Abstract
GABAA receptors mediate the majority of the fast inhibition in the mature brain and play an important role in the pathogenesis of many neurological and psychiatric disorders. The αβδ GABAA receptor localizes extra- or perisynaptically and mediates GABAergic tonic inhibition. Compared with synaptically localized αβγ receptors, αβδ receptors are more sensitive to GABA, display relatively slower desensitization and exhibit lower efficacy to GABA agonism. Interestingly, αβδ receptors can be positively modulated by a variety of structurally different compounds, even at saturating GABA concentrations. This review focuses on allosteric modulation of recombinant αβδ receptor currents and αβδ receptor-mediated tonic currents by anesthetics and ethanol. The possible mechanisms for the positive modulation of αβδ receptors by these compounds will also be discussed.
1. Introduction
GABAergic neurotransmission mediates the prevalent inhibition in the mature brain [1,2,3]. The neurotransmitter involves in this signaling is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is biosynthesized from glutamate by glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) and degraded by GABA transaminase (GABA-T) [3]. GABA is purported to act as a primary neurotransmitter by 30-40% of all CNS neurons [2,4]. GABA is released from vesicles at synapses in a Ca2+-dependent manner [3,5]. Also, a Ca2+-independent cytoplasmic GABA release occurs mainly at extrasynaptic site, which may be caused by reversal transport of GABA molecules by GABA transporters (GAT) [2,3]. Upon release, GABA activates ionotropic GABAA and GABAC receptors as well as metabotropic GABAB receptors. Termination of GABA action in the synaptic cleft is achieved by diffusion and active reuptake by GAT localized on presynaptic nerve endings and astrocytes [3]. Four GAT subtypes have been identified [6], and neurons mainly express GAT-1 and GAT-2/3 [7].
GABAA receptors mediate the majority of fast inhibition in the adult brain [1,2]. Activation of GABAA receptors results in two types of GABAergic inhibition: phasic and tonic inhibition. While phasic inhibition, mediated by inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs), is produced by brief exposure of postsynaptic GABAA receptors to high concentrations of GABA, tonic inhibition is generated by continuous activation of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors by low ambient concentrations of GABA [8,9,10,11]. In many brain regions such as thalamus and hippocampus, GABAA receptor-mediated currents are predominantly contributed by tonic currents, which account for ~75%-90% of total inhibitory currents [8,12,13]. Therefore, the tonic inhibition plays a major role in modulating neuronal excitability in these brain areas.
GABAA receptors are heteropentameric chloride ion channels, and multiple GABAA receptor subunit subtypes as well as splice variants have been identified, including α1-α6, β1-β3, γ1-γ3, δ, ε, π and θ [1]. Like the other members of the cys-loop receptor family, each GABAA receptor subunit is composed of a long extracellular N terminus, four transmembrane domains (M1-M4), one extracellular M2-3 loop, two intracellular loops (M1-2 and M3-4) and a short extracellular C terminus (Figure 1). It has been reported that αbg and αbd receptors are the predominant isoforms present in vivo [14], primarily mediating phasic and tonic inhibition, respectively [9]. The α1β2γ2 isoform is the ubiquitous and predominant synaptic receptors in the brain [14,15]. On the other hand, the αbd GABAA receptor is localized extra- or perisynaptically [9,10]. The δ subunit mainly co-assembles with the α6 subunit in the cerebellum [16,17] and with the α4 subunit in several brain regions such as thalamus and cortex [18,19,20,21]. An intimate association between δ and α1 subunits was observed in hippocampus [22], but was not detected in thalamus [19]. The α4βd receptor is the major δ subunit-containing GABAA receptor in the brain [14].
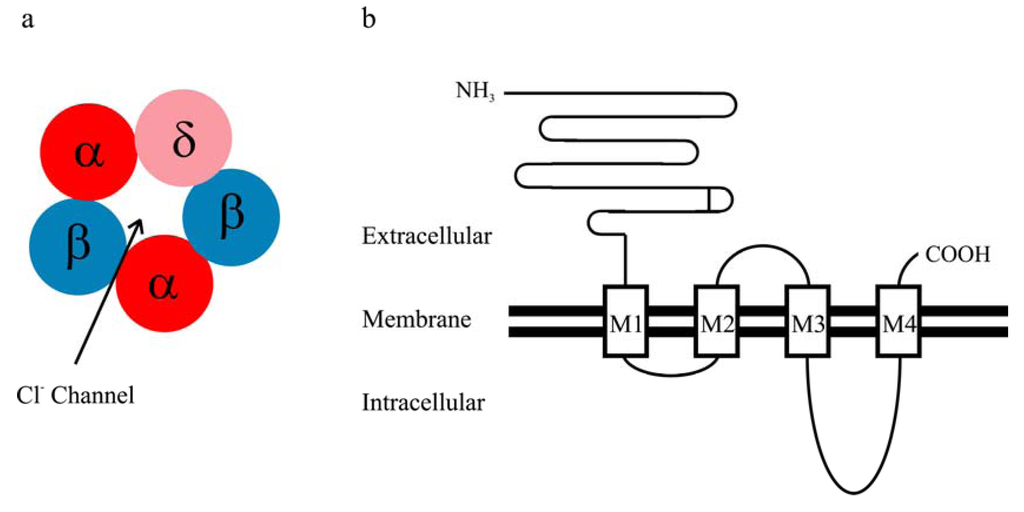
Figure 1.
(a) The assumed stoichiometry of the αβδ receptor (α:β:δ = 2:2:1); (b) Schematic presentation of the topology of a GABAA receptor subunit.
2. Kinetic Properties of αβδ GABAA Receptor Currents
Whole cell currents evoked by saturating concentrations of GABA are always smaller for α1β3δ receptors than for α1β3γ2L receptors (Figure 2a,c) [23,24,25,26]. The extent of desensitization of αβδ receptor currents is dependent on the α subunit (Table 1). α4β2/3δ or α6β3δ currents evoked by saturating concentrations of GABA display considerable extent of desensitization [25,27,28,29]. However, compared with their counterpart α4β3γ2L and α6β3γ2L receptors [25,30], the desensitization of α4β3δ and α6β3δ receptors is relatively slower, lacking the fast component. α5β3δ receptors are poorly expressed in HEK293T cells, and the desensitization of this receptor isoform seems to be slower than that of α5β3γ2L receptors [29]. α1β2/3δ currents evoked by saturating concentrations of GABA exhibit very slow desensitization, some of which have minimal or no desensitization (Figure 2a) [23,26,31]. Structural investigations using δ-γ2L chimeras showed that the N terminus and two adjacent residues (V233, Y234) in M1 of the δ subunit contributed to the slow desensitization of α1β3δ receptors [32]. α1β3δ and α4β3δ currents deactivate faster than α1β3γ2L and α4β3γ2L currents, respectively [26,29]. The deactivation of α5β3δ and α6β3δ currents is slower than that of α1β3δ and α4β3δ currents and may not be different from their counterpart γ2L subunit-containing receptor currents (Table 1) [29].

