system activity. The endocannabinoid system comprises the naturally occurring endogenous ligands (endocannabinoids), the best characterized of which are anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonyl glycerol (2-AG); the enzymes involved in the synthesis and degradation of these lipid mediators; and the G-protein coupled cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, through which the endocannabinoids mediate their effects. Endocannabinoids are synthesized on demand, with the phospholipase D catalysed hydrolysis of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine being primarily responsible for the synthesis of anandamide [1], while 2-AG synthesis is catalysed by the enzymes phospholipase C and diacylglycerol lipase [2]. The enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolyase (FAAH) preferentially catabolises anandamide and although 2-AG also acts as a substrate for FAAH, monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) is considered the primary enzyme involved in 2-AG inactivation [3]. In addition to CB1 and CB2 receptors, endocannabinoids also have affinity for, and activity at, transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and GPR55 [4,5,6,7]. Elements of this novel signaling system are widely and densely expressed in the mammalian brain [8,9], implying crucial roles in central nervous system function.
The cannabinoid CB1 receptor has been well characterised and is thought to mediate the majority of the psychoactive effects of cannabinoids due to its high level of expression in key central nervous system regions involved in movement, affective responding, cognition, temperature, appetite and neuroendocrine function [10,11,12]. Its localisation is predominantly presynaptic, and its direct activation by synthetic agonists, or by endocannabinoids that signal retrogradely, inhibits the release of neurotransmitters including GABA and glutamate [13]. However, the clinical utility of cannabinoids acting at CB1 receptors is limited due to confounding adverse central side effects and the development of tolerance [14,15]. This has led to increased interest in the possible clinical utility of endocannabinoid modulators and selective CB2 receptor ligands. The CB2 receptor has been categorised classically as the peripheral cannabinoid receptor due to its presence on the cells and tissues of the immune, reproductive, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and respiratory systems and numerous reports which were unable to detect CB2 receptor transcripts in normal healthy brain [12,16,17,18,19]. However, recent evidence, reviewed in detail in Section 2 below, suggests that CB2 receptors are present in the brain under normal and, in particular, under pathological conditions, although to a much lesser extent than the ubiquitously expressed CB1 receptors.
The CB2 receptor is encoded by a gene located on chromosome 1p36, and was first identified and cloned in 1993 [12]. It shares 48% homology with the CB1 receptor, and there is 82% sequence identity between the mouse and human CB2 receptor [20]. CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors are both seven-transmembrane domain receptors coupled to Gi/o proteins, activation of which inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity and initiates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt pathways [20]. The kinases in the MAPK signal transduction pathways activated by CB2 receptors include Jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 and p38. CB2 receptor-mediated inhibition of cAMP and activation of MAPK and PI3K-Akt signaling has been demonstrated in several cell types including those involved in central nervous system function such as microglial cells [21,22,23,24], neural progenitor cells [25,26] and cerebromicrovascular endothelial cells [27]. In addition, CB2 receptor activation enhances the synthesis of ceramide, a sphingolipid messenger, particularly in tumour cell lines including human leukemia cell line [28], prostate cancer PC3 cells [29] and DLD-1 and HT29 colon cancer cells [30] and also in neuroglioma [31,32] and human astrocytoma cells [33], a mechanism which induces apoptotic cell death. Based on the ability to inhibit forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation, it has been demonstrated that anandamide has low intrinsic activity at the CB2 receptor while 2-AG acts as a full agonist [34,35,36,37] and potentially the true natural agonist at the CB2 receptor. However, under pathological conditions anandamide levels are enhanced and have been proposed to mediate significant effects via CB2 receptors [22,38].
Due to the high density of CB2 receptors on peripheral tissues, particularly in cells and tissues of the immune system, the anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of CB2 receptor activation have received a great deal of attention. This research has led to the development of an ever increasing number of selective agonists for the CB2 receptor [39] some of which have undergone clinical evaluation. For example, Pharmos Corporation demonstrated that Cannabinor (formally PRS-211,375) did not elicit significant analgesic effects on capsaicin-induced pain but did so on pressure-induced and heat-induced pain and was well tolerated by patients in Phase 2 of clinical trials [40]. However according to their website [40] Pharmos Corporation has since decided to cease the development of Cannabinor for pain indications and explore possible collaborations towards retargeting this CB2 receptor agonist. Similarly, GlaxoSmithKline have also completed Phase 2 clinical trials evaluating the effects of the selective CB2 agonist GW842166, in osteoarthritis [41] and dental pain [42], although the results of these studies have not been published to date. Identification of CB2 receptors in the central nervous system has also led to increasing investigation into its involvement in neuroimmunological and neurodegeneratative disorders, topics which have been covered in detail by several recent reviews [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. The present review will provide an overview of the evidence demonstrating the presence of functional CB2 receptors in the brain, the role of this receptor in neurophysiology and highlight the potential involvement of these receptors in neuropsychiatric disorders.
2. Expression and Distribution of CB2 Receptors in the Central Nervous System
Several researchers have failed to identify CB2 receptor mRNA or protein in the brain under non-pathological conditions [12,16,17,18,19]. However, with the development of increasingly selective and sensitive tools for identifying CB2 receptors, there is now evidence demonstrating low expression of this receptor in the brain, although the functional significance of this expression remains to be fully elucidated. CB2 receptors have been identified on human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells [27], human foetal astrocytes [51] and limited populations of microglia [52,53] in the healthy human brain. A recent study employing in situ hybridization using specific riboprobes demonstrated CB2 receptor transcripts within the cerebral cortex, hippocampus and the globus pallidus of adult male Macaca fascicularis primate [54]. Comparably, CB2 receptor expression has been demonstrated in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, striatum, amygdala, thalamic nuclei, periaquaductal grey, cerebellum and several brain stem nuclei of the rodent brain [55,56,57,58,59,60,61]. Although many studies have identified central CB2 receptors on glial and endothelial cells, there is mounting evidence to support the expression of CB2 receptors on sub-populations of neurons within the central nervous system. In vitro studies have demonstrated the presence of CB2 receptor mRNA and/or protein on human sensory nerve fibres [62], dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord neurons [63,64], hippocampal neuronal cultures [25,26,56] and cerebellar Purkinje neurons [63].
One of the first studies to demonstrate CB2 receptor expression on neurons in situ in the brain was that of Skaper et al., who reported expression on cerebellar granular cells in the neonatal mouse brain [65]. At the time, research suggested that CB2 receptors were absent from the brain and therefore the authors concluded that agonism of a CB2-like receptor downregulates excitotoxic neuronal injury. The presence of CB2 receptors on neurons, microglia and capillary endothelia, but not astrocytes, in the cerebellum was subsequently confirmed in several studies [56,57,58,60,66]. However, the precise location and distribution of CB2 receptors on cerebellar neurons remains to be fully characterised. Several studies have demonstrated an association between the CB2 receptor and Purkinje cell bodies and dendrites [56,57,60], however a recent study failed to confirm this association [58]. This latter study identified CB2 receptors on cluster basket cell axons and parallel fibres in the molecular layer which may be associated with granular cells or mossy fibres in the granular layer. Similarly, CB2 receptors were originally postulated to be located post-synaptically on the cerebellar Purkinje dendrites [56], however, recent evidence suggests that both CB1 and CB2 receptors in the cerebellum are principally located pre-synaptically [58], suggesting that they, like CB1 receptors, may also play a role in endocannabinoid retrograde neurotransmission.
CB2 receptors have also been localised on neurons in various rodent brainstem nuclei including the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus, the nucleus ambiguous, spinal trigeminal nucleus [59], vestibular and cochlear nuclei [56,58,67] and inferior olive [58]. The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus is the integration site of emetic reflexes and co-activation of CB1 and CB2 receptors on neurons in this region induces anti-emetic effects in the ferret [59]. This was one of the first studies to highlight that although CB2 receptor expression in the brain is low under normal non-pathological conditions, its presence on brainstem neurons is of functional significance.
Expression of CB2 receptors outside the cerebellum and brainstem under non-pathological conditions has been controversial. Several investigators have failed to identify CB2 receptor transcripts or protein in forebrain regions [12,16,17,18,19]. However, Gong et al. provided the first evidence indicating that CB2 receptors may have a wider distribution in the brain when they demonstrated (using immunohistochemistry) CB2 receptor expression on both neuronal and glial processes in various rat brain regions including the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, striatum, amygdala, thalamic nuclei, periaquaductal grey, cerebellum and several brain stem nuclei [56,60]. However, in the same study [56], CB2 receptor mRNA expression was only identified in the striatum and hypothalamus and not in the olfactory bulb, cortex, thalamus or spinal cord. Further evidence for the expression of CB2 receptors in cortical areas includes reports of a small proportion of CB2 receptors identified on neocortical neurons [68] and moderate to heavy immunolabelling of dendrites and cell bodies of pyramidal neurons in the rat and mouse cerebral cortex [69]. In addition, recent evidence demonstrated CB2 expression on pyramidal neurons within layers III and V of the primate cerebral cortex [54]. CB2 receptors have also been identified on neural progenitor cells of the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus in the hippocampus [25] and interneurons primarily in CA1 and CA3 areas of the primate and rodent hippocampus [54,56,70,71]. The expression pattern of CB2 receptors in the hippocampus appears somewhat at odds between that reported for pre-pubertal [70] and adult [56] rats suggesting that CB2 receptor expression may change as a consequence of development. Evidence suggests that CB2 receptors are located primarily in cell bodies and dendrites, but not axons, in cortical areas and the hippocampus [55,60,70,71], indicating a post-synaptic localisation of these receptors. In comparison, both small unmyelinated axons and small dendrites in the substantia nigra exhibit CB2 receptor immunoreactivity, suggesting both pre- and post-synaptic localisation in this region [55]. The specific type of neurons expressing CB2 receptors and the functional significance of pre- and post-synaptic CB2 receptors remain to be determined. Recent evidence suggests that CB2 receptors may modulate GABAergic neurotransmission, at least in the entorhinal cortex [72]. In this study, CB2 receptor agonism with JWH-133 or 2-AG resulted in suppression of GABAergic inhibition in the medial entorhinal cortex while addition of the CB2 receptor antagonist/inverse agonist JTE-907 alone enhanced GABAergic transmission in this region.
Liu and colleagues recently identified two different isoforms of the CB2 receptor gene, the expression of which are species- and tissue-specific [73]. In this study, a new isoform of the human CB2 gene was identified, CB2 gene promoter transcribing testis (CB2A), which has a starting exon located 45kb upstream of the previously identified isoform from the spleen (CB2B). The authors demonstrate that CB2A mRNA expression is highest in the human testis, and to a lesser extent (<1% of testis expression) in the brain, when compared to the CB2B isoform which is expressed predominantly in the spleen, with very low levels (<0.1% of spleen expression) observed in the brain. CB2A mRNA expression was observed in the human amygdala, caudate, putamen, nucleus accumbens, hippocampus, cortex and cerebellum. It is possible that the failure of previous studies to demonstrate CB2 mRNA expression in the human brain may be due to the use of primers targeting the CB2B isoform rather than the CB2A isoform which appears to be more abundant in the brain. Identification of the different isoforms of the CB2 receptor has important implications for the development of agents targeting central receptor isoforms that may be devoid of associated widespread anti-inflammatory effects and vice-versa. In comparison to the human, mouse and rat homologues of both the CB2A and CB2B isoforms were identified in the spleen and in brain regions including the frontal cortex, striatum and brainstem (1% of the expression levels in the spleen). Expression of CB2A was approximately 5-fold greater than CB2B in the rodent brain [73]. This further highlights the difference between the human and rodent CB2 receptor genes and has important implications for the interpretation of results across species. Deletion of the C-terminus of the CB2 receptor is the most common means of generating the CB2 receptor knockout mouse [74]. Lui et al. demonstrated that in C-terminus CB2 receptor knockout mice, CB2A expression is downregulated and CB2B expression is enhanced in the spleen. In comparison, both CB2A and CB2B promoter activity and expression are enhanced in the brainstem of these knockout mice [73]. The authors suggest that enhanced levels of the CB2A and CB2B isoforms may reflect enhanced expression of a truncated CB2 receptor in the brain which may still be functionally active. Although further confirmatory studies are required, these findings may have important implications for the interpretation of results from studies using these mice.
The high expression of CB2 receptors on all components of the immune system and the potent anti-inflammatory effects of CB2 receptor agonists has lead to increased interest in the involvement of CB2 receptors in immune responses in the CNS. The first evidence for the possible involvement of brain CB2 receptors in neuroinflammation was provided by Benito and colleagues, who demonstrated the presence of CB2 receptors on microglia associated with neuritic plaques in Alzheimer’s disease [52]. CB2 expression has since been demonstrated in several other pathologies including adult and paediatric brain tumours [75], multiple sclerosis [76,77], amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [77], Down’s syndrome [78], Huntington’s disease [79] and HIV-induced encephalitis [80]. The involvement of CB2 receptors in the brain in these pathologies is further supported by preclinical studies demonstrating enhanced expression in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of multiple sclerosis [81,82], ischemia-reperfusion injury [83,84], R6/2 transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease [79], transgenic model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [85] and in response to simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis [80] and lipopolysaccharide injection [86]. Therefore, neuroinflammation is associated with enhanced CB2 receptor expression in the brain while CB1 receptor expression may be unaltered [52], reduced [87,88,89] or increased [82,90] under these conditions.
In addition to neuroinflammatory disorders, drugs of abuse and other pharmacological agents also modulate brain CB2 receptor expression. Enhanced CB2 receptor mRNA expression in whole brain extracts have been demonstrated following chronic administration of cocaine and heroin [91]. In addition, Torres and colleagues recently demonstrated enhanced CB2 receptor immunoreactivity in the frontal cortex of rats 3 hours following MDMA administration, an effect attenuated by repeated administration of the CB2 receptor agonist JWH-015 [92]. In contrast, preference for alcohol consumption was associated with a reduction in CB2 receptor transcripts in the ventral midbrain and striatum [69,93]. Chronic administration of the non-selective CB1/CB2 receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 significantly enhances CB2 receptor expression in the cerebellum but not frontal cortex, hippocampus, striatum, spleen or testis [73]. There was no effect of repeated administration of CB1 (AM251) or CB2 (AM630) antagonists on CB2 expression in the mouse brain [73].
