Combining Biofilm-Controlling Compounds and Antibiotics as a Promising New Way to Control Biofilm Infections
Abstract
:1. Biofilm Infections Are Difficult to Treat Due to Complex Protection Mechanisms
2. Microbes Communicate by Autoinducers to Form Biofilms
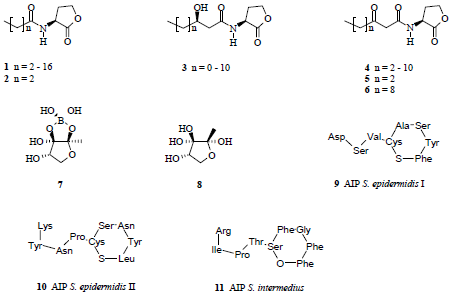
3. Quorum-Quenching Is a Novel Target of Biofilm Control but Not the Only One
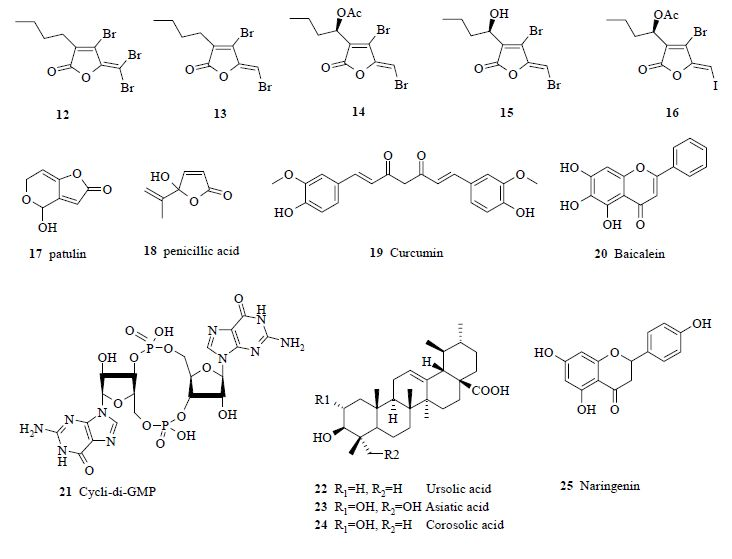
3.1. Natural products as leads for quorum-quenching drugs
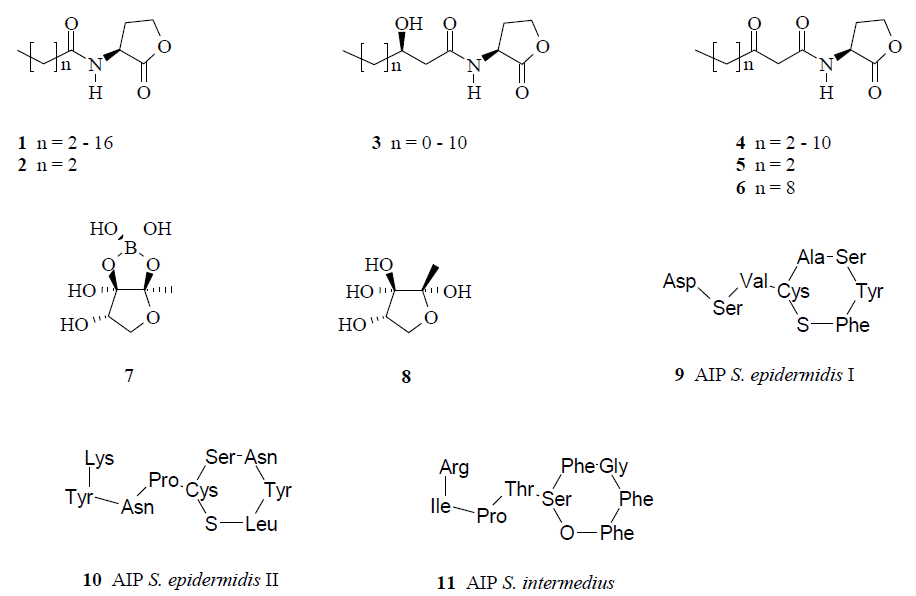
3.2. Synthetic analogues as quorum-quenchers
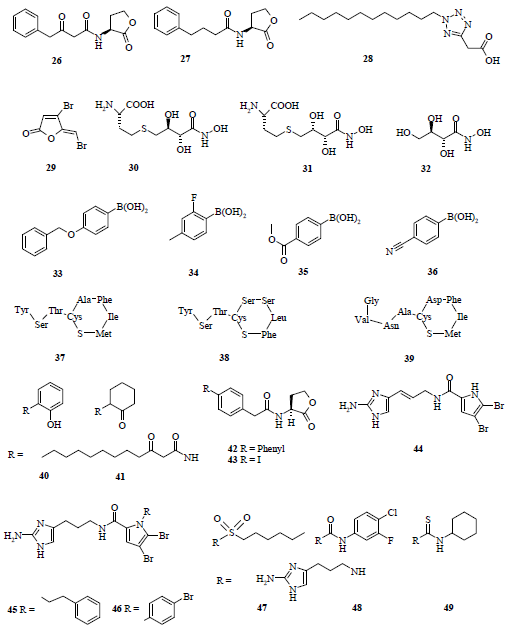
3.3. Antagonists of AIPs
4. There Are More Ways to Control Biofilms Than Interference with the Quorum-Sensing System
4.1. Fatty acids acting as diffusible signal factor
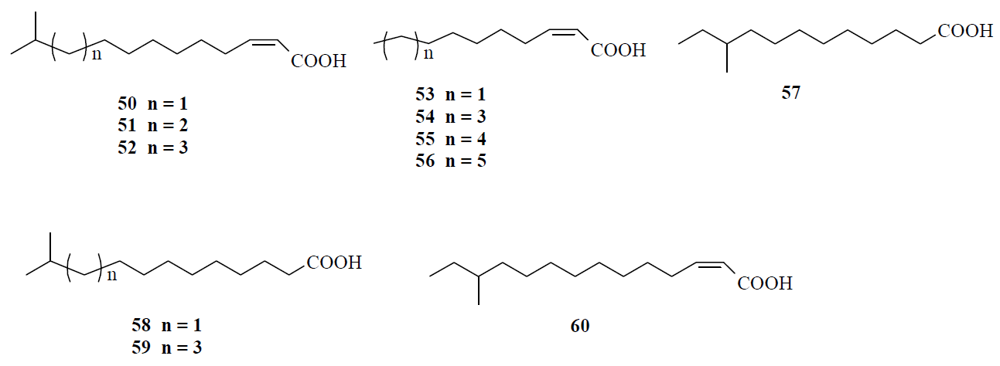
4.2. Nitric oxide (NO) can disperse biofilms
4.3. Hydrolysis of extracellular DNA (eDNA)
5. Dispersion of the Biofilm Can Increase the Virulence
6. Combining Quorum-Quenching Compounds with Antibiotics Can Treat Biofilm Infections
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Singh, P.K.; Schaefer, A.L.; Parsek, M.R.; Moninger, T.O.; Welsh, M.J.; Greenberg, E.P. Quorum-sensing signals indicate that cystic fibrosis lungs are infected with bacterial biofilms. Nature 2000, 407, 762–764. [Google Scholar]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Hu, F.Z.; Gieseke, A.; Nistico, L.; Nguyen, D.; Hayes, J.; Forbes, M.; Greenberg, D.P.; Dice, B.; Burrows, A.; Wackym, P.A.; Stoodley, P.; Post, J.C.; Ehrlich, G.D.; Kerschner, J.E. Direct detection of bacterial biofilms on the middle-ear mucosa of children with chronic otitis media. JAMA 2006, 296, 202–211. [Google Scholar]
- Carron, M.A.; Tran, V.R.; Sugawa, C.; Coticchia, J.M. Identification of Helicobacter pylori biofilms in human gastric mucosa. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2006, 10, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: From the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, M.; Dillon, L.R. Catheter outcomes in home infusion. J. Infus. Nurs. 2008, 31, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteley, M.; Bangera, M.G.; Bumgarner, R.E.; Parsek, M.R.; Teitzel, G.M.; Lory, S.; Greenberg, E.P. Gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Nature 2001, 413, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stewart, P.S.; Costerton, J.W. Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet 2001, 358, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Joly, V.; Pangon, B.; Vallois, J.M.; Abel, L.; Brion, N.; Bure, A.; Chau, N.P.; Contrepois, A.; Carbon, C. Value of antibiotic levels in serum and cardiac vegetations for predicting antibacterial effect of ceftriaxone in experimental Escherichia coli endocarditis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1987, 31, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Lostroh, C.P.; Ogi, T.; Greenberg, E.P. Identification, timing, and signal specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-controlled genes: A transcriptome analysis. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2066–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, T.-F.; Pitts, B.; Pellock, B.; Walker, G.C.; Stewart, P.S.; O’Toole, G.A. A genetic basis for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm antibiotic resistance. Nature 2003, 426, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.T.; Wang, Q.; Harshey, R.M. Cell density and mobility protect swarming bacteria against antibiotics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3776–3781. [Google Scholar]
- Schauder, S.; Bassler, B.L. The languages of bacteria. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1468–1480. [Google Scholar]