Table 1.
Comparison of GABA current kinetics among αβ3δ receptors with different α subunits. Adapted from [29].
| α1β3δ | α4β3δ | α5β3δ | α6β3δ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Desensitization | 24.8 ± 6.5% | 53.4 ± 2.1% | 36.2 ± 4.4% | 44.7 ± 3.9% |
| Deactivation | 125.3 ± 10.5 ms | 117.8 ± 13.5 ms | 345.7 ± 87.4 ms | 449.1 ± 80.9 ms |
3. Modulation of αβδ Receptors by Anesthetics
3.1. Barbiturates
Barbiturates are widely used general anesthetics and exert their actions in the brain by interacting with GABAA receptors [33]. Pentobarbital, the prototypic barbiturate commonly tested in laboratories, affects GABAA receptor function in a concentration- and use-dependent manner. That is, at low concentrations, pentobarbital potentiates GABAA receptor currents [26,34,35]. At higher concentrations, pentobarbital can directly activate GABAA receptors [26,34,35,36]. At very high concentrations (mM), pentobarbital suppresses GABAA receptor function via an open channel block mechanism [26,37,38,39]. These concentration- and use-dependent properties of barbiturates on GABAA receptor function are also observed in other GABAA receptor modulators [40,41].
Interestingly, chronic treatment with and subsequent withdrawal of pentobarbital in animals alter the expression of GABAA receptor δ subunit in certain brain region [42], suggesting anesthetics may exert effects on αβδ receptors. Using a novel fluorescence resonance energy transfer-derived measurement of membrane potential, Adkins et al. reported that α4β3δ receptor response was markedly potentiated by pentobarbital [43]. Subsequent electrophysiological study showed that pentobarbital produced a greater potentiation of α4β3δ currents than α4β3γ2 currents evoked by sub-maximal concentrations of GABA [27]. We compared allosteric modulation by pentobarbital of α1β3δ and α1β3γ2L currents evoked by sub-maximal as well as saturating concentrations of GABA using a rapid drug application device. At a sub-maximal concentration of GABA (1 μM), pentobarbital at 100 μM enhanced peak current amplitude, increased the desensitization and prolonged the deactivation of α1β3δ and α1β3γ2L currents to a similar extent [26]. On the other hand, pentobarbital differentially modulated α1β3δ and α1β3γ2L currents evoked by a saturating concentration of GABA (1 mM). Pentobarbital substantially enhanced the peak current amplitude and increased the desensitization of α1β3δ currents, but it failed to potentiate the peak current amplitude and decreased the desensitization of α1β3γ2L currents induced by 1 mM GABA (Figure 2) [26]. In order to determine the structural domains of the δ subunit that are involved in the unique modulation by pentobarbital of α1β3δ currents evoked by a saturating concentration of GABA, a series of chimeras between δ and γ2L subunits were constructed and transfected with wild type α1 and β3 subunits. By comparing the current properties of the chimeric receptors with those of the wild type receptors in the presence of pentobarbital, we concluded that enhancement of α1β3δ currents by pentobarbital required the amino acid sequence from the N terminus to proline 241 in M1 of the δ subunit. We also observed that increasing desensitization of α1β3δ currents by pentobarbital required the amino acid sequence from the N terminus to isoleucine 235 in M1 of the δ subunit [44].
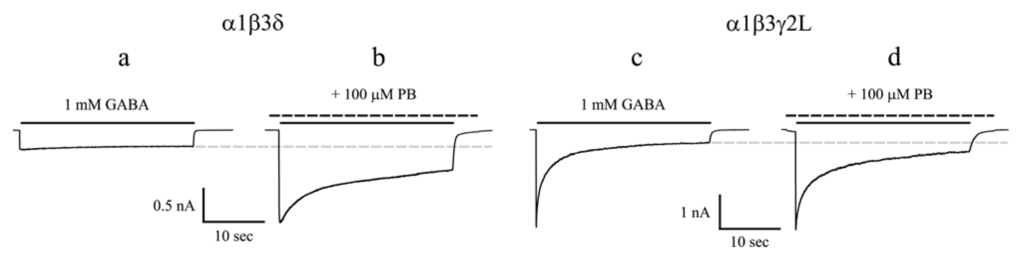
Figure 2.
(a) The whole-cell current trace of α1β3δ receptors evoked by a saturating concentration of GABA displayed slow desensitization; (b) Pentobarbital substantially enhanced the peak and steady-state current amplitudes and increased the desensitization of α1β3δ receptors; (c) The whole-cell current trace of α1β3γ2L receptors evoked by a saturating concentration of GABA exhibited extensive and fast desensitization; (d) Pentobarbital did not potentiate the peak current amplitude but enhanced the steady-state current amplitude of α1β3γ2L receptors. Pentobarbital decreased the desensitization of α1β3γ2L receptors. The solid line above each current trace denotes the duration of GABA application (28 sec), and the dashed line denotes that of pentobarbital application. The gray dashed line indicates the level of steady-state current for GABA controls. PB, Pentobarbital. Modified from [26].
Like αβγ receptors, pentobarbital can directly activate αβδ receptors. The peak pentobarbital current amplitude reached its maximal value at 1 mM for α1β3γ2L receptors. However, the peak pentobarbital current amplitude continued to increase up to 3 mM for α1β3δ receptors [26]. It seems that the maximal peak current amplitude evoked by pentobarbital is greater than that evoked by a saturating concentration of GABA for αβδ receptors [26,45].
3.2. Neurosteroids
The anesthetic action of neurosteroids is achieved by interacting with GABAA receptors [46]. Neurosteroids can either positively or negatively modulate GABAA receptor function. This review focuses on the effect of positive modulators of neurosteroids on αβδ receptor function. Endogenous neurosteroids are produced mainly from glial cells in the brain [40,47], and extracellular concentrations of neurosteroids are in the nanomolar range (10-300 nM), which are dynamically regulated during certain physiological conditions such as pregnancy [10]. Neurosteroids at physiological concentrations predominantly modulate the function of extra- or perisynaptic αβδ receptors [48]. In accord with this, along with the fluctuation of neurosteroid level during pregnancy, the function and expression of αβδ receptors undergo plastic changes in the hippocampus of rodents [49,50,51], which may contribute to alterations of seizure susceptibility and anxiety. It has also been reported that α4βd receptor expression is markedly increased at the onset of puberty in female rodents when some learning processes are impaired [52,53]. Neurosteroids may play an important role in shaping learning deficits at this developmental stage of rodents [53].