3. Neurophysiological Functions Mediated by Central CB2 Receptors
Several studies have reported that CB2 receptor agonists/antagonists are devoid of psychoactive effects and have attributed the CNS effects of CB2 ligands to non-selective activity at CB1 or other non-cannabinoid receptors [94]. However, with increasing evidence for the presence of CB2 receptors in the brain, particularly on sub-populations of neurons, the involvement of this receptor in mediating possible neurological and psychoactive effects is receiving increasing attention. Alterations in locomotor responses and stereotyped behaviour observed in mice following the administration of high doses of selective CB2 receptor agonists/antagonists provides some evidence for a neurophysiological role of brain CB2 receptors, although non-selective effects at these doses cannot be ruled out. Acute blockade of the CB2 receptor using the antagonist SR144528 induces biphasic effects, increasing spontaneous locomotor activity in the DBA/2 mouse at low doses (1-10mg/kg) and reducing activity at high doses (20 mg/kg) [91]. In comparison, genetic deletion of the CB2 receptor is not associated with any change in motor co-ordination [95,96]. Increasing doses of the CB2 receptor agonist JWH-015 reduced locomotor activity and stereotyped behaviour, with females of three different mouse strains more affected than their male counterparts [60]. However, the authors did not determine if these effects were mediated specifically by CB2 receptor activation or due to effects at other non-selective targets. Similar locomotor depressant effects were observed following administration of an alternative CB2 receptor agonist GW405833 (100 mg/kg) [97], however a follow-up study determined that the central effects of GW405833 were not mediated by CB2 receptors, determined using CB2-/- mice [95]. In addition, the selective CB2 receptor agonists HU308 and AM1214, at doses that induced appreciable antinociceptive effects, did not affect locomotor activity [98,99]. Recent evidence has also demonstrated that administration of the selective CB2 receptor agonist AM1241, or antagonist AM630, failed to elicit a change in brain activity assessed by fMRI [100], leading these authors to conclude that CB2 receptors in the brain may not be functionally active under non-pathological conditions. However, it is also possible that the extent to which the CB2 receptor was modulated pharmacologically in this study may not have been of sufficient magnitude to elicit changes in neuronal activity detectable with fMRI methodology.
It has been proposed that functional interaction or co-operation between CB1 and CB2 receptors is required in order regulate neurophysiological function. This would account for the low intrinsic activity of CB2 ligands, administered alone, on CNS function. In line with this theory, Van Sickle and colleagues demonstrated that co-activation of both CB1 and CB2 receptors on neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus in the brainstem reduces emetic responses to morphine-6-glucuronide in the ferret [59]. However, CB2 receptor activation on dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus neurons using the selective agonist AM1241, or the endocannabinoid 2-AG, was not sufficient to inhibit emetic reflexes in the absence of CB1 receptor stimulation. Thus, activation of brain CB2 receptors alone may not be sufficient to modulate significant physiological effects such as emesis under non-pathological conditions.
It is well known that CB1 receptors are involved in the regulation of food intake and energy expenditure, prompting several companies to develop CB1 receptor antagonists/inverse agonists such as rimonabant, as potential anti-obesity agents [101]. However, repeated administration of these agents was associated with adverse psychiatric effects such as anxiety and depression in a small number of individuals, resulting in the withdrawal of the rimonabant from the European market. As such, attention has now turned to the involvement of endocannabinoids and CB2 receptors in regulating energy balance. Eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa have recently been associated with a Q63R polymorphism of the CB2 gene, with the R allele significantly more abundant in these individuals than controls [102]. Peripheral administration of the CB2 receptor partial agonist palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), and the CB2 receptor antagonist AM630, decreased food intake in non-fasting C57Bl/6 and DBA/2 mice [103]. The appetite suppressant effects of PEA were not affected by 12 hour food deprivation. However, following food deprivation, AM630 increased food intake in C57Bl/6 mice [103]. Similarly, intracerebroventricular administration of AM630 (5 µg) increased deprivation-induced food intake in male Lewis rats although no effect was observed at higher doses [104]. Thus, while antagonism of the CB1 receptor induces anorexia irrespective of fasting state, the effects of CB2 receptor ligands on food intake appear to depend on metabolic state. Thus, both CB1 and CB2 receptors in the brain appear to influence food intake in rodents although the precise mechanisms by which this occurs remain to be determined.
CB2 receptor agonists induce potent anti-hyperalgesic effects in models of acute, neuropathic and inflammatory pain [for reviews see [105,106,107]] although the involvement of central CB2 receptors in this response has not received a great deal of attention. One of the few studies to demonstrate an involvement of brain CB2 receptors in modulating nociceptive responding reported a reduction of noxious and non-noxious evoked responses in a rat model of neuropathic pain following the administration of the CB2 receptor agonist JWH-133 into the ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus [108]. Similarly, intrathecal but not peripheral administration of JWH-133 reversed mechanical allodynia associated with peripheral nerve injury in mice [109], further highlighting the involvement of central CB2 receptors in mediating neuropathic pain. The molecular mechanism mediating central CB2-induced anti-hyperalgesic effects is unknown, however, evidence indicates a functional interaction between CB2 and µ-opioid receptors, with SR144528 inhibition of CB2 receptors attenuating a noladin ether-induced decrease in µ-opioid receptor activity in the forebrain [110] while SR144528 alone reduces µ-opioid receptor activity and expression in the brainstem and cerebellum [111,112]. It is also possible that CB2 receptor agonists mediate their analgesic effects by inhibition of neuroinflammatory activity associated with neuropathic pain. Recent evidence has demonstrated a slight but non-significant increase in CB2 receptor expression in the spinal cord of a rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain [113], however it remains to be determined if central expression of this receptor is altered in other neuropathic pain states. It should also be noted that intra-thalamic administration of JWH-133 or SR144528 does not alter nociceptive responding in sham-controls [108]. Similarly, intracerebroventricular administration of JWH-133 did not alter inflammatory nociceptive responding following intra-plantar formalin administration [114] and intra-amygdaloid administration of the non-selective CB1/CB2 receptor agonist WIN55-212,2 attenuated formalin-induced nociceptive behaviour in rats via activity at CB1 but not CB2 receptors [115]. These findings further indicate that the physiological effects of brain CB2 receptors on nociceptive processing under non-pathological conditions may be minimal, but these receptors do appear to play a role under conditions of neuropathic pain.
4. Neuroinflammation and CB2 Receptors
Neuroinflammation encompasses a wide array of cellular processes including activation of microglia and astrocytes, enhanced pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, eicosanoids, complement activation and acute phase proteins. Cannabinoid compounds, plant-derived, synthetic and endogenous, are well known to elicit potent effects on inflammation, both peripherally and centrally. The presence of CB2 receptors on glia and neurons in the brain, has prompted several groups to investigate the role of this receptor in neuroinflammation and neuroprotection, a topic which has been covered in detail by several recent reviews [43,44,45,46,47,48,49]. This body of evidence suggests that CB2 receptor activation elicits glial-dependant anti-inflammatory effects, thereby reducing neuroinflammation associated with several neurodegenerative diseases. Neuroinflammatory processes have also been proposed to underlie the pathophysiology of several neuropsychiatric disorders and for this reason a brief overview of the role of CB2 receptors in neuroinflammation and its implications for psychiatric disorders will be presented here.
Enhanced CB2 receptor expression, primarily on activated microglia, occurs in several neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis and Huntington’s disease, and in experimental models of neuroinflammation [75,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,86]. Selective CB2 receptor agonists reduce symptoms and slow the progression of neurodegeneration in an animal model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [85] and in the EAE model of multiple sclerosis [82]. In turn, CB2 receptor deletion is associated with exacerbated neuroinflammatory responses and symptomatology in several animal models including EAE [82] and cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury [116]. Expression of CB2 receptors on microglia alters depending on their state of activation, with little to no receptors observed on microglia in the healthy brain [24,44,117,118]. Upregulation of CB2 receptors on microglia, as occurs in response to inflammatory conditions, modulates the activation, proliferation, differentiation and migration of these cells [21,24,119]. It is widely accepted that CB2 receptor activation is associated with potent anti-inflammatory responses, including inhibition of the release of inflammatory mediators including nitric oxide and cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1, tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α and IL-6 from both rodent and human microglial [22,23,120,121] and astrocytic [51,122,123] cells and enhanced release of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) [122,124]. In vivo studies have demonstrated that stimulation of CB2 receptors reduces microglial activation and the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in models of neuroinflammation [119,125], hypoxia-ischemia [90] and Huntington’s disease [79,126]. In the case of Alzheimer’s disease, pro-inflammatory cytokines in neuritic plaques interfere with the ability of microglia to phagocytose Aβ [127]. CB2 receptor activation is associated with enhanced removal of Aβ by THP-1 derived macrophages in Alzheimer’s disease brain sections [128]. Thus, it has been proposed that the increased ability of microglial cells to phagocytose Aβ is a consequence of the anti-inflammatory effects of CB2 receptor activation. Overall, the upregulation of CB2 receptors observed in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders possibly acts as a regulatory mechanism controlling the production and release of toxic inflammatory mediators from microglia and/or enhancing the neuroprotective effects of astrocytes.
CB2 receptors also regulate neuronal proliferation and survival [25,26,66,129]. CB2 receptor deficient mice exhibit reduced neural progenitor proliferation [25] and CB2 receptor antagonism is associated with a reduction in the development of new neurons in the olfactory bulb [129]. In comparison, selective agonism of the CB2 receptor results in enhanced neural stem cell proliferation, possibly via stimulation of MAPK-ERK and Akt pathways [25,26,129]. Increasing endocannabinoid tone using a reuptake inhibitor protects against AMPA-induced excitotoxicity, via modulation of CB1, CB2 and PPARγ signalling [130] and CB2 receptor agonism protects the striatum from malonate-induced neurotoxicity [126]. Furthermore, chronic administration of the non-selective CB1/CB2 agonist HU210 enhances neurogenesis in adult mice [131], and WIN55,212-2 triggers neurogenesis in the hippocampus of aged rats [132], effects which may, in part, be mediated by activity at CB2 receptors. Although these findings have important implications for the development of novel therapeutics for acute brain injury and chronic neurodegenerative disorders, it is possible that CB2 receptors may also have a role to play in psychiatric disorders such as depression and schizophrenia which are associated with enhanced inflammatory responses and reduced neurogenesis.
5. CB2 Receptors and Neuropsychiatric Disorders
5.1. Stress and Anxiety
The role of the endocannabinoid system in mediating fear, stress and anxiety has been researched extensively over the past decade (for recent reviews see [133,134,135]). In general, CB1 receptor activation elicits complex bi-phasic effects on stress-responding and recent evidence indicates that this may in part be due to differential activation of CB1 on forebrain glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons that elicit anxiolytic and anxiogenic effects respectively [136]. As mentioned in earlier sections, several studies have demonstrated a lack of psychoactive effects such as catalepsy, hypolocomotion and hypothermia following pharmacological modulation of the CB2 receptor [98,99,137] and, as a consequence, the role of CB2 receptors in regulating stress and anxiety has received little attention. The data reviewed above in Section 2 demonstrating expression of CB2 receptors in key brain areas involved in modulating the stress response including the amygdala, hippocampus, prefrontal cortex and hypothalamus [56,60,70,71,138], suggest that the potential role of CB2 receptors in regulation of emotional responding is at least worthy of investigation. To date, most studies examining the effect of selective CB2 receptor agonists on CNS function have examined the ability of ligands to modulate locomotor activity, with few studies examining effects in validated models of emotionality/anxiety. Unconditioned responding in stressful environments or conditioned responses to a previously learned aversive stimulus are the most commonly used means of assessing anxiety-related behaviour in animals. Onaivi and colleagues have assessed stress-induced anxiety-related behaviour in the two-compartment black and white test (also known as the light-dark test) and in the elevated plus maze following the administration of CB2 receptor ligands [60,91]. Acute systemic administration of JWH-015 (1-20 mg/kg) dose dependantly induced an anxiogenic response in the black and white box, with females slightly more sensitive than males [60,139]. In contrast, JWH-015 (20 mg/kg) attenuated stress-induced gender-specific aversion to the open arms of the elevated plus maze [139] and administration of the CB2 receptor agonist GW405833 (100 mg/kg) induced anxiolytic effects in the marble burying test [97]. However, it should be noted that the behavioural effects of CB2 receptor stimulation in these studies was accompanied by reduced locomotor activity at the doses used [60,97,139], and administration of a CB2 receptor antagonist failed to reverse either the locomotor depressant or the anxiolytic effects observed in the marble burying test [95], which may have important implications for the interpretation of the effects observed. Chronic administration of JWH-015 results in an anxiolytic behavioural profile in the black and white box [60] and reduces stereotypic behaviour in non-stressed but not stressed BALB/c mice [139], which the authors interpret as an anxiolytic profile. However, it should be noted that stereotypic behaviour represents locomotor activity and rearing and, as such, may be more accurately interpreted as a measure of general activity rather than a measure of anxiety-like behaviour.
In contrast to the effects observed following CB2 receptor stimulation, CB2 receptor antagonism using SR144528 had little or no effect in the black and white box, with the exception of a decrease in time spent in the white chamber in DBA/2 male mice at 20 mg/kg SR144528 [91], again possibly a result of reduced locomotor activity observed at this dose. Repeated (3 day) intracerebroventricular administration of CB2 antisense oligonucleotide increased the amount of time spent on the open arms of the elevated plus maze indicative of an anxiolytic-like effect [61,139], however, the effect of this treatment on locomotor activity in the maze was not reported. Only one published study to date has examined the role of brain CB2 receptors in conditioned aversion/learning, demonstrating that infusion of JWH-015 or PEA into the CA1 region of the hippocampus does not affect novel object recognition or long-term memory retention [140]. Overall, the results obtained from behavioural studies of the role of CB2 receptors in modulating the response to aversion are far from clear, highlighting the need for further studies examining the effects of selective deletion, blockade or stimulation of brain CB2 receptors on the regulation of emotional responding.
A critical component of the stress response is the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the subsequent increase in glucocorticoid levels and several studies have examined the role of the endocannabinoid system in mediating this response [141]. CB2 receptor mRNA and protein have been identified in the brain regions that modulate HPA axis activity including the hippocampus, amygdala and hypothalamus [56,71], while in comparison, CB2 receptors are not expressed in the adrenal cortex [142], indicating that should CB2 ligands modulate the neuroendocrine response to stress, this would most likely occur at the level of the brain. Our studies have indicated that endotoxin-induced increases in circulating corticosterone levels are not altered by administration of the non-selective CB1/2 receptor agonist HU-210 or the CB2 receptor antagonist/inverse agonist SR144528 [125]. Further studies will be required to determine whether CB2 receptors are involved in the endocannabinoid-mediated modulation of neuroendocrine activity under basal and stress conditions.
