Abstract
In the past twenty years, 14 new antiepileptic drugs have been approved for use in the United States and/or Europe. These drugs are eslicarbazepine acetate, felbamate, gabapentin, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, pregabalin, rufinamide, stiripentol, tiagabine, topiramate, vigabatrin and zonisamide. In general, the clinical utility of therapeutic drug monitoring has not been established in clinical trials for these new anticonvulsants, and clear guidelines for drug monitoring have yet to be defined. The antiepileptic drugs with the strongest justifications for drug monitoring are lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine, stiripentol, and zonisamide. Stiripentol and tiagabine are strongly protein bound and are candidates for free drug monitoring. Therapeutic drug monitoring has lower utility for gabapentin, pregabalin, and vigabatrin. Measurement of salivary drug concentrations has potential utility for therapeutic drug monitoring of lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and topiramate. Therapeutic drug monitoring of the new antiepileptic drugs will be discussed in managing patients with epilepsy.
1. Background on Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Antiepileptic Medications
Drugs used to prevent and treat seizures (antiepileptic drugs, AEDs) have been among the most common medications for which therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is performed [1,2]. Traditionally, TDM has been applied mainly to the 'older' or first-generation AEDs that have been on the market in the United States and Europe for several decades, namely carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, and valproic acid. These first-generation AEDs in general have narrow therapeutic ranges and significant inter-individual variability in their pharmacokinetics (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion). Somewhat surprisingly, given the common practice of utilizing TDM for AEDs, the evidence that TDM of AEDs significantly helps clinical management is mostly anecdotal and retrospective. Only two randomized, controlled studies of AED TDM have been conducted and neither showed clinical benefits. Both studies did show, however, that physicians often apply information from TDM incorrectly, diminishing the clinical impact of TDM [3,4]. Better education of medical practitioners on TDM is a priority for the future.
TDM of AEDs faces three main challenges [2]. Firstly, seizures occur irregularly, sometimes with long periods of time between episodes. Consequently, long-term observation of any therapy for seizures may be needed to assess clinical benefit. Secondly, some AEDs produce adverse effects that may be difficult to distinguish from the underlying neurologic disease. Lastly, there are no simple laboratory tests or diagnostic procedures that can assess the clinical efficacy of AEDs. Clinical observation and relatively labor-intensive procedures such as the electroencephalogram (EEG) remain the mainstays of clinical assessment.
In applying TDM to any drug, the most basic assumption is that the concentration being measured correlates with the concentration at the target site of action (e.g., ion channel in the brain). TDM is usually performed on serum or plasma, or occasionally on some other body fluid such as saliva, urine or cerebrospinal fluid. Factors that can negatively affect the correlation between clinical effect and serum/plasma concentration include tolerance to the drug, irreversibility of drug action and active metabolites. For drugs with active metabolites, TDM can include measurement of the concentrations of both parent drug and its metabolite(s) or just of the metabolite(s). As an example, TDM of oxcarbazepine focuses on 10-hydroxycarbazepine (major metabolite), as will be discussed below.
TDM of newer AEDs in saliva has not yet been widely applied [5], but has been studied for six drugs: gabapentin [6], lamotrigine [7], levetiracetam [8], oxcarbazepine (main metabolite 10-hydroxycarbazepine) [9], topiramate [10] and zonisamide [11]. Of these six drugs, gabapentin appears to be clearly unsuited for salivary concentration analysis due to the low concentration in saliva versus plasma (salivary concentrations are ~5–10% that of serum or plasma). General concerns with monitoring salivary concentrations are shorter half-life of some drugs in saliva compared to serum and difficulties in analyzing patients who have little saliva or viscous saliva. However, a key advantage of monitoring saliva is ease of collection, especially in the pediatric and geriatric populations. A study has demonstrated that salivary samples for monitoring AEDs can be collected by the patient and mailed to a clinical laboratory without significant degradation of sample [12].
2. Reasons for Applying TDM to AEDS
There are multiple reasons why TDM may be useful in the clinical management of AED therapy. A common reason is that the pharmacokinetics of the drug shows significant inter-individual variability [13,14,15]. If the pharmacokinetics is very consistent and predictable, then dosing of the drug can often be done without TDM. Metabolism (biotransformation) is a major pharmacokinetic factor that can affect AEDs. Variability in metabolism may be due to impaired organ function (typically kidney or liver), genetic factors (pharmacogenetics), or drug-drug or drug-food interactions. Several AEDs, namely carbamazepine, phenobarbital, and phenytoin, are well-known 'inducers' (stimulators) of 'drug-metabolizing' enzymes in the liver and other organs [16]. Carbamazepine, phenobarbital, and phenytoin act on nuclear hormone receptors such as the pregnane X receptor (PXR, NR1I2) or the constitutive androstane receptor (CAR, NR1I3). When activated by ligands such as carbamazepine, PXR and CAR increase the expression of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, phase II enzymes (e.g., glucuronidating enzymes), and efflux transporters, all of which can accelerate the elimination of AEDs and other drugs [17,18].
AEDs are often used in patients with some degree of renal impairment. Renal insufficiency can alter AED pharmacokinetics by decreased clearance of drug and/or metabolites, or by removal of drug during dialysis procedures. For some AEDs, there has been little investigation of the effect of dialysis on AED plasma concentration. In general, AEDs with low degrees of plasma protein binding are cleared more effectively by dialysis than those AEDs with high degrees of protein binding [19]. In the discussion of the specific AEDs in this review, studies of the effect of dialysis on AED are mentioned if available in the published literature.
Carbamazepine represents an example of a drug that shows 'autoinduction', namely that the metabolism of carbamazepine increases as the drug is used chronically [20]. This means that the carbamazepine dose needs to be increased over time to keep pace with the increases in metabolism, until the induction finally plateaus. Other known enzymes inducers include rifampin (a tuberculosis drug) and St. John's wort (a herbal antidepressant) [16]. Some drugs may also inhibit metabolism of AEDs (typically by blocking CYP enzyme catalytic activity), potentially leading to excessively high concentrations of drug unless the dose is reduced appropriately. As an example, valproic acid is an inhibitor of multiple liver enzymes and has been well-documented to cause drug-drug interactions with other AEDs [1]. Variability in pharmacokinetics may also occur due to alterations in drug absorption or distribution. AEDs that show variable and unpredictable pharmacokinetics are good candidates for TDM [2].
For some medications that are highly (>90%) bound to serum proteins, monitoring of free (unbound) drug concentrations may be clinically useful [21]. A number of factors may alter serum protein concentrations including liver disease, old age, and pregnancy. Concomitant medications (e.g., valproic acid) or endogenous substances may displace drugs from serum protein binding sites, potentially leading to higher free drug concentrations. Uremia, as may occur in renal failure, may also increase free AED concentrations by displacement from serum protein binding sites. Free drug concentrations are typically measured by analyzing the concentration of drug present in an ultrafiltrate of plasma or serum. The technical challenge is that free drug concentrations for drugs that are highly protein bound are substantially lower than total drug concentrations. Some analytical methods that may be suitable for measuring total drug concentrations may have insufficient analytical sensitivity to accurately measure the full range of clinically useful free drug concentrations [21]. In addition, the ultrafiltration process is not easily automated and thus adds manual processing time to the clinical laboratory analysis of AEDs that require determination of free drug concentration.
TDM may also be used to assess adherence (compliance) to therapy [2]. Given that AEDs may be prescribed for years, even in the absence of seizures, patients may skip doses or stop taking the medication altogether. The presence of adverse effects or cost of medications can be other reasons that patients stop taking their medication.
3. The Newer Generation of AEDs
In the last twenty years, 14 new AEDs have entered the market in the United States and/or Europe [22,23]. These drugs are eslicarbazepine acetate, felbamate, gabapentin, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, pregabalin, rufinamide, stiripentol, tiagabine, topiramate, vigabatrin and zonisamide. Eslicarbazepine acetate, lacosamide, rufinamide, and stiripentol are not yet approved in the United States. The newer AEDs are sometimes characterized as second- or third-generation drugs. In comparison to the older AEDs, the newer agents often have wider therapeutic ranges and fewer serious adverse effects. Like some of the older AEDs, the newer agents may also be used for other conditions such as bipolar disorder ('manic depression'), chronic pain syndromes (e.g., fibromyalgia, trigeminal neuralgia), or migraine headaches [22,24]. This manuscript focuses on TDM of the newer AEDs in treatment of epilepsy, emphasizing whether the pharmacokinetics and clinical effects of the drug make TDM useful.
4. The Challenge of Establishing Reference Ranges for AEDs
Reference ranges for the newer AEDs have generally been difficult to establish [2]. These drugs are usually effective over a wide range of serum/plasma concentrations but with substantial inter-individual variation in response. Ideally, TDM would guide physicians towards serum/plasma concentrations that optimize seizure control, while avoiding or at least minimizing toxic effects. The 'reference range' of an AED can be defined by two limits—a lower limit below which therapeutic effect is unlikely and an upper limit above which toxicity is likely [2]. However, any particular individual may have good clinical response at AED concentrations outside the reference range. In addition, reference ranges may vary with different types of seizures, or when AEDs are used to treat other clinical conditions such as neuropathic pain or bipolar disorder. For example, the original reference range for an AED may have been derived from studies of patients with refractory epilepsy, a population that may respond quite differently from patients with more easily treatable disease. Furthermore, many of the newer AEDs were first studied as adjunctive therapy and not as monotherapy. Perucca has promoted the concept of 'individual therapeutic concentrations' for AEDs [25] wherein a patient is treated until good seizure control is achieved. The serum/plasma concentration is determined and then serves as the patient's individual therapeutic concentration. TDM can then be applied periodically to determine whether the concentration is staying near the individual therapeutic concentration [25,26]. Drug monitoring can be especially important when changes in the patient occur that alter AED pharmacokinetics, e.g., pregnancy, impaired kidney or liver function, or concomitant therapy with enzyme-inducing or -inhibiting drugs. One limitation of the individual therapeutic concentration is that changes in the underlying seizure condition may require establishment of a new individual therapeutic concentration.