Neurosteroids such as alphaxalone (5α-pregnan-3α-ol-11,20-di-one) and THDOC (5α-pregnan-3α, 21-diol-20-one) potentiated α4β3δ receptor responses [27,43]. It seems that THDOC evokes a greater enhancement of maximal GABA currents for α1β3δ receptors than for α4β3δ or α6β3δ receptors [24,27,54,55]. THDOC at 1 μM dramatically potentiated the peak current amplitude and increased the desensitization of α1β3δ currents evoked by a saturating concentration of GABA (1 mM). However, THDOC reduced the peak current amplitude and had little effect on desensitization of α1β3γ2L currents evoked by 1 mM GABA. For both receptor isoforms, THDOC prolonged current deactivation [24]. Like pentobarbital, THDOC only slightly enhanced α1β3 currents [24,29], suggesting that the δ subunit plays an important role in modulating α1β3δ currents by these compounds. Interestingly, it was reported that some general anesthetics including THDOC enhanced maximal GABA currents to the similar extent for α4β3δ and α4β3 receptors [55]. These data indicate that it is the α4 subunit instead of the δ subunit that confers the potentiation of α4β3δ currents by THDOC and other anesthetics. Therefore, α subunits may also play a role in modulating αβδ currents by THDOC and general anesthetics. The structural domains of the δ subunit that confer enhancement of αβδ currents by THDOC are not fully elucidated. Preliminary studies suggest that δ subunit domains required for maximal potentiation of α1β3δ currents by neurosteroids may be different from those by barbiturates [44].
Application of THDOC (10 nM) suppressed neuronal excitability by enhancing tonic currents mediated by δ subunit-containing receptors in hippocampus [48]. However, for thalamocortical neurons, THDOC at 10 nM had no effect on tonic currents, but application of THDOC at 100 nM did enhance tonic current amplitude [13]. The reasons for this region-specific sensitivity of tonic currents to neurosteroid modulation are currently unclear. Several factors may contribute to this variability. First, neuronal GABAA receptors are highly heterogeneous [14,15]. The composition of αβδ receptors may be different in hippocampal and thalamic neurons. Actually, in thalamus, the major δ subunit-containing receptors are α4βd isoform, and no α1βd isoform is detectable [18,19]. But, both α4βd and α1βd isoforms exist in hippocampus [20,22]. The sensitivity of α1βd and α4βd receptors to the actions of neurosteroids was reported to differ (see above). Second, neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptor function is dependent on its phosphorylation state. For example, the neurosteroid allopregnanolone prolonged IPSC decay only when the receptors were in a phosphorylated state [56]. Also, PKC activation enhanced the potentiating effect of THDOC on α1β2γ2L currents [57]. Interestingly, the function of α4β3δ receptors was modulated by PKA [58]. Therefore, it is possible that the differential sensitivity of hippocampal and thalamic neurons to neurosteroids is partly due to different phosphorylation levels of αβδ receptors.
3.3. Other Anesthetics
In additional to barbiturates and anesthetic neurosteroids, many other general anesthetics also positively modulate the function of αβδ receptors. For example, etomidate enhances α4β3δ currents [27,55] and augments tonic currents in thalamocortical neurons [12]. Moreover, isoflurane and sevoflurane potentiate recombinant α1β1δ or α6β2δ currents evoked by a sub-maximal concentration of GABA [59,60]. Consistent with these findings, application of isoflurane can lead to enhancement of tonic currents in hippocampal, thalamic and cardiac vagal neurons [61,62,63]. In addition, propofol, a widely used general anesthetic, may also exert its action in the brain partly by modulating tonic inhibition mediated by αβδ receptors. Recent investigations showed that propofol potentiated αβδ currents [25,27,60]. Propofol at 10 μM produced similar alterations for α1β3γ2L and α6β3γ2L currents evoked by a saturating concentration of GABA; peak currents were not changed, desensitization was decreased and deactivation was prolonged [25]. However, propofol at this concentration produced differential effects on α1β3δ and α6β3δ currents. Although propofol potentiated peak current amplitude for both α1β3δ and α6β3δ receptors, the potentiation was greater for α1β3δ than for α6β3δ receptors. Propofol prolonged the deactivation of α6β3δ currents but did not change that of α1β3δ currents. For both receptor isoforms, propofol did not alter the desensitization [25]. In line with these data from recombinant receptors, it has been shown that propofol enhances tonic currents [63,64,65,66,67] and prolongs the duration of miniature IPSCs in neurons [64,67]. Importantly, at clinically relevant concentrations (~0.4 μM) [68], propofol can directly activate α1β3γ2L receptors but produce negligible effect on α1β3δ receptors [25]. Taken together, the evidence suggests that propofol achieves its anesthetic effect in the brain by positively modulating tonic and phasic inhibition as well as by directly activating synaptic GABAA receptors.
4. Modulation of αβδ Receptors by Ethanol
Ethanol is a widely used drug of abuse and exerts its actions in the CNS by interacting with multiple neurotransmission systems including GABAergic transmission [69,70,71]. Previous studies using GABAA receptor δ subunit knockout mice suggest that the δ subunit may play a role in ethanol actions in the CNS [72]. It was subsequently reported that α4βd and α6βd receptors were highly sensitive to ethanol modulation [73,74]. The β3 subunit- other than β2 subunit-containing α4βd and α6βd receptor was considered to be the target for low concentration of ethanol (<30 mM) [74,75]. Ligand binding and electrophysiological studies using alcohol antagonist Ro 15-4513 as a probe indicate that ethanol binds to recombinant and native α4/6β3δ receptors [76,77]. Recent studies investigating the structural domains of the δ subunit have identified key regions of the δ subunit that may be important in conferring ethanol sensitivity in αβδ receptors. It has been reported that loop 2 of the extracellular domain of the GABAA receptor is coupled with channel gating [78], and mutations of the loop 2 residues in the glycine receptor, another member of cys-loop receptors, can affect ethanol sensitivity [79,80]. αβγ receptors are relatively insensitive to ethanol modulation [74]. Interestingly, when loop 2 sequence of the γ2 subunit was replaced with that of the δ subunit, ethanol sensitivity of the chimeric receptor was substantially increased [81], suggesting that loop 2 of the δ subunit plays an important role in conferring high sensitivity of αβδ receptors to ethanol.
Since the αβδ receptor is the predominant isoform to mediate tonic inhibition and the major contributor to the total GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition in several brain regions [8,13], it is expected that ethanol enhances tonic currents in these areas. In accordance with this, ethanol was reported to potentiate the tonic currents from dentate gyrus granule cells in hippocampus [82,83,84] and thalamocortical neurons in thalamus [85]. In hippocampal interneurons, δ subunits coassemble with α1 subunits to form α1βd receptors, which exhibit high sensitivity to ethanol [22]. Two α6 subunit variants (100R, 100Q) were identified in rat population, and rats carrying the 100Q variant were behaviorally more sensitive to ethanol [87,88,89]. Electrophysiological recordings were performed on cerebellar granule cells in brain slices prepared from rats that were homozygous for either α6 (100R) or α6 (100Q). It was observed that tonic currents were enhanced by ethanol in both genotypes, but the enhancement was greater in slices from the rats with homozygosity of α6 (100Q) [90].