Although Onaivi and colleagues demonstrated similar effects of the CB2 receptor ligand JWH-015 on locomotor activity and stereotypic behaviour in three strains of mice, namely C57Bl6/J, DBA/2 and BABL/c, they did not compare behavioural responses between these different strains in tests of emotionality and anxiety [139]. BALB/c mice have been proposed as a model of anxiety and are regarded as more stress-sensitive than other mouse strains including C57Bl6/J and DBA/2 mice [143,144,145]. For example, BALB/c mice exhibit an anxiogenic profile in the black and white box, manifested as a reduced time in the white compartment of the test apparatus when compared to C57Bl6/J counterparts [145]. Therefore, due to the contribution of genetic background to stress responding, it is possible that CB2 ligands may elicit differential effects depending on the strain of mouse used. In accordance, low doses of JWH-015 (5 mg/kg) increased stereotypic behaviour in male DBA/2 but not C57Bl6/J or BALB/C mice [60]. No significant difference in whole brain CB2 receptor expression prior to or following chronic stress was observed between the three different mouse strains [139]. However, it remains to be determined if the density or function of CB2 receptors or other components of the endocannabinoid system are differentially altered between these different strains of mice in brain regions associated with stress responding. Accordingly, early life stress such as maternal deprivation induces an anxiogenic behavioural phenotype [146] which has recently been associated with enhanced CB2 receptor expression in the hippocampus [70]. Thus, greater understanding of the role of CB2 receptors in pathological anxiety states will be reached by examining the expression, distribution and functional activity of these receptors in preclinical models that exhibit ethological validity.
5.2. Depression
The involvement of the endocannabinoid system in the regulation of mood and affective responding has received increasing interest in the past few years (for recent reviews see [147,148,149]), particularly in light of the withdrawal of rimonabant (CB1 receptor antagonist/inverse agonist) as an anti-obesity agent due to the increased risk of psychiatric side effects, including depression. The involvement of CB1 receptors in regulating mood is further supported by the upregulation of CB1 receptor expression and function in the prefrontal cortex of depressed suicide victims [150] and enhanced CB1 receptor density in the prefrontal cortex of alcoholic suicide victims compared with alcoholic controls [151]. Furthermore, allele variations in the CB1 receptor gene CNR1, plays a role in the antidepressant response in major depressed patients [152] and a cohort of elderly depressed Parkinsonian patients have demonstrated a polymorphism (AATn) of the CNR1 [153]. Preclinical evidence further supports the involvement of CB1 receptors in depressive-like behaviour [154,155] and suggests that the effects of currently used antidepressants might depend upon endocannabinoid system modification. For example, endocannabinoid-CB1 receptor signaling in the brain is altered by several interventions that elicit antidepressant activity in humans, including chronic tricyclic antidepressant treatment [156,157], repeated electroconvulsive therapy [158] and sleep deprivation [159]. In contrast, the involvement of the CB2 receptor in affective responding has not received similar attention. A recent study has, however, demonstrated an association between depression and a polymorphism in the CB2 receptor gene at position Q63R in Japanese patients [69]. Polymorphisms in the Q63R in the CB2 gene have also been linked with eating disorders, alcoholism, osteoporosis, autoimmune disease and schizophrenia [93,102,160,161], many of which often demonstrate co-morbidity with depressive illness. Although it remains to be determined if this genetic link exists across other ethnic groups, it is possible that genetic variation in the CB2 gene may be a predisposing factor in the development of depression. CB2 receptor mediated effects of cannabinoid agonists such as WIN55,212-2 and 2-AG are reduced in the presence of the Q63R polymorphism [160,162] and serum levels of 2-AG and anandamide are reduced in patients with major depression, an effect directly correlated with the duration of the depressive episode [163]. Although further studies are required, in addition to alterations in endocannabinoid levels and CB1 receptor signaling, central CB2 receptor expression or function may be altered in depressed patients.
The association between adverse life events and the development of depression is widely acknowledged, and, as a consequence, many of the preclinical models of depression or antidepressant-like activity exploit this link by examining behavioural and physiological responses to stress. One of the most widely used behavioural tests for antidepressant-like activity is the forced swim test, where rodents exposed to a confined swim arena will initially attempt to escape but after some time will assume a floating posture (immobility) that is thought to be related to a state of behavioural despair [164]. Antidepressant agents increase escape behaviour thereby reducing the duration of immobility, while in comparison, an increase in immobility is regarded as a depressive-like state. Antidepressant-like activity of cannabinoid ligands and endocannabinoid modulators such as FAAH and anandamide reuptake inhibitors, have been demonstrated in the forced swim test [131,155,165,166,167,168,169,170,171]. In many of the studies, the antidepressant-like effects have primarily been attributed to activity at the CB1 receptor, confirmed using receptor antagonists and/or genetic deletion. Recent evidence has indicated that CB1 receptors on subpopulations of glutamatergic, but not GABAergic, neurons appear to mediate the forced swim stress-induced behavioural and neuroendocrine effects [172]. However, non-selective CB1/CB2 receptor agonists and endocannabinoid modulators may also activate CB2 receptors. Antidepressant-like activity following chronic CB1/CB2 receptor stimulation using HU210, but not CB1 receptor agonism (AM281) alone, was observed in the forced swim test [131]. In addition, intra-hippocampal administration of HU210 induced an antidepressant-like effect in the forced swim test, an effect only partially attenuated by pharmacological blockade of the CB1 receptor [169]. Although further studies are required in order to further determine the mechanism of action underpinning these effects of non-selective CB1/CB2 agonists, it is possible that activation of central CB2 receptors may co-operatively augment the effects of CB1 receptor activation on stress-induced behaviour and monoaminergic function. Presently, only one study has been published directly assessing the effect of pharmacological CB2 agonism in the forced swim test, reporting that acute administration of the CB2 agonist GW405833 did not alter time spent immobile in the forced swim test [173]. However, in the presence of neuropathic pain, CB2 receptor activation reduced nociceptive responding to a mechanical stimulus while concurrently attenuating the enhanced immobility observed in the forced swim test [173]. The present results indicate that CB2 receptor agonism may alleviate neuropathic pain and the co-morbid depressive symptoms that often accompany this disorder. In an interesting study published recently, García-Gutiérrez and colleagues employed both pharmacological and genetic approaches to investigate the role of the CB2 receptor in depressive-like behaviour [138]. Transgenic mice engineered to over-express the CB2 receptor (including over-expression in key brain regions implicated in depression) exhibited reduced depressive-like behaviour in the tail suspension test and in a novelty suppressed feeding test, compared with wildtype controls. However, acute intraperitoneal administration of the CB2 receptor antagonist AM630, at doses that had no effect on locomotor activity, had an antidepressant-like effect in the forced swim test in wildtype mice, but not in CB2 over-expressing mice [138]. Though the depression-resistant endophenotype associated with CB2 over-expression and the antidepressant-like effects of CB2 receptor blockade pose an apparent discrepancy which is difficult to reconcile, these data do at least demonstrate an important role for the CB2 receptor in regulating depressive state in mice. More studies examining the effects of direct activation/inhibition of brain CB2 receptors are required in order to determine conclusively the role this receptor plays a role in stress-induced behavioural changes.
A detailed understanding of the neurobiological underpinnings of depression requires pre-clinical models that mimic the neurological and physiological alterations that characterise this psychiatric disorder. Chronic mild or unpredictable stress (CMS) is a widely used and validated preclinical model of depression displaying several behavioural and physiological alterations that mimic those observed in the clinical setting [174,175]. CMS is associated with reduced 2-AG levels in the hippocampus, enhanced anandamide levels in limbic and cortical areas and differential expression of CB1 receptor with increased receptor expression in the prefrontal cortex and a concurrent decrease in the hippocampus, hypothalamus and ventral striatum [156,176]. One of the first studies to imply that the CB2 receptor may be implicated in depression was that of Onaivi et al., where they demonstrated that CB2 protein levels measured by western immunoblotting in whole brain extract were enhanced in mice subjected to CMS for a period of 4 weeks [61,69]. However, the anatomical region(s) associated with the enhanced CB2 protein expression or the identity of the cells that express this receptor, i.e., glia or neurons, were not identified. CB2 receptor mRNA was detected in the striatum, midbrain and hippocampus of control and CMS exposed mice, however, no significant difference in expression was observed between the groups [61]. More recently, García-Gutiérrez and colleagues demonstrated that CMS in mice for 7-8 weeks resulted in reduced levels of CB2 mRNA in the hippocampus of mice, compared with non-stressed controls. Moreover, this stress-induced reduction was prevented by chronic administration of the CB2 receptor antagonist AM630 [138]. Behaviourally, acute treatment with JWH-015 reduced stereotypic behaviour in stressed but not non-stressed mice whereas the converse was observed following chronic treatment [139]. This group have also reported that reduced spontaneous locomotor activity of mice subjected to CMS was enhanced by acute and chronic treatment with JWH-015. In addition, CMS-induced anxiogenic behaviour in the elevated plus maze was attenuated by acute administration of JWH-015 [60,69]. CMS is associated with reduced intake of palatable solutions such as sucrose, used as a measure of anhedonia, a hallmark of depressive-illness. Daily administration of either the CB2 receptor agonist JWH-015 or the CB2 receptor antagonist AM630 did not alter chronic stress-induced decreases in sucrose consumption [69,91]. Administration of JWH-015 for a period of 2 weeks increased sucrose consumption in control but not stressed animals, an effect not observed at later time points. Although the authors report no effect of AM630 on sucrose consumption, examination of the data indicates that sucrose consumption was reduced in control, but not stressed mice, from week 2 of treatment with this CB2 receptor antagonist (3 mg/kg) [69]. Based on these findings it would appear that stress blocks CB2 receptor modulation of hedonic responses. Similarly, although CB2 receptor ligands elicit no effect on alcohol consumption in control mice, enhanced alcohol consumption following CMS is augmented by JWH-015 and slightly attenuated by AM630 [93]. In addition to providing further evidence for a differential role of CB2 receptors in modulating behaviour in stressed versus non-stressed animals, the results of this latter study also raise the possibility of a role for CB2 receptors in the co-morbidity of depression and alcohol abuse. Recently it has been shown that transgenic mice engineered to over-express the CB2 receptor are resistant to CMS-induced reductions in sucrose consumption and increases in tail suspension test immobility time [138]. The CB2 over-expressing mice were also resistant to CMS-induced reductions in brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in the hippocampus. While these results suggest that the CB2 over-expression results in a depression-resistant endophenotype, the same study also reported that pharmacological blockade of CB2, with chronic administration of the CB2 receptor antagonist AM630 for 4 weeks, prevented the effects of CMS on tail suspension test, sucrose intake, CB2 receptor gene, BDNF gene and protein expression in wildtype mice. The authors speculate that the chronic antagonist treatment may have lead to increased expression of CB2 in key brain regions, thereby mimicking the phenotype of the CB2 over-expressing transgenic mice. Taken together, these results indicate that CB2 receptors may play an important role in mediating behavioural and molecular effects associated with CMS.
Early life stress has been linked with a predisposition to psychiatric disorders in later life, resulting in the development of several preclinical models based on this association. One such model is the maternal deprivation (MD) model which involves separation of neonatal rats from the dam for a single 24 hour episode resulting in long-lasting behavioural, neurochemical and immune changes and has been proposed as a model of several neuropsychiatric disorders including depression. The depressive-like phenotype associated with MD includes decreased latency to immobility in the forced swim test [177,178], reduced locomotor activity and social investigatory behaviour [178] and enhanced impulsivity [179]. Alterations in the endocannabinoid system have been demonstrated in this model where MD is associated with enhanced hippocampal 2-AG levels [180] and reduced CB1 and increased CB2 receptor expression in the hippocampus [70]. Although both male and female MD rats exhibited a comparable increase in hippocampal CB2 receptor expression, CB1 receptor expression demonstrated sexual dimorphism, with a greater MD-related decrease observed in males when compared to females [70]. Examination of gender-specific effects is of particularly importance due to the enhanced prevalence of neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders in women. Detailed examination of the location of these receptors demonstrates that hippocampal CB2 receptors are located on dendritic terminals and not microglia [70]. This is consistent with the finding that CB2 receptors are located post-synaptically in the hippocampus [55] in comparison to the CB1 receptor that is primarily located on pre-synaptic GABAergic and glutamatergic terminals [181,182]. It remains to be determined if similar alterations in the expression of cannabinoid receptors occurs in other brain regions in this model. Thus, MD-induced changes in CB2 receptor expression, and other components of the endocannabinoid system may underlie some of the behavioural, cognitive and neuroendocrine changes observed in this model and in the neuropsychiatric disorders it models.
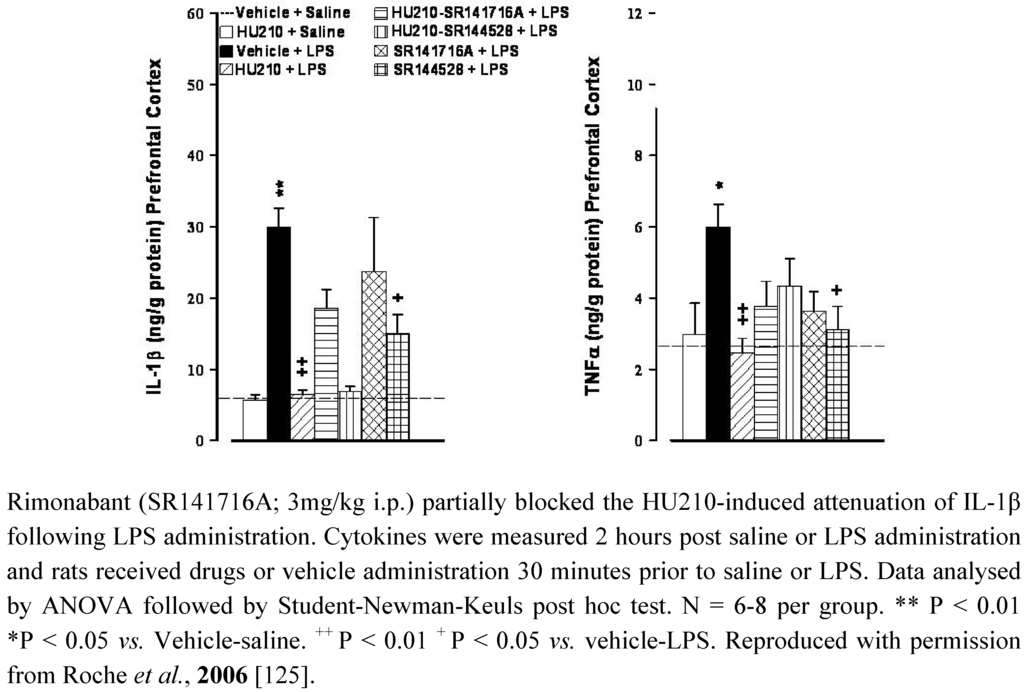
Figure 1.