- Camilli, A.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial small-molecule signaling pathways. Science 2006, 311, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Shrout, J.D.; Chopp, D.L.; Just, C.L.; Hentzer, M.; Givskov, M.; Parsek, M.R. The impact of quorum sensing and swarming motility on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation is nutritionally conditional. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, K.; Surette, M.G. Environmental regulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Las and Rhl quorum-sensing systems. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 4827–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollinger, N.; Hassett, D.J.; Iglewski, B.H.; Costerton, J.W.; McDermott, T.R. Gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Evidence of iron override effects on quorum sensing and biofilm-specific gene regulation. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, V.E.; Gillis, R.J.; Iglewski, B.H. Transcriptome analysis of quorum-sensing regulation and virulence factor expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Vaccine 2004, 22 (Suppl.1), S15–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, W.-R. Controlling Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria by interfering with their biofilm formation. Drug Design Rev. Online 2005, 2, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Schauder, S.; Potier, N.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Pelczer, I.; Bassler, B.L.; Hughson, F.M. Structural identification of a bacterial quorum-sensing signal containing boron. Nature 2002, 415, 545–549. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.T.; Xavier, K.B.; Campagna, S.R.; Taga, M.E.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L.; Hughson, F.M. Salmonella typhimurium recognizes a chemically distinct form of the bacterial quorum-sensing signal AI-2. Mol. Cell 2004, 15, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, K.B.; Miller, S.T.; Lu, W.; Kim, J.H.; Rabinowitz, J.; Pelczer, I.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L. Phosphorylation and processing of the quorum-sensing molecule autoinducer-2 in enteric bacteria. Chem. Biol. 2007, 2, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Taga, M.E.; Semmelhack, J.L.; Bassler, B.L. The LuxS-dependent autoinducer AI-2 controls the expression of an ABC transporter that functions in AI-2 uptake in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 42, 777–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taga, M.E.; Miller, S.T.; Bassler, B.L. Lsr-mediated transport and processing of AI-2 in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 1411–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezzonico, F.; Duffy, B. Lack of genomic evidence of AI-2 receptors suggests a non-quorum sensing role for luxS in most bacteria. BMC Microbiology 2008, 8, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, N.; Holden, M.T.; Qazi, S.N.; Williams, P.; Winzer, K. Functional analysis of luxS in Staphylococcus aureus reveals a role in metabolism but not quorum sensing. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 2885–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, G.J.; Novick, R.P. Peptide signaling in Staphylococcus aureus and other Gram-positive bacteria. Peptides 2004, 25, 1389–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, P.; Affas, Z.; Reynolds, C.; Holden, M.T.G.; Wood, S.J.; Saint, S.; Cockayne, A.; Hill, P.J.; Dodd, C.E.R.; Bycroft, B.W.; Chan, W.C.; Williams, P. Structure, activity and evolution of the group I thiolactone peptide quorum-sensing system of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, W.-R. Controlling the biofilm formation of Gram-positive pathogenic bacteria. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 1509–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M.; Süssmuth, R.; Jung, G.; Götz, F. Structure of the pheromone peptide of the Staphylococcus epidermidis agr system. FEBS Lett. 1998, 424, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.; Beavis, R.; Novick, R.P. Bacterial interference caused by autoinducing peptide variants. Science 1997, 276, 2027–2030. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, L.; Surette, M.G. Communication in bacteria: An ecological and evolutionary perspective. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, T.; Jesudhasan, P.; Pillai, S.; Wood, T.K.; Jayaraman, A. Temporal regulation of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli virulence mediated by autoinducer-2. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 78, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, K.; Hentzer, M.; Geisenberger, O.; Huber, B.; Steidle, A.; Wu, H.; Høiby, N.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Eberl, L. N-Acylhomoserine-lactone-mediated communication between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia in mixed biofilms. Microbiology 2001, 147, 3249–3262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burmølle, M.; Webb, J.S.; Rao, D.; Hansen, L.H.; Sørensen, S.J.; Kjelleberg, S. Enhanced biofilm formation and increased resistance to antimicrobial agents and bacterial invasion are caused by synergistic interactions in multispecies biofilms. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3916–3923. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, K.; Dammel, C.; Stein, J.; Rabin, H.; Surette, M.G. Modulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa gene expression by host microflora through interspecies communication. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 1477–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, G.F.; Sartorio, R.; Lee, S.-H.; Rogers, C.J.; Meijler, M.M.; Moss, J.A.; Clapham, B.; Brogan, A.P.; Dickerson, T.J.; Janda, K.D. Revisiting quorum sensing: Discovery of additional chemical and biological functions for 3-oxo-N-acylhomoserine lactones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- de Nys, R.; Wright, A.D.; König, G.M.; Sticher, O. New halogenated furanones from the marine red alga Delisea pulchra (cf.fimbriata). Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 11213–11220. [Google Scholar]
- Manefield, M.; de Nys, R.; Kumar, N.; Read, R.; Givskov, M.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S. Evidence that halogenated furanones from Delisea pulchra inhibit acylated homoserine lactone (AHL)-mediated gene expression by displacing the AHL signal from its receptor protein. Microbiol. 1999, 145, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelmgaard, T.; Persson, T.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Givskov, M.; Nielsen, J. Synthesis of furanone-based natural product analogues with quorum sensing antagonist activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 3261–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estephane, J.; Dauvergne, J.; Soulère, L.; Reverchon, S.; Queneau, Y.; Doutheu, A. N-Acyl-3-amino-5H-furanone derivatives as new inhibitors of LuxR-dependent quorum sensing: Synthesis, biological evaluation and binding mode study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4321–4324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Kim, J.; Park, H.Y.; Park, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.K.; Yoon, J. Furanone derivatives as quorum-sensing antagonists of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 80, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Sims, J.J.; Wood, T.K. Inhibition of biofilm formation and swarming of Escherichia coli by (5Z)-4-bromo-5-(bromomethylene)-3-butyl-2(5H)-furanone. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Song, Z.; Givskov, M.; Doring, G.; Worlitzsch, D.; Mathee, K.; Rygaard, J.; Høiby, N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutations in lasI and rhlI quorum sensing systems result in milder chronic lung infection. Microbiology 2001, 147, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Song, Z.; Hentzer, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M.; Høiby, N. Synthetic furanones inhibit quorum-sensing and enhance bacterial clearance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in mice. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harjai, K.; Kumar, R.; Singh, S. Garlic blocks quorum sensing and attenuates the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 58, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, A.R.; Cifelli, P.M.; Ortori, C.A.; Righetti, K.; Lewis, S.; Erskine, P.; Holland, E.D.; Givskov, M.; Williams, P.; Cámara, M.; Barrett, D.A.; Knox, A. Garlic as an inhibitor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing in cystic fibrosis--a pilot randomized controlled trial. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2010, 45, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rudrappa, T.; Bais, H.P. Curcumin, a known phenolic from Curcuma longa, attenuates the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 in whole plant and animal pathogenicity models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikram, A.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Jesudhasan, P.R.; Pillai, S.D.; Patil, B.S. Suppression of bacterial cell-cell signalling, biofilm formation and type III secretion system by citrus flavonoids. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverchon, S.; Chantegrel, B.; Deshayes, C.; Doutheau, A.; Cotte-Pattat, N. New synthetic analogues of N-acyl homoserine lactones as agonists or antagonists of transcriptional regulators involved in bacterial quorum sensing. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müh, U.; Schuster, M.; Heim, R.; Singh, A.; Olson, E.R.; Greenberg, E.P. Novel Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing inhibitors identified in an ultra-high-throughput screen. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 3674–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.M.; Bu, Y.; Suga, H. Library screening for synthetic agonists and antagonists of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa autoinducer. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.M.; Bu, Y.; Suga, H. Induction and inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing by synthetic autoinducer analogs. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattmann, M.E.; Geske, G.D.; Worzalla, G.A.; Chandler, J.R.; Sappington, K.J.; Greenberg, E.P.; Blackwell, H.E. Synthetic ligands that activate and inhibit a quorum-sensing regulator in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 3072–3075. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geske, G.D.; O'Neill, J.C.; Blackwell, H.E. N-phenylacetanoyl-L-homoserine lactones can strongly antagonize or superagonize quorum sensing in Vibrio fischeri. ACS Chem. Biol. 2007, 2, 315–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geske, G.D.; Wezeman, R.J.; Siegel, A.P.; Blackwell, H.E. Small molecule inhibitors of bacterial quorum sensing and biofilm formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12762–12763. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geske, G.D.; O'Neill, J.C.; Miller, D.M.; Mattmann, M.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Modulation of bacterial quorum sensing with synthetic ligands: systematic evaluation of N-acylated homoserine lactones in multiple species and new insights into their mechanisms of action. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 13613–13625. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forenza, S.; Minale, L.; Riccio, R.; Fattorusso, E. New bromo-pyrrole derivatives from the sponge. Agelas oroides. J. Chem. Soc. D 1971, 1129–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, S.R.; Jensen, P.R.; Henkel, T.P.; Fenical, W.; Pawlik, J.R. Effects of Caribbean sponge extracts on bacterial attachment. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 31, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.J.; Reyes, S.; Stowe, S.D.; Tucker, A.T.; Ballard, T.E.; Mathies, L.D.; Cavanagh, J.; Melander, C. Amide isosteres of oroidin: assessment of antibiofilm activity and C. elegans toxicity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 4582–4585. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ballard, T.E.; Richards, J.J.; Aquino, A.; Reed, C.S.; Melander, C. Antibiofilm activity of a diverse oroidin library generated through reductive acylation. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Rajan, R.; Zhu, J.; Bell, C.E.; Pei, D. Design and synthesis of substrate and intermediate analogue inhibitors of S-ribosylhomocysteinase. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3003–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, N.; Chou, H.-T.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Lu, C.-D.; Tai, P.C.; Wang, B. Identification of boronic acids as antagonists of bacterial quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2008, 369, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayville, P.; Ji, G.; Beavis, R.; Yang, H.; Goger, M.; Novick, R.P.; Muir, T.W. Structure-activity analysis of synthetic autoinducing thiolactone peptides from Staphylococcus aureus responsible for virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Wright III, J.S.; Lyon, G.J.; George, E.A.; Muir, T.W.; Novick, R.P. Hydrophobic interactions drive ligand-receptor recognition for activation and inhibition of staphylococcal quorum sensing. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16168–16173. [Google Scholar]
- McDowell, P.; Affas, Z.; Reynolds, C.; Holden, M.T.G.; Wood, S.J.; Saint, S.; Cockayne, A.; Hill, P.J.; Dodd, C.E.R.; Bycroft, B.W.; Chan, W.C.; Williams, P. Structure, activity and evolution of the group I thiolactone peptide quorum-sensing system of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lyon, G.J.; Wright, J.S.; Muir, T.W.; Novick, R.P. Key determinants of receptor activation in the agr autoinducing peptides of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 10095–10104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harraghy, N.; Kerdudou, S.; Herrmann, M. Quorum-sensing systems in staphylococci as therapeutic targets. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjelleberg, S.; Molin, S. Is there a role for quorum sensing signals in bacterial biofilms? Curr. Opinion Microbiol. 2002, 5, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, M. Diversification of the function of cell-to-cell signaling in regulation of virulence within plant pathogenic xanthomonads. Sci. Signal. 2008, 1, pe23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looney, W.J. Role of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in hospital-acquired infection. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2005, 62, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.P.; Wong, A.C. Extracellular fatty acids facilitate flagella-independent translocation by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Res. Microbiol. 2007, 158, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.P.; Fouhy, Y.; Garcia, B.F.; Watt, S.A.; Niehaus, K.; Yang, L.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Dow, J.M. Interspecies signalling via the Stenotrophomonas maltophilia diffusible signal factor influences biofilm formation and polymyxin tolerance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 68, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Shingaki, R.; Fukui, K. Inhibition of swarming motility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by branched-chain fatty acids. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 281, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, C.; Deng, Y.; Wang, L.-H.; He, Y.; Xu, J.-L.; Fan, Y.; Pan, S.Q.; Zhang, L.-H. A novel DSF-like signal from Burkholderia cenocepacia interferes with Candida albicans morphological transition. ISME J. 2008, 2, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snider, J. Molecule that induces biofilm dispersion discovered. JADA 2006, 137, 1643–1646. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davies, D.G.; Marques, C.N.H. A fatty acid messenger is responsible for inducing dispersion in microbial biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, T. When the party is over: A signal for dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7325–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlag, S.; Nerz, C.; Birkenstock, T.A.; Altenberend, F.; Götz, F. Inhibition of Staphylococcal biofilm formation by nitrite. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 7911–7919. [Google Scholar]
- Hetrick, E.M.; Shin, J.H.; Paul, H.S.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Anti-biofilm efficacy of nitric oxide-releasing silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2782–2789. [Google Scholar]