With the background and theory on TDM above, each of the newer AEDs will be discussed in turn with regard to TDM. This manuscript focuses on monitoring of serum or plasma, although as mentioned above there has been some clinical application of measuring AED concentrations in other fluids (e.g., saliva) [5]. For discussion of the analytical methods that can be used for measurement of AED serum/plasma concentrations, selected numbers of representative references are cited. Table 1 summarizes the pharmacokinetic properties of the newer AEDs, while Table 2 presents a summary of the factors that influence the use and interpretation of TDM for the AEDs. The chemical structures of the AEDs are in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Pharmacokinetic properties and reference ranges for the AEDs.
| Drug | Oral Bioavailability (%) | Serum protein binding (%) | Time to peak concentration (h) | Half-life in Absence of Concomitant Enzyme Inducersa | Half-life in Presence of Concomitant Enzyme Inducersa | Reference Range in Serum (mg/L)f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eslicarbazepine acetate | ≥80 | 30 | 1–4 | 20–24 | 20–24 | Not established |
| Felbamate | >90 | 25 | 2–6 | 16–22 | 10–18 | 30–60 |
| Gabapentin | <60 | 0 | 2–3 | 5–9 | 5–9 | 2–20 |
| Lacosamide | ≥95 | 15 | 0.5–4 | 12–13 | 12–13 | 5–10 |
| Lamotrigine | ≥95 | 55 | 1–3 | 15–35b | 8–20 | 3–14 |
| Levetiracetam | ≥95 | 0 | 1 | 6–8 | 6–8 | 12–46 |
| Oxcarbazepinec | 90 | 40 | 3–6 | 8–15 | 7–12 | 3–35 |
| Pregabalin | ≥90 | 0 | 1–2 | 5–7 | 5–7 | 2.8–8.3 |
| Rufinamide | 85 | 30 | 5–6 | 8–12 | ≤8 | Not established |
| Stiripentold | ≥90 | 99 | 1–2 | Variablee | Variablee | 4–22 |
| Tiagabined | ≥90 | 96 | 1–2 | 5–9 | 2–4 | 0.02–0.2 |
| Topiramate | ≥80 | 15 | 2–4 | 20–30 | 10–15 | 5–20 |
| Vigabatrin | ≥60 | 0 | 1–2 | 5–8 | 5–8 | 0.8–36 |
| Zonisamide | ≥65 | 50 | 2–5 | 50–70 | 25–35 | 10–40 |
a Enzyme inducers include carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampicin, and St. John's wort. References for drugs whose half-lives are altered in patients receiving liver enzyme inducers: felbamate [36], lamotrigine [37], oxcarbazepine [38], rufinamide [39], tiagabine [40], topiramate [41] and zonisamide [15]. b Half-life increases to 30–90 h during concomitant therapy with valproic acid (enzyme inhibitor). c All parameters refer to the active metabolite 10-hydroxycarbazepine. d Monitoring of free drug may be useful for these drugs. e Drug shows zero-order elimination kinetics. f References for reference ranges: felbamate [42,43], gabapentin [44], lacosamide [45], lamotrigine [46], levetiracetam [47], oxcarbazepine (10-hydroxycarbazepine metabolite) [48], pregabalin [2], stiripentol [49], tiagabine [50], topiramate [51], vigabatrin [23], zonisamide [52].

Table 2.
Summary of factors that influence use and interpretation of TDM for newer AEDs.
| Drug | Factors that Favor Use of TDM | Factors that May Limit Use of TDM and/or Complicate Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Eslicarbazepine acetate | Auto-induction with chronic dosing | Has active metabolite (oxcarbazepine) |
| Liver failure | ||
| Felbamate | Variable metabolism | Unclear toxic concentrations |
| Potential for severe toxicity | ||
| Gabapentin | Variable absorption | Wide range of clinically effective serum concentrations |
| Renal failure | ||
| Low incidence of toxicity | ||
| Lacosamide | Liver failure | Generally predictable pharmacokinetics Drug-drug interactions uncommon |
| Renal failure | ||
| Lamotrigine | Variable metabolism | |
| Common drug-drug interactions | ||
| Well-defined toxic concentrations | ||
| Common use in pregnancy | ||
| Levetiracetam | Renal failure | Wide range of clinically effective serum concentrations |
| Low incidence of toxicity | ||
| Oxcarbazepine | Variable metabolism | |
| Well-defined toxic concentrations | ||
| Pregabalin | Variable absorption | Wide range of clinically effective serum concentrations |
| Renal failure | ||
| Low incidence of toxicityShort half-life | ||
| Rufinamide | Variable absorption | |
| Common drug-drug interactions Renal failure | ||
| Stiripentol | Extensive first-pass metabolism High serum protein binding | High serum protein binding can complicate interpretation of total drug concentrations (free drug levels may be helpful) |
| Zero-order elimination kinetics | ||
| Tiagabine | High serum protein bindingLiver failure | High serum protein binding can complicate interpretation of total drug concentrations (free drug levels may be helpful) |
| Common drug-drug interactions | ||
| Topiramate | Common drug-drug interactions | |
| Vigabatrin | Renal failure | Poor correlation of serum concentrations and therapeutic effect (irreversible effect) |
| Zonisamide | Variable metabolism | |
| Common drug-drug interactions | ||
| Well-defined toxic concentrations |
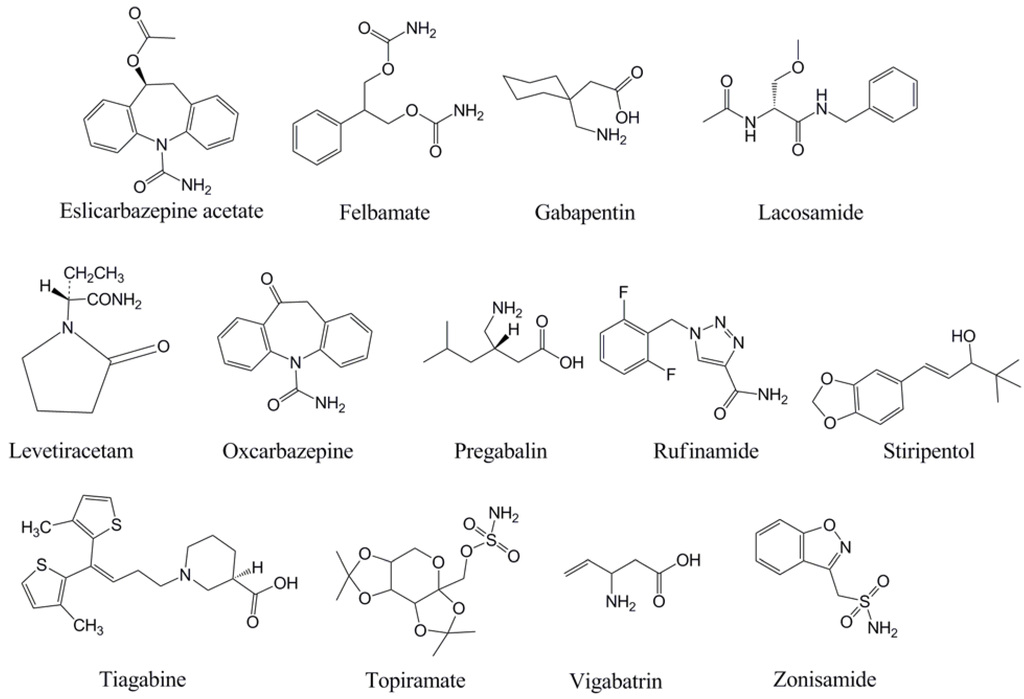
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of the antiepileptic drugs discussed in this review.
5. Eslicarbazepine Acetate
Eslicarbazepine acetate [(S)-licarbazepine acetate] is a pro-drug that is rapidly metabolized by liver esterases to form eslicarbazepine, a compound that inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels [27]. Following oral administration, approximately 95% of eslicarbazepine acetate is converted to eslicarbazepine in plasma [28]. TDM focuses on eslicarbazepine (active metabolite). Minor metabolites of eslicarbazepine acetate are oxcarbazepine (also used as an AED) and (R)-licarbazepine. Unlike carbamazepine, eslicarbazepine acetate is not converted to carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide and does not exhibit auto-induction in metabolism. Eslicarbazepine has low (~30%) binding to serum proteins and an elimination half-life of 20–24 h during chronic administration [29]. Eslicarbazepine has low potential for drug-drug interactions [30,31]. The pharmacokinetics of eslicarbazepine are not significantly affected by mild to moderate hepatic failure [32]. Clearance of eslicarbazepine and minor metabolites of eslicarbazepine acetate is predominantly by the kidney, with significant increases in area under the curve (AUC) in patients with moderate or severe renal failure. Hemodialysis effectively clears eslicarbazepine and other metabolites of eslicarbazepine acetate [33].
Overall, TDM has a minimal role in the therapeutic use of eslicarbazepine due to the relatively predictable pharmacokinetics of the drug. An enantioselective high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet (HPLC-UV) method has been developed for the specific monitoring of eslicarbazepine and its metabolites [34]. It remains to be seen if eslicarbazepine acetate, like carbamazepine, has a therapeutic role in the management of bipolar disorder [35].
6. Felbamate
Felbamate was approved in 1993 in the United States for the treatment of partial seizures in adults and for Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome, a type of childhood epilepsy that is often refractory to AED therapy [53]. By 1994, cases of aplastic anemia and later severe liver failure were identified and associated with felbamate therapy. The drug has remained on the market but with revised labeling and much restricted use [53]. In terms of pharmacokinetics, felbamate has high bioavailability (>90%). Approximately 50% of the parent drug is ultimately metabolized by the liver to inactive metabolites [54]. It is suspected that one or more of the metabolites mediates the rare but serious adverse effects [55]. Inducers of liver metabolism (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, rifampin, St. John's wort) increase the metabolism of felbamate [56], while valproic acid inhibits the metabolism [57]. Felbamate does not have a clear reference range but typical doses used in epilepsy management usually result in serum/plasma concentrations of 30–60 mg/L [43]. The clearance of felbamate is 20–65% higher in children than in adults [14].
The variable metabolism of felbamate and differences between children and adults in clearance suggest that TDM may be helpful in felbamate therapy. Multiple analytical methodologies have been reported for the measurement of felbamate in plasma/serum including HPLC [58,59], gas chromatography (GC) [60] and capillary electrophoresis [61]. However, the rare adverse effects have severely limited the use of felbamate [53]. Close monitoring of blood counts and liver function are advised during felbamate therapy.
