Role of Leukotrienes and Leukotriene Modifiers in Asthma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biosynthesis and Metabolism of Leukotrienes
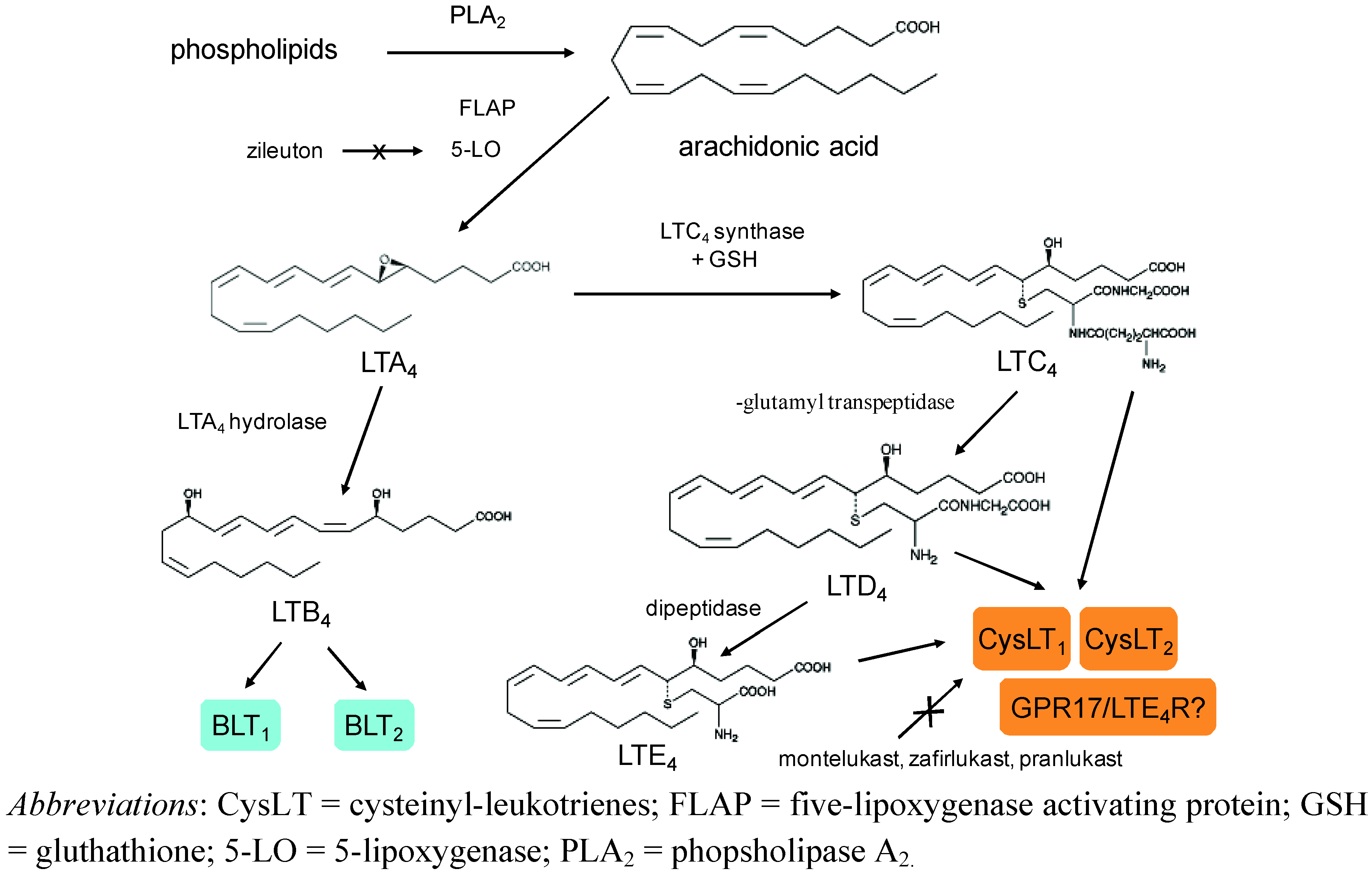
3. Receptors and Mechanism of Action of Leukotrienes
4. Biological Effects of Leukotrienes in the Airways
5. Measurement of LTs in Biological Fluids in Patients with Asthma
6. Effects of Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists in Asthma
| Drug | Mechanism of action | Indication | Benefits | Side effects | Dose | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montelukast | CysLT1 receptor antagonism | asthma, allergic rhinitis | as monotherapy in children with mild persistent asthma; particularly effective in exercise-induced asthma, ASA, allergen-induced asthma; as add-on therapy with ICS | headache, abdominal pain; possible association with Churg-Strauss syndrome | adults: 10 mg o.d. children 6 to 14 years of age: 5 mg o.d. children 2 to 5 years of age: 4 mg o.d. | most widely prescribed CysLT1 receptor antagonist |
| Pranlukast | CysLT1 receptor antagonism | asthma, allergic rhinitis | particularly effective in exercise-induced asthma, ASA, allergen-induced asthma; as add-on therapy with ICS | abdominal pain, liver enzymes elevations; possible association with Churg-Strauss syndrome | adults: 225 mg b.i.d. | only marketed in Asia |
| Zafirlukast | CysLT1 receptor antagonism | asthma | particularly effective in exercise-induced asthma, ASA, allergen-induced asthma; as add-on therapy with ICS | headache, abdominal pain, liver enzymes elevations; possible association with Churg-Strauss syndrome | children ≥ 12 years of age and adults: 20 mg b.i.d. children 5 to 11 years of age: 10 mg b.i.d. | first CysLT1 receptor antagonist to be approved; food and drug interactions |
| Zileuton | 5-LO inhibition | asthma | particularly effective in exercise-induced asthma and ASA | headache, abdominal pain; liver enzymes elevations (5%) | adults and children 12 years of age and older: 600 mg q.i.d. | virtually abandoned because of poor compliance and hepatic toxicity |

7. Conclusions
Ackowledgements
References
- Peters-Golden, M.; Henderson, W.R. Leukotrienes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1841–1854. [Google Scholar]
- Montuschi, P.; Sala, A.; Dahlén, S.-E.; Folco, G. Pharmacological modulation of the leukotriene pathway in allergic airway disease. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 404–412. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlen, S.E. Treatment of asthma with antileukotrienes: First line or last resort therapy? Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 533, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busse, W.; Kraft, M. Cysteinyl leukotrienes in allergic inflammation: Strategic target for therapy. Chest 2005, 127, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Folco, G.; Murphy, R.C. Eicosanoid transcellular biosynthesis: From cell-cell interactions to in vivo tissue responses. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallstrand, T.S.; Henderson, W.R., Jr. An update on the role of leukotrienes in asthma. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 10, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, S.E.; Trudeau, J.B.; Kaminsky, D.A.; Cohn, J.; Martin, R.J.; Wescott, J.Y. Effect of 5-lipoxygenase inhibition on bronchoconstriction and airway inflammation in nocturnal asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 897–905. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, S.; Moodley, Y.P.; Thompson, P.J.; Misso, N.L. Prostaglandin E2 and cysteinyl leukotriene concentrations in sputum: Association with asthma severity and eosinophilic inflammation. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Montuschi, P.; Mondino, C.; Koch, P.; Barnes, P.J.; Ciabattoni, G. Effect of a leukotriene receptor antagonist on exhaled leukotriene E4 and prostanoids in asthmatic children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 347–353. [Google Scholar]