- Nabloa, B.J.; Prichard, H.L.; Butler, R.D.; Klitzman, B.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Inhibition of implant-associated infections via nitric oxide release. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6984–6990. [Google Scholar]
- Thormann, K.M.; Duttler, S.; Saville, R.M.; Hyodo, M.; Shukla, S.; Hayakawa, Y.; Spormann, A.M. Control of formation and cellular detachment from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 biofilms by cyclic di-GMP. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 2681–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamayo, R.; Pratt, J.T.; Camilli, A. Roles of cyclic diguanylate in the regulation of bacterial pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.P.; Fouhy, Y.; Lucey, J.F.; Dow, J.M. Cyclic di-GMP signaling in bacteria: Recent advances and new puzzles. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 8327–8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenal, U.; Malone, J. Mechanisms of cyclic-di-GMP signaling in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2006, 40, 385–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitchurch, C.B.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Ragas, P.C.; Mattick, J.S. Extracellular DNA required for bacterial biofilm formation. Science 2002, 295, 1487–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Ou, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Molin, S.; Qu, D. Role of autolysin-mediated DNA release in biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Microbiology. 2007, 153, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izano, E.A.; Amarante, M.A.; Kher, W.B.; Kaplan, J.B. Differential roles of poly-N-acetylglucosamine surface polysaccharide and extracellular DNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.G.; Marques, C.N.; Amari, D.T.; Hong, B.Y.; Mavor, J.L. Characterization of induction of biofilm dispersion by cis-2-decenoic acid. ASM Biofilms 2009, Cancun, Mexico, Book of abstracts 2009, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Yahr, T.L.; Wolfgang, M.C. Transcriptional regulation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Gotz, F.; Häussler, S.; Jordan, D.; Saravanamuthu, S.S.; Wehmhöner, D.; Strüssmann, A.; Lauber, J.; Attree, I.; Buer, J.; Tümmler, B.; Steinmetz, I. Expression analysis of a highly adherent and cytotoxic small colony variant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from a lung of a patient with cystic fibrosis. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 3837–3847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, H.; Bond, N.J.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Givskov, M.; Lilley, K.S.; Welch, M. Biofilms and type III secretion are not mutually exclusive in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 2009, 155, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamber, S.; Cheung, A.L. SarZ promotes the expression of virulence factors and represses biofilm formation by modulating SarA and agr in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, H.A.; Kottkamp, G.S.; Eppelbaum, J.L.; Stubblefield, B.A.; Gilbert, S.E.; Gilbert, E.S. Influences of biofilm structure and antibiotic resistance mechanisms on indirect pathogenicity in a model polymicrobial biofilm. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5013–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Jensen, P.O.; Burmolle, M.; Hentzer, M.; Haagensen, J.A.J.; Hougen, H.P.; Calum, H.; Madsen, K.G.; Moser, C.; Molin, S.; Hoiby, N.; Givskov, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa tolerance to tobramycin, hydrogen peroxide and polymorphonuclear leukocytes is quorum-sensing dependent. Microbiology 2005, 151, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Wu, H.; Andersen, J.B.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bagge, N.; Kumar, N.; Schembri, M.A.; Song, Z.; Kristoffersen, P.; Manefield, M.; Costerton, J.W.; Molin, S.; Eberl, L.