It should be noted that not all investigations have been able to confirm the aforementioned findings, resulting in some controversy regarding the ethanol sensitivity of αβδ receptors [75,91,92,93]. For example, several groups failed to observe that ethanol enhanced αβδ currents or bound to αβδ receptors at low concentrations [60,94,95,96]. It was also reported that native αβδ receptors on cultured neurons or on neurons in acute slices were not sensitive to ethanol [60,94,97,98]. A study indicated that the sensitivity of tonic currents to ethanol was not increased for the α6 (100Q) variant in rats [99]. Many confounding factors can lead to the discrepant results such as differences in heterologous expression system, the state of posttranslational modifications of αβδ receptors. It has been recently reported that ethanol enhancement of tonic currents is dependent on the phosphorylation of αβδ receptors mediated by PKCδ [100]. Interestingly, the expression of PKCδ was considerably low in L(tk−) cells [100], which were used in a previous study indicating that αβδ receptors were not sensitive to ethanol modulation [94]. This raises a possibility that some of the controversial results may result, at least in part, from the different phosphorylation states of αβδ receptors. That being said, the exact reasons for these discrepancies are largely unknown, and this topic is an area of active research in the alcohol field.
5. Mechanisms for Positive Modulation of αβδ Receptors
Besides anesthetics and ethanol, αβδ receptors can also be positively modulated by many other structurally different compounds such as protons [101,102], gaboxadol (THIP) [43,103], dihydropyrimidinone [104], Tracazolate [105,106] and AA29504 [107]. Although the binding sites for most of these compounds on GABAA receptors have not been identified yet, it seems unlikely that the δ subunit is critically involved in binding of these compounds on αβδ receptors. Previous studies using δ subunit knockout mice suggest that many general anesthetics like barbiturates, etomidate and propofol may not have binding sites on δ subunits [48,108]. Therefore, most anesthetics may modulate αβδ receptor function by modifying the allosteric transduction and gating kinetics of this receptor isoform.
Whole cell currents evoked by saturating concentrations of GABA were consistently smaller for α1β3δ receptors than for α1β3γ2L receptors [24,25,26]. Consistent with this notion, single channel recordings found that α1β3δ channel activity was characterized by brief openings and only had two open states, leading to a shorter mean open time than α1β2/3γ2L receptors [24,26,45,109,110,111]. Additionally, gaboxadol and pentobarbital produced a greater activation than GABA on α1/4β2/3δ receptors [26,43,45]. These aforementioned studies suggest that GABA is a partial agonist for αβδ receptors, leaving much room for potentiation by modulators [112]. Both pentobarbital and THDOC enhanced α1β3δ steady-state current amplitude evoked by a saturating concentration of GABA (see Figure 2a, 2b). Steady-state single channel recordings found that these modulators increased mean open time of α1β3δ currents mainly by introducing a third open state into this receptor isoform [24,26,45]. However, α1β3δ single channel currents activated by pentobarbital (100 μM) or THDOC (1 μM) in the absence of GABA exhibited three open states [24,26]. It is unclear whether the third open state introduced by pentobarbital or THDOC is caused by direct activation or allosteric modulation of α1β3δ receptors. To address this issue, we examined the effect of lowered pH on α1β3δ receptor function since protons allosterically modulate GABAA receptor function without direct activation of it. Lowered pH substantially augmented the steady-state current amplitude of α1β3δ receptors [102]. In line with this, steady-state single channel analysis indicated that at physiological pH, α1β3δ single channel currents were characterized with brief openings and had two open states (Figure 3a1, 3a2) whereas at lowered pH, α1β3δ single channel currents exhibited both brief- and long-duration openings and had three open states (Figure 3b1,b2). These data indicated that lowered pH introduced an additional open state into α1β3δ receptors [102]. Given that the proportion of the third open state in the presence of GABA and pentobarbital (THDOC) is larger than that in the presence of pentobarbital (THDOC) alone, it is conclusive that, like protons, positive modulation of α1β3δ receptors by pentobarbital or THDOC is achieved mainly by introduction of an additional open state.
Note that pentobarbital also potentiated steady-state current amplitude of α1β3γ2L receptors evoked by a saturating concentration of GABA (see Figure 2c,d). But, pentobarbital achieved this by a different mechanism from that of α1β3δ receptors. Instead of introducing an additional open state, pentobarbital increased steady-state single channel current mean open time by increasing the relative proportion and duration of the third open state for α1β3γ2L receptors [26].
6. Conclusions
Although αβδ receptors only constitute a small proportion of all GABAA receptors expressed in the brain, they are the major contributor to GABAergic tonic inhibition in many brain regions. A wealth of studies has demonstrated that tonic inhibition plays an important role in mediating neuronal excitability under physiological conditions. In addition to its involvement in anesthetic and ethanol actions, recent studies showed that defects in αβδ receptor function or tonic inhibition led to pathogenesis of neurological disorders such as epilepsy [31,113,114,115], suggesting that the αβδ receptor is a potential therapeutic target for epilepsy and alcohol abuse. A better understanding of the kinetic properties and mechanisms of allosteric modulation of αβδ receptors should lead to the development of not only highly selective modulators that produce effective anesthesia but also novel treatment strategies to control neurological disorders as well as to reduce the abuse and dependence of alcohol.
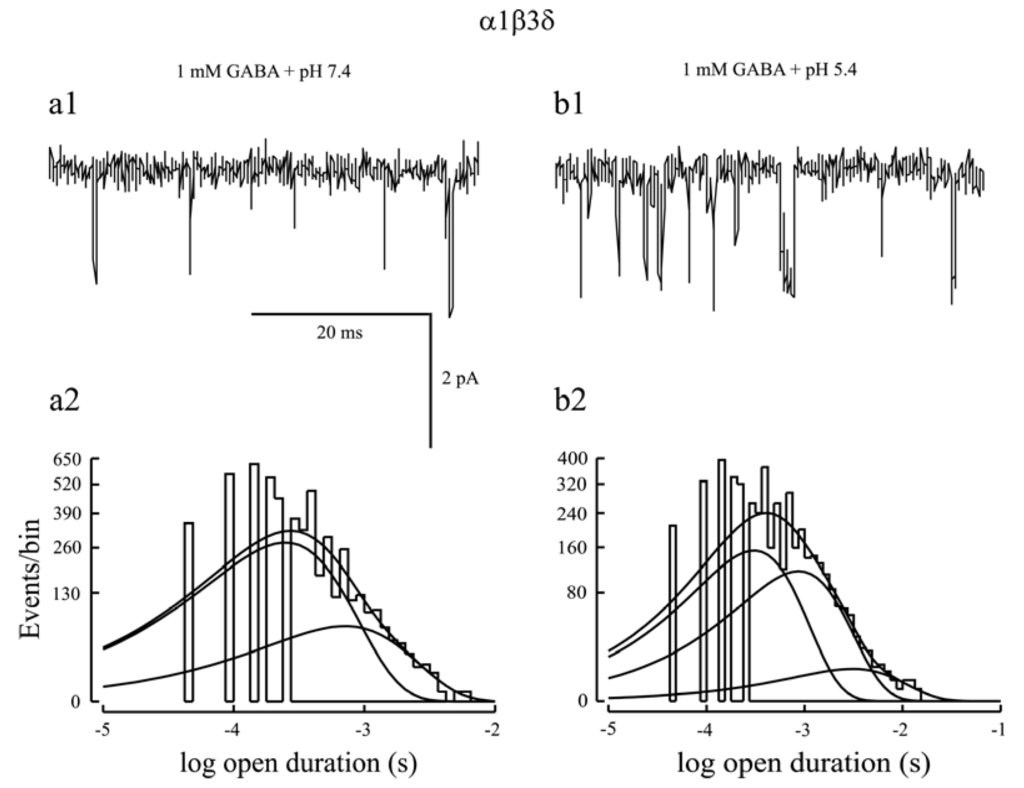
Figure 3.
