Interactions of Extracts from Selected Plant Materials Supporting the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease with Free Radicals—EPR and UV-Vis Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results of EPR Examination of the Interaction of Extracts Obtained from the Plant Raw Materials Such as Ginkgo biloba, Ginseng, Yerba Mate, and Green Tea, with Free Radicals
2.1.1. The Reduction in the EPR Spectra of Free Radicals by the Tested Extracts
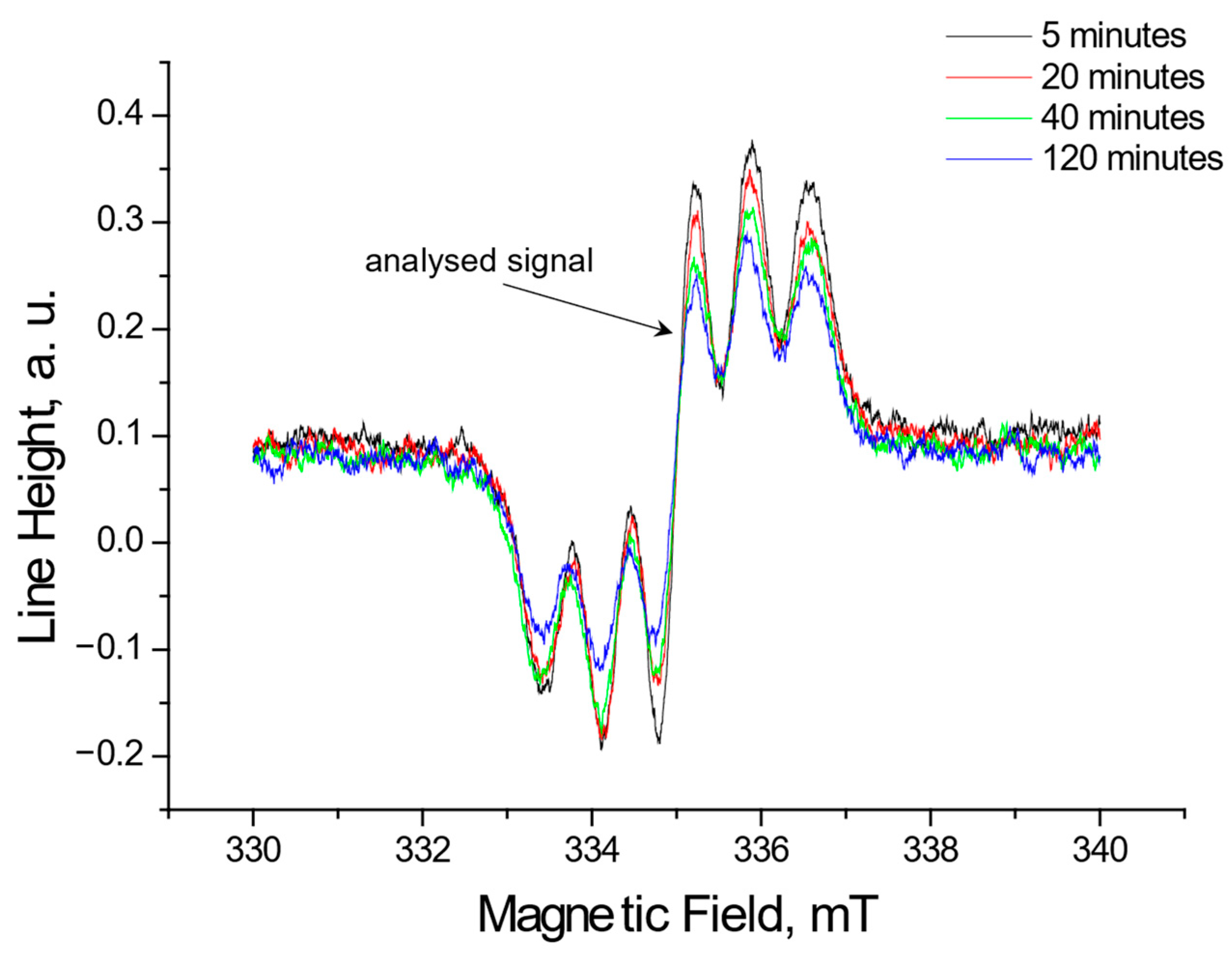
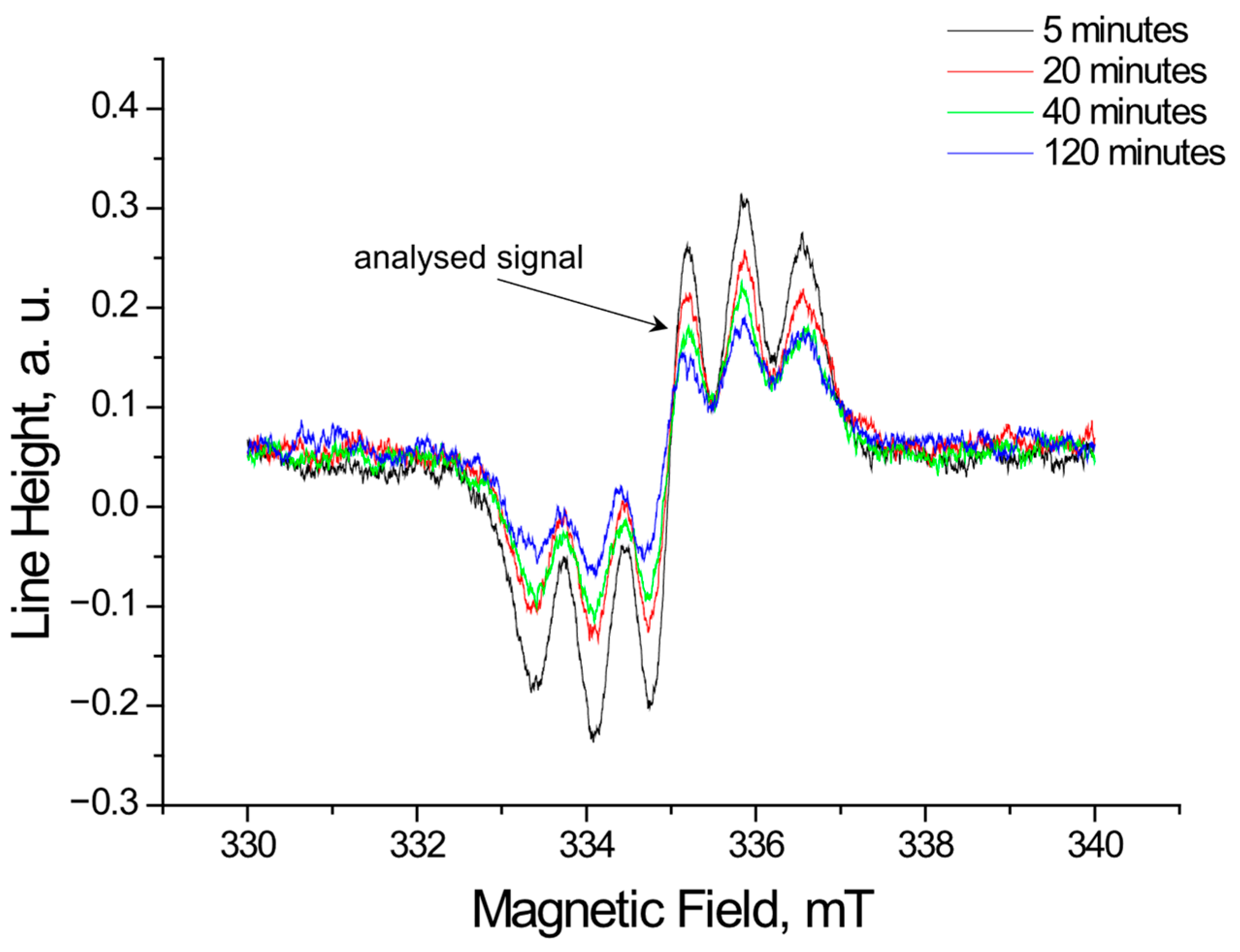
2.1.2. The Changes in the EPR Spectra with Increasing Contact Time of Free Radicals with the Tested Extracts
2.2. Results of UV-Vis Examination of the Interaction of Extracts Obtained from the Plant Raw Materials Such as Ginkgo biloba, Ginseng, Yerba Mate, and Green Tea, with Free Radicals
2.2.1. The Reduction in the UV-Vis Spectra of Free Radicals by the Tested Extracts
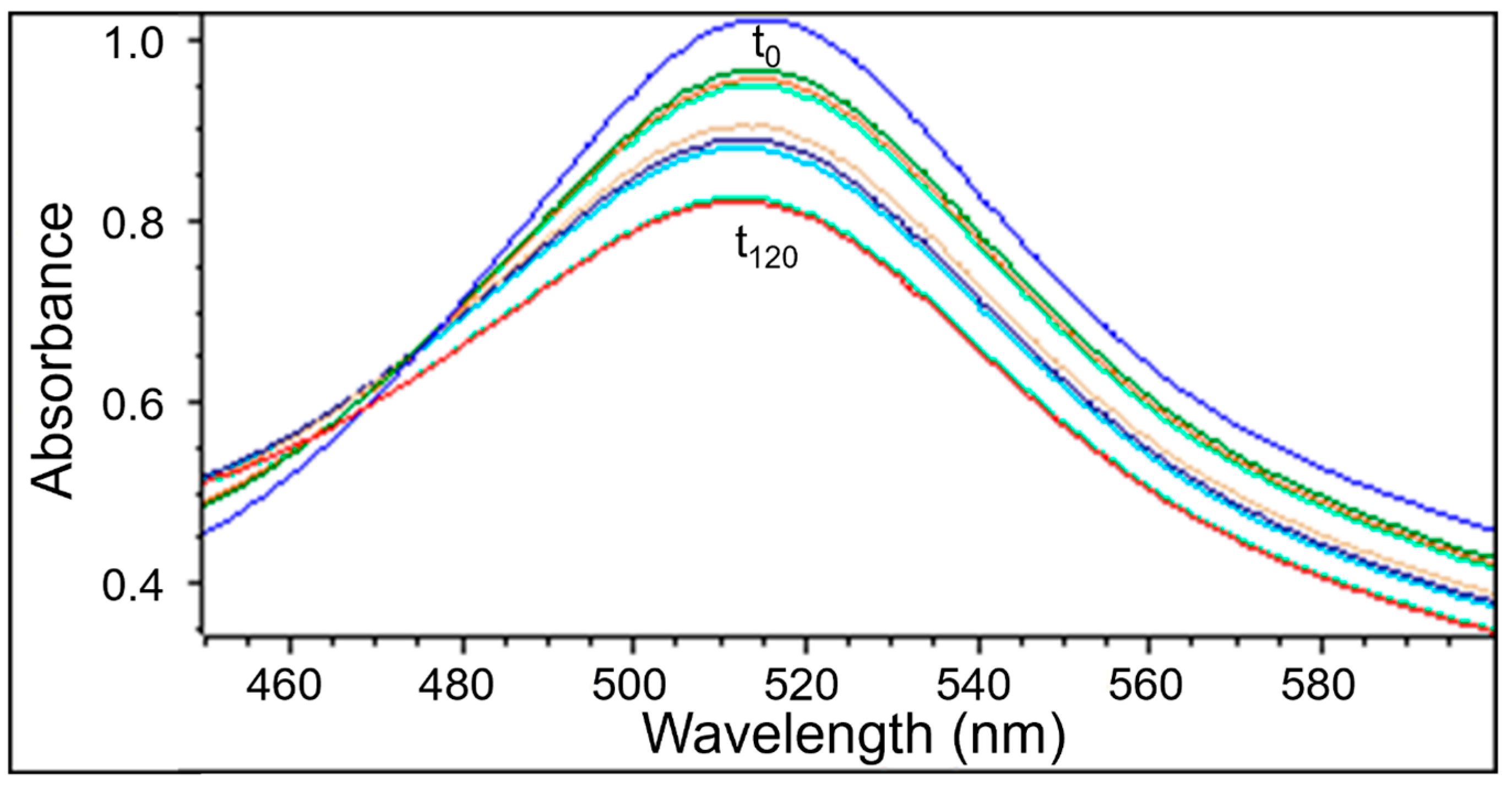
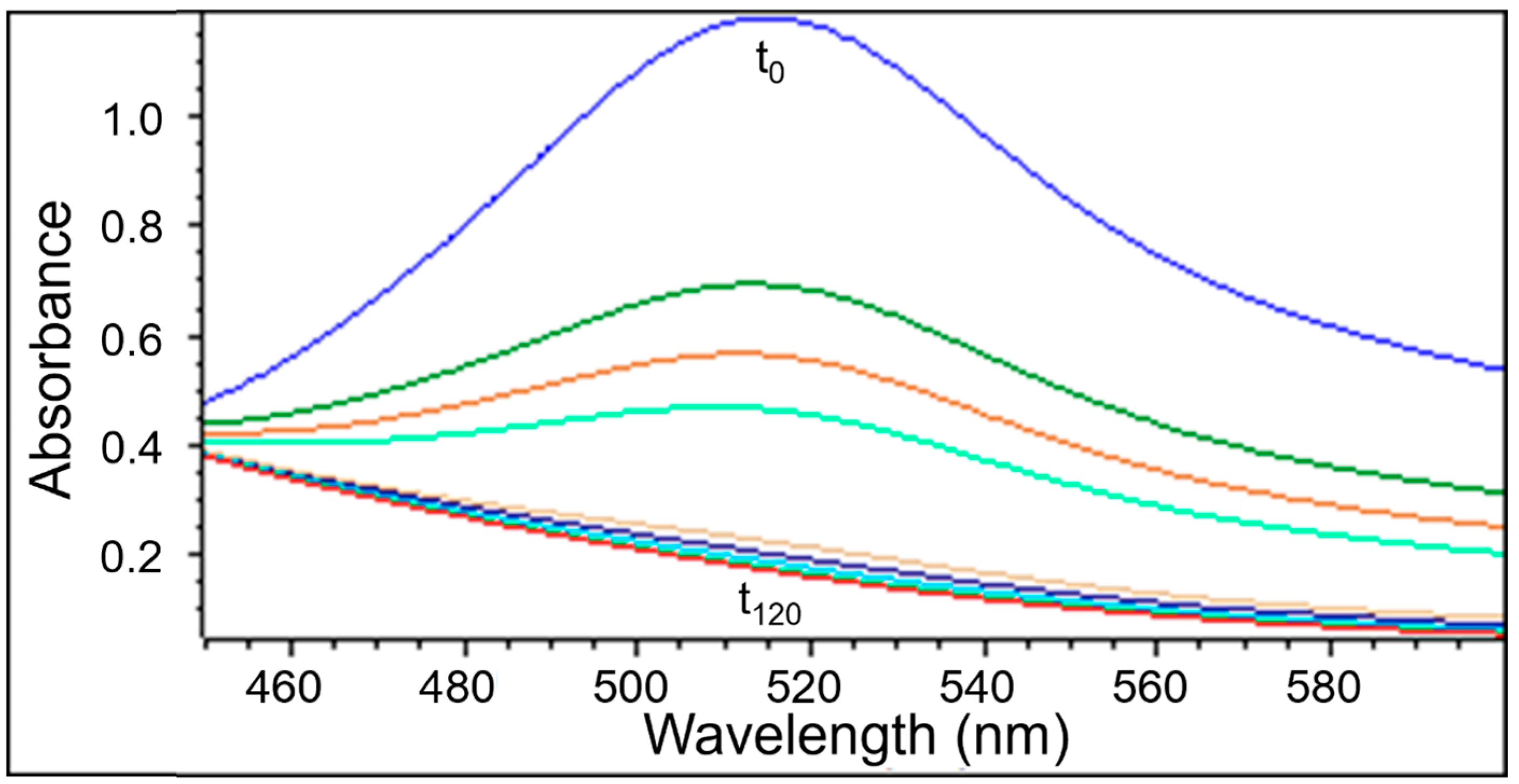
2.2.2. The Changes in the UV-Vis Spectra with Increasing Contact Time of Free Radicals with the Tested Extracts
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. The Examined Extracts from the Single Plant Raw Materials
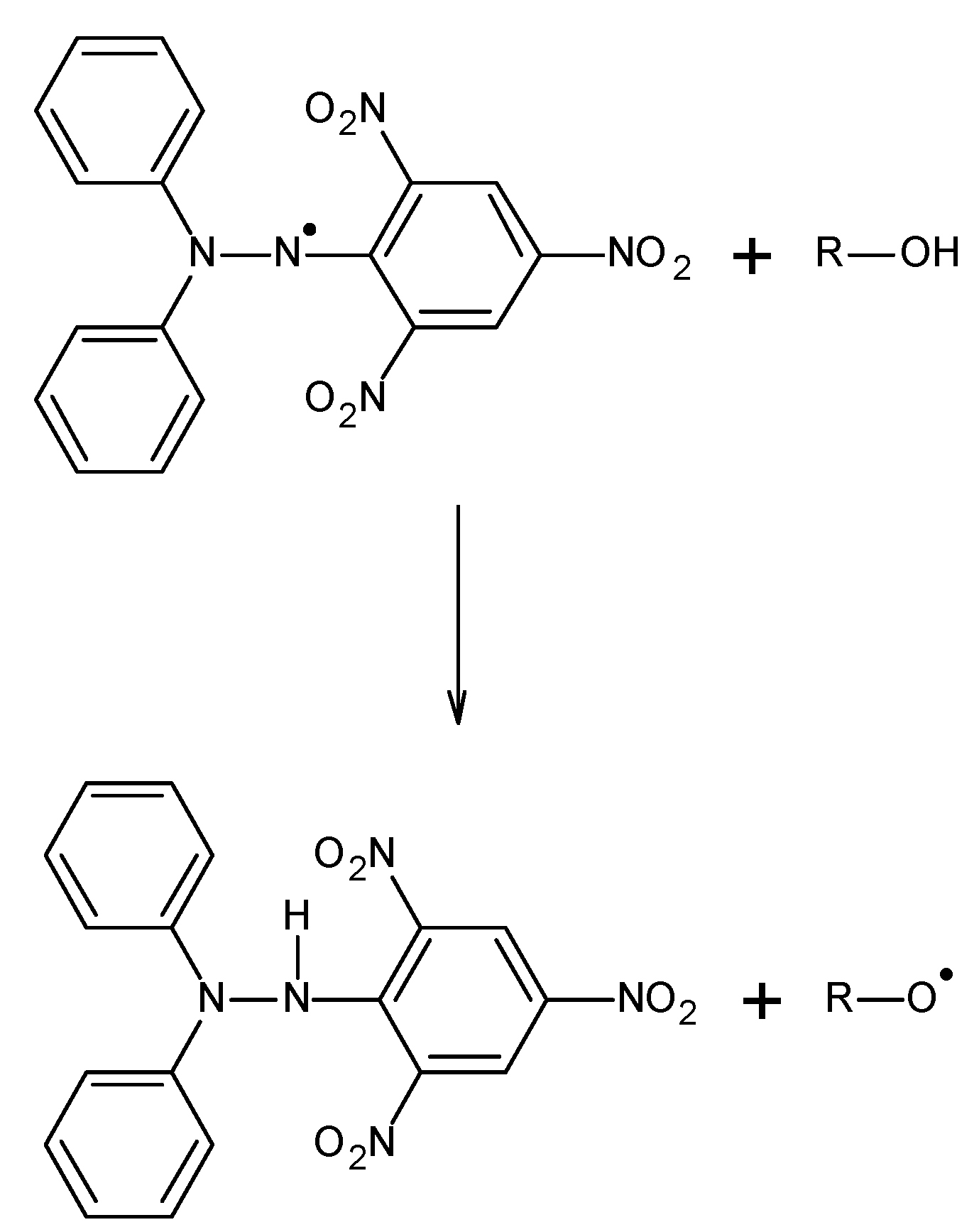
3.2. The Used DPPH Free Radicals and the Scheme of Their Interactions with Antioxidants
3.3. EPR Examination of Antioxidant Properties of the Tested Plant Extracts
3.4. UV-Vis Examination of Antioxidant Properties of the Tested Plant Extracts