7. Gabapentin
Gabapentin was originally approved in 1994 in the United States for the treatment in epilepsy but has achieved greater popularity as an adjunctive therapy for chronic pain. Although structurally related to the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), gabapentin does not appear to interact with GABA receptors in the brain or spinal cord [22,62]. Gabapentin is rapidly absorbed by the L-amino acid transport system [63]. A study published in 1998 showed a decrease in bioavailability at doses of 4800 mg/day of gabapentin as compared to lower doses, suggesting possible saturability of the L-amino acid transport system [64]. However, a later study demonstrated linear absorption up to 4800 mg/day [6]. Salivary concentrations of gabapentin are only 5–10% those in plasma, limiting the utility of salivary gabapentin concentrations for TDM [6]. Gabapentin is not metabolized and shows little binding to serum proteins [63]. The majority of drug is excreted renally and the half-life of the drug increases in renal failure [62]. Gabapentin is effectively cleared by hemodialysis [65]. A wide range of serum/plasma concentrations are associated with clinical effect [66] although effective control of seizures typically requires concentrations above 2 mg/L [67]. An approximate reference range of 2–20 mg/L has been proposed [44]. Multiple analytical methodologies have been reported for the measurement of gabapentin in plasma/serum including HPLC [68,69], HPLC-tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) [70], gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) [71] and GC/MS/MS [72].
8. Lacosamide
Lacosamide is a novel functionalized amino acid whose mechanism of action is thought to involve enhancement of slow inactivation of sodium channels [73]. Lacosamide was approved in Europe in September 2008 for partial-onset seizures in patients 16 years and older [74]. Lacosamide has a bioavailability of ~100% with minimal first-pass metabolism and serum protein binding [75]. Approximately 40% of the drug is ultimately excreted by the kidney with the remainder cleared by metabolism. Although the effect of hemodialysis on lacosamide pharmacokinetics has not been reported, the low plasma protein binding of lacosamide suggests that this drug should be effectively cleared by dialysis [19]. CYP2C19 (an enzyme that can show pharmacogenetic variation) catalyzes the metabolism of lacosamide to an inactive metabolite. The half-life of lacosamide is approximately 12 hours. Clinically significant drug-drug interactions involving lacosamide are minimal [76], including a detailed study showing a lack of interaction between carbamazepine and lacosamide [77]. Both HPLC [78] and LC/MS/MS [79] procedures for measuring lacosamide concentrations in plasma or serum have been reported. Overall, lacosamide has predictable pharmacokinetics with no clinically significant differences in pharmacokinetics between children, young adults, and elderly patients. Other than to establish individualized references ranges, TDM of lacosamide is likely best focused on patients with liver and/or kidney failure [80].
9. Lamotrigine
Lamotrigine was approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in late 1994 as an adjunctive therapy for partial seizures [22]. Lamotrigine has since gained indications as monotherapy for partial seizures and also as a treatment for bipolar disorder [1,2]. Lamotrigine has also accumulated a solid safety record in pregnancy, leading to the common use of this AED in pregnant women with epilepsy [81,82]. Lamotrigine is rapidly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is only 50–60% bound to serum proteins. Lamotrigine distributes into saliva, with salivary lamotrigine concentrations being on average approximately 0.4–0.5 that of serum concentrations in patients receiving chronic lamotrigine therapy. Salivary lamotrigine concentrations correlate well with those in serum, which makes saliva an alternative sample to perform TDM [83,84]. The parent drug is extensively metabolized, mainly by glucuronidation to an inactive metabolite [85]. Similar to carbamazepine, the metabolism of lamotrigine shows the phenomenon of autoinduction. For most patients, autoinduction is complete within two weeks, with a ~20% reduction in steady-state serum/plasma concentrations if the dose is not changed [86]. The metabolism of lamotrigine is significantly affected by concomitant use of classic liver enzyme inducers [85]. Oral contraceptives containing ethinyl estradiol also significantly reduce the serum concentrations of lamotrigine [87,88]. The serum half-life of lamotrigrine typically is 15–35 h when used as monotherapy but only 8–20 h when use concomitantly with a liver enzyme inducers, and up to 60 h when used together with valproic acid, a CYP enzyme inhibitor [85]. The half-life of lamotrigine increases to ~50 h in patients with severe renal failure. Lamotrigine is effectively cleared by hemodialysis [89]. The clearance of lamotrigine is higher in children [14,46] and markedly higher (~300%) in pregnancy [14]. There is not a tight relationship between clinical response and serum/plasma concentrations [46], but a reference range of 3–14 mg/L has been proposed for refractory epilepsy therapy [90]. The incidence of toxic effects are significantly increased when serum/plasma concentrations exceed 15 mg/L [90].
Three factors of lamotrigine make TDM clinically useful. First, the drug shows significant interindividual variation in dose versus serum/plasma, in large part due to multiple factors that can affect liver metabolism of the drug. Second, the clearance of lamotrigine varies substantially during pregnancy and also across age groups [91]. Lastly, there is a fairly clear concentration threshold above which toxic side effects become more common [90,91]. Multiple analytical methodologies have been reported for the measurement of lamotrigine in plasma/serum including HPLC [92,93,94], radioimmunoassay [95], homogeneous immunoassay [96], immunofluorometric assay [97], capillary electrophoresis [98], capillary zone electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry [99], gas chromatography (GC) with a nitrogen-phosphorus detector [100], GC/MS [101], LC/MS [102], LC/MS/MS [103] and micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography [104].
10. Levetiracetam
Levetiracetam is a novel anticonvulsant [105] whose mechanism of action is thought to involve binding of the synaptic vesicle protein SV2A, a protein involved in neurotransmitter vesicle exocytosis [106]. Levetiracetam is rapidly and nearly completely absorbed following oral administration, although the rate of oral absorption is slowed by co-ingestion with food [107]. Levetiracetam distributes well into saliva, with salivary levetiracetam concentrations being on average slightly higher than serum concentrations in patients receiving chronic levetiracetam therapy [108]. Salivary levetiracetam concentrations correlate well with those in serum, which makes saliva an alternative sample to perform TDM [109]. Levetiracetam does not bind serum proteins and has linear pharmacokinetics. Approximately 100% of the absorbed drug is excreted by the kidneys [110], with approximately two-thirds as the parent drug and the remainder as the metabolite LO57, formed by hydrolysis in the blood [111]. Although the effect of hemodialysis on levetiracetam pharmacokinetics has not been reported, the low plasma protein binding of levetiracetam suggests that this drug should be effectively cleared by dialysis [19]. In performing TDM, it is important to separate serum or plasma from whole blood rapidly, as artefactual hydrolysis of levetiracetam can occur in the blood tube [111]. Because levetiracetam is not metabolized by the liver, significant drug-drug interactions are uncommon [76]. The serum half-life of levetiracetam is longer (16–18 h) in neonates compared to adults (6–8 h) [2]. An approximately 60% decrease in serum concentrations is observed in pregnancy [82]. From evaluation of 470 patients in a specialty epilepsy clinic, a reference range of 12–46 mg/L has been proposed [47]. Multiple analytical methodologies have been reported for the measurement of levetiracetam in plasma/serum including HPLC [112,113], GC [114,115], GC/MS [116], LC/MS/MS [117], microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography [118] and capillary electrophoresis [119]. Other than to evaluate potential toxicity or to assess compliance, the value of TDM for levetiracetam is mostly in adjusting dosage for renal insufficiency [120].
11. Oxcarbazepine
Oxcarbazepine is structurally related to carbamazepine but does not produce nearly as much induction of liver enzymes as carbamazepine and also shows a lower incidence of agranulocytosis [38,121]. Oxcarbazepine is rapidly and completely absorbed [38] and metabolized via 10-keto reduction to its monohydroxy derivative 10-hydroxycarbazepine. 10-Hydroxycarbazepine has equal potency to oxcarbazepine in antiseizure activity, but accumulates to higher concentrations in serum [122]. 10-Hydroxycarbazepine also distributes into saliva, with salivary 10-hydroxycarbazepine concentrations ranging from 0.3 to 1.7 that of serum concentrations [9]. However, the use of saliva as an alternative specimen type for TDM of oxcarbazepine is limited by dose-dependent variations in the correlation between 10-hydroxycarbazepine saliva and serum concentrations and a shorter half-life of 10-hydroxycarbazepine in saliva as compared to serum [9,123].
For the purposes of TDM, oxcarbazepine is treated like a pro-drug, with monitoring focusing on the monohydroxy metabolite as the main mediator of the antiseizure effects [2]. 10-Hydroxycarbazepine is further metabolized, primarily by glucuronidation. The clearance of 10-hydroxycarbazepine is reduced in the elderly [14] and also in the setting of renal insufficiency [124]. There is little data on the effect of hemodialysis on oxcarbazepine or 10-hydroxycarbazepine except for a case report of the successful treatment of massive oxcarbazepine overdose by hemodialysis [125]. The clearance of 10-hydroxycarbazepine is increased in pregnancy [126] and in patients taking liver enzyme-inducing drugs [38]. Young children require higher doses of oxcarbazepine per body weight than adults [127].
In a study of 947 patients, a wide range of 10-hydroxycarbazepine serum concentrations (3–35 mg/L) were observed to be clinically effective in seizure treatment [48], with toxic side effects being more common at serum/plasma concentrations of 35 mg/L or higher [128]. Multiple analytical methodologies have been reported for the measurement of 10-hydroxycarbazepine in plasma/serum including GC [129], GC/MS [130], HPLC [131,132], LC/MS [133], LC/MS/MS [134] and micellar electrokinetic chromatography [135]. TDM is justified when changes are expected that might alter 10-hydroxycarbazepine clearance including changes in renal function, pregnancy, and concomitant use of liver enzyme-inducing drugs.