The CB1/CB2 receptor agonist HU210 (100 µg/kg i.p.) and CB2 receptor antagonist SR144528 (3mg/kg i.p.) attenuated LPS (100 µg/kg i.p)-induced increases in IL-1β and TNFα levels in the prefrontal cortex in rats.
The functional significance of the alterations in cannabinoid receptor expression in animal models of depression remains to be determined however, as previously highlighted, CB1 and CB2 receptors modulate neural stem cell proliferation in culture [26,183]) and/or in adult mice [25,129,184,185]. Impaired hippocampal neurogenesis has been proposed to underlie the pathophysiology of depression (for reviews see [186,187,188]). Neurogenesis relies on several factors including neurotrophins such as brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a reduction in which has been observed in depressed patients [189,190,191] and in preclinical models including CMS [192] and MD [193]. Antidepressants, as a class, reverse pathological stress-induced reductions in adult hippocampal neurogenesis [194], an effect at least partially mediated by enhancing BDNF, TrkB receptor signaling and activation of MAPK/ERK pathways [195,196,197,198]. Similarly, chronic, but not acute, treatment of rats with the CB1/CB2 agonist HU210, but not the selective CB1 agonist AM281, enhanced hippocampal neurogenesis and elicited antidepressant-like behavioural effects [131]. The inability of AM281 to modulate neurogenesis or immobility behaviour may indicate a role for CB2 receptors in the effects of HU210, promoting neuronal survival and differentiation in the hippocampus. In addition, WIN55,212-2 induced activation of both CB1 and CB2 receptors enhances neurogenesis in the hippocampus of aged rats [132]. As highlighted earlier, immunological mediators also modulate neurogenesis, with high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines considered detrimental to neuronal viability. It has been proposed that the reduced neurogenesis observed in depression is due, at least in part, to the enhanced immune activation and elevated cytokine levels that are a feature of this psychiatric disorder [199], an effect also demonstrated in several animal models including CMS and MD [178,200,201]. Furthermore, immune stimuli such as endotoxins activate microglia and enhance inflammatory cytokine levels in the brain resulting in reduced BDNF [202], reduced neurogenesis [203,204] and depressive-like symptoms [205]. We have previously shown that HU210 attenuates endotoxin-induced increases in IL-1β and TNFα in rat brain, effects partially mediated by CB1, but not CB2, receptors [125]. However, blockade of either CB1 or CB2 receptors, using rimonabant or SR144528 respectively, also attenuated lipopolysaccaride (LPS)-induced cytokine levels in the brain [125] (Figure 1). In addition, administration of the endotoxin LPS enhances endocannabinoid levels [206,207,208] and increases CB2 receptor protein expression in the brain (detected using western immunoblotting) [86]. Based on the clinical and preclinical evidence, we hypothesise that depression is associated with altered endocannabinoid function including that of the brain CB2 receptors, activation of which would reduce inflammatory responses, enhance neurogenesis and result in antidepressant activity (Figure 2).
5.3. Schizophrenia
The role of the endocannabinoid system in schizophrenia has received considerable attention and has be covered in detail in several recent reviews [209,210] including those within this special issue [211,212]. Therefore, this section will concentrate primarily on the putative role of the CB2 receptor in this disorder.
Ishiguro and colleagues have recently demonstrated that Japanese schizophrenic patients exhibit an increase in the frequency of two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the CB2 receptor gene, namely rs12744386 and Q63R, which confer lower functioning of the CB2 receptor [160]. Low levels of CB2 receptor mRNA and protein in the brain and lympohocytes were associated with the C allele of rs1274486 gene, a genotype commonly observed in schizophrenic patients.
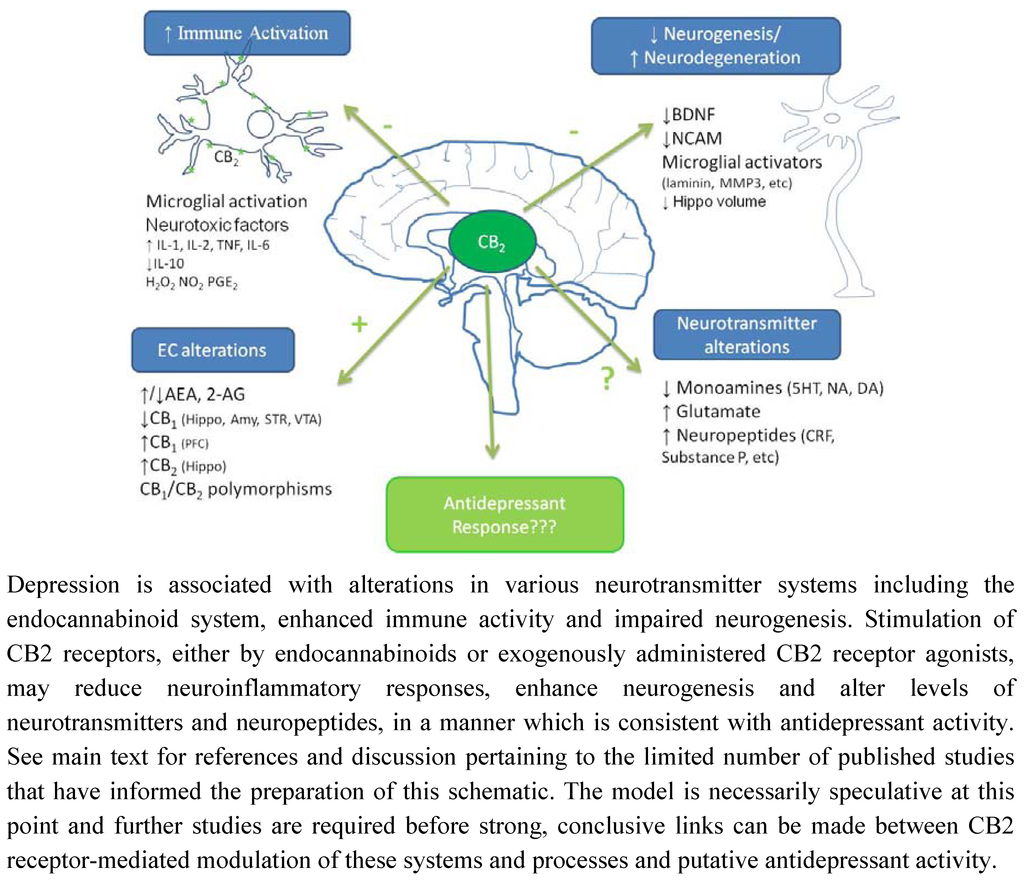
Figure 2.
Putative mechanisms underpinning potential antidepressant effect of CB2 receptor stimulation.
As mentioned earlier, the other SNP (rs2501432) is a mismatch Q63R, the presence of which leads to poor response to CB2 ligands [160]. Thus, the presence of both SNPs may synergistically confer enhanced susceptibility to schizophrenia. In line with these observations, schizophrenia is associated with enhanced cerebrospinal fluid levels of anandamide and PEA, and remission from which is associated with reduced anandamide levels and peripheral blood mononuclear cell CB2 receptor mRNA expression [213,214,215]. It is unknown if similar changes in CB2 receptor expression are observed in the brain, however, neuroleptic treatment reduces G-protein functioning in schizophrenic patients [216], and as such may induce similar effects on G-protein coupled cannabinoid receptors.
The effect of CB2 receptor antagonists on MK-801- or methamphetamine-induced disturbances in pre-pulse inhibition (PPI) have also been examined. PPI is a widely used behavioural test of sensorimotor gating, deficits in which are commonly observed in schizophrenic patients [217,218]. Essentially, PPI refers to the ability of a weak pre-stimulus, a pre-pulse, to inhibit the startle reflex elicited by a subsequent intense stimulus. Administration of the CB2 receptor antagonist, AM630, alone, did not alter PPI, however AM630 did augment the MK-801- and metamphetamine-induced reduction in PPI and increase in locomotor activity [160]. It has been proposed that that a decrease in CB2 receptor functioning alone does not lead to the development of schizophrenia but that in the presence of other risk factors, reduced CB2 receptor functioning may confer enhanced susceptibility to the development of this disorder.
Disorganised stereotypic behaviour is common in psychotic individuals, mediated by hyperdopaminergic functioning and alleviated by antipsychotic treatment. CB1 receptor desensitization due to chronic cannabinoid treatment or CB1 receptor antagonism exacerbates dopamine receptor-induced stereotypic behaviours [219,220]. Although the role of CB2 receptors in directly mediating or modulating dopamine-induced effects has not been investigated, CB2 receptor agonists reduce stereotypic behaviour in a dose-dependent and gender specific manner [60] as outlined in previous sections. In addition, CB2 receptors modulate key neurotransmitter systems involved in schizophrenia such as dopaminergic and glutamatergic function, possibly via microglial inhibition. For example, CB2 receptor agonists prevent 6-hydroxydopamine induced dopamine depletion [221] and glutamate receptor (AMPA, kainate and NMDA) mediated excitotoxicity [25,79,122,222]. Alterations in cannabinoid receptor expression may induce profound alterations in neurotransmission (dopaminergic and/or glutamatergic) and/or, modulation of hippocampal axonal growth and plasticity, which may confer a predisposition to the development of schizophrenia. MD and/or exposure to cannabinoids during critical neurodevelopmental periods have been proposed to induce such neurochemical alterations which may underlie the psychotic-like behavioural alterations. In addition to the depressive-like phenotype exhibited following MD, this model also results in long-term behavioural alterations that resemble symptoms observed in schizophrenia, including deficits in PPI, latent inhibition and auditory sensory gating [223,224]. The behavioural alterations associated with MD, combined with the neuronal, endocrine and immune alterations observed, support its usefulness and relevance as a model based on the neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia. As previously mentioned MD is associated with alterations in the endocannabinoid signalling system including reduced CB1 expression and enhanced CB2 receptor expression in the hippocampus [70,146,180]. Although an increase in CB2 receptor expression in the hippocampus of MD rats may seem at odds with data suggesting that schizophrenia is associated with reduced CB2 receptor functioning, it should be noted that although the density of CB2 receptors is enhanced, significant impairment in function may exist. In addition, CB2 receptor expression was assessed in pre-pubertal MD rats and the density and distribution pattern of this receptor may be different in adults.
Schizophrenia is associated with altered neuroimmune functioning, primarily an imbalance between type-1 and type-2 immune responses, which is thought to underlie altered neuronal function including neurotransmitter alterations and reduced neurogenesis (for review see [225,226,227,228]). In addition, epidemiological data have demonstrated an association between prenatal infection, enhanced pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and increased risk of psychiatric disorders in later life, including schizophrenia [229], an association exploited in order to develop more ethologically valid models of schizophrenia. This imbalance in immune function is also observed in neurodevelopmental models such as MD [178,200]. Antipsychotic medication and anti-inflammatory agents such as COX-2 inhibitors alleviate psychotic symptoms, correct the imbalance in type-1 and type-2 responses and reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine release [225,226]. It remains to be determined whether the anti-inflammatory effects of CB2 receptor agonism might confer protection and enhancement of neuronal function of sufficient magnitude to alleviate psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia.
The enhanced prevalence of schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders such as anxiety and depression in women highlights the need for more studies examining gender differences in the development of these disorders. Gonadal hormones have been demonstrated to alter expression of cannabinoid receptors [230] and females in general are more sensitive than males to the behavioural effects of cannabinoids [231]. As highlighted in earlier sections, few studies have examined the effect of CB2 ligands in animal models of neuropsychiatric disorder and for the most part these studies have been confined to examining effects in male animals. However, it has been demonstrated that the CB2 receptor agonist JWH-015 reduces stereotypic behaviour in female mice at a dose (10 mg/kg) that is ineffective in male counterparts [60]. In addition, sexually dimorphic effects on hippocampal CB1 receptor expression have been demonstrated in the MD neurodevelopmental animal model, with a more marked MD-related decrease observed in male rats compared with female rats [70]. In comparison, comparable increases in CB2 receptor expression were observed in male and female rats. As such further studies are required in order to determine if gender-specific alterations in endocannabinoid function may underlie the development of, and differential susceptibility to, neuropsychiatric disorders.
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Due to the increased availability of tools which have allowed for a more specific analysis of the neuroanatomical distribution, neurophysiology and neuropharmacology of the CB2 receptor, considerable evidence now exists to support the presence of CB2 receptors on microglia and subpopulations of neurons within the brain, contrary to the belief widely held previously that this receptor was restricted to peripheral locations. Further studies are required in order to elucidate the role of this receptor under non-pathological conditions, however, central endocannabinoids may act primarily at CB1 receptors with possible co-operative effects at CB2 receptors, in order to maintain normal homeostasis. In comparison, several pathophysiological conditions are associated with altered CB1 and CB2 receptor expression and/or function, and under such conditions, endocannabinoid activity at CB2 receptors may have greater significance. Such a mechanism would explain why CB2 receptor ligands elicit little or no psychoactive effects in experimental settings mimicking normal acute physiological responding, but may exert potent effects in models of disease states such as neurodegenerative disorders and chronic pain. This may have important therapeutic implications as CB2 receptor agonists may be devoid of psychoactivity under normal non-pathological conditions and in disorders associated with increased CB2 receptor expression in peripheral tissues. However, in conditions associated with increased CB2 receptor expression in the brain, these receptors may elicit appreciable CNS effects. For example, increased central CB2 receptor expression on microglia as observed in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders may be targeted to induce an anti-inflammatory environment that promotes neuroprotection and/or neuroregeneration. Similarly, CB2 receptors on microglia and neurons in critical brain regions involved in regulating emotion may be altered in psychiatric disorders such as anxiety, depression and schizophrenia, and targeting these receptors may reduce neuroinflammatory processes, enhance neurogenesis and modulate neurotransmitter systems thereby alleviating symptoms associated with these disorders (Figure 2).