(a1, b1) Representative α1β3δ receptor single channel current traces evoked by a saturating concentration of GABA at physiological pH (7.4) and acidic pH (5.4) were presented. The single channel activity at pH 7.4 exhibited brief openings, but that at pH 5.4 displayed a mixture of brief- and long-duration openings; (a2, b2) Single channel open probability histograms at physiological pH (7.4) and acidic pH (5.4) were presented. At pH 7.4, the histogram was fitted by two components, indicating two open states. However, at pH 5.4, the histogram was fitted by three components, suggesting that lowered pH introduced an additional open state into α1β3δ receptors to enhance the efficacy of this receptor isoform. Since protons could not directly activate GABAA receptors, the third open state was caused by allosteric modulation of α1β3δ receptors by protons. Modified from [102].
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to thank Daryl Davies for critical reading of the manuscript and the people in Robert Macdonald’s lab for technical assistance and discussion.
References
- Olsen, R.W.; Macdonald, R.L. GABAA receptor complex: structure and function. In Glutamate and GABA Receptors and Transporters: Structure, Function and Pharmacology; Egebjerg, J., Schousboe, A., Krogsgaard-Larsen, P., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: London, U.K., 2002; pp. 202–235. [Google Scholar]
- Beleboni, R.O.; Carolino, R.O.; Pizzo, A.B.; Castellan-Baldan, L.; Coutinho-Netto, J.; dos Santos, W.F.; Coimbra, N.C. Pharmacological and biochemical aspects of GABAergic neurotransmission: pathological and neuropsychobiological relationships. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2004, 24, 707–728. [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe, A.; Waagepetersen, H.S. GABA: homeostatic and pharmacological aspects. Prog. Brain Res. 2007, 160, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, E. GABA: the road to neurotransmitter status. In Benzodiazepine/GABA Receptors and Chloride Channels: Structure and Functional Properties; Olsen, R.W., Venter, C.J., Eds.; Wiley: New York, USA, 1986; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, M. Establishment of GABA as an inhibitory neurotransmitter at Crustacean neuromuscular junction and in the mammalian central nervous system. In GABA: Receptors, Transporters and Metabolism; Tanaka, C., Bowery, N.G., Eds.; Birkhauser: Basel, Switzerland, 1996; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Soudijn, W.; van Wijngaarden, I. The GABA transporter and its inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2000, 7, 1063–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Keros, S.; Hablitz, J.J. Subtype-specific GABA transporter antagonists synergistically modulate phasic and tonic GABAA conductances in rat neocortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 94, 2073–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Mody, I.; Pearce, R.A. Diversity of inhibitory neurotransmission through GABAA receptors. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 569–575. [Google Scholar]
- Farrant, M.; Nusser, Z. Variation on an inhibitory theme: phasic and tonic activation of GABAA receptors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 215–229. [Google Scholar]
- Belelli, D.; Harrison, N.L.; Maguire, J.; Macdonald, R.L.; Walker, M.C.; Cope, D.W. Extrasynaptic GABAA receptors: form, pharmacology, and function. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 12757–12763. [Google Scholar]
- Zheleznova, N.N.; Sedelnikova, A.; Weiss, D.S. Function and modulation of δ-containing GABAA receptors. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34S, S67–S73. [Google Scholar]
- Belelli, D.; Peden, D.R.; Rosahl, T.W.; Wafford, K.A.; Lambert, J.J. Extrasynaptic GABAA receptors of thalamocortical neurons: a molecular target for hypnotics. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 11513–11520. [Google Scholar]
- Cope, D.W.; Hughes, S.W.; Crunelli, V. GABAA receptor-mediated tonic inhibition in thalamic neurons. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 11553–11563. [Google Scholar]
- McKernan, R.M.; Whiting, P.J. Which GABAA-receptor subtypes really occur in the brain? Trends Neurosci. 1996, 19, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Pirker, S.; Schwarzer, C.; Wieselthaler, A.; Sieghart, W.; Sperk, G. GABAA receptors: immunocytochemical distribution of 13 subunits in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience 2000, 101, 815–850. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.; Korpi, E.R.; McKernan, R.M.; Pelz, R.; Nusser, Z.; Makela, R.; Mellor, J.R.; Pollard, S.; Bahn, S.; Stephenson, F.A.; Randall, A.D.; Sieghart, W.; Somogyi, P.; Smith, A.J.; Wisden, W. Ligand-gated ion channel subunit partnerships: GABAA receptor α6 subunit gene inactivation inhibits δ subunit expression. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar]
- Poltl, A.; Hauer, B.; Fuchs, K.; Tretter, V.; Sieghart, W. Subunit composition and quantitative importance of GABAA receptor subtypes in the cerebellum of of mouse and rat. J. Neurochem. 2003, 87, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Sur, C.; Farrar, S.J.; Kerby, J.; Whiting, P.J.; Atack, J.R.; McKernan, R.M. Preferential coassembly of α4 and δ subunits of the γ-aminobutyric acidA receptor in rat thalamus. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 56, 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, F.; Pignataro, L.; Schofield, C.M.; Yue, M.; Harrison, N.L.; Goldstein, P.A. An extrasynaptic GABAA receptor mediates tonic inhibition in thalamic VB neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 94, 4491–4501. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, D.; Jia, F.; Liang, J.; Peng, Z.; Suryanarayanan, A.; Werner, D.F.; Spigelman, I.; Houser, C.R.; Olsen, R.W.; Harrison, N.L.; Homanics, G.E. GABAA receptor α4 subunits mediate extrasynaptic inhibition in thalamus and dentate gyrus and the action of gaboxadol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15230–15235. [Google Scholar]
- Drasbek, K.R.; Hoestgaard-Jensen, K.; Jensen, K. Modulation of extrasynaptic THIP conductances by GABAA-receptor modulators in mouse neocortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 2293–2300. [Google Scholar]
- Glykys, J.; Peng, Z.; Chandra, D.; Homanics, G.E.; Houser, C.R.; Mody, I. A new naturally occurring GABAA receptor subunit partnership with high sensitivity to ethanol. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, N.C.; Macdonald, R.L. Assembly of GABAA receptor subunit: role of the δ subunit. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 7077–7086. [Google Scholar]
- Wohlfarth, K.M.; Bianchi, M.T.; Macdonald, R.L. Enhanced neurosteroid potentiation of ternary GABAA receptors containing the δ subunit. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.J.; Macdonald, R.L. Multiple actions of propofol on αβγ and αβδ GABAA receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.J.; Bianchi, M.T.; Macdonald, R.L. Pentobarbital differentially modulates α1β3δ and α1β3γ2L GABAA receptor currents. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 988–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, N.; Kerby, J.; Bonnert, T.P.; Whiting, P.J.; Wafford, K.A. Pharmacological characterization of a novel cell line expressing human α4β3δ GABAA receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 136, 965–974. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.J.; Kang, J.Q.; Song, L.; Dibbens, L.; Mulley, J.; Macdonald, R.L. δ subunit susceptibility variants E177A and R220H associated with complex epilepsy alter channel gating and surface expression of α4β2δ GABAA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.J.; Botzolakis, E.J.; Macdonald, R.L. Context-dependent modulation of αβγ and αβδ GABAA receptors by penicillin: implication for phasic and tonic inhibition. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 161–173. [Google Scholar]