12. Pregabalin
Pregabalin was designed to be a more potent analog of gabapentin [136]. Like gabapentin, pregabalin has shown effectiveness in treating chronic pain and additionally gained an indication in the United States for the treatment of fibromyalgia [22]. Pregabalin has predictable pharmacokinetics with excellent bioavailability [137], essentially no metabolism, no reported drug-drug interactions and minimal binding to serum proteins. The majority of the absorbed dose (~98%) is excreted unchanged in the urine with a clearance that approximates glomerular filtration rate (GFR) [138]. Renal failure patients require reduced dosage and it is also seems prudent to consider age-related changes in renal function in pharmacotherapy with gabapentin [139]. Pregabalin is effectively cleared by hemodialysis [139]. No clear reference range has been established but an approximate range of 2.8–8.3 mg/L has been proposed [2]. The short half-life of pregabalin (4.6–6.8 h) [140] means that care must be taken in drawing blood for TDM. Similar to gabapentin, other than to adjust dosing during renal failure or to assess compliance, pregabalin is not a good candidate for routine TDM. Plasma and serum concentrations of pregabalin can be determined by HPLC following derivitization [141] or by LC/MS/MS [142].
13. Rufinamide
Rufinamide is a novel anticonvulsant whose mechanism of action is to prolong the inactivated state of voltage-gated sodium channels [143]. Rufinamide was approved for use in Europe in January 2007 and by the FDA in the United States in December 2008 for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Rufinamide is well-absorbed (~85%) following oral administration, with the absorption enhanced significantly when the drug is taken together with food [39]. The peak exposure (Cmax) to rufinamide may increase up to 50% when taken with food as compared to an empty stomach. For this reason, it is advised that patients consistently take rufinamide in the same temporal relation to meals. Rufinamide is extensively metabolized with only trace amounts of the parent drug being recovered in urine and feces. The primary route of metabolism is not via CYP enzymes but instead from carboxyesterase-mediated enzymatic hydrolysis to form an inactive derivative that is excreted in the urine.
The metabolism of rufinamide is accelerated by classic liver enzyme inducers such as carbamazepine, and rifampin [39]. The clearance of rufinamide is not affected much by impaired renal function; however, increased doses of rufinamide are generally needed in patients receiving hemodialysis due to removal of the drug by the dialysis procedure. TDM for rufinamide can be useful because serum levels correlate well with seizure control, allowing for determination of an individual therapeutic concentration [39,143,144]. However, there is currently insufficient data to define a general therapeutic range for rufinamide [39]. Rufinamide serum or plasma concentrations can be determined by HPLC [145]. Monitoring of serum levels can be especially helpful in patients taking concomitant liver enzyme inducers or who are receiving hemodialysis.
14. Stiripentol
Stiripentol is an AED that inhibits GABA reuptake and also produces barbiturate-like positive allosteric modulation of GABAA receptors [146,147]. Stiripentol was originally approved in Europe in 2001. Stiripentol is rapidly absorbed following oral administration but has high first-pass metabolism and thus low bioavailability. There are at least 13 metabolites of stiripentol in humans involving 5 or more different metabolic pathways. A major challenge to the dosing of stiripentol is that the drug shows non-linear pharmacokinetics, with a marked decrease in clearance with increased dosage [148]. Stiripentol is also highly (>99%) protein bound which likely limits clearance of this drug by hemodialysis procedures [19]. The reference range for stiripentol is not well-defined but serum concentrations of 4–22 mg/L correlate with control of absence seizures in children [49].
The complex pharmacokinetics of stiripentol (non-linear pharmacokinetics, high serum protein binding, extensive metabolism) resemble those of the classic AED phenytoin [144]. Monitoring of the free drug fraction of stiripentol would be theoretically advantageous although methods to measure free fractions have not yet been reported. Care must also be taken with the use of stiripentol with carbamazepine, clobazam, phenobarbital, phenytoin, and valproic because stiripentol inhibits the metabolism of these drugs and/or their metabolites [149,150]. An HPLC method has been reported for the analysis of stiripentol concentrations in plasma or serum [151].
15. Tiagabine
Tiagabine is currently infrequently used in the United States and Europe [22]. The major limitation of tiagabine is a propensity to cause non-convulsive status epilepticus which has been well-documented in many case reports and retrospective studies [152,153,154]. The mechanism of anti-convulsive action of tiagabine is not clear although inhibition of GABA reuptake has been proposed [22]. Tiagabine is rapidly absorbed with excellent bioavailability [155]. Unlike many of the other newer anticonvulsants, tiagabine is highly bound to proteins (>96%). Valproic acid can displace tiagabine from plasma protein binding sites, leading to increased free concentrations of tiagabine [156]. Tiagabine is extensively metabolized with less than 1% of the absorbed parent drug excreted unchanged [50,155]. The metabolism of tiagabine is increased during concomitant therapy with classic liver enzyme inducers. Renal impairment has no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of tiagabine [157]. The serum half-life is 2–4 h in patients receiving enzyme inducers and 5–9 h in those not receiving enzyme inducers [40]. The serum half-life increases to 12–16 h in severe liver failure [158]. Children have higher clearance than adults [159].
The inter-individual variation in liver metabolism makes tiagabine a strong candidate for TDM. However, the relatively short half-life of tiagabine under most conditions means that care must be taken in drawing blood for TDM, with trough levels obtained if feasible. The high binding to serum proteins further suggests that measurement of free drug concentrations may be useful [21]. However, there has been little investigation of the relationship between serum/plasma concentrations and therapeutic efficacy [2]. A broad reference range of 20–200 ng/mL has been proposed [50]. Analytical issues have been a challenging problem in measurement of tiagabine serum/plasma concentrations, with some assays not achieving a low enough limit of sensitivity to measure the full range of clinically relevant free drug concentrations [160]. Multiple analytical methodologies have been reported for the measurement of tiagabine in plasma/serum including GC/MS [161] and HPLC [162]. Research aimed at development of improved methodology for measurement of free drug concentrations may be stimulated if the clinical popularity of tiagabine increases in the future.
16. Topiramate
Topiramate has approval for treatment of epilepsy of children and adults, and also for the treatment of migraine headaches [22]. Following oral administration, topiramate is absorbed rapidly with a high bioavailability (~80%) and low binding to serum proteins [163]. Topiramate distributes into saliva, with salivary topiramate concentrations being on average approximately 0.9 that of serum concentrations in patients receiving chronic topiramate therapy. Salivary topiramate concentrations correlate well with those in serum, which makes saliva an alternative sample to perform TDM [10]. Approximately 50% of the absorbed dose is metabolized by the liver, with an increase in metabolism seen in patients concomitantly receiving therapy with classic enzyme inducers. Enzyme inducers can decrease the serum half-life from 20–30 h to approximately 12 h [41,164]. Children generally eliminate topiramate faster than adults [14,165]. Although the effect of hemodialysis on topiramate pharmacokinetics has not been reported, the low plasma protein binding of topiramate suggests that this drug should be effectively cleared by dialysis [19]. A reference range of 5–20 mg/L has been proposed for topiramate for epilepsy therapy [51]. The value of TDM of topiramate is mainly due to inter-individual variation in metabolism. Multiple analytical methodologies have been reported for the measurement of topiramate in plasma/serum including GC [166], GC/MS [167], HPLC [168], LC/MS [169,170], LC/MS/MS [171] and immunoassay [172,173].
17. Vigabatrin
Vigabatrin is an irreversible inhibitor of GABA transaminase, an enzyme that catalyzes the elimination of GABA [174,175]. The drug is supplied as a racemic mixture, with the S(+) enantiomer being active and R(-) enantiomer being therapeutically inactive [175]. The drug has high bioavailability (60–80%) [176], low binding to serum proteins and is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine [174]. Clearance of vigabatrin increased during hemodialysis [177]. Doses of vigabatrin generally need to be decreased during renal failure [174].
The irreversible effect of vigabatrin on its molecular target undermines one of the principle assumptions of TDM, namely that the concentration in serum/plasma clearly correlates with that at the target site of action. This may be one reason why a wide range of trough serum/plasma concentrations (0.8–36 mg/L) have been found in patients successfully treated with vigabatrin [23]. Multiple analytical methodologies have been reported for the measurement of vigabatrin in plasma/serum including capillary electrophoresis [178], GC/MS [71] and HPLC [179]. Other than to assess compliance or possible drug overdose, there is little justification for monitoring of vigabatrin plasma/serum concentrations [23].
18. Zonisamide
Zonisamide is approved in the United States for adjunctive treatment of partial seizures but is also used 'off-label' for bipolar disorder, chronic pain, and migraine headaches [22,52]. Zonisamide is also marketed in Asia and Europe. Zonisamide is rapidly absorbed after oral administration and is only 40–60% bound to serum proteins. Zonisamide distributes into saliva, but there is only limited data published on the relation between salivary and serum zonisamide concentrations [11]. Zonisamide displays linear pharmacokinetics but is extensively metabolized by oxidation, acetylation, and other pathways [180]. CYP3A4, the major liver drug-metabolizing enzyme in most people, is responsible for some of the metabolism of zonisamide. The metabolism of zonisamide can be significantly affected by CYP enzyme inhibitors (e.g., cimetidine, erythromycin, ketoconazole, valproic acid) and inducers. The serum half-life of zonisamide is approximately 50–70 h for patients receiving zonisamide as monotherapy but decreases to 25–35 h in patients concomitantly taking enzyme inducers. Conversely, liver enzyme inhibitors such as valproic acid and ketoconazole may prolong zonisamide half-life [15]. Zonisamide is effectively cleared by hemodialysis [181]. Children require higher doses by weight than adults [14]. Toxic side effects are uncommon at serum concentrations below 30 mg/L [182]. A serum/plasma reference range of 10–40 mg/L has been proposed for seizure management [52,183]. Multiple analytical methodologies have been reported for the measurement of zonisamide in plasma/serum including HPLC [184,185], LC/MS [186] and micellar electrokinetic capillary electrophoresis [187]. The inter-individual variability in metabolism of zonisamide, especially seen in those receiving concomitant therapy with other drugs that can affect liver enzyme expression, makes zonisamide an attractive candidate for TDM.