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S.; Høiby, N.; Givskov, M. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3803–3815. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Phipps, R.K.; Christensen, K.B.; Jensen, P.O.; Andersen, J.B.; Koch, B.; Larsen, T.O.; Hentzer, M.; Eberl, L.; Hoiby, N.; Givskov, M. Identity and effects of quorum-sensing inhibitors produced by Penicillium species. Microbiol. 2005, 151, 1325–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Zuo, R.; Barrios, A.F.G.; Bedzyk, L.A.; Eldridge, G.R.; Pasmore, M.E.; Wood, T.K. Differential gene expression for investigation of Escherichia coli biofilm inhibition by plant extract ursolic acid. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4022–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garo, E.; Eldridge, G.R.; Goering, M.G.; Pulcini, E.D.; Hamilton, M.A.; Costerton, J.W.; James, G.A. Asiatic acid and corosolic acid enhance the susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms to tobramycin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1813–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Qian, L.; Cao, L.; Tan, H.; Huang, Y.; Xue, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, S. Virtual screening for novel quorum sensing inhibitors to eradicate biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 79, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barraud, N.; Hassett, D.J.; Hwang, S.-H.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Webb, J.S. Involvement of nitric oxide in biofilm dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7344–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, S.A.; Krayer, M.; Lindsey, J.S.; Melander, C. Tandem dispersion and killing of bacteria from a biofilm. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, S.A.; Huigens, R.W., III.; Cavanagh, J.; Melander, C. Synergistic effects between conventional antibiotics and 2-aminoimidazole-derived antibiofilm agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010. [Epub ahead of print]. [Google Scholar]
- Donelli, G.; Francolini, I.; Romoli, D.; Guaglianone, E.; Piozzi, A.; Ragunath, C.; Kaplan, J.B. Synergistic activity of dispersin B and cefamandole nafate in inhibition of staphylococcal biofilm growth in polyurethanes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2733–2740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geske, G.D.; O’Neill, J.C.; Blackwell, H.E. N-(phenylacetanoyl)-l-homoserine lactones can strongly antagonize or superagonize quorum sensing in Vibrio fischeri. ACS Chem. Biol. 2007, 2, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kievit, T.R. Minireview: Quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Env. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, E.; Humair, B.; Denervaud, V.; Riedel, K.; Spahr, S.; Eberl, L.; Valverde, C.; Haas, D. Two GacA-dependent small RNAs modulate the quorum-sensing response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 6026–6033. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Estrela, A.B.; Abraham, W.-R. Combining Biofilm-Controlling Compounds and Antibiotics as a Promising New Way to Control Biofilm Infections. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 1374-1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3051374
Estrela AB, Abraham W-R. Combining Biofilm-Controlling Compounds and Antibiotics as a Promising New Way to Control Biofilm Infections. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(5):1374-1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3051374
Chicago/Turabian StyleEstrela, Andréia Bergamo, and Wolf-Rainer Abraham. 2010. "Combining Biofilm-Controlling Compounds and Antibiotics as a Promising New Way to Control Biofilm Infections" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 5: 1374-1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3051374
APA StyleEstrela, A. B., & Abraham, W.-R. (2010). Combining Biofilm-Controlling Compounds and Antibiotics as a Promising New Way to Control Biofilm Infections. Pharmaceuticals, 3(5), 1374-1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3051374