- Lagrange, A.H.; Botzolakis, E.J.; Macdonald, R.L. Enhanced macroscopic desensitization shapes the response of α4 subtype-containing GABAA receptors to synaptic and extrasynaptic GABA. J. Physiol. 2007, 578, 655–676. [Google Scholar]
- Dibbens, L.M.; Feng, H.J.; Richards, M.C.; Harkin, L.A.; Hodgson, B.L.; Scott, D.; Jenkins, M.; Petrou, S.; Sutherland, G.R.; Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.F.; Macdonald, R.L.; Mulley, J.C. GABRD encoding a protein for extra- or peri-synaptic GABAA receptors is a susceptibility locus for generalized epilepsies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, M.T.; Haas, K.F.; Macdonald, R.L. Structural determinants of fast desensitization and desensitization-deactivation coupling in GABAA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Henschel, O.; Gipson, K.E.; Bordey, A. GABAA receptors, anesthetics and anticonvulsants in brain development. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2008, 7, 211–224. [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll, R.A.; Wojtowicz, J.M. The effects of pentobarbital and related compounds on frog motoneurons. Brain Res. 1980, 191, 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, D.W.; Macdonald, R.L. Barbiturate enhancement of GABA-mediated inhibition and activation of chloride ion conductance: correlation with anticonvulsant and anesthetic actions. Brain Res. 1981, 209, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Krampfl, K.; Wolfes, H.; Dengler, R.; Bufler, J. Kinetic analysis of the agonistic and blocking properties of pentobarbital on recombinant rat α1β2γ2S GABAA receptor channels. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 435, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, N.; Maruyama, T.; Tokutomi, N. Kinetic properties of the pentobarbitone-gated chloride current in frog sensory neurones. J. Physiol. 1987, 394, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, J.M.; Donevan, S.D.; Rogawski, M.A. Direct activation of GABAA receptors by barbiturates in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J. Physiol. 1996, 497, 509–522. [Google Scholar]
- Akk, G.; Steinbach, J.H. Activation and block of recombinant GABAA receptors by pentobarbitone: a single-channel study. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 130, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, J.J.; Belelli, D.; Hill-Venning, C.; Peters, J.A. Neurosteroids and GABAA receptor function. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1995, 16, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht, R.; Holsboer, F. Neuroactive steroids: mechanisms of action and neuropsychopharmacological perspectives. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 410–416. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.H.; Wang, L.H. Region-specific changes in GABAA receptor δ subunit mRNA level by tolerance to and withdrawal from pentobarbital. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 202, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Adkins, C.E.; Pillai, G.V.; Kerby, J.; Bonnert, T.P.; Haldon, C.; McKeman, R.M.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Oades, K.; Whiting, P.J.; Simpson, P.B. α4β3δ GABAA receptors characterized by fluorescence resonance energy transfer-derived measurements of membrane potential. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38934–38939. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.J.; Macdonald, R.L. Barbiturates require the N terminus and first transmembrane domain of the δ subunit for enhancement of α1β3δ GABAA receptor currents. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 23614–23621. [Google Scholar]
- Akk, G.; Bracamontes, J.; Steinbach, J.H. Activation of GABAA receptors containing the α4 subunit by GABA and pentobarbital. J. Physiol. 2004, 556, 387–399. [Google Scholar]
- Akk, G.; Covey, D.F.; Evers, A.S.; Steinbach, J.H.; Zorumski, C.F.; Mennerick, S. Mechanisms of neurosteroid interactions with GABAA receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 116, 35–57. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, E.A.; Herd, M.B.; Gunn, B.G.; Lambert, J.J.; Belelli, D. Neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptors: molecular determinants and significance in health and disease. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Stell, B.M.; Brickley, S.G.; Tang, C.Y.; Farrant, M.; Mody, I. Neuroactive steroids reduce neuronal excitability by selectively enhancing tonic inhibition mediated by δ subunit-containing GABAA receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14439–14444. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, J.L.; Stell, B.M.; Rafizadeh, M.; Mody, I. Ovarian cycle-linked changes in GABAA receptors mediating tonic inhibition alter seizure susceptibility and anxiety. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 797–804. [Google Scholar]
- Sanna, E.; Mostallino, M.C.; Murru, L.; Carta, M.; Talani, G.; Zucca, S.; Mura, M.L.; Maciocco, E.; Biggio, G. Changes in expression and function of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in the rat hippocampus during pregnancy and after delivery. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, J.; Mody, I. Steroid hormone fluctuations and GABAAR plasticity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34S, S84–S90. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.S.; Aoki, C.; Shen, H. Puberty, steroids and GABAA receptor plasticity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34S, S91–S103. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Sabaliauskas, N.; Sherpa, A.; Fenton, A.A.; Stelzer, A.; Aoki, C.; Smith, S.S. A critical role for α4βd GABAA receptors in shaping learning deficits at puberty in mice. Science 2010, 327, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, K.H.; Baur, R.; Sigel, E. Unanticipated structural and functional properties of δ-subunit-containing GABAA receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 7889–7896. [Google Scholar]
- Meera, P.; Olsen, R.W.; Otis, T.S.; Wallner, M. Etomidate, propofol and the neurosteroid THDOC increase the GABA efficacy of recombinant α4β3δ and α4β3 GABAA receptors expressed in HEK cells. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Fancsik, A.; Linn, D.M.; Tasker, J.G. Neurosteroid modulation of GABA IPSCs is phosphorylation dependent. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3067–3075. [Google Scholar]