19. Summary and Further Applications
The newer generation of AEDs offers attractive pharmacological alternatives to the traditional AEDs for treatment of epilepsy and other disorders such as chronic pain, migraine headaches, and fibromyalgia. The newer AEDs generally have fewer adverse effects and wider therapeutic margins. The strongest cases for routine TDM can be made for lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine (mono-hydroxy metabolite), stiripentol, tiagabine, and zonisamide, mainly due to inter-individual variation in metabolism and clearance. For other drugs, TDM may be clinically useful to assess adherence or to adjust dosing in organ failure. Generalized reference ranges have yet to be proposed for some newer AEDs; however, even in the absence of generalized reference ranges, individual reference ranges can be established for patients treated with newer AEDs, allowing for expanded use of TDM. Future research is needed to better define reference ranges and to better document the value of TDM in clinical practice.
Acknowledgements
MDK is supported by a Physician-Scientist Career Development Award K08-GM074238 from the National Institutes of Health.
References
- Neels, H.M.; Sierens, A.C.; Naelerts, K.; Scharpé, S.L.; Hatfield, G.M.; Lambert, W.E. Therapeutic drug monitoring of old and newer anti-epileptic drugs. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2004, 42, 1228–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Patsalos, P.N.; Berry, D.J.; Bourgeois, B.F.D.; Cloyd, J.C.; Glauser, T.A.; Johannessen, S.I.; Tomson, T.; Perucca, E. Antiepileptic drugs—Best practice guidelines for therapeutic drug monitoring: A position paper by the subcommission on therapeutic drug monitoring, ILAE commission on therapeutic strategies. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 1239–1276. [Google Scholar]
- Fröscher, W.; Eichelbaum, M.; Gugler, R.; Hildebrand, G.; Penin, H. A prospective randomized trial on the effect of monitoring plasma anticonvulsant levels in epilepsy. J. Neurol. 1981, 224, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Januzzi, G.; Cian, P.; Fattore, C.; Gatti, G.; Bartoli, A.; Monaco, F.; Perucca, E. A multicenter randomized controlled trial on the clinical impact of therapeutic drug monitoring in patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Delgado, M.R. Therapeutic drug concentration monitoring using saliva samples. Focus on anticonvulsants. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1999, 36, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, D.J.; Beran, R.G.; Plunkeft, M.J.; Clarke, L.A.; Hung, W.T. The absorption of gabapentin following high dose escalation. Seizure 2003, 12, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiropoulos, I.; Kristensen, O.; Klitgaard, N.A. Saliva and serum concentration of lamotrigine in patients with epilepsy. Ther. Drug. Monit. 2000, 22, 517–521. [Google Scholar]
- Mecarelli, O.; Li Voti, P.; Pro, S.; Romolo, F.S.; Rotolo, M.; Pulitano, P.; Accornero, N.; Vanacore, N. Saliva and serum levetiracetam concentrations in patients with epilepsy. Ther. Drug. Monit. 2007, 29, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, M.V.; Tang, P.H.; Ryan, M.A.; Grim, S.A.; Fakhoury, T.A.; Strawsburg, R.H.; DeGrauw, T.J.; Baumann, R.J. Feasibility and limitations of oxcarbazepine monitoring using salivary monohydroxycarbamazepine (MHD). Ther. Drug. Monit. 2004, 26, 300–304. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, M.V.; Tang, P.H.; Glauser, T.A.; Ryan, M.A.; Grim, S.A.; Strawsburg, R.H.; deGrauw, T.J.; Baumann, R.J. Topiramate concentration in saliva: An alternative to serum monitoring. Pediatr. Neurol. 2003, 29, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai, N.; Seki, T.; Yamada, T.; Takuma, Y.; Hirai, K. Concentrations of zonisamide in serum, free fraction, mixed saliva and cerebrospinal fluid in epileptic children treated with monotherapy. Jpn. J. Psychiatry Neurol. 1993, 47, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.D.; Ryan, M.; Miles, M.V.; Tang, P.H.; Fakhoury, T.A.; Degrauw, T.J.; Baumann, R.J. Stability of salivary concentrations of the newer antiepileptic drugs in the postal system. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 576–579. [Google Scholar]
- Bialer, M. The pharmacokinetics and interactions of new antiepileptic drugs: An overview. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 722–726. [Google Scholar]
- Perucca, E. Clinical pharmacokinetics of new-generation antiepileptic drugs at the extremes of age. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 45, 351–364. [Google Scholar]
- Perucca, E.; Bialer, M. The clinical pharmacokinetics of the newer antiepileptic drugs. Focus on topiramate, zonisamide and tiagabine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1996, 31, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, E.G. Induction of cytochromes P450. Curr. Drug Metab. 2001, 2, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Tien, E.S.; Negishi, M. Nuclear receptors CAR and PXR in the regulation of hepatic metabolism. Xenobiotica 2006, 36, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, W.; Krasowski, M.D. PXR: A xenobiotic receptor of diverse function implicated in pharmacogenetics. Pharmacogenomics 2008, 9, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar]
- Lacerda, G.; Krummel, T.; Sabourdy, C.; Ryvlin, P.; Hirsch, E. Optimizing therapy of seizures in patients with renal or hepatic dysfunction. Neurology 2006, 67, S28–S33. [Google Scholar]
- Pitlick, W.H.; Levy, R.H. Time-dependent kinetics I: Exponential autoinduction of carbamazepine in monkeys. J. Pharm. Sci. 1977, 66, 647–649. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, A. Usefulness of monitoring free (unbound) concentrations of therapeutic drugs in patient management. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 377, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- LaRoche, S.M.; Helmers, S.L. The new antiepileptic drugs: Clinical applications. JAMA 2004, 291, 615–620. [Google Scholar]
- Patsalos, P.N. New antiepileptic drugs. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1999, 36, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Johannessen Landmark, C. Antiepileptic drugs in non-epilepsy disorders: Relations between mechanisms of action and clinical efficacy. CNS Drugs 2008, 22, 27–47. [Google Scholar]
- Perucca, E. Is there a role for therapeutic drug monitoring of new anticonvulsants? Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2000, 38, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannessen, S.I.; Tomson, T. Pharmacokinetic variability of newer epileptic drugs? Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 45, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosio, A.F.; Silva, A.P.; Malva, J.O.; Soares-da-Silva, P.; Carvalho, A.P.; Carvalho, C.M. Inhibition of glutamate release by BIA 2-093 and BIA 2-024, two novel derivatives of carbamazepine, due to blockade of sodium but not calcium channels. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 61, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maia, J.; Vaz-da-Silva, M.; Almeida, L.; Falcao, A.; Silveira, P.; Guimaraes, S.; Graziela, P.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Effect of food on the pharmacokinetic profile of eslicarbazepine acetate (BIA 2-093). Drugs R D 2005, 6, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, L.; Falcao, A.; Maia, J.; Mazur, D.; Gellert, M.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Single-dose and steady-state pharmacokinetics of eslicarbazepine acetate (BIA 2-093) in healthy elderly and young subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, L.; Nunes, T.; Sicard, E.; Rocha, J.F.; Falcao, A.; Brunet, J.S.; Lefebvre, M.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Pharmacokinetic interaction study between eslicarbazepine acetate and lamotrigine in healthy subjects. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2010, 121, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Bialer, M.; Johannessen, S.I.; Levy, R.H.; Perucca, E.; Tomson, T.; White, H.S. Progress report on new antiepileptic drugs: A summary of the ninth eilat conference (EILAT IX). Epilepsy Res. 2009, 83, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, L.; Potgieter, J.H.; Maia, J.; Potgieter, M.A.; Mota, F.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Pharmacokinetics of eslicarbazepine acetate in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 64, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, J.; Almeida, L.; Falcao, A.; Soares, E.; Mota, F.; Potgieter, M.A.; Potgieter, J.H.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of eslicarbazepine acetate. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 46, 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, G.; Figueiredo, I.; Castel-Branco, M.; Loureiro, A.; Fortuna, A.; Falcao, A.; Caramona, M. Enantioselective HPLC-UV method for determination of eslicarbazepine acetate (BIA 2-093) and its metabolites in human plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Popova, E.; Leighton, C.; Bernabarre, A.; Bernardo, M.; Vieta, E. Oxcarbazepine in the treatment of bipolar and schizoaffective disorders. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2007, 7, 617–626. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, M.L.; Graves, N.M.; Marienau, K.; Holmes, G.B.; Remmel, R.P.; Leppik, I.E. Discontinuation of phenytoin and carbamazepine in patients receiving felbamate. Epilepsia 1991, 32, 398–406. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay, R.E.; Pellock, J.M.; Garnett, W.R.; Sanchez, R.M.; Valakas, A.M.; Wargin, W.A.; Lai, A.A.; Hubbell, J.; Chern, W.H.; Allsup, T.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of lamotrigine (Lamictal) in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 1991, 10, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, T.W.; Korn-Merker, E.; Rambeck, B. Clinical pharmacokinetics of oxcarbazepine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2003, 42, 1023–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Perucca, E.; Cloyd, J.; Critchley, D.; Fuseau, E. Rufinamide: Clinical pharmacokinetics and concentration-response relationships in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 1123–1141. [Google Scholar]
- So, E.L.; Wolff, D.; Graves, N.M.; Leppik, I.E.; Cascino, G.D.; Pixton, G.C.; Gustavson, L.E. Pharmacokinetics of tiagabine as add-on therapy in patients taking enzyme-inducing antiepilepsy drugs. Epilepsy Res. 1995, 22, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Britzi, M.; Perucca, E.; Soback, S.; Levy, R.H.; Fattore, C.; Crema, F.; Gatti, G.; Doose, D.R.; Maryanoff, B.E.; Bialer, M. Pharmacokinetic and metabolic investigation of topiramate disposition in healthy subjects in the absence and in the presence of enzyme induction by carbamazepine. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 378–384. [Google Scholar]
- Faught, E.; Sachdeo, R.C.; Remler, M.P.; Chayasirisobhon, S.; Iragui-Madoz, V.J.; Ramsay, R.E.; Sutula, T.P.; Kanner, A.; Harner, R.N.; Kuzniecky, R.; Kramer, L.D.; Karmin, M.; Rosenberg, A. Felbamate monotherapy for partial-onset seizures: An active-controlled trial. Neurology 1993, 43, 688–692. [Google Scholar]
- Sachdeo, R.C.; Kramer, L.D.; Rosenberg, A.; Sachdeo, S. Felbamate monotherapy: Controlled trial in patients with partial onset seizures. Ann. Neurol. 1992, 32, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Lindberger, M.; Luhr, O.; Johannessen, S.I.; Larsson, S.; Tomson, T. Serum concentrations and effects of gabapentin and vigabatrin: Observations from a dose titration study. Ther. Drug Monit. 2003, 25, 457–462. [Google Scholar]