More studies evaluating the involvement of CB2 receptors in psychiatric disorders are both justified and required. Such studies should employ the full range of tools that are available to study the CB2 receptor, including reliable, well-characterised and validated antibodies and primers, selective CB2 receptor agonists and antagonists and CB2 receptor transgenic mice (knockouts or overexpressing) to evaluate the interaction between these receptors and other components of the endocannabinoid system in appropriate animal models. The selectivity of CB2 receptor ligands continues to improve with several compounds entering clinical trials for non-psychiatric disorders (e.g., osteoarthritis, dental pain). Careful evaluation of the side effects associated with chronic treatment of these agents will provide further insight into the potential role of CB2 in regulating neurophysiological function. In addition, the development of more selective probes such as high quality antibodies, and studies which employ a variety of anatomical, functional and biochemical techniques in order to evaluate the expression and function of CB2 receptors will lead to increased knowledge on the role of this receptor in the brain. As we have seen, some very interesting data have begun to emerge. However, the evidence to-date for a role of CB2 receptors in neuropsychiatric disorders is largely indirect, and so further studies are required to determine the precise pathophysiological contribution of the CB2 receptor and its true potential as a viable therapeutic target in neuropsychiatric disease.
Abbreviations
| 2-AG | 2-arachidonyl glycerolc |
| AEA | anandamide |
| AMPA | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptor |
| BDNF | brain derived neurotrophic factor |
| CMS | chronic mild stress |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| EAE | experimental auto- immune encephalomyelitis |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| FAAH | fatty acid amide hydrolyase |
| IL-1 | interleukin-1 |
| JNK | Jun N-terminal protein kinase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MD | maternal deprivation |
| MAGL | monoacylglycerol lipase |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartic acid |
| OEA | N-oleoylethanolamide |
| PEA | Palmitoylethanolamide |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PPAR | peroxisome proliferator- activated receptors |
| PPI | pre-pulse inhibition |
| TNFα | tumour necrosis factor-α |
| TRPV1 | transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 |
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge funding received from Health Research Board of Ireland, Science Foundation Ireland and the National University of Ireland Galway, Millennium Fund.
Endogenous Ligands and Pharmacological Agents Cited
Endocannabinoids: 2-AG, AEA
Fatty acid amides: PEA, OEA
Non-selective cannabinoid receptor agonists: HU210, WIN55,212-2
CB1 receptor agonists: AM281
CB1 receptor antagonists/inverse agonists: Rimonabant (SR141617A), AM251
CB2 receptor agonists: JWH-015, JWH-133, AM1241, GW405833, PEA (partial)
CB2 receptor antagonists: AM630, SR144528, JTE-907
References
- Di Marzo, V.; De Petrocellis, L.; Sepe, N.; Buono, A. Biosynthesis of anandamide and related acylethanolamides in mouse J774 macrophages and N18 neuroblastoma cells. Biochem. J. 1996, 316, 977–984. [Google Scholar]
- Stella, N.; Schweitzer, P.; Piomelli, D. A second endogenous cannabinoid that modulates long-term potentiation. Nature 1997, 388, 773–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, K.; McKinney, M.K.; Cravatt, B.F. Enzymatic pathways that regulate endocannabinoid signaling in the nervous system. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 1687–1707. [Google Scholar]
- Ryberg, E.; Larsson, N.; Sjogren, S.; Hjorth, S.; Hermansson, N.O.; Leonova, J.; Elebring, T.; Nilsson, K.; Drmota, T.; Greasley, P.J. The orphan receptor GPR55 is a novel cannabinoid receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Pertwee, R.G. GPR55: a new member of the cannabinoid receptor clan? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 984–986. [Google Scholar]
- Burstein, S. PPAR-gamma: a nuclear receptor with affinity for cannabinoids. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Alexander, S.P.; Kendall, D.A.; Bennett, A.J. Cannabinoids and PPARalpha signalling. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 1095–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham, M.; Lynn, A.B.; Little, M.D.; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; de Costa, B.R.; Rice, K.C. Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1932–1936. [Google Scholar]
- Egertova, M.; Giang, D.K.; Cravatt, B.F.; Elphick, M.R. A new perspective on cannabinoid signalling: complementary localization of fatty acid amide hydrolase and the CB1 receptor in rat brain. Proc. Biol. Sci. 1998, 265, 2081–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Devane, W.A.; Dysarz, F.A., 3rd; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; Howlett, A.C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988, 34, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, L.A.; Lolait, S.J.; Brownstein, M.J.; Young, A.C.; Bonner, T.I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 1990, 346, 561–564. [Google Scholar]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Rea, K.; Roche, M.; Finn, D.P. Supraspinal modulation of pain by cannabinoids: the role of GABA and glutamate. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 633–648. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, S.; Cebeira, M.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J. Cannabinoid tolerance and dependence: a review of studies in laboratory animals. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 81, 300–318. [Google Scholar]
- De Vry, J.; Jentzsch, K.R.; Kuhl, E.; Eckel, G. Behavioral effects of cannabinoids show differential sensitivity to cannabinoid receptor blockade and tolerance development. Behav. Pharmacol. 2004, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Derbenev, A.V.; Stuart, T.C.; Smith, B.N. Cannabinoids suppress synaptic input to neurones of the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve. J. Physiol. 2004, 559, 923–938. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, G.; Wray, E.J.; Tao, Q.; McAllister, S.D.; Rorrer, W.K.; Aung, M.M.; Martin, B.R.; Abood, M.E. Evaluation of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor-selective antagonist, SR144528: further evidence for cannabinoid CB2 receptor absence in the rat central nervous system. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 377, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer, A.; Zimmer, A.M.; Hohmann, A.G.; Herkenham, M.; Bonner, T.I. Increased mortality, hypoactivity, and hypoalgesia in cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5780–5785. [Google Scholar]
- Facci, L.; Dal Toso, R.; Romanello, S.; Buriani, A.; Skaper, S.D.; Leon, A. Mast cells express a peripheral cannabinoid receptor with differential sensitivity to anandamide and palmitoylethanolamide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 3376–3380. [Google Scholar]
- Howlett, A.C.; Barth, F.; Bonner, T.I.; Cabral, G.; Casellas, P.; Devane, W.A.; Felder, C.C.; Herkenham, M.; Mackie, K.; Martin, B.R.; et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 161–202. [Google Scholar]
- Carrier, E.J.; Kearn, C.S.; Barkmeier, A.J.; Breese, N.M.; Yang, W.; Nithipatikom, K.; Pfister, S.L.; Campbell, W.B.; Hillard, C.J. Cultured rat microglial cells synthesize the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonylglycerol, which increases proliferation via a CB2 receptor-dependent mechanism. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 999–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Correa, F.; Docagne, F.; Mestre, L.; Clemente, D.; Hernangomez, M.; Loria, F.; Guaza, C. A role for CB2 receptors in anandamide signalling pathways involved in the regulation of IL-12 and IL-23 in microglial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 86–100. [Google Scholar]
- Facchinetti, F.; Del Giudice, E.; Furegato, S.; Passarotto, M.; Leon, A. Cannabinoids ablate release of TNFalpha in rat microglial cells stimulated with lypopolysaccharide. Glia 2003, 41, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, L.; Franklin, A.; Witting, A.; Wade, C.; Xie, Y.; Kunos, G.; Mackie, K.; Stella, N. Nonpsychotropic cannabinoid receptors regulate microglial cell migration. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Palazuelos, J.; Aguado, T.; Egia, A.; Mechoulam, R.; Guzman, M.; Galve-Roperh, I. Non-psychoactive CB2 cannabinoid agonists stimulate neural progenitor proliferation. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2405–2407. [Google Scholar]
- Molina-Holgado, F.; Rubio-Araiz, A.; Garcia-Ovejero, D.; Williams, R.J.; Moore, J.D.; Arevalo-Martin, A.; Gomez-Torres, O.; Molina-Holgado, E. CB2 cannabinoid receptors promote mouse neural stem cell proliferation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 629–634. [Google Scholar]
- Golech, S.A.; McCarron, R.M.; Chen, Y.; Bembry, J.; Lenz, F.; Mechoulam, R.; Shohami, E.; Spatz, M. Human brain endothelium: coexpression and function of vanilloid and endocannabinoid receptors. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2004, 132, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, B.; Carracedo, A.; Diez-Zaera, M.; Gomez del Pulgar, T.; Guzman, M.; Velasco, G. The CB2 cannabinoid receptor signals apoptosis via ceramide-dependent activation of the mitochondrial intrinsic pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Olea-Herrero, N.; Vara, D.; Malagarie-Cazenave, S.; Diaz-Laviada, I. Inhibition of human tumour prostate PC-3 cell growth by cannabinoids R(+)-Methanandamide and JWH-015: involvement of CB2. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 940–950. [Google Scholar]
- ianchi, F.; Papucci, L.; Schiavone, N.; Lulli, M.; Magnelli, L.; Vinci, M.C.; Messerini, L.; Manera, C.; Ronconi, E.; Romagnani, P.; et al. Cannabinoid receptor activation induces apoptosis through tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated ceramide de novo synthesis in colon cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7691–7700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramer, R.; Weinzierl, U.; Schwind, B.; Brune, K.; Hinz, B. Ceramide is involved in r(+)-methanandamide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human neuroglioma cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Hinz, B.; Ramer, R.; Eichele, K.; Weinzierl, U.; Brune, K. Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression is involved in R(+)-methanandamide-induced apoptotic death of human neuroglioma cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, C.; de Ceballos, M.L.; Gomez del Pulgar, T.; Rueda, D.; Corbacho, C.; Velasco, G.; Galve-Roperh, I.; Huffman, J.W.; Ramon y Cajal, S.; Guzman, M. Inhibition of glioma growth in vivo by selective activation of the CB(2) cannabinoid receptor. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5784–5789. [Google Scholar]
- Felder, C.C.; Joyce, K.E.; Briley, E.M.; Mansouri, J.; Mackie, K.; Blond, O.; Lai, Y.; Ma, A.L.; Mitchell, R.L. Comparison of the pharmacology and signal transduction of the human cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 48, 443–450. [Google Scholar]
- Hillard, C.J.; Manna, S.; Greenberg, M.J.; DiCamelli, R.; Ross, R.A.; Stevenson, L.A.; Murphy, V.; Pertwee, R.G.; Campbell, W.B. Synthesis and characterization of potent and selective agonists of the neuronal cannabinoid receptor (CB1). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Gonsiorek, W.; Lunn, C.; Fan, X.; Narula, S.; Lundell, D.; Hipkin, R.W. Endocannabinoid 2-arachidonyl glycerol is a full agonist through human type 2 cannabinoid receptor: antagonism by anandamide. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Slipetz, D.M.; O'Neill, G.P.; Favreau, L.; Dufresne, C.; Gallant, M.; Gareau, Y.; Guay, D.; Labelle, M.; Metters, K.M. Activation of the human peripheral cannabinoid receptor results in inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 48, 352–361. [Google Scholar]
- Eljaschewitsch, E.; Witting, A.; Mawrin, C.; Lee, T.; Schmidt, P.M.; Wolf, S.; Hoertnagl, H.; Raine, C.S.; Schneider-Stock, R.; Nitsch, R.; Ullrich, O. The endocannabinoid anandamide protects neurons during CNS inflammation by induction of MKP-1 in microglial cells. Neuron 2006, 49, 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- Marriott, K.S.; Huffman, J.W. Recent advances in the development of selective ligands for the cannabinoid CB(2) receptor. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 187–204. [Google Scholar]
- PharmosCorporation CB2-selective program: Cannabinor. Available online: http://www.pharmoscorp.com/development/cannabinor.html/ accessed on 9 August 2010.
- GlaxoSmithKlein. A study of the effects of CB2 compound GW842166 in patients with osteoarthritis. Clin. Trial. Gov. 2010. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00444769?term=CB2+agonist+and+pain&rank=1/ accessed on 9 August 2010.
- GlaxoSmithKlein. Dental Pain 3rd molar tooth extraction GW842166. Clinical Trial. Gov. 2010. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00444769?term=CB2+agonists&rank=2/ accessed on 9 August 2010.