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, S.; Benoist, C.; Weidner, W. World Alzheimer Report 2023: Reducing Dementia Risk: Never too Early, Never too Late; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2023; pp. 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Barcikowska, M. Przyczyny choroby Alzheimera. W: Barcikowska M, Parnowski T, (Red). Choroba Alzheimera 1906–2021, Seria: Choroby mózgu, Warszawa: PZWL Wydawnictwo Lekarskie; 2021, str. 1–9. Available online: https://pzwl.pl/choroba-alzheimera-1906-2021-105001.html (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Jack, C.R.; Albert, M.S.; Knopman, D.S.; McKhann, G.M.; Sperling, R.A.; Carrillo, M.C.; Thies, B.; Phelps, C.H. Introduction to the recommendation from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s continuum: An update. Free Neuropathol. 2020, 1, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczygieł, B.; Gaweł, M.; Ukleja, A.; Boniecka, I. Rola wybranych składników odżywczych we wspomaganiu leczenia farmakologicznego choroby Alzheimera. Medycyna Wieku Podeszłego 2014, 4, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Kant, R.; Goldstein, L.S.B.; Ossenkoppele, R. Amyloid-β-independent regulators of tau pathology in Alzheimer dissease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Zhamg, D.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, T.Y.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s dissease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doiphode, M.S.; Jadhav, P.T. Novel Pharmacological Approach to the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Multidisc. Res. 2022, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, M.W.; Edmonds, E.C.; Salomon, D.S. Alzheimer’s Disease: Past, Present, and Future. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2017, 23, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabro, M.; Rinaldi, C.; Santoro, G.; Crisafulli, C. The biological pathways of Alzheimer disease: A review. AIMS Neurosci. 2021, 8, 86–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.; Słupski, W.; Rutkowska, M. Nowe strategie terapeutyczne choroby Alzheimera. Postępy Hig. Med. Dośw. 2021, 75, 474–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Bautista, C.; Baquero, M.; Vento, M.; Consuelo Cháfer-Pericás, C. Free radicals in Alzheimer’s disease: Lipid peroxidation biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 491, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulbacka, J.; Saczko, J.; Chwiłkowska, A. Stres oksydacyjny w procesie uszkodzenia komórek. Pol. Merk. Lek. 2009, XXVII, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gaweł, M.; Potulska-Chromik, A. Choroby neurodegeneracyjne: Choroba Alzheimera i Parkinsona. Postępy Nauk Med. 2015, 7, 468–476. [Google Scholar]
- Barczak, A. Jak rozpoznać pierwsze objawy otępienia? Med. Dypl. 2017, 26, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Barczak, A. Choroba Alzehimera—co powinien wiedzieć lekarz POZ. Med. Dypl. 2021, 30, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Barczak, A. Niezbędnik Choroby Alzheimera; Wydawnictwo Termedia: Poznań, Poland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Barczak, A. Aktualne możliwości wykrywania i terapii choroby Alzheimera. Lekarz POZ 2021, 7, 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Broczek, K. Czy Można Zapobiegać Chorobie Alzheimera? W: Barcikowska, M.; Parnowski, T.; (Red). Choroba Alzheimera 1906–2021, Seria: Choroby Mózgu, Warszawa: PZWL Wydawnictwo Lekarskie: Warszawa, Poland, 2021; str. 147–171. Available online: https://www.medicon.pl/choroba-alzheimera-1906-2021/32509 (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Barcikowska, M.; Gabryelewicz, T. Choroba Alzheimera. W: Rozpoznawanie i leczenie otępień. Gabryelewicz, T.; Barczak, A.; Barcikowska, M. (Red.). Wydawnictwo Termedia: Poznań, Poland, 2021, str. 59–77. Available online: https://search.worldcat.org/title/1273740931 (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Parnowski, T. Leczenie Stosowane w Chorobie Alzheimera. W: Barcikowska, M.; Parnowski, T. (Red). Choroba Alzheimera 1906–2021, Seria: Choroby Mózgu, PZWL Wydawnictwo Lekarskie: Warszawa, Poland, 2021, str. 173–233. Available online: https://www.ibuk.pl/fiszka/259464/choroba-alzheimera-1906-2021.html (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Bartosz, G. Druga Twarz Tlenu. Wolne Rodniki w Przyrodzie; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, M.; Nawaz, A. Effects of medicinal plants on Alzheimer’s disease and memory deficits. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rami, L.; Ji-Hun, K.; Won-Woo, K.; Sung-Hee, H.; Sun-Hye, C.; Jong-Hoon, K.; Ik-Hyun, C.; Manho, K.; Seung-Yeol, N. Emerging evidence that ginseng components improve cognition in subjective memory impairment, mild cognitive impairment, and early Alzheimer’s disease dementia. J. Gins. Res. 2024, 48, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najman, K.; Rajewski, R.; Sadowska, A.; Hallmann, E.; Buczak, K. Changes in the Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties of Yerba Mate Depending on the Brewing Conditions. Molecules 2024, 29, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, K.; Nakamura, Y. Green Tea Suppresses Brain Aging. Molecules. Molecules 2021, 26, 4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, Y.; Inagaki, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Kaneko, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Takihara, T. Effect of Daily Intake of Green Tea Catechins on Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Subjects: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Arendash, G.W.; Hou, H.; Fernandez, F.; Jensen, M.; Runfeldt, M.; Shytle, R.D.; Tan, J. Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reduces β-amyloid mediated cognitive impairment and modulates tau pathology in Alzheimer transgenic mice. Brain Res. 2008, 1214, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londzin, P.; Zamora, M.; Kąkol, B.; Taborek, A.; Folwarczna, J. Potential of Caffeine in Alzheimer’s Disease—A Review of Experimental Studies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor-E-Tabassum; Das, R.; Lami, M.S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Mitra, S.; Tallei, T.E.; Idroes, R.; Mohamed, A.A.R.; Hossain, M.J.; Dhama, K.; et al. Ginkgo biloba: A Treasure of Functional Phytochemicals with Multimedicinal Applications. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, 2022, 8288818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Kojder, K.; Zielonka-Brzezicka, J.; Wróbel, J.; Bosiacki, M.; Fabiańska, M.; Wróbel, M.; Sołek-Pastuszka, J.; Klimowicz, A. The Use of Ginkgo biloba L. as a Neuroprotective Agent in the Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 775034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, N.