- Mondino, C.; Ciabattoni, G.; Koch, P.; Pistelli, R.; Trové, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Montuschi, P. Effects of inhaled corticosteroids on exhaled leukotrienes and prostanoids in asthmatic children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 761–767. [Google Scholar]
- Holgate, S.T.; Peters-Golden, M.; Panettieri, R.A.; Henderson, W.R. Roles of cysteinyl leukotrienes in airway inflammation, smooth muscle function, and remodeling. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, S18–S36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, A.K.; Henderson, W.R., Jr. The role of leukotrienes in airway remodeling. Curr. Mol. Med. 2009, 9, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, K.R.; O'Neill, G.P.; Liu, Q.; Im, D.S.; Sawyer, N.; Metters, K.M.; Coulombe, N.; Abramovitz, M.; Figueroa, D.J.; Zeng, Z.; Connolly, B.M.; Bai, C.; Austin, C.P.; Chateauneuf, A.; Stocco, R.; Greig, G.M.; Kargman, S.; Hooks, S.B.; Hosfield, E.; Williams, D.L., Jr.; Ford-Hutchinson, A.W.; Caskey, C.T.; Evans, J.F. Characterization of the human cysteinyl leukotriene CysLT1 receptor. Nature 1999, 399, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mellor, E.A.; Frank, N.; Soler, D.; Hodge, M.R.; Lora, J.M.; Austen, K.F.; Boyce, J.A. Expression of the type 2 receptor for cysteinyl leukotrienes (CysLT2R) by human mast cells: Functional distinction from CysLT1R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11589–11593. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa, D.J.; Breyer, R.M.; Defoe, S.K.; Kargman, S.; Daugherty, B.L.; Waldburger, K.; Liu, Q.; Clements, M.; Zeng, Z.; O'Neill, G.P.; Jones, T.R.; Lynch, K.R.; Austin, C.P.; Evans, J.F. Expression of the cysteinyl leukotriene 1 receptor in normal human lung and peripheral blood leukocytes. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 226–233. [Google Scholar]
- Leigh, R.; Vethanayagam, D.; Yoshida, M.; Watson, R.M.; Rerecich, T.; Inman, M.D.; O'Byrne, P.M. Effects of montelukast and budesonide on airway responses and airway inflammation in asthma. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Leff, J.A.; Busse, W.W.; Pearlman, D.; Bronsky, E.A.; Kemp, J.; Hendeles, L.; Dockhorn, R.; Kundu, S.; Zhang, J.; Seidenberg, B.C.; Reiss, T.F. Montelukast, a leukotriene-receptor antagonist, for the treatment of mild asthma and exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlen, S.E.; Malmström, K.; Nizankowska, E.; Dahlén, B.; Kuna, P.; Kowalski, M.; Lumry, W.R.; Picado, C.; Stevenson, D.D.; Bousquet, J.; Pauwels, R.; Holgate, S.T.; Shahane, A.; Zhang, J.; Reiss, T.F.; Szczeklik, A. Improvement of aspirin-intolerant asthma by montelukast, a leukotriene antagonist: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Price, D.B.; Hernandez, D.; Magyar, P.; Fiterman, J.; Beeh, K.M.; James, I.G.; Konstantopoulos, S.; Rojas, R.; van Noord, J.A.; Pons, M.; Gilles, L.; Leff, J.A. Randomised controlled trial of montelukast plus inhaled budesonide versus double dose inhaled budesonide in adult patients with asthma. Thorax 2003, 58, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Busse, W.; Raphael, G.D.; Galant, S.; Kalberg, C.; Goode-Sellers, S.; Srebro, S.; Edwards, L.; Rickard, K. Low-dose fluticasone propionate compared with montelukast for first-line treatment of persistent asthma: A randomized clinical trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 461–468. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, W.R., Jr.; Chiang, G.K.; Tien, Y.T.; Chi, E.Y. Reversal of allergen-induced airway remodeling by CysLT1 receptor blockade. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 718–728. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.M.; Chakir, J.; Vethanayagam, D.; Boulet, L.P.; Laviolette, M.; Gauldie, J.; O'Byrne, P.M. Montelukast treatment attenuates the increase in myofibroblasts following low-dose allergen challenge. Chest 2006, 130, 741–753. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, S.E.; Szefler, S.J.; Leung, D.Y.; Sloan, S.I.; Rex, M.D.; Martin, R.J. Bronchoscopic evaluation of severe asthma. Persistent inflammation associated with high dose glucocorticoids. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 737–743. [Google Scholar]