- Leidenheimer, N.J.; Chapell, R. Effects of PKC activation and receptor desensitization on neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptors. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1997, 52, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Hernandez, C.C.; Macdonald, R.L. Modulation of spontaneous and GABA-evoked tonic α4β3δ and α4β3γ2L GABAA receptor currents by protein kinase A. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Lees, G.; Edwards, M.D. Modulation of recombinant human γ-aminobutyric acidA receptors by isoflurane: influence of the δ subunit. Anesthesiology 1998, 88, 206–217. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, M.; Marszalec, W.; Yeh, J.Z.; Narahashi, T. Effects of ethanol on tonic GABA currents in cerebellar granule cells and mammalian cells recombinantly expressing GABAA receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 319, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Caraiscos, V.B.; Newell, J.G.; You-Ten, K.E.; Elliott, E.M.; Rosahl, T.W.; Wafford, K.A.; MacDonald, J.F.; Orser, B.A. Selective enhancement of tonic GABAergic inhibition in murine hippocampal neurons by low concentration of the volatile anesthetic isoflurane. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8454–8458. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, F.; Yue, M.; Chandra, D.; Homanics, G.E.; Goldstein, P.A.; Harrison, N.L. Isoflurane is a potent modulator of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in the thalamus. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 324, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Propofol and isoflurane enhancement of tonic γ-aminobutyric acid type A current in cardiac vagal neurons in the nucleus ambiguus. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 108, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, D.; Zhu, G.; Pennefather, P.; Jackson, M.F.; MacDonald, J.F.; Orser, B.A. Distinct functional and pharmacological properties of tonic and quantal inhibitory postsynaptic currents mediated by γ-aminobutyric acidA receptors in hippocampal neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 814–824. [Google Scholar]
- Bieda, M.C.; MacIver, M.B. Major role for tonic GABAA conductances in anesthetic suppression of intrinsic neuronal excitability. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 92, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, A.; Mashimo, T.; Uchida, I. GABAergic tonic inhibition of substantia gelatinosa neurons in mouse spinal cord. Neuroreport 2006, 17, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar]
- McDougall, S.J.; Bailey, T.W.; Mendelowitz, D.; Andresen, M.C. Propofol enhances both tonic and phasic inhibitory currents in second-order neurons of the solitary tract nucleus (NTS). Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 552–563. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.P.; Xu, T.L. The actions of propofol on γ-aminobutyric acid-A and glycine receptors in acutely dissociated spinal dorsal horn neurons of the rat. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 95, 907–914. [Google Scholar]
- Faingold, C.L.; N’Gouemo, P.; Riaz, A. Ethanol and neurotransmitter interactions-from molecular to integrative effects. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 55, 509–535. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.J.; Faingold, C.L. The effects of chronic ethanol administration on amygdala neuronal firing and ethanol withdrawal seizures. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 648–653. [Google Scholar]
- Silberman, Y.; Bajo, M.; Chappell, A.M.; Christian, D.T.; Cruz, M.; Diaz, M.R.; Kash, T.; Lack, A.K.; Messing, R.O.; Siggins, G.R.; Winder, D.; Roberto, M.; McCool, B.A.; Weiner, J.L. Neurobiological mechanisms contributing to alcohol-stress-anxiety interactions. Alcohol 2009, 43, 509–519. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalek, R.M.; Bowers, B.J.; Wehner, J.M.; Kralic, J.E.; VanDoren, M.J.; Morrow, A.L.; Homanics, G.E. GABAA-receptor δ subunit knockout mice have multiple defects in behavioral responses to ethanol. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 1708–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom-Poromaa, I.; Smith, D.H.; Gong, Q.H.; Sabado, T.N.; Li, X.; Light, A.; Wiedmann, M.; Williams, K.; Smith, S.S. Hormonally regulated α4β2δ GABAA receptors are a target for alcohol. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 721–722. [Google Scholar]
- Wallner, M.; Hanchar, H.J.; Olsen, R.W. Ethanol enhances α4β3δ and α6β3δγ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors at low concentrations known to affect humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15218–15223. [Google Scholar]
- Santhakumar, V.; Wallner, M.; Otis, T.S. Ethanol acts directly on extrasynaptic subtypes of GABAA receptors to increase tonic inhibition. Alcohol 2007, 41, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Hanchar, H.J.; Chutsrinopkun, P.; Meera, P.; Supavilai, P.; Sieghart, W.; Wallner, M.; Olsen, R.W. Ethanol potently and competitively inhibits binding of the alcohol antagonist Ro 15-4513 to α4/6β3δ GABAA receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8546–8551. [Google Scholar]
- Wallner, M.; Hanchar, H.J.; Olsen, R.W. Low-dose alcohol actions on α4β3δ GABAA receptors are reversed by the behavioral alcohol antagonist Ro 15-4513. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8540–8545. [Google Scholar]
- Kash, T.L.; Jenkins, A.; Kelley, J.C.; Trudell, J.R.; Harrison, N.L. Coupling of agonist binding to channel gating in the GABAA receptor. Nature 2003, 421, 272–275. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, D.K.; Trudell, J.R.; Bertaccini, E.J.; Li, K.; Davies, D.L.; Alkana, R.L. Evidence that ethanol acts on a target in loop 2 of the extracellular domain of α1 glycine receptors. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 2097–2109. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, D.I.; Trudell, J.R.; Crawford, D.K.; Alkana, R.L.; Davies, D.L. Targets for ethanol action and antagonism in loop 2 of the extracellular domain of glycine receptors. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, D.I.; Trudell, J.R.; Crawford, D.K.; Asatryan, L.; Alkana, R.L.; Davies, D.L. Loop 2 structure in glycine and GABAA receptors plays a key role in determining ethanol sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27304–27314. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Faria, L.C.; Mody, I. Low ethanol concentrations selectively augment the tonic inhibition mediated by δ subunit-containing GABAA receptors in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8379–8382. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, N.; Cagetti, E.; Houser, C.R.; Olsen, R.W.; Spigelman, I. Chronic intermittent ethanol-induced switch of ethanol actions from extrasynaptic to synaptic hippocampal GABAA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, R.L.; Wilson, W.A.; Swartzwelder, H.S. Magnitude and ethanol sensitivity of tonic GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition in dentate gyrus changes from adolescence to adulthood. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 3806–3811. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, F.; Chandra, D.; Homanics, G.E.; Harrison, N.L. Ethanol modulates synaptic and extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in the thalamus. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 475–482. [Google Scholar]