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, B. Neuroprotective Effects of Ginseng Phytochemicals: Recent Perspectives. Molecules 2019, 24, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razgonova, M.P.; Veselov, V.V.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Golokhvast, K.S.; Nosyrev, A.E.; Cravotto, G.; Tsatsakis, A.; Spandidos, D.A. Panax ginseng components and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 2975–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawron-Gzella, A.; Chanaj-Kaczmarek, J.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Yerba Mate—A Long but Current History. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutomski, P.; Goździewska, M.; Florek-Łuszczki, M. Health properties of Yerba Mate. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2020, 27, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musial, C.; Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M. Beneficial properties of green tea catechins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde-Salazar, V.; Ruiz-Gabarre, D.; García-Escudero, V. Alzheimer’s Disease and Green Tea: Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate as a Modulator of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozmelj, T.R.; Voinov, M.A.; Grilc, M.; Smirnov, A.I.; Jasiukaitytė-Grojzdek, E.; Lucia, L.; Likozar, B. Lignin Structural Characterization and Its Antioxidant Potential: A Comparative Evaluation by EPR, UV-Vis Spectroscopy, and DPPH Assays. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaj, R.; Pilawa, B.; Zdybel, M.; Chodurek, E.; Witczyk, D.; Kroemer, M.; Chwałowska, M. Neutralization of free radicals by an infusion obtained from a mixture of plant raw materials suitable for supporting lactation. Herba Pol. 2025, 71, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical Methods Used in Determining Antioxidant Activity: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirzis, G.; Bartosz, G. Determination of antiradical and antioxidant activity: Basic principles and new insights. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2010, 57, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Łomankiewicz, D.; Pilawa, B.; Chodurek, E.; Zdybel, M. Interactions of Extracts from Selected Plant Materials Supporting the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease with Free Radicals—EPR and UV-Vis Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091421
Łomankiewicz D, Pilawa B, Chodurek E, Zdybel M. Interactions of Extracts from Selected Plant Materials Supporting the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease with Free Radicals—EPR and UV-Vis Studies. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091421
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁomankiewicz, Damian, Barbara Pilawa, Ewa Chodurek, and Magdalena Zdybel. 2025. "Interactions of Extracts from Selected Plant Materials Supporting the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease with Free Radicals—EPR and UV-Vis Studies" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091421
APA StyleŁomankiewicz, D., Pilawa, B., Chodurek, E., & Zdybel, M. (2025). Interactions of Extracts from Selected Plant Materials Supporting the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease with Free Radicals—EPR and UV-Vis Studies. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091421