- Montuschi, P.; Barnes, P.J. Exhaled leukotrienes and prostaglandins in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 615–620. [Google Scholar]
- Montuschi, P.; Martello, S.; Felli, M.; Mondino, C.; Chiarotti, M. Ion trap liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry analysis of leukotriene B4 in exhaled breath condensate. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 2723–2729. [Google Scholar]
- Montuschi, P.; Martello, S.; Felli, M.; Mondino, C.; Chiarotti, C. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis of exhaled leukotriene B4 in asthmatic children. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Kostikas, K.; Gaga, M.; Papatheodorou, G.; Karamanis, T.; Orphanidou, D.; Loukides, S. Leukotriene B4 in exhaled breath condensate and sputum supernatant in patients with COPD and asthma. Chest 2005, 127, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Montuschi, P. New Perspectives in Monitoring Lung Inflammation: Analysis of Exhaled Breath Condensate; Montuschi, P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D.J.; Barnes, P.J.; Spaethe, S.M.; van Alstyne, E.L.; Mitchell, M.I.; O'Connor, B.J. Effect of a leukotriene B4 receptor antagonist, LY293111, on allergen-induced responses in asthma. Thorax 1996, 51, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, N.L.; Riley, J.P; Banie, H.; Xue, X.; Sun, B.; Crawford, S.; Lundeen, K.A.; Yu, F.; Karlsson, L.; Fourie, A.M.; Dunford, P.J. Leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibition attenuates allergic airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyahara, N.; Ohnishi, H.; Matsuda, H.; Miyahara, S.; Takeda, K.; Koya, T.; Matsubara, S.; Okamoto, M.; Dakhama, A.; Haribabu, B.; Gelfand, E.W. Leukotriene B4 receptor 1 expression on dendritic cells is required for the development of Th2 responses and allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi, H.; Miyahara, N.; Dakhama, A.; Takeda, K.; Mathis, S.; Haribabu, B.; Gelfand, E.W. Corticosteroids enhance CD8+ T cell-mediated airway hyperresponsiveness and allergic inflammation by upregulating leukotriene B4 receptor 1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 864–871. [Google Scholar]
- James, A.J.; Penrose, J.F.; Cazaly, A.M.; Holgate, S.T.; Sampson, A.P. Human bronchial fibroblasts express the 5-lipoxygenase pathway. Resp. Res. 2006, 7, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa, A.; Kanaoka, Y.; Xing, W.; Austen, K.F. Functional recognition of a distinct receptor preferential for leukotriene E4 in mice lacking the cysteinyl leukotriene 1 and 2 receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16695–11700. [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa, C.; Balestrieri, B.; Austen, K.F.; Kanaoka, Y. GPR17 is a negative regulator for the cysteinyl leukotriene 1 receptor response to leukotriene D4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11685–11690. [Google Scholar]
- Paruchuri, S.; Tashimo, H.; Feng, C.; Maekawa, A.; Xing, W.; Jiang, Y.; Kanaoka, Y.; Conley, P.; Boyce, J.A. Leukotriene E4-induced pulmonary inflammation is mediated by the P2Y12 receptor. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 2543–2555. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.H. Leukotriene E4: Perspective on the forgotten mediator. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 417–421. [Google Scholar]