- Glykys, J.; Peng, Z.; Chandra, D.; Homanics, G.E.; Houser, C.R.; Mody, I. A new naturally occurring GABAA receptor subunit partnership with high sensitivity to ethanol. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Saba, L.; Porcella, A.; Congeddu, E.; Colombo, G.; Peis, M.; Pistis, M.; Gessa, G.L.; Pani, L. The R100Q mutation of the GABAA α6 receptor subunit may contribute to voluntary aversion to ethanol in the sNP rat line. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2001, 87, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, L.G.; Spence, J.P.; Peter Eriksson, C.J.; Lumeng, L.; Li, T.K. AA and ANA rats exhibit the R100Q mutation in the GABAA receptor α6 subunit. Alcohol 2003, 31, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Santhakumar, V.; Hanchar, H.J.; Wallner, M.; Olsen, R.W.; Otis, T.S. Contributions of the GABAA receptor α6 subunit to phasic and tonic inhibition revealed by a naturally occurring polymorphism in the α6 gene. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar]
- Hanchar, H.J.; Dodson, P.D.; Olsen, R.W.; Otis, T.S.; Wallner, M. Alcohol-induced motor impairment caused by increased extrasynaptic GABAA receptor activity. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 339–345. [Google Scholar]
- Borghese, C.M.; Harris, R.A. Studies of ethanol actions on recombinant δ-containingγ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors yield contradictory results. Alcohol 2007, 41, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Korpi, E.R.; Debus, F.; Linden, A.M.; Malecot, C.; Leppa, E.; Vekovischeva, O.; Rabe, H.; Bohme, I.; Aller, M.I.; Wisden, W.; Luddens, H. Does ethanol act preferentially via selected brain GABAA receptor subtypes? The current evidence is ambiguous. Alcohol 2007, 41, 163–176. [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger, D.M.; Homanics, G.E. Tonic for what ails us? High-affinity GABAA receptors and alcohol. Alcohol 2007, 41, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Borghese, C.M.; Storustovu, S.; Ebert, B.; Herd, M.B.; Belelli, D.; Lambert, J.J.; Marshall, G.; Wafford, K.A.; Harris, R.A. The δ subunit of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors does not confer sensitivity to low concentrations of ethanol. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, A.K.; Marutha Ravindran, C.R.; Ticku, M.K. Low concentrations of ethanol do not affect radioligand binding to the δ-subunit-containing GABAA receptors in the brain. Brain Res. 2007, 1165, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Baur, R.; Kaur, K.H.; Sigel, E. Structure of α6β3δ GABAA receptors and their lack of ethanol sensitivity. J. Neurochem. 2009, 111, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Carta, M.; Mameli, M.; Valenzuela, C.F. Alcohol enhances GABAergic transmission to cerebellar granule cells via an increase in Golgi cell excitability. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 3746–3751. [Google Scholar]
- Casagrande, S.; Cupello, A.; Pellistri, F.; Robello, M. Only high concentrations of ethanol affect GABAA receptors of rat cerebellum granule cells in culture. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 414, 273–276. [Google Scholar]
- Botta, P.; Mameli, M.; Floyd, K.L.; Radcliffe, R.A.; Valenzuela, C.F. Ethanol sensitivity of GABAergic currents in cerebellar granule neurons is not increased by a single amino acid change (R100Q) in the α6 GABAA receptor subunit. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 323, 684–691. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, D.S.; Wei, W.; Deitchman, J.K.; Kharazia, V.N.; Lesscher, H.M.B.; McMahon, T.; Wang, D.; Qi, Z.H.; Sieghart, W.; Zhang, C.; Shokat, K.M.; Mody, I.; Messing, R.O. Protein kinase Cδ regulates ethanol intoxication and enhancement of GABA-stimulated tonic current. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11890–11899. [Google Scholar]
- Krishek, B.J.; Amato, A.; Connolly, C.N.; Moss, S.J.; Smart, T.G. Proton sensitivity of the GABAA receptor is associated with the receptor subunit composition. J. Physiol. 1996, 492, 431–443. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.J.; Macdonald, R.L. Proton modulation of α1β3δ GABAA receptor channel gating and desensitization. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 92, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Drasbek, K.R.; Jensen, K. THIP, a hypnotic and antinociceptive drug, enhances an extrasynaptic GABAA receptor-mediated conductance in mouse neocortex. Cereb. Cortex 2006, 16, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.W.; Mabry, J.; Polisar, J.G.; Eagen, K.P.; Ganem, B.; Hess, G.P. Dihydropyrimidinone positively modulation of δ-subunit-containing γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors, including an epilepsy-linked mutant variant. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4841–4851. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, S.A.; Wingrove, P.B.; Connelly, L.; Whiting, P.J.; Wafford, K.A. Tracazolate reveals a novel type of allosteric interaction with recombinant γ-aminobutyric acidA receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 861–869. [Google Scholar]
- Zheleznova, N.; Sedelnikova, A.; Weiss, D.S. α1β2δ, a silent GABAA receptor: recruitment by tracazolate and neurosteroids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Hoestgaard-Jensen, K.; Dalby, N.O.; Wolinsky, T.D.; Murphey, C.; Jones, K.A.; Rottlander, M.; Frederiksen, K.; Watson, W.P.; Jensen, K.; Ebert, B. Pharmacological characterization of a novel positive modulator at α4β3δ-containing extrasynaptic GABAA receptors. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 702–711. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalek, R.M.; Banerjee, P.K.; Korpi, E.R.; Quinlan, J.J.; Firestone, L.L.; Mi, Z.P.; Lagenaur, C.; Tretter, V.; Sieghart, W.; Anagnostaras, S.G.; Sage, J.R.; Fanselow, M.S.; Guidotti, A.; Spigelman, I.; Li, Z.; DeLorey, T.M.; Olsen, R.W.; Homanics, G.E. Attenuated sensitivity to neuroactive steroids in γ-aminobutyrate type A receptor δ subunit knockout mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12905–12910. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, J.L.; Macdonald, R.L. Single channel properties of recombinant GABAA receptors containing γ2 or δ subtypes expressed with α1 and β3 subtypes in mouse L929 cells. J. Physiol. 1997, 505, 283–297. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, K.F.; Macdonald, R.L. GABAA receptor subunit γ2 and δ subtypes confer unique kinetic properties on recombinant GABAA receptor currents in mouse fibroblasts. J. Physiol. 1999, 514, 27–45. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach, J.H.; Akk, G. Modulation of GABAA receptor channel gating by pentobarbital. J. Physiol. 2001, 537, 715–733. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, M.T.; Macdonald, R.L. Neurosteroids shift partial agonist activation of GABAA receptor channels from low- to high-efficacy gating patterns. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10934–10943. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.S.; Yao, J.; Fang, C.; Luscher, B.; Chen, G. Downregulation of tonic GABA currents following epileptogenic stimulation of rat hippocampal cultures. J. Physiol. 2006, 577, 579–590. [Google Scholar]
- Cope, D.W.; Di Giovanni, G.; Fyson, S.J.; Orban, G.; Errington, A.C.; Lorincz, M.L.; Gould, T.M.; Carter, D.A.; Crunelli, V. Enhanced tonic GABAA inhibition in typical absence epilepsy. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch, B.; Qashu, F.; Figueiredo, T.H.; Aroniadou-Anderjaska, V.; Rogawski, M.A.; Braga, M.F. Pathological alterations in GABAergic interneurons and reduced tonic inhibition in the basolateral amygdale during epileptogenesis. Neuroscience 2009, 163, 415–429. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).