- Kellinghaus, C. Lacosamide as treatment for partial epilepsy: Mechanisms of action, pharmacology, effects, and safety. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2009, 5, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli, A.; Guerrini, R.; Belmonte, A.; Alessandri, M.G.; Gatti, G.; Perucca, E. The influence of dosage, age, and comedication on steady state plasma lamotrigine concentrations in epileptic children: A prospective study with preliminary assessments of correlations with clinical response. Ther. Drug Monit. 1997, 19, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leppik, I.E.; Rarick, J.O.; Walczak, T.S.; Tran, T.A.; White, J.R.; Gumnit, R.J. Effective levetiracetam doses and serum concentrations: Age effects. Epilepsia 2002, 43, 240. [Google Scholar]
- Friis, M.L.; Kristensen, O.; Boas, J.; Dalby, M.; Deth, S.H.; Gram, L.; Mikkelsen, M.; Pedersen, B.; Sabers, A.; Worm-Petersen, J. Therapeutic experiences with 947 epileptic out-patients in oxcarbazepine treatment. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1993, 87, 224–227. [Google Scholar]
- Farwell, J.R.; Anderson, G.D.; Kerr, B.M.; Tor, J.A.; Levy, R.H. Stiripentol in atypical absence seizures in children: An open trial. Epilepsia 1993, 34, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Uthman, B.M.; Rowan, A.J.; Ahmann, P.A.; Leppik, I.E.; Schachter, S.C.; Sommerville, K.W.; Shu, V. Tiagabine for complex partial seizures: A randomized, add-on, dose-response trial. Arch. Neurol. 1998, 55, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johannessen, S.I.; Battino, D.; Berry, D.J.; Bialer, M.; Kramer, G.; Tomson, T.; Patsalos, P.N. Therapeutic drug monitoring of the newer antiepileptic drugs. Ther. Drug Monit. 2003, 25, 347–363. [Google Scholar]
- Mimaki, T. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutic drug monitoring of zonisamide. Ther. Drug Monit. 1998, 20, 593–597. [Google Scholar]
- Pellock, J.M.; Faught, E.; Leppik, I.E.; Shinnar, S.; Zupanc, M.L. Felbamate: Consensus of current clinical experience. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 71, 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, C.D.; Barthen, M.T.; Hopper, D.W.; Miller, T.A.; Quigg, M.; Hudspeth, C.; Montouris, G.; Marsh, L.; Perhach, J.L.; Sofia, R.D.; Macdonald, T.L. Quantification in patient urine samples of felbamate and three metabolites: Acid carbamate and two mercapturic acids. Epilepsia 1999, 40, 769–776. [Google Scholar]
- Shumaker, R.C.; Fantel, C.; Kelton, E.; Wong, K.; Weliky, I. Evaluation of the elimination of (14C) felbamate in healthy men. Epilepsia 1990, 31, 642. [Google Scholar]
- Sachdeo, R.C.; Narang-Sachdeo, S.K.; Howard, J.R.; Dix, R.K.; Shumaker, R.C.; Perhach, J.L.; Rosenberg, A. Steady-state pharmacokinetics and dose-proportionality of felbamate after oral administration of 1200, 2400, and 3600 mg/day of felbamate. Epilepsia 1993, 34, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, D.L.; Wagner, M.L.; Perhach, J.L.; Kramer, L.; Graves, N.; Leppik, I.; Shumaker, R.C. Felbamate steady-state pharmacokinetics during co-administration of valproate. Epilepsia 1991, 32, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Annesley, T.M.; Clayton, L.T. Determination of felbamate in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography. Ther. Drug Monit. 1994, 16, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Behnke, C.E.; Reddy, M.N. Determination of felbamate concentration in pediatric samples by high-performance liquid chromatography. Ther. Drug Monit. 1997, 19, 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Poquette, M.A. Isothermal gas chromatographic method for the rapid determination of felbamate concentration in human serum. Ther. Drug Monit. 1995, 17, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Shihabi, Z.K.; Oles, K.S. Felbamate measured in serum by two methods: HPLC and capillary electrophoresis. Clin. Chem. 1994, 40, 1904–1908. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, M.J. Gabapentin. Epilepsia 1995, 36, S57–S86. [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer, K.O.; von Hodenberg, A.; Kölle, E.U. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of gabapentin in rat, dog and man. Arzneimittelforschung 1988, 36, 830–839. [Google Scholar]
- Gidal, B.E.; DeCerce, J.; Bockbrader, H.N.; Gonzalez, J.; Kruger, S.; Pitterle, M.E.; Rutecki, P.; Ramsay, R.E. Gabapentin bioavailability: Effect of dose and frequency of administration in adult patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 1998, 31, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, M.O.; Eldon, M.A.; Keane, W.F.; Turck, D.; Bockbrader, H.N.; Underwood, B.A.; Sedman, A.J.; Halstenson, C.E. Disposition of gabapentin in anuric subjects on hemodialysis. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 35, 622–626. [Google Scholar]
- Armijo, J.A.; Perna, M.A.; Adin, J.; Vega-Gil, N. Association between patient age and gabapentin serum concentration-to-dose ratio: A preliminary multivariate analysis. Ther. Drug Monit. 2004, 26, 633–637. [Google Scholar]
- Sivenius, J.; Kälviäinen, R.; Ylinen, A.; Riekkinen, P. A double-blind study of gabapentin in the treatment of partial seizures. Epilepsia 1991, 32, 539–542. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrami, G.; Kiani, A. Sensitive high-performance liquid chromatographic quantitation of gabapentin in human serum using liquid-liquid extraction and pre-column derivatization with 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 835, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Juenke, J.M.; Brown, P.I.; McMillin, G.A.; Urry, F.M. Procedure for the monitoring of gabapentin with 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid derivatization followed by HPLC with ultraviolet detection. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Ifa, D.R.; Falci, M.; Moraes, M.E.; Bezerra, F.A.; Moraes, M.O.; de Nucci, G. Gabapentin quantification in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Application to bioequivalence study. J. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 36, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrey, D.C.; Godderis, K.O.; Engelrelst, V.I.; Bernard, D.R.; Langlois, M.R. Quantitative determination of vigabatrin and gabapentin in human serum by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 354, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Gambelunghe, C.; Mariucci, G.; Tantucci, M.; Ambrosini, M.V. Gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of gabapentin in serum. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2005, 19, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Curia, G.; Biagini, G.; Perucca, E.; Avoli, M. Lacosamide: A new approach to target voltage-gated sodium currents in epileptic disorders. CNS Drugs 2009, 23, 555–568. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.; Sperling, M.R.; Biton, V.; Krauss, G.; Hebert, D.; Rudd, G.D.; Doty, P. Lacosamide as adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures: A randomized controlled trial. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Menachem, E.; Biton, V.; Jatuzis, D.; Abou-Khalil, B.; Doty, P.; Rudd, G.D. Efficacy and safety of oral lacosamide as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial-onset seizures. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Johannessen Landmark, C.; Patsalos, P.N. Drug interactions involving the new second- and third-generation antiepileptic drugs. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2010, 10, 119–140. [Google Scholar]
- Beydoun, A.; D'Souza, J.; Hebert, D.; Doty, P. Lacosamide: Pharmacology, mechanisms of action and pooled efficacy and safety data in partial-onset seizures. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2009, 9, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gidal, B.E.; Privitera, M.D.; Sheth, R.D.; Gilman, J.T. Vigabatrin: A novel therapy for seizure disorders. Ann. Pharmacother. 1999, 33, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Cawello, W.; Nickel, B.; Eggert-Formella, A. No pharmacokinetic interaction between lacosamide and carbamazepine in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 50, 459–471. [Google Scholar]
- Halford, J.J.; Lapointe, M. Clinical perspectives on lacosamide. Epilepsy Curr. 2009, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sabers, A.; Tomson, T. Managing antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy and lactation. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2009, 22, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Tomson, T.; Battino, D. Pharmacokinetics and therapeutic drug monitoring of newer antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy and the puerperium. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2007, 46, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Incecayir, T.; Agabeyoglu, I.; Gucuyener, K. Comparison of plasma and saliva concentrations of lamotrigine in healthy volunteers. Arzneimittelforschung 2007, 57, 517–521. [Google Scholar]
- Malone, S.A.; Eadie, M.J.; Addison, R.S.; Wright, A.W.; Dickinson, R.G. Monitoring salivary lamotrigine concentrations. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 13, 902–907. [Google Scholar]
- Biton, V. Pharmacokinetics, toxicology and safety of lamotrigine in epilepsy. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2006, 2, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, Z.; Posner, J. Population pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine monotherapy in patients with epilepsy: Retrospective analysis of routine monitoring data. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 43, 457–464. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, A.; Helde, G.; Brodtkorb, E. Ethinyl estradiol, not progestogens, reduces lamotrigine serum concentrations. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1414–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabers, A.; Buchholt, J.M.; Uldall, P.; Hansen, E.L. Lamotrigine plasma levels reduced by oral contraceptives. Epilepsy Res. 2001, 47, 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Fillastre, J.P.; Taburet, A.M.; Fialaire, A.; Etienne, I.; Bidault, R.; Singlas, E. Pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine in patients with renal impairment: Influence of haemodialysis. Drug. Exp. Clin. Res. 1993, 19, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, R.G.; Black, A.B.; Harris, A.L.; Batty, A.B.; Sallustio, B.C. Lamotrigine and therapeutic drug monitoring: retrospective survey following the introduction of a routine service. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 46, 547–551. [Google Scholar]
- Pennell, P.B.; Peng, L.; Newport, D.J.; Ritchie, J.C.; Koganti, A.; Holley, D.K.; Newman, M.; Stowe, Z.N. Lamotrigine in pregnancy: Clearance, therapeutic drug monitoring, and seizure frequency. Neurology 2008, 70, 2130–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelis-Stoforidis, P.; Morgan, D.J.; O'Brien, T.J.; Vajda, F.J. Determination of lamotrigine in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 1999, 727, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Forssblad, E.; Eriksson, A.S.; Beck, O. Liquid chromatographic determination of plasma lamotrigine in pediatric samples. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal. 1996, 14, 755–758. [Google Scholar]