- Benito, C.; Tolon, R.M.; Pazos, M.R.; Nunez, E.; Castillo, A.I.; Romero, J. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors in human brain inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, G.A.; Raborn, E.S.; Griffin, L.; Dennis, J.; Marciano-Cabral, F. CB2 receptors in the brain: role in central immune function. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 240–251. [Google Scholar]
- Ashton, J.C.; Glass, M. The Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor as a Target for Inflammation-Dependent Neurodegeneration. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2007, 5, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Ruiz, J.; Pazos, M.R.; Garcia-Arencibia, M.; Sagredo, O.; Ramos, J.A. Role of CB2 receptors in neuroprotective effects of cannabinoids. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2008, 286, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- De Filippis, D.; Steardo, A.; D'Amico, A.; Scuderi, C.; Cipriano, M.; Esposito, G.; Iuvone, T. Differential cannabinoid receptor expression during reactive gliosis: a possible implication for a nonpsychotropic neuroprotection. Sci. World J. 2009, 9, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Ruiz, J.; Romero, J.; Velasco, G.; Tolon, R.M.; Ramos, J.A.; Guzman, M. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor: a new target for controlling neural cell survival? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Rivers, J.R.; Ashton, J.C. The development of cannabinoid CBII receptor agonists for the treatment of central neuropathies. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Atwood, B.K.; Mackie, K. CB2: a cannabinoid receptor with an identity crisis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Sheng, W.S.; Hu, S.; Min, X.; Cabral, G.A.; Lokensgard, J.R.; Peterson, P.K. Synthetic cannabinoid WIN55,212-2 inhibits generation of inflammatory mediators by IL-1beta-stimulated human astrocytes. Glia 2005, 49, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Benito, C.; Nunez, E.; Tolon, R.M.; Carrier, E.J.; Rabano, A.; Hillard, C.J.; Romero, J. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors and fatty acid amide hydrolase are selectively overexpressed in neuritic plaque-associated glia in Alzheimer's disease brains. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 11136–11141. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Nunez, E.; Benito, C.; Pazos, M.R.; Barbachano, A.; Fajardo, O.; Gonzalez, S.; Tolon, R.M.; Romero, J. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors are expressed by perivascular microglial cells in the human brain: an immunohistochemical study. Synapse 2004, 53, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Lanciego, J.L.; Barroso-Chinea, P.; Rico, A.J.; Conte-Perales, L.; Callen, L.; Roda, E.; Gomez-Bautista, V.; Lopez, I.P.; Lluis, C.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; et al. Expression of the mRNA coding the cannabinoid receptor 2 in the pallidal complex of Macaca fascicularis. J. Psychopharmacol. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brusco, A.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Saez, T.; Onaivi, E.S. Ultrastructural localization of neuronal brain CB2 cannabinoid receptors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1139, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Gong, J.P.; Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Liu, Q.R.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Brusco, A.; Uhl, G.R. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain. Brain Res. 2006, 1071, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ashton, J.C.; Friberg, D.; Darlington, C.L.; Smith, P.F. Expression of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in the rat cerebellum: an immunohistochemical study. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 396, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Suarez, J.; Bermudez-Silva, F.J.; Mackie, K.; Ledent, C.; Zimmer, A.; Cravatt, B.F.; de Fonseca, F.R. Immunohistochemical description of the endogenous cannabinoid system in the rat cerebellum and functionally related nuclei. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 509, 400–421. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Van Sickle, M.D.; Duncan, M.; Kingsley, P.J.; Mouihate, A.; Urbani, P.; Mackie, K.; Stella, N.; Makriyannis, A.; Piomelli, D.; Davison, J.S.; et al. Identification and functional characterization of brainstem cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Science 2005, 310, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gong, J.P.; Patel, S.; Perchuk, A.; Meozzi, P.A.; Myers, L.; Mora, Z.; Tagliaferro, P.; Gardner, E.; et al. Discovery of the presence and functional expression of cannabinoid CB2 receptors in brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1074, 514–536. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Sejal, P.; Meozzi, P.A.; Myers, L.; Tagliaferro, P.; Hope, B.; Leonard, C.M.; Uhl, G.R.; Brusco, A.; Gardner, E. Methods to study the behavioral effects and expression of CB2 cannabinoid receptor and its gene transcripts in the chronic mild stress model of depression. Methods Mol. Med. 2006, 123, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Stander, S.; Schmelz, M.; Metze, D.; Luger, T.; Rukwied, R. Distribution of cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2) on sensory nerve fibers and adnexal structures in human skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2005, 38, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Beltramo, M.; Bernardini, N.; Bertorelli, R.; Campanella, M.; Nicolussi, E.; Fredduzzi, S.; Reggiani, A. CB2 receptor-mediated antihyperalgesia: possible direct involvement of neural mechanisms. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ross, R.A.; Coutts, A.A.; McFarlane, S.M.; Anavi-Goffer, S.; Irving, A.J.; Pertwee, R.G.; MacEwan, D.J.; Scott, R.H. Actions of cannabinoid receptor ligands on rat cultured sensory neurones: implications for antinociception. Neuropharmacology 2001, 40, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Skaper, S.D.; Buriani, A.; Dal Toso, R.; Petrelli, L.; Romanello, S.; Facci, L.; Leon, A. The ALIAmide palmitoylethanolamide and cannabinoids, but not anandamide, are protective in a delayed postglutamate paradigm of excitotoxic death in cerebellar granule neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 3984–3989. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Viscomi, M.T.; Oddi, S.; Latini, L.; Pasquariello, N.; Florenzano, F.; Bernardi, G.; Molinari, M.; Maccarrone, M. Selective CB2 receptor agonism protects central neurons from remote axotomy-induced apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4564–4570. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Baek, J.H.; Zheng, Y.; Darlington, C.L.; Smith, P.F. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor expression in the rat brainstem cochlear and vestibular nuclei. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008, 128, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hill, E.L.; Gallopin, T.; Ferezou, I.; Cauli, B.; Rossier, J.; Schweitzer, P.; Lambolez, B. Functional CB1 receptors are broadly expressed in neocortical GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 2580–2589. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gong, J.P.; Patel, S.; Meozzi, P.A.; Myers, L.; Perchuk, A.; Mora, Z.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Gardner, E.; et al. Functional expression of brain neuronal CB2 cannabinoid receptors are involved in the effects of drugs of abuse and in depression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1139, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Suarez, J.; Llorente, R.; Romero-Zerbo, S.Y.; Mateos, B.; Bermudez-Silva, F.J.; de Fonseca, F.R.; Viveros, M.P. Early maternal deprivation induces gender-dependent changes on the expression of hippocampal CB(1) and CB(2) cannabinoid receptors of neonatal rats. Hippocampus 2009, 19, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Brusco, A.; Tagliaferro, P.; Saez, T.; Onaivi, E.S. Postsynaptic localization of CB2 cannabinoid receptors in the rat hippocampus. Synapse 2008, 62, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Morgan, N.H.; Stanford, I.M.; Woodhall, G.L. Functional CB2 type cannabinoid receptors at CNS synapses. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.R.; Pan, C.H.; Hishimoto, A.; Li, C.Y.; Xi, Z.X.; Llorente-Berzal, A.; Viveros, M.P.; Ishiguro, H.; Arinami, T.; Onaivi, E.S.; et al. Species differences in cannabinoid receptor 2 (CNR2 gene): identification of novel human and rodent CB2 isoforms, differential tissue expression and regulation by cannabinoid receptor ligands. Genes Brain Behav. 2009, 8, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Buckley, N.E.; McCoy, K.L.; Mezey, E.; Bonner, T.; Zimmer, A.; Felder, C.C.; Glass, M. Immunomodulation by cannabinoids is absent in mice deficient for the cannabinoid CB(2) receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 396, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ellert-Miklaszewska, A.; Grajkowska, W.; Gabrusiewicz, K.; Kaminska, B.; Konarska, L. Distinctive pattern of cannabinoid receptor type II (CB2) expression in adult and pediatric brain tumors. Brain Res. 2007, 1137, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Benito, C.; Romero, J.P.; Tolon, R.M.; Clemente, D.; Docagne, F.; Hillard, C.J.; Guaza, C.; Romero, J. Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors and fatty acid amide hydrolase are specific markers of plaque cell subtypes in human multiple sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2396–2402. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Yiangou, Y.; Facer, P.; Durrenberger, P.; Chessell, I.P.; Naylor, A.; Bountra, C.; Banati, R.R.; Anand, P. COX-2, CB2 and P2X7-immunoreactivities are increased in activated microglial cells/macrophages of multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord. BMC Neurol. 2006, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Nunez, E.; Benito, C.; Tolon, R.M.; Hillard, C.J.; Griffin, W.S.; Romero, J. Glial expression of cannabinoid CB(2) receptors and fatty acid amide hydrolase are beta amyloid-linked events in Down's syndrome. Neuroscience 2008, 151, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Palazuelos, J.; Aguado, T.; Pazos, M.R.; Julien, B.; Carrasco, C.; Resel, E.; Sagredo, O.; Benito, C.; Romero, J.; Azcoitia, I.; et al. Microglial CB2 cannabinoid receptors are neuroprotective in Huntington's disease excitotoxicity. Brain 2009, 132, 3152–3164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Benito, C.; Kim, W.K.; Chavarria, I.; Hillard, C.J.; Mackie, K.; Tolon, R.M.; Williams, K.; Romero, J. A glial endogenous cannabinoid system is upregulated in the brains of macaques with simian immunodeficiency virus-induced encephalitis. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2530–2536. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Maresz, K.; Carrier, E.J.; Ponomarev, E.D.; Hillard, C.J.; Dittel, B.N. Modulation of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in microglial cells in response to inflammatory stimuli. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Palazuelos, J.; Davoust, N.; Julien, B.; Hatterer, E.; Aguado, T.; Mechoulam, R.; Benito, C.; Romero, J.; Silva, A.; Guzman, M.; Nataf, S.; Galve-Roperh, I. The CB(2) cannabinoid receptor controls myeloid progenitor trafficking: involvement in the pathogenesis of an animal model of multiple sclerosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13320–13329. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ashton, J.C.; Rahman, R.M.; Nair, S.M.; Sutherland, B.A.; Glass, M.; Appleton, I. Cerebral hypoxia-ischemia and middle cerebral artery occlusion induce expression of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in the brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 412, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Martin, B.R.; Adler, M.W.; Razdan, R.K.; Jallo, J.I.; Tuma, R.F. Cannabinoid CB(2) receptor activation decreases cerebral infarction in a mouse focal ischemia/reperfusion model. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Shoemaker, J.L.; Seely, K.A.; Reed, R.L.; Crow, J.P.; Prather, P.L. The CB2 cannabinoid agonist AM-1241 prolongs survival in a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis when initiated at symptom onset. J. Neurochem. 2007, 101, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Das, S.; Williams, E.A.; Moore, D.; Jones, J.D.; Zahm, D.S.; Ndengele, M.M.; Lechner, A.J.; Howlett, A.C. Lipopolysaccharide and cyclic AMP regulation of CB(2) cannabinoid receptor levels in rat brain and mouse RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 181, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Cabranes, A.; Venderova, K.; de Lago, E.; Fezza, F.; Sanchez, A.; Mestre, L.; Valenti, M.; Garcia-Merino, A.; Ramos, J.A.; Di Marzo, V.; et al. Decreased endocannabinoid levels in the brain and beneficial effects of agents activating cannabinoid and/or vanilloid receptors in a rat model of multiple sclerosis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2005, 20, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Lastres-Becker, I.; Berrendero, F.; Lucas, J.J.; Martin-Aparicio, E.; Yamamoto, A.; Ramos, J.A.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J.J. Loss of mRNA levels, binding and activation of GTP-binding proteins for cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the basal ganglia of a transgenic model of Huntington's disease. Brain Res. 2002, 929, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Westlake, T.M.; Howlett, A.C.; Bonner, T.I.; Matsuda, L.A.; Herkenham, M. Cannabinoid receptor binding and messenger RNA expression in human brain: an in vitro receptor autoradiography and in situ hybridization histochemistry study of normal aged and Alzheimer's brains. Neuroscience 1994, 63, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Lopez, D.; Martinez-Orgado, J.; Nunez, E.; Romero, J.; Lorenzo, P.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I. Characterization of the neuroprotective effect of the cannabinoid agonist WIN-55212 in an in vitro model of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in newborn rats. Pediatr. Res. 2006, 60, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gong, J.P.; Patel, S.; Meozzi, P.A.; Myers, L.; Perchuk, A.; Mora, Z.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Gardner, E.; et al. Brain neuronal CB2 cannabinoid receptors in drug abuse and depression: from mice to human subjects. PLoS One 2008, 3, e1640. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Torres, E.; Gutierrez-Lopez, M.D.; Borcel, E.; Peraile, I.; Mayado, A.; O'Shea, E.; Colado, M.I. Evidence that MDMA ('ecstasy') increases cannabinoid CB2 receptor expression in microglial cells: role in the neuroinflammatory response in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro, H.; Iwasaki, S.; Teasenfitz, L.; Higuchi, S.; Horiuchi, Y.; Saito, T.; Arinami, T.; Onaivi, E.S. Involvement of cannabinoid CB2 receptor in alcohol preference in mice and alcoholism in humans. Pharmacogenomics J. 2007, 7, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Pryce, G.; Baker, D. Control of spasticity in a multiple sclerosis model is mediated by CB1, not CB2, cannabinoid receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Whiteside, G.T.; Gottshall, S.L.; Boulet, J.M.; Chaffer, S.M.; Harrison, J.E.; Pearson, M.S.; Turchin, P.I.; Mark, L.; Garrison, A.E.; Valenzano, K.J. A role for cannabinoid receptors, but not endogenous opioids, in the antinociceptive activity of the CB2-selective agonist, GW405833. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 528, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Sain, N.M.; Liang, A.; Kane, S.A.; Urban, M.O. Antinociceptive effects of the non-selective cannabinoid receptor agonist CP 55,940 are absent in CB1(-/-) and not CB2(-/-) mice in models of acute and persistent pain. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Valenzano, K.J.; Tafesse, L.; Lee, G.; Harrison, J.E.; Boulet, J.M.; Gottshall, S.L.; Mark, L.; Pearson, M.S.; Miller, W.; Shan, S.; et al. Pharmacological and pharmacokinetic characterization of the cannabinoid receptor 2 agonist, GW405833, utilizing rodent models of acute and chronic pain, anxiety, ataxia and catalepsy. Neuropharmacology 2005, 48, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hanus, L.; Breuer, A.; Tchilibon, S.; Shiloah, S.; Goldenberg, D.; Horowitz, M.; Pertwee, R.G.; Ross, R.A.; Mechoulam, R.; Fride, E. HU-308: a specific agonist for CB(2), a peripheral cannabinoid receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14228–14233. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Malan, T.P., Jr.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Deng, H.; Liu, Q.; Mata, H.P.; Vanderah, T.; Porreca, F.; Makriyannis, A. CB2 cannabinoid receptor-mediated peripheral antinociception. Pain 2001, 93, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Chin, C.L.; Tovcimak, A.E.; Hradil, V.P.; Seifert, T.R.; Hollingsworth, P.R.; Chandran, P.; Zhu, C.Z.; Gauvin, D.; Pai, M.; Wetter, J.; et al. Differential effects of cannabinoid receptor agonists on regional brain activity using pharmacological MRI. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bermudez-Silva, F.J.; Viveros, M.P.; McPartland, J.M.; Rodriguez de Fonseca, F. The endocannabinoid system, eating behavior and energy homeostasis: The end or a new beginning? Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro, H.; Carpio, O.; Horiuchi, Y.; Shu, A.; Higuchi, S.; Schanz, N.; Benno, R.; Arinami, T.; Onaivi, E.S. A nonsynonymous polymorphism in cannabinoid CB2 receptor gene is associated with eating disorders in humans and food intake is modified in mice by its ligands. Synapse 2010, 64, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Carpio, O.; Ishiguro, H.; Schanz, N.; Uhl, G.R.; Benno, R. Behavioral effects of CB2 cannabinoid receptor activation and its influence on food and alcohol consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1139, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Werner, N.A.; Koch, J.E. Effects of the cannabinoid antagonists AM281 and AM630 on deprivation-induced intake in Lewis rats. Brain Res. 2003, 967, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Anand, P.; Whiteside, G.; Fowler, C.J.; Hohmann, A.G. Targeting CB2 receptors and the endocannabinoid system for the treatment of pain. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 60, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Guindon, J.; Hohmann, A.G. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: a therapeutic target for the treatment of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Jhaveri, M.D.; Sagar, D.R.; Elmes, S.J.; Kendall, D.A.; Chapman, V. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor-mediated anti-nociception in models of acute and chronic pain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2007, 36, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Jhaveri, M.D.; Elmes, S.J.; Richardson, D.; Barrett, D.A.; Kendall, D.A.; Mason, R.; Chapman, V. Evidence for a novel functional role of cannabinoid CB(2) receptors in the thalamus of neuropathic rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, W.; Mikami, T.; Iwamura, H. Involvement of central cannabinoid CB2 receptor in reducing mechanical allodynia in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 583, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Paldyova, E.; Bereczki, E.; Santha, M.; Wenger, T.; Borsodi, A.; Benyhe, S. Noladin ether, a putative endocannabinoid, inhibits mu-opioid receptor activation via CB2 cannabinoid receptors. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Paldy, E.; Bereczki, E.; Santha, M.; Wenger, T.; Borsodi, A.; Zimmer, A.; Benyhe, S. CB(2) cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR144528 decreases mu-opioid receptor expression and activation in mouse brainstem: role of CB(2) receptor in pain. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 53, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Paldyova, E.; Bereczki, E.; Santha, M.; Wenger, T.; Borsodi, A.; Benyhe, S. Altered gene expression and functional activity of opioid receptors in the cerebellum of CB1 cannabinoid receptor knockout mice after acute treatments with cannabinoids. Acta Biol. Hung. 2007, 58, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Toth, C.C.; Jedrzejewski, N.M.; Ellis, C.L.; Frey, W.H., 2nd. Cannabinoid-mediated modulation of neuropathic pain and microglial accumulation in a model of murine type I diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2010, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Jafari, M.R.; Golmohammadi, S.; Ghiasvand, F.; Zarrindast, M.R.; Djahanguiri, B. Influence of nicotinic receptor modulators on CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist (JWH133)-induced antinociception in mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 2007, 18, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hasanein, P.; Parviz, M.; Keshavarz, M.; Javanmardi, K. CB1 receptor activation in the basolateral amygdala produces antinociception in animal models of acute and tonic nociception. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Adler, M.W.; Abood, M.E.; Ganea, D.; Jallo, J.; Tuma, R.F. CB2 receptor activation attenuates microcirculatory dysfunction during cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury. Microvasc. Res. 2009, 78, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Carlisle, S.J.; Marciano-Cabral, F.; Staab, A.; Ludwick, C.; Cabral, G.A. Differential expression of the CB2 cannabinoid receptor by rodent macrophages and macrophage-like cells in relation to cell activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2002, 2, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Stella, N. Cannabinoid signaling in glial cells. Glia 2004, 48, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ehrhart, J.; Obregon, D.; Mori, T.; Hou, H.; Sun, N.; Bai, Y.; Klein, T.; Fernandez, F.; Tan, J.; Shytle, R.D. Stimulation of cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2) suppresses microglial activation. J. Neuroinflammation 2005, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Puffenbarger, R.A.; Boothe, A.C.; Cabral, G.A. Cannabinoids inhibit LPS-inducible cytokine mRNA expression in rat microglial cells. Glia 2000, 29, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Klegeris, A.; Bissonnette, C.J.; McGeer, P.L. Reduction of human monocytic cell neurotoxicity and cytokine secretion by ligands of the cannabinoid-type CB2 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Molina-Holgado, F.; Pinteaux, E.; Moore, J.D.; Molina-Holgado, E.; Guaza, C.; Gibson, R.M.; Rothwell, N.J. Endogenous interleukin-1 receptor antagonist mediates anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions of cannabinoids in neurons and glia. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 6470–6474. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Molina-Holgado, F.; Molina-Holgado, E.; Guaza, C.; Rothwell, N.J. Role of CB1 and CB2 receptors in the inhibitory effects of cannabinoids on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide release in astrocyte cultures. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 67, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Correa, F.; Hernangomez, M.; Mestre, L.; Loria, F.; Spagnolo, A.; Docagne, F.; Di Marzo, V.; Guaza, C. Anandamide enhances IL-10 production in activated microglia by targeting CB(2) receptors: roles of ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-kappaB. Glia 2010, 58, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Roche, M.; Diamond, M.; Kelly, J.P.; Finn, D.P. In vivo modulation of LPS-induced alterations in brain and peripheral cytokines and HPA axis activity by cannabinoids. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 181, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Sagredo, O.; Gonzalez, S.; Aroyo, I.; Pazos, M.R.; Benito, C.; Lastres-Becker, I.; Romero, J.P.; Tolon, R.M.; Mechoulam, R.; Brouillet, E.; et al. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonists protect the striatum against malonate toxicity: relevance for Huntington's disease. Glia 2009, 57, 1154–1167. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Koenigsknecht-Talboo, J.; Landreth, G.E. Microglial phagocytosis induced by fibrillar beta-amyloid and IgGs are differentially regulated by proinflammatory cytokines. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8240–8249. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Tolon, R.M.; Nunez, E.; Pazos, M.R.; Benito, C.; Castillo, A.I.; Martinez-Orgado, J.A.; Romero, J. The activation of cannabinoid CB2 receptors stimulates in situ and in vitro beta-amyloid removal by human macrophages. Brain Res. 2009, 1283, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Goncalves, M.B.; Suetterlin, P.; Yip, P.; Molina-Holgado, F.; Walker, D.J.; Oudin, M.J.; Zentar, M.P.; Pollard, S.; Yanez-Munoz, R.J.; Williams, G.; Walsh, F.S.; Pangalos, M.N.; Doherty, P. A diacylglycerol lipase-CB2 cannabinoid pathway regulates adult subventricular zone neurogenesis in an age-dependent manner. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2008, 38, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Loria, F.; Petrosino, S.; Hernangomez, M.; Mestre, L.; Spagnolo, A.; Correa, F.; Di Marzo, V.; Docagne, F.; Guaza, C. An endocannabinoid tone limits excitotoxicity in vitro and in a model of multiple sclerosis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Van Cleemput, J.; Ji, S.P.; Bai, G.; Zhang, X. Cannabinoids promote embryonic and adult hippocampus neurogenesis and produce anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3104–3116. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Marchalant, Y.; Brothers, H.M.; Norman, G.J.; Karelina, K.; DeVries, A.C.; Wenk, G.L. Cannabinoids attenuate the effects of aging upon neuroinflammation and neurogenesis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 34, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Lafenetre, P.; Chaouloff, F.; Marsicano, G. The endocannabinoid system in the processing of anxiety and fear and how CB1 receptors may modulate fear extinction. Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 56, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Finn, D.P. Endocannabinoid-mediated modulation of stress responses: Physiological and pathophysiological significance. Immunobiology 2010, 215, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hill, M.N.; Gorzalka, B.B. The endocannabinoid system and the treatment of mood and anxiety disorders. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2009, 8, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Lutz, B.; Aparisi, A.; Viveros, M.P. The dual role of the endocannabinoid system as a regulator of anxiety responses. FENS Abstr. 2010, 5, 088.035. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Deng, H.; Zvonok, A.; Cockayne, D.A.; Kwan, J.; Mata, H.P.; Vanderah, T.W.; Lai, J.; Porreca, F.; Makriyannis, A.; et al. Activation of CB2 cannabinoid receptors by AM1241 inhibits experimental neuropathic pain: pain inhibition by receptors not present in the CNS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10529–10533. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Pérez-Ortiz, J.M.; Gutiérrez-Adán, A.; Manzanares, J. Depression-resistant endophenotype in mice overexpressing cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Onaivi, E.S. Neuropsychobiological evidence for the functional presence and expression of cannabinoid CB2 receptors in the brain. Neuropsychobiology 2006, 54, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Clarke, J.R.; Rossato, J.I.; Monteiro, S.; Bevilaqua, L.R.; Izquierdo, I.; Cammarota, M. Posttraining activation of CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus impairs object recognition long-term memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2008, 90, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Steiner, M.A.; Wotjak, C.T. Role of the endocannabinoid system in regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 170, 397–432. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, C.G.; Mohn, C.; Lamounier-Zepter, V.; Rettori, V.; Bornstein, S.R.; Krug, A.W.; Ehrhart-Bornstein, M. Expression and function of endocannabinoid receptors in the human adrenal cortex. Horm. Metab. Res. 2010, 42, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Avgustinovich, D.F.; Lipina, T.V.; Bondar, N.P.; Alekseyenko, O.V.; Kudryavtseva, N.N. Features of the genetically defined anxiety in mice. Behav. Genet. 2000, 30, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Griebel, G.; Belzung, C.; Perrault, G.; Sanger, D.J. Differences in anxiety-related behaviours and in sensitivity to diazepam in inbred and outbred strains of mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000, 148, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- O'Mahony, C.M.; Sweeney, F.F.; Daly, E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Restraint stress-induced brain activation patterns in two strains of mice differing in their anxiety behaviour. Behav. Brain Res. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Marco, E.M.; Adriani, W.; Llorente, R.; Laviola, G.; Viveros, M.P. Detrimental psychophysiological effects of early maternal deprivation in adolescent and adult rodents: altered responses to cannabinoid exposure. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Mangieri, R.A.; Piomelli, D. Enhancement of endocannabinoid signaling and the pharmacotherapy of depression. Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 56, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Moreira, F.A.; Grieb, M.; Lutz, B. Central side-effects of therapies based on CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonists and antagonists: focus on anxiety and depression. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 23, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Serra, G.; Fratta, W. A possible role for the endocannabinoid system in the neurobiology of depression. Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2007, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hungund, B.L.; Vinod, K.Y.; Kassir, S.A.; Basavarajappa, B.S.; Yalamanchili, R.; Cooper, T.B.; Mann, J.J.; Arango, V. Upregulation of CB1 receptors and agonist-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding in the prefrontal cortex of depressed suicide victims. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Vinod, K.Y.; Hungund, B.L. Role of the endocannabinoid system in depression and suicide. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Domschke, K.; Dannlowski, U.; Ohrmann, P.; Lawford, B.; Bauer, J.; Kugel, H.; Heindel, W.; Young, R.; Morris, P.; Arolt, V.; Deckert, J.; Suslow, T.; Baune, B.T. Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1) gene: Impact on antidepressant treatment response and emotion processing in Major Depression. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 18, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Barrero, F.J.; Ampuero, I.; Morales, B.; Vives, F.; de Dios Luna Del Castillo, J.; Hoenicka, J.; Garcia Yebenes, J. Depression in Parkinson's disease is related to a genetic polymorphism of the cannabinoid receptor gene (CNR1). Pharmacogenomics J. 2005, 5, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Beyer, C.E.; Dwyer, J.M.; Piesla, M.J.; Platt, B.J.; Shen, R.; Rahman, Z.; Chan, K.; Manners, M.T.; Samad, T.A.; Kennedy, J.D.; Bingham, B.; Whiteside, G.T. Depression-like phenotype following chronic CB(1) receptor antagonism. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Morrish, A.C.; Hill, M.N.; Riebe, C.J.; Gorzalka, B.B. Protracted cannabinoid administration elicits antidepressant behavioral responses in rats: role of gender and noradrenergic transmission. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 98, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hill, M.N.; Carrier, E.J.; McLaughlin, R.J.; Morrish, A.C.; Meier, S.E.; Hillard, C.J.; Gorzalka, B.B. Regional alterations in the endocannabinoid system in an animal model of depression: effects of concurrent antidepressant treatment. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 2322–2336. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hill, M.N.; Ho, W.S.; Sinopoli, K.J.; Viau, V.; Hillard, C.J.; Gorzalka, B.B. Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in the ability of long-term tricyclic antidepressant treatment to suppress stress-induced activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 2591–2599. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hill, M.N.; Barr, A.M.; Ho, W.S.; Carrier, E.J.; Gorzalka, B.B.; Hillard, C.J. Electroconvulsive shock treatment differentially modulates cortical and subcortical endocannabinoid activity. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Bazan, N.G. Lipid signaling: sleep, synaptic plasticity, and neuroprotection. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005, 77, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ishiguro, H.; Horiuchi, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Koga, M.; Imai, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Morikawa, M.; Inada, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Brain Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Karsak, M.; Cohen-Solal, M.; Freudenberg, J.; Ostertag, A.; Morieux, C.; Kornak, U.; Essig, J.; Erxlebe, E.; Bab, I.; Kubisch, C.; et al. Cannabinoid receptor type 2 gene is associated with human osteoporosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 3389–3396. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Carrasquer, A.; Nebane, N.M.; Williams, W.M.; Song, Z.H. Functional consequences of nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in the CB2 cannabinoid receptor. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 2010, 20, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hill, M.N.; Miller, G.E.; Carrier, E.J.; Gorzalka, B.B.; Hillard, C.J. Circulating endocannabinoids and N-acyl ethanolamines are differentially regulated in major depression and following exposure to social stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Bertin, A.; Jalfre, M. "Behavioural despair" in rats and mice: strain differences and the effects of imipramine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1978, 51, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Gobbi, G.; Bambico, F.R.; Mangieri, R.; Bortolato, M.; Campolongo, P.; Solinas, M.; Cassano, T.; Morgese, M.G.; Debonnel, G.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Tarzia, G.; Mor, M.; Trezza, V.; Goldberg, S.R.; Cuomo, V.; Piomelli, D. Antidepressant-like activity and modulation of brain monoaminergic transmission by blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18620–18625. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Adamczyk, P.; Golda, A.; McCreary, A.C.; Filip, M.; Przegalinski, E. Activation of endocannabinoid transmission induces antidepressant-like effects in rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008, 59, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Egashira, N.; Matsuda, T.; Koushi, E.; Higashihara, F.; Mishima, K.; Chidori, S.; Hasebe, N.; Iwasaki, K.; Nishimura, R.; Oishi, R.; Fujiwara, M. Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol prolongs the immobility time in the mouse forced swim test: involvement of cannabinoid CB(1) receptor and serotonergic system. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 589, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bambico, F.R.; Katz, N.; Debonnel, G.; Gobbi, G. Cannabinoids elicit antidepressant-like behavior and activate serotonergic neurons through the medial prefrontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 11700–11711. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- McLaughlin, R.J.; Hill, M.N.; Morrish, A.C.; Gorzalka, B.B. Local enhancement of cannabinoid CB1 receptor signalling in the dorsal hippocampus elicits an antidepressant-like effect. Behav. Pharmacol. 2007, 18, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Steiner, M.A.; Wanisch, K.; Monory, K.; Marsicano, G.; Borroni, E.; Bachli, H.; Holsboer, F.; Lutz, B.; Wotjak, C.T. Impaired cannabinoid receptor type 1 signaling interferes with stress-coping behavior in mice. Pharmacogenomics J. 2008, 8, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hill, M.N.; Gorzalka, B.B. Pharmacological enhancement of cannabinoid CB1 receptor activity elicits an antidepressant-like response in the rat forced swim test. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2005, 15, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Steiner, M.A.; Marsicano, G.; Wotjak, C.T.; Lutz, B. Conditional cannabinoid receptor type 1 mutants reveal neuron subpopulation-specific effects on behavioral and neuroendocrine stress responses. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2008, 33, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Doods, H.; Treede, R.D.; Ceci, A. Depression-like behaviour in rats with mononeuropathy is reduced by the CB2-selective agonist GW405833. Pain 2009, 143, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Willner, P.; Mitchell, P.J. The validity of animal models of predisposition to depression. Behav. Pharmacol. 2002, 13, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Willner, P. Chronic mild stress (CMS) revisited: consistency and behavioural-neurobiological concordance in the effects of CMS. Neuropsychobiology 2005, 52, 90–110. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hill, M.N.; Patel, S.; Carrier, E.J.; Rademacher, D.J.; Ormerod, B.K.; Hillard, C.J.; Gorzalka, B.B. Downregulation of endocannabinoid signaling in the hippocampus following chronic unpredictable stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Macri, S.; Laviola, G. Single episode of maternal deprivation and adult depressive profile in mice: interaction with cannabinoid exposure during adolescence. Behav. Brain Res. 2004, 154, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Llorente, R.; Arranz, L.; Marco, E.M.; Moreno, E.; Puerto, M.; Guaza, C.; De la Fuente, M.; Viveros, M.P. Early maternal deprivation and neonatal single administration with a cannabinoid agonist induce long-term sex-dependent psychoimmunoendocrine effects in adolescent rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2007, 32, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Marco, E.M.; Adriani, W.; Canese, R.; Podo, F.; Viveros, M.P.; Laviola, G. Enhancement of endocannabinoid signalling during adolescence: Modulation of impulsivity and long-term consequences on metabolic brain parameters in early maternally deprived rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2007, 86, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Llorente, R.; Llorente-Berzal, A.; Petrosino, S.; Marco, E.M.; Guaza, C.; Prada, C.; Lopez-Gallardo, M.; Di Marzo, V.; Viveros, M.P. Gender-dependent cellular and biochemical effects of maternal deprivation on the hippocampus of neonatal rats: a possible role for the endocannabinoid system. Dev. Neurobiol. 2008, 68, 1334–1347. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Kawamura, Y.; Fukaya, M.; Maejima, T.; Yoshida, T.; Miura, E.; Watanabe, M.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Kano, M. The CB1 cannabinoid receptor is the major cannabinoid receptor at excitatory presynaptic sites in the hippocampus and cerebellum. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 2991–3001. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Katona, I.; Sperlagh, B.; Sik, A.; Kafalvi, A.; Vizi, E.S.; Mackie, K.; Freund, T.F. Presynaptically located CB1 cannabinoid receptors regulate GABA release from axon terminals of specific hippocampal interneurons. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 4544–4558. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Rueda, D.; Navarro, B.; Martinez-Serrano, A.; Guzman, M.; Galve-Roperh, I. The endocannabinoid anandamide inhibits neuronal progenitor cell differentiation through attenuation of the Rap1/B-Raf/ERK pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 46645–46650. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Aguado, T.; Monory, K.; Palazuelos, J.; Stella, N.; Cravatt, B.; Lutz, B.; Marsicano, G.; Kokaia, Z.; Guzman, M.; Galve-Roperh, I. The endocannabinoid system drives neural progenitor proliferation. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1704–1706. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Jin, K.; Xie, L.; Kim, S.H.; Parmentier-Batteur, S.; Sun, Y.; Mao, X.O.; Childs, J.; Greenberg, D.A. Defective adult neurogenesis in CB1 cannabinoid receptor knockout mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Vaidya, V.A.; Fernandes, K.; Jha, S. Regulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis: relevance to depression. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2007, 7, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Thomas, R.M.; Peterson, D.A. Even neural stem cells get the blues: evidence for a molecular link between modulation of adult neurogenesis and depression. Gene Expr. 2008, 14, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Sahay, A.; Hen, R. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in depression. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, E.; Hashimoto, K.; Okamura, N.; Koike, K.; Komatsu, N.; Kumakiri, C.; Nakazato, M.; Watanabe, H.; Shinoda, N.; Okada, S.; et al. Alterations of serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in depressed patients with or without antidepressants. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Aydemir, C.; Yalcin, E.S.; Aksaray, S.; Kisa, C.; Yildirim, S.G.; Uzbay, T.; Goka, E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) changes in the serum of depressed women. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 30, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Brunoni, A.R.; Lopes, M.; Fregni, F. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies on major depression and BDNF levels: implications for the role of neuroplasticity in depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 11, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Gronli, J.; Bramham, C.; Murison, R.; Kanhema, T.; Fiske, E.; Bjorvatn, B.; Ursin, R.; Portas, C.M. Chronic mild stress inhibits BDNF protein expression and CREB activation in the dentate gyrus but not in the hippocampus proper. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 85, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Roceri, M.; Hendriks, W.; Racagni, G.; Ellenbroek, B.A.; Riva, M.A. Early maternal deprivation reduces the expression of BDNF and NMDA receptor subunits in rat hippocampus. Mol. Psychiatry 2002, 7, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Santarelli, L.; Saxe, M.; Gross, C.; Surget, A.; Battaglia, F.; Dulawa, S.; Weisstaub, N.; Lee, J.; Duman, R.; Arancio, O.; et al. Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 2003, 301, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Saarelainen, T.; Hendolin, P.; Lucas, G.; Koponen, E.; Sairanen, M.; MacDonald, E.; Agerman, K.; Haapasalo, A.; Nawa, H.; Aloyz, R.; et al. Activation of the TrkB neurotrophin receptor is induced by antidepressant drugs and is required for antidepressant-induced behavioral effects. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Peng, C.H.; Chiou, S.H.; Chen, S.J.; Chou, Y.C.; Ku, H.H.; Cheng, C.K.; Yen, C.J.; Tsai, T.H.; Chang, Y.L.; Kao, C.L. Neuroprotection by Imipramine against lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis in hippocampus-derived neural stem cells mediated by activation of BDNF and the MAPK pathway. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 18, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Peng, Q.; Masuda, N.; Jiang, M.; Li, Q.; Zhao, M.; Ross, C.A.; Duan, W. The antidepressant sertraline improves the phenotype, promotes neurogenesis and increases BDNF levels in the R6/2 Huntington's disease mouse model. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 210, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Luikart, B.W.; Birnbaum, S.; Chen, J.; Kwon, C.H.; Kernie, S.G.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Parada, L.F. TrkB regulates hippocampal neurogenesis and governs sensitivity to antidepressive treatment. Neuron 2008, 59, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Lucassen, P.J.; Meerlo, P.; Naylor, A.S.; van Dam, A.M.; Dayer, A.G.; Fuchs, E.; Oomen, C.A.; Czeh, B. Regulation of adult neurogenesis by stress, sleep disruption, exercise and inflammation: Implications for depression and antidepressant action. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- De la Fuente, M.; Llorente, R.; Baeza, I.; De Castro, N.M.; Arranz, L.; Cruces, J.; Viveros, M.P. Early maternal deprivation in rats: a proposed animal model for the study of developmental neuroimmunoendocrine interactions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1153, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Grippo, A.J.; Francis, J.; Beltz, T.G.; Felder, R.B.; Johnson, A.K. Neuroendocrine and cytokine profile of chronic mild stress-induced anhedonia. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 84, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Guan, Z.; Fang, J. Peripheral immune activation by lipopolysaccharide decreases neurotrophins in the cortex and hippocampus in rats. Brain Behav. Immun. 2006, 20, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Qin, L.; He, J.; Hanes, R.N.; Pluzarev, O.; Hong, J.S.; Crews, F.T. Increased systemic and brain cytokine production and neuroinflammation by endotoxin following ethanol treatment. J. Neuroinflammation 2008, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Koo, J.W.; Duman, R.S. IL-1beta is an essential mediator of the antineurogenic and anhedonic effects of stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- DellaGioia, N.; Hannestad, J. A critical review of human endotoxin administration as an experimental paradigm of depression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Maccarrone, M.; De Petrocellis, L.; Bari, M.; Fezza, F.; Salvati, S.; Di Marzo, V.; Finazzi-Agro, A. Lipopolysaccharide downregulates fatty acid amide hydrolase expression and increases anandamide levels in human peripheral lymphocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 393, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Di Marzo, V.; Bisogno, T.; De Petrocellis, L.; Melck, D.; Orlando, P.; Wagner, J.A.; Kunos, G. Biosynthesis and inactivation of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol in circulating and tumoral macrophages. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Solari, J.; Prestifilippo, J.P.; Bornstein, S.R.; McCann, S.M.; Rettori, V. Participation of the endocannabinoid system in the effect of TNF-alpha on hypothalamic release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1088, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Muller-Vahl, K.R.; Emrich, H.M. Cannabis and schizophrenia: towards a cannabinoid hypothesis of schizophrenia. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2008, 8, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Espejo, E.; Viveros, M.P.; Nunez, L.; Ellenbroek, B.A.; Rodriguez de Fonseca, F. Role of cannabis and endocannabinoids in the genesis of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2009, 206, 531–549. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bortolato, M. Role of Cannabinoids in Cognitive Control: Focus on Schizophrenia. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3. Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Desfossés, J.; Potvin, S.; Kouassi, E.; Stip, E. Endocannabinoids and Schizophrenia. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3. Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- De Marchi, N.; De Petrocellis, L.; Orlando, P.; Daniele, F.; Fezza, F.; Di Marzo, V. Endocannabinoid signalling in the blood of patients with schizophrenia. Lipids Health Dis. 2003, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Leweke, F.M.; Giuffrida, A.; Wurster, U.; Emrich, H.M.; Piomelli, D. Elevated endogenous cannabinoids in schizophrenia. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Giuffrida, A.; Leweke, F.M.; Gerth, C.W.; Schreiber, D.; Koethe, D.; Faulhaber, J.; Klosterkotter, J.; Piomelli, D. Cerebrospinal anandamide levels are elevated in acute schizophrenia and are inversely correlated with psychotic symptoms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 2108–2114. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Avissar, S.; Roitman, G.; Schreiber, G. Differential effects of the antipsychotics haloperidol and clozapine on G protein measures in mononuclear leukocytes of patients with schizophrenia. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2001, 21, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Swerdlow, N.R.; Weber, M.; Qu, Y.; Light, G.A.; Braff, D.L. Realistic expectations of prepulse inhibition in translational models for schizophrenia research. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2008, 199, 331–388. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Braff, D.L.; Light, G.A.; Ellwanger, J.; Sprock, J.; Swerdlow, N.R. Female schizophrenia patients have prepulse inhibition deficits. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ferrer, B.; Gorriti, M.A.; Palomino, A.; Gornemann, I.; de Diego, Y.; Bermudez-Silva, F.J.; Bilbao, A.; Fernandez-Espejo, E.; Moratalla, R.; Navarro, M.; Rodriguez de Fonseca, F. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonism markedly increases dopamine receptor-mediated stereotypies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 559, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Beltramo, M.; de Fonseca, F.R.; Navarro, M.; Calignano, A.; Gorriti, M.A.; Grammatikopoulos, G.; Sadile, A.G.; Giuffrida, A.; Piomelli, D. Reversal of dopamine D(2) receptor responses by an anandamide transport inhibitor. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3401–3407. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Arencibia, M.; Gonzalez, S.; de Lago, E.; Ramos, J.A.; Mechoulam, R.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J. Evaluation of the neuroprotective effect of cannabinoids in a rat model of Parkinson's disease: importance of antioxidant and cannabinoid receptor-independent properties. Brain Res. 2007, 1134, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Docagne, F.; Muneton, V.; Clemente, D.; Ali, C.; Loria, F.; Correa, F.; Hernangomez, M.; Mestre, L.; Vivien, D.; Guaza, C. Excitotoxicity in a chronic model of multiple sclerosis: Neuroprotective effects of cannabinoids through CB1 and CB2 receptor activation. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2007, 34, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ellenbroek, B.A.; de Bruin, N.M.; van Den Kroonenburg, P.T.; van Luijtelaar, E.L.; Cools, A.R. The effects of early maternal deprivation on auditory information processing in adult Wistar rats. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 55, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ellenbroek, B.A.; Cools, A.R. Early maternal deprivation and prepulse inhibition: the role of the postdeprivation environment. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 73, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Miuller, N.; Schwarz, M.J. The immunological basis of glutamatergic disturbance in schizophrenia: towards an integrated view. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 2007, 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Monji, A.; Kato, T.; Kanba, S. Cytokines and schizophrenia: Microglia hypothesis of schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 63, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Yum, S.Y.; Yum, S.K.; Kim, T.; Hwang, M.Y. Clinical perspectives on autoimmune processes in schizophrenia. Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 2009, 32, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bernstein, H.G.; Steiner, J.; Bogerts, B. Glial cells in schizophrenia: pathophysiological significance and possible consequences for therapy. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2009, 9, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Boksa, P. Effects of prenatal infection on brain development and behavior: A review of findings from animal models. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez de Fonseca, F.; Cebeira, M.; Ramos, J.A.; Martin, M.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J.J. Cannabinoid receptors in rat brain areas: sexual differences, fluctuations during estrous cycle and changes after gonadectomy and sex steroid replacement. Life Sci. 1994, 54, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Craft, R.M. Sex differences in behavioral effects of cannabinoids. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 2471–2478. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an Open Access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).