- Ciana, P.; Fumagalli, M.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Verderio, C.; Rosa, P.; Lecca, D.; Ferrario, S.; Parravicini, C.; Capra, V.; Gelosa, P.; Guerrini, U.; Belcredito, S.; Cimino, M.; Sironi, L.; Tremoli, E.; Rovati, G.E.; Martini, C.; Abbracchio, M.P. The orphan receptor GPR17 identified as a new dual uracil nucleotides/cysteinyl-leukotrienes receptor. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4615–4627. [Google Scholar]
- Gauvreau, G.M.; Plitt, J.R.; Baatjes, A.; MacGlashan, D.W. Expression of functional cysteinyl leukotriene receptors by human basophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Di Gennaro, A.; Carnini, C.; Buccellati, C.; Ballerino, R.; Zarini, S.; Fumagalli, F.; Viappiani, S.; Librizzi, L.; Hernandez, A.; Murphy, R.C.; Constantin, G.; De Curtis, M.; Folco, G.; Sala, A. Cysteinyl-leukotrienes receptor activation in brain inflammatory reactions and cerebral edema formation: A role for transcellular biosynthesis of cysteinyl-leukotrienes. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 842–844. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa, D.J.; Borish, L.; Barami, D.; Philip, G.; Austin, C.P.; Evans, J.F. Expression of cysteinyl leukotriene synthetic and signalling proteins in inflammatory cells in active seasonal allergic rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, M.; Tanaka, H.; Abe, S. Interferon-γ up-regulates expression of cysteinyl leukotriene type 2 receptors on eosinophils in asthmatic patients. Chest 2005, 128, 3148–3155. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, S.; Billington, C.K.; Pascual, R.M.; Deshpande, D.A.; Stefano, F.P.; Kohout, T.A.; Eckman, D.M.; Benovic, J.L.; Penn, R.B. Regulation of cysteinyl leukotriene type 1 receptor internalization and signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 8722–8732. [Google Scholar]
- Yokomizo, T.; Izumi, T.; Chang, K.; Takuwa, Y.; Shimizu, T. A G-protein-coupled receptor for leukotriene B4 that mediates chemotaxis. Nature 1997, 387, 620–624. [Google Scholar]
- Yokomizo, T.; Kato, K.; Terawaki, K.; Izumi, T.; Shimizu, T. A second leukotriene B4 receptor, BLT2. A new therapeutic target in inflammation and immunological disorders. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundeen, K.A.; Sun, B.; Karlsson, L.; Furie, A.M. Leukotriene B4 receptors BLT1and BLT2: Expression and function in human and murine mast cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 339–347. [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand, E.W.; Dakhama, A. CD8+ T lymphocytes and leukotriene B4: novel interactions in the persistence and progression of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 577–582. [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara, N.; Takeda, K.; Miyahara, S.; Taube, C.; Joetham, A.; Koya, T.; Matsubara, S.; Dakhama, A.; Tager, A.M.; Lustre, A.D.; Gelfand, E.W. Leukotriene B4 receptor-1 is essential for allergen-mediated recruitment of CD8+ T cells and airway hyperresponsiveness. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 4979–4984. [Google Scholar]
- Diamant, Z.; Hiltermann, J.T.; van Rensen, E.L.; Callenbach, P.M.; Veselic-Charvat, M.; van der Veen, H.; Sont, J.K.; Sterk, P.J. The effect of inhaled leukotriene D4 and methacholine on sputum cell differentials in asthma. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Peters-Golden, M. Expanding roles for leukotrienes in airway inflammation. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2008, 8, 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.C.; Hsu, F.I.; Barrett, N.A.; Friend, D.S.; Grenningloh, R.; Ho, I.C.; Al-Garawi, A.; Lora, J.M.; Lam, B.K.; Austen, K.F.; Kanaoka, Y. Cysteinyl leukotrienes regulate Th2 cell-dependent pulmonary inflammation. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4440–4448. [Google Scholar]