- Greiner-Sosanko, E.; Lower, D.R.; Virji, M.A.; Krasowski, M.D. Simultaneous determination of lamotrigine, zonisamide, and carbamazepine in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddlecombe, R.A.; Dean, K.L.; Smith, C.D.; Jeal, S.C. Validation of a radioimmunoassay for the determination of human plasma concentrations of lamotrigine. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal. 1990, 8, 691–694. [Google Scholar]
- Westley, I.S.; Morris, R.G. Seradyn quantitative microsphere system lamotrigine immunoassay on a Hitachi 911 analyzer compared with HPLC-UV. Ther. Drug Monit. 2008, 30, 634–637. [Google Scholar]
- Sailstad, J.M.; Findlay, J.W. Immunofluorometric assay for lamotrigine (Lamictal) in human plasma. Ther. Drug Monit. 1991, 13, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Theurillat, R.; Kuhn, M.; Thormann, W. Therapeutic drug monitoring of lamotrigine using capillary electrophoresis. Evaluation of assay performance and quality assurance over a 4-year period in the routine arena. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 979, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Jann, M.W.; Hon, Y.Y.; Shamsi, S.A. Development of capillary zone electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry for the determination of lamotrigine in human plasma. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 2033–2043. [Google Scholar]
- Watelle, M.; Demedts, P.; Franck, F.; De Deyn, P.P.; Wauters, A.; Neels, H. Analysis of the antiepileptic phenyltriazine compound lamotrigine using gas chromatography with nitrogen phosphorus detection. Ther. Drug Monit. 1997, 19, 460–464. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, A.; Hart, A.P. Lamotrigine analysis in plasma by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry after conversion to a tert.-butyldimethylsilyl derivative. J. Chromatogr. B 1997, 693, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, O.; Ohman, I.; Nordgren, H.K. Determination of lamotrigine and its metabolites in human plasma by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Ther. Drug Monit. 2006, 28, 603–607. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kwon, O.H.; Lee, B.I.; Heo, K. Determination of lamotrigine in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Neurol. Sci. 2010, in press.. [Google Scholar]
- Pucci, V.; Bugamelli, F.; Baccini, C.; Raggi, M.A. Analysis of lamotrigine and its metabolites in human plasma and urine by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Leppik, I.E. The place of levetiracetam in the treatment of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2001, 42, S44–S45. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, B.A.; Lambeng, N.; Nocka, K.; Kensel-Hammes, P.; Bajjalieh, S.M.; Matagne, A.; Fuks, B. The synaptic vesicle protein SV2A is the binding site for the antiepileptic drug levetiracetam. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004, 101, 9861–9866. [Google Scholar]
- Fay, M.A.; Sheth, R.D.; Gidal, B.E. Oral absorption kinetics of levetiracetam: The effect of mixing with food or enteral nutrition formulas. Clin. Ther. 2005, 27, 594–598. [Google Scholar]
- Lins, R.L.; Otoul, C.; De Smedt, F.; Coupez, R.; Stockis, A. Comparison of plasma and saliva concentrations of levetiracetam following administration orally as a tablet and as a solution in healthy adult volunteers. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 45, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Grim, S.A.; Ryan, M.; Miles, M.V.; Tang, P.H.; Strawsburg, R.H.; de Grauw, T.J.; Fakhoury, T.A.; Baumann, R.J. Correlation of levetiracetam concentrations between serum and plasma. Ther. Drug Monit. 2003, 25, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Patsalos, P.N. Clinical pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 43, 707–724. [Google Scholar]
- Patsalos, P.N.; Ghattaura, S.; Ratnaraj, N.; Sander, J.W. In situ metabolism of levetiracetam in blood of patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 1818–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci, V.; Bugamelli, F.; Mandrioli, R.; Ferranti, A.; Kenndler, E.; Raggi, M.A. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of Levetiracetam in human plasma: Comparison of different sample clean-up procedures. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2004, 18, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnaraj, N.; Doheny, H.C.; Patsalos, P.N. A micromethod for the determination of the new antiepileptic drug levetiracetam (ucb LO59) in serum or plasma by high performance liquid chromatography. Ther. Drug Monit. 1996, 18, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Greiner-Sosanko, E.; Giannoutsos, S.; Lower, D.R.; Virji, M.A.; Krasowski, M.D. Drug monitoring: Simultaneous analysis of lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine, 10-hydroxycarbazepine, and zonisamide by HPLC-UV and a rapid GC method using a nitrogen-phosphorus detector for levetiracetam. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2007, 45, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vermeij, T.A.; Edelbroek, P.M. High-performance liquid chromatographic and megabore gas-liquid chromatographic determination of levetiracetam (ucb L059) in human serum after solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. B 1994, 662, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Isoherranen, N.; Roeder, M.; Soback, S.; Yagen, B.; Schurig, V.; Bialer, M. Enantioselective analysis of levetiracetam and its enantiomer R-alpha-ethyl-2-oxo-pyrrolidine acetamide using gas chromatography and ion trap mass spectrometric detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2000, 745, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Oswald, L.M.; Mendu, D.R.; Soldin, S.J. Determination of levetiracetam in human plasma/serum/saliva by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 375, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, M.; Piunti, A.; Marziali, E.; Komarova, N.; Raggi, M.A.; Kenndler, E. Microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography applied for separation of levetiracetam from other antiepileptic drugs in polypharmacy. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 992–998. [Google Scholar]
- Shihabi, Z.K.; Oles, K.; Hinsdale, M. Analysis of the antiepileptic drug keppra by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1004, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, R.A. Pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, J.G.; McKee, P.J.; Forrest, G.; Beastall, G.H.; Park, B.K.; Lowrie, J.I.; Lloyd, P.; Brodie, M.J. Lack of enzyme induction with oxcarbazepine (600 mg daily) in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1991, 31, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, P.; Flesch, G.; Dieterle, W. Clinical pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of oxcarbazepine. Epilepsia 2007, 35, S10–S13. [Google Scholar]
- Cardot, J.M.; Degen, P.; Flesch, G.; Menge, P.; Dieterle, W. Comparison of plasma and saliva concentrations of the active monohydroxy metabolite of oxcarbazepine in patients at steady state. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1995, 16, 603–614. [Google Scholar]
- Rouan, M.C.; Lecaillon, J.B.; Godbillon, J.; Menard, F.; Darragon, T.; Meyer, P.; Kourilsky, O.; Hillion, D.; Aldigier, J.C.; Jungers, P. The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of oxcarbazepine and its metabolites. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1994, 47, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Furlanut, M.; Franceschi, L.; Poz, D.; Silvestri, L.; Pecorari, M. Acute oxcarbazepine, benazepril, and hydrochlorothiazide overdose with alcohol. Ther. Drug Monit. 2006, 28, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzucchelli, I.; Onat, F.Y.; Ozkara, C.; Atakli, D.; Specchio, L.M.; Neve, A.L.; Gatti, G.; Perucca, E. Changes in the disposition of oxcarbazepine and its metabolites during pregnancy and the puerperium. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 504–509. [Google Scholar]
- Battino, D.; Estienne, M.; Avanzini, G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of antiepileptic drugs in pediatric patients. Part II. Phenytoin, carbamazepine, sulthiame, lamotrigine, vigabatrin, oxcarbazepine and felbamate. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1995, 29, 341–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striano, S.; Striano, P.; Di Nocera, P.; Italiano, D.; Fasiello, C.; Ruosi, P.; Bilo, L.; Pisani, F. Relationship between serum mono-hydroxy-carbazepine concentrations and adverse effects in patients with epilepsy on high-dose oxcabazepine therapy. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 69, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- von Unruh, G.E.; Paar, W.D. Gas chromatographic assay for oxcarbazepine and its main metabolites in plasma. J. Chromatogr. 1985, 345, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- von Unruh, G.E.; Paar, W.D. Gas chromatographic/mass spectrometric assays for oxcarbazepine and its main metabolites, 10-hydroxy-carbazepine and carbazepine-10,11-trans-diol. Biol. Mass Spectrom. 1986, 13, 651–656. [Google Scholar]
- Juenke, J.M.; Brown, P.I.; Urry, F.M.; McMillin, G.A. Drug monitoring and toxicology: A procedure for the monitoring of oxcarbazepine metabolite by HPLC-UV. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2006, 44, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeij, T.A.; Edelbroek, P.M. Robust isocratic high performance liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of seven antiepileptic drugs including lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine and zonisamide in serum after solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 857, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Breton, H.; Cociglio, M.; Bressolle, F.; Peyriere, H.; Blayac, J.P.; Hillaire-Buys, D. Liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry determination of carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine and eight of their metabolites in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 828, 80–90. [Google Scholar]
- Paglia, G.; D'Apolito, O.; Garofalo, D.; Scarano, C.; Corso, G. Development and validation of a LC/MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of oxcarbazepine and its main metabolites in human serum. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 860, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Pucci, V.; Kenndler, E.; Raggi, M.A. Quantitation of oxcarbazepine and its metabolites in human plasma by micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2003, 17, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Selak, I. Pregabalin (Pfizer). Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 2001, 2, 828–834. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, J.A.; Strand, J.C.; Posvar, E.L.; Bockbrader, H.N.; Radulovic, L.L. Pregabalin (CI-1008) single-dose pharmacokinetics and safety/tolerance in healthy subjects after oral administration of pregabalin solution or capsule doses. Epilepsia 1998, 39, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Corrigan, B.W.; Poole, W.F.; Posvar, E.L.; Strand, J.C.; Alvey, C.W.; Radulovic, L.L. Metabolic disposition of pregabalin in healthy volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, P18. [Google Scholar]
- Randinitis, E.J.; Posvar, E.L.; Alvey, C.W.; Sedman, A.J.; Cook, J.A.; Bockbrader, H.N. Pharmacokinetics of pregabalin in subjects with various degrees of renal functions. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 43, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Bockbrader, H.N.; Hunt, T.; Strand, J.; Posvar, E.L.; Sedman, A. Pregabalin pharmacokinetics and safety in health volunteers: Results from two phase I studies. Neurology 2000, 11, 412. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, D.; Millington, C. Analysis of pregabalin at therapeutic concentrations in human plasma/serum by reversed-phase HPLC. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Nirogi, R.; Kandikere, V.; Mudigonda, K.; Komarneni, P.; Aleti, R. Liquid chromatography atmospheric pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of pregabalin in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 3899–3906. [Google Scholar]
- Wheless, J.W.; Vazquez, B. Rufinamide: A novel broad-spectrum antiepileptic drug. Epilepsy Curr. 2010, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Luszczki, J.J. Third-generation antiepileptic drugs: Mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics and interactions. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 197–216. [Google Scholar]
- Contin, M.; Mohamed, S.; Candela, C.; Albani, F.; Riva, R.; Baruzzi, A. Simultaneous HPLC-UV analysis of rufinamide, zonisamide, lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine monohydroxy derivative and felbamate in deproteinized plasma of patients with epilepsy. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiron, C. Stiripentol. Neurotherapeutics 2007, 4, 123–125. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, J.L. The anti-convulsant stiripentol acts directly on the GABA(A) receptor as a positive allosteric modulator. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 190–197. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, R.H.; Lin, H.S.; Blehaut, H.M.; Tor, J.A. Pharmacokinetics of stiripentol in normal man: evidence of nonlinearity. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1983, 23, 523–533. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, R.H.; Loiseau, P.; Guyot, M.; Blehaut, H.M.; Tor, J.; Moreland, T.A. Stiripentol kinetics in epilepsy: Nonlinearity and interactions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1984, 36, 661–669. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, A.; Rey, E.; Pons, G.; Rousseau, M.; d'Athis, P.; Olive, G.; Mather, G.G.; Bishop, F.E.; Wurden, C.J.; Labroo, R.; Trager, W.F.; Kunze, K.L.; Thummel, K.E.; Vincent, J.C.; Gillardin, J.M.; Lepage, F.; Levy, R.H. Influence of stiripentol on cytochrome P450-mediated metabolic pathways in humans: In vitro and in vivo comparison and calculation of in vivo inhibition constants. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 62, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arends, R.H.; Zhang, K.; Levy, R.H.; Baillie, T.A.; Shen, D.D. Stereoselective pharmacokinetics of stiripentol: An explanation for the development of tolerance to anticonvulsant effect. Epilepsy Res. 1994, 18, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Schapel, G.; Chadwick, D. Tiagabine and non-convulsive status epilepticus. Seizure 1996, 5, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Balslev, T.; Uldall, P.; Buchholt, J. Provocation of non-convulsive status epilepticus by tiagabine in three adolescent patients. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2000, 4, 169–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kellinghaus, C.; Dziewas, R.; Ludemann, P. Tiagabine-related non-convulsive status epilepticus in partial epilepsy: Three case reports and a review of the literature. Seizure 2002, 11, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Gustavson, L.E.; Mengel, H.B. Pharmacokinetics of tiagabine, a γ-aminobutyric acid-uptake inhibitor, in healthy subjects after single and multiple doses. Epilepsia 1995, 36, 605–611. [Google Scholar]
- Patsalos, P.N.; Elyas, A.A.; Ratnaraj, N.; Iley, J. Concentration-dependent displacement of tiagabine by valproic acid. Epilepsia 2002, 43, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Cato, A., III; Gustavson, L.E.; Qian, J.; El-Shourbagy, T.; Kelly, E.A. Effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics and tolerability of tiagabine. Epilepsia 1998, 39, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.H.; Gustavson, L.E.; Sperelakis, R.; Lam, N.P.; El-Shourbagy, T.; Qian, J.X.; Layden, T. Pharmacokinetics and safety of tiagabine in subjects with various degrees of hepatic function. Epilepsia 1997, 38, 445–451. [Google Scholar]
- Gustavson, L.E.; Boellner, S.W.; Granneman, G.R.; Qian, J.X.; Guenther, H.J.; el-Shourbagy, T.; Sommerville, K.W. A single-dose study to define tiagabine pharmacokinetics in pediatric patients with complex partial seizures. Neurology 1997, 48, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.; Bialer, M.; Johannessen, S.I.; Krämer, G.; Levy, R.; Mattson, R.H.; Perucca, E.; Patsalos, P.N.; Wilson, J.F. Interlaboratory variability in the quantification of new generation antiepileptic drugs based on external quality assessment data. Epilepsia 2003, 44, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, D.F.; Castella, E.; Goumaz, L.; Anderegg, G. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry assay method for the therapeutic drug monitoring of the antiepileptic drug tiagabine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 21, 641–646. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ratnaraj, N.; Patsalos, P.N. The pharmacokinetic inter-relationship of tiagabine in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and brain extracellular fluid (frontal cortex and hippocampus). Seizure 2004, 13, 574–581. [Google Scholar]
- Easterling, D.E.; Zakszewski, T.; Moyer, M.D.; Margul, B.L.; Marriott, T.B.; Nayak, R.K. Plasma pharmacokinetics of topiramate, a new anticonvulsants in humans. Epilepsia 1988, 29, 662. [Google Scholar]
- Mimrod, D.; Specchio, L.M.; Britzi, M.; Perucca, E.; Specchio, N.; La Neve, A.; Soback, S.; Levy, R.H.; Gatti, G.; Doose, D.R.; Maryanoff, B.E.; Bialer, M. A comparative study of the effect of carbamazepine and valproic acid on the pharmacokinetics and metabolic profile of topiramate at steady state in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, W.E.; Doose, D.R.; Walker, S.A.; Baldassarre, J.S.; Reifer, R.A. A study of topiramate pharmacokinetics and tolerability in children with epilepsy. Pediatr. Neurol. 1999, 20, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Riffitts, J.M.; Gisclon, L.G.; Stubbs, R.J.; Palmer, M.E. A capillary gas chromatographic assay with nitrogen phosphorus detection for the quantification of topiramate in human plasma, urine and whole blood. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 19, 363–371. [Google Scholar]
- Mozayani, A.; Carter, J.; Nix, R. Distribution of topiramate in a medical examiner's case. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1999, 23, 556–558. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrami, G.; Mirzaeei, S.; Kiani, A. Sensitive analytical method for Topiramate in human serum by HPLC with pre-column fluorescent derivatization and its application in human pharmacokinetic studies. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 813, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Britzi, M.; Soback, S.; Isoherranen, N.; Levy, R.H.; Perucca, E.; Doose, D.R.; Maryanoff, B.E.; Bialer, M. Analysis of topiramate and its metabolites in plasma and urine of healthy subjects and patients with epilepsy by use of a novel liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry assay. Ther. Drug Monit. 2003, 25, 314–322. [Google Scholar]
- Contin, M.; Riva, R.; Albani, F.; Baruzzi, A. Simple and rapid liquid chromatographic-turbo ion spray mass spectrometric determination of topiramate in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2001, 761, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, J.; Hojskov, C.S.; Poulsen, J.H. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry assay for topiramate analysis in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid: Validation and comparison with fluorescence-polarization immunoassay. Ther. Drug Monit. 2002, 24, 658–664. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, D.J.; Patsalos, P.N. Comparison of topiramate concentrations in plasma and serum by fluorescence polarization immunoassay. Ther. Drug Monit. 2000, 22, 460–464. [Google Scholar]
- Snozek, C.L.; Rollins, L.A.; Peterson, P.W.; Langman, L.J. Comparison of a new serum topiramate immunoassay to fluorescence polarization immunoassay. Ther. Drug Monit. 2010, 32, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, E.; Pons, G.; Olive, G. Vigabatrin. Clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1992, 23, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schechter, P.J. Clinical pharmacology of vigabatrin. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1989, 27, S19–S22. [Google Scholar]
- Durham, S.L.; Hoke, J.F.; Chen, T.M. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of vigabatrin following a single oral dose of [14C]vigabatrin in healthy male volunteers. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1993, 21, 480–484. [Google Scholar]
- Jacqz-Aigrain, E.; Guillonneau, M.; Rey, E.; Macher, M.A.; Montes, C.; Chiron, C.; Loirat, C. Pharmacokinetics of the S(+) and R(-) enantiomers of vigabatrin during chronic dosing in a patient with renal failure. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 44, 183–185. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.Y.; Lin, W.C. Determination of vigabatrin by capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 794, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Erturk, S.; Aktas, E.S.; Atmaca, S. Determination of vigabatrin in human plasma and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2001, 760, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, R.; Bockbrader, H.N.; Chang, T.; Sedman, A.J. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of zonisamide. Epilepsia 1996, 37, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Ijiri, Y.; Inoue, T.; Fukuda, F.; Suzuki, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Shibahara, N.; Takenaka, H.; Tanaka, K. Dialyzability of the antiepileptic drug zonisamide in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Epilepsia 2004, 45, 924–927. [Google Scholar]
- Berent, S.; Sackellares, J.C.; Giordani, B.; Wagner, J.G.; Donofrio, P.D.; Abou-Khalil, B. Zonisamide (CI-912) and cognition:Results from preliminary study. Epilepsia 1987, 28, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Glauser, T.A.; Pippenger, C.E. Controversies in blood-level monitoring: re-examining its role in the treatment of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2000, 41, S6–S15. [Google Scholar]
- Juenke, J.; Brown, P.I.; Urry, F.M.; McMillin, G.A. Drug monitoring and toxicology: A procedure for the monitoring of levetiracetam and zonisamide by HPLC-UV. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2006, 30, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, M.; Hirade, K.; Sugiyama, T.; Katagiri, Y. High-performance liquid chromatographic assay of zonisamide in human plasma using a non-porous silica column. J. Chromatogr. B 2001, 755, 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, M.; Birnbaum, A.K.; Remmel, R.P. High-speed simultaneous determination of nine antiepileptic drugs using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Ther. Drug Monit. 2008, 30, 347–356. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, K.; Goto, Y.; Sueyasu, M.; Futagami, K.; Kataoka, Y.; Oishi, R. Micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography for therapeutic drug monitoring of zonisamide. J. Chromatogr. B 1997, 695, 417–425. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an Open Access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).