- Sampson, A.P.; Castling, D.P.; Green, C.P.; Price, J.F. Persistent increase in plasma and urinary leukotrienes after acute asthma. Arch. Dis. Chil. 1995, 73, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Fourie, A.M. Modulation of inflammatory disease by inhibitors of leukotriene A4 hydrolase. Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 2009, 10, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlen, B.; Nizankowska, E.; Szczeklik, A.; Zetterström, O.; Bochenek, G.; Kumlin, M.; Mastalerz, L.; Pinis, G.; Swanson, L.J.; Boodhoo, T.I.; Wright, S.; Dubé, L.M.; Dahlén, S.E. Benefits from adding the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor zileuton to conventional therapy in aspirin-intolerant asthmatics. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.R.; McFadden, C.A.; Frantz, R.; Awni, W.M.; Cohn, J.; Drazen, J.M.; Israel, E. Effect of chronic 5-lipoxygenase inhibition on airway hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic subjects. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Riccioni, G.; Vecchia, R.D.; D'Orazio, N.; Sensi, S.; Guagnano, M.T. Comparison of montelukast and budesonide on bronchial reactivity in subjects with mild-moderate persistent asthma. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 16, 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Berges-Gimeno, M.P.; Simon, R.A.; Stevenson, D.D. The effect of leukotriene-modifier drugs on aspirin-induced asthma and rhinitis reactions. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen, L.A.; Laitinen, A.; Haahtela, T.; Vilkka, V.; Spur, B.W.; Lee, T.H. Leukotriene E4 and granulocytic infiltration into asthmatic airways. Lancet 1993, 341, 989–990. [Google Scholar]
- Gauvreau, G.M.; Parameswaran, K.N.; Watson, R.M.; O'Byrne, P.M. Inhaled leukotriene E4, but not leukotriene D4, increased airway inflammatory cells in subjects with aopic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O'Hickey, S.P.; Arm, J.P.; Rees, P.J.; Spur, B.W.; Lee, T.H. The relative responsiveness to inhaled leukotriene E4, methacholine and histamine in normal and asthmatic subjects. Eur. Respir. J. 1988, 1, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Antczak, A.; Montuschi, P.; Kharitonov, S.; Gorski, P.; Barnes, P.J. Increased exhaled cysteinyl leukotrienes and 8-isoprostane in aspirin-induced asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Zanconato, S.; Carraro, S.; Corradi, M.; Alinovi, R.; Pasquale, M.F.; Piacentini, G.; Zacchello, F.; Baraldi, E. Leukotrienes and 8-isoprostane in exhaled breath condensate of children with stable and unstable asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Katsunuma, T.; Tomikawa, M.; Tan, A.; Yuki, K.; Akashi, K.; Eto, Y. Increased leukotriene E4 in the exhaled breath condensate of children with mild asthma. Chest 2006, 130, 1718–1722. [Google Scholar]
- Csoma, Z.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Balint, B.; Bush, A.; Wilson, N.M.; Barnes, P.J. Increased leukotrienes in exhaled breath condensate in childhood asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Pavord, I.D.; Ward, R.; Woltmann, G.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Sheller, J.R.; Dworski, R. Induced sputum eicosanoid concentrations in asthma. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 1905–1909. [Google Scholar]
- Kumlin, M. Measurement of leukotrienes in humans. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, S102–S106. [Google Scholar]
- Higashi, N.; Taniguchi, M.; Mita, H.; Kawagishi, Y.; Ishii, T.; Higashi, A.; Osame, M.; Akiyama, K. Clinical features of asthmatic patients with increased urinary leukotriene E4 excretion (hyperleukotrienuria): Involvement of chronic hyperplastic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Green, S.A.; Malice, M.P.; Tanaka, W.; Tozzi, C.A.; Reiss, T.F. Increase in urinary leukotriene LTE4 levels in acute asthma: correlation with airflow limitation. Thorax 2004, 59, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, I.; Hunt, J.; Barnes, P.J.; Alving, K.; Antczak, A.; Baraldi, E.; Becher, G.; van Beurden, W.J.; Corradi, M.; Dekhuijzen, R.; Dweik, R.A.; Dwyer, T.; Effros, R.; Erzurum, S.; Gaston, B.; Gessner, C.; Greening, A.; Ho, L.P.; Hohlfeld, J.; Jöbsis, Q.; Laskowski, D.; Loukides, S.; Marlin, D.; Montuschi, P.; Olin, A.C.; Redington, A.E.; Reinhold, P.; van Rensen, E.L.; Rubinstein, I.; Silkoff, P.; Toren, K.; Vass, G.; Vogelberg, C.; Wirtz, H. ATS/ERS Task Force on exhaled breath condensate. Exhaled breath condensate: Methodological recommendations and unresolved questions. Eur. Resp. J. 2005, 26, 523–548. [Google Scholar]
- Montuschi, P. Analysis of exhaled breath condensate in respiratory medicine: Methodological aspects and potential clinical applications. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2007, 1, 5–23. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, B.; Antó, J.M.; Barreiro, E.; Bel, E.H.D.; Bousquet, J.; Castellsagud, J.; Chanez, P.; Dahién, B.; Dahién, S.E.; Dews, Ń.; Djukanovic, R.; Fabbri, L.M.; Folkerts, G.; Gaga, M.; Gratziou, C.; Holgate, S.T.; Howarth, P.H.; Johnston, S.L.; Kanniess, F. The ENFUMOSA cross-sectional European multicentre study of the clinical phenotype of chronic severe asthma. Eur. Resp. J. 2003, 22, 470–477. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Smithline, H.A.; Malice, M.P.; Green, S.A.; Reiss, T.F. A randomized controlled trial of intravenous montelukast in acute asthma. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 528–533. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Gurner, D.M.; Smithline, H.A.; Chapela, R.; Fabbri, L.M.; Green, S.A.; Malice, M.P.; Legrand, C.; Dass, S.B.; Knorr, B.A.; Reiss, T.F. A randomized placebo-controlled study of intravenous montelukast for the treatment of acute asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 374–380. [Google Scholar]
- Roquet, A.; Dahlén, B.; Kumlin, M.; Ihre, E.; Anstrén, G.; Binks, S.; Dahlén, S.E. Combined antagonism of leukotrienes and histamine produces predominant inhibition of allergen-induced early and late phase airway obstruction in asthmatics. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 1856–1863. [Google Scholar]
- Phipatanakul, W.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A.; Eggleston, P.A.; Van Natta, M.; Kesavan, J.; Schuberth, K.; Wood, R.A. The efficacy of montelukast in the treatment of cat allergen-induced asthma in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 794–799. [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman, D.S.; van Adelsberg, J.; Philip, G.; Tilles, S.A.; Busse, W.; Hendeles, L.; Loeys, T.; Dass, S.B.; Reiss, T.F. Onset and duration of protection against exercise-induced bronchoconstriction by a single oral dose of montelukast. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006, 97, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, G.; Pearlman, D.S.; Villarán, C.; Legrand, C.; Loeys, T.; Langdon, R.B.; Reiss, T.F. Single-dose montelukast or salmeterol as protection against exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Chest 2007, 132, 875–883. [Google Scholar]
- Villaran, C.; O'Neill, S.J.; Helbling, A.; van Noord, J.A.; Lee, T.H.; Chuchalin, A.G.; Langley, S.J.; Gunawardena, K.A.; Suskovic, S.; Laurenzi, M.; Jasan, J.; Menten, J.; Leff, J.A. Montelukast versus salmeterol in patients with asthma and exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Montelukast/salmeterol exercise study group. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Melo, R.E.; Solé, D.; Naspitz, C.K. Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children: Montelukast attenuates the immediate-phase and late-phase responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald, J.M.; Shahidi, N. Achieving asthma control in patients with moderate disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert Panel Report (EPR-3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma-Summary Report 2007. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, S94–S138. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szefler, S.J.; Phillips, B.R.; Martinez, F.D.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Lemanske, R.F.; Strunk, R.C.; Geiger, R.S.; Larsen, G.; Spahn, J.D.; Bacharier, L.B.; Bloomberg, G.R.; Guilbert, T.W.; Heldt, G.; Morgan, W.J.; Moss, M.H.; Sorkness, C.A.; Taussig, L.M. Characterization of within-subject responses to fluticasone and montelukast in childhood asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Vaquerizo, M.J.; Casan, P.; Castello, J.; Perpiña, M.; Sanchis, J.; Sobradillo, V.; Valencia, A.; Verea, H.; Viejo, J.L.; Villasante, C.; Gonzalez-Esteban, J.; Picado, C. Effect of montelukast added to inhaled budesonide on control of mild to moderate asthma. Thorax 2003, 58, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Bjermer, L.; Bisgaard, H.; Bousquet, J.; Fabbri, L.M.; Greening, A.P.; Haahtela, T.; Holgate, S.T.; Picado, C.; Menten, J.; Dass, S.B.; Leff, J.A.; Polos, P.G. Montelukast and fluticasone compared with salmeterol and fluticasone in protecting against asthma exacerbation in adults: One year, double blind, randomised, comparative trial. BMJ 2003, 327, 891. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ducharme, F.M.; Lasserson, T.J.; Cates, C.J. Addition of long-acting β2-agonists vs. anti-leukotrienes as add-on therapy to inhaled corticosteroids for chronic asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, (4), CD003137. [Google Scholar]
- Lemanske, R.F., Jr.; Mauger, D.T.; Sorkness, C.A.; Jackson, D.J.; Boehmer, S.J.; Martinez, F.D.; Strunk, R.C.; Szefler, S.J.; Zeiger, R.S.; Bacharier, L.B.; Covar, R.A.; Guilbert, T.W.; Larsen, G.; Morgan, W.J.; Moss, M.H.; Spahn, J.D.; Taussig, L.M. Childhood Asthma Research and Education (CARE) Network of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Step-up therapy for children with uncontrolled asthma receiving inhaled corticosteroids. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohbayashi, H.; Shibata, N.; Hirose, T.; Adachi, M. Additional effects of pranlukast in salmeterol/fluticasone combination therapy for the asthmatic distal airway in a randomized crossover study. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 22, 574–579. [Google Scholar]
- Tomari, S.; Matsuse, H.; Hirose, H.; Tsuchida, T.; Fukahori, S.; Fukushima, C.; Kawano, T.; Matsuo, N.; Kohno, S. Observational study of the additive effects of pranlukast on inflammatory markers of clinically stable asthma with inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta 2 agonists. Respiration 2008, 76, 398–402. [Google Scholar]
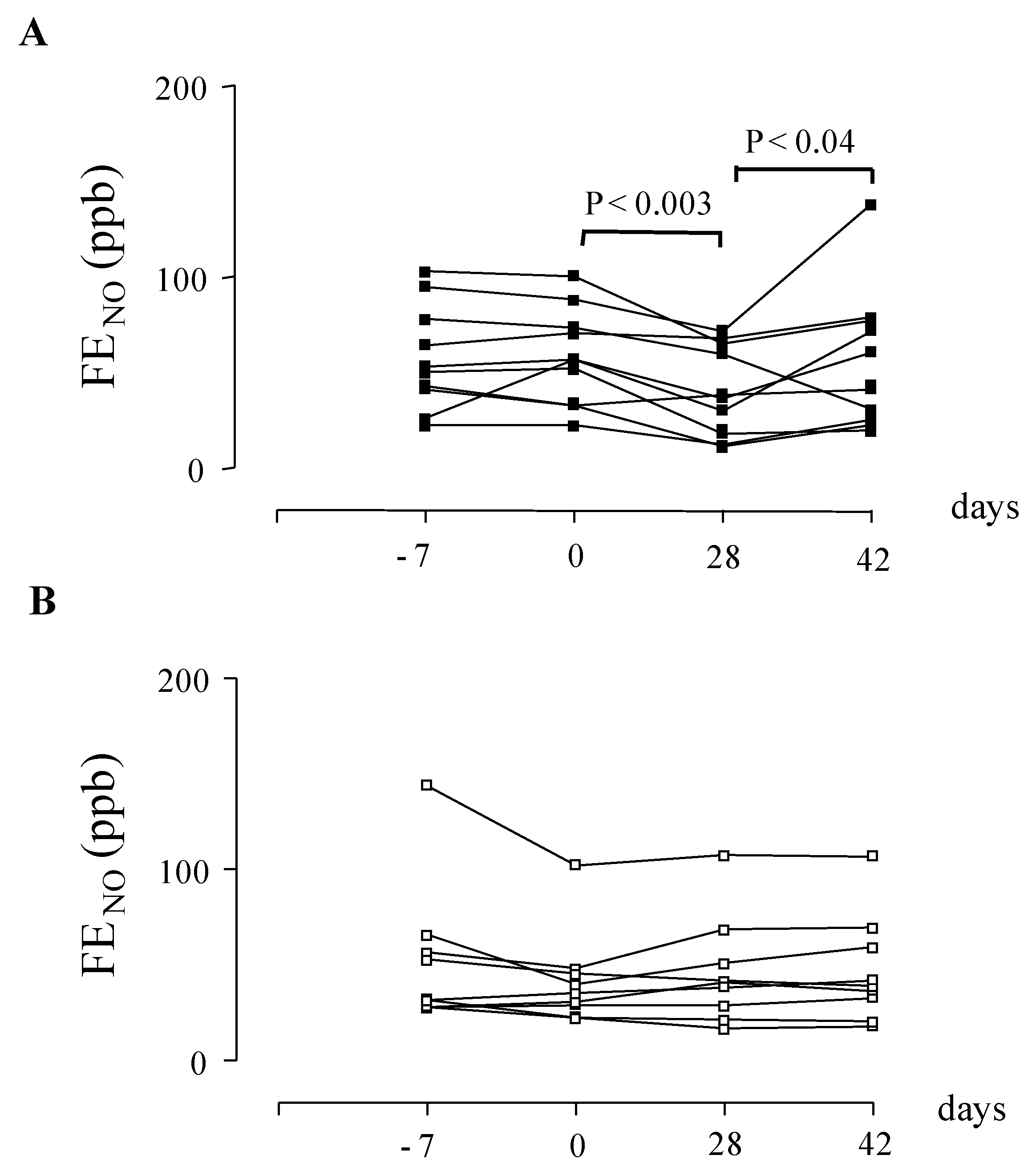
- Montuschi, P.; Mondino, C.; Koch, P.; Ciabattoni, G.; Barnes, P.J.; Baviera, G. Effects of montelukast treatment and withdrawal on fractional exhaled nitric oxide and lung function in children with asthma. Chest 2007, 132, 1876–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Lofdahl, C.G.; Reiss, T.F.; Leff, J.A.; Israel, E.; Noonan, M.J.; Finn, A.F.; Seidenberg, B.C.; Capizzi, T.; Kundu, S.; Godard, P. Randomised, placebo controlled trial of effect of a leukotriene receptor antagonist, montelukast, on tapering inhaled corticosteroids in asthmatic patients. BMJ 1999, 319, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gyllfors, P.; Dahlén, S.E.; Kumlin, M.; Larsson, K.; Dahlén, B. Bronchial responsiveness to leukotriene D4 is resistant to inhaled fluticasone propionate. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Szefler, S.J.; Martin, R.J. Lessons learned from variation in response to therapy in clinical trials. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Malmstrom, K.; Rodriguez-Gomez, G.; Guerra, J.; Villaran, C.; Pineiro, A.; Wei, L.X.; Seidenberg, B.C.; Reiss, T.F. Oral montelukast, inhaled beclomethasone, and placebo for chronic asthma. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 487–495. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, J.J.; Zhang, S.; Grant, A.; Shao, L.; Tantisira, K.G.; Allayee, H.; Wang, J.; Sylvester, J.; Holbrook, J.; Wise, R.; Weiss, S.T.; Barnes, K. Influence of leukotriene pathway polymorphisms on response to montelukast in asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.; Pais, M.; Bish, R.; Reid, D.; Feltis, B.; Johns, D.; Walter, H. Airway inflammation, basement membrane thickening and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthma. Thorax 2002, 57, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino, M.; Takahashi, M.; Takai, Y.; Sim, J. Inhaled corticosteroids decrease subepithelial collagen deposition by modulation of the balance between matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 expression in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaard, H.; Hermansen, M.N.; Loland, L.; Halkjaer, L.B.; Buchvald, F. Intermittent inhaled corticosteroids in infants with episodic wheezing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1998–2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bibby, S.; Healy, B.; Steele, R.; Kumareswaran, K.; Nelson, H.; Beasley, R. Association between leukotriene receptor antagonist therapy and Churg-Strauss syndrome: An analysis of the FDA AERS database. Thorax 2010, 65, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, G.; Hustad, C.; Noonan, G.; Malice, M.P.; Ezekowitz, A.; Reiss, T.F.; Knorr, B. Reports of suicidality in clinical trials of montelukast. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 691–696. [Google Scholar]
- Manalai, P.; Woo, J.M.; Postolache, T.T. Suicidality and montelukast. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2009, 8, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holbrook, J.T.; Harik-Khan, R. Montelukast and emotional well-being as a marker for depression: results from 3 randomized, double-masked clinical trials. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 828–829. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, M.; Koren, G.; Kalra, S.; Ying, A.; Smorlesi, C.; De Santis, M.; Diav-Citrin, O.; Avgil, M.; Voyer Lavigne, S.; Berkovich, M.; Einarson, A. Montelukast use during pregnancy: A multicentre, prospective, comparative study of infant outcomes. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhireva, L.N.; Jones, K.L.; Schatz, M.; Klonoff-Cohen, H.S.; Johnson, D.; Slymen, D.J.; Chambers, C.D. Organization of Teratology Information Specialists Collaborative Research Group. Safety of leukotriene receptor antagonists in pregnancy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.B.; Swern, A.; Tozzi, C.A.; Philip, G.; Polos, P. Effect of montelukast on lung function in asthma patients with allergic rhinitis: analysis from the COMPACT trial. Allergy 2006, 61, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an Open Access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Montuschi, P. Role of Leukotrienes and Leukotriene Modifiers in Asthma. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 1792-1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3061792
Montuschi P. Role of Leukotrienes and Leukotriene Modifiers in Asthma. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(6):1792-1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3061792
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontuschi, Paolo. 2010. "Role of Leukotrienes and Leukotriene Modifiers in Asthma" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 6: 1792-1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3061792
APA StyleMontuschi, P. (2010). Role of Leukotrienes and Leukotriene Modifiers in Asthma. Pharmaceuticals, 3(6), 1792